5d7088e496f38c4c70b942f4faa468a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 TRADERS’ DECISION-MAKING PROCESSES: RESULTS FROM AN INVESTMENT SIMULATION MONITORED WITH AN EEG Prof. Dr. Roberto Ivo da R. Lima Filho roberto. ivo@poli. ufrj. br June / 2015
TRADERS’ DECISION-MAKING PROCESSES: RESULTS FROM AN INVESTMENT SIMULATION MONITORED WITH AN EEG Prof. Dr. Roberto Ivo da R. Lima Filho roberto. ivo@poli. ufrj. br June / 2015
 Objective The objective of this article is to identify, with the aid of an electroencephalogram (EEG), that traders use different areas of the brain (and therefore different levels of neuronal activity) in their decisionmaking process when it comes to making a financial investment.
Objective The objective of this article is to identify, with the aid of an electroencephalogram (EEG), that traders use different areas of the brain (and therefore different levels of neuronal activity) in their decisionmaking process when it comes to making a financial investment.
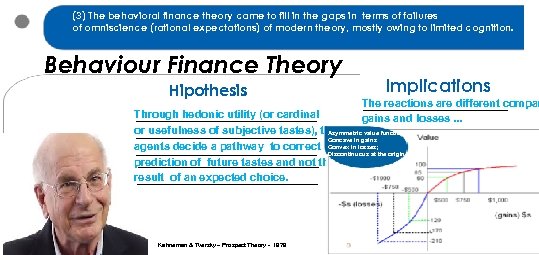 (3) The behavioral finance theory came to fill in the gaps in terms of failures of omniscience (rational expectations) of modern theory, mostly owing to limited cognition. Behaviour Finance Theory Hipothesis Implications The reactions are different compar gains and losses. . . Through hedonic utility (or cardinal or usefulness of subjective tastes), the Asymmetric value function: Concave in gains agents decide a pathway to correct Convex in losses; Discontinuous at the origin. prediction of future tastes and not the result of an expected choice. Kahneman & Tversky – Prospect Theory - 1979
(3) The behavioral finance theory came to fill in the gaps in terms of failures of omniscience (rational expectations) of modern theory, mostly owing to limited cognition. Behaviour Finance Theory Hipothesis Implications The reactions are different compar gains and losses. . . Through hedonic utility (or cardinal or usefulness of subjective tastes), the Asymmetric value function: Concave in gains agents decide a pathway to correct Convex in losses; Discontinuous at the origin. prediction of future tastes and not the result of an expected choice. Kahneman & Tversky – Prospect Theory - 1979
 Behavioural Biases Heuristics Representativeness: judgment based on stereotypes Availability: frequency with which assesses the chances of occurrence of an event, given the memory of them. Risk Aversion The fear of losing is responsible for bringing the agents to make choices not rational manner, disregarding the odds and the historical data available. Anchorage Individuals make reviews based on taking an initial value, adjusting it to reach a final decision onwards. Brands of bounded rationality of economic agents. . . Overconfidence Tendency to take credit for positive outcomes and assign the blame for negative outcomes to external events. Certainty Effect Overvaluation of a specific event, due to the inability to understand the odds and calculate their expected values. Herd Behaviour & Contagion Individuals react in a chain process, with the feeling of wandering in the company of others would be less uncomfortable than the embarrassment of making his/her. Kahnemanmistake. Judgement under Uncertainty own & Tversky – - 1974
