d20f1982f87d40e24fcd0db4947e73ba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 138
 Traditional Remedies for Clinical Trials and Healthcare Information: Patient Care Data in Support of Clinical Research Liora Alschuler, Landen Bain, Rebecca Kush, Ph. D, Meredith Nahm, Roberto Ruggeri December, 2003 copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial http: //www. idealliance. org/proceedings/xml 03/slides/alschuler&bain. ppt
Traditional Remedies for Clinical Trials and Healthcare Information: Patient Care Data in Support of Clinical Research Liora Alschuler, Landen Bain, Rebecca Kush, Ph. D, Meredith Nahm, Roberto Ruggeri December, 2003 copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial http: //www. idealliance. org/proceedings/xml 03/slides/alschuler&bain. ppt
 – alschuler. spinosa, consultants – Co-chair HL 7 Structured Documents TC & Marketing Committee – Co-editor, Clinical Document Architecture (ANSI/HL 7 CDA) – liora@the-word-electric. com • Landen Bain – CDISC Board – Co-chair HL 7 Marketing Committee • Rebecca Kush, Ph. D – Founder and President, CDISC • Meredith Nahm – Manager, Clinical Data Management, Duke Clinical Research Institute • Roberto Ruggeri – Microsoft Healthcare Evangelist copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial • Liora Alschuler
– alschuler. spinosa, consultants – Co-chair HL 7 Structured Documents TC & Marketing Committee – Co-editor, Clinical Document Architecture (ANSI/HL 7 CDA) – liora@the-word-electric. com • Landen Bain – CDISC Board – Co-chair HL 7 Marketing Committee • Rebecca Kush, Ph. D – Founder and President, CDISC • Meredith Nahm – Manager, Clinical Data Management, Duke Clinical Research Institute • Roberto Ruggeri – Microsoft Healthcare Evangelist copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial • Liora Alschuler
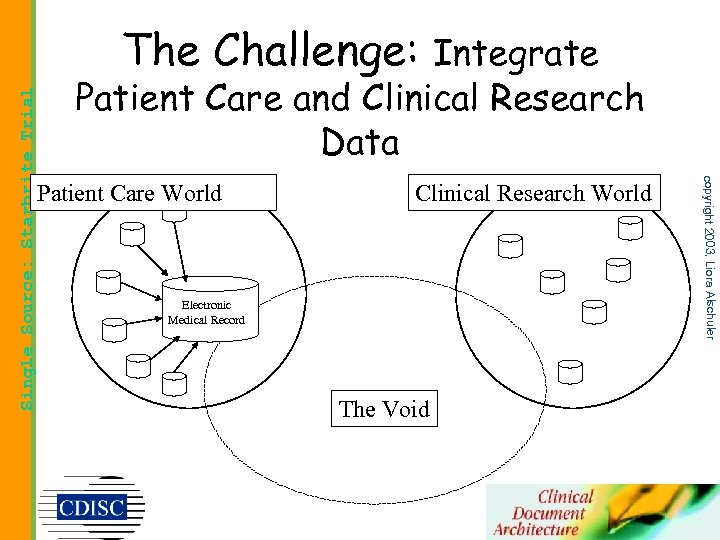 Patient Care and Clinical Research Data Patient Care World Clinical Research World Electronic Medical Record The Void copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial The Challenge: Integrate
Patient Care and Clinical Research Data Patient Care World Clinical Research World Electronic Medical Record The Void copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial The Challenge: Integrate
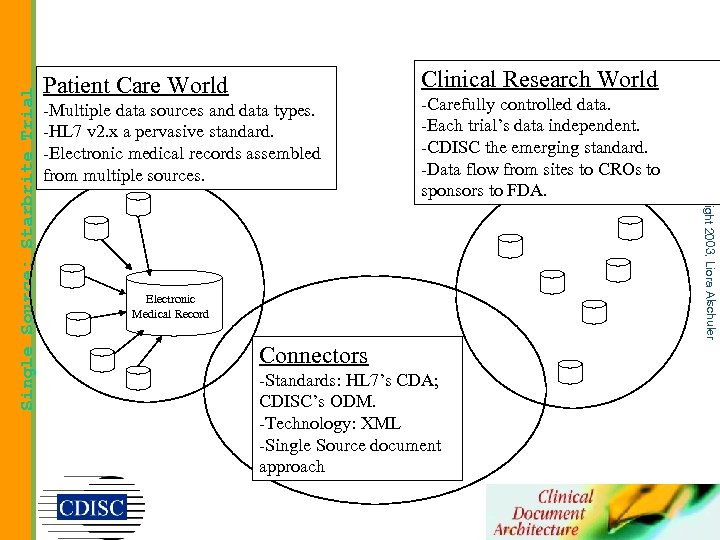 -Multiple data sources and data types. -HL 7 v 2. x a pervasive standard. -Electronic medical records assembled from multiple sources. -Carefully controlled data. -Each trial’s data independent. -CDISC the emerging standard. -Data flow from sites to CROs to sponsors to FDA. Electronic Medical Record Connectors -Standards: HL 7’s CDA; CDISC’s ODM. -Technology: XML -Single Source document approach copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Clinical Research World Patient Care World
-Multiple data sources and data types. -HL 7 v 2. x a pervasive standard. -Electronic medical records assembled from multiple sources. -Carefully controlled data. -Each trial’s data independent. -CDISC the emerging standard. -Data flow from sites to CROs to sponsors to FDA. Electronic Medical Record Connectors -Standards: HL 7’s CDA; CDISC’s ODM. -Technology: XML -Single Source document approach copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Clinical Research World Patient Care World
 • Steve Ruberg, Applied Clinical Trials, February, 2002: “The essential kernal of the whole clinical development processs is the data… Thus, without a data-centric approach to developing any e-clinical solution, we are unlikely to be fully successful. The data is the foundation on which we build our entire effort. ” copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Impact on Healthcare and Drug Information
• Steve Ruberg, Applied Clinical Trials, February, 2002: “The essential kernal of the whole clinical development processs is the data… Thus, without a data-centric approach to developing any e-clinical solution, we are unlikely to be fully successful. The data is the foundation on which we build our entire effort. ” copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Impact on Healthcare and Drug Information
 • Need to shorten cycle time of drug development: – Drug company R & D is too high; – Government pressure. • Drive for personalized, prospective medicine. • Patient and investigator convenience. • HHS desire to link research data to physician behavior. • Rationalize provider document workflow. copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Business Drivers
• Need to shorten cycle time of drug development: – Drug company R & D is too high; – Government pressure. • Drive for personalized, prospective medicine. • Patient and investigator convenience. • HHS desire to link research data to physician behavior. • Rationalize provider document workflow. copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Business Drivers
 • Starbright – a small clinical trial at Duke’s Clinical Research Institute (DCRI) – DCRI’s Data Mgt and IT groups are cooperating with the trial’s investigator. – Goal is to capture both patient care and clinical trial data at the front end, and populate both data streams, using CDA and CDISC standards copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Project opportunities
• Starbright – a small clinical trial at Duke’s Clinical Research Institute (DCRI) – DCRI’s Data Mgt and IT groups are cooperating with the trial’s investigator. – Goal is to capture both patient care and clinical trial data at the front end, and populate both data streams, using CDA and CDISC standards copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Project opportunities
 • Two different world views between patient care and clinical research: – Bio-statisticians want perfect data; – Clinicians want everything they can grab. • Lack of a structured vocabulary. • Privacy concerns. • CDISC, HL 7 divergent data models copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Obstacles
• Two different world views between patient care and clinical research: – Bio-statisticians want perfect data; – Clinicians want everything they can grab. • Lack of a structured vocabulary. • Privacy concerns. • CDISC, HL 7 divergent data models copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Obstacles
 • Participants: – – CDISC Duke Clinical Research Institute (DCRI) investigatiors • Liora Alschuler, Landen Bain, Rebecca Kush, Ph. D, Meredith Nahm, Steve Woody, Sally Cassells, Richard Low, John Madden, MD – technology partners, Microsoft (primary), Arbortext, Topsail, Sentillion copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial
• Participants: – – CDISC Duke Clinical Research Institute (DCRI) investigatiors • Liora Alschuler, Landen Bain, Rebecca Kush, Ph. D, Meredith Nahm, Steve Woody, Sally Cassells, Richard Low, John Madden, MD – technology partners, Microsoft (primary), Arbortext, Topsail, Sentillion copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial
 CDISC is an open, multidisciplinary, non-profit organization committed to the development of worldwide industry standards to support the electronic acquisition, exchange, submission and archiving of clinical trials data and metadata for medical and biopharmaceutical product development. The CDISC mission is to lead the development of global, vendor-neutral, platform-independent standards to improve data quality and accelerate product development in our industry. copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium
CDISC is an open, multidisciplinary, non-profit organization committed to the development of worldwide industry standards to support the electronic acquisition, exchange, submission and archiving of clinical trials data and metadata for medical and biopharmaceutical product development. The CDISC mission is to lead the development of global, vendor-neutral, platform-independent standards to improve data quality and accelerate product development in our industry. copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium
 • Formed in 1997 as a volunteer group • As of 2000, funded as non-profit organization • Now supported by >140 corporate members: pharmaceutical companies; biotech companies; CROs; technology providers • CDISC Groups now growing in Japan, Europe; initiated in India • Standards developed through consensusbased approach by teams of volunteers; public reviews • No fee for use of the standards; freely available on CDISC website (www. cdisc. org) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDISC
• Formed in 1997 as a volunteer group • As of 2000, funded as non-profit organization • Now supported by >140 corporate members: pharmaceutical companies; biotech companies; CROs; technology providers • CDISC Groups now growing in Japan, Europe; initiated in India • Standards developed through consensusbased approach by teams of volunteers; public reviews • No fee for use of the standards; freely available on CDISC website (www. cdisc. org) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDISC
 • CDISC developed standards for submission of clinical trial data, which was beyond the scope of ICH since only FDA requires that data be included in regulatory submissions at this time. • The current plan is for FDA to reference the HL 7 -approved CDISC Submission Data Standards (SDS) as a specification in their FDA Guidance on the implementation of the ICH electronic Common Technical Document (e. CTD). copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial ICH and CDISC
• CDISC developed standards for submission of clinical trial data, which was beyond the scope of ICH since only FDA requires that data be included in regulatory submissions at this time. • The current plan is for FDA to reference the HL 7 -approved CDISC Submission Data Standards (SDS) as a specification in their FDA Guidance on the implementation of the ICH electronic Common Technical Document (e. CTD). copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial ICH and CDISC
 • ANSI-accredited Standards Development Organization • Established 1987 • Approx. 2000 members • 23 affiliates in Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Africa copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Health Level Seven
• ANSI-accredited Standards Development Organization • Established 1987 • Approx. 2000 members • 23 affiliates in Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, Africa copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Health Level Seven
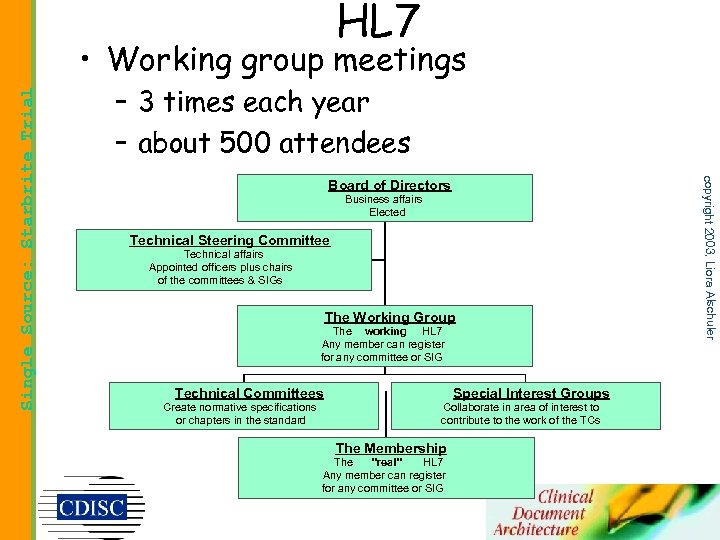 HL 7 – 3 times each year – about 500 attendees Board of Directors Business affairs Elected Technical Steering Committee Technical affairs Appointed officers plus chairs of the committees & SIGs The Working Group The working HL 7 Any member can register for any committee or SIG Technical Committees Create normative specifications or chapters in the standard Special Interest Groups Collaborate in area of interest to contribute to the work of the TCs The Membership "real" The HL 7 Any member can register for any committee or SIG copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial • Working group meetings
HL 7 – 3 times each year – about 500 attendees Board of Directors Business affairs Elected Technical Steering Committee Technical affairs Appointed officers plus chairs of the committees & SIGs The Working Group The working HL 7 Any member can register for any committee or SIG Technical Committees Create normative specifications or chapters in the standard Special Interest Groups Collaborate in area of interest to contribute to the work of the TCs The Membership "real" The HL 7 Any member can register for any committee or SIG copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial • Working group meetings
 • • Modeling & Methodology Patient Care Orders & Observations Structured Documents: Clinical Document Architecture (CDA, SPL) • RCRIM: Regulated Clinical Research Information Management • CCOW: Context Management copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial a few of the HL 7 TCs
• • Modeling & Methodology Patient Care Orders & Observations Structured Documents: Clinical Document Architecture (CDA, SPL) • RCRIM: Regulated Clinical Research Information Management • CCOW: Context Management copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial a few of the HL 7 TCs
 • • XML Genomics Clinical Guidelines Electronic Health Record JAVA Imaging Integration Medication copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial a few of the HL 7 SIGs
• • XML Genomics Clinical Guidelines Electronic Health Record JAVA Imaging Integration Medication copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial a few of the HL 7 SIGs
 • Version 2. x – used worldwide, 90% of US hospitals – “pipe & hat”: HL 7 -proprietary, EDI-like PID||2247^^^Primary|098018500^^^MRN||FIX -INTF^PAT||19650618|Female| • Version 2. XML – a normative XML encoding for V 2
• Version 2. x – used worldwide, 90% of US hospitals – “pipe & hat”: HL 7 -proprietary, EDI-like PID||2247^^^Primary|098018500^^^MRN||FIX -INTF^PAT||19650618|Female| • Version 2. XML – a normative XML encoding for V 2
 • Version 3 – based on Reference Information Model (RIM) – technology independent: so far, developing XML schemas, JAVA API • RCRIM/CDISC lab reporting is a V 3 draft standard, as is SPL • First normative V 3 spec was CDA copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial HL 7 Standards
• Version 3 – based on Reference Information Model (RIM) – technology independent: so far, developing XML schemas, JAVA API • RCRIM/CDISC lab reporting is a V 3 draft standard, as is SPL • First normative V 3 spec was CDA copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial HL 7 Standards
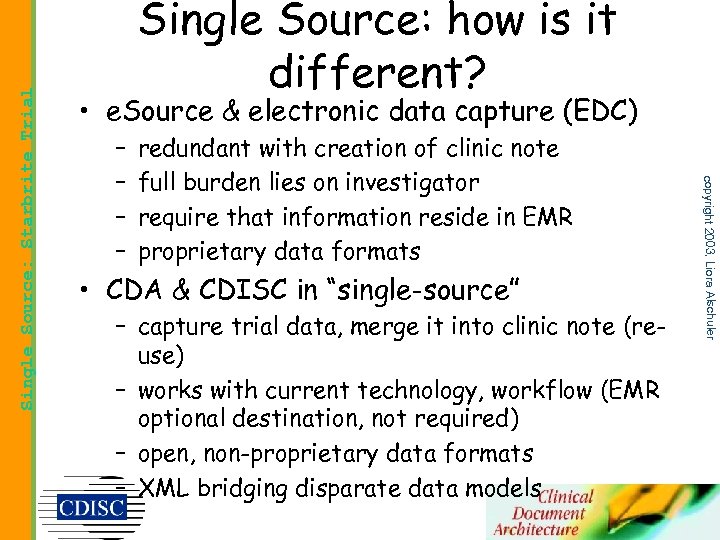 • e. Source & electronic data capture (EDC) – – redundant with creation of clinic note full burden lies on investigator require that information reside in EMR proprietary data formats • CDA & CDISC in “single-source” – capture trial data, merge it into clinic note (reuse) – works with current technology, workflow (EMR optional destination, not required) – open, non-proprietary data formats – XML bridging disparate data models copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Single Source: how is it different?
