31b2d89a852db7fed6a29975527780aa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Translating molecular testing into sepsis diagnosis: the challenge in clinical practices. Dr Ngo Tat Trung, Ph. D (Dept. Molecular biology 108 Military Central Hospital) Danang– September 2015
Translating molecular testing into sepsis diagnosis: the challenge in clinical practices. Dr Ngo Tat Trung, Ph. D (Dept. Molecular biology 108 Military Central Hospital) Danang– September 2015
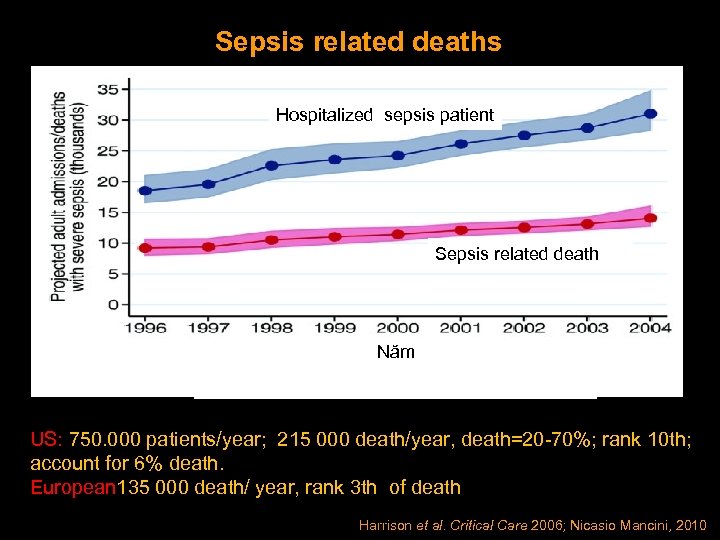 Sepsis related deaths Hospitalized sepsis patient Sepsis related death Năm US: 750. 000 patients/year; 215 000 death/year, death=20 -70%; rank 10 th; account for 6% death. European 135 000 death/ year, rank 3 th of death Harrison et al. Critical Care 2006; Nicasio Mancini, 2010
Sepsis related deaths Hospitalized sepsis patient Sepsis related death Năm US: 750. 000 patients/year; 215 000 death/year, death=20 -70%; rank 10 th; account for 6% death. European 135 000 death/ year, rank 3 th of death Harrison et al. Critical Care 2006; Nicasio Mancini, 2010
 Classical Sepsis detection tools CÁC PHƯƠNG PHÁP CHẨN ĐOÁN NN G Y NKH Clinical symptoms Immune response monitor Blood culture
Classical Sepsis detection tools CÁC PHƯƠNG PHÁP CHẨN ĐOÁN NN G Y NKH Clinical symptoms Immune response monitor Blood culture