Behavioural Biases Heuristics Representativeness: judgment based on stereotypes Availability: frequency with which assesses the chances of occurrence of an event, given the memory of them. Risk Aversion The fear of losing is responsible for bringing the agents to make choices not rational manner, disregarding the odds and the historical data available. Anchorage Individuals make reviews based on taking an initial value, adjusting it to reach a final decision onwards. Brands of bounded rationality of economic agents. . . Overconfidence Tendency to take credit for positive outcomes and assign the blame for negative outcomes to external events. Certainty Effect Overvaluation of a specific event, due to the inability to understand the odds and calculate their expected values. Herd Behaviour & Contagion Individuals react in a chain process, with the feeling of wandering in the company of others would be less uncomfortable than the embarrassment of making his/her. Kahnemanmistake. Judgement under Uncertainty own & Tversky – - 1974
 (4) To better understand the brain executive functions, some theories and hypotheses have been suggested Dynamic Filtering Theory Describes the prefrontal cortex acts as a high level "gating”, where there is a filtering mechanism that improves goal-directed activations and inhibits irrelevant. activations Pre-Frontal Cortex Maintaining a connection with the limbic system there is an association with long-term memory, in addition to affect and motivation. Shimamura - the role of prefrontal cortex in dynamic filtering - 2000
(4) To better understand the brain executive functions, some theories and hypotheses have been suggested Dynamic Filtering Theory Describes the prefrontal cortex acts as a high level "gating”, where there is a filtering mechanism that improves goal-directed activations and inhibits irrelevant. activations Pre-Frontal Cortex Maintaining a connection with the limbic system there is an association with long-term memory, in addition to affect and motivation. Shimamura - the role of prefrontal cortex in dynamic filtering - 2000
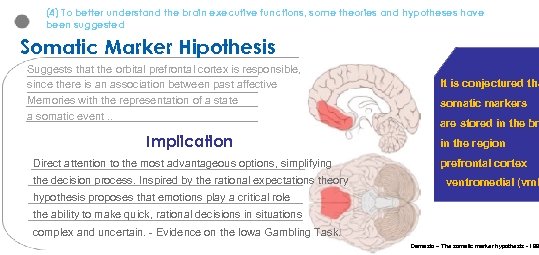 (4) To better understand the brain executive functions, some theories and hypotheses have been suggested Somatic Marker Hipothesis Suggests that the orbital prefrontal cortex is responsible, since there is an association between past affective Memories with the representation of a state a somatic event. . Implication It is conjectured tha somatic markers are stored in the br in the region Direct attention to the most advantageous options, simplifying prefrontal cortex the decision process. Inspired by the rational expectations theory ventromedial (vm. P hypothesis proposes that emotions play a critical role the ability to make quick, rational decisions in situations complex and uncertain. - Evidence on the Iowa Gambling Task. Damasio – The somatic marker hypothesis - 199
(4) To better understand the brain executive functions, some theories and hypotheses have been suggested Somatic Marker Hipothesis Suggests that the orbital prefrontal cortex is responsible, since there is an association between past affective Memories with the representation of a state a somatic event. . Implication It is conjectured tha somatic markers are stored in the br in the region Direct attention to the most advantageous options, simplifying prefrontal cortex the decision process. Inspired by the rational expectations theory ventromedial (vm. P hypothesis proposes that emotions play a critical role the ability to make quick, rational decisions in situations complex and uncertain. - Evidence on the Iowa Gambling Task. Damasio – The somatic marker hypothesis - 199