• e. Source & electronic data capture (EDC) – – redundant with creation of clinic note full burden lies on investigator require that information reside in EMR proprietary data formats • CDA & CDISC in “single-source” – capture trial data, merge it into clinic note (reuse) – works with current technology, workflow (EMR optional destination, not required) – open, non-proprietary data formats – XML bridging disparate data models copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Single Source: how is it different?
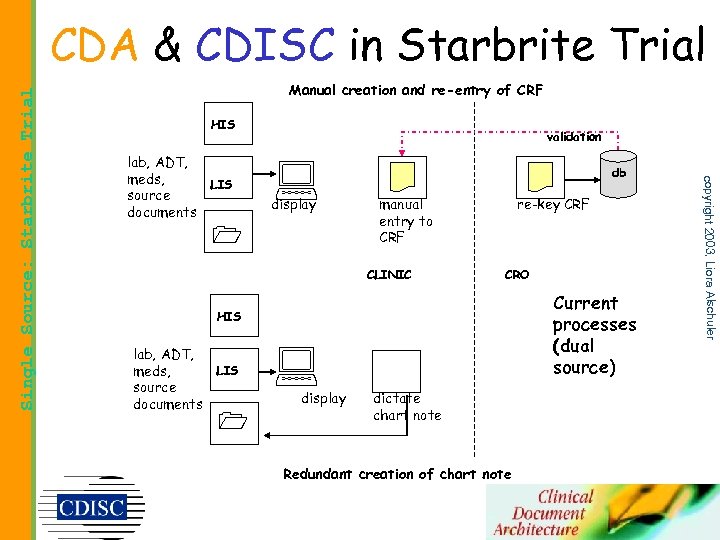 Manual creation and re-entry of CRF HIS lab, ADT, meds, source documents LIS validation display db manual entry to CRF CLINIC re-key CRF CRO Current processes (dual source) HIS lab, ADT, meds, source documents LIS display dictate chart note Redundant creation of chart note copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
Manual creation and re-entry of CRF HIS lab, ADT, meds, source documents LIS validation display db manual entry to CRF CLINIC re-key CRF CRO Current processes (dual source) HIS lab, ADT, meds, source documents LIS display dictate chart note Redundant creation of chart note copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
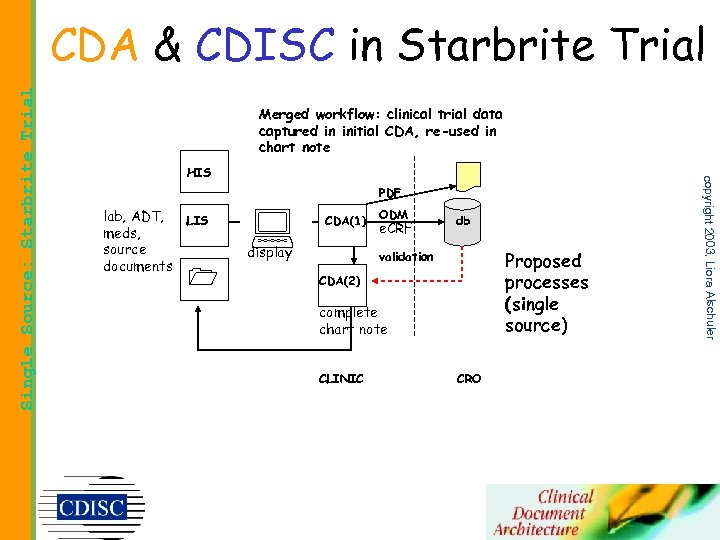 Merged workflow: clinical trial data captured in initial CDA, re-used in chart note HIS lab, ADT, meds, source documents LIS PDF CDA(1) display ODM e. CRF db Proposed processes (single source) validation CDA(2) complete chart note CLINIC CRO copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
Merged workflow: clinical trial data captured in initial CDA, re-used in chart note HIS lab, ADT, meds, source documents LIS PDF CDA(1) display ODM e. CRF db Proposed processes (single source) validation CDA(2) complete chart note CLINIC CRO copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
 • features: – contributes to patient chart, not the reverse, optimizes clinical workflow – no requirement to create/extract from EMR – fewer privacy and regulatory issues – can be driven from electronic protocol – uses HL 7 CDA and CDISC ODM copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
• features: – contributes to patient chart, not the reverse, optimizes clinical workflow – no requirement to create/extract from EMR – fewer privacy and regulatory issues – can be driven from electronic protocol – uses HL 7 CDA and CDISC ODM copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
 • System features/requirements: • • multi-stage, incremental document creation optimal re-use (minimal redundant entry) minimal change to current workflow create both ODM-compliant XML for trials and CDA-compliant XML for clinical records, mapping between ODM. xml and CDA. xml • low cost • rapid development • optimal use of technology partners, off-theshelf technology copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
• System features/requirements: • • multi-stage, incremental document creation optimal re-use (minimal redundant entry) minimal change to current workflow create both ODM-compliant XML for trials and CDA-compliant XML for clinical records, mapping between ODM. xml and CDA. xml • low cost • rapid development • optimal use of technology partners, off-theshelf technology copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
 • With a few simple tags, and controlled vocabulary, XML can describe anything • but… • the tags need to be defined:
• With a few simple tags, and controlled vocabulary, XML can describe anything • but… • the tags need to be defined:
 • Clinical Document Architecture • ANSI/HL 7 CDA R 1. 0 -2000 • first certified XML spec for healthcare • first balloted portion of HL 7’s “V 3” • first RIM-based specification • created & maintained by HL 7 Structured Documents Technical Committee (SDTC) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA
• Clinical Document Architecture • ANSI/HL 7 CDA R 1. 0 -2000 • first certified XML spec for healthcare • first balloted portion of HL 7’s “V 3” • first RIM-based specification • created & maintained by HL 7 Structured Documents Technical Committee (SDTC) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA
 • The scope of the CDA is the standardization of clinical documents for exchange. • CDA enables, but does not constrain: – – – authoring document management storage distribution display copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA: scope
• The scope of the CDA is the standardization of clinical documents for exchange. • CDA enables, but does not constrain: – – – authoring document management storage distribution display copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA: scope
 • priority is patient care, other applications facilitated • minimize technical barriers to implementation • promote longevity of clinical records • scoped by exchange, independent of transfer or storage • enable policy-makers to control information requirements copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA: Release 1. 0
• priority is patient care, other applications facilitated • minimize technical barriers to implementation • promote longevity of clinical records • scoped by exchange, independent of transfer or storage • enable policy-makers to control information requirements copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA: Release 1. 0
 • access/portability/exchange – query/locate by patient, provider, practioner, setting, encounter, date • integration – multiple transcription systems – with EHR records • re-use/derivative data – summaries – billing copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial What can you do Applications of the CDA…or with a few tags?
• access/portability/exchange – query/locate by patient, provider, practioner, setting, encounter, date • integration – multiple transcription systems – with EHR records • re-use/derivative data – summaries – billing copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial What can you do Applications of the CDA…or with a few tags?
 Single Source: Starbrite Trial PICNIC (European Union) SCIPHOX (Germany) HYGEIAnet/Web. On. Coll (Greece) NHS South Staffordshire (United Kingdom) Aluetietojärjestelmä (Finland) MERIT-9 (Japan) • e-Claims Supporting Doc Arch (Canada); HIPAA Claims Attachments (US, proposed) • Mayo Clinic (US) • Buenos Aires project (Argentina) • Dalhousie U, QEII Health Sci Ctr (Canada) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler • • • CDA: Major Implementations
Single Source: Starbrite Trial PICNIC (European Union) SCIPHOX (Germany) HYGEIAnet/Web. On. Coll (Greece) NHS South Staffordshire (United Kingdom) Aluetietojärjestelmä (Finland) MERIT-9 (Japan) • e-Claims Supporting Doc Arch (Canada); HIPAA Claims Attachments (US, proposed) • Mayo Clinic (US) • Buenos Aires project (Argentina) • Dalhousie U, QEII Health Sci Ctr (Canada) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler • • • CDA: Major Implementations
 CDA Release 2 (draft), section 2. 1: A clinical document. . . has the following characteristics: · Persistence · Stewardship · Potential for authentication · Context · Wholeness · Human readability “Context - Contents of a clinical document share a common context unless all or part of that context is overridden or nullified. ” (material in blue is quoted from the Clinical Document Architecture Release 1. 0) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial The CDA document defined
CDA Release 2 (draft), section 2. 1: A clinical document. . . has the following characteristics: · Persistence · Stewardship · Potential for authentication · Context · Wholeness · Human readability “Context - Contents of a clinical document share a common context unless all or part of that context is overridden or nullified. ” (material in blue is quoted from the Clinical Document Architecture Release 1. 0) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial The CDA document defined
 • Span full range of technical sophistication • Minimal constraint on content • Makes all types of information human readable and, to the greatest extent possible, also machine processible copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Requirements for a universal clinical document
• Span full range of technical sophistication • Minimal constraint on content • Makes all types of information human readable and, to the greatest extent possible, also machine processible copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Requirements for a universal clinical document
 • CDA documents are “human readable” = – This principle means that CDA documents are human readable using: a) widely-available and commonly deployed XMLaware browsers and print drivers and b) a generic CDA style sheet written in a standard style sheet language. • CDA documents are also “machine processable” to the degree that markup has been added – required markup provides initial functionality – optional markup can augment processing copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA: : Readability
• CDA documents are “human readable” = – This principle means that CDA documents are human readable using: a) widely-available and commonly deployed XMLaware browsers and print drivers and b) a generic CDA style sheet written in a standard style sheet language. • CDA documents are also “machine processable” to the degree that markup has been added – required markup provides initial functionality – optional markup can augment processing copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA: : Readability
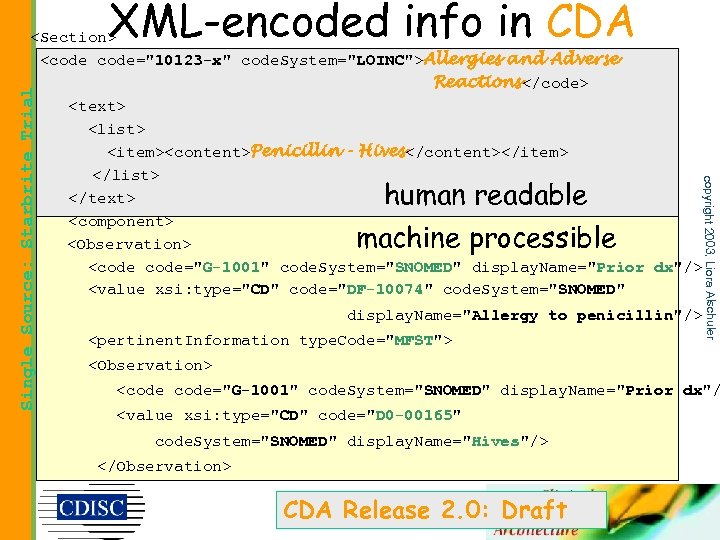 XML-encoded info in CDA Single Source: Starbrite Trial human readable machine processible copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler
XML-encoded info in CDA Single Source: Starbrite Trial human readable machine processible copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler
 • Operational Data Model – ver. 1. 1, April, 2002 – www. CDISC. org • Defined by set of XML DTDs • A database insertion schema copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDISC ODM
• Operational Data Model – ver. 1. 1, April, 2002 – www. CDISC. org • Defined by set of XML DTDs • A database insertion schema copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDISC ODM
 • The technical focus in the development of ODM 1. 0 was the definition of structures to represent the three major information components relating to a clinical trial: – clinical study metadata (item definitions and protocol) – clinical study administrative data (users and access privileges) – clinical study data (complete record of patient data and audit trail) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDISC ODM
• The technical focus in the development of ODM 1. 0 was the definition of structures to represent the three major information components relating to a clinical trial: – clinical study metadata (item definitions and protocol) – clinical study administrative data (users and access privileges) – clinical study data (complete record of patient data and audit trail) copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDISC ODM
 • Study allows representation of more than one study in a single file • Admin. Data includes information about the users of the system, the clinical sites involved in the study, and associated security information • Reference. Data provides information relevant to the interpretation of data that is not necessarily study specific, such as lab normal ranges • Clinical. Data contains the actual data item values associated with each study. copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDISC ODM