 Blood culture Classical method, widely implemented but still far from making clinician satisfied because of its intrinsic drawbacks: 1. Impractical for fastidious pathogens 2. Time required for first wave of microbial colonies to appear is too long that might switch patients into worse deleterious situation 3. Large volumes blood is mandatory for proper culturing of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria
Blood culture Classical method, widely implemented but still far from making clinician satisfied because of its intrinsic drawbacks: 1. Impractical for fastidious pathogens 2. Time required for first wave of microbial colonies to appear is too long that might switch patients into worse deleterious situation 3. Large volumes blood is mandatory for proper culturing of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria
 Consequence of mis/late detection • • Risk to be sepsis shock: Reduce chances to survive Increased hospital cost Drug resistance clones emerge → need to develop relevent approaches that work complimentary to blood culture *Nicasio. Mancini et al, 2010
Consequence of mis/late detection • • Risk to be sepsis shock: Reduce chances to survive Increased hospital cost Drug resistance clones emerge → need to develop relevent approaches that work complimentary to blood culture *Nicasio. Mancini et al, 2010
 Nucleic acid test(NAT) PCR combined mass spectrometric DNA sequencing
Nucleic acid test(NAT) PCR combined mass spectrometric DNA sequencing
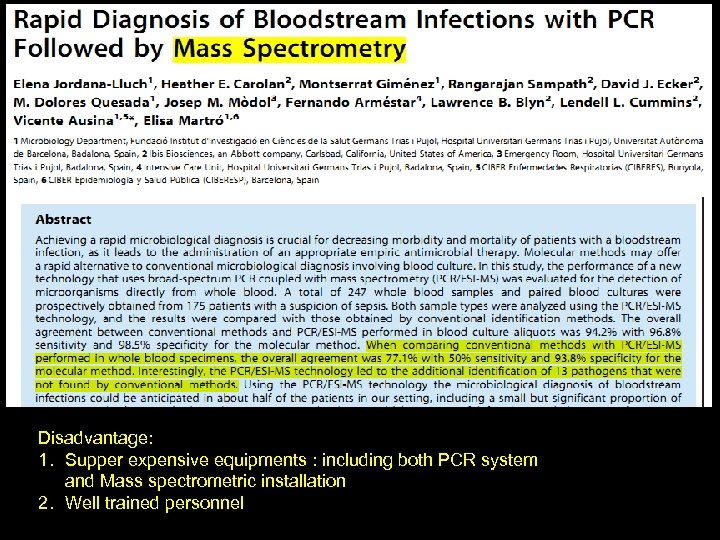 Disadvantage: 1. Supper expensive equipments : including both PCR system and Mass spectrometric installation 2. Well trained personnel
