37e1b3ad0185120fab2e369fb031853d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Trading of Complex Commodities Josh Johnson Committee: Eugene Fink Lawrence Hall Srinivas Katkoori
Trading of Complex Commodities Josh Johnson Committee: Eugene Fink Lawrence Hall Srinivas Katkoori
 Introduction Motivation • Build an automated exchange for trading goods and services
Introduction Motivation • Build an automated exchange for trading goods and services
 Introduction Motivation • Build an automated exchange for trading goods and services • Combine the speed and liquidity of the stock exchange
Introduction Motivation • Build an automated exchange for trading goods and services • Combine the speed and liquidity of the stock exchange
 Introduction Motivation • Build an automated exchange for trading goods and services • Combine the speed and liquidity of the stock exchange with the flexibility of e. Bay +
Introduction Motivation • Build an automated exchange for trading goods and services • Combine the speed and liquidity of the stock exchange with the flexibility of e. Bay +
 Outline • Main concepts • Previous work • Data structures • Performance
Outline • Main concepts • Previous work • Data structures • Performance
 Concepts • Market • Orders • Matches • Fills
Concepts • Market • Orders • Matches • Fills
 Market All items that can be traded form a market. Example: All conceivable vehicles compose a car market.
Market All items that can be traded form a market. Example: All conceivable vehicles compose a car market.
 Orders An order is a subset of the market along with a price function. Order example: Any Mustang or Corvette; Mustang for $38, 000 or Corvette for $40, 000 , . -$1 for every ten miles.
Orders An order is a subset of the market along with a price function. Order example: Any Mustang or Corvette; Mustang for $38, 000 or Corvette for $40, 000 , . -$1 for every ten miles.
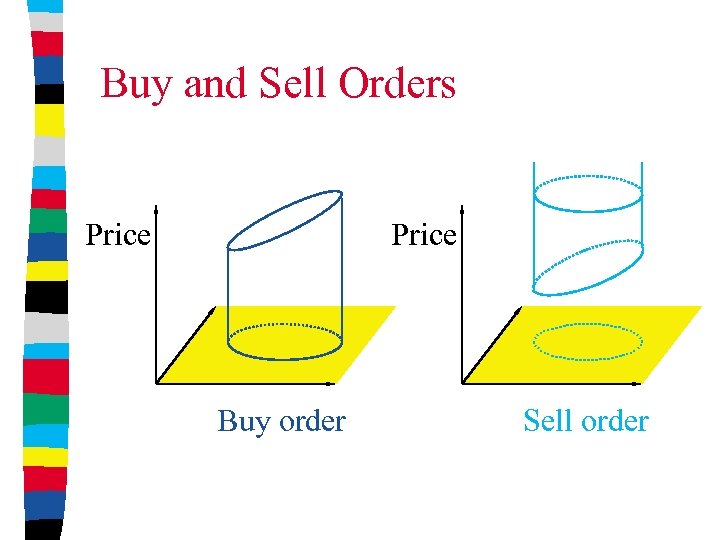 Buy and Sell Orders Price Buy order Sell order
Buy and Sell Orders Price Buy order Sell order
 Matching A buy order matches a sell order if: item buy-region sell-region, buy-price(item) sell-price(item).
Matching A buy order matches a sell order if: item buy-region sell-region, buy-price(item) sell-price(item).
