4b017ef8f3b8cb822b87b879beee8cb5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63

Training Module 1 A Patent Basics ip 4 inno 1 3/15/2018

Goals for Today You will: • Gain an insight into patent functions • Gain an insight into patent process • Gain an insight into patent strategies • Learn about the roles of important partners • Briefly be introduced to supplementary protection possibilities ip 4 inno 2 3/15/2018

Programme • Patent – definitions and demands • Patent document • Patent process • Patent strategies • Utility models • Other supplementary rights and certificates • Case ip 4 inno 3 3/15/2018

Registered intellectual property IP rights with a certificate Utility models Patents Duration: until 10 years Duration: 20 until years Designs Trademarks Duration: until 5 x 5 years Duration: until 10 years or life ip 4 inno 4 3/15/2018

Examples of unregistered IP Literature Pieces of music Paintings Drawings Films Construction works and scientific and technical representations Unregistered IP = Copy right The right will be in force until 70 years after the death of the originator Trademarks and designs can be unregistered as well ip 4 inno 5 3/15/2018

Patents Definitions and Demands ip 4 inno 6 3/15/2018

What is a Patent? You can say it is: • An agreement between the inventor and society Alternative definition (legal): • A patent is an exclusive right to commercially exploit the invention in this country. Protection up to 20 years • A patent is a prohibitive right ip 4 inno 7 3/15/2018

Prohibitive right A patent forbid others commercially to: – produce, sell, work, use, import and possess the invention But… …A patent does not extend to: – acts performed for non-commercial purposes – acts performed for experimental purposes – Acts concerning products which are commercially worked by, or with the consent of, the patentee – Individual production of a medicinal product at a pharmacy ip 4 inno 8 3/15/2018
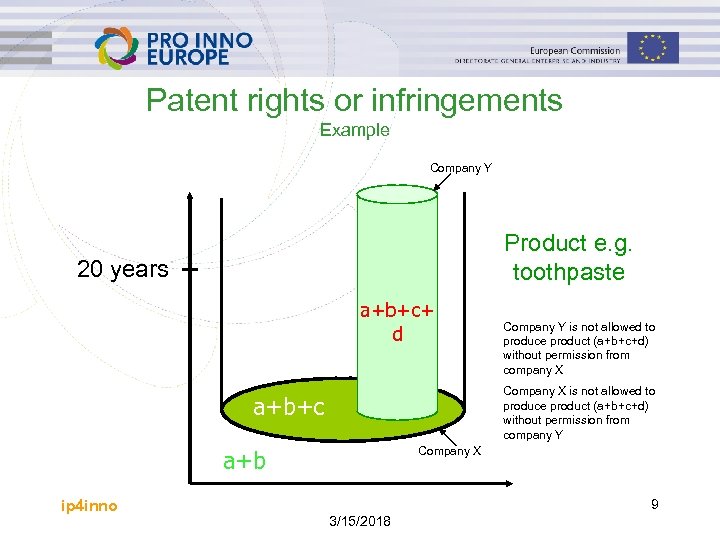
Patent rights or infringements Example Company Y Product e. g. toothpaste 20 years a+b+c+ d Company X is not allowed to produce product (a+b+c+d) without permission from company Y a+b+c Company X a+b ip 4 inno Company Y is not allowed to produce product (a+b+c+d) without permission from company X 9 3/15/2018
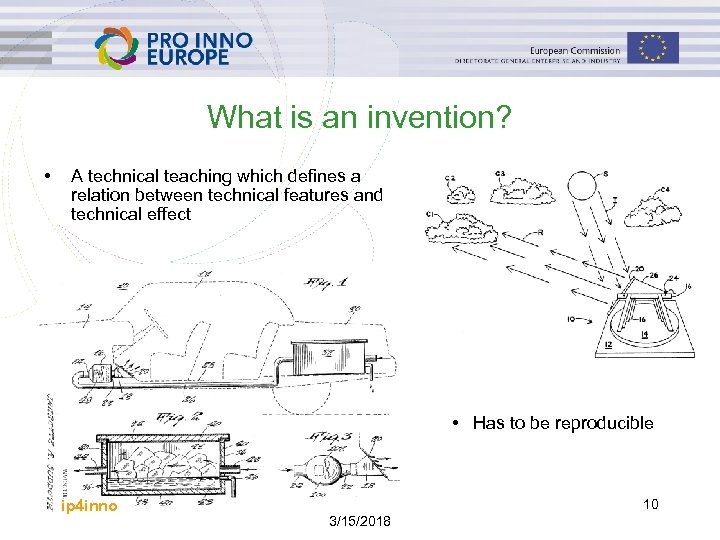
What is an invention? • A technical teaching which defines a relation between technical features and technical effect • Has to be reproducible ip 4 inno 10 3/15/2018