 (4) The cognitive neuroscience of emotion also supports the Review of decisions in two major strands called Sloman - Empirical case of two systems of reasoning - 1996 Dual Process Theory Associative / Heuristics Is based from past experiences, with only a "reproductive" allusion. Such information is relevant for the current situation. Reason / Analitical Uses a logical structure to reach different conclusions from the associative system. Useful for "situations" unpublished,
(4) The cognitive neuroscience of emotion also supports the Review of decisions in two major strands called Sloman - Empirical case of two systems of reasoning - 1996 Dual Process Theory Associative / Heuristics Is based from past experiences, with only a "reproductive" allusion. Such information is relevant for the current situation. Reason / Analitical Uses a logical structure to reach different conclusions from the associative system. Useful for "situations" unpublished,
 (4) Some features can be identified. . . Sistem 1 (~Associative) Be fast and automatic, with strong emotional ties included in the reasoning process. Evidence in the ventral medial prefrontal cortex. Sistem 2 (~Reason) Have r slower speed and is much more volatil being subject to conscious judgments and atti It is evolutionarily recent and specific to the be humans. It relates to the prefrontal co Dominance on the right side denotes a negative emotion, while the left suggests positive emotion. Sloman - Empirical case of two systems of reasoning - 1996
(4) Some features can be identified. . . Sistem 1 (~Associative) Be fast and automatic, with strong emotional ties included in the reasoning process. Evidence in the ventral medial prefrontal cortex. Sistem 2 (~Reason) Have r slower speed and is much more volatil being subject to conscious judgments and atti It is evolutionarily recent and specific to the be humans. It relates to the prefrontal co Dominance on the right side denotes a negative emotion, while the left suggests positive emotion. Sloman - Empirical case of two systems of reasoning - 1996
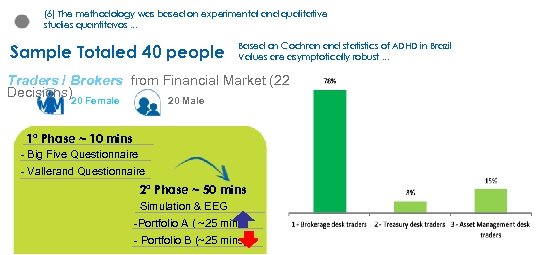 (6) The methodology was based on experimental and qualitative studies quantitavos. . . Sample Totaled 40 people Based on Cochran and statistics of ADHD in Brazil Values are asymptotically robust. . . Traders / Brokers from Financial Market (22 Decisions)20 Female 20 Male 1ª Phase ~ 10 mins - Big Five Questionnaire - Vallerand Questionnaire 2ª Phase ~ 50 mins Simulation & EEG -Portfolio A ( ~25 mins) - Portfolio B (~25 mins)
(6) The methodology was based on experimental and qualitative studies quantitavos. . . Sample Totaled 40 people Based on Cochran and statistics of ADHD in Brazil Values are asymptotically robust. . . Traders / Brokers from Financial Market (22 Decisions)20 Female 20 Male 1ª Phase ~ 10 mins - Big Five Questionnaire - Vallerand Questionnaire 2ª Phase ~ 50 mins Simulation & EEG -Portfolio A ( ~25 mins) - Portfolio B (~25 mins)
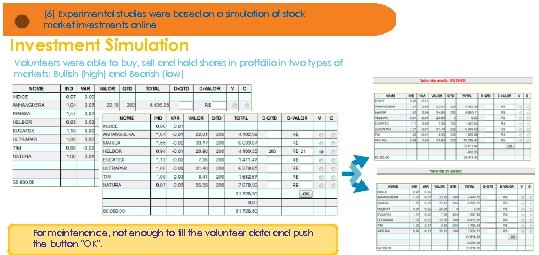 (6) Experimental studies were based on a simulation of stock market investments online Investment Simulation Volunteers were able to buy, sell and hold shares in protfóliio in two types of markets: Bullish (high) and Bearish (low) For maintenance, not enough to fill the volunteer data and push the button "OK".
(6) Experimental studies were based on a simulation of stock market investments online Investment Simulation Volunteers were able to buy, sell and hold shares in protfóliio in two types of markets: Bullish (high) and Bearish (low) For maintenance, not enough to fill the volunteer data and push the button "OK".
