f2cd234d59cf31e9192e60a2277894d1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 TRANSFORMING PATHOLOGY: Emerging technology driving practice innovation
TRANSFORMING PATHOLOGY: Emerging technology driving practice innovation
 Personalized Medicine & Pathology Friend or Foe? Mara G. Aspinall CAP Foundation Chicago, Illinois June 7, 2008
Personalized Medicine & Pathology Friend or Foe? Mara G. Aspinall CAP Foundation Chicago, Illinois June 7, 2008
 Personalized Medicine - Friend or Foe? o What is it? o Why now? o When will it be real? o Call to Action for Pathologists
Personalized Medicine - Friend or Foe? o What is it? o Why now? o When will it be real? o Call to Action for Pathologists
 Personalized Medicine Old Paradigm: Trial and Error Medicine Successful When it Leads to Innovation and Improves Standard of Care. Fails When We Settle for “Trial and Error” Medicine AS the Standard of Care.
Personalized Medicine Old Paradigm: Trial and Error Medicine Successful When it Leads to Innovation and Improves Standard of Care. Fails When We Settle for “Trial and Error” Medicine AS the Standard of Care.
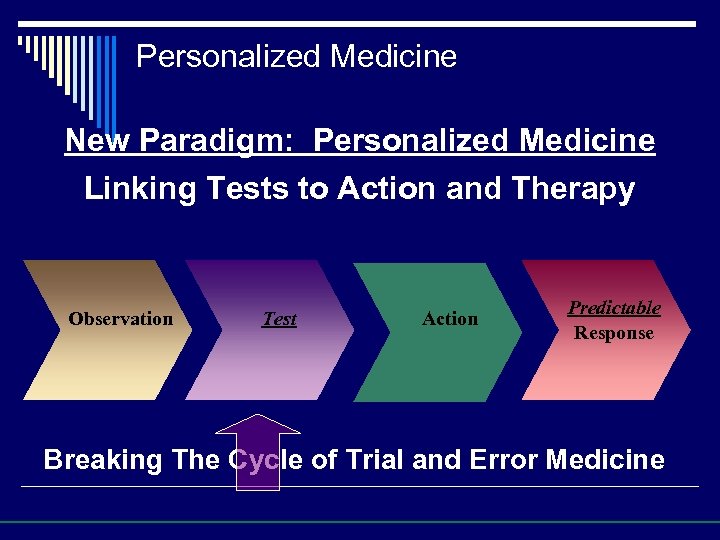 Personalized Medicine New Paradigm: Personalized Medicine Linking Tests to Action and Therapy Observation Test Action Predictable Response Breaking The Cycle of Trial and Error Medicine
Personalized Medicine New Paradigm: Personalized Medicine Linking Tests to Action and Therapy Observation Test Action Predictable Response Breaking The Cycle of Trial and Error Medicine
 Personalized Medicine Why is it Important? Diagnosis Save Lives Diagnosis Save Money
Personalized Medicine Why is it Important? Diagnosis Save Lives Diagnosis Save Money
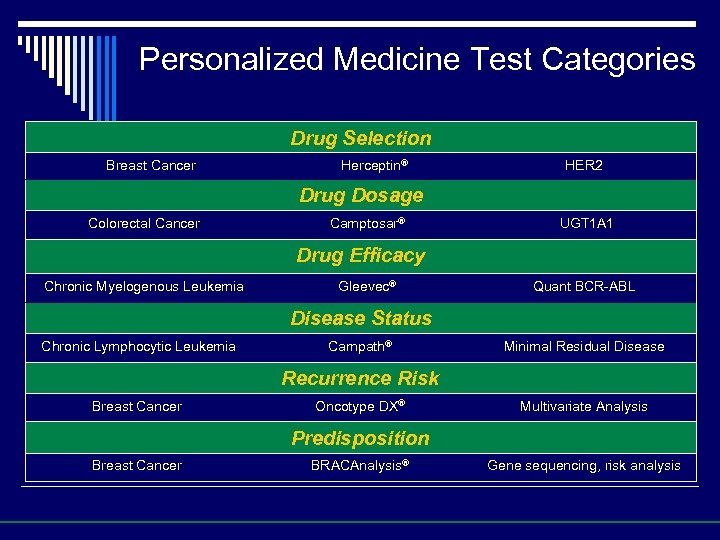 Personalized Medicine Test Categories Drug Selection Breast Cancer Herceptin® HER 2 Drug Dosage Colorectal Cancer Camptosar® UGT 1 A 1 Drug Efficacy Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Gleevec® Quant BCR-ABL Disease Status Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Campath® Minimal Residual Disease Recurrence Risk Breast Cancer Oncotype DX® Multivariate Analysis Predisposition Breast Cancer BRACAnalysis® Gene sequencing, risk analysis
Personalized Medicine Test Categories Drug Selection Breast Cancer Herceptin® HER 2 Drug Dosage Colorectal Cancer Camptosar® UGT 1 A 1 Drug Efficacy Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Gleevec® Quant BCR-ABL Disease Status Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Campath® Minimal Residual Disease Recurrence Risk Breast Cancer Oncotype DX® Multivariate Analysis Predisposition Breast Cancer BRACAnalysis® Gene sequencing, risk analysis
 Personalized Medicine Saves Lives 100 Years Ago 80 Years Ago 60 Years Ago 5 Year Survival “Disease of the Blood” Leukemia or Lymphoma Chronic Leukemia Acute Leukemia Preleukemia Today ~ 0% Indolent Lymphoma Aggressive Lymphoma 38 Leukemia types identified: 51 Lymphomas identified: Acute myeloid leukemia ( 12 types) Mature B-cell lymphomas ( 14 types) Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (2 types) Mature T-cell lymphomas (15 types) Acute promyelocytic leukemia (2 types) Plasma cell neoplasm (3 types) Acute monocytic leukemia (2 types) Immature (precursor) lymphomas (2 types) Acute erythroid leukemia (2 types) Hodgkin’s lymphoma (5 types) Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia Immunodeficiency associated lymphomas Acute myelomonocytic leukemia (2 types) ( 5 types) Chronic myeloid leukemia Other hematolymphoid neoplasms ( 7 types) Chronic myeloproliferative disorders (5 types) Myelodysplastic syndromes (6 types) Mixed myeloproliferative/myelodysplastic syndromes (3 types) 70% Ries LAG, Eisner MP, Kosary CL, Hankey BF, Miller BA, Clegg L, Mariotto A, Feuer EJ, Edwards BK (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975 -2002, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http: //seer. cancer. gov/csr/1975_2002/, based on Nov 2004 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site 2005.
