84019f7ae2e7d7a59b921189cc373235.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Transaction I 02/23/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Transaction I 02/23/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Outline n n Transaction and OLTP Designed properties of transactions 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Outline n n Transaction and OLTP Designed properties of transactions 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Transaction n A multi-billion dollar business OLTP http: //www. tpc. org/default. asp 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Transaction n A multi-billion dollar business OLTP http: //www. tpc. org/default. asp 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Transaction Definition n n A unit of program execution that accesses and possibly updates various data items Transactions? ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Book an airline ticket from DFW to Paris Buy “The Dilbert Principle” from amazon. com Sell 1000 shares of LU from your ameritrade account Withdraw $100 from a ATM machine Issue a SQL statement to sqlplus of Oracle 9 i Look at your grade of homework 3 Check out your groceries at Walmart 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Transaction Definition n n A unit of program execution that accesses and possibly updates various data items Transactions? ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Book an airline ticket from DFW to Paris Buy “The Dilbert Principle” from amazon. com Sell 1000 shares of LU from your ameritrade account Withdraw $100 from a ATM machine Issue a SQL statement to sqlplus of Oracle 9 i Look at your grade of homework 3 Check out your groceries at Walmart 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Challenges to Maintain Transactions n Hardware failures ¡ ¡ n Software failures ¡ ¡ n Programming errors System crash… User interference ¡ n Cashed stuck in ATM machine Power failure… Termination of transactions Concurrent users ¡ Multiple users accessing the same item 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Challenges to Maintain Transactions n Hardware failures ¡ ¡ n Software failures ¡ ¡ n Programming errors System crash… User interference ¡ n Cashed stuck in ATM machine Power failure… Termination of transactions Concurrent users ¡ Multiple users accessing the same item 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Designed Properties of Database Systems n n Atomicity Consistency Isolation Durability 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Designed Properties of Database Systems n n Atomicity Consistency Isolation Durability 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Atomicity n n Transaction needs to be executed as a unit Example ¡ n You should not cause the quantity of “The Dilbert Principle” of amazon. com decrease if you place your order and the order does not get through due to server errors Who are responsible for atomicity? ¡ ¡ Transaction management system and Recovery system 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Atomicity n n Transaction needs to be executed as a unit Example ¡ n You should not cause the quantity of “The Dilbert Principle” of amazon. com decrease if you place your order and the order does not get through due to server errors Who are responsible for atomicity? ¡ ¡ Transaction management system and Recovery system 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Consistency n n Database implicit/explicit constraints need to be maintained Example: ¡ n Transferring money from one account to another in the same bank should not change your total amount of money Who are responsible for consistency? ¡ ¡ Transaction management system and Programmer 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Consistency n n Database implicit/explicit constraints need to be maintained Example: ¡ n Transferring money from one account to another in the same bank should not change your total amount of money Who are responsible for consistency? ¡ ¡ Transaction management system and Programmer 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Isolation n n Transaction A should not see partial results of transaction B Analogy: ¡ n When I update my website here and there, you should not see and think a tentative version as my final version Who are responsible for isolation? ¡ Transaction management system 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Isolation n n Transaction A should not see partial results of transaction B Analogy: ¡ n When I update my website here and there, you should not see and think a tentative version as my final version Who are responsible for isolation? ¡ Transaction management system 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Durability n n Any transaction committed needs to be in database for ever Example: ¡ After you get the receipt of the water melon you buy from Alberson, the transaction is final and permanently reflected in the database system n n If you want to cancel it, that is another transaction Who are responsible for durability? ¡ ¡ Transaction management system and Recovery system 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Durability n n Any transaction committed needs to be in database for ever Example: ¡ After you get the receipt of the water melon you buy from Alberson, the transaction is final and permanently reflected in the database system n n If you want to cancel it, that is another transaction Who are responsible for durability? ¡ ¡ Transaction management system and Recovery system 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
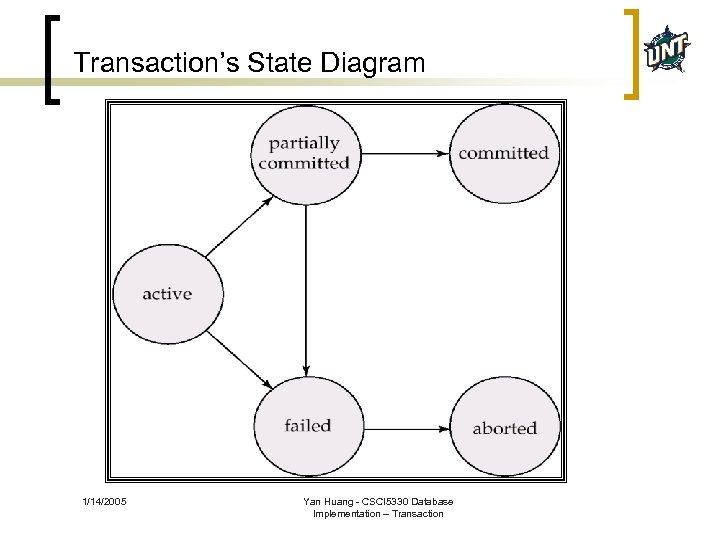 Transaction’s State Diagram 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Transaction’s State Diagram 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 An Ideal World n n No hardware failures No software failures No programming errors Do we still need transaction management? 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
An Ideal World n n No hardware failures No software failures No programming errors Do we still need transaction management? 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Why Concurrent Transactions? n n Parallelism Improved response time 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Why Concurrent Transactions? n n Parallelism Improved response time 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Schedule n Schedules – sequences that indicate the chronological order in which instructions of concurrent transactions are executed ¡ ¡ a schedule for a set of transactions must consist of all instructions of those transactions must preserve the order in which the instructions appear in each individual transaction. 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Schedule n Schedules – sequences that indicate the chronological order in which instructions of concurrent transactions are executed ¡ ¡ a schedule for a set of transactions must consist of all instructions of those transactions must preserve the order in which the instructions appear in each individual transaction. 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
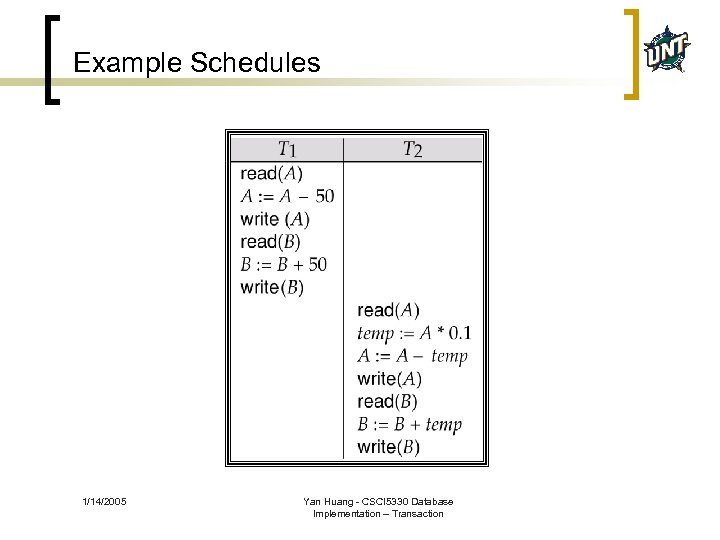 Example Schedules 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Example Schedules 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
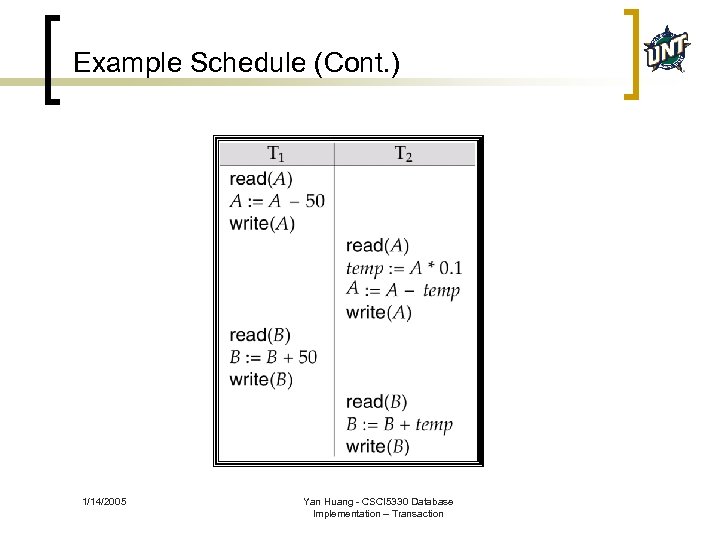 Example Schedule (Cont. ) 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Example Schedule (Cont. ) 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
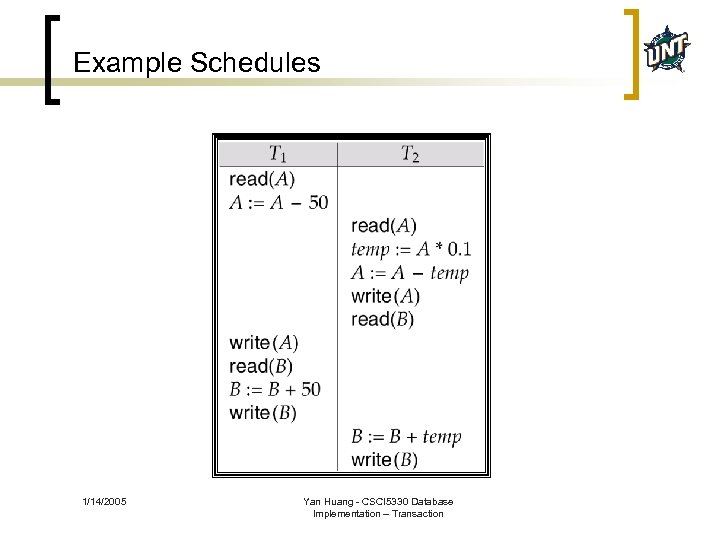 Example Schedules 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Example Schedules 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
 Concurrency Control n Some schedules are bad because the outcome of the schedule is not “predictable” 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction
Concurrency Control n Some schedules are bad because the outcome of the schedule is not “predictable” 1/14/2005 Yan Huang - CSCI 5330 Database Implementation – Transaction


