b5c7632d54c042fab491e2d08dd6ad56.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 Transition and End State Issues in Complex Emergencies
Transition and End State Issues in Complex Emergencies
 Since the end of the cold war the UN, Regional Organizations, the US, and other Nations have been involved in more than a dozen peace operations that involved internal conflicts. Despite limited operational success, sustainable peace has proven elusive.
Since the end of the cold war the UN, Regional Organizations, the US, and other Nations have been involved in more than a dozen peace operations that involved internal conflicts. Despite limited operational success, sustainable peace has proven elusive.
 Concerns • • Managing the Political Process to an End State Translating the Political Mandate Managing the Transition to Sustainable Peace Lack of Support from International Stakeholders • Insufficient Preparation of the Military for the Complex Emergency • The Lack of Surge Capacity in the Civilian Side of Peace Operations • Failure to Resource Critical Aspects
Concerns • • Managing the Political Process to an End State Translating the Political Mandate Managing the Transition to Sustainable Peace Lack of Support from International Stakeholders • Insufficient Preparation of the Military for the Complex Emergency • The Lack of Surge Capacity in the Civilian Side of Peace Operations • Failure to Resource Critical Aspects
 The question that must be answered is, “What is the desired End State? ”
The question that must be answered is, “What is the desired End State? ”
 Evaluating Effective End states A transition from peace operation to local government (end state) was determined to be completely effective if: q Significant armed conflict did not begin again q There were no politically-motivated violent disruptions of civil society q The political system survived an indigenously and internationally recognized national level election From a presentation prepared for OSD/OASD PK/HA 1997
Evaluating Effective End states A transition from peace operation to local government (end state) was determined to be completely effective if: q Significant armed conflict did not begin again q There were no politically-motivated violent disruptions of civil society q The political system survived an indigenously and internationally recognized national level election From a presentation prepared for OSD/OASD PK/HA 1997
 Examine the possible “end state or country conditions at exit” using seven categories. Political Resolution Demilitarization Basic Needs Public Security Governance Economy Civil Society
Examine the possible “end state or country conditions at exit” using seven categories. Political Resolution Demilitarization Basic Needs Public Security Governance Economy Civil Society
 Political Resolution • An agreed Peace Plan – scope and objectives meet the major political goals • Political will of the factions/parties to resolve issues • Supporting role of external parties – International actors – Neighboring states • Implementation of the mandate • Buy-in from the major stakeholders