Personalized Medicine Saves Lives 100 Years Ago 80 Years Ago 60 Years Ago 5 Year Survival “Disease of the Blood” Leukemia or Lymphoma Chronic Leukemia Acute Leukemia Preleukemia Today ~ 0% Indolent Lymphoma Aggressive Lymphoma 38 Leukemia types identified: 51 Lymphomas identified: Acute myeloid leukemia ( 12 types) Mature B-cell lymphomas ( 14 types) Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (2 types) Mature T-cell lymphomas (15 types) Acute promyelocytic leukemia (2 types) Plasma cell neoplasm (3 types) Acute monocytic leukemia (2 types) Immature (precursor) lymphomas (2 types) Acute erythroid leukemia (2 types) Hodgkin’s lymphoma (5 types) Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia Immunodeficiency associated lymphomas Acute myelomonocytic leukemia (2 types) ( 5 types) Chronic myeloid leukemia Other hematolymphoid neoplasms ( 7 types) Chronic myeloproliferative disorders (5 types) Myelodysplastic syndromes (6 types) Mixed myeloproliferative/myelodysplastic syndromes (3 types) 70% Ries LAG, Eisner MP, Kosary CL, Hankey BF, Miller BA, Clegg L, Mariotto A, Feuer EJ, Edwards BK (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975 -2002, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, http: //seer. cancer. gov/csr/1975_2002/, based on Nov 2004 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site 2005.
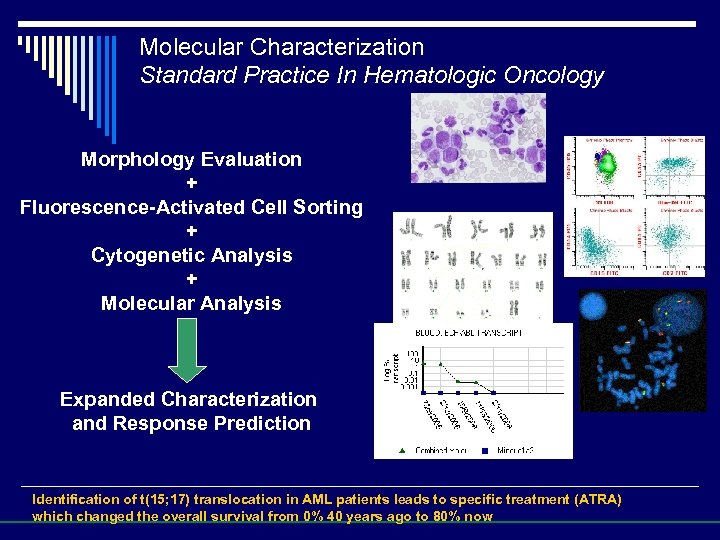 Molecular Characterization Standard Practice In Hematologic Oncology Morphology Evaluation + Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting + Cytogenetic Analysis + Molecular Analysis Expanded Characterization and Response Prediction Identification of t(15; 17) translocation in AML patients leads to specific treatment (ATRA) which changed the overall survival from 0% 40 years ago to 80% now
Molecular Characterization Standard Practice In Hematologic Oncology Morphology Evaluation + Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting + Cytogenetic Analysis + Molecular Analysis Expanded Characterization and Response Prediction Identification of t(15; 17) translocation in AML patients leads to specific treatment (ATRA) which changed the overall survival from 0% 40 years ago to 80% now
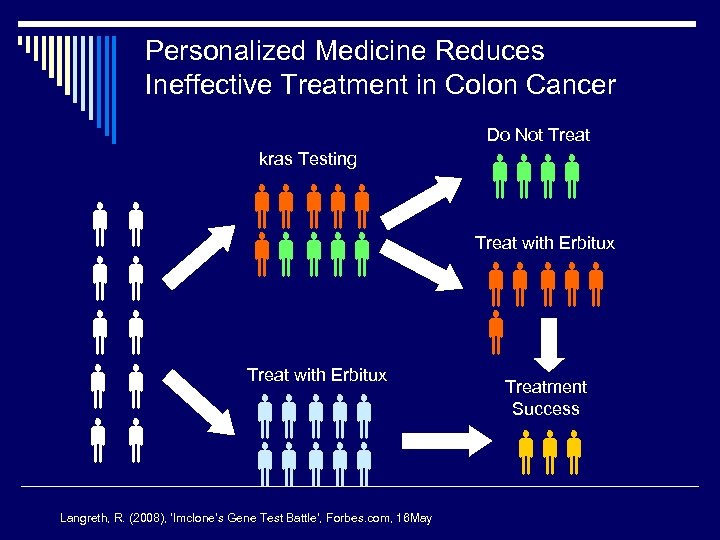 Personalized Medicine Reduces Ineffective Treatment in Colon Cancer Do Not Treat kras Testing Treat with Erbitux Langreth, R. (2008), ‘Imclone’s Gene Test Battle’, Forbes. com, 16 May Treat with Erbitux Treatment Success
Personalized Medicine Reduces Ineffective Treatment in Colon Cancer Do Not Treat kras Testing Treat with Erbitux Langreth, R. (2008), ‘Imclone’s Gene Test Battle’, Forbes. com, 16 May Treat with Erbitux Treatment Success
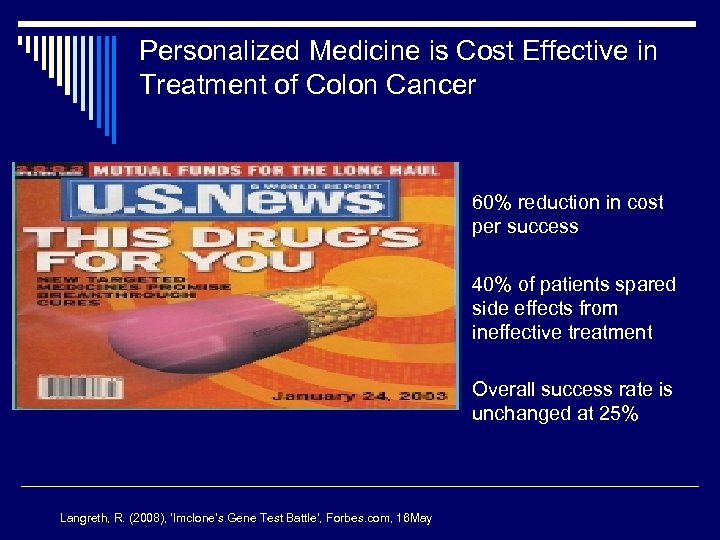 Personalized Medicine is Cost Effective in Treatment of Colon Cancer o 60% reduction in cost per success o 40% of patients spared side effects from ineffective treatment o Overall success rate is unchanged at 25% Langreth, R. (2008), ‘Imclone’s Gene Test Battle’, Forbes. com, 16 May
Personalized Medicine is Cost Effective in Treatment of Colon Cancer o 60% reduction in cost per success o 40% of patients spared side effects from ineffective treatment o Overall success rate is unchanged at 25% Langreth, R. (2008), ‘Imclone’s Gene Test Battle’, Forbes. com, 16 May