• Study allows representation of more than one study in a single file • Admin. Data includes information about the users of the system, the clinical sites involved in the study, and associated security information • Reference. Data provides information relevant to the interpretation of data that is not necessarily study specific, such as lab normal ranges • Clinical. Data contains the actual data item values associated with each study. copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDISC ODM
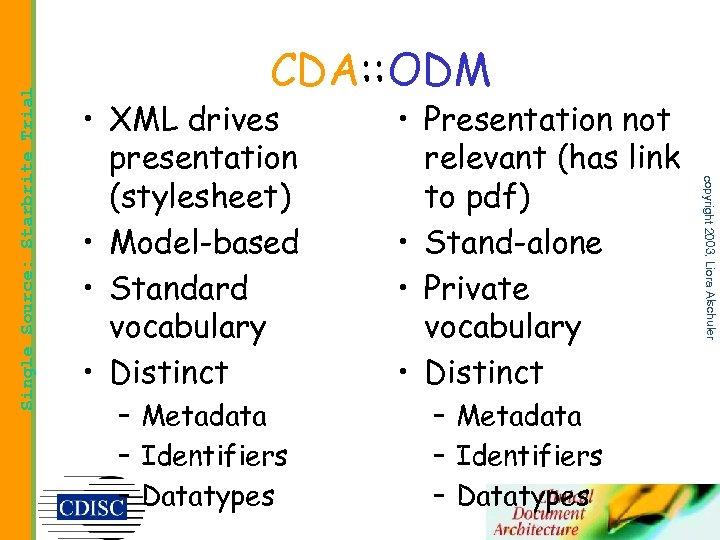 • XML drives presentation (stylesheet) • Model-based • Standard vocabulary • Distinct – Metadata – Identifiers – Datatypes • Presentation not relevant (has link to pdf) • Stand-alone • Private vocabulary • Distinct – Metadata – Identifiers – Datatypes copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA: : ODM
• XML drives presentation (stylesheet) • Model-based • Standard vocabulary • Distinct – Metadata – Identifiers – Datatypes • Presentation not relevant (has link to pdf) • Stand-alone • Private vocabulary • Distinct – Metadata – Identifiers – Datatypes copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA: : ODM
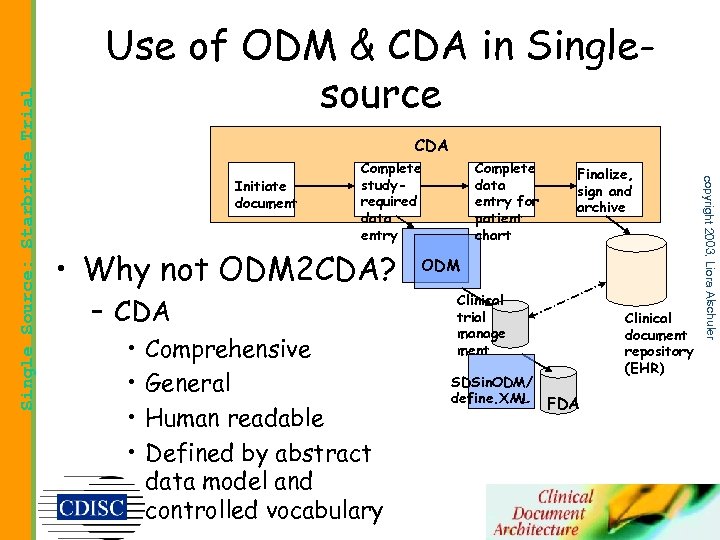 CDA Initiate document Complete studyrequired data entry • Why not ODM 2 CDA? – CDA • • Comprehensive General Human readable Defined by abstract data model and controlled vocabulary Complete data entry for patient chart Finalize, sign and archive ODM Clinical trial manage ment SDSin. ODM/ define. XML Clinical document repository (EHR) FDA copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Use of ODM & CDA in Singlesource
CDA Initiate document Complete studyrequired data entry • Why not ODM 2 CDA? – CDA • • Comprehensive General Human readable Defined by abstract data model and controlled vocabulary Complete data entry for patient chart Finalize, sign and archive ODM Clinical trial manage ment SDSin. ODM/ define. XML Clinical document repository (EHR) FDA copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Use of ODM & CDA in Singlesource
 BNPDATA (TYPE 4) F DOMAIN
BNPDATA (TYPE 4) F DOMAIN
 CSSEQ
CSSEQ
 • • • BNP Data Endpoint Summary Weight Orthopnea Weight gain copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Five sample data elements
• • • BNP Data Endpoint Summary Weight Orthopnea Weight gain copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Five sample data elements
 Single Source: Starbrite Trial copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler
Single Source: Starbrite Trial copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler
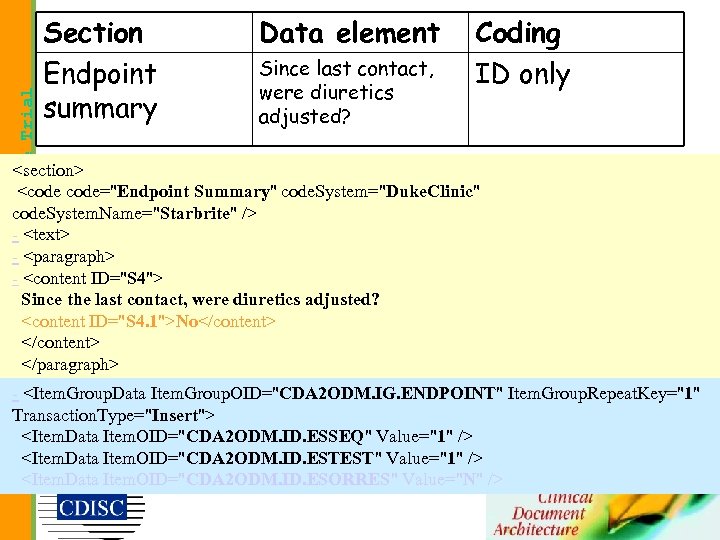 Data element Since last contact, were diuretics adjusted? Coding ID only
Data element Since last contact, were diuretics adjusted? Coding ID only
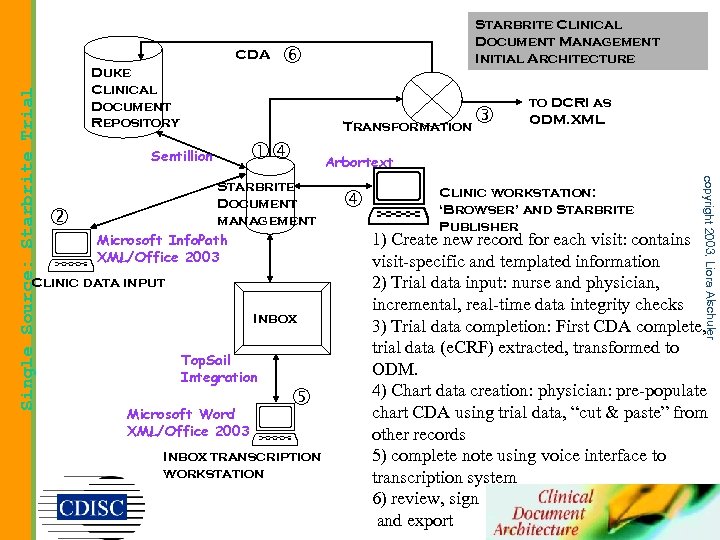 Duke Clinical Document Repository Transformation Sentillion Starbrite Document management Microsoft Info. Path XML/Office 2003 Clinic data input Inbox Top. Sail Integration Microsoft Word XML/Office 2003 Inbox transcription workstation to DCRI as ODM. XML Arbortext Clinic workstation: ‘Browser’ and Starbrite Publisher copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA Starbrite Clinical Document Management Initial Architecture 1) Create new record for each visit: contains visit-specific and templated information 2) Trial data input: nurse and physician, incremental, real-time data integrity checks 3) Trial data completion: First CDA complete, trial data (e. CRF) extracted, transformed to ODM. 4) Chart data creation: physician: pre-populate chart CDA using trial data, “cut & paste” from other records 5) complete note using voice interface to transcription system 6) review, sign and export
Duke Clinical Document Repository Transformation Sentillion Starbrite Document management Microsoft Info. Path XML/Office 2003 Clinic data input Inbox Top. Sail Integration Microsoft Word XML/Office 2003 Inbox transcription workstation to DCRI as ODM. XML Arbortext Clinic workstation: ‘Browser’ and Starbrite Publisher copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA Starbrite Clinical Document Management Initial Architecture 1) Create new record for each visit: contains visit-specific and templated information 2) Trial data input: nurse and physician, incremental, real-time data integrity checks 3) Trial data completion: First CDA complete, trial data (e. CRF) extracted, transformed to ODM. 4) Chart data creation: physician: pre-populate chart CDA using trial data, “cut & paste” from other records 5) complete note using voice interface to transcription system 6) review, sign and export
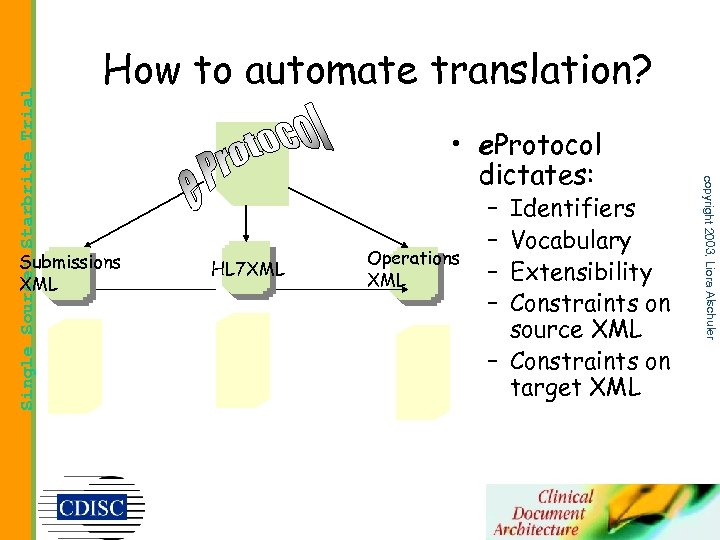 Submissions XML • e. Protocol dictates: HL 7 XML Operations XML – – Identifiers Vocabulary Extensibility Constraints on source XML – Constraints on target XML copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial How to automate translation?
Submissions XML • e. Protocol dictates: HL 7 XML Operations XML – – Identifiers Vocabulary Extensibility Constraints on source XML – Constraints on target XML copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial How to automate translation?
 • Status, October, 2003: – preliminary technical design and information analysis complete – information design, in progress: Liora Alschuler, Sally Cassells (Lincoln Technologies, CDISC) completing data CDA/ODM data mapping – technical implementation: kick-off meeting October 14, Durham, NC (attending: Microsoft, Arbortext, Topsail, DCRI) – project pilot in place Q 1, 2004 copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
• Status, October, 2003: – preliminary technical design and information analysis complete – information design, in progress: Liora Alschuler, Sally Cassells (Lincoln Technologies, CDISC) completing data CDA/ODM data mapping – technical implementation: kick-off meeting October 14, Durham, NC (attending: Microsoft, Arbortext, Topsail, DCRI) – project pilot in place Q 1, 2004 copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial CDA & CDISC in Starbrite Trial
 • Next steps: – Design and prototype a general solution – Expand scope: integrate with standardsbased electronic protocol – Implement at one or more additional sites • Establish base of industry partnerships to sustain second stage design, testing, implementation copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Single-source: beyond Starbrite
• Next steps: – Design and prototype a general solution – Expand scope: integrate with standardsbased electronic protocol – Implement at one or more additional sites • Establish base of industry partnerships to sustain second stage design, testing, implementation copyright 2003, Liora Alschuler Single Source: Starbrite Trial Single-source: beyond Starbrite
 Content and Interoperability Standards Panel: HL 7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA: : CCR: : CCD) June 9, 2006 Liora Alschuler 48 http: //www. ahima. org/meetings/ltc/documents/Alschuler_HITin. LTCPanel. June 06. rev. ppt
Content and Interoperability Standards Panel: HL 7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA: : CCR: : CCD) June 9, 2006 Liora Alschuler 48 http: //www. ahima. org/meetings/ltc/documents/Alschuler_HITin. LTCPanel. June 06. rev. ppt
 About me • Liora Alschuler –Consultant, Alschuler Associates, LLC • Tricare Management Activity, Department of Defense, Enterprise Wide Referrals & Authorizations; Documents, Files, Images (DFI) • Subcontractor, HITSP Standards Harmonization • Industry-leading PHR, EMR and RHIO solution vendors –Co-editor, CDA –Co-chair HL 7 Structured Documents TC –Co-author, CDA & CRS Quick Start Guides –Member, HL 7 Board of Directors –HL 7 IHE Liaison –past Chair, KEG & XML SIG & HL 7 Marketing Committee –Author ABCD. . . SGML: A Managers Guide to Structured Information, 1995 –www. Alschuler. Associates. com , liora@alschulerassociates. com 49
About me • Liora Alschuler –Consultant, Alschuler Associates, LLC • Tricare Management Activity, Department of Defense, Enterprise Wide Referrals & Authorizations; Documents, Files, Images (DFI) • Subcontractor, HITSP Standards Harmonization • Industry-leading PHR, EMR and RHIO solution vendors –Co-editor, CDA –Co-chair HL 7 Structured Documents TC –Co-author, CDA & CRS Quick Start Guides –Member, HL 7 Board of Directors –HL 7 IHE Liaison –past Chair, KEG & XML SIG & HL 7 Marketing Committee –Author ABCD. . . SGML: A Managers Guide to Structured Information, 1995 –www. Alschuler. Associates. com , liora@alschulerassociates. com 49
 Healthcare IT 101 • Largely a failed endeavor • IOM perspective – Institute of Medicine, To Err Is Human – 98, 000 preventable deaths each year • MOM perspective – Post discharge – What meds? – Office visit: no value • Problems known • Why not fixed? 50
Healthcare IT 101 • Largely a failed endeavor • IOM perspective – Institute of Medicine, To Err Is Human – 98, 000 preventable deaths each year • MOM perspective – Post discharge – What meds? – Office visit: no value • Problems known • Why not fixed? 50
 Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 51
Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 51
 Health Level Seven (HL 7. org) • Standards Development Organization • Developing standards for interoperability • • – – Patient care Public health Clinical trials Reimbursement HIPAA DSMO 20 years, 2000 members 30+ international affiliates “A model community”: building standards to a single information model 52
Health Level Seven (HL 7. org) • Standards Development Organization • Developing standards for interoperability • • – – Patient care Public health Clinical trials Reimbursement HIPAA DSMO 20 years, 2000 members 30+ international affiliates “A model community”: building standards to a single information model 52
 Committees & Special Interest Groups n n n n Anatomic Pathology Anesthesia Architecture Review Board** Arden Syntax Attachments Cardiology Common Message Element Types*** CCOW* Clinical Decision Support* Clinical Genomics Clinical Guidelines Community Based Health Services Conformance Infrastructure & Messaging* Education** Electronic Health Records* n n n n n Electronic Services** Emergency Dept. Financial Management* Government Projects (US) Imaging Integration Implementation** International Affiliates** Java Laboratory Health Care Devices Marketing** Medical Records/ Information Management* Modeling & Methodology* Orders & Observations* Organization Review** Outreach for Clinical Research* Patient Administration* Patient Care* Patient Safety n n n n Pediatric Data Standards Personnel Management* Pharmacy Process Improvement** Public Health & Emergency Response Publishing** Regulated Clinical Research Information Management (RCRIM)* (formerly Clinical Trials) n n n n n Scheduling & Logistics* Security* Service Oriented Arch. Structured Documents* Technical Steering Committee** Templates Tooling** Vocabulary* XML * Technical Committees, ** Board Committees, ***Task Force 53 As of 06/06