Political Resolution • An agreed Peace Plan – scope and objectives meet the major political goals • Political will of the factions/parties to resolve issues • Supporting role of external parties – International actors – Neighboring states • Implementation of the mandate • Buy-in from the major stakeholders
 Demilitarization • Political Role - establish constitutional control of forces • Cease-fires and separation of forces • Removal of foreign troops • Internal Security Functions • Control of Heavy Weapons • Reduction in Light weapons
Demilitarization • Political Role - establish constitutional control of forces • Cease-fires and separation of forces • Removal of foreign troops • Internal Security Functions • Control of Heavy Weapons • Reduction in Light weapons
 Demilitarization - cont. • Demobilization of Military forces / militias to reasonable level • Reintegration of Former combatants into society • Restructure of Forces • Reduction in civil unrest • Control lawlessness of combatants
Demilitarization - cont. • Demobilization of Military forces / militias to reasonable level • Reintegration of Former combatants into society • Restructure of Forces • Reduction in civil unrest • Control lawlessness of combatants
 Basic Needs • • Food and Water Availability of Shelter De-mining Health Support System in place Re-housing of Internally Displaced Return of refugees - repatriation to former homes Freedom of Movement Infrastructure Restoration - power, sewage, running water, medical facilities, transportation • Market availability of food products
Basic Needs • • Food and Water Availability of Shelter De-mining Health Support System in place Re-housing of Internally Displaced Return of refugees - repatriation to former homes Freedom of Movement Infrastructure Restoration - power, sewage, running water, medical facilities, transportation • Market availability of food products
 Public Security • Political Role - re-establish reliable security apparatus • Provide for the physical security of the population • Compliance with security aspects of Peace Agreement • Restructure of Police • Training of police • Police - Civil relations
Public Security • Political Role - re-establish reliable security apparatus • Provide for the physical security of the population • Compliance with security aspects of Peace Agreement • Restructure of Police • Training of police • Police - Civil relations
 Public Security - cont. • • • Re-establishing the Judicial structure Judges - trained and working Legal constructs - Rule of law Re-establish the Prison System Banditry reduced
Public Security - cont. • • • Re-establishing the Judicial structure Judges - trained and working Legal constructs - Rule of law Re-establish the Prison System Banditry reduced