A patentable invention must be: • Capable of industrial application • New / Novelty • Essentially differ from that which is already known = inventive step ip 4 inno 11 3/15/2018

What can be patented? • A product • The apparatus for producing the product • The process for producing the product • The use of the product ip 4 inno 12 3/15/2018

What cannot be patented? • Computer programmes • Medical and surgical treatments • Mathematical methods • Business methods • Discoveries • Aesthetic creations • New species of plant or animal • Inventions which are contrary to moral standards and public order (e. g. instruments of torture) • The human body and any non-separate part/s thereof ip 4 inno 13 3/15/2018

Industrial Application • The invention must have at least one practical purpose and must be reproducible • There is no evaluation of quality or economical factors! • Only the technical qualities are relevant ip 4 inno 14 3/15/2018

Novelty • Novelty: An objective, global demand • New in relation to that which is known prior to the date of filing the application • Known = general availability through the written word, spoken word (lectures, etc. ), usage, etc. ip 4 inno 15 3/15/2018

The Inventive Step To differ essentially = Inventive step = Not obvious to a person skilled in the art ip 4 inno 16 3/15/2018

Patent Document ip 4 inno 17 3/15/2018
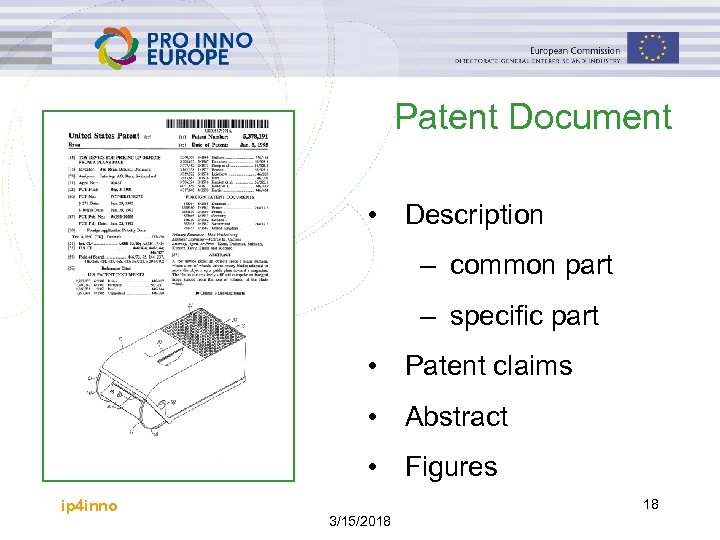
Patent Document • Description – common part – specific part • Patent claims • Abstract • Figures ip 4 inno 18 3/15/2018

The Patent’s Composition Dema nds Title Drawings 1. Title 2. Description – common part – what the patent concerns – prior art, the disadvantages – the purpose and advantages of the invention – how and by which means the advantages are achieved must correspond with the patent claims – mode of operation, by means of which describes how the inventive effect is achieved ip 4 inno 19 3/15/2018

The Patent’s Composition cont. 3. 4. 5. Description specific part, and any figures – detailed technical description with specific explanation of embodiment with reference to any figures Claims – independent claim/s apparatus method use of. . . product – dependent claim/s Abstract ip 4 inno 20 3/15/2018

