67251a35ef4584dada533ced2988eacc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Trade Facilitation (TF) and its Economic Benefits Serguei Kouzmine UNECE GTS 8 December 2010 1
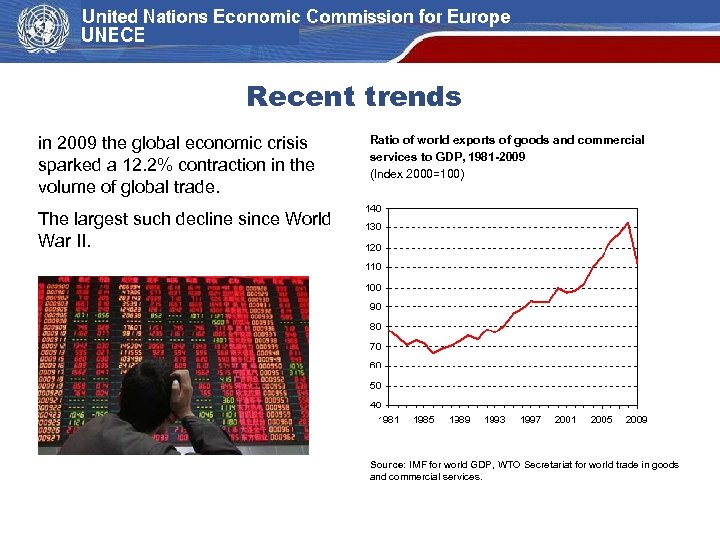
Recent trends in 2009 the global economic crisis sparked a 12. 2% contraction in the volume of global trade. Ratio of world exports of goods and commercial services to GDP, 1981 -2009 (Index 2000=100) The largest such decline since World War II. Source: IMF for world GDP, WTO Secretariat for world trade in goods and commercial services.

Importance of trade facilitation « International Trade is one of the most important arenas in which we must combat the real effects of the crisis. Trade itself is a stimulus. » Source: Simon Crean, Australian Minister of Trade « Where the trade environment is more favorable, businesses are better positioned to take advantage of new opportunties, to grow and to great jobs when the global economy picks up again. » Source: WB, World Business Report, 2010
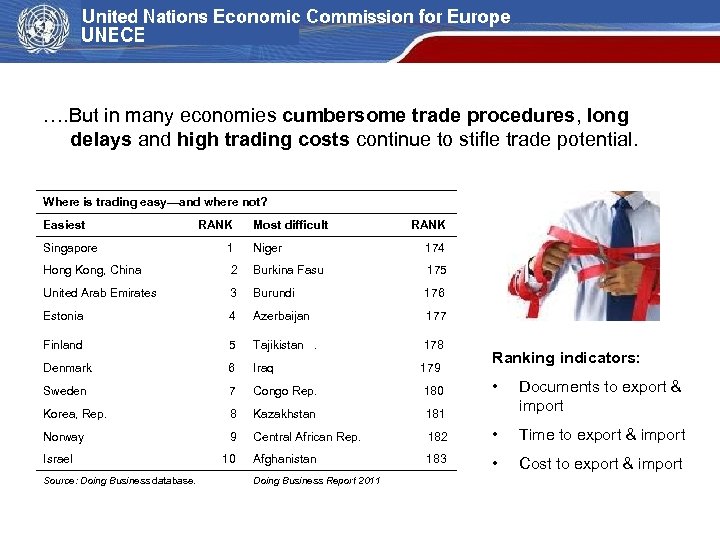
…. But in many economies cumbersome trade procedures, long delays and high trading costs continue to stifle trade potential. Where is trading easy—and where not? Easiest RANK Most difficult RANK Singapore 1 Niger 174 Hong Kong, China 2 Burkina Fasu 175 United Arab Emirates 3 Burundi 176 Estonia 4 Azerbaijan 177 Finland 5 Tajikistan . 178 Denmark 6 Iraq 179 Sweden 7 Congo Rep. 180 Korea, Rep. 8 Kazakhstan 181 Norway 9 Ranking indicators: • Documents to export & import Central African Rep. 182 • Time to export & import Israel 10 Afghanistan 183 • Cost to export & import Source: Doing Business database. Doing Business Report 2011
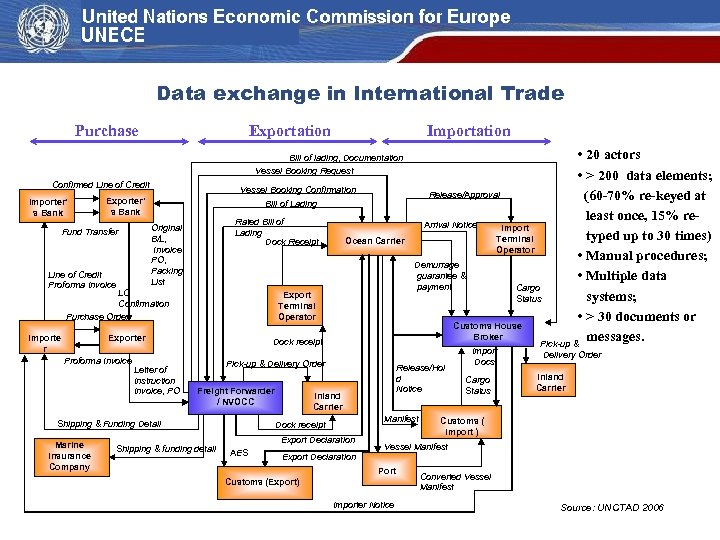
Data exchange in International Trade Purchase Exportation Importation Bill of lading, Documentation Vessel Booking Request Confirmed Line of Credit Importer’ s Bank Vessel Booking Confirmation Exporter’ s Bank Bill of Lading Rated Bill of Lading Dock Receipt Original B/L, Invoice, PO, Packing List Fund Transfer Line of Credit Proforma Invoice LC Confirmation Purchase Order Export Terminal Operator Exporter Importe r Proforma Invoice Letter of Instruction Invoice, PO Dock receipt Pick-up & Delivery Order Freight Forwarder / NVOCC Shipping & Funding Detail Marine Insurance Company Ocean Carrier Shipping & funding detail Release/Hol d Notice Inland Carrier Manifest Dock receipt Export Declaration AES • 20 actors • > 200 data elements; Release/Approval (60 -70% re-keyed at least once, 15% re. Arrival Notice Import typed up to 30 times) Terminal Operator • Manual procedures; Demurrage guarantee & • Multiple data payment Cargo systems; Status • > 30 documents or Customs House Broker messages. Pick-up & Export Declaration Import Docs Cargo Status Delivery Order Inland Carrier Customs ( Import ) Vessel Manifest Port Customs (Export) Importer Notice Converted Vessel Manifest Source: UNCTAD 2006

