Traditional economy.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Traditional economy KOLYADA VICTOR, E 206
Traditional economy KOLYADA VICTOR, E 206
 Presentation plan 1. Introduction 1. What traditional economy is? 2. Where? 2. Main body 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Characteristics of a traditional Economy Traditional Mixed Economies Advantages Disadvantages The difference Example 3. Conclusion
Presentation plan 1. Introduction 1. What traditional economy is? 2. Where? 2. Main body 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Characteristics of a traditional Economy Traditional Mixed Economies Advantages Disadvantages The difference Example 3. Conclusion
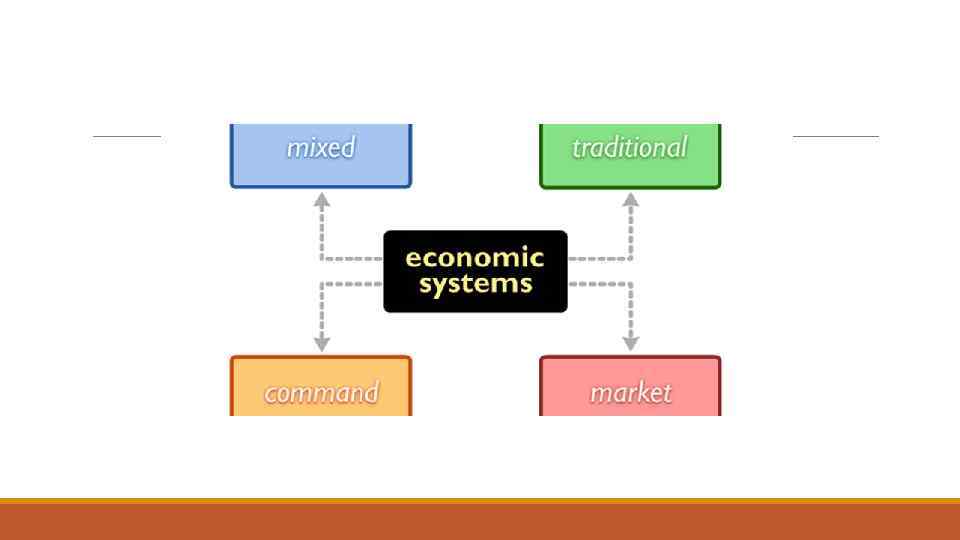
 What traditional economy is? A traditional economy is a system where traditions, customs, and beliefs shape the goods and products the society creates. Countries that use this type of economic system are often rural and farm-based. Traditional economy is defined by bartering and trading.
What traditional economy is? A traditional economy is a system where traditions, customs, and beliefs shape the goods and products the society creates. Countries that use this type of economic system are often rural and farm-based. Traditional economy is defined by bartering and trading.
 Where? Most traditional economies operate in emerging markets and developing countries. They are in Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. Asia South Africa Latin America
Where? Most traditional economies operate in emerging markets and developing countries. They are in Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. Asia South Africa Latin America
 Characteristics of a traditional Economy Traditional economies center around a family or tribe. They use traditions gained from the elders' experience to guide day-to-day life. That's why they base economic decisions on these traditions.
Characteristics of a traditional Economy Traditional economies center around a family or tribe. They use traditions gained from the elders' experience to guide day-to-day life. That's why they base economic decisions on these traditions.
 Characteristics of a traditional Economy Most traditional economies use all they can produce. There is rarely surplus or leftovers. That makes it unnecessary to trade or create money.
Characteristics of a traditional Economy Most traditional economies use all they can produce. There is rarely surplus or leftovers. That makes it unnecessary to trade or create money.
 Characteristics of a traditional Economy Some traditional economies do trade rely on barter.
Characteristics of a traditional Economy Some traditional economies do trade rely on barter.
 Characteristics of a Traditional Economy Traditional economies start to evolve once they start farming and settle down. They are more likely to have a surplus, such as crop, that they use for trade. When that happens, economy creates some form of money. That facilitates trading over long distances.
Characteristics of a Traditional Economy Traditional economies start to evolve once they start farming and settle down. They are more likely to have a surplus, such as crop, that they use for trade. When that happens, economy creates some form of money. That facilitates trading over long distances.
 Traditional Mixed Economies When traditional economies interact with market or command economies, things change. Cash takes on a more important role. It enables those in the traditional economy to buy better equipment. That makes their farming, hunting, or fishing more profitable. When that happens, they become a traditional mixed economy.
Traditional Mixed Economies When traditional economies interact with market or command economies, things change. Cash takes on a more important role. It enables those in the traditional economy to buy better equipment. That makes their farming, hunting, or fishing more profitable. When that happens, they become a traditional mixed economy.
 Traditional Mixed Economies Traditional economies can have elements of capitalism, socialism, and communism. It depends on how they are set up. Agricultural societies that allow private ownership of farmland incorporate capitalism.
Traditional Mixed Economies Traditional economies can have elements of capitalism, socialism, and communism. It depends on how they are set up. Agricultural societies that allow private ownership of farmland incorporate capitalism.
 Advantages + Custom and tradition dictate the distribution of resources. Everyone knows their contribution toward production, whether it's as a farmer or hunter. Members also understand what they are likely to receive. Even if they aren't satisfied, they don't rebel. They understand that it's what's kept the society together and functioning for generations. Since traditional economies are smaller, they are less destructive to the environment.
Advantages + Custom and tradition dictate the distribution of resources. Everyone knows their contribution toward production, whether it's as a farmer or hunter. Members also understand what they are likely to receive. Even if they aren't satisfied, they don't rebel. They understand that it's what's kept the society together and functioning for generations. Since traditional economies are smaller, they are less destructive to the environment.
 Disadvantages Traditional economies are vulnerable to changes in nature, especially the weather. For this reason, traditional economies limit population growth. When the harvest or hunting is poor, people starve.
Disadvantages Traditional economies are vulnerable to changes in nature, especially the weather. For this reason, traditional economies limit population growth. When the harvest or hunting is poor, people starve.
 The main difference with market economy In command economies, prices and supplies are determined by the government, while, in contrast, prices in a market economy are set by supply and demand. A mixed economy includes both private enterprise and some degree of government control.
The main difference with market economy In command economies, prices and supplies are determined by the government, while, in contrast, prices in a market economy are set by supply and demand. A mixed economy includes both private enterprise and some degree of government control.
 Example The Inuit tribe of northern Canada is one example of a society that still uses a traditional economy. Families teach their children the same customs and allocation of resources that have been practiced for hundreds of years. Children in this society are taught how to hunt, fish, make tools, and build shelter
Example The Inuit tribe of northern Canada is one example of a society that still uses a traditional economy. Families teach their children the same customs and allocation of resources that have been practiced for hundreds of years. Children in this society are taught how to hunt, fish, make tools, and build shelter
 Conclusion In a society with traditional economy nearly all economic activity is the result of ritual and custom. Habit and custom also prescribe most social behaviour. Individuals are not free to make decisions based on what they want or would like to have. Instead, their roles are defined. They know what goods and services will be produced, how to produce them, and how such goods and services will be distributed.
Conclusion In a society with traditional economy nearly all economic activity is the result of ritual and custom. Habit and custom also prescribe most social behaviour. Individuals are not free to make decisions based on what they want or would like to have. Instead, their roles are defined. They know what goods and services will be produced, how to produce them, and how such goods and services will be distributed.
 Thank you for your attention!
Thank you for your attention!