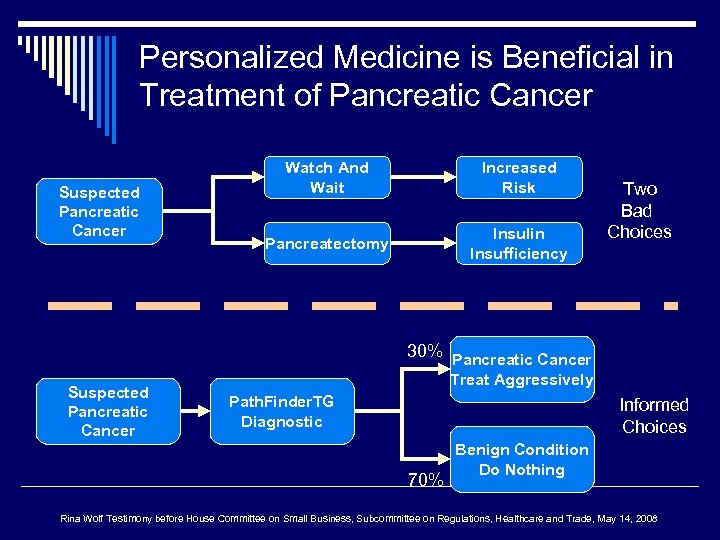 Personalized Medicine is Beneficial in Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer Suspected Pancreatic Cancer Watch And Wait Increased Risk Pancreatectomy Insulin Insufficiency Two Bad Choices 30% Pancreatic Cancer Suspected Pancreatic Cancer Treat Aggressively Path. Finder. TG Diagnostic Informed Choices 70% Benign Condition Do Nothing Rina Wolf Testimony before House Committee on Small Business, Subcommittee on Regulations, Healthcare and Trade, May 14, 2008
Personalized Medicine is Beneficial in Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer Suspected Pancreatic Cancer Watch And Wait Increased Risk Pancreatectomy Insulin Insufficiency Two Bad Choices 30% Pancreatic Cancer Suspected Pancreatic Cancer Treat Aggressively Path. Finder. TG Diagnostic Informed Choices 70% Benign Condition Do Nothing Rina Wolf Testimony before House Committee on Small Business, Subcommittee on Regulations, Healthcare and Trade, May 14, 2008
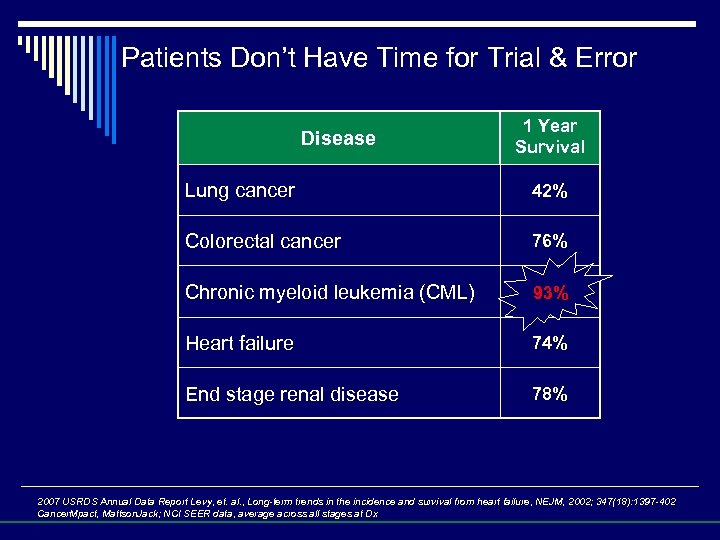 Patients Don’t Have Time for Trial & Error Disease 1 Year Survival Lung cancer 42% Colorectal cancer 76% Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) 63% 93% Heart failure 74% End stage renal disease 78% 2007 USRDS Annual Data Report Levy, et. al. , Long-term trends in the incidence and survival from heart failure, NEJM, 2002; 347(18): 1397 -402 Cancer. Mpact, Mattson. Jack; NCI SEER data, average across all stages at Dx
Patients Don’t Have Time for Trial & Error Disease 1 Year Survival Lung cancer 42% Colorectal cancer 76% Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) 63% 93% Heart failure 74% End stage renal disease 78% 2007 USRDS Annual Data Report Levy, et. al. , Long-term trends in the incidence and survival from heart failure, NEJM, 2002; 347(18): 1397 -402 Cancer. Mpact, Mattson. Jack; NCI SEER data, average across all stages at Dx
 Personalized Medicine - Friend or Foe? o What is it? o Why now? o When will it be real? o Call to Action
Personalized Medicine - Friend or Foe? o What is it? o Why now? o When will it be real? o Call to Action
 Why Now? The Human Genome Project
Why Now? The Human Genome Project
 Why Now? Explosion of the “Omics” o o o o Proteomics Allergenomics Bibliomics Biomics Cardiogenomics Cellomics Chemogenomics Chemoproteomics Chromatinomics Chromosomics Combinatorial Peptidomics Computational RNomics Cryobionomics http: //www. genomicglossaries. com o o o o Crystallomics Cytochromics Cytomics Degradomics Ecotoxicogenomics Eicosanomics Embryogenomics Enviromics Epigenomics Epitomics Expressomics Fluxomics Fragmentomics Fragonomics Etc…
Why Now? Explosion of the “Omics” o o o o Proteomics Allergenomics Bibliomics Biomics Cardiogenomics Cellomics Chemogenomics Chemoproteomics Chromatinomics Chromosomics Combinatorial Peptidomics Computational RNomics Cryobionomics http: //www. genomicglossaries. com o o o o Crystallomics Cytochromics Cytomics Degradomics Ecotoxicogenomics Eicosanomics Embryogenomics Enviromics Epigenomics Epitomics Expressomics Fluxomics Fragmentomics Fragonomics Etc…
 Why Now? Diagnostic Technology Has Improved Past – Macro Level Testing Tests differentiated disease from non-disease Disease defined by location and size Today – Molecular Level Testing Disease defined by individual biology and /or DNA of tumor or virus Tests to subcategorize disease: predict outcomes of specific therapeutic screen for adverse events monitor disease