Too many documents… l l l l Enquiry Order Despatch advice Collection order Payment order Documentary credit Forwarding instructions Forwarder's invoice Goods receipt Air waybill Road consignment note Rail consignment note Bill of lading l l l Freight invoice Cargo manifest Export licence Exchange control doc. Phytosanitary certificate Veterinary certificate Certificate of origin Consular invoice Dangerous goods declaration Import licence Customs delivery note TIR carnet Source: UNCTAD 2006
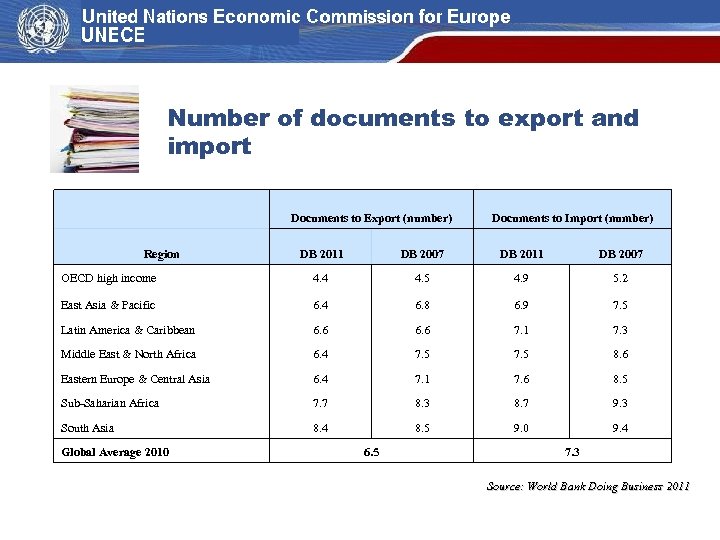
Number of documents to export and import Documents to Export (number) Region Documents to Import (number) DB 2011 DB 2007 OECD high income 4. 4 4. 5 4. 9 5. 2 East Asia & Pacific 6. 4 6. 8 6. 9 7. 5 Latin America & Caribbean 6. 6 7. 1 7. 3 Middle East & North Africa 6. 4 7. 5 8. 6 Eastern Europe & Central Asia 6. 4 7. 1 7. 6 8. 5 Sub-Saharian Africa 7. 7 8. 3 8. 7 9. 3 South Asia 8. 4 8. 5 9. 0 9. 4 Global Average 2010 6. 5 7. 3 Source: World Bank Doing Business 2011
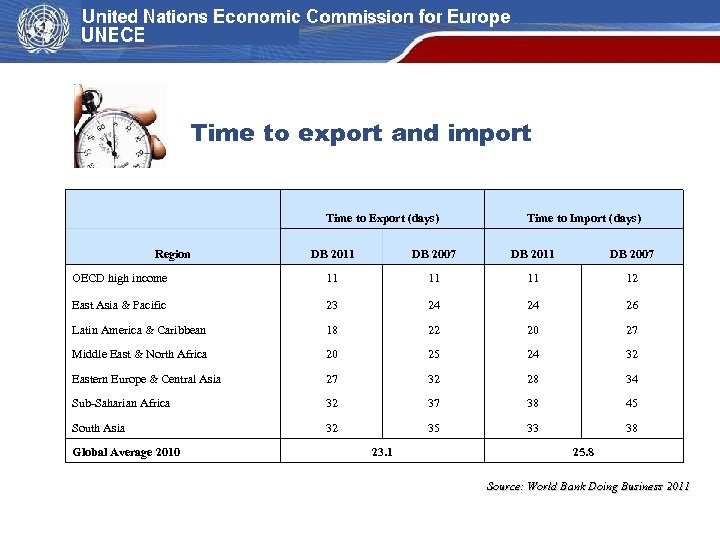
Time to export and import Time to Export (days) Region Time to Import (days) DB 2011 DB 2007 OECD high income 11 11 11 12 East Asia & Pacific 23 24 24 26 Latin America & Caribbean 18 22 20 27 Middle East & North Africa 20 25 24 32 Eastern Europe & Central Asia 27 32 28 34 Sub-Saharian Africa 32 37 38 45 South Asia 32 35 33 38 Global Average 2010 23. 1 25. 8 Source: World Bank Doing Business 2011