Committees & Special Interest Groups n n n n Anatomic Pathology Anesthesia Architecture Review Board** Arden Syntax Attachments Cardiology Common Message Element Types*** CCOW* Clinical Decision Support* Clinical Genomics Clinical Guidelines Community Based Health Services Conformance Infrastructure & Messaging* Education** Electronic Health Records* n n n n n Electronic Services** Emergency Dept. Financial Management* Government Projects (US) Imaging Integration Implementation** International Affiliates** Java Laboratory Health Care Devices Marketing** Medical Records/ Information Management* Modeling & Methodology* Orders & Observations* Organization Review** Outreach for Clinical Research* Patient Administration* Patient Care* Patient Safety n n n n Pediatric Data Standards Personnel Management* Pharmacy Process Improvement** Public Health & Emergency Response Publishing** Regulated Clinical Research Information Management (RCRIM)* (formerly Clinical Trials) n n n n n Scheduling & Logistics* Security* Service Oriented Arch. Structured Documents* Technical Steering Committee** Templates Tooling** Vocabulary* XML * Technical Committees, ** Board Committees, ***Task Force 53 As of 06/06
 HL 7 for messaging • It’s all about the interface: • Hospital-centric view of HIT 54
HL 7 for messaging • It’s all about the interface: • Hospital-centric view of HIT 54
 HL 7 beyond the hospital interface Enterprise Facility Region Network 55 National
HL 7 beyond the hospital interface Enterprise Facility Region Network 55 National
 HL 7 beyond the messaging interface • CCOW: multi-application context management, single sign-on • Arden Syntax: decision support, guidelines • Electronic Health Record: functional, system and interoperability models • Reference Information Model (RIM) • Clinical Document Architecture 56
HL 7 beyond the messaging interface • CCOW: multi-application context management, single sign-on • Arden Syntax: decision support, guidelines • Electronic Health Record: functional, system and interoperability models • Reference Information Model (RIM) • Clinical Document Architecture 56
 Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 57
Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 57
 CDA • • Clinical Document Architecture ANSI/HL 7 CDA R 1. 0 -2000 ANSI/HL 7 CDA R 2. 0 -2005 A specification for document exchange using – – XML, the HL 7 Reference Information Model (RIM) Version 3 methodology and vocabulary (SNOMED, ICD, local, …) 58
CDA • • Clinical Document Architecture ANSI/HL 7 CDA R 1. 0 -2000 ANSI/HL 7 CDA R 2. 0 -2005 A specification for document exchange using – – XML, the HL 7 Reference Information Model (RIM) Version 3 methodology and vocabulary (SNOMED, ICD, local, …) 58
 CDA: A Document Exchange Specification • This is a CDA • and this • and this 59
CDA: A Document Exchange Specification • This is a CDA • and this • and this 59
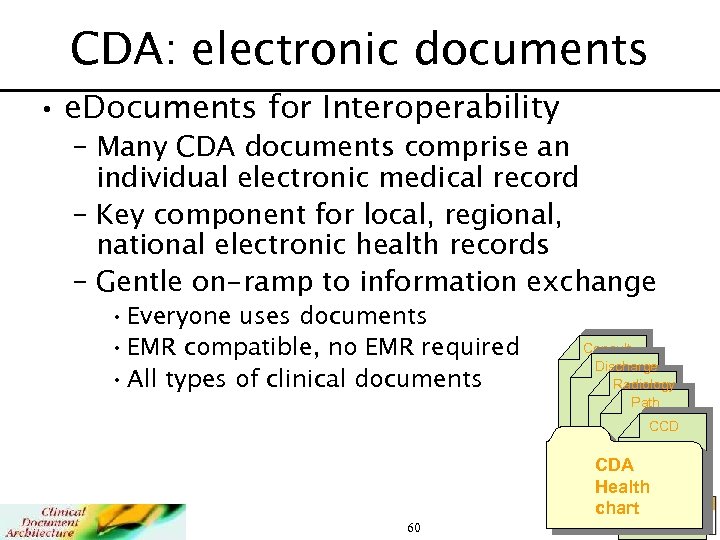 CDA: electronic documents • e. Documents for Interoperability – Many CDA documents comprise an individual electronic medical record – Key component for local, regional, national electronic health records – Gentle on-ramp to information exchange • Everyone uses documents • EMR compatible, no EMR required • All types of clinical documents Consult Discharge Radiology Path CCD CDA Health chart 60
CDA: electronic documents • e. Documents for Interoperability – Many CDA documents comprise an individual electronic medical record – Key component for local, regional, national electronic health records – Gentle on-ramp to information exchange • Everyone uses documents • EMR compatible, no EMR required • All types of clinical documents Consult Discharge Radiology Path CCD CDA Health chart 60
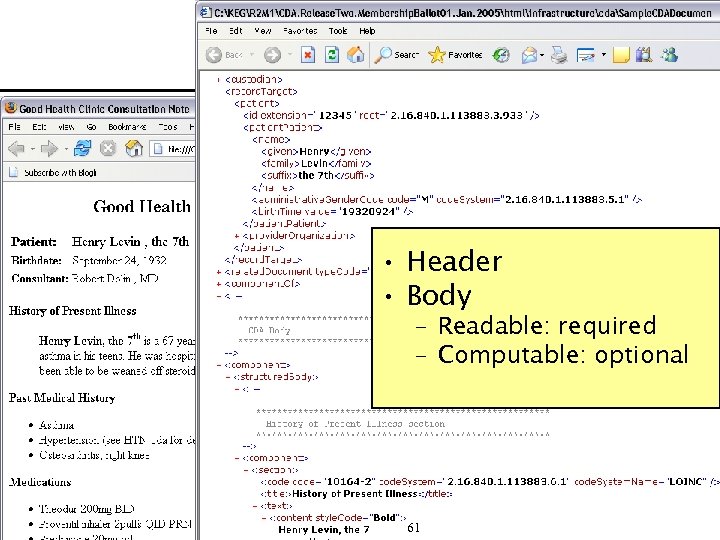 Sample CDA • Header • Body – Readable: required – Computable: optional 61
Sample CDA • Header • Body – Readable: required – Computable: optional 61
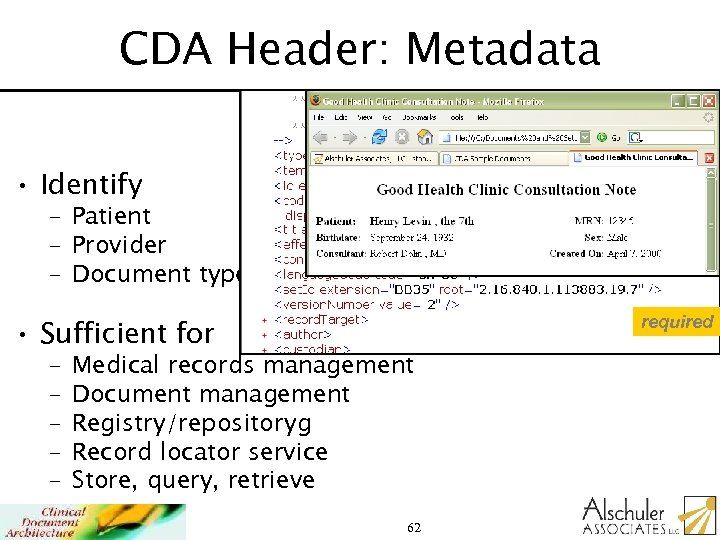 CDA Header: Metadata • Identify – Patient – Provider – Document type. . . required • Sufficient for – – – Medical records management Document management Registry/repositoryg Record locator service Store, query, retrieve 62
CDA Header: Metadata • Identify – Patient – Provider – Document type. . . required • Sufficient for – – – Medical records management Document management Registry/repositoryg Record locator service Store, query, retrieve 62
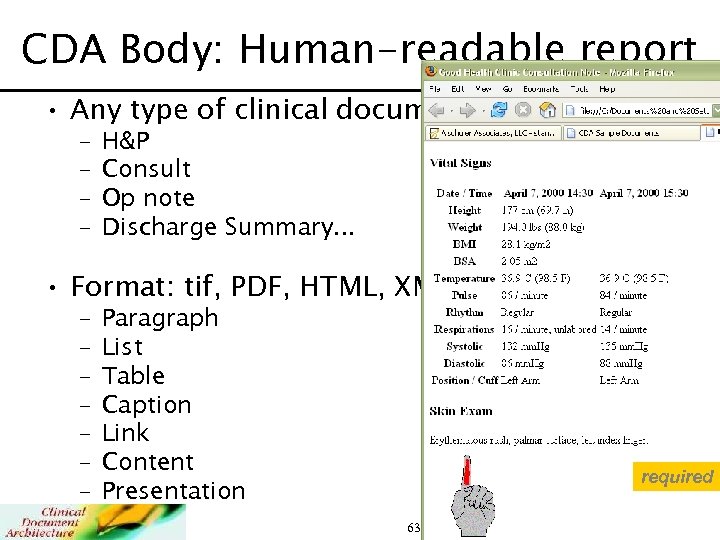 CDA Body: Human-readable report • Any type of clinical document – – H&P Consult Op note Discharge Summary. . . • Format: tif, PDF, HTML, XML: – – – – Paragraph List Table Caption Link Content Presentation required 63
CDA Body: Human-readable report • Any type of clinical document – – H&P Consult Op note Discharge Summary. . . • Format: tif, PDF, HTML, XML: – – – – Paragraph List Table Caption Link Content Presentation required 63
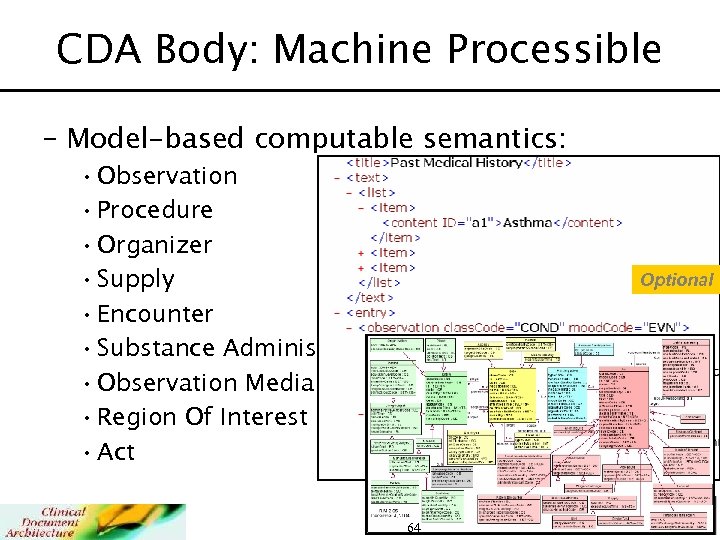 CDA Body: Machine Processible – Model-based computable semantics: • Observation • Procedure • Organizer • Supply • Encounter • Substance Administration • Observation Media • Region Of Interest • Act Optional 64
CDA Body: Machine Processible – Model-based computable semantics: • Observation • Procedure • Organizer • Supply • Encounter • Substance Administration • Observation Media • Region Of Interest • Act Optional 64
 CDA: Incremental Computability • Standard HL 7 metadata • Simple XML for point of care human readability • RIM semantics for reusable computability (“semantic interoperability”) 65
CDA: Incremental Computability • Standard HL 7 metadata • Simple XML for point of care human readability • RIM semantics for reusable computability (“semantic interoperability”) 65
 Investing in Information • CDA can be simple • CDA can be complex • Simple encoding relatively inexpensive • Complex encoding costs more • You get what you pay for: – like charging a battery, – the more detailed the encoding – the greater the potential for reuse 67
Investing in Information • CDA can be simple • CDA can be complex • Simple encoding relatively inexpensive • Complex encoding costs more • You get what you pay for: – like charging a battery, – the more detailed the encoding – the greater the potential for reuse 67
 Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 68
Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 68
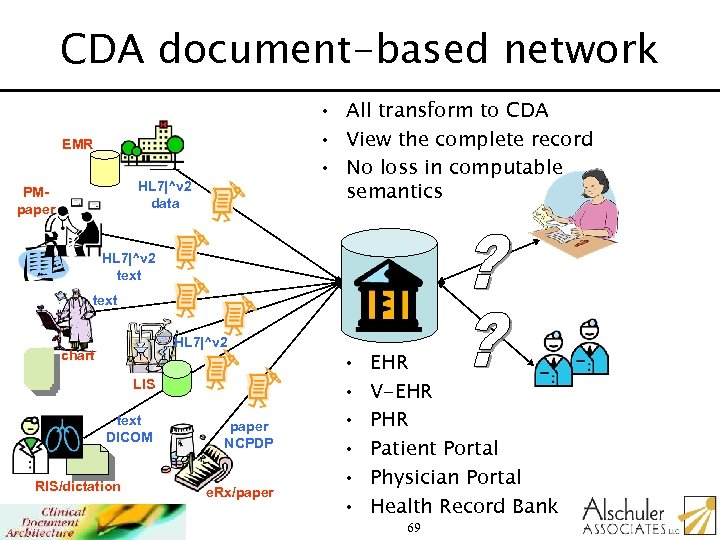 CDA document-based network • All transform to CDA • View the complete record • No loss in computable semantics EMR HL 7|^v 2 data PMpaper HL 7|^v 2 text HL 7|^v 2 chart LIS text DICOM RIS/dictation paper NCPDP e. Rx/paper • • • EHR V-EHR Patient Portal Physician Portal Health Record Bank 69
CDA document-based network • All transform to CDA • View the complete record • No loss in computable semantics EMR HL 7|^v 2 data PMpaper HL 7|^v 2 text HL 7|^v 2 chart LIS text DICOM RIS/dictation paper NCPDP e. Rx/paper • • • EHR V-EHR Patient Portal Physician Portal Health Record Bank 69
 CDA for Information Exchange • International: basis of interoperability in most advanced national networks – Finland, Greece, Canada, Germany, Japan, Korea, France, Italy, New Zealand, Australia, and more • US: Federal Health Architecture/CHI – CMS Notice of Proposed Rule Making • Claims attachments using CDA + X 12 • First pilot concluded, others underway – VA/Do. D bi-directional exchange • US: Document format for NHIN pilots, RHIO design – NHIN Pilots: preliminary architecture – HITSP: preliminary choice – IHE Medical Summary – CDA for NHIN/RHIO exchange 70
CDA for Information Exchange • International: basis of interoperability in most advanced national networks – Finland, Greece, Canada, Germany, Japan, Korea, France, Italy, New Zealand, Australia, and more • US: Federal Health Architecture/CHI – CMS Notice of Proposed Rule Making • Claims attachments using CDA + X 12 • First pilot concluded, others underway – VA/Do. D bi-directional exchange • US: Document format for NHIN pilots, RHIO design – NHIN Pilots: preliminary architecture – HITSP: preliminary choice – IHE Medical Summary – CDA for NHIN/RHIO exchange 70
 • • • Major Implementations (outside US) PICNIC (European Union) SCIPHOX (Germany) HYGEIAnet/Web. On. Coll (Greece) Aluetietojärjestelmä (Finland) Health Information Summaries (New Zealand) Referrals (Australia) MERIT-9 (Japan) NHS (Wales) Buenos Aires HMO project (Argentina) Plus projects in France, Italy, Russia, Estonia, Taiwan, Korea… 71
• • • Major Implementations (outside US) PICNIC (European Union) SCIPHOX (Germany) HYGEIAnet/Web. On. Coll (Greece) Aluetietojärjestelmä (Finland) Health Information Summaries (New Zealand) Referrals (Australia) MERIT-9 (Japan) NHS (Wales) Buenos Aires HMO project (Argentina) Plus projects in France, Italy, Russia, Estonia, Taiwan, Korea… 71
 CDA: an international standard 72
CDA: an international standard 72
 CDA: Investing in Information • CDA at the Mayo Clinic – Initiated in 1999 – About 50, 000 documents each week – Clinical documents: Most important capital asset • CDA at New York Presbyterian (was Col. Pres) – “CDA Philosophy” – Clinical notes contain critical information in narrative – Best format for information mining and aggregation across applications – 1/3 of all discharges summaries 73
CDA: Investing in Information • CDA at the Mayo Clinic – Initiated in 1999 – About 50, 000 documents each week – Clinical documents: Most important capital asset • CDA at New York Presbyterian (was Col. Pres) – “CDA Philosophy” – Clinical notes contain critical information in narrative – Best format for information mining and aggregation across applications – 1/3 of all discharges summaries 73
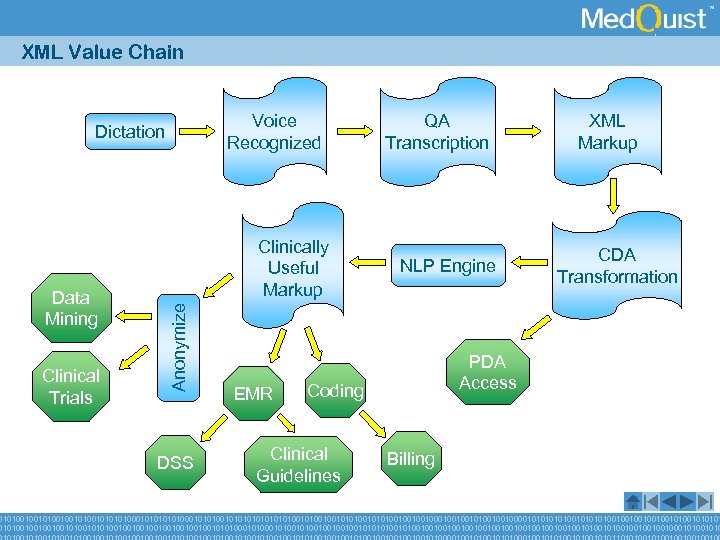 XML Value Chain Voice Recognized Dictation Clinical Trials Anonymize Data Mining Clinically Useful Markup DSS EMR QA Transcription NLP Engine CDA Transformation PDA Access Coding Clinical Guidelines XML Markup Billing 010100100101010100010101001010101001010010010101001000100100100001010100101001001001010101001001010010010010010010101000101001001010101001001001001001001001010010010001010
XML Value Chain Voice Recognized Dictation Clinical Trials Anonymize Data Mining Clinically Useful Markup DSS EMR QA Transcription NLP Engine CDA Transformation PDA Access Coding Clinical Guidelines XML Markup Billing 010100100101010100010101001010101001010010010101001000100100100001010100101001001001010101001001010010010010010010101000101001001010101001001001001001001001010010010001010
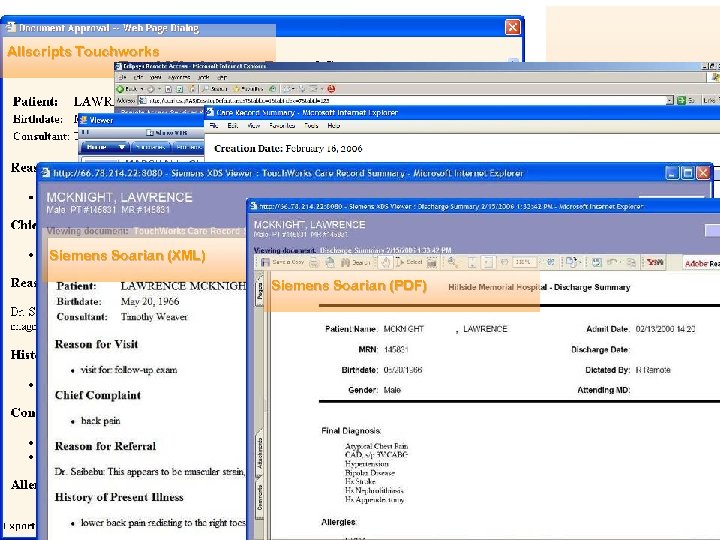 Allscripts Touchworks IHE Medical Summaries HIMSS 2006: a CDA Gallery GE Centricity Siemens Soarian (XML) Medi. Notes e Siemens Soarian (PDF) Eclipsys Sunrise
Allscripts Touchworks IHE Medical Summaries HIMSS 2006: a CDA Gallery GE Centricity Siemens Soarian (XML) Medi. Notes e Siemens Soarian (PDF) Eclipsys Sunrise
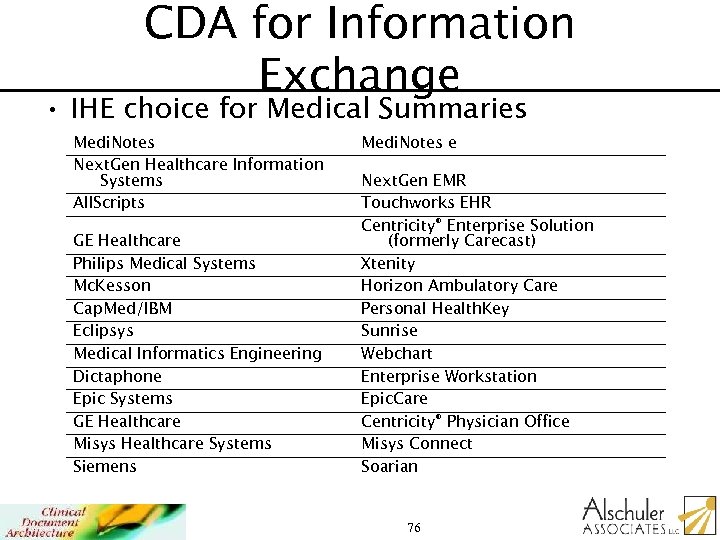 CDA for Information Exchange • IHE choice for Medical Summaries Medi. Notes Next. Gen Healthcare Information Systems All. Scripts GE Healthcare Philips Medical Systems Mc. Kesson Cap. Med/IBM Eclipsys Medical Informatics Engineering Dictaphone Epic Systems GE Healthcare Misys Healthcare Systems Siemens Medi. Notes e Next. Gen EMR Touchworks EHR Centricity® Enterprise Solution (formerly Carecast) Xtenity Horizon Ambulatory Care Personal Health. Key Sunrise Webchart Enterprise Workstation Epic. Care Centricity® Physician Office Misys Connect Soarian 76