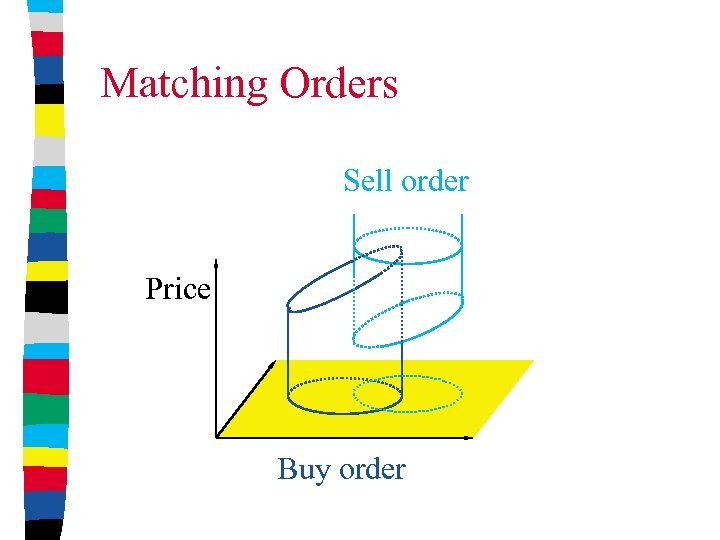 Matching Orders Sell order Price Buy order
Matching Orders Sell order Price Buy order
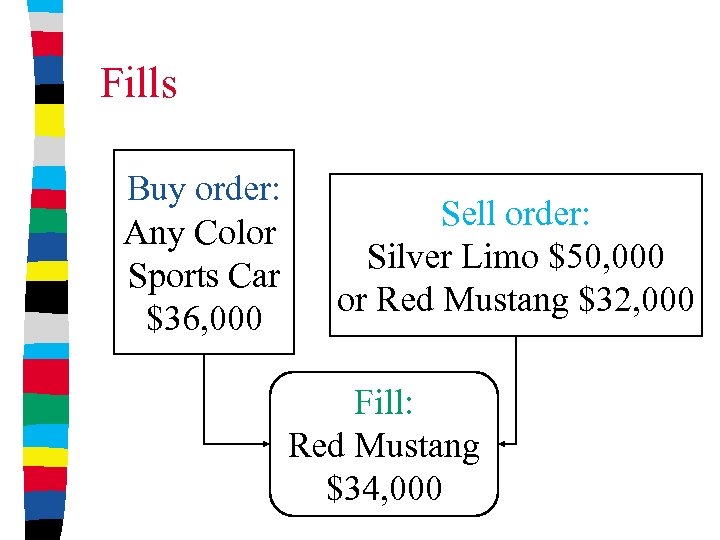 Fills Buy order: Any Color Sports Car $36, 000 Sell order: Silver Limo $50, 000 or Red Mustang $32, 000 Fill: Red Mustang $34, 000
Fills Buy order: Any Color Sports Car $36, 000 Sell order: Silver Limo $50, 000 or Red Mustang $32, 000 Fill: Red Mustang $34, 000
 Implemented Exchange System Specific sell orders Good: Sell a red Mustang made in 1999. Bad: Sell any color Mustang made before 1999.
Implemented Exchange System Specific sell orders Good: Sell a red Mustang made in 1999. Bad: Sell any color Mustang made before 1999.
 Outline • Main concepts • Previous work • Data structures • Performance
Outline • Main concepts • Previous work • Data structures • Performance
 Previous Work • Auctions • Exchanges
Previous Work • Auctions • Exchanges
 Auctions • Complex commodities • Asymmetry between buyers and sellers • Illiquid Examples: e. Bay, Free. Markets, e. Mediator
Auctions • Complex commodities • Asymmetry between buyers and sellers • Illiquid Examples: e. Bay, Free. Markets, e. Mediator
 Exchanges • Simple commodities • Symmetry between buyers and sellers • Liquid Examples: Stocks, Futures
