9b25cb2ad4ecc1fc38021972740b22a0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

Trade and Globalisation Indicators work at OECD Presentation to the WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 A. Lindner, Head Trade and Globalisation Statistics, OECD Andreas. lindner@oecd. org 19 -May-2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 1

Integrated set of detailed, policyrelevant databases and indicators • OECD data warehouse OECD. Stat Ø data at your fingertips, including customized ways to search, visualize, re-arrange and export data Ø Arranged by themes Ø Fully integrated flow from collection, processing, dissemination and publication using unique (especially developed) tools (e. g. Stat. Link) Ø Permanently linked to OECD analysis 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 2

How to ensure relevance? • Internally: • Work Programme through WPTGS (OECD Working Party on Trade in Goods and Trade in Services Statistics) • Embedded in OECDs statistical coordination (SPG, ASTF, CSTAT) • Users across OECD provide feedback and request special compilations (e. g. high-tech trade, ISIC – breakdown, etc. ) • Participation in other relevant WPs or Expert Groups at OECD 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 3

How to ensure relevance? • Externally: • Close and permanent contact with OECD countries experts, WPTGS delegates, National data sources • Active participation in international co-ordination bodies with focus on methodologies and measurement issues (e. g. the two Inter-Agency Trade Task Forces, UN city groups, etc. ) • Active participation in relevant statistical meetings organised by other IO’s 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 4

Where to find it? : OECD. Stat 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 5
External access easy through the Statistics Portal 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 6

General country coverage • 30 OECD countries and world-wide trading partners • Plus the 5 OECD accession countries (Russian Federation, Chile, Israel, Estonia and Slovenia) • Plus the 5 Enhanced Engagement countries (Brazil, India, Indonesia, China, South Africa) • Why 30+5+5? 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 7
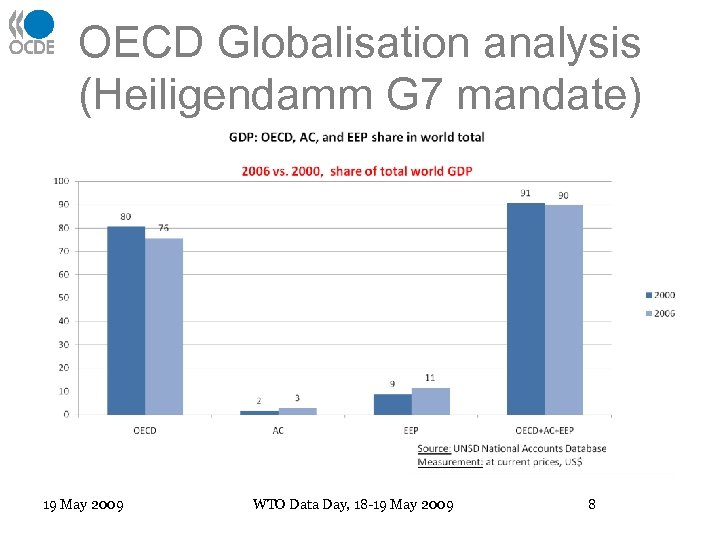
OECD Globalisation analysis (Heiligendamm G 7 mandate) 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 8
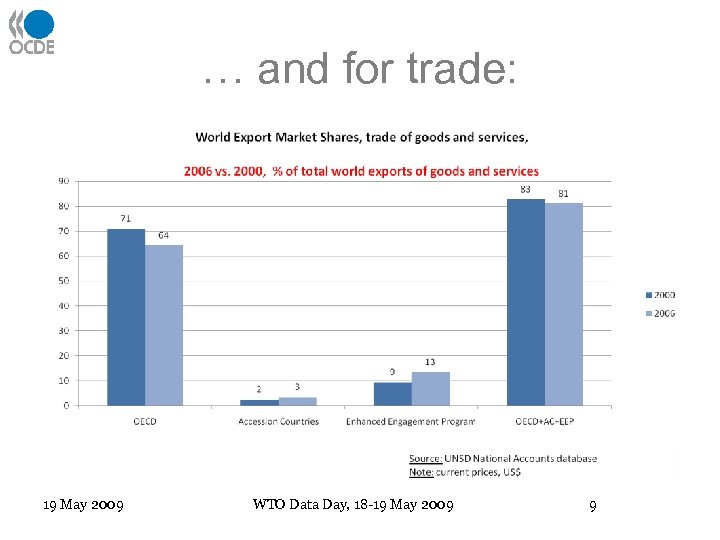
… and for trade: 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 9