CDA for Information Exchange • IHE choice for Medical Summaries Medi. Notes Next. Gen Healthcare Information Systems All. Scripts GE Healthcare Philips Medical Systems Mc. Kesson Cap. Med/IBM Eclipsys Medical Informatics Engineering Dictaphone Epic Systems GE Healthcare Misys Healthcare Systems Siemens Medi. Notes e Next. Gen EMR Touchworks EHR Centricity® Enterprise Solution (formerly Carecast) Xtenity Horizon Ambulatory Care Personal Health. Key Sunrise Webchart Enterprise Workstation Epic. Care Centricity® Physician Office Misys Connect Soarian 76
 Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 77
Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 77
 Agreements/MOUs * Accredited Standards Committee X 12 — ASC-X 12 * American Dental Association — ADA o ADA Joint Project Statement * American Society for Testing Materials — ASTM * CEN/TC 251 * Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium — CDISC * Digital Imaging and Communication In Medicine — DICOM * e. Health Initiative – e. HI * Institute for Electrical and Electronic Engineers — IEEE * Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise — IHE * Medbiquitous * National Council for Prescription Drug Program — NCPDP * OASIS * Object Management Group — OMG * University of Nevada Las Vegas — UNLV * College of American Pathologists - SNOMED International Division — SNOMED 78
Agreements/MOUs * Accredited Standards Committee X 12 — ASC-X 12 * American Dental Association — ADA o ADA Joint Project Statement * American Society for Testing Materials — ASTM * CEN/TC 251 * Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium — CDISC * Digital Imaging and Communication In Medicine — DICOM * e. Health Initiative – e. HI * Institute for Electrical and Electronic Engineers — IEEE * Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise — IHE * Medbiquitous * National Council for Prescription Drug Program — NCPDP * OASIS * Object Management Group — OMG * University of Nevada Las Vegas — UNLV * College of American Pathologists - SNOMED International Division — SNOMED 78
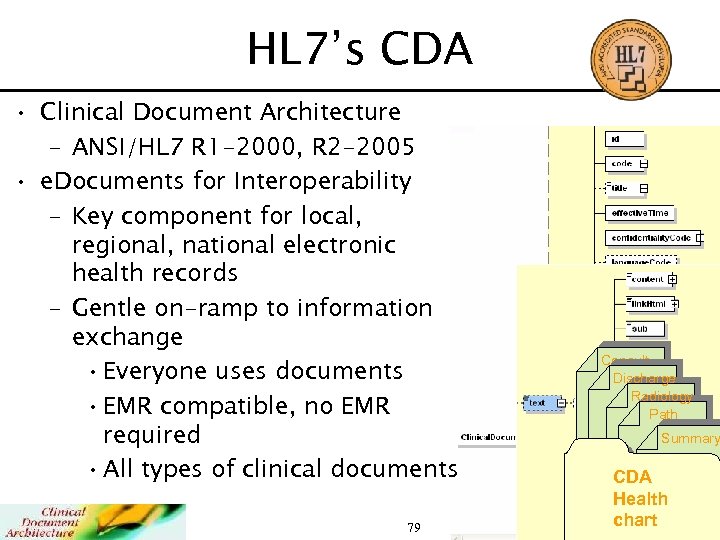 HL 7’s CDA • Clinical Document Architecture – ANSI/HL 7 R 1 -2000, R 2 -2005 • e. Documents for Interoperability – Key component for local, regional, national electronic health records – Gentle on-ramp to information exchange • Everyone uses documents • EMR compatible, no EMR required • All types of clinical documents 79 Consult Discharge Radiology Path Summary CDA Health chart
HL 7’s CDA • Clinical Document Architecture – ANSI/HL 7 R 1 -2000, R 2 -2005 • e. Documents for Interoperability – Key component for local, regional, national electronic health records – Gentle on-ramp to information exchange • Everyone uses documents • EMR compatible, no EMR required • All types of clinical documents 79 Consult Discharge Radiology Path Summary CDA Health chart
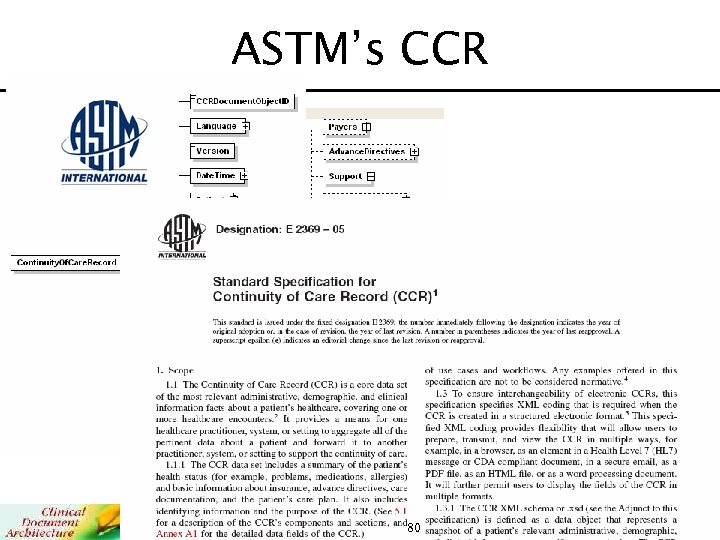 ASTM’s CCR 80
ASTM’s CCR 80
 ASTM CCR vs. HL 7 CDA • Conflicting? • Overlapping? • What if you could have both!#*? I!! – What if you could have your data elements – And send them in a common exchange framework? 82
ASTM CCR vs. HL 7 CDA • Conflicting? • Overlapping? • What if you could have both!#*? I!! – What if you could have your data elements – And send them in a common exchange framework? 82
 ASTM CCR + HL 7 CDA = CCD • CDA is designed to support professional society recommendations, national clinical practice guidelines, standardized data sets, etc. • From the perspective of CDA, the ASTM CCR is a standardized data set that can be used to constrain CDA specifically for summary documents. • The resulting specification, known as the Continuity of Care Document (CCD), is being developed as a collaborative effort between ASTM and HL 7. 83
ASTM CCR + HL 7 CDA = CCD • CDA is designed to support professional society recommendations, national clinical practice guidelines, standardized data sets, etc. • From the perspective of CDA, the ASTM CCR is a standardized data set that can be used to constrain CDA specifically for summary documents. • The resulting specification, known as the Continuity of Care Document (CCD), is being developed as a collaborative effort between ASTM and HL 7. 83
 ASTM’s CCR 84
ASTM’s CCR 84
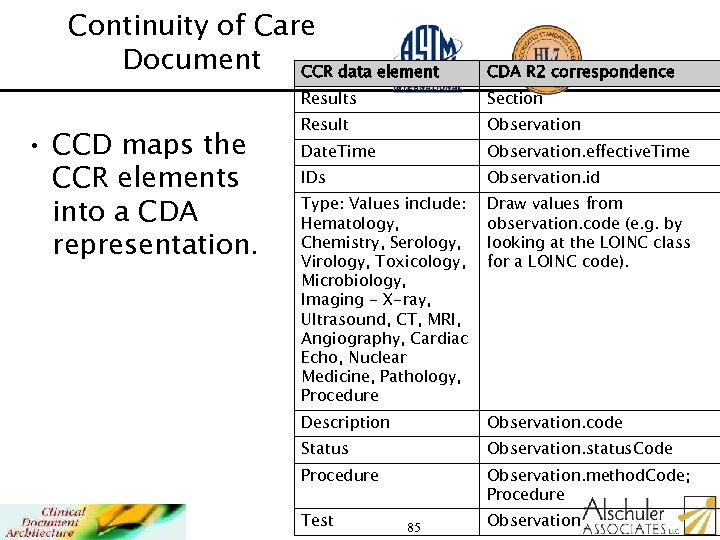 Continuity of Care Document CCR data element CDA R 2 correspondence Results • CCD maps the CCR elements into a CDA representation. Section Result Observation Date. Time Observation. effective. Time IDs Observation. id Type: Values include: Hematology, Chemistry, Serology, Virology, Toxicology, Microbiology, Imaging - X-ray, Ultrasound, CT, MRI, Angiography, Cardiac Echo, Nuclear Medicine, Pathology, Procedure Draw values from observation. code (e. g. by looking at the LOINC class for a LOINC code). Description Observation. code Status Observation. status. Code Procedure Observation. method. Code; Procedure Test 85 Observation
Continuity of Care Document CCR data element CDA R 2 correspondence Results • CCD maps the CCR elements into a CDA representation. Section Result Observation Date. Time Observation. effective. Time IDs Observation. id Type: Values include: Hematology, Chemistry, Serology, Virology, Toxicology, Microbiology, Imaging - X-ray, Ultrasound, CT, MRI, Angiography, Cardiac Echo, Nuclear Medicine, Pathology, Procedure Draw values from observation. code (e. g. by looking at the LOINC class for a LOINC code). Description Observation. code Status Observation. status. Code Procedure Observation. method. Code; Procedure Test 85 Observation
 Continuity of Care Document • • Did this come out of the blue? There is a history of collaboration – – Many people have participated in both efforts Presentation on CDA for continuity of care at ASTM CCR meeting, August, 2003 Memorandum of Understanding, 2004 Acapulco demo: CDA for CCR, October, 2004 – Initial HL 7 Care Record Summary ballot, April, 2005: – HL 7 ballot on CCR, Spring 2005: incorporated changes required for bi-directional exchange and semantic interoperability 86 • • • HL 7 partnered with Massachusetts Medical Society, Microsoft, Ramsey Systems (UK) Limited to CDA header, no detailed section coding Anticipated: “Development of detailed (CDA Level 3) Implementation Guides for “continuity of care” (CCR) in collaboration with the ASTM E 31 under the 2004 Memorandum of Understanding”
Continuity of Care Document • • Did this come out of the blue? There is a history of collaboration – – Many people have participated in both efforts Presentation on CDA for continuity of care at ASTM CCR meeting, August, 2003 Memorandum of Understanding, 2004 Acapulco demo: CDA for CCR, October, 2004 – Initial HL 7 Care Record Summary ballot, April, 2005: – HL 7 ballot on CCR, Spring 2005: incorporated changes required for bi-directional exchange and semantic interoperability 86 • • • HL 7 partnered with Massachusetts Medical Society, Microsoft, Ramsey Systems (UK) Limited to CDA header, no detailed section coding Anticipated: “Development of detailed (CDA Level 3) Implementation Guides for “continuity of care” (CCR) in collaboration with the ASTM E 31 under the 2004 Memorandum of Understanding”
 Continuity of Care Document • “ASTM is dedicated and privileged to work in collaboration with HL 7 on the expression of ASTM's Continuity of Care Record content within HL 7's CDA XML syntax and the seamless transformation of clinical and administrative data between the two standards. ” • Rick Peters, MD, E 31. 28 87
Continuity of Care Document • “ASTM is dedicated and privileged to work in collaboration with HL 7 on the expression of ASTM's Continuity of Care Record content within HL 7's CDA XML syntax and the seamless transformation of clinical and administrative data between the two standards. ” • Rick Peters, MD, E 31. 28 87
 Continuity of Care Document • Benefits – Industry concensus on summary document contents and requirements through ASTM ballots (2004, 2005) – Industry concensus on document exchange framework through HL 7 ballots (1999 -2005) – Summaries for continuity of care • Interoperable with full range of document types • Interoperable with HL 7 V 3 messages, all RIM-based specifications (public health reporting, clinical trials, structured product labels and more) 88
Continuity of Care Document • Benefits – Industry concensus on summary document contents and requirements through ASTM ballots (2004, 2005) – Industry concensus on document exchange framework through HL 7 ballots (1999 -2005) – Summaries for continuity of care • Interoperable with full range of document types • Interoperable with HL 7 V 3 messages, all RIM-based specifications (public health reporting, clinical trials, structured product labels and more) 88
 Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 89
Outline • • • HL 7 CDA for exchange networks CDA+CCR=CCD Summary, Resources & Questions 89
 CDA for Interoperability • HL 7/ANSI specification based on – Reference Information Model (RIM) – Extensible Markup Language (XML) – Standard Terminology • The spec: – Header+Human-readable report+(optional) computable semantics • Industry acceptance: – Internationally implemented for 6 years – US: FHA, CHI, CMS, VA, Do. D, NHIN, HITSP. . . – Vendor support: strong & growing • Interoperability – Full patient record, not just the data that can be coded today – Full patient record – summaries and more, implementation guides in the works from multiple professional societies and agencies 90
CDA for Interoperability • HL 7/ANSI specification based on – Reference Information Model (RIM) – Extensible Markup Language (XML) – Standard Terminology • The spec: – Header+Human-readable report+(optional) computable semantics • Industry acceptance: – Internationally implemented for 6 years – US: FHA, CHI, CMS, VA, Do. D, NHIN, HITSP. . . – Vendor support: strong & growing • Interoperability – Full patient record, not just the data that can be coded today – Full patient record – summaries and more, implementation guides in the works from multiple professional societies and agencies 90
 Current Work • HL 7 – – – – – Continuity of Care Document (with ASTM) Pathology reports (with CAP) Imaging reports (with DICOM) Claims attachments, migrate from R 1 (with CMS) Medical Summary (with IHE, EHR Vendors Association) Dental reports (with ADA) Anesthesiology Reports (with Anes SIG) Public health reports (with CDC). . . What should we be doing to develop standard documents for LTC? 91
Current Work • HL 7 – – – – – Continuity of Care Document (with ASTM) Pathology reports (with CAP) Imaging reports (with DICOM) Claims attachments, migrate from R 1 (with CMS) Medical Summary (with IHE, EHR Vendors Association) Dental reports (with ADA) Anesthesiology Reports (with Anes SIG) Public health reports (with CDC). . . What should we be doing to develop standard documents for LTC? 91
 References & More Info www. HL 7. org Structured Documents Technical Committee web page All meetings, listservs, open to all JAMIA Dolin RH, Alschuler L, Boyer S, Beebe C, Behlen FM, Biron PV, Shabo A. HL 7 Clinical Document Architecture, Release 2. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006; 13: 30– 39. http: //www. jamia. org/cgi/reprint/13/1/30 Care Record Summary http: //www. hl 7. org/Library/Committees/structure/Care. Record. Sum mary%5 FI 2%5 F 2005 SEP%2 Ezip CDA Release 2. 0 Normative Edition: see HL 7. org Alschuler. Associates. com Quick Start Guides CDA/CRS Validator CDA Gallery liora@alschulerassociates. com 92