Exchanges • Simple commodities • Symmetry between buyers and sellers • Liquid Examples: Stocks, Futures
 Outline • Main concepts • Previous work • Data structures • Performance
Outline • Main concepts • Previous work • Data structures • Performance
 Main Structures • Tree of sell orders • List of buy orders
Main Structures • Tree of sell orders • List of buy orders
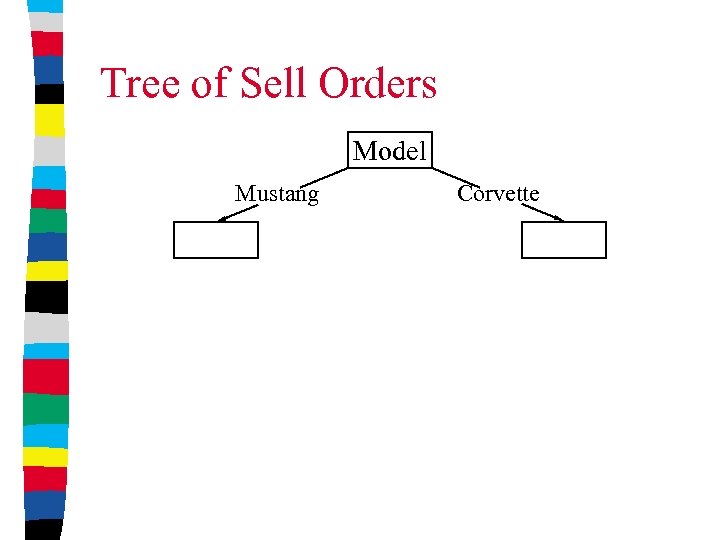 Tree of Sell Orders Model Mustang Corvette
Tree of Sell Orders Model Mustang Corvette
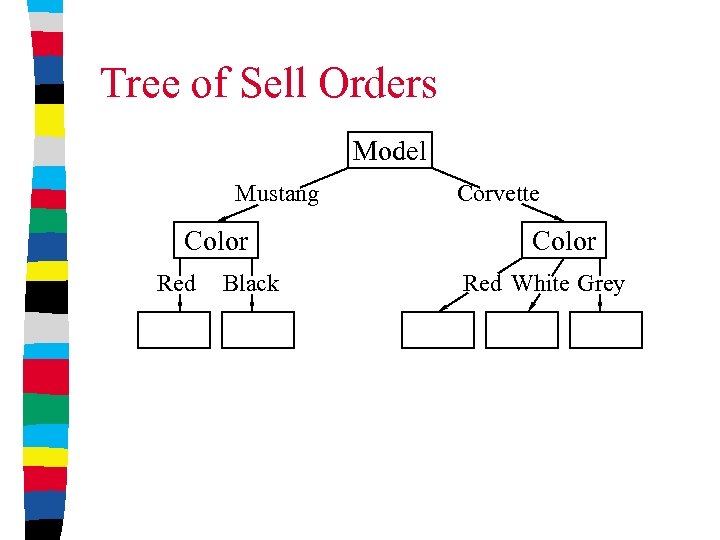 Tree of Sell Orders Model Mustang Color Red Black Corvette Color Red White Grey
Tree of Sell Orders Model Mustang Color Red Black Corvette Color Red White Grey
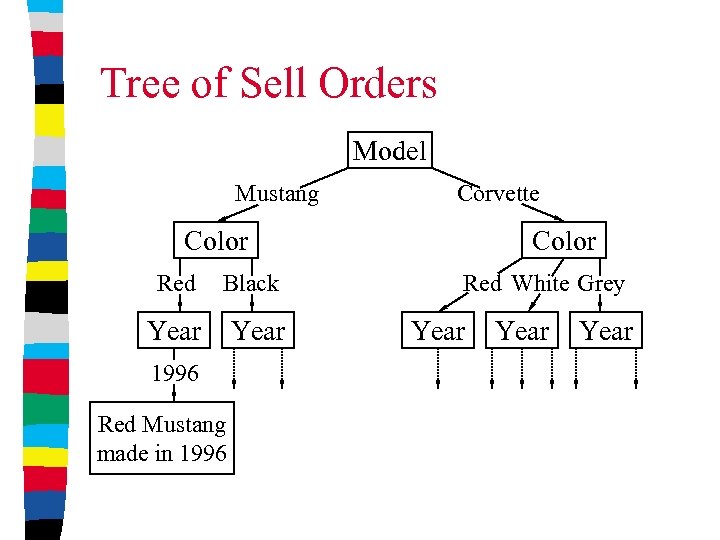 Tree of Sell Orders Model Mustang Corvette Color Red Black Year 1996 Red Mustang made in 1996 Color Red White Grey Year
Tree of Sell Orders Model Mustang Corvette Color Red Black Year 1996 Red Mustang made in 1996 Color Red White Grey Year
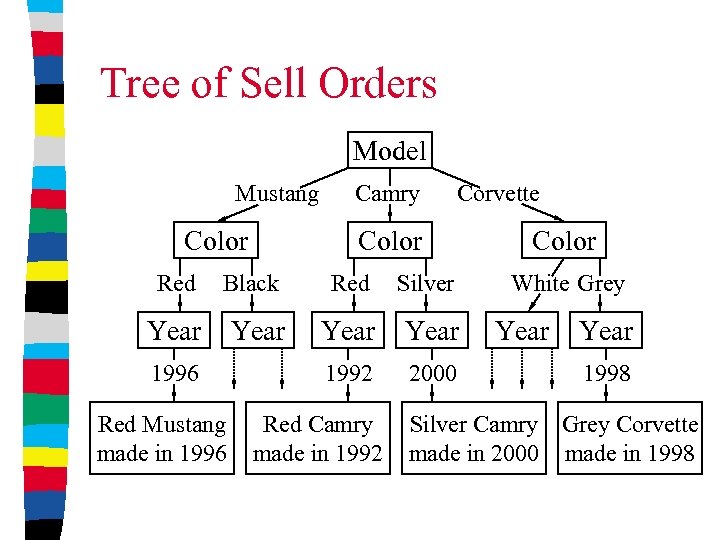 Tree of Sell Orders Model Mustang Color Camry Corvette Color Red Black Red Silver Year 1992 2000 1996 Red Mustang made in 1996 Red Camry made in 1992 Color White Grey Year 1998 Silver Camry Grey Corvette made in 2000 made in 1998