 Governance • • National Electoral process Electoral Laws established Political process - opposition party process Administrative Bureaucracy restored Judicial system operating Reduction in levels of corruption Restoration of local government structures
Governance • • National Electoral process Electoral Laws established Political process - opposition party process Administrative Bureaucracy restored Judicial system operating Reduction in levels of corruption Restoration of local government structures
 Economic • • Jobs Control of the Inflation rate Access to secure Banking Access to consumer Goods Economic reconstruction Structural adjustment programs Access to loans/investment capital
Economic • • Jobs Control of the Inflation rate Access to secure Banking Access to consumer Goods Economic reconstruction Structural adjustment programs Access to loans/investment capital
 Civil Society • Media, both government and opposition established • Freedom of Speech • Norms of Human rights guaranteed • Grievance /reconciliation process • Presence of national private/ NGO organizations • Education system re-established
Civil Society • Media, both government and opposition established • Freedom of Speech • Norms of Human rights guaranteed • Grievance /reconciliation process • Presence of national private/ NGO organizations • Education system re-established
 The question is: “Should every aspect of these requirements be met? ” Examine the minimum requirement - Sustainable Security
The question is: “Should every aspect of these requirements be met? ” Examine the minimum requirement - Sustainable Security
 Sustainable Security • The capacity of a society to solve it’s own problems peacefully without an external administrative or military presence • A common conceptual approach and a common standard of sustainable security will greatly assist the determination of an end state. Pauline Baker & Angeli Weller
Sustainable Security • The capacity of a society to solve it’s own problems peacefully without an external administrative or military presence • A common conceptual approach and a common standard of sustainable security will greatly assist the determination of an end state. Pauline Baker & Angeli Weller
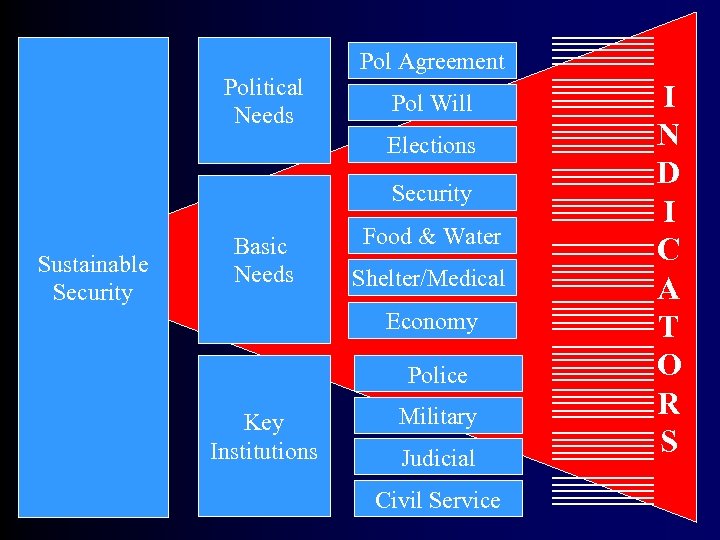
 Minimum Standards of Sustainable Security • Political Framework – Acceptable Agreement – Political will • Provide for the basic needs of the people – – – Security Shelter Food & Water Medical Care Basic Economy • Rebuild four Key State Institutions – – Military Police Judiciary Civil Service
Minimum Standards of Sustainable Security • Political Framework – Acceptable Agreement – Political will • Provide for the basic needs of the people – – – Security Shelter Food & Water Medical Care Basic Economy • Rebuild four Key State Institutions – – Military Police Judiciary Civil Service
 Benefits of the Sustainable Security Approach • • Define the mission more precisely Develop Measures of Effectiveness Evaluate success criteria Assess the military, humanitarian and political end state • Develop the transition plan to hand over to civil authorities