References & More Info www. HL 7. org Structured Documents Technical Committee web page All meetings, listservs, open to all JAMIA Dolin RH, Alschuler L, Boyer S, Beebe C, Behlen FM, Biron PV, Shabo A. HL 7 Clinical Document Architecture, Release 2. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006; 13: 30– 39. http: //www. jamia. org/cgi/reprint/13/1/30 Care Record Summary http: //www. hl 7. org/Library/Committees/structure/Care. Record. Sum mary%5 FI 2%5 F 2005 SEP%2 Ezip CDA Release 2. 0 Normative Edition: see HL 7. org Alschuler. Associates. com Quick Start Guides CDA/CRS Validator CDA Gallery liora@alschulerassociates. com 92
 Thank you! Questions? 93
Thank you! Questions? 93
 http: //www. alschulerassociates. com/library/presentations/CDA 4 CDT. PEHRC. June 07. ppt Clinical Document Architecture for Common Document Types PEHRC June 18, 2007 Liora Alschuler
http: //www. alschulerassociates. com/library/presentations/CDA 4 CDT. PEHRC. June 07. ppt Clinical Document Architecture for Common Document Types PEHRC June 18, 2007 Liora Alschuler
 Liora Alschuler – Consultant in healthcare IT 1997 -present • Background in electronic text, industry analyst with Seybold Publications, xml. com • Author, ABCD. . . SGML: A Manager’s Guide to Structured Information, 1995 • Founded consulting firm in 2005 – Volunteer standards work • Health Level Seven Board of Directors (2005 -2008) • Co-chair Structured Documents Technical Committee • Co-editor Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) – liora@alschulerassociates. com
Liora Alschuler – Consultant in healthcare IT 1997 -present • Background in electronic text, industry analyst with Seybold Publications, xml. com • Author, ABCD. . . SGML: A Manager’s Guide to Structured Information, 1995 • Founded consulting firm in 2005 – Volunteer standards work • Health Level Seven Board of Directors (2005 -2008) • Co-chair Structured Documents Technical Committee • Co-editor Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) – liora@alschulerassociates. com
 Alschuler Associates, LLC • Consultants in standards-based solutions for healthcare information working with vendors, providers, standards developers • Clients – Military Health System • Enterprise-wide documents, files, images (DFIEA) – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention • Implementation Guide for infectious disease reporting (NHSN) – North American Association of Central Cancer Registries • Implementation Guide for cancer abstracts – Department of Health and Human Services • Subcontracts on Health IT Standards Panel (HITSP) and Health Information Standards for Privacy and Confidentiality (HISPC) – American Hospital Association • Use case development for healthcare IT standards initiative – CDA 4 CDT • Co-founder & Project Management – Private, commercial clients: Fortune 100 and startups • www. alschulerassociates. com
Alschuler Associates, LLC • Consultants in standards-based solutions for healthcare information working with vendors, providers, standards developers • Clients – Military Health System • Enterprise-wide documents, files, images (DFIEA) – Centers for Disease Control and Prevention • Implementation Guide for infectious disease reporting (NHSN) – North American Association of Central Cancer Registries • Implementation Guide for cancer abstracts – Department of Health and Human Services • Subcontracts on Health IT Standards Panel (HITSP) and Health Information Standards for Privacy and Confidentiality (HISPC) – American Hospital Association • Use case development for healthcare IT standards initiative – CDA 4 CDT • Co-founder & Project Management – Private, commercial clients: Fortune 100 and startups • www. alschulerassociates. com
 • HL 7 • CDA – what is it – where is it used • CCD • CDA 4 CDT – & the PEHRC
• HL 7 • CDA – what is it – where is it used • CCD • CDA 4 CDT – & the PEHRC
 Health Level Seven • Non-profit ANSI Standards Development Organization • 20 years old • 2000+ members – individual, corporate • 30 affiliates – US affiliate in near future • “A model community”: building standards to a single information model
Health Level Seven • Non-profit ANSI Standards Development Organization • 20 years old • 2000+ members – individual, corporate • 30 affiliates – US affiliate in near future • “A model community”: building standards to a single information model
 HL 7 Steering Divisions Foundation & Technologies • Implementable Technology Specifications Structure & Semantic Design • Implementation/Conformance • Clinical & Messaging • Infrastructure Context Object Workgroup • Java • Clinical Decision Support • Modeling & Methodology • Electronic Health Record • Security • Financial Management • Service Oriented Architecture • Genomics • Templates • Orders • Vocabulary & Observations • Patient Administration • Scheduling & Logistics • Structured Documents Domain Experts • Anesthesiology • Attachments • Cardiology • Clinical Guidelines • Community Based Collaborative Care • Emergency Care • Government Projects • Health Care Devices • Imaging Integration • Laboratory • Patient Care • Patient Safety • Pediatrics Data Standards • Public Health Emergency Response • Pharmacy • Regulated Clinical Research Information Management
HL 7 Steering Divisions Foundation & Technologies • Implementable Technology Specifications Structure & Semantic Design • Implementation/Conformance • Clinical & Messaging • Infrastructure Context Object Workgroup • Java • Clinical Decision Support • Modeling & Methodology • Electronic Health Record • Security • Financial Management • Service Oriented Architecture • Genomics • Templates • Orders • Vocabulary & Observations • Patient Administration • Scheduling & Logistics • Structured Documents Domain Experts • Anesthesiology • Attachments • Cardiology • Clinical Guidelines • Community Based Collaborative Care • Emergency Care • Government Projects • Health Care Devices • Imaging Integration • Laboratory • Patient Care • Patient Safety • Pediatrics Data Standards • Public Health Emergency Response • Pharmacy • Regulated Clinical Research Information Management
 CDA: A Document Exchange Specification • • This is a CDA and this and this
CDA: A Document Exchange Specification • • This is a CDA and this and this
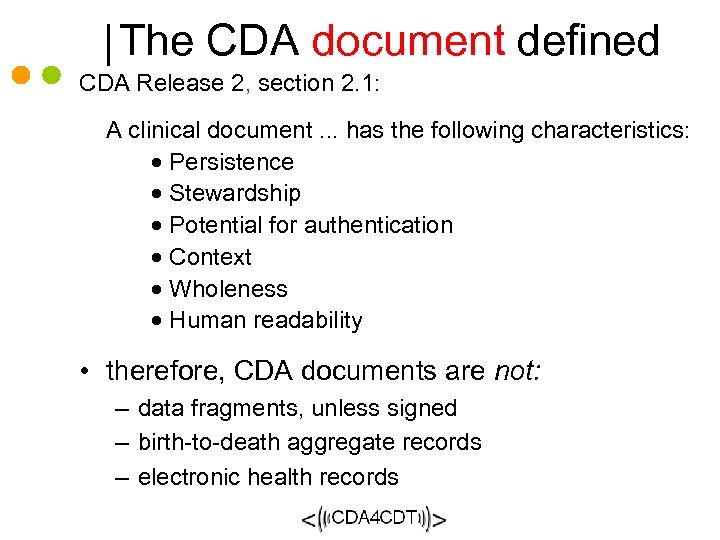 The CDA document defined CDA Release 2, section 2. 1: A clinical document. . . has the following characteristics: · Persistence · Stewardship · Potential for authentication · Context · Wholeness · Human readability • therefore, CDA documents are not: – data fragments, unless signed – birth-to-death aggregate records – electronic health records
The CDA document defined CDA Release 2, section 2. 1: A clinical document. . . has the following characteristics: · Persistence · Stewardship · Potential for authentication · Context · Wholeness · Human readability • therefore, CDA documents are not: – data fragments, unless signed – birth-to-death aggregate records – electronic health records
 CDA Design Principles • priority is patient care, other applications facilitated • minimize technical barriers to implementation • promote longevity of clinical records • scoped by exchange, independent of transfer or storage • enable policy-makers to control information requirements
CDA Design Principles • priority is patient care, other applications facilitated • minimize technical barriers to implementation • promote longevity of clinical records • scoped by exchange, independent of transfer or storage • enable policy-makers to control information requirements
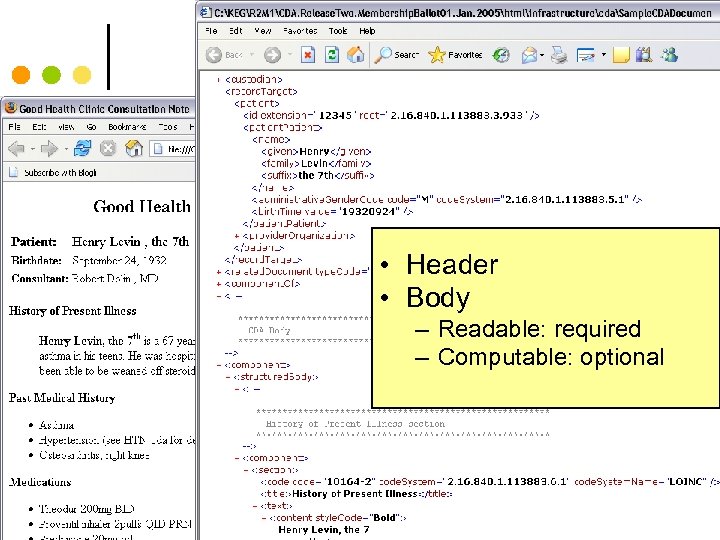 Sample CDA • Header • Body – Readable: required – Computable: optional
Sample CDA • Header • Body – Readable: required – Computable: optional
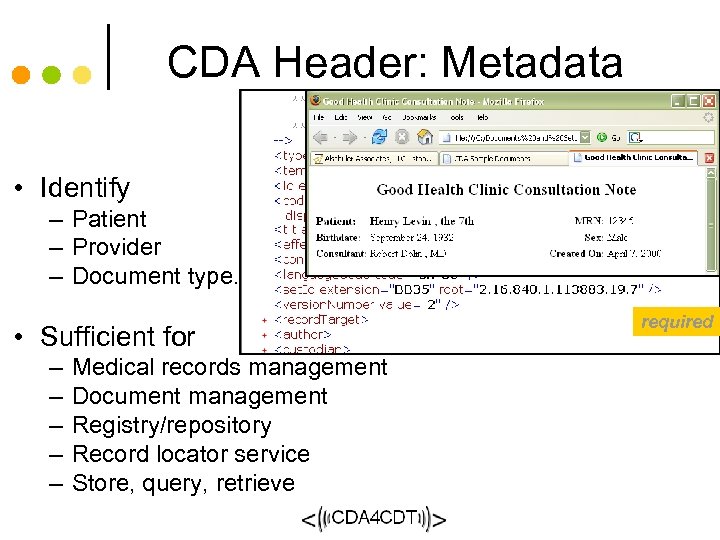 CDA Header: Metadata • Identify – Patient – Provider – Document type. . . • Sufficient for – – – Medical records management Document management Registry/repository Record locator service Store, query, retrieve required
CDA Header: Metadata • Identify – Patient – Provider – Document type. . . • Sufficient for – – – Medical records management Document management Registry/repository Record locator service Store, query, retrieve required
 CDA Body: Human-readable report • Any type of clinical document – – H&P Consult Op note Discharge Summary. . . • Format: tif, PDF, HTML, XML: – – – – Paragraph List Table Caption Link Content Presentation required
CDA Body: Human-readable report • Any type of clinical document – – H&P Consult Op note Discharge Summary. . . • Format: tif, PDF, HTML, XML: – – – – Paragraph List Table Caption Link Content Presentation required
 CDA Body: Machine Processible – Model-based computable semantics: • • • Observation Procedure Organizer Supply Encounter Substance Administration Observation Media Region Of Interest Act Optional
CDA Body: Machine Processible – Model-based computable semantics: • • • Observation Procedure Organizer Supply Encounter Substance Administration Observation Media Region Of Interest Act Optional
 CDA: Incremental Semantic Interoperability • Standard HL 7 metadata • Simple XML for point of care human readability • RIM semantics for reusable computability (“semantic interoperability”)
CDA: Incremental Semantic Interoperability • Standard HL 7 metadata • Simple XML for point of care human readability • RIM semantics for reusable computability (“semantic interoperability”)
 Primary Use Cases • access/portability/exchange – query/locate by patient, provider, practitioner, setting, encounter, date – access distributed information through common metadata – document management • integration – transcription systems – EHR records • re-use/derivative data – summaries, reports – decision support
Primary Use Cases • access/portability/exchange – query/locate by patient, provider, practitioner, setting, encounter, date – access distributed information through common metadata – document management • integration – transcription systems – EHR records • re-use/derivative data – summaries, reports – decision support
 CDA for Information Exchange in the US • Recommended by Health Information Technology Standards Panel (HITSP) work groups • CMS Notice of Proposed Rule Making – Claims attachments using CDA + X 12 – First pilot concluded, others underway • Widespread vendor adoption: – Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise – CDA 4 CDT – Other
CDA for Information Exchange in the US • Recommended by Health Information Technology Standards Panel (HITSP) work groups • CMS Notice of Proposed Rule Making – Claims attachments using CDA + X 12 – First pilot concluded, others underway • Widespread vendor adoption: – Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise – CDA 4 CDT – Other
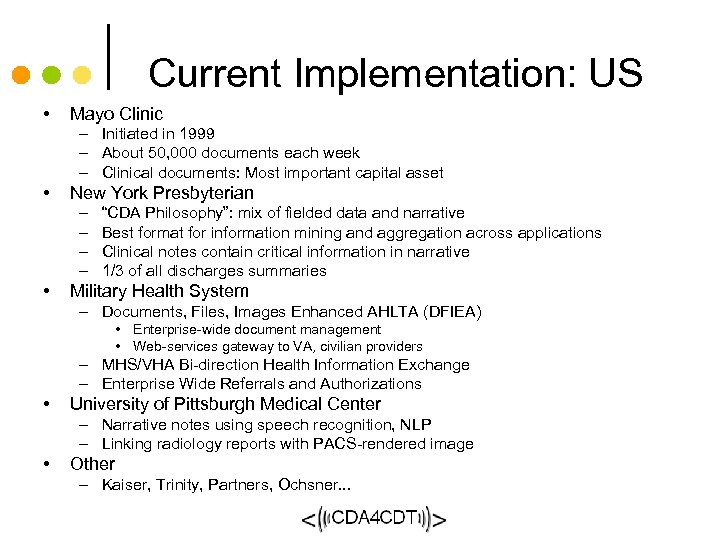 Current Implementation: US • Mayo Clinic – Initiated in 1999 – About 50, 000 documents each week – Clinical documents: Most important capital asset • New York Presbyterian – – • “CDA Philosophy”: mix of fielded data and narrative Best format for information mining and aggregation across applications Clinical notes contain critical information in narrative 1/3 of all discharges summaries Military Health System – Documents, Files, Images Enhanced AHLTA (DFIEA) • Enterprise-wide document management • Web-services gateway to VA, civilian providers – MHS/VHA Bi-direction Health Information Exchange – Enterprise Wide Referrals and Authorizations • University of Pittsburgh Medical Center – Narrative notes using speech recognition, NLP – Linking radiology reports with PACS-rendered image • Other – Kaiser, Trinity, Partners, Ochsner. . .
