bb2591474227549c93c797559d3a81d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11

Trade-off Analysis • Basic questions – “Are the solutions that are being suggested as good as possible, i. e. , are they on the frontier? ” – “How much must I give up to get a little more of what I want most? ” – Pareto Optimality
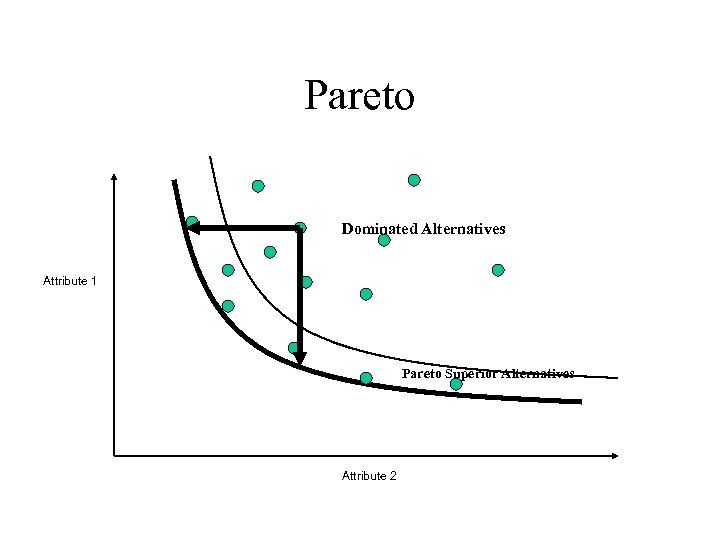
Pareto Dominated Alternatives Attribute 1 Pareto Superior Alternatives Attribute 2

Trade-off Analysis: Attributes • Quantifiable characteristics of the problem • “How could / would we define a bad / worse; good / better outcome? ” – Reduced cost of service – Improved reliability in delivery – Reduced air emission – Less use of land – No use of Chlorine in the production process

Trade-off Analysis: Uncertainties • Events over which the analyst has no control • “… it might but then again…” – International economic conditions – International oil prices – Regulatory change – Resource ($; land; human skills …) Availability

Trade-off Analysis: Options • Actions that could / can be taken • “We can build / buy / legislate / regulate …” – Build a new power plant – Invest in energy conservation / demand side management – Purchase scrubbers for old power plants – Close the power plants and build new clean plants – Move all power generation “off shore”