Why Now? Diagnostic Technology Has Improved Past – Macro Level Testing Tests differentiated disease from non-disease Disease defined by location and size Today – Molecular Level Testing Disease defined by individual biology and /or DNA of tumor or virus Tests to subcategorize disease: predict outcomes of specific therapeutic screen for adverse events monitor disease
 Why Now? Diagnostic Technology Has Improved Tomorrow – Predictive Testing Multiple technology platforms needed for higher analytic validity Multi-factorial testing for common, complex diseases Multi-gene signatures as standard for cancer New Sample Types – Urine, Saliva, Breath, others? Increased Use of Diagnostic Imaging
Why Now? Diagnostic Technology Has Improved Tomorrow – Predictive Testing Multiple technology platforms needed for higher analytic validity Multi-factorial testing for common, complex diseases Multi-gene signatures as standard for cancer New Sample Types – Urine, Saliva, Breath, others? Increased Use of Diagnostic Imaging
 Why Now: Increased Government Interest o FDA n In-vitro Diagnostic Multivariate Index Assay (IVD MIA) Draft Guidance n Pharmacogenomics voluntary data submission o HHS Secretary’s Committee on Genetics, Health and Society (SACGHS) n Report recommending filling gaps in oversight of genetic tests o President’s Council on Science and Technology n Upcoming Report of Personalized Medicine
Why Now: Increased Government Interest o FDA n In-vitro Diagnostic Multivariate Index Assay (IVD MIA) Draft Guidance n Pharmacogenomics voluntary data submission o HHS Secretary’s Committee on Genetics, Health and Society (SACGHS) n Report recommending filling gaps in oversight of genetic tests o President’s Council on Science and Technology n Upcoming Report of Personalized Medicine
 Personalized Medicine - Friend or Foe? o What is it? o Why now? o When will it be real? o Call to Action for Pathologists
Personalized Medicine - Friend or Foe? o What is it? o Why now? o When will it be real? o Call to Action for Pathologists
 The Personalized Medicine Timeline Fear Value Acceptance
The Personalized Medicine Timeline Fear Value Acceptance
 The Personalized Medicine Timeline Fear Payers: Adds to My Cost Without Return Treating Physicians: Too Prescriptive for Me Patients: Will I Be Denied Access to New Drugs? Regulators: How Do We Handle New Complexities? Diagnostics: More Tests With Poor Reimbursement Pharma: Reduces My Market Pathologists: Reduces My Market
The Personalized Medicine Timeline Fear Payers: Adds to My Cost Without Return Treating Physicians: Too Prescriptive for Me Patients: Will I Be Denied Access to New Drugs? Regulators: How Do We Handle New Complexities? Diagnostics: More Tests With Poor Reimbursement Pharma: Reduces My Market Pathologists: Reduces My Market
 Pharma Fear Spending Up but New Drug Approvals Not Pharmaceutical Research and Manufactures of America: Pharmaceutical Industry Profile 2006 www. fda. gof/oc/initiatives/criticalpath/whitepaper. html
Pharma Fear Spending Up but New Drug Approvals Not Pharmaceutical Research and Manufactures of America: Pharmaceutical Industry Profile 2006 www. fda. gof/oc/initiatives/criticalpath/whitepaper. html
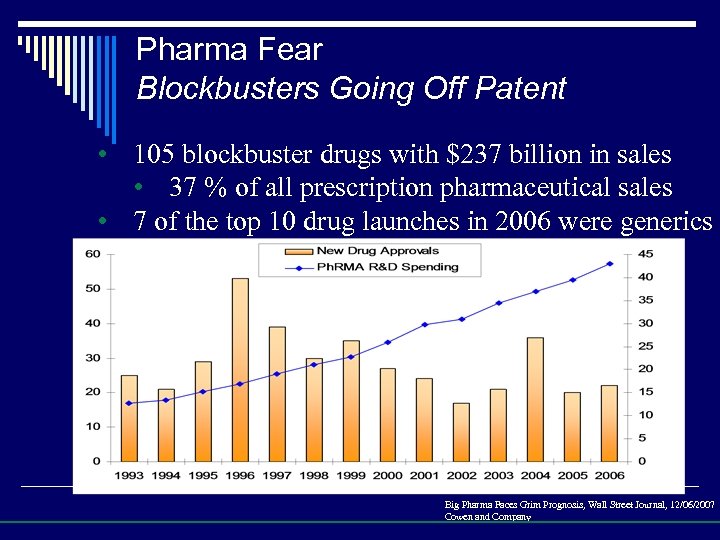 Pharma Fear Blockbusters Going Off Patent • 105 blockbuster drugs with $237 billion in sales • 37 % of all prescription pharmaceutical sales • 7 of the top 10 drug launches in 2006 were generics Big Pharma Faces Grim Prognosis, Wall Street Journal, 12/06/2007 Cowen and Company