Tree of Sell Orders Model Mustang Color Camry Corvette Color Red Black Red Silver Year 1992 2000 1996 Red Mustang made in 1996 Red Camry made in 1992 Color White Grey Year 1998 Silver Camry Grey Corvette made in 2000 made in 1998
 Node in the Tree Each node contains a red-black tree for one attribute. If there are k values for an attribute, search within the node takes O(lg k).
Node in the Tree Each node contains a red-black tree for one attribute. If there are k values for an attribute, search within the node takes O(lg k).
 Matching a Buy Order Let S be the number of sell orders and m be the number of matches. Best case: Time = O(m + lg S) Worse case: Time = O(m lg S) Worst case: Time = O(S)
Matching a Buy Order Let S be the number of sell orders and m be the number of matches. Best case: Time = O(m + lg S) Worse case: Time = O(m lg S) Worst case: Time = O(S)
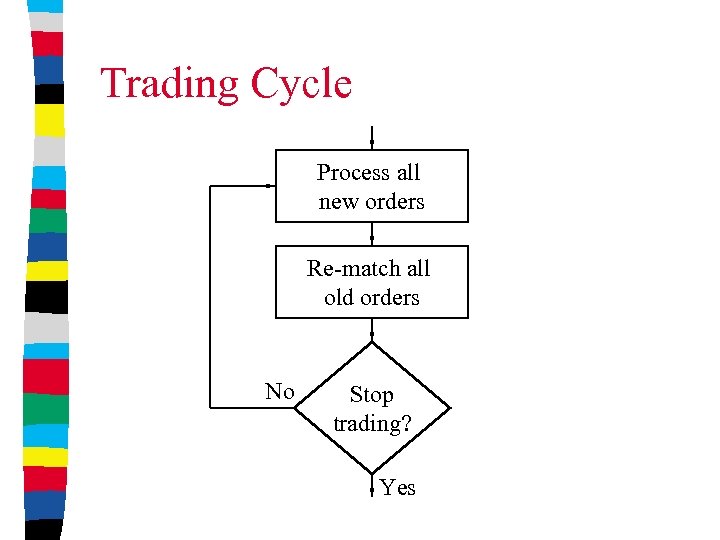 Trading Cycle Process all new orders Re-match all old orders No Stop trading? Yes
Trading Cycle Process all new orders Re-match all old orders No Stop trading? Yes
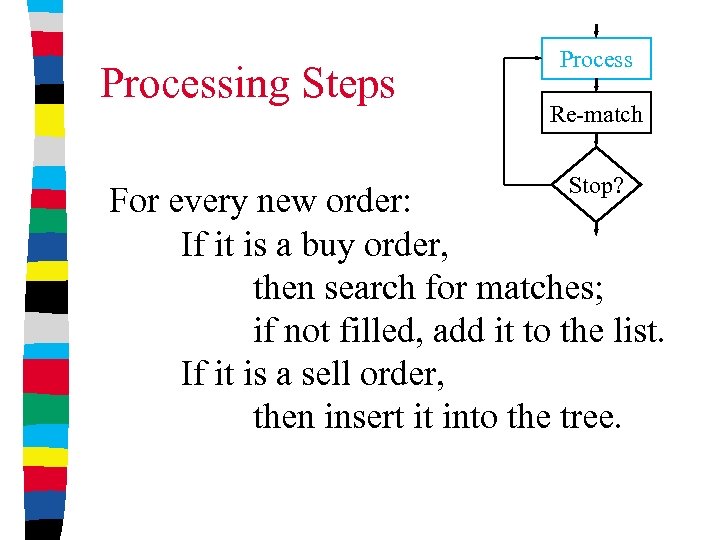 Processing Steps Process Re-match Stop? For every new order: If it is a buy order, then search for matches; if not filled, add it to the list. If it is a sell order, then insert it into the tree.