Benefits of the Sustainable Security Approach • • Define the mission more precisely Develop Measures of Effectiveness Evaluate success criteria Assess the military, humanitarian and political end state • Develop the transition plan to hand over to civil authorities
 MOEs & Endstate Primary Use: • Evaluate whether mission is succeeding or failing Secondary Uses: • Establishes planning partnerships • Brings together organizations that need to support each other • Establish a common approach • Minimizes confusion & risk • Provides end-point or trend analysis
MOEs & Endstate Primary Use: • Evaluate whether mission is succeeding or failing Secondary Uses: • Establishes planning partnerships • Brings together organizations that need to support each other • Establish a common approach • Minimizes confusion & risk • Provides end-point or trend analysis
 Political Needs Pol Agreement Pol Will Elections Security Sustainable Security Basic Needs Food & Water Shelter/Medical Economy Police Key Institutions Military Judicial Civil Service I N D I C A T O R S
Political Needs Pol Agreement Pol Will Elections Security Sustainable Security Basic Needs Food & Water Shelter/Medical Economy Police Key Institutions Military Judicial Civil Service I N D I C A T O R S
 Continuous Analysis • Before the conflict – approaches for preventive diplomacy – provides overall perspective • During a conflict – define limits of external operations – work with local and other intervening agencies – prepare exit strategies • After containment of a conflict – plan transition strategies – link political framework with plan to rebuild
Continuous Analysis • Before the conflict – approaches for preventive diplomacy – provides overall perspective • During a conflict – define limits of external operations – work with local and other intervening agencies – prepare exit strategies • After containment of a conflict – plan transition strategies – link political framework with plan to rebuild
 Who Evaluates? • Professional soldiers – security, indigenous armies, • Humanitarians – basic needs • External police – professionalism, competence, level of training and autonomy • International Judges and Lawyers – local judicial system, standards, training & support requirements • Public Administration Specialists – the civil service, medical services, elections
Who Evaluates? • Professional soldiers – security, indigenous armies, • Humanitarians – basic needs • External police – professionalism, competence, level of training and autonomy • International Judges and Lawyers – local judicial system, standards, training & support requirements • Public Administration Specialists – the civil service, medical services, elections
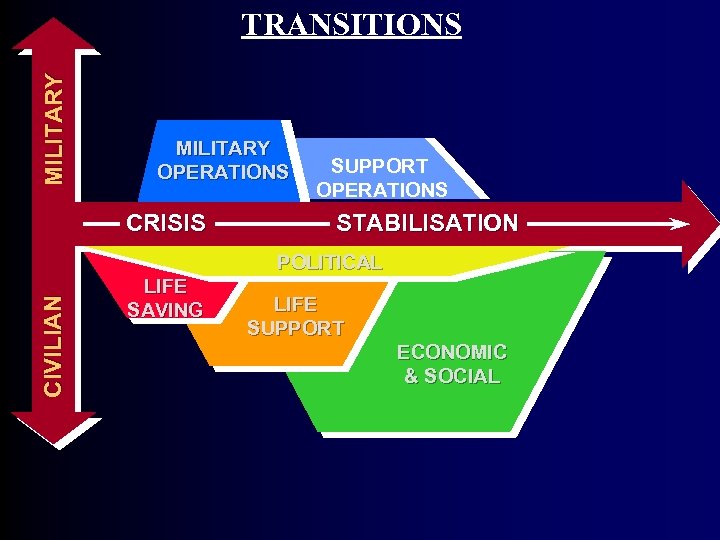
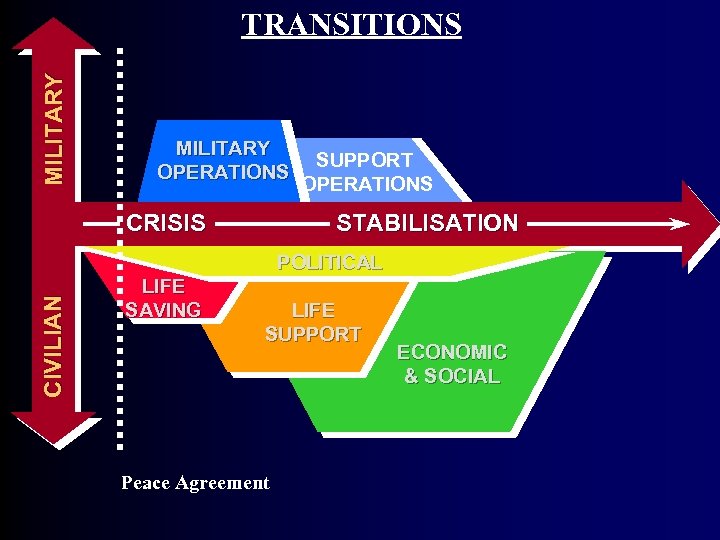
 Many Transitions or End States Exist • • • Conflict Peace Agreement Peace Enforcement Peacekeeping Sustainable Security Sustainable Peace Let’s Examine the Transitions