Pharma Fear Blockbusters Going Off Patent • 105 blockbuster drugs with $237 billion in sales • 37 % of all prescription pharmaceutical sales • 7 of the top 10 drug launches in 2006 were generics Big Pharma Faces Grim Prognosis, Wall Street Journal, 12/06/2007 Cowen and Company
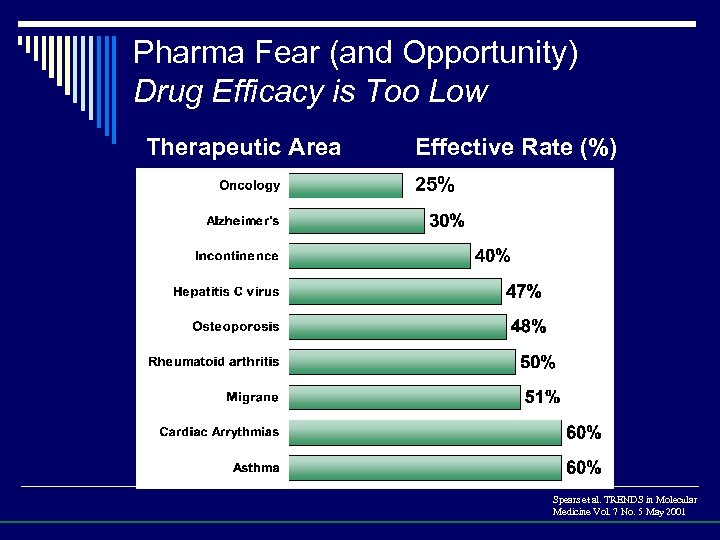 Pharma Fear (and Opportunity) Drug Efficacy is Too Low Therapeutic Area Effective Rate (%) 25% Spears et al. TRENDS in Molecular Medicine Vol. 7 No. 5 May 2001
Pharma Fear (and Opportunity) Drug Efficacy is Too Low Therapeutic Area Effective Rate (%) 25% Spears et al. TRENDS in Molecular Medicine Vol. 7 No. 5 May 2001
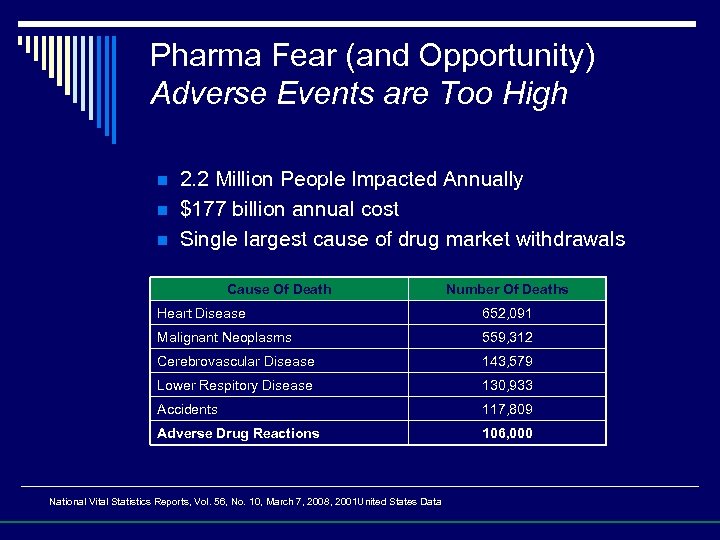 Pharma Fear (and Opportunity) Adverse Events are Too High n n n 2. 2 Million People Impacted Annually $177 billion annual cost Single largest cause of drug market withdrawals Cause Of Death Number Of Deaths Heart Disease 652, 091 Malignant Neoplasms 559, 312 Cerebrovascular Disease 143, 579 Lower Respitory Disease 130, 933 Accidents 117, 809 Adverse Drug Reactions 106, 000 National Vital Statistics Reports, Vol. 56, No. 10, March 7, 2008, 2001 United States Data
Pharma Fear (and Opportunity) Adverse Events are Too High n n n 2. 2 Million People Impacted Annually $177 billion annual cost Single largest cause of drug market withdrawals Cause Of Death Number Of Deaths Heart Disease 652, 091 Malignant Neoplasms 559, 312 Cerebrovascular Disease 143, 579 Lower Respitory Disease 130, 933 Accidents 117, 809 Adverse Drug Reactions 106, 000 National Vital Statistics Reports, Vol. 56, No. 10, March 7, 2008, 2001 United States Data
 Pharma Fear (and Opportunity) Prescription Compliance is Too Low Source: American Heart Association
Pharma Fear (and Opportunity) Prescription Compliance is Too Low Source: American Heart Association
 Pharma Fear (and Opportunity) Drug Reimbursement System Changing? • Reimbursement ONLY if patient benefits from drug • REFUND if patient does not benefit after treatment • Current Examples: • Velcade for multiple myeloma • • • Johnson & Johnson and Government Payors in UK and France Full refund to payor if patient does not achieve 50% biomarker reduction Oncotype DX • • Genomic Health and United Healthcare Price adjusted if tests do not show change in clinical practice Pricing Pills by the Results, New York Times, July 14, 2007
Pharma Fear (and Opportunity) Drug Reimbursement System Changing? • Reimbursement ONLY if patient benefits from drug • REFUND if patient does not benefit after treatment • Current Examples: • Velcade for multiple myeloma • • • Johnson & Johnson and Government Payors in UK and France Full refund to payor if patient does not achieve 50% biomarker reduction Oncotype DX • • Genomic Health and United Healthcare Price adjusted if tests do not show change in clinical practice Pricing Pills by the Results, New York Times, July 14, 2007
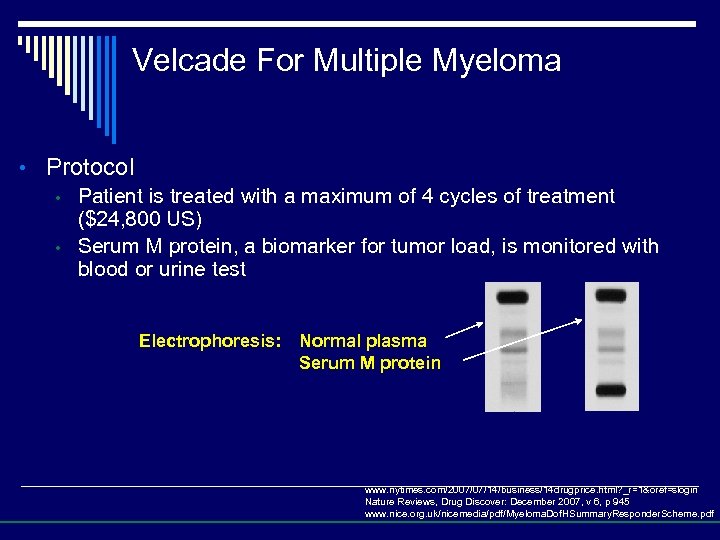 Velcade For Multiple Myeloma • Protocol • Patient is treated with a maximum of 4 cycles of treatment ($24, 800 US) • Serum M protein, a biomarker for tumor load, is monitored with blood or urine test Electrophoresis: Normal plasma Serum M protein www. nytimes. com/2007/07/14/business/14 drugprice. html? _r=1&oref=slogin Nature Reviews, Drug Discover: December 2007, v 6, p 945 www. nice. org. uk/nicemedia/pdf/Myeloma. Dof. HSummary. Responder. Scheme. pdf