Processing Steps Process Re-match Stop? For every new order: If it is a buy order, then search for matches; if not filled, add it to the list. If it is a sell order, then insert it into the tree.
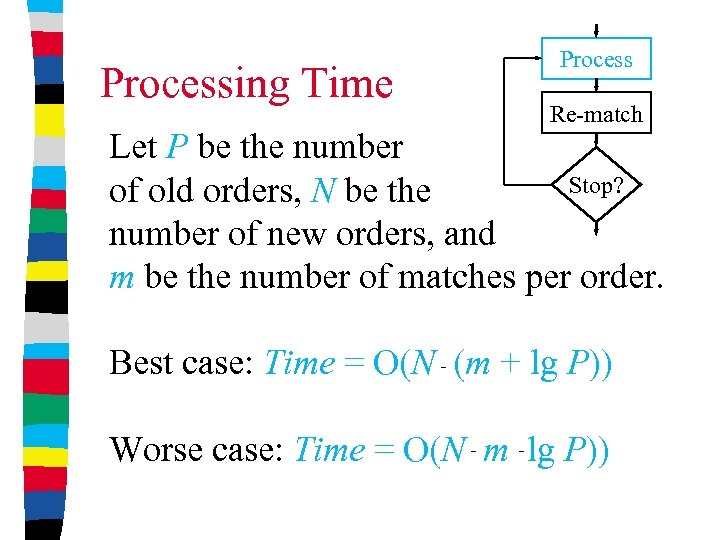 Processing Time Process Re-match Let P be the number Stop? of old orders, N be the number of new orders, and m be the number of matches per order. Best case: Time = O(N (m + lg P)) Worse case: Time = O(N m lg P))
Processing Time Process Re-match Let P be the number Stop? of old orders, N be the number of new orders, and m be the number of matches per order. Best case: Time = O(N (m + lg P)) Worse case: Time = O(N m lg P))
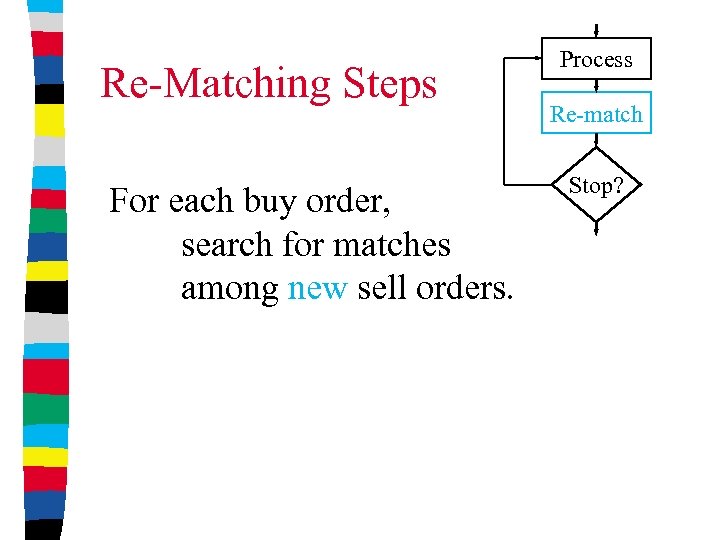 Re-Matching Steps For each buy order, search for matches among new sell orders. Process Re-match Stop?