Part I: Merchandise Trade: annual • ITCS (International Trade by Commodities Statistics), available online, on DVDs, and paper publications • All OECD countries provide to OECD the detailed annual data which OECD then provides to UNSD (Mo. U) and ITC • This data sharing ensures consistent redissemination of data across international organisations (i. e. UN’s COMTRADE is sourced from OECD for all OECD countries) 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 10
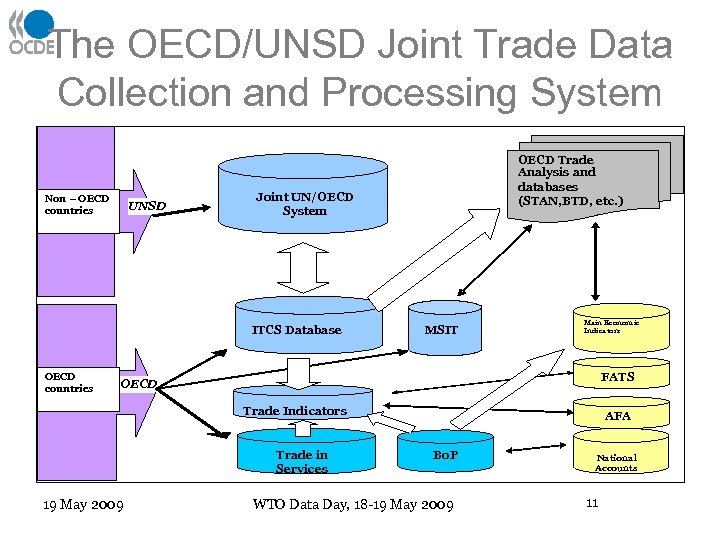
The OECD/UNSD Joint Trade Data Collection and Processing System Non – OECD countries UNSD Joint UN/OECD System ITCS Database OECD countries OECD Trade Analysis and databases (STAN, BTD, etc. ) MSIT Main Economic Indicators FATS OECD Trade Indicators Trade in Services 19 May 2009 AFA Bo. P WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 National Accounts 11
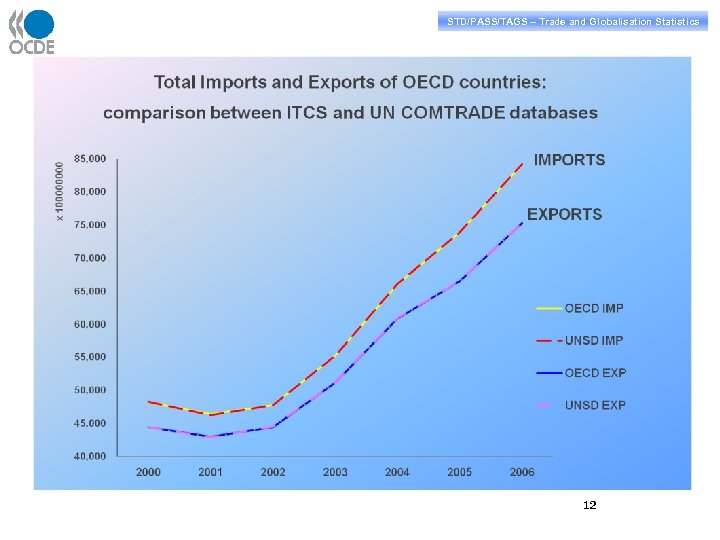
STD/PASS/TAGS – Trade and Globalisation Statistics 12
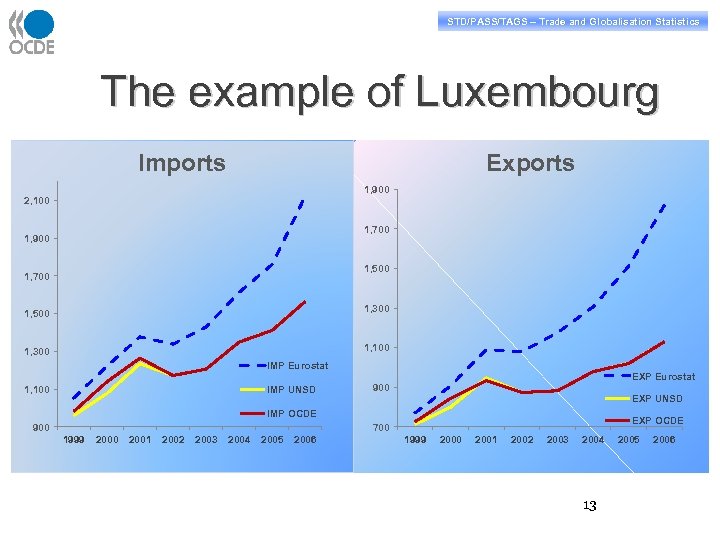
STD/PASS/TAGS – Trade and Globalisation Statistics The example of Luxembourg Imports Exports 1, 900 2, 100 1, 700 1, 900 1, 500 1, 700 1, 300 1, 500 1, 100 1, 300 IMP Eurostat 1, 100 IMP UNSD EXP Eurostat 900 EXP UNSD IMP OCDE EXP OCDE 700 900 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 13 2005 2006

Merchandise Trade: annual • Besides the “traditional "classifications HS and SITC, additional official classifications have been added: – ISIC – ICT goods (OECD classification) – High-Tech products classification (OECD list) • Full OECD. Stat functionality is ensured – Pivot dimensions – Rankings – Customized and saved queries – Export in various formats 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 14