Current Implementation: US • Mayo Clinic – Initiated in 1999 – About 50, 000 documents each week – Clinical documents: Most important capital asset • New York Presbyterian – – • “CDA Philosophy”: mix of fielded data and narrative Best format for information mining and aggregation across applications Clinical notes contain critical information in narrative 1/3 of all discharges summaries Military Health System – Documents, Files, Images Enhanced AHLTA (DFIEA) • Enterprise-wide document management • Web-services gateway to VA, civilian providers – MHS/VHA Bi-direction Health Information Exchange – Enterprise Wide Referrals and Authorizations • University of Pittsburgh Medical Center – Narrative notes using speech recognition, NLP – Linking radiology reports with PACS-rendered image • Other – Kaiser, Trinity, Partners, Ochsner. . .
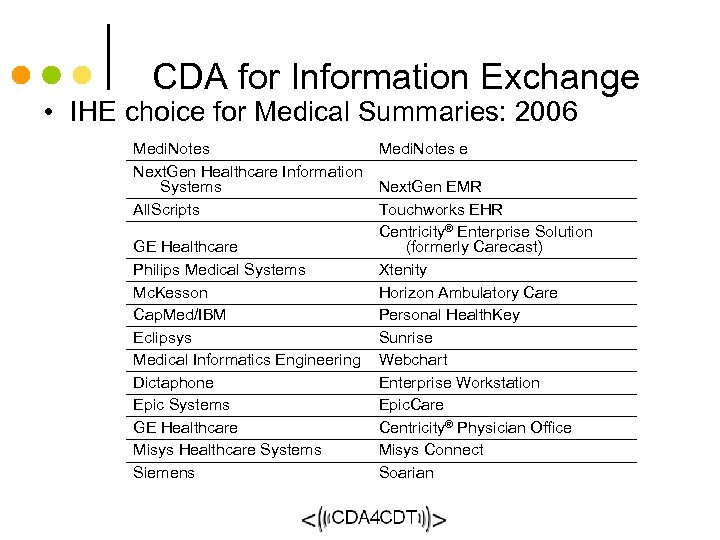 CDA for Information Exchange • IHE choice for Medical Summaries: 2006 Medi. Notes Next. Gen Healthcare Information Systems All. Scripts GE Healthcare Philips Medical Systems Mc. Kesson Cap. Med/IBM Eclipsys Medical Informatics Engineering Dictaphone Epic Systems GE Healthcare Misys Healthcare Systems Siemens Medi. Notes e Next. Gen EMR Touchworks EHR Centricity® Enterprise Solution (formerly Carecast) Xtenity Horizon Ambulatory Care Personal Health. Key Sunrise Webchart Enterprise Workstation Epic. Care Centricity® Physician Office Misys Connect Soarian
CDA for Information Exchange • IHE choice for Medical Summaries: 2006 Medi. Notes Next. Gen Healthcare Information Systems All. Scripts GE Healthcare Philips Medical Systems Mc. Kesson Cap. Med/IBM Eclipsys Medical Informatics Engineering Dictaphone Epic Systems GE Healthcare Misys Healthcare Systems Siemens Medi. Notes e Next. Gen EMR Touchworks EHR Centricity® Enterprise Solution (formerly Carecast) Xtenity Horizon Ambulatory Care Personal Health. Key Sunrise Webchart Enterprise Workstation Epic. Care Centricity® Physician Office Misys Connect Soarian
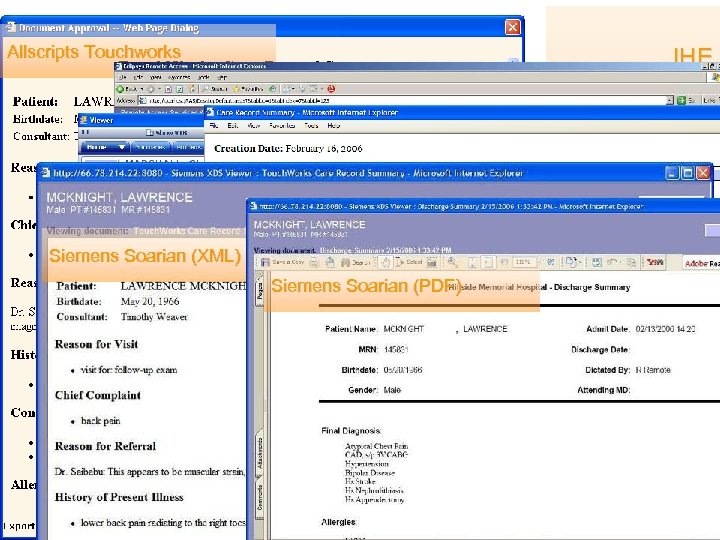 Allscripts Touchworks GE Centricity Siemens Soarian (XML) Medi. Notes e Siemens Soarian (PDF) Eclipsys Sunrise IHE Medical Summaries HIMSS 2006: a CDA Gallery
Allscripts Touchworks GE Centricity Siemens Soarian (XML) Medi. Notes e Siemens Soarian (PDF) Eclipsys Sunrise IHE Medical Summaries HIMSS 2006: a CDA Gallery
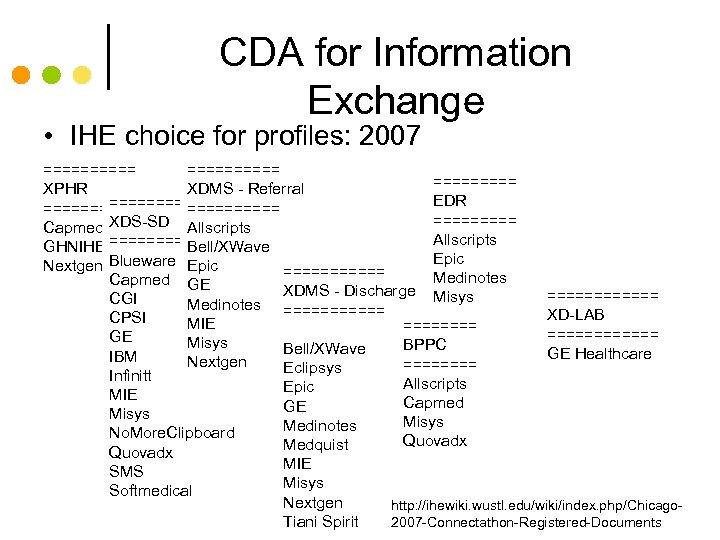 CDA for Information Exchange • IHE choice for profiles: 2007 ========== XPHR XDMS - Referral EDR =========== Capmed XDS-SD Allscripts GHNIHE ====== Bell/XWave Epic Nextgen Blueware Epic ====== Medinotes Capmed GE XDMS - Discharge Misys ====== CGI Medinotes ====== XD-LAB CPSI MIE ============ GE Misys BPPC Bell/XWave GE Healthcare IBM Nextgen ==== Eclipsys Infinitt Allscripts Epic MIE Capmed GE Misys Medinotes No. More. Clipboard Quovadx Medquist Quovadx MIE SMS Misys Softmedical Nextgen http: //ihewiki. wustl. edu/wiki/index. php/Chicago. Tiani Spirit 2007 -Connectathon-Registered-Documents
CDA for Information Exchange • IHE choice for profiles: 2007 ========== XPHR XDMS - Referral EDR =========== Capmed XDS-SD Allscripts GHNIHE ====== Bell/XWave Epic Nextgen Blueware Epic ====== Medinotes Capmed GE XDMS - Discharge Misys ====== CGI Medinotes ====== XD-LAB CPSI MIE ============ GE Misys BPPC Bell/XWave GE Healthcare IBM Nextgen ==== Eclipsys Infinitt Allscripts Epic MIE Capmed GE Misys Medinotes No. More. Clipboard Quovadx Medquist Quovadx MIE SMS Misys Softmedical Nextgen http: //ihewiki. wustl. edu/wiki/index. php/Chicago. Tiani Spirit 2007 -Connectathon-Registered-Documents
 CDA & CCD • IHE Profiles 2005 -2007 based on the Care Record Summary (CRS) – first standard implementation guide for CDA – restricted to “level 2” to avoid competition w/CCR – covered a wider number of use cases • IHE 2007 -2008 will move to conform with CCD • New CDA implementation guides also conform with CCD
CDA & CCD • IHE Profiles 2005 -2007 based on the Care Record Summary (CRS) – first standard implementation guide for CDA – restricted to “level 2” to avoid competition w/CCR – covered a wider number of use cases • IHE 2007 -2008 will move to conform with CCD • New CDA implementation guides also conform with CCD
 ASTM CCR+HL 7 CDA = CCD • The primary use case for the ASTM CCR is to provide a snapshot in time containing a summary of the pertinent clinical, demographic, and administrative data for a specific patient. • From its inception, CDA has supported the ability to represent professional society recommendations, national clinical practice guidelines, standardized data sets, etc. • From the perspective of CDA, the ASTM CCR is a standardized data set that can be used to constrain CDA specifically for summary documents. • The resulting specification is known as the Continuity of Care Document (CCD).
ASTM CCR+HL 7 CDA = CCD • The primary use case for the ASTM CCR is to provide a snapshot in time containing a summary of the pertinent clinical, demographic, and administrative data for a specific patient. • From its inception, CDA has supported the ability to represent professional society recommendations, national clinical practice guidelines, standardized data sets, etc. • From the perspective of CDA, the ASTM CCR is a standardized data set that can be used to constrain CDA specifically for summary documents. • The resulting specification is known as the Continuity of Care Document (CCD).
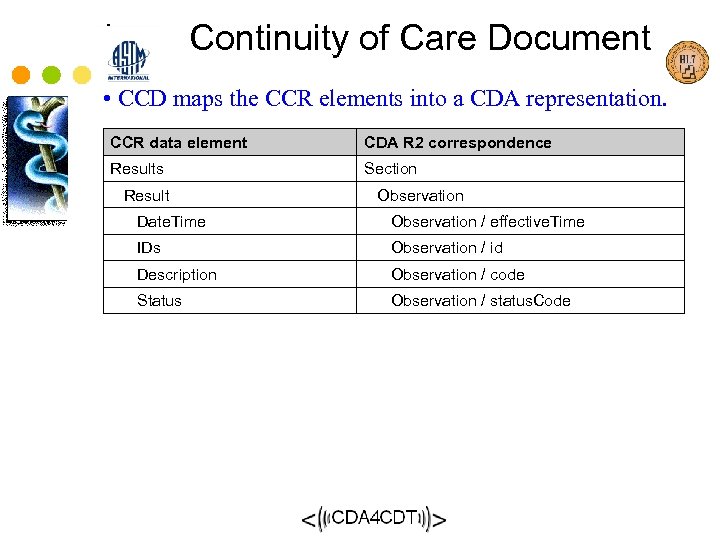 Continuity of Care Document • CCD maps the CCR elements into a CDA representation. CCR data element CDA R 2 correspondence Results Section Result Observation Date. Time Observation / effective. Time IDs Observation / id Description Observation / code Status Observation / status. Code
Continuity of Care Document • CCD maps the CCR elements into a CDA representation. CCR data element CDA R 2 correspondence Results Section Result Observation Date. Time Observation / effective. Time IDs Observation / id Description Observation / code Status Observation / status. Code
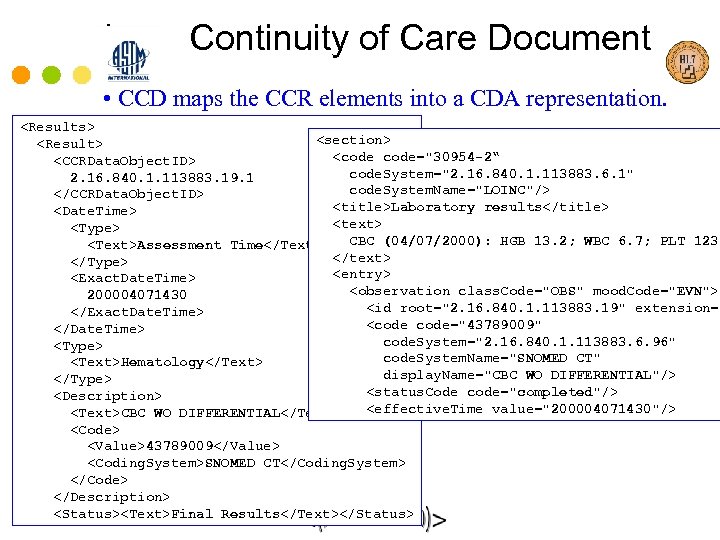 Continuity of Care Document • CCD maps the CCR elements into a CDA representation.
Continuity of Care Document • CCD maps the CCR elements into a CDA representation.
 CDA Business Case • Gentle on-ramp to information exchange - CDA is straight-forward to implement, and provides a mechanism for incremental semantic interoperability. • Improved patient care - CDA provides a mechanism for inserting best practices and evidence-based medicine directly into the process of care (via the same “template” mechanism used to build CCD), thereby making it easier to do the right thing. • Lower costs – CDA provides necessary information to coordinate care, reducing redundant testing and optimizing care delivery for quality and cost. • CDA hits the “sweet spot” – CDA encompasses all of clinical documents. A single standard for the entire EHR is too broad. Multiple standards and/or messages for each EHR function may be difficult to implement. CDA is “just right”.
CDA Business Case • Gentle on-ramp to information exchange - CDA is straight-forward to implement, and provides a mechanism for incremental semantic interoperability. • Improved patient care - CDA provides a mechanism for inserting best practices and evidence-based medicine directly into the process of care (via the same “template” mechanism used to build CCD), thereby making it easier to do the right thing. • Lower costs – CDA provides necessary information to coordinate care, reducing redundant testing and optimizing care delivery for quality and cost. • CDA hits the “sweet spot” – CDA encompasses all of clinical documents. A single standard for the entire EHR is too broad. Multiple standards and/or messages for each EHR function may be difficult to implement. CDA is “just right”.
 CDA beyond CCD • Not everything we want to exchange is a summary • Let’s look at what’s happening with development of other document types. . .
CDA beyond CCD • Not everything we want to exchange is a summary • Let’s look at what’s happening with development of other document types. . .