Disadvantage: 1. Supper expensive equipments : including both PCR system and Mass spectrometric installation 2. Well trained personnel
 Promising technology, especially for multi-readout assays
Promising technology, especially for multi-readout assays
 Challenges to PCR’s sensitivity An optimized PCR reaction using DNA extracted by Qiagen, Zymo blood extraction kits can only sense pathogen’s ribosomal 16 S pieces if the bacterial load exceeds roughly 500 CFU/ml Patients would present sepsis – related clinical symptoms if bacterial load exceed 10 - 500 CFU/ml Klouche and Schröder 2008
Challenges to PCR’s sensitivity An optimized PCR reaction using DNA extracted by Qiagen, Zymo blood extraction kits can only sense pathogen’s ribosomal 16 S pieces if the bacterial load exceeds roughly 500 CFU/ml Patients would present sepsis – related clinical symptoms if bacterial load exceed 10 - 500 CFU/ml Klouche and Schröder 2008
 How the primers mis-pairing to human DNA happens NATURE | VOL 431 | 9 SEPTEMBER 2004
How the primers mis-pairing to human DNA happens NATURE | VOL 431 | 9 SEPTEMBER 2004
 Virut Two aspects must be focused to harness PCR into sepsis diagnosis 1. Human DNA removal/bacterial DNA enrichment 2. Optimize the conditions for PCR diagnostic algorithm
Virut Two aspects must be focused to harness PCR into sepsis diagnosis 1. Human DNA removal/bacterial DNA enrichment 2. Optimize the conditions for PCR diagnostic algorithm
 Virut Our strategic resolution
Virut Our strategic resolution