Merchandise Trade: ITCS challenges • Not major ones, works well • Ensure continuity of smooth Inter-Agency sharing and coordination • Better coverage of re-imports and re-exports • Deal with the IMTS Rev 3 BPM 6 “discordance” – Goods for processing measurement – Possible data collection gaps in future • Quantities and unit values 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 15

Merchandise Trade: monthly • MSIT (Monthly Statistics of International Trade) provides most up-to-date merchandise trade aggregates (totals, volume and unit value indices, by SITC Section, by detailed partner country) • OECD seasonally adjusts and deflates data • Available online, by subscription, on paper • Due to the current crisis, an additional advance aggregates series is under development, by which real-time monitoring of OECD countries’ monthly trade news releases will become possible • The objective is to have, for instance, in May as many countries’ aggregates available for March 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 16
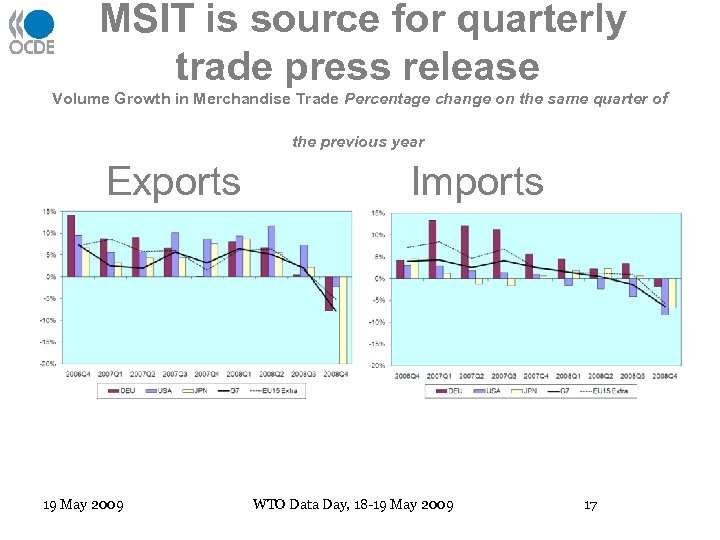
MSIT is source for quarterly trade press release Volume Growth in Merchandise Trade Percentage change on the same quarter of the previous year Exports 19 May 2009 Imports WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 17
MSIT in OECD. Stat 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 18

Monthly Merchandise Trade: challenges • Add “monitoring” total aggregates data to have minus two months picture of trends • Necessity to apply similar procedure to trade in services BOP-based data aggregates • Add to OECDs crisis response Website • Value and volume indices too incomplete 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 19

Trade by Enterprise Characteristics • In co-operation with Eurostat • Matching of trade registers and business registers • Important element for globalisation analysis, SME policies, etc. • Standard indicators (value added, number of enterprises, employees) available by – enterprise size classes – top enterprises – Partner zones and countries – Number of partner countries – Commodity groups 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 20
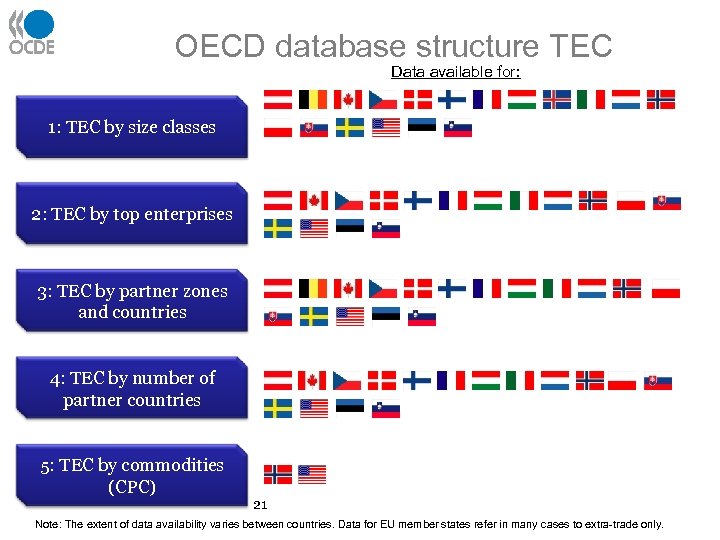
OECD database structure TEC Data available for: 1: TEC by size classes 2: TEC by top enterprises 3: TEC by partner zones and countries 4: TEC by number of partner countries 5: TEC by commodities (CPC) 21 Note: The extent of data availability varies between countries. Data for EU member states refer in many cases to extra-trade only.

Data access • A theme called “Trade by Enterprise Characteristics” has been added to the OECD data warehouse, OECD. STAT, within the Globalisation cube: • The theme consists of the five data subsets, called I to V (‘TEC by size classes’ up to ‘TEC by commodity groups (CPC)’). • While datasets I, III and IV come with two indicators each, one of them referring to each ‘number of enterprises’ and the other one to ‘Trade value’, datasets II and V deliver value figures ($US). 22

Data access Concentration of trade (showcase example from dataset II) This new OECD. STAT theme within the Globalisation cube of course offers the usual functionalities that OECD. STAT provides for all datasets (drag & dropfunctionality, individual queries, individual user-defined views, standard charts, download