Re-Matching Steps For each buy order, search for matches among new sell orders. Process Re-match Stop?
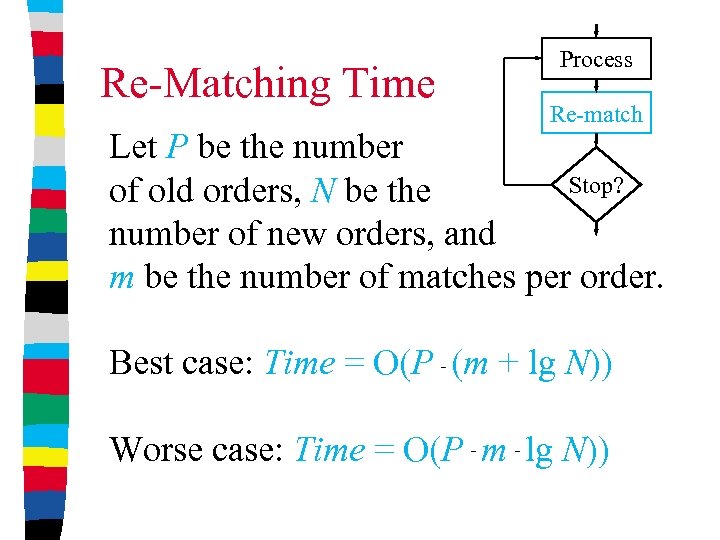 Re-Matching Time Process Re-match Let P be the number Stop? of old orders, N be the number of new orders, and m be the number of matches per order. Best case: Time = O(P (m + lg N)) Worse case: Time = O(P m lg N))
Re-Matching Time Process Re-match Let P be the number Stop? of old orders, N be the number of new orders, and m be the number of matches per order. Best case: Time = O(P (m + lg N)) Worse case: Time = O(P m lg N))
 Outline • Main concepts • Previous work • Data structures • Performance
Outline • Main concepts • Previous work • Data structures • Performance
 Performance Extensive empirical evaluation: • 400 MHz CPU • 1, 024 Mbyte memory • 100 MHz bus
Performance Extensive empirical evaluation: • 400 MHz CPU • 1, 024 Mbyte memory • 100 MHz bus
 Control Variables • Number of old orders • Number of new orders • Length of item description
Control Variables • Number of old orders • Number of new orders • Length of item description
 Measurements • Processing time • Re-matching time • Response time • Throughput