Velcade For Multiple Myeloma • Protocol • Patient is treated with a maximum of 4 cycles of treatment ($24, 800 US) • Serum M protein, a biomarker for tumor load, is monitored with blood or urine test Electrophoresis: Normal plasma Serum M protein www. nytimes. com/2007/07/14/business/14 drugprice. html? _r=1&oref=slogin Nature Reviews, Drug Discover: December 2007, v 6, p 945 www. nice. org. uk/nicemedia/pdf/Myeloma. Dof. HSummary. Responder. Scheme. pdf
 Velcade For Multiple Myeloma • • Biomarker is linked to drug efficacy Biomarker results are then linked to payment • Complete response (CR): minimal / no serum M protein - PAID • Partial response (PR): > 50 % reduction of serum M protein – PAID • Minor or Minimal response (MR): < 50 % reduction of serum M protein - REFUND www. nytimes. com/2007/07/14/business/14 drugprice. html? _r=1&oref=slogin Nature Reviews, Drug Discover: December 2007, v 6, p 945 www. nice. org. uk/nicemedia/pdf/Myeloma. Dof. HSummary. Responder. Scheme. pdf
Velcade For Multiple Myeloma • • Biomarker is linked to drug efficacy Biomarker results are then linked to payment • Complete response (CR): minimal / no serum M protein - PAID • Partial response (PR): > 50 % reduction of serum M protein – PAID • Minor or Minimal response (MR): < 50 % reduction of serum M protein - REFUND www. nytimes. com/2007/07/14/business/14 drugprice. html? _r=1&oref=slogin Nature Reviews, Drug Discover: December 2007, v 6, p 945 www. nice. org. uk/nicemedia/pdf/Myeloma. Dof. HSummary. Responder. Scheme. pdf
 Pathologist Fear? New Sample Types Beyond Tissue • Molecular Blood Tests • Breath Tests • Urine Tests
Pathologist Fear? New Sample Types Beyond Tissue • Molecular Blood Tests • Breath Tests • Urine Tests
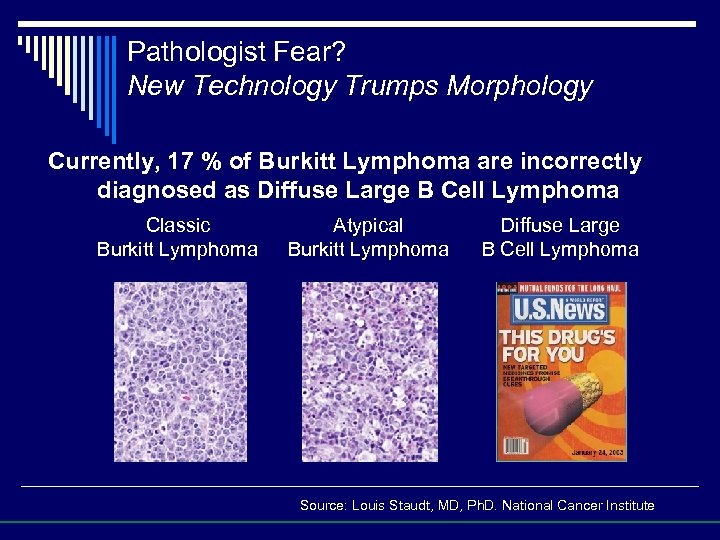 Pathologist Fear? New Technology Trumps Morphology Currently, 17 % of Burkitt Lymphoma are incorrectly diagnosed as Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Classic Burkitt Lymphoma Atypical Burkitt Lymphoma Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Source: Louis Staudt, MD, Ph. D. National Cancer Institute
Pathologist Fear? New Technology Trumps Morphology Currently, 17 % of Burkitt Lymphoma are incorrectly diagnosed as Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Classic Burkitt Lymphoma Atypical Burkitt Lymphoma Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Source: Louis Staudt, MD, Ph. D. National Cancer Institute
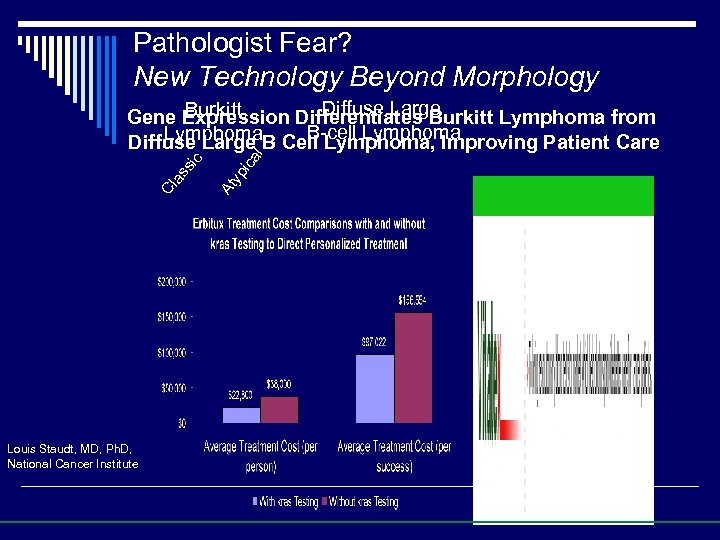 Pathologist Fear? New Technology Beyond Morphology Louis Staudt, MD, Ph. D, National Cancer Institute ca yp i At Cl as sic l Diffuse Large Burkitt Gene Expression Differentiates Burkitt Lymphoma from B-cell Lymphoma Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma, Improving Patient Care
Pathologist Fear? New Technology Beyond Morphology Louis Staudt, MD, Ph. D, National Cancer Institute ca yp i At Cl as sic l Diffuse Large Burkitt Gene Expression Differentiates Burkitt Lymphoma from B-cell Lymphoma Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma, Improving Patient Care
 Pathologist Fear? Molecular Tests are Exploding Source: In Development – Coalition for 21 st Century Medicine Survey 2007
Pathologist Fear? Molecular Tests are Exploding Source: In Development – Coalition for 21 st Century Medicine Survey 2007
 Venture Capital is focused on DX Increased Venture Capital Spending Nature Biotechnology Volume 24 Number 8 August 2006, Bio. Century's BCIQ, Genzyme Analysis
Venture Capital is focused on DX Increased Venture Capital Spending Nature Biotechnology Volume 24 Number 8 August 2006, Bio. Century's BCIQ, Genzyme Analysis