 (6) Experimental studies were based on a simulation of stock market investments online Investiment Simulation Newspapers and graphs were presented
(6) Experimental studies were based on a simulation of stock market investments online Investiment Simulation Newspapers and graphs were presented
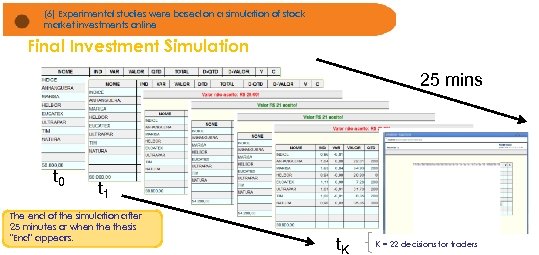 (6) Experimental studies were based on a simulation of stock market investments online Final Investment Simulation 25 mins t 0 t 1 The end of the simulation after 25 minutes or when thesis "End" appears. t. K K = 22 decisions for traders
(6) Experimental studies were based on a simulation of stock market investments online Final Investment Simulation 25 mins t 0 t 1 The end of the simulation after 25 minutes or when thesis "End" appears. t. K K = 22 decisions for traders
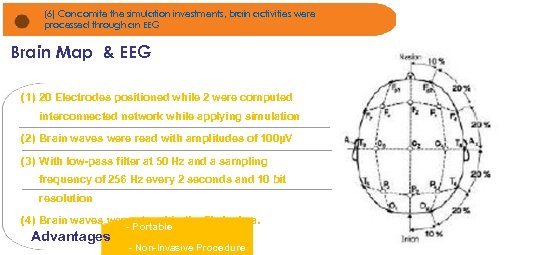 (6) Concomite the simulation investments, brain activities were processed through an EEG Brain Map & EEG Notícias de Jornais e gráficos foram apresentados (1) 20 Electrodes positioned while 2 were computed interconnected network while applying simulation (2) Brain waves were read with amplitudes of 100μV (3) With low-pass filter at 50 Hz and a sampling frequency of 256 Hz every 2 seconds and 10 bit resolution (4) Brain waves were stored in the file Icelera. - Portable Advantages - Non-Invasive Procedure
(6) Concomite the simulation investments, brain activities were processed through an EEG Brain Map & EEG Notícias de Jornais e gráficos foram apresentados (1) 20 Electrodes positioned while 2 were computed interconnected network while applying simulation (2) Brain waves were read with amplitudes of 100μV (3) With low-pass filter at 50 Hz and a sampling frequency of 256 Hz every 2 seconds and 10 bit resolution (4) Brain waves were stored in the file Icelera. - Portable Advantages - Non-Invasive Procedure
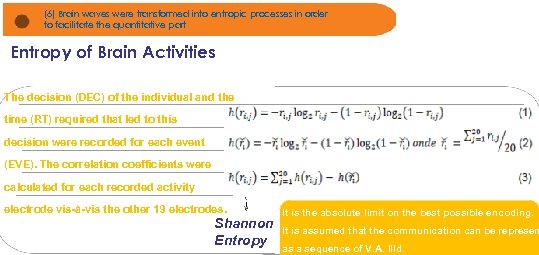 (6) Brain waves were transformed into entropic processes in order to facilitate the quantitative part Entropy of Brain Activities Notícias de Jornais e gráficos foram apresentados The decision (DEC) of the individual and the time (RT) required that led to this decision were recorded for each event (EVE). The correlation coefficients were calculated for each recorded activity electrode vis-à-vis the other 19 electrodes. Shannon Entropy It is the absolute limit on the best possible encoding. It is assumed that the communication can be represen as a sequence of V. A. IIId.
(6) Brain waves were transformed into entropic processes in order to facilitate the quantitative part Entropy of Brain Activities Notícias de Jornais e gráficos foram apresentados The decision (DEC) of the individual and the time (RT) required that led to this decision were recorded for each event (EVE). The correlation coefficients were calculated for each recorded activity electrode vis-à-vis the other 19 electrodes. Shannon Entropy It is the absolute limit on the best possible encoding. It is assumed that the communication can be represen as a sequence of V. A. IIId.