What do traders want ? l Simple and smooth processing of formalities l Means to allow goods to proceed promptly to their final destination. No longer itineraries, no unpacking, no delays l A single control point for all public services l Standard forms, assembled into a ‘single bunch of documents’, compatible with trade documents and transport contracts l Predictable and transparent rules and procedures Source: UNCTAD
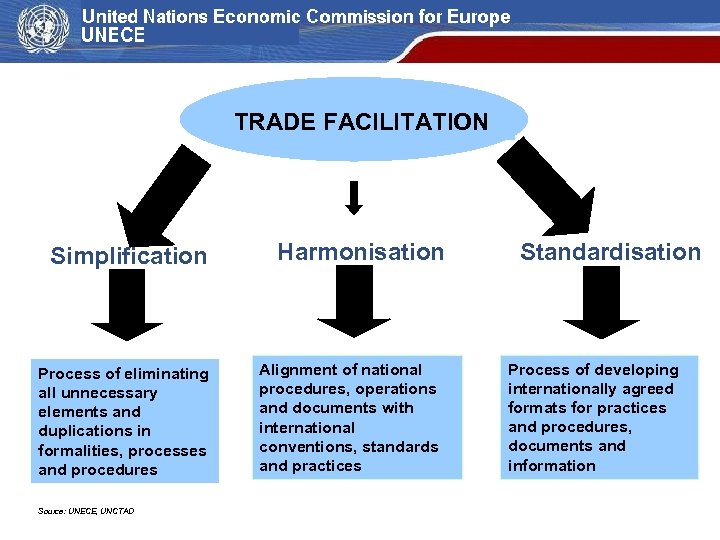
TRADE FACILITATION Simplification Process of eliminating all unnecessary elements and duplications in formalities, processes and procedures CSDAT Aug 2010 Source: UNECE, UNCTAD Harmonisation Alignment of national procedures, operations and documents with international conventions, standards and practices Standardisation Process of developing internationally agreed formats for practices and procedures, documents and information 10