 Pharma and Pathologist Fear and Opportunity FDA Stance On Valid Genomic Biomarkers In The Context of Approved Drug Labels o Drugs with Labels Containing Pharmacogenomic Information – 121 n n Drugs with Tests Required - 2 Drugs with Tests Recommended - 3 Drugs with Tests for Information Only – 16 Drugs with No Test Mentioned – 100 Clinical Ligand Assay Society 32 nd International Meeting Louisville, KY May 22, 2006 Felix W. Frueh, Ph. D Associate Director for Genomics, Office of Clinical Pharmacology CDER/FDA
Pharma and Pathologist Fear and Opportunity FDA Stance On Valid Genomic Biomarkers In The Context of Approved Drug Labels o Drugs with Labels Containing Pharmacogenomic Information – 121 n n Drugs with Tests Required - 2 Drugs with Tests Recommended - 3 Drugs with Tests for Information Only – 16 Drugs with No Test Mentioned – 100 Clinical Ligand Assay Society 32 nd International Meeting Louisville, KY May 22, 2006 Felix W. Frueh, Ph. D Associate Director for Genomics, Office of Clinical Pharmacology CDER/FDA
 Personalized Medicine - Friend or Foe? o What is it? o Why now? o When will it be real? o Call to Action
Personalized Medicine - Friend or Foe? o What is it? o Why now? o When will it be real? o Call to Action
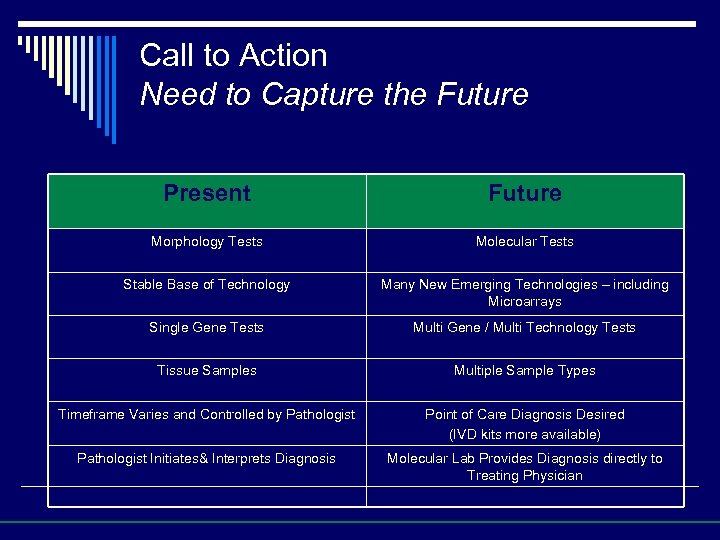 Call to Action Need to Capture the Future Present Future Morphology Tests Molecular Tests Stable Base of Technology Many New Emerging Technologies – including Microarrays Single Gene Tests Multi Gene / Multi Technology Tests Tissue Samples Multiple Sample Types Timeframe Varies and Controlled by Pathologist Point of Care Diagnosis Desired (IVD kits more available) Pathologist Initiates& Interprets Diagnosis Molecular Lab Provides Diagnosis directly to Treating Physician
Call to Action Need to Capture the Future Present Future Morphology Tests Molecular Tests Stable Base of Technology Many New Emerging Technologies – including Microarrays Single Gene Tests Multi Gene / Multi Technology Tests Tissue Samples Multiple Sample Types Timeframe Varies and Controlled by Pathologist Point of Care Diagnosis Desired (IVD kits more available) Pathologist Initiates& Interprets Diagnosis Molecular Lab Provides Diagnosis directly to Treating Physician
 Call to Action Friend or Foe? Personalized Medicine Needs to be a Friend Pathologists Need to : - Own Personalized Medicine - Source of expertise on all tests available - Interpreter and consolidator of all test results - Educator of all other physicians on diagnosis Move Industry from Fear to Acceptance
Call to Action Friend or Foe? Personalized Medicine Needs to be a Friend Pathologists Need to : - Own Personalized Medicine - Source of expertise on all tests available - Interpreter and consolidator of all test results - Educator of all other physicians on diagnosis Move Industry from Fear to Acceptance
 Moving From Fear To Acceptance o Physician Education o Data – Integration into the EHR / EMR o Policy – Reimbursement and Regulatory Aspinall and Hamermesh, Harvard Business Review, Oct 2007
Moving From Fear To Acceptance o Physician Education o Data – Integration into the EHR / EMR o Policy – Reimbursement and Regulatory Aspinall and Hamermesh, Harvard Business Review, Oct 2007