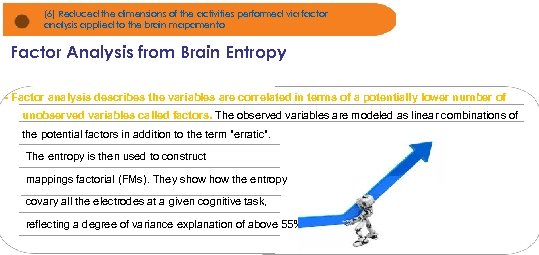 (6) Reduced the dimensions of the activities performed via factor analysis applied to the brain mapamento Factor Analysis from Brain Entropy Notícias de Jornais e gráficos foram apresentados - Factor analysis describes the variables are correlated in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. The observed variables are modeled as linear combinations of the potential factors in addition to the term "erratic". The entropy is then used to construct mappings factorial (FMs). They show the entropy covary all the electrodes at a given cognitive task, reflecting a degree of variance explanation of above 55%.
(6) Reduced the dimensions of the activities performed via factor analysis applied to the brain mapamento Factor Analysis from Brain Entropy Notícias de Jornais e gráficos foram apresentados - Factor analysis describes the variables are correlated in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. The observed variables are modeled as linear combinations of the potential factors in addition to the term "erratic". The entropy is then used to construct mappings factorial (FMs). They show the entropy covary all the electrodes at a given cognitive task, reflecting a degree of variance explanation of above 55%.
 (6) Resultando em três grandes padrões Action Factor Analysis from Brain Entropy (A) The P 1 pattern reveals the activity of neural circuits Notícias de Jornais e gráficos foram apresentados for recognizing solutions and also assess the risks and benefits; (B) P 3 reveals the activity of neural circuits responsible the calculation and adequacy of the action of P 1; (C) P 2 triggers the whole process of decision making. If you select the action to be implemented with information provided by P 1 and P 3 P 2 Decision P 1 Necessity
(6) Resultando em três grandes padrões Action Factor Analysis from Brain Entropy (A) The P 1 pattern reveals the activity of neural circuits Notícias de Jornais e gráficos foram apresentados for recognizing solutions and also assess the risks and benefits; (B) P 3 reveals the activity of neural circuits responsible the calculation and adequacy of the action of P 1; (C) P 2 triggers the whole process of decision making. If you select the action to be implemented with information provided by P 1 and P 3 P 2 Decision P 1 Necessity
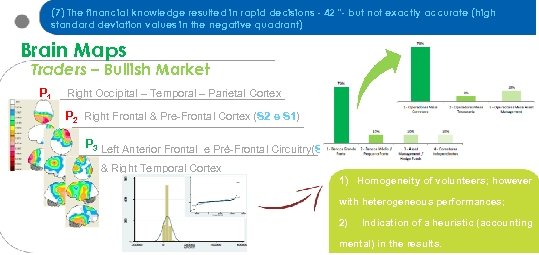 (7) The financial knowledge resulted in rapid decisions - 42 "- but not exactly accurate (high standard deviation values in the negative quadrant) Brain Maps Traders – Bullish Market P 1 Right Occipital – Temporal – Parietal Cortex P 2 Right Frontal & Pre-Frontal Cortex (S 2 e S 1) P 3 Left Anterior Frontal e Pré-Frontal Circuitry(S 1) & Right Temporal Cortex 1) Homogeneity of volunteers; however with heterogeneous performances; 2) Indication of a heuristic (accounting mental) in the results.
(7) The financial knowledge resulted in rapid decisions - 42 "- but not exactly accurate (high standard deviation values in the negative quadrant) Brain Maps Traders – Bullish Market P 1 Right Occipital – Temporal – Parietal Cortex P 2 Right Frontal & Pre-Frontal Cortex (S 2 e S 1) P 3 Left Anterior Frontal e Pré-Frontal Circuitry(S 1) & Right Temporal Cortex 1) Homogeneity of volunteers; however with heterogeneous performances; 2) Indication of a heuristic (accounting mental) in the results.