Trade-off Analysis: Scenarios • Combining the options into a set of rational plans that can be analyzed • “What could / can actually be done given reality and resource constraints? ” – Give growth in demand (and uncertainty) • Close the dirtiest power plant, added one new, clean unit and invest $100 million in demand side management. • Invest in scrubbers for all old plants and build one new, high efficiency, clean power plant (no DSM)
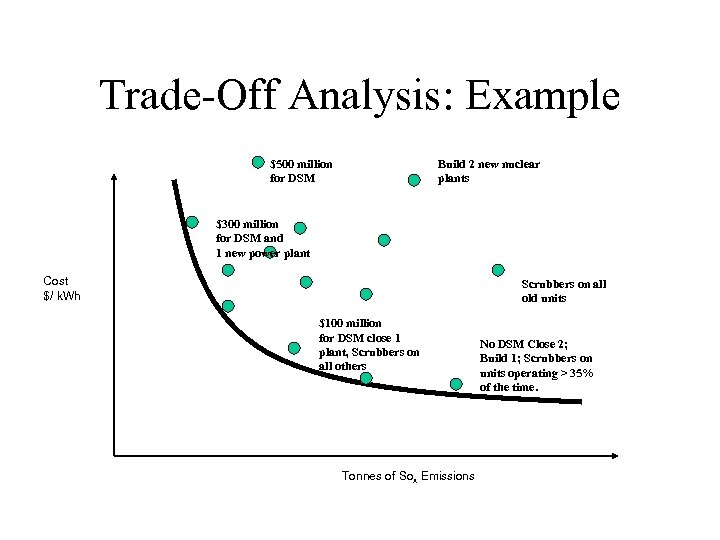
Trade-Off Analysis: Example $500 million for DSM Build 2 new nuclear plants $300 million for DSM and 1 new power plant Cost $/ k. Wh Scrubbers on all old units $100 million for DSM close 1 plant, Scrubbers on all others Tonnes of Sox Emissions No DSM Close 2; Build 1; Scrubbers on units operating > 35% of the time.
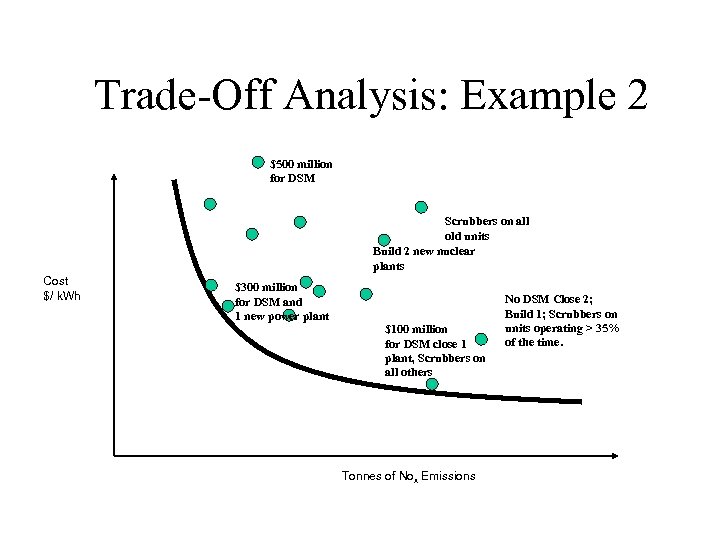
Trade-Off Analysis: Example 2 $500 million for DSM Scrubbers on all old units Build 2 new nuclear plants Cost $/ k. Wh $300 million for DSM and 1 new power plant $100 million for DSM close 1 plant, Scrubbers on all others Tonnes of Nox Emissions No DSM Close 2; Build 1; Scrubbers on units operating > 35% of the time.
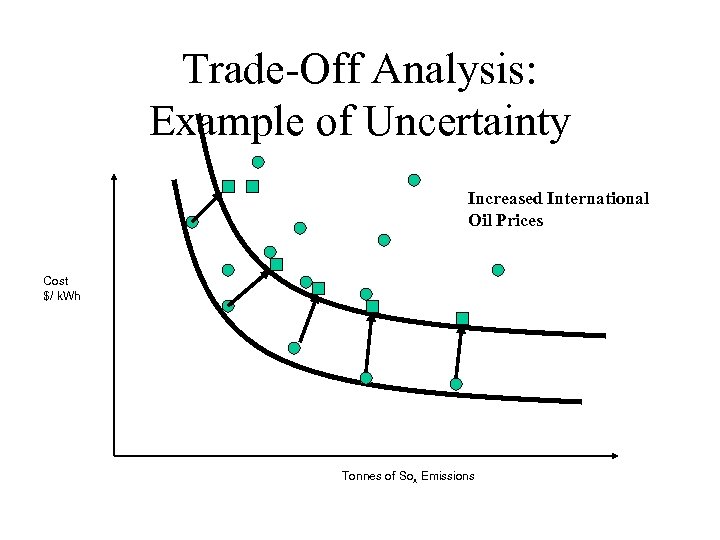
Trade-Off Analysis: Example of Uncertainty Increased International Oil Prices Cost $/ k. Wh Tonnes of Sox Emissions
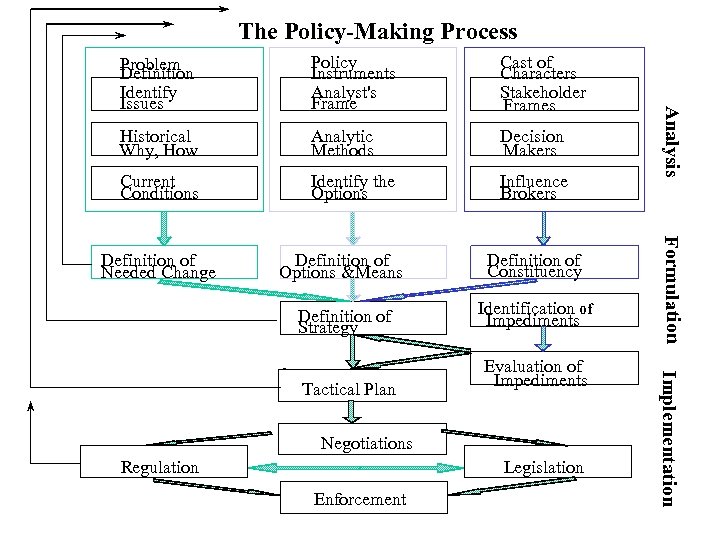
The Policy-Making Process Policy Instruments Analyst's Frame Cast of Characters Stakeholder Frames Historical Why, How Analytic Methods Decision Makers Current Conditions Identify the Options Influence Brokers Definition of Constituency Definition of Strategy Identification of Impediments Tactical Plan Evaluation of Impediments Negotiations Regulation Legislation Enforcement Implementation Definition of Options &Means Formulation Definition of Needed Change Analysis Problem Definition Identify Issues

Policy Analysis: “Truths” • Question / challenge the assumptions • THE forecast is always wrong • Communication is the key: Make it more understandable not more complicated • Measure the important variables not the variables that are easy to measure
bb2591474227549c93c797559d3a81d5.ppt