 Move From Fear to Acceptance o Physician Education n Build commitment through education for community physicians n Publish new PM practice guidelines – tests and technologies o Data & Integration into EHR n Create Convincing Data on the positive outcomes and health economics of appropriate use of PM diagnostics n Leadership in the build of the EHR / EMR o Policies Needed n Reimbursement based on value rather than activity n Regulatory options that encourage diagnostic and drug combinations o Embrace “Era of Diagnostics” For Improved Outcomes
Move From Fear to Acceptance o Physician Education n Build commitment through education for community physicians n Publish new PM practice guidelines – tests and technologies o Data & Integration into EHR n Create Convincing Data on the positive outcomes and health economics of appropriate use of PM diagnostics n Leadership in the build of the EHR / EMR o Policies Needed n Reimbursement based on value rather than activity n Regulatory options that encourage diagnostic and drug combinations o Embrace “Era of Diagnostics” For Improved Outcomes
 Move From Fear to Acceptance o Physician Education – PATHOLOGIST LEAD n Build commitment through education for community physicians n Publish new PM practice guidelines – tests and technologies o Data & Integration into EHR – PATHOLOGIST LEAD n Create Convincing Data on the positive outcomes and health economics of appropriate use of PM diagnostics n Leadership in the build of the EHR / EMR o Policies Needed – PATHOLOGIST LEAD n Reimbursement based on value rather than activity n Regulatory options that encourage diagnostic and drug combinations o Embrace “Era of Diagnostics” For Improved Outcomes
Move From Fear to Acceptance o Physician Education – PATHOLOGIST LEAD n Build commitment through education for community physicians n Publish new PM practice guidelines – tests and technologies o Data & Integration into EHR – PATHOLOGIST LEAD n Create Convincing Data on the positive outcomes and health economics of appropriate use of PM diagnostics n Leadership in the build of the EHR / EMR o Policies Needed – PATHOLOGIST LEAD n Reimbursement based on value rather than activity n Regulatory options that encourage diagnostic and drug combinations o Embrace “Era of Diagnostics” For Improved Outcomes
 Call to Action Opportunities… • • Expand scope of practice Increase impact on patient treatment Institutional Knowledge Coordinator Cutting edge expertise • Leadership in Personalized Medicine – it is here to stay
Call to Action Opportunities… • • Expand scope of practice Increase impact on patient treatment Institutional Knowledge Coordinator Cutting edge expertise • Leadership in Personalized Medicine – it is here to stay
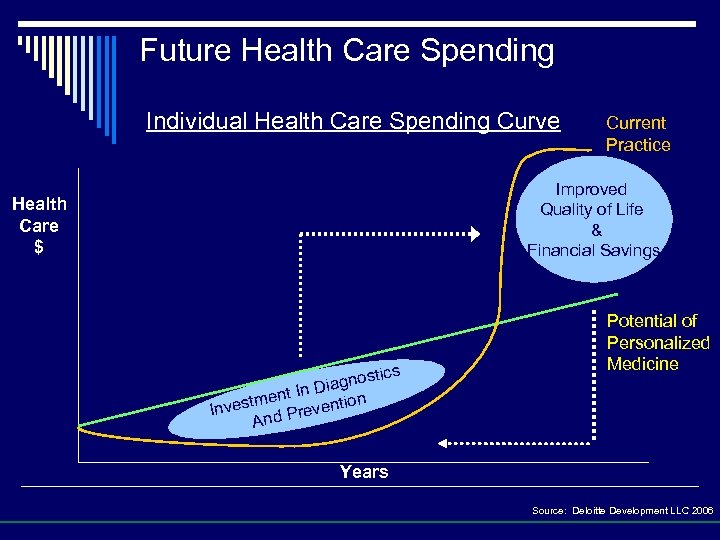 Future Health Care Spending Individual Health Care Spending Curve Current Practice Improved Quality of Life & Financial Savings Health Care $ stics iagno In D tment vention Inves d Pre An Potential of Personalized Medicine Years Source: Deloitte Development LLC 2006
Future Health Care Spending Individual Health Care Spending Curve Current Practice Improved Quality of Life & Financial Savings Health Care $ stics iagno In D tment vention Inves d Pre An Potential of Personalized Medicine Years Source: Deloitte Development LLC 2006
 Acknowledgements o David Turnquist, Boston College o Deloitte Center for Health Solutions o Personalized Medicine Coalition
Acknowledgements o David Turnquist, Boston College o Deloitte Center for Health Solutions o Personalized Medicine Coalition
 TRANSFORMING PATHOLOGY: Emerging technology driving practice innovation
TRANSFORMING PATHOLOGY: Emerging technology driving practice innovation