Patent Process ip 4 inno 21 3/15/2018

The Patent Process (simplified) Application Examination for official secrets Application refused Formal examination Storage Search and examination Decision Application approved Publication A Further examination ip 4 inno Publication B Opposition Expiration after max. 20 years 22 3/15/2018
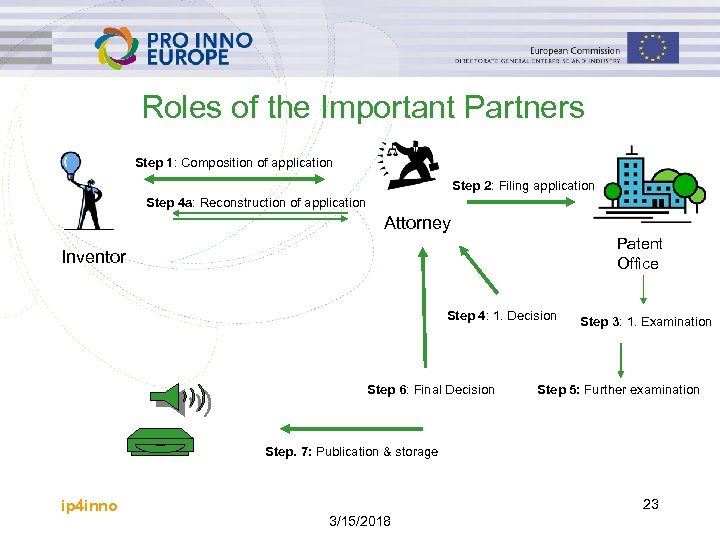
Roles of the Important Partners Step 1: Composition of application Step 2: Filing application Step 4 a: Reconstruction of application Attorney Patent Office Inventor Step 4: 1. Decision Step 6: Final Decision Step 3: 1. Examination Step 5: Further examination Step. 7: Publication & storage ip 4 inno 23 3/15/2018

Patent Strategy ip 4 inno 24 3/15/2018

Why apply for a patent? To: • Provide insurance for one’s invention and investments in developing technology • Prevent others from patenting the invention and secure one’s place in the market • Attract investors for further development, and to hold on to current investors • Sell the patent rights in the future as a single commodity or business • Marketing value ip 4 inno 25 3/15/2018

Patent Strategy Options: • Patent protection – national patent – international patent application – regional patent system • Concealment • Patent prophylaxis – publication ip 4 inno 26 3/15/2018
Patents ip 4 inno 27 3/15/2018

Which Type of Patent? National patent can be used: • For protection in the home country market or in a few countries • As a basis for extending protection to other countries or regions International patent applications can be used: • For protection in many countries and for extending the prepublication period (up to 30 months) Regional patent can be used: • For protection in a number of countries in the same region at a lower cost ip 4 inno 28 3/15/2018

International Patent Systems Basic principle: • Patent in each country The systems: • Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) • European Patent Convention (EPC) • Other regional systems (OAPI, ARIPO, EURASIAN) ip 4 inno 29 3/15/2018

Priority Within 1 year from filing you can: â File your application in other countries with inclusion of priority established in the first country of filing the application For patent applications this means that: â ip 4 inno Novelty is valid from the application filing date of the first country 30 3/15/2018

European Patent Convention (EPC) • Single place of filing • Single place of completion • Single place of granting EPO • More economical than group of countries ip 4 inno 31 3/15/2018

Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) • International novelty and patentability search • Single place of filing • Final decision for countries Main advantages: • One application place • One set of rules • Postponement for 30/31 months from priority date and by that buying time! ip 4 inno 32 3/15/2018
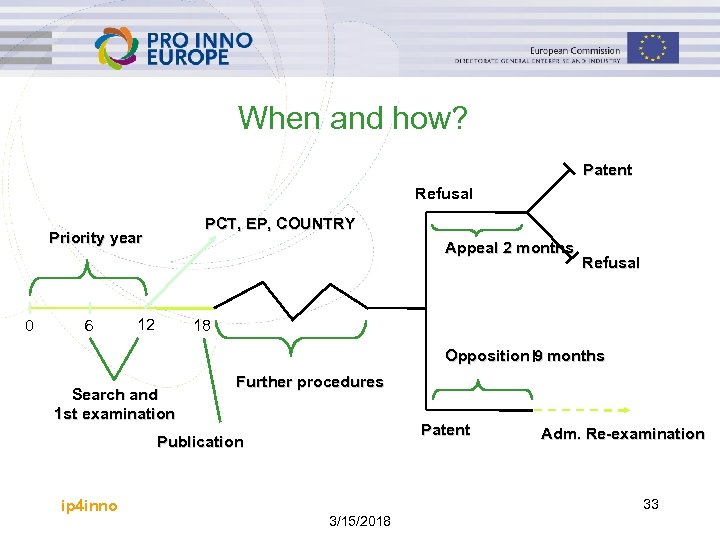
When and how? Patent Refusal PCT, EP, COUNTRY Priority year 0 6 Appeal 2 months 12 Refusal 18 Opposition 9 months Search and 1 st examination Further procedures Patent Publication ip 4 inno Adm. Re-examination 33 3/15/2018