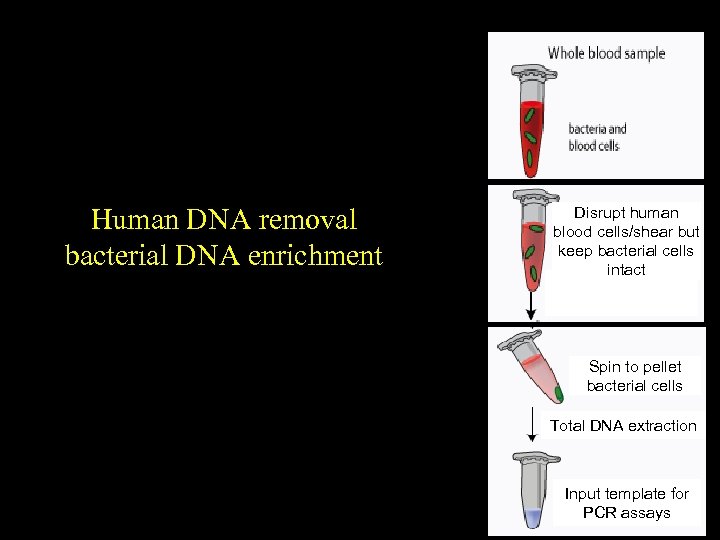 Human DNA removal bacterial DNA enrichment Disrupt human blood cells/shear but keep bacterial cells intact Spin to pellet bacterial cells Total DNA extraction Input template for PCR assays
Human DNA removal bacterial DNA enrichment Disrupt human blood cells/shear but keep bacterial cells intact Spin to pellet bacterial cells Total DNA extraction Input template for PCR assays
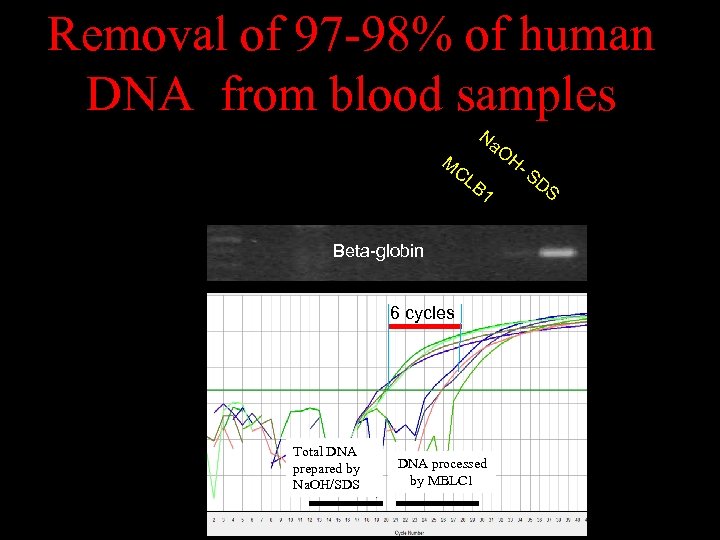 Removal of 97 -98% of human DNA from blood samples M Na OH CL B 1 Beta-globin 6 cycles Total DNA prepared by Na. OH/SDS DNA processed by MBLC 1 - S DS
Removal of 97 -98% of human DNA from blood samples M Na OH CL B 1 Beta-globin 6 cycles Total DNA prepared by Na. OH/SDS DNA processed by MBLC 1 - S DS
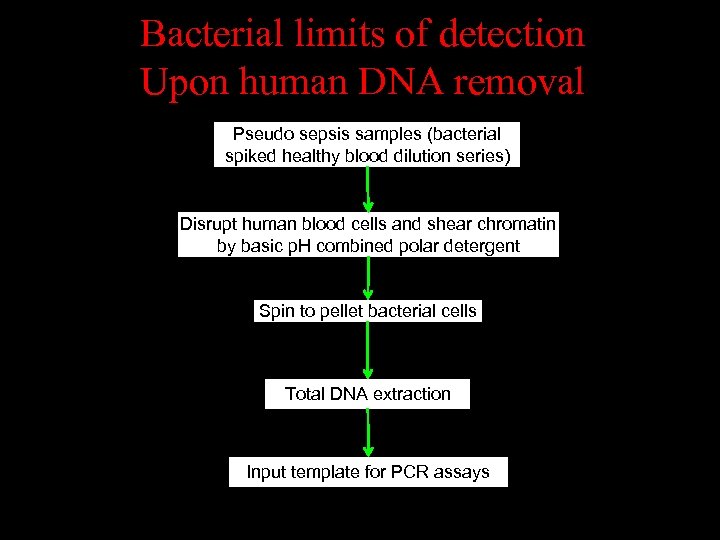 Bacterial limits of detection Upon human DNA removal Pseudo sepsis samples (bacterial spiked healthy blood dilution series) Disrupt human blood cells and shear chromatin by basic p. H combined polar detergent / Spin to pellet bacterial cells Total DNA extraction Input template for PCR assays
Bacterial limits of detection Upon human DNA removal Pseudo sepsis samples (bacterial spiked healthy blood dilution series) Disrupt human blood cells and shear chromatin by basic p. H combined polar detergent / Spin to pellet bacterial cells Total DNA extraction Input template for PCR assays
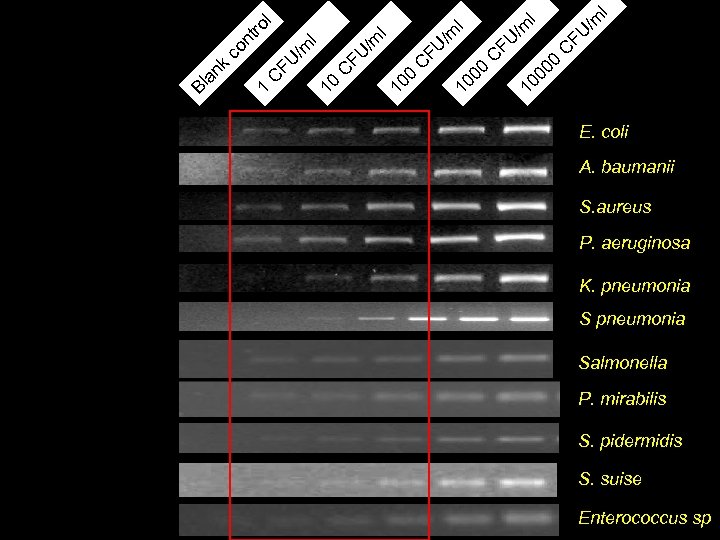 l k co nt ro 1 l C FU /m l 10 00 C FU /m 10 l 00 0 C FU /m Bl an E. coli A. baumanii S. aureus P. aeruginosa K. pneumonia Salmonella P. mirabilis S. pidermidis S. suise Enterococcus sp