Measurements • Processing time • Re-matching time • Response time • Throughput
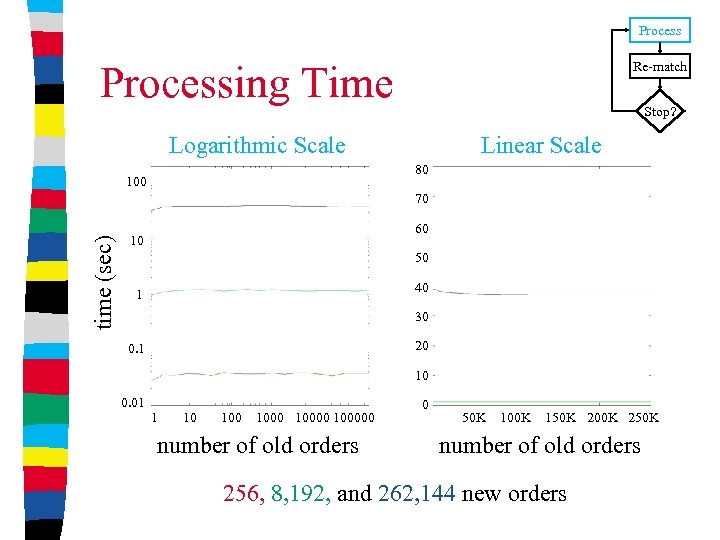 Processing Time Re-match Stop? Logarithmic Scale Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
Processing Time Re-match Stop? Logarithmic Scale Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
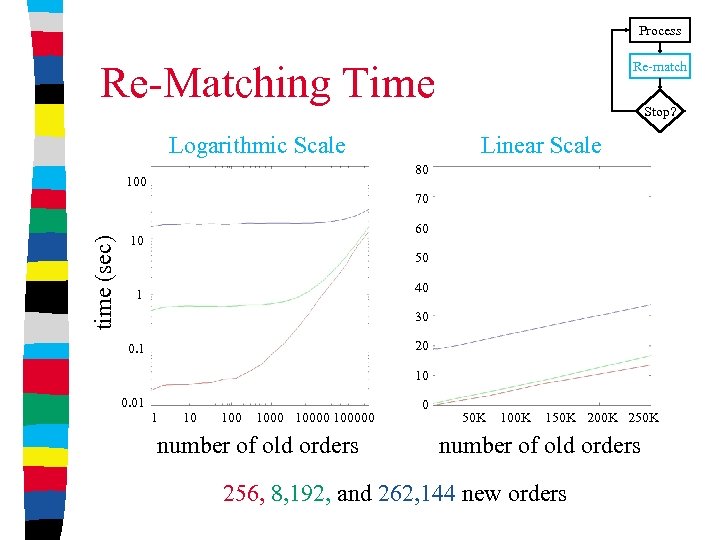 Process Re-Matching Time Logarithmic Scale Re-match Stop? Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
Process Re-Matching Time Logarithmic Scale Re-match Stop? Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
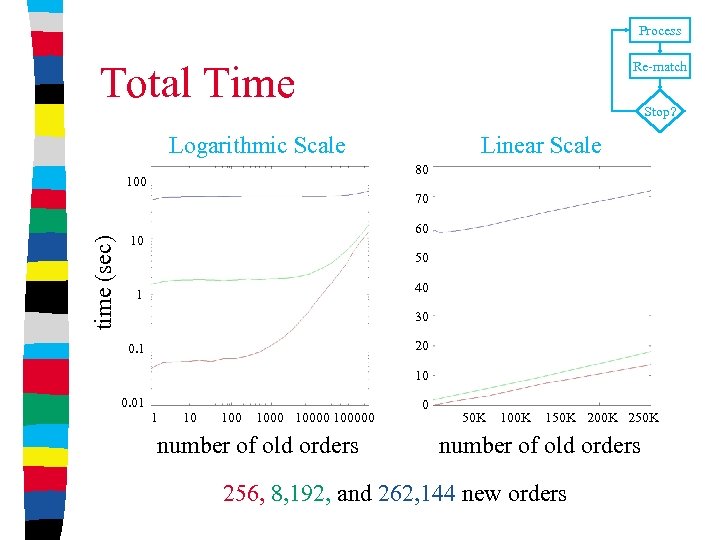 Process Total Time Re-match Stop? Logarithmic Scale Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
Process Total Time Re-match Stop? Logarithmic Scale Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
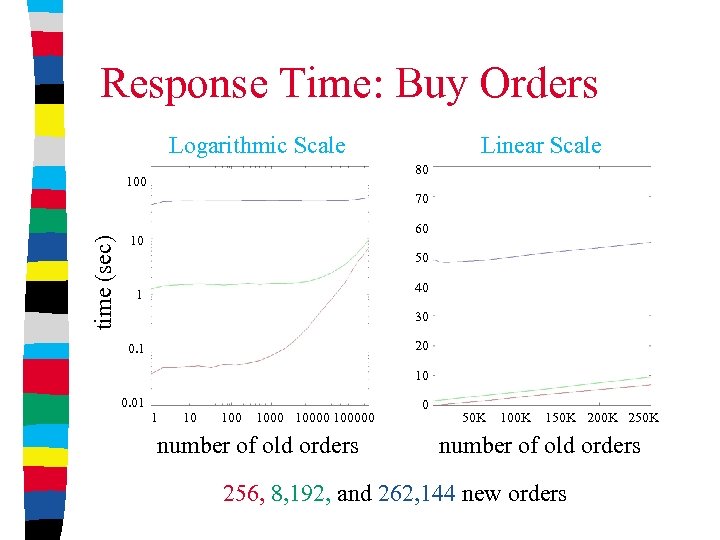 Response Time: Buy Orders Logarithmic Scale Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
Response Time: Buy Orders Logarithmic Scale Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
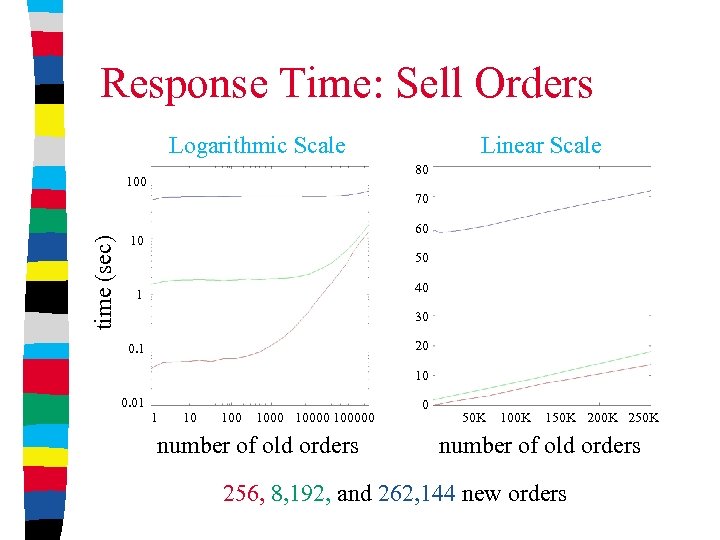 Response Time: Sell Orders Logarithmic Scale Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