PCT system - Important Dates ip 4 inno 34 3/15/2018

PCT Organisation - units Application RO/NO ISA RO/IB Functions: 1. Performs Search and opinion 1. Publication of ISR+WO 2. Transmits ISR+WO to IB and applicant Functions: 1. Collect fees 2. Receive appl. 3. Check formality 4. IB Transmits record copy to IB and search copy to ISA Demand? IB NO Functions: YES 1. Establish IPRP and send to designated offices IB Functions: RO/IB = Receiving office is International Bureau (WIPO) ISA = International searching authority 1. Transmit copy of demand to IB+notify applicant 2. Performs WO/IPER 3. RO/NO = Receiving office is national office Functions: 1. IB = International bureau (WIPO) IPEA Transmit IPER to IB and applicant Transmit IPER to elected offices IPEA = International preliminary examination authority ip 4 inno 35 3/15/2018
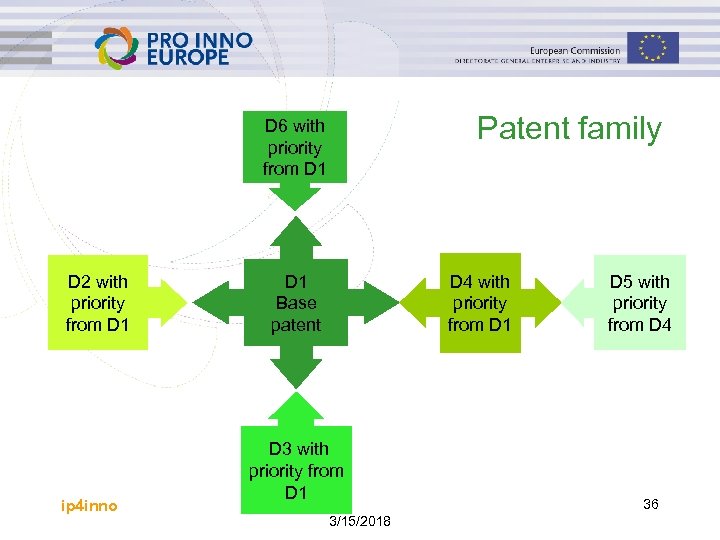
Patent family D 6 with priority from D 1 D 2 with priority from D 1 ip 4 inno D 1 Base patent D 4 with priority from D 1 D 3 with priority from D 1 3/15/2018 D 5 with priority from D 4 36

Utility Models ip 4 inno 37 3/15/2018

Utility Model • The ”Patent-system” for smaller inventions • Conditions: – solve a technical problem – new – inventive step (in some countries e. g. Turkey not necessary) • Often used for inventions concerning: – household goods – hand tools – furniture ip 4 inno 38 3/15/2018

The utility model It looks like a patent. The U in the publication number marks the utility model U as - utility - utilité - utilidad - utilità ip 4 inno 39 3/15/2018

The utility model is similar to a patent Similar in terms that: – a utility model is an exclusive right – allows the right holder to prevent others from commercially using the protected invention – may also be sold or licensed – within 12 months a national utility model application can be turned into a European patent application, if the utility model application fits to the requirements of the European patent application ip 4 inno 40 3/15/2018

Example of utility model ip 4 inno 41 3/15/2018

The utility model is similar to a patent but … – – – the lifetime is only 10 years granted within a few months may be granted without examination (e. g. in Germany) the fees for application and maintenance are cheaper it only protects products NOT processes A product … The assembling of … can be protected ip 4 inno cannot be protected 42 3/15/2018

The utility model and the concept of novelty • • • The nature of an invention is that it is new Normally, new means new to the world Concerning the patent law new means "does not form part of state of the art" which is in accordance with our understanding of novelty • In contrast to a patent, in some countries the novelty requirement to obtain a utility model is "relative" (e. g. Germany, Spain) – only a public written disclosure of the invention in Spain/Germany is prejudicial against the novelty of the invention – in Germany a description within the 6 months preceding the date relevant for the priority of the application shall not be taken into consideration if it is based on the conception of the applicant or his predecessor in title. ip 4 inno 43 3/15/2018

Some possible consequences from the "relative" novelty requirement Assume that a certain canvas chair is used at a hotel pool in Croatia. The chair is not described in public prints, especially not in Germany or Spain. Utility models may be granted for the same canvas chair in Germany and Spain. ip 4 inno 44 3/15/2018