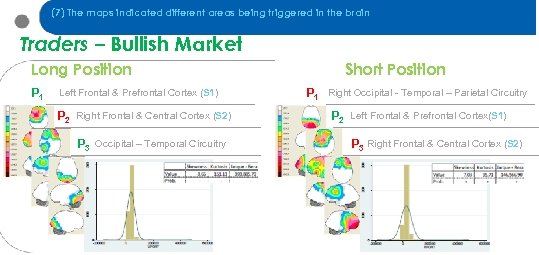 (7) The maps indicated different areas being triggered in the brain Traders – Bullish Market Long Position P 1 Left Frontal & Prefrontal Cortex (S 1) P 2 Right Frontal & Central Cortex (S 2) P 3 Occipital – Temporal Circuitry Short Position P 1 Right Occipital - Temporal – Parietal Circuitry P 2 Left Frontal & Prefrontal Cortex(S 1) P 3 Right Frontal & Central Cortex (S 2)
(7) The maps indicated different areas being triggered in the brain Traders – Bullish Market Long Position P 1 Left Frontal & Prefrontal Cortex (S 1) P 2 Right Frontal & Central Cortex (S 2) P 3 Occipital – Temporal Circuitry Short Position P 1 Right Occipital - Temporal – Parietal Circuitry P 2 Left Frontal & Prefrontal Cortex(S 1) P 3 Right Frontal & Central Cortex (S 2)
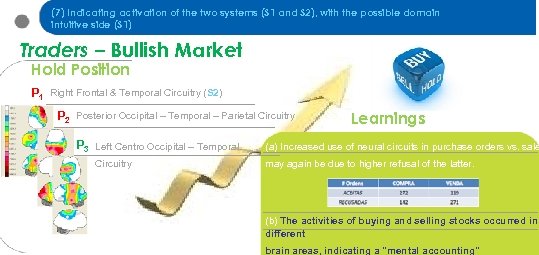 (7) Indicating activation of the two systems (S 1 and S 2), with the possible domain intuitive side (S 1) Traders – Bullish Market Hold Position P 1 Right Frontal & Temporal Circuitry (S 2) P 2 Posterior Occipital – Temporal – Parietal Circuitry P 3 Left Centro Occipital – Temporal Circuitry Learnings (a) Increased use of neural circuits in purchase orders vs. sale may again be due to higher refusal of the latter. (b) The activities of buying and selling stocks occurred in different brain areas, indicating a "mental accounting"
(7) Indicating activation of the two systems (S 1 and S 2), with the possible domain intuitive side (S 1) Traders – Bullish Market Hold Position P 1 Right Frontal & Temporal Circuitry (S 2) P 2 Posterior Occipital – Temporal – Parietal Circuitry P 3 Left Centro Occipital – Temporal Circuitry Learnings (a) Increased use of neural circuits in purchase orders vs. sale may again be due to higher refusal of the latter. (b) The activities of buying and selling stocks occurred in different brain areas, indicating a "mental accounting"
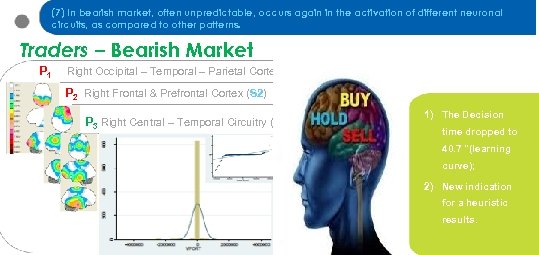 (7) In bearish market, often unpredictable, occurs again in the activation of different neuronal circuits, as compared to other patterns. Traders – Bearish Market P 1 Right Occipital – Temporal – Parietal Cortex P 2 Right Frontal & Prefrontal Cortex (S 2) P 3 Right Central – Temporal Circuitry (S 1) 1) The Decision time dropped to 40. 7 "(learning curve); 2) New indication for a heuristic results.
(7) In bearish market, often unpredictable, occurs again in the activation of different neuronal circuits, as compared to other patterns. Traders – Bearish Market P 1 Right Occipital – Temporal – Parietal Cortex P 2 Right Frontal & Prefrontal Cortex (S 2) P 3 Right Central – Temporal Circuitry (S 1) 1) The Decision time dropped to 40. 7 "(learning curve); 2) New indication for a heuristic results.