l k co nt ro 1 l C FU /m l 10 00 C FU /m 10 l 00 0 C FU /m Bl an E. coli A. baumanii S. aureus P. aeruginosa K. pneumonia Salmonella P. mirabilis S. pidermidis S. suise Enterococcus sp
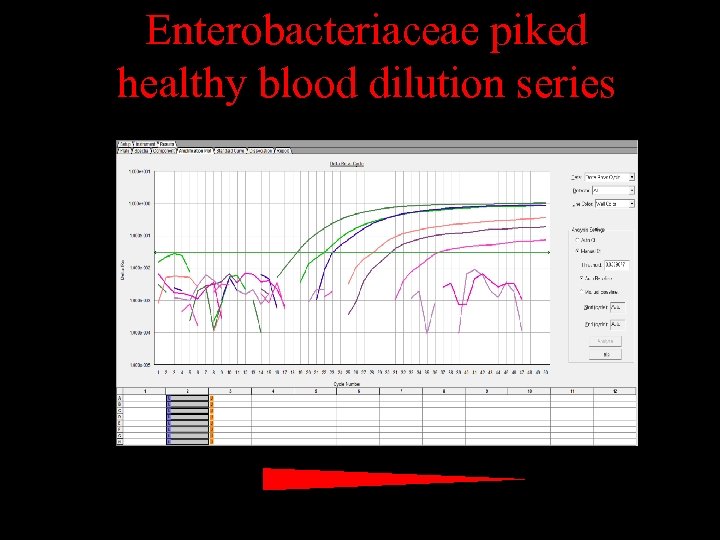 Enterobacteriaceae piked healthy blood dilution series
Enterobacteriaceae piked healthy blood dilution series
 Optimize the conditions for PCR diagnostic algorithm
Optimize the conditions for PCR diagnostic algorithm
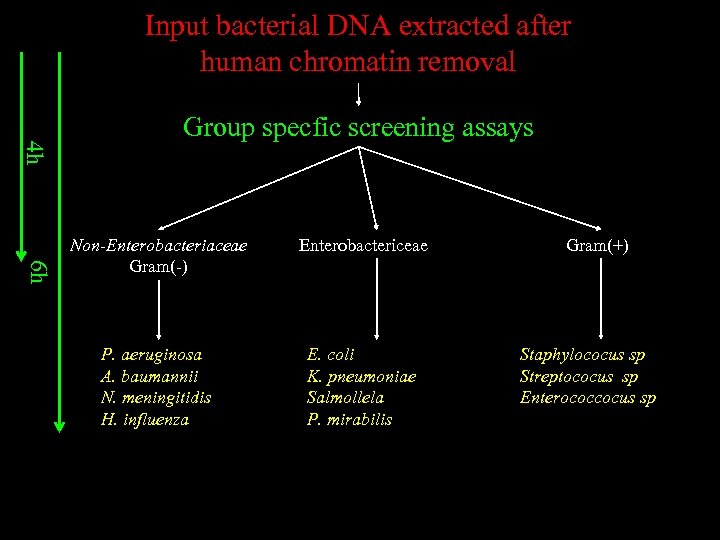 Input bacterial DNA extracted after human chromatin removal 4 h Group specfic screening assays 6 h Non-Enterobacteriaceae Gram(-) Enterobactericeae P. aeruginosa A. baumannii N. meningitidis H. influenza E. coli K. pneumoniae Salmollela P. mirabilis Gram(+) Staphylococus sp Streptococus sp Enterococcocus sp
Input bacterial DNA extracted after human chromatin removal 4 h Group specfic screening assays 6 h Non-Enterobacteriaceae Gram(-) Enterobactericeae P. aeruginosa A. baumannii N. meningitidis H. influenza E. coli K. pneumoniae Salmollela P. mirabilis Gram(+) Staphylococus sp Streptococus sp Enterococcocus sp
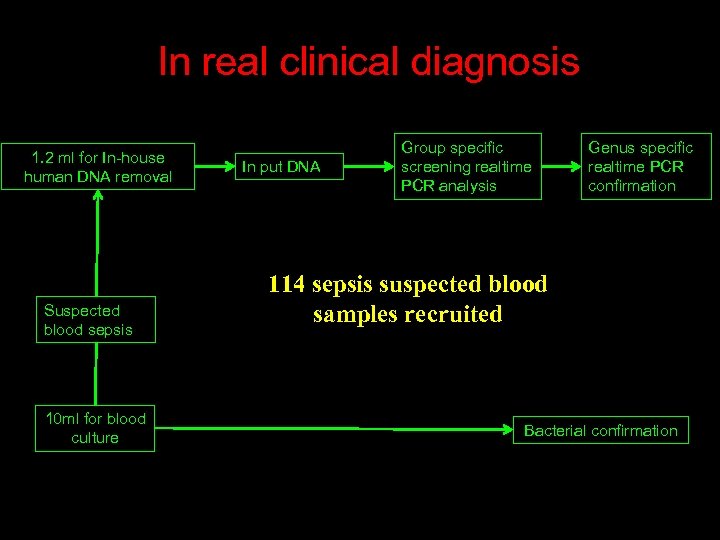 In real clinical diagnosis 1. 2 ml for In-house human DNA removal Suspected blood sepsis 10 ml for blood culture In put DNA Group specific screening realtime PCR analysis Genus specific realtime PCR confirmation 114 sepsis suspected blood samples recruited Bacterial confirmation