Where can utility models be acquired? Countries and regions providing utility model protection are: Australia Argentina Armenia Austria ARIPO Belarus Belgium Brazil Bulgaria China Colombia Costa Rica Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Ethiopia Finland (France)* Georgia Germany Greece Guatemala Hungary Ireland Italy Japan Kazakhstan Kenya Kyrgyzstan Malaysia Mexico Netherlands OAPI Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Republic of Korea Republic of Moldova Russian Federation Slovakia Spain Tajikistan Trinidad & Tobago Turkey Ukraine Uruguay Uzbekistan Source: http: //www. wipo. int/sme/en/ip_business/utility_models/where. htm ip 4 inno 45 3/15/2018

Why a Utility Model? • • • Protects minor inventions excluded from patent protection Protects inventions where a shorter protection period is required Speedy protection Easy Cheap Use utility model as a strategic weapon - example: In DK the furniture industry uses utility models to ”pack in” patents. If one company has a patent for e. g. a chair, a number of competitors will file utility model applications with tiny developments of the chair. The patent holder cannot change his chair in any way without infringing the utility models. Hence he has to make a licence agreement or buy the utility models from his competitors! ip 4 inno 46 3/15/2018

Other Supplementary Rights and Certificates (1) Plant Varieties – Objects of Verification • Varieties of all botanical genera and species, including, inter alia, hybrids between genera or species • Variety – a plant grouping within a single botanical taxon of the lowest known rank ip 4 inno 47 3/15/2018

Other Supplementary Rights and Certificates (2) Supplementary Protection Certificates for products which constitute: • The “active ingredient”, or combination of active ingredients, of a “medicinal product”; or • The “active substance”, or combination of active substances, of a “plant protection product” ip 4 inno 48 3/15/2018

Patent and Business Is my invention new? What is state of the art? Which solutions already exist? Am I free to use or do I infringe someone’s patent? ip 4 inno Who are my competitors, or potential partners and what do they do? What’s going on in a specific technical field? 49 3/15/2018

Links • www. epo. org (European Patent Office) • www. wipo. int (World Intellectual Property Office) • www. uspto. gov/patft/ (US Patent and Trademark Office) • www. espacenet. com (Europe’s network of patent databases) ip 4 inno 50 3/15/2018

Discussion A general discussion of today’s topics ip 4 inno 51 3/15/2018

CASE ip 4 inno 52 3/15/2018

Øvelse Patenting a reflecting bike tape ip 4 inno 53 3/15/2018

Reflective tape 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe the construction of the tape. What is new – compared to already known tapes. If new – what is patentable ? Set up a claim ip 4 inno 54 3/15/2018

Example of a claim Bike clip or tape including an oblong flexible sleeve characterized by the spring function of the sleeve, which without external influence keeps the tape coiled in a cylindrical roll with overlapping ends. ip 4 inno 55 3/15/2018
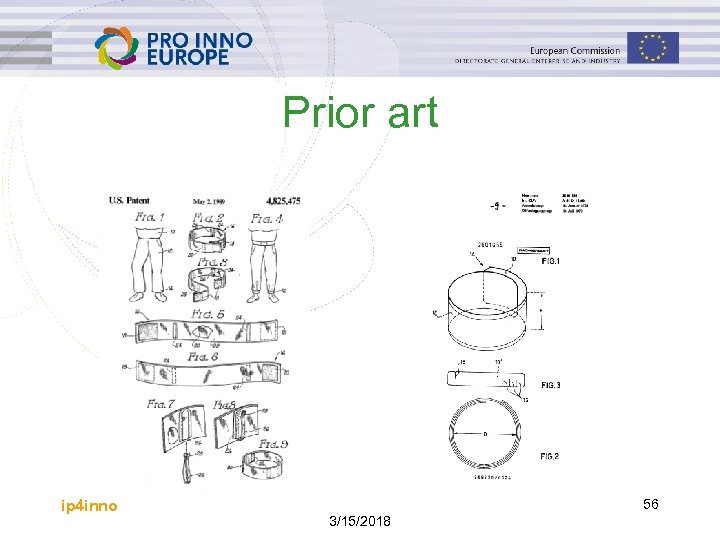
Prior art ip 4 inno 56 3/15/2018