Response Time: Sell Orders Logarithmic Scale Linear Scale 80 100 time (sec) 70 60 10 50 40 1 30 20 0. 1 10 0. 01 1 10 100000 number of old orders 0 50 K 100 K 150 K 200 K 250 K number of old orders 256, 8, 192, and 262, 144 new orders
 Throughput Market with ten attributes: 5, 600 new orders per second.
Throughput Market with ten attributes: 5, 600 new orders per second.
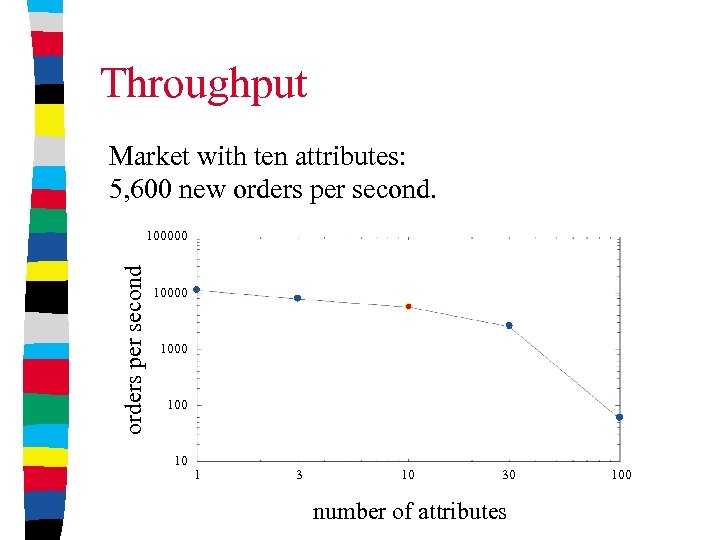 Throughput Market with ten attributes: 5, 600 new orders per second 100000 1000 10 1 3 10 30 number of attributes 100
Throughput Market with ten attributes: 5, 600 new orders per second 100000 1000 10 1 3 10 30 number of attributes 100
 Main Results • Formal model of complex markets • Exchange system for limited order semantics • Evaluation of its performance
Main Results • Formal model of complex markets • Exchange system for limited order semantics • Evaluation of its performance
 Future Work Short-term • Reducing response time • Improving data structures Long-term • Extend order semantics • Search for optimal matches • Use multiple CPUs
Future Work Short-term • Reducing response time • Improving data structures Long-term • Extend order semantics • Search for optimal matches • Use multiple CPUs