The economic benefits of TF By reducing trade related transaction costs, delays at the borders, number of documents required, improving custom administration……. , trade facilitation: l Fosters businesses’ competitiveness l Increases trade volumes and gains l Raises countries’ GDP l Boosts government tax revenues

Some evidence…. Worldwide l Trade related transaction costs are estimated to lie between 2 and 15% the value of imported goods (OECD 2001, 2003) l Each 1% reduction of such costs is worth up an economic prize of USD 43 billion worldwide (OECD 2003)

Some evidence (con’t d)… In APEC l If APEC members, who perform below average, were able to improve their TF performance to half the APEC average, intra. APEC trade could increase by USD 254 billion and raise average APEC region GDP by 4, 3 % (Wilson et al. 2004) l If APEC members would reduce border delays by 1 day, they would increase exports by 1% (Martinez-Zarzosa et Marquez-Ramos 2008)

Towards smart regulation Over the past 5 years, economies that rank high on the ease of trading across borders have: 1. Introduced or improved electronic data interchange systems 2. Introduced or improved risk-based inspections 3. Improved customs administration 4. Reduced number of trade documents 5. Improved procedures at ports 6. Introduced or improved single window 7. Implemented border cooperation agreements Source: WB, World Business Report, 2010

Opening a single window (SW) in Singapore & Korea ● In Singapore, the SW System (Trade Net) allows the business community to: Ø submit 100 % of trade applications (9 mln per year) to all concerned government authorities Ø with a processing time of 10 minutes ● In Korea, the SW System: Ø Processes 80% of all import applications (3, 000 per day) Ø It is s used by 17 participating organizations and about 16, 068 businesses from the trade community (as of December 2009). ● In both countries Firms’ savings in labor, printing, paper delivery, storage, inventory costs, etc. amount to approx US$ 1 billion per year . Source: UN/CEFACT Single Window Repository 2010
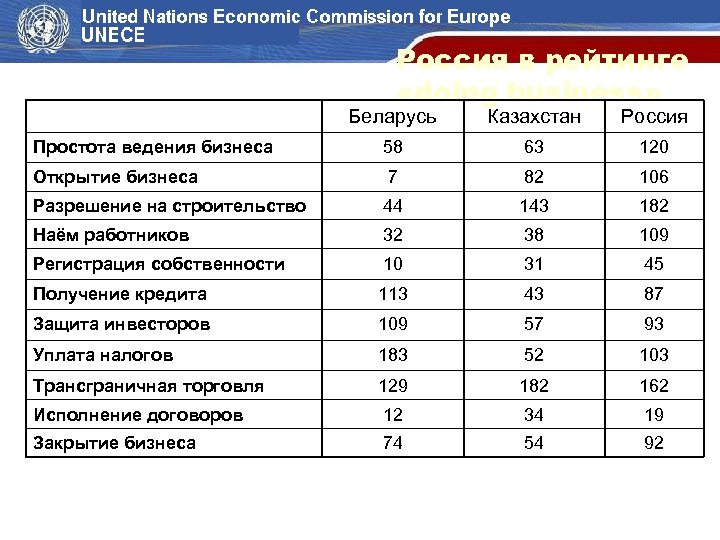
Россия в рейтинге «doing business» Беларусь Казахстан Россия Простота ведения бизнеса 58 63 120 Открытие бизнеса 7 82 106 Разрешение на строительство 44 143 182 Наём работников 32 38 109 Регистрация собственности 10 31 45 Получение кредита 113 43 87 Защита инвесторов 109 57 93 Уплата налогов 183 52 103 Трансграничная торговля 129 182 162 Исполнение договоров 12 34 19 Закрытие бизнеса 74 54 92

Как видят Россию? l « Индекс развития ИКТ » - Россия - 48 место (Швеция-1; Германия-13; Франция-18: Беларусь-55; Казахстан-69; . . ) l « Индекс логистики » -Россия- 94 место (Германия-1; Швеция-3; Франция-17; Казахстан-62; Украина-102; . . ) l « Делать бизнес» - Россия - 120 место (Сингапур – 1; США – 4; Германия – 25; Франция – 31; Беларусь- 58; Казахстан – 63, . . )

In summary Trade facilitation: l Gives businesses a competitive edge l Allows greater integration in the global economy l Enhances government revenues Contacts: Sergei Kouzmine UNECE Global Trade Solution Section serguei. kouzmine@unece. org www. unece. org/trade
67251a35ef4584dada533ced2988eacc.ppt