In real clinical diagnosis 1. 2 ml for In-house human DNA removal Suspected blood sepsis 10 ml for blood culture In put DNA Group specific screening realtime PCR analysis Genus specific realtime PCR confirmation 114 sepsis suspected blood samples recruited Bacterial confirmation
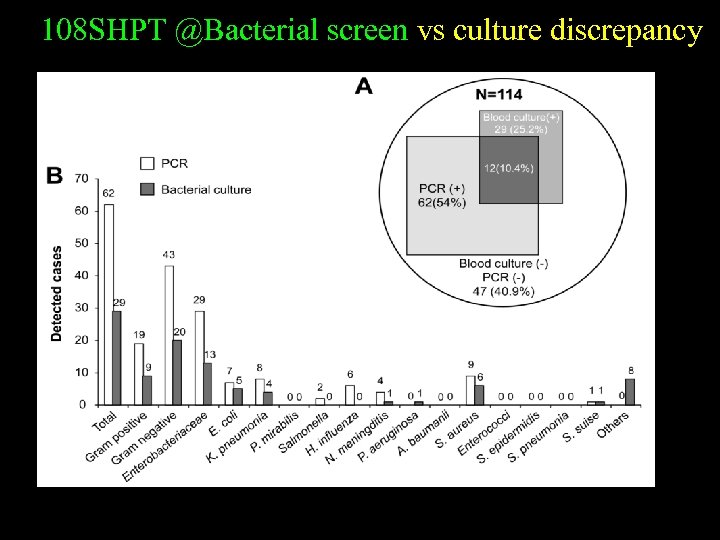 108 SHPT @Bacterial screen vs culture discrepancy
108 SHPT @Bacterial screen vs culture discrepancy
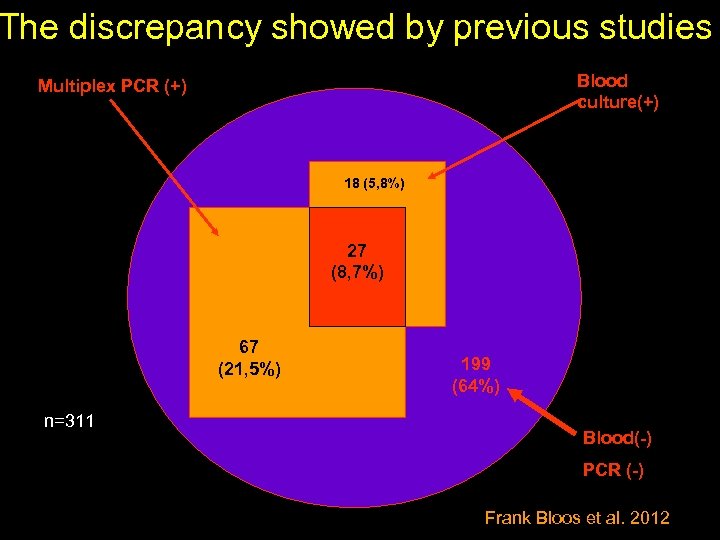 The discrepancy showed by previous studies Blood culture(+) Multiplex PCR (+) 18 (5, 8%) 27 (8, 7%) 67 (21, 5%) n=311 199 (64%) Blood(-) PCR (-) Frank Bloos et al. 2012
The discrepancy showed by previous studies Blood culture(+) Multiplex PCR (+) 18 (5, 8%) 27 (8, 7%) 67 (21, 5%) n=311 199 (64%) Blood(-) PCR (-) Frank Bloos et al. 2012
 In conclude: Targeted enrichment of bacterial DNA as consequence of human DNA removal significantly enhances the sensitivity of downstream PCR based sepsis diagnostics
In conclude: Targeted enrichment of bacterial DNA as consequence of human DNA removal significantly enhances the sensitivity of downstream PCR based sepsis diagnostics
 We would like to acknowledge the funding from Vietnamese Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant: KC-10. 43/11 -15) for this study Thank you for your attention
We would like to acknowledge the funding from Vietnamese Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant: KC-10. 43/11 -15) for this study Thank you for your attention