 Other CDA content profile development – Within HL 7: • Clinical domains: anatomic pathology, imaging, lab, anesthesiology, pediatrics, long term care, others? • ASIG: HIPAA Attachments – adding dental – Outside HL 7: Public health & MDS • NAACCR Cancer abstracts (no HL 7 ballot) • CDC Infectious Disease Reports (will be HL 7 ballot) • MDS: soon, from HHS – IHE • 2006: 1 content type built on HL 7 CRS • 2007: 7 content types, some constrain CRS, others new • Current cycle: – updating all to be consistent with CCD – adding Discharge Summary – CDA 4 CDT
Other CDA content profile development – Within HL 7: • Clinical domains: anatomic pathology, imaging, lab, anesthesiology, pediatrics, long term care, others? • ASIG: HIPAA Attachments – adding dental – Outside HL 7: Public health & MDS • NAACCR Cancer abstracts (no HL 7 ballot) • CDC Infectious Disease Reports (will be HL 7 ballot) • MDS: soon, from HHS – IHE • 2006: 1 content type built on HL 7 CRS • 2007: 7 content types, some constrain CRS, others new • Current cycle: – updating all to be consistent with CCD – adding Discharge Summary – CDA 4 CDT
 CDA for Common Document Types • Project initiated in January, 2007 – M*Modal – AHDI(was AAMT)/MTIA – AHIMA • Strong support from dictation / transcription and document management industries • Cooperation/coordination with HL 7, IHE, EHR vendors and providers
CDA for Common Document Types • Project initiated in January, 2007 – M*Modal – AHDI(was AAMT)/MTIA – AHIMA • Strong support from dictation / transcription and document management industries • Cooperation/coordination with HL 7, IHE, EHR vendors and providers
 CDA 4 CDT Mission • Develop CDA Implementation Guides (IGs) for common types of electronic healthcare documents • Bring them through the HL 7 ballot process • Promote their use and adoption by healthcare organizations and health information exchange networks
CDA 4 CDT Mission • Develop CDA Implementation Guides (IGs) for common types of electronic healthcare documents • Bring them through the HL 7 ballot process • Promote their use and adoption by healthcare organizations and health information exchange networks
 Rationale • Enlarge and enrich the flow of data into the electronic health record • Speed the development of interoperable clinical document repositories • Bridge the gap between narrative documents produced through dictation and the structured, computable records within an EHR
Rationale • Enlarge and enrich the flow of data into the electronic health record • Speed the development of interoperable clinical document repositories • Bridge the gap between narrative documents produced through dictation and the structured, computable records within an EHR
 Why would physicians promoting the EHR have an interest in documents? • Assumptions: – EMR/EHR is the solution – Documents are the problem • Questions: – Are they mutually exclusive or complementary? – Can e. Documents bridge the gap?
Why would physicians promoting the EHR have an interest in documents? • Assumptions: – EMR/EHR is the solution – Documents are the problem • Questions: – Are they mutually exclusive or complementary? – Can e. Documents bridge the gap?
 Problems with Documents • Can’t compute • Can’t automate decision support • Can’t validate conformance to content requirements • And why are they still prevalent? – – Nuanced & precise Support human decision making Retain current workflow e. Documents support narrative & codes • multiple indices optimized for reimbursement, decision support, quality metrics, research • Document management completes the EMR
Problems with Documents • Can’t compute • Can’t automate decision support • Can’t validate conformance to content requirements • And why are they still prevalent? – – Nuanced & precise Support human decision making Retain current workflow e. Documents support narrative & codes • multiple indices optimized for reimbursement, decision support, quality metrics, research • Document management completes the EMR
 Why encourage continued use of documents? • Worst case: – no computable clinical data – no reuse – + information at the point of care • Best case: – fully computable data to populate EHR • Likely case: – section-level reuse (i. e. HPI pre-populates Discharge Summary) – we can do this now – gradual rise in semantic interoperability
Why encourage continued use of documents? • Worst case: – no computable clinical data – no reuse – + information at the point of care • Best case: – fully computable data to populate EHR • Likely case: – section-level reuse (i. e. HPI pre-populates Discharge Summary) – we can do this now – gradual rise in semantic interoperability
 Why not keep pushing for fully interoperable records? • Semantic interoperability is hard – over 250, 000 concepts in SNOMED CT – we can’t give up, we need safe computability • Need information at the point of care • Networks need data: self-sustaining networks have Big Data – Initial ROI will spur further investment – MTIA members process 300 M documents/year • Complex systems are built from simple systems • CDA: no loss of computability minimum metadata today future
Why not keep pushing for fully interoperable records? • Semantic interoperability is hard – over 250, 000 concepts in SNOMED CT – we can’t give up, we need safe computability • Need information at the point of care • Networks need data: self-sustaining networks have Big Data – Initial ROI will spur further investment – MTIA members process 300 M documents/year • Complex systems are built from simple systems • CDA: no loss of computability minimum metadata today future
 CDA 4 CDT: bridging the gap between EHRs and e. Documents • CDA 4 CDT will: – Establish consensus on content using CDA e. Document format – Propagate support for CDA within the dictation/transcription industry – Create consistent electronic documents for importation into EMR, document repositories and health information exchanges – Increase EMR adoption • Highest potential: – Massively increase amount of data in fledgling exchange networks because minimally disruptive to current workflow • Defining success: – At least 25% of RFPs for transcription, EMRs, integration and information exchange cite compliance as a requirement
CDA 4 CDT: bridging the gap between EHRs and e. Documents • CDA 4 CDT will: – Establish consensus on content using CDA e. Document format – Propagate support for CDA within the dictation/transcription industry – Create consistent electronic documents for importation into EMR, document repositories and health information exchanges – Increase EMR adoption • Highest potential: – Massively increase amount of data in fledgling exchange networks because minimally disruptive to current workflow • Defining success: – At least 25% of RFPs for transcription, EMRs, integration and information exchange cite compliance as a requirement
 CDA 4 CDT • Scope – Develop implementation guide for use across the industry – Rapid development, leverage framework, precedents – Establish section-level content, reuse section templates • H&P Timeline – Initial draft in 7 weeks – Balloted as HL 7 Draft Standard for Trial Use • March 26 ballot open, April 24 close • Ballot reconciliation approximately 5 weeks • Revised draft to ballot in August • Consult Note Timeline – Target August 2007 initial ballot • Discharge Summary: Coordinating with IHE on publication – Target publication fall 2007
CDA 4 CDT • Scope – Develop implementation guide for use across the industry – Rapid development, leverage framework, precedents – Establish section-level content, reuse section templates • H&P Timeline – Initial draft in 7 weeks – Balloted as HL 7 Draft Standard for Trial Use • March 26 ballot open, April 24 close • Ballot reconciliation approximately 5 weeks • Revised draft to ballot in August • Consult Note Timeline – Target August 2007 initial ballot • Discharge Summary: Coordinating with IHE on publication – Target publication fall 2007
 Technical working group • A focused group of working volunteers – prior knowledge of CDA – experience implementing CDA – familiarity with the current set of CDA implementation guides • Participation is open at all stages of the ballot and ballot review process • CDA 4 CDT retains no copyright of balloted material
Technical working group • A focused group of working volunteers – prior knowledge of CDA – experience implementing CDA – familiarity with the current set of CDA implementation guides • Participation is open at all stages of the ballot and ballot review process • CDA 4 CDT retains no copyright of balloted material
 H&P Method • Review precedents: – ASTM’s Standard Specifications for Healthcare Document Formats (E 2184. 02) (Headings and subheadings used in the healthcare industry and associated with specific report types) – HL 7/ASTM Continuity of Care Document (CCD) – Clinical LOINC document and section codes – HL 7 ASIG CDA R 2 Attachment for Clinical Notes – HL 7 Care Record Summary (CRS) – IHE profiles, including the content profiles within Patient Care Coordination – MHS/Do. D-VA-IM-IT Demo Project Discharge Summary and SOAP HL 7 CDA R 2 Implementation Guides • Review samples/templates: – Sample CDA documents developed for local provider institutions (Mayo Clinic, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, New York Presbyterian, and others) – Non-CDA sample documents supplied by participating providers and vendors – H&P templates from AHIMA, vendors, providers • Statistical analysis: over 15, 000 dictated H&Ps by M*Modal • Test design against samples
H&P Method • Review precedents: – ASTM’s Standard Specifications for Healthcare Document Formats (E 2184. 02) (Headings and subheadings used in the healthcare industry and associated with specific report types) – HL 7/ASTM Continuity of Care Document (CCD) – Clinical LOINC document and section codes – HL 7 ASIG CDA R 2 Attachment for Clinical Notes – HL 7 Care Record Summary (CRS) – IHE profiles, including the content profiles within Patient Care Coordination – MHS/Do. D-VA-IM-IT Demo Project Discharge Summary and SOAP HL 7 CDA R 2 Implementation Guides • Review samples/templates: – Sample CDA documents developed for local provider institutions (Mayo Clinic, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, New York Presbyterian, and others) – Non-CDA sample documents supplied by participating providers and vendors – H&P templates from AHIMA, vendors, providers • Statistical analysis: over 15, 000 dictated H&Ps by M*Modal • Test design against samples
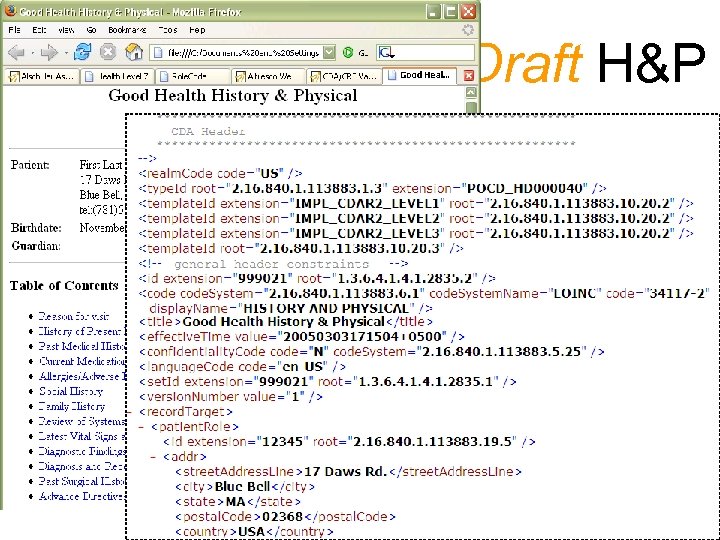 Draft H&P
Draft H&P
 Ballot results • 78 comments received – ACP, Trinity Health, Kaiser Permanente, VHA, Regenstreif – Epic, GE, Medquist, Northrop • All comments addressed – All negatives will be withdrawn – Draft in revision – Will re-ballot in August/September • If passed, will be “Draft Standard for Trial Use” (DSTU) – stable platform for implementation – within 2 years either normative or revised
Ballot results • 78 comments received – ACP, Trinity Health, Kaiser Permanente, VHA, Regenstreif – Epic, GE, Medquist, Northrop • All comments addressed – All negatives will be withdrawn – Draft in revision – Will re-ballot in August/September • If passed, will be “Draft Standard for Trial Use” (DSTU) – stable platform for implementation – within 2 years either normative or revised
 Ballot issues • Most difficult – balance diversity of current practice against desire for consistency – where can you lead the industry, where must you follow? • Clarify intended content – Past Medical History vs. Surgical History • Physical exam: diversity of practice – Define full set of sub-headings – Allow narrative &/or sub-sections
Ballot issues • Most difficult – balance diversity of current practice against desire for consistency – where can you lead the industry, where must you follow? • Clarify intended content – Past Medical History vs. Surgical History • Physical exam: diversity of practice – Define full set of sub-headings – Allow narrative &/or sub-sections
 Consult Note • Same method as H&P – – consistent with precedents large scale analysis of dictated notes reuse section-level content review E&M guidelines • Examine required metadata • Examine report contents – Require “reason for referral” – Relationship with “reason for visit”, “chief complaint” • Seeking pre-ballot review
Consult Note • Same method as H&P – – consistent with precedents large scale analysis of dictated notes reuse section-level content review E&M guidelines • Examine required metadata • Examine report contents – Require “reason for referral” – Relationship with “reason for visit”, “chief complaint” • Seeking pre-ballot review
 Future work • Horizontal: additional document types – Op note – Specialize the History & Physical • Vertical: supporting implementation – Quick Start Guides for implementers – Training for implementers • Promotion: Among providers – Education on utility, strategic value – End-user training for compliance • Whatever it takes to support and promote widespread adoption
Future work • Horizontal: additional document types – Op note – Specialize the History & Physical • Vertical: supporting implementation – Quick Start Guides for implementers – Training for implementers • Promotion: Among providers – Education on utility, strategic value – End-user training for compliance • Whatever it takes to support and promote widespread adoption
 How can PEHRC, PEHRC members get involved? • Participate in design review – through CDA 4 CDT – through HL 7 Structured Documents TC – through HL 7 Board of Directors • Participate in the ballot – as HL 7 member or non-member • Encourage implementation – within professional society – within practice group
How can PEHRC, PEHRC members get involved? • Participate in design review – through CDA 4 CDT – through HL 7 Structured Documents TC – through HL 7 Board of Directors • Participate in the ballot – as HL 7 member or non-member • Encourage implementation – within professional society – within practice group
 CDA for Common Document Types • Founders: • Benefactors: • Participants: Acusis, Kaiser Permanente, Mayo Clinic, Military Health System, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, GE Healthcare • Management:
CDA for Common Document Types • Founders: • Benefactors: • Participants: Acusis, Kaiser Permanente, Mayo Clinic, Military Health System, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, GE Healthcare • Management:
 HL 7: patient-centered health information HL 7 TC/SIG RCRIM SDTC Pharmacy Lab Image Int. Patient Care Decision Support Public Health Pharmacy Discharge medications PCP followup Consult New drug information PHR/EHR Vocabulary Services Knowledge Base R&D Study Develop Report HL 7 Standards RIM-Data. Types-ITS SPL CDA: Discharge Sum V 3 msg: Med Order CDA: lab, imaging V 2: lab Arden ICSR a. ECG CT Lab Stability MOUs X 12, ADA ASTM, CEN CDISC, DICOM, e. HI IEEE, IHE, OASIS, OMG, NCPDP, CAP, WEDI
HL 7: patient-centered health information HL 7 TC/SIG RCRIM SDTC Pharmacy Lab Image Int. Patient Care Decision Support Public Health Pharmacy Discharge medications PCP followup Consult New drug information PHR/EHR Vocabulary Services Knowledge Base R&D Study Develop Report HL 7 Standards RIM-Data. Types-ITS SPL CDA: Discharge Sum V 3 msg: Med Order CDA: lab, imaging V 2: lab Arden ICSR a. ECG CT Lab Stability MOUs X 12, ADA ASTM, CEN CDISC, DICOM, e. HI IEEE, IHE, OASIS, OMG, NCPDP, CAP, WEDI
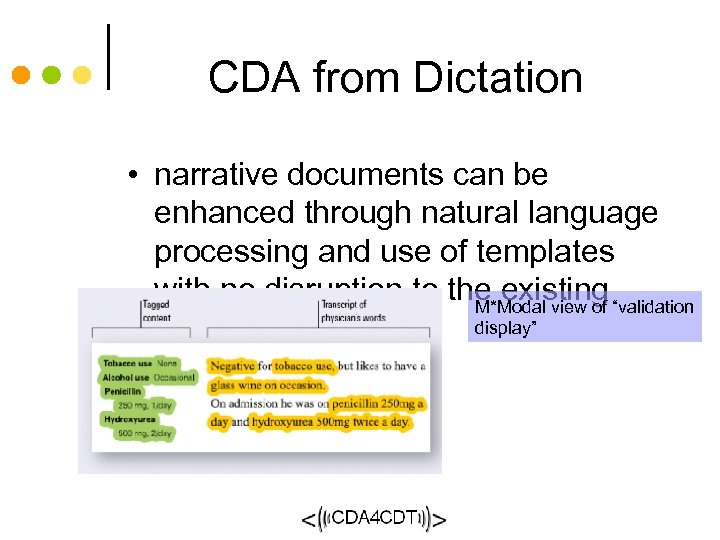 CDA from Dictation • narrative documents can be enhanced through natural language processing and use of templates with no disruption to the existing “validation M*Modal view of display” workflow
CDA from Dictation • narrative documents can be enhanced through natural language processing and use of templates with no disruption to the existing “validation M*Modal view of display” workflow