Reflective bike tape Invention: Reflective bike tape Technical remedies: Known technique 1 technique 2 US 4 825 475 + Bike clips or tape DE 28 01 655 + Flexible cuff + Encapsulated spring function + + Coils by external action + + Overlapping ends + + Technical functions: Reaches around an arm or a leg Unaided attached ip 4 inno + 57 3/15/2018
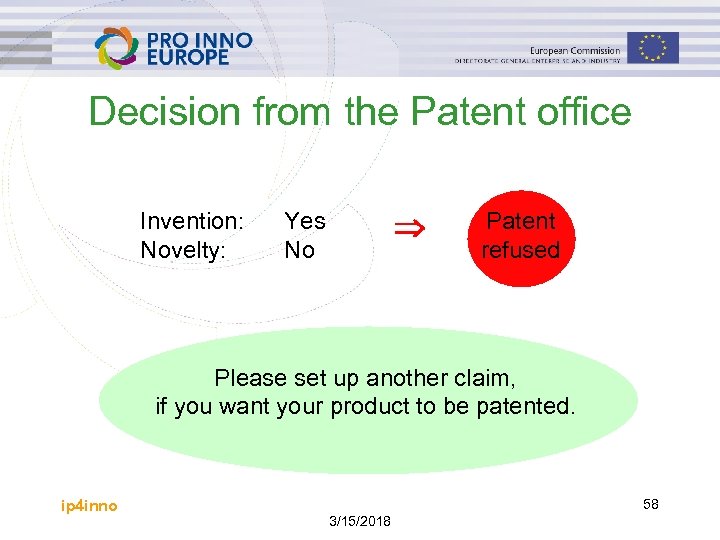
Decision from the Patent office Invention: Novelty: Yes No Patent refused Please set up another claim, if you want your product to be patented. ip 4 inno 58 3/15/2018

Renewed Analysis Does the invention still have any patentable left? • Check of the revealed material: – does it fit with the impression of relevant techniques at the applicant ? – problems / weaknesses by the revealed technique compared to the invention. • Has any important features about the invention been overseen by the patent office ? • Elaboration of reply. Changes in application, explanation of the invention in relation to the revealed material ip 4 inno 59 3/15/2018

Example of claim(s) 1. Bike clip or tape including an oblong flexible sleeve characterized by the spring function of the sleeve, which without external influence keeps the tape coiled in a cylindrical roll with overlapping ends. 2. Bike clip or tape according to claim 1 characterized by the spring function established by a core of bistable spring material which allows the tape to be stable in the outstretched plane state. ip 4 inno 60 3/15/2018
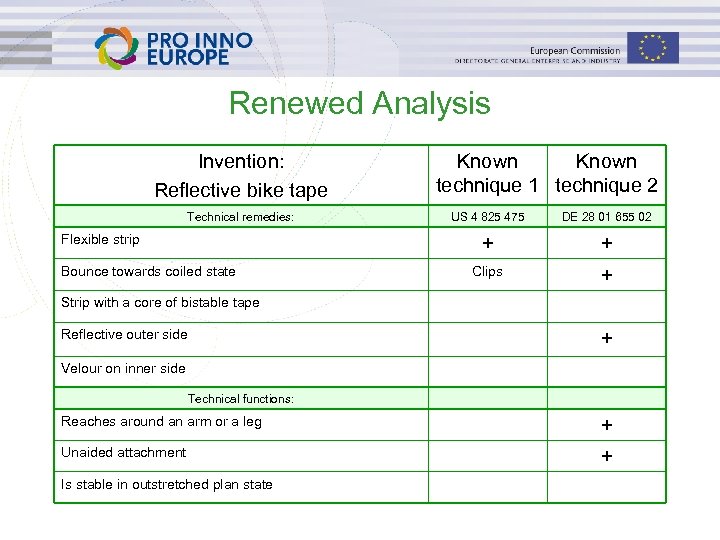
Renewed Analysis Invention: Reflective bike tape Technical remedies: Known technique 1 technique 2 Bounce towards coiled state DE 28 01 655 02 + Flexible strip US 4 825 475 + Clips + Strip with a core of bistable tape Reflective outer side + Velour on inner side Technical functions: Reaches around an arm or a leg + Unaided attachment + Is stable in outstretched plan state

Decision from the Patent office Invention: Yes Novelty: Yes Patent Granted ip 4 inno 62 3/15/2018

THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION ip 4 inno 63 3/15/2018
4b017ef8f3b8cb822b87b879beee8cb5.ppt