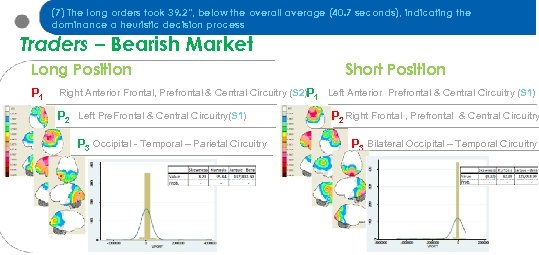 (7) The long orders took 39. 2“, below the overall average (40. 7 seconds), indicating the dominance a heuristic decision process Traders – Bearish Market Long Position P 1 Short Position Right Anterior Frontal, Prefrontal & Central Circuitry (S 2)P 1 Left Anterior Prefrontal & Central Circuitry (S 1) P 2 Left Pre. Frontal & Central Circuitry(S 1) P 3 Occipital - Temporal – Parietal Circuitry P 2 Right Frontal , Prefrontal & Central Circuitry P 3 Bilateral Occipital – Temporal Circuitry
(7) The long orders took 39. 2“, below the overall average (40. 7 seconds), indicating the dominance a heuristic decision process Traders – Bearish Market Long Position P 1 Short Position Right Anterior Frontal, Prefrontal & Central Circuitry (S 2)P 1 Left Anterior Prefrontal & Central Circuitry (S 1) P 2 Left Pre. Frontal & Central Circuitry(S 1) P 3 Occipital - Temporal – Parietal Circuitry P 2 Right Frontal , Prefrontal & Central Circuitry P 3 Bilateral Occipital – Temporal Circuitry
 (7) Pointing to the predominance of an associative / analytic strategy that Traders – Bearish Market Learnings Hold Position P 1 Bilateral Posterior Occipital - Temporal – Parietal Circuitry P 2 Right Anterior Frontal & Prefrontal Circuitry (S 2) (a) In short positions, it is identified that the losses were great P 3 Right Frontal & Prefrontal Circuitry (S 2) compared with tlong ones; (b) Indication of a greater involvement of "instance-based" rule Follow. . . some experience anchored in the past, as advocated by Rocha (2013) and Sloman (1996). This is true. . . including the decision time and intensity of neuronal circuits. .
(7) Pointing to the predominance of an associative / analytic strategy that Traders – Bearish Market Learnings Hold Position P 1 Bilateral Posterior Occipital - Temporal – Parietal Circuitry P 2 Right Anterior Frontal & Prefrontal Circuitry (S 2) (a) In short positions, it is identified that the losses were great P 3 Right Frontal & Prefrontal Circuitry (S 2) compared with tlong ones; (b) Indication of a greater involvement of "instance-based" rule Follow. . . some experience anchored in the past, as advocated by Rocha (2013) and Sloman (1996). This is true. . . including the decision time and intensity of neuronal circuits. .
 (8) Key Takeaways Ø One should take into account the emotion, since it has a fundamental role in the process of decision making both proven empirically and qualitatively Ø The simulation was applied to trader’s groups, with the same conditions of information, suggesting the falsiability of the hypothesis of market efficiency considering different final values of portfolios Ø Suitable given the intensity of neuronal activities in the decision and response, ie: Ø Traders use different areas of the brain (intuition) and were faster decisionmakers (40 "), suggesting" associative - based rule “
(8) Key Takeaways Ø One should take into account the emotion, since it has a fundamental role in the process of decision making both proven empirically and qualitatively Ø The simulation was applied to trader’s groups, with the same conditions of information, suggesting the falsiability of the hypothesis of market efficiency considering different final values of portfolios Ø Suitable given the intensity of neuronal activities in the decision and response, ie: Ø Traders use different areas of the brain (intuition) and were faster decisionmakers (40 "), suggesting" associative - based rule “