Many Transitions or End States Exist • • • Conflict Peace Agreement Peace Enforcement Peacekeeping Sustainable Security Sustainable Peace Let’s Examine the Transitions
 MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS CRISIS SUPPORT OPERATIONS STABILISATION CI V I L I AN POLITICAL LIFE SAVING LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL
MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS CRISIS SUPPORT OPERATIONS STABILISATION CI V I L I AN POLITICAL LIFE SAVING LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL
 MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CRISIS STABILISATION CI V I L I AN POLITICAL LIFE SAVING LIFE SUPPORT Peace Agreement ECONOMIC & SOCIAL
MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CRISIS STABILISATION CI V I L I AN POLITICAL LIFE SAVING LIFE SUPPORT Peace Agreement ECONOMIC & SOCIAL
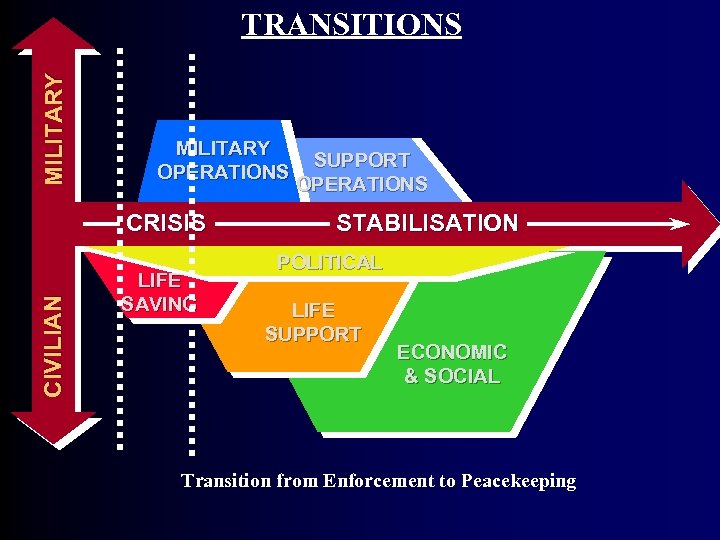 MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition from Enforcement to Peacekeeping
MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition from Enforcement to Peacekeeping
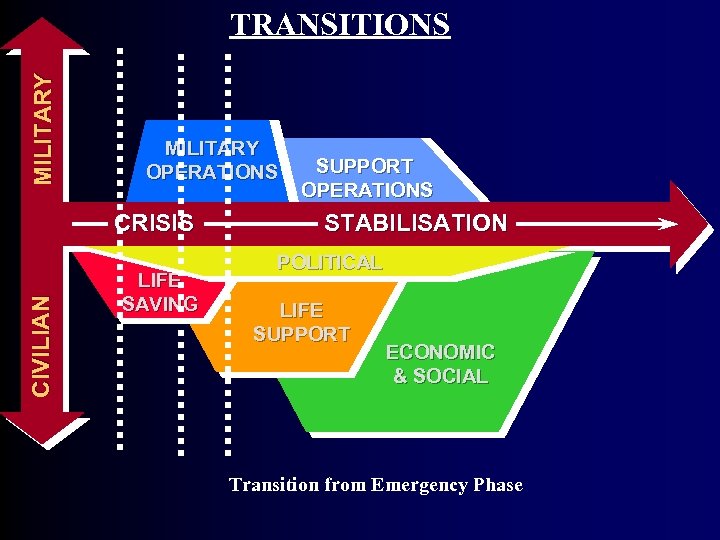 MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition from Emergency Phase
MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition from Emergency Phase
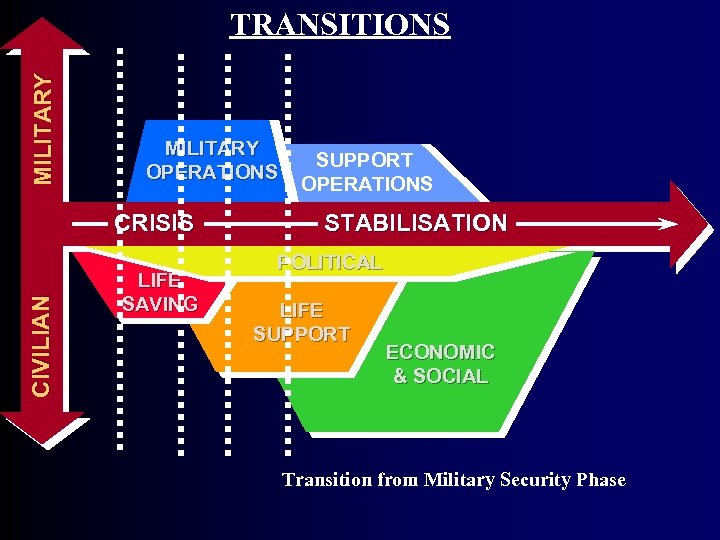 MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition from Military Security Phase
MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition from Military Security Phase
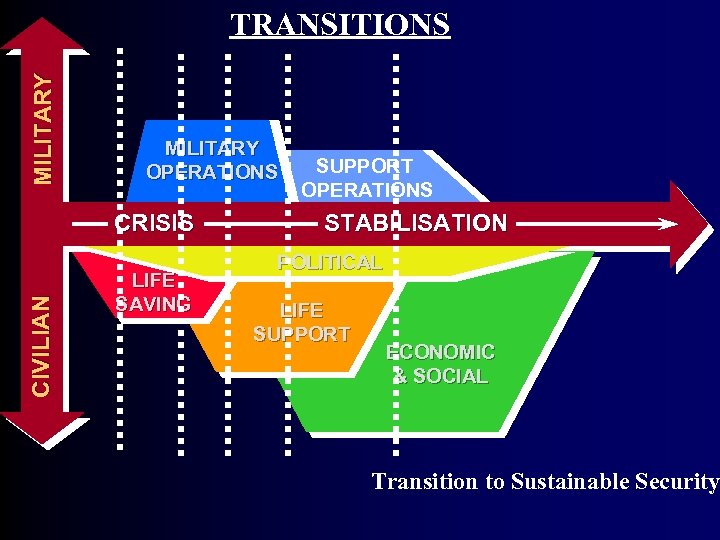 MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition to Sustainable Security
MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition to Sustainable Security
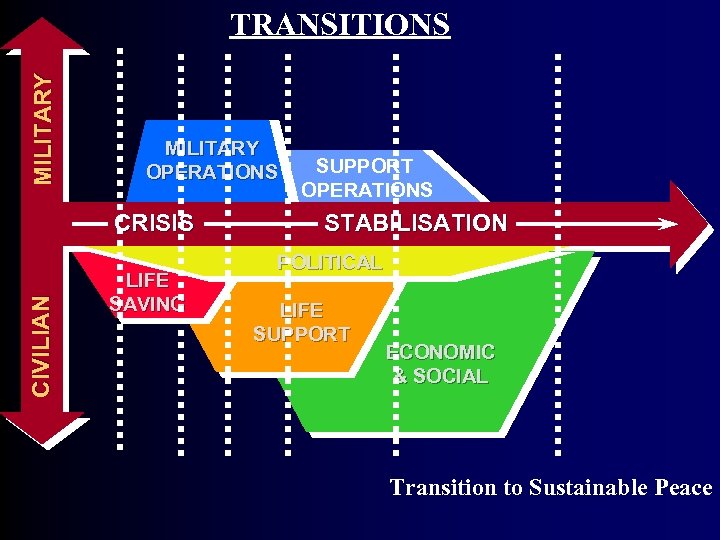 MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition to Sustainable Peace
MI L I T A R Y TRANSITIONS MILITARY OPERATIONS SUPPORT OPERATIONS CI V I L I AN CRISIS LIFE SAVING STABILISATION POLITICAL LIFE SUPPORT ECONOMIC & SOCIAL Transition to Sustainable Peace
 Considerations for Transition & End State • Plan for transition when you plan for intervention plan in conjunction with others • Transition or end-state for one component is not necessarily the same for another • Your successful transition may depend on others • Develop MOEs based on success in the key areas of sustainable security • Use working elements of indigenous capacity • Understand the transition strategy will evolve • Support elements in the domain of other components
Considerations for Transition & End State • Plan for transition when you plan for intervention plan in conjunction with others • Transition or end-state for one component is not necessarily the same for another • Your successful transition may depend on others • Develop MOEs based on success in the key areas of sustainable security • Use working elements of indigenous capacity • Understand the transition strategy will evolve • Support elements in the domain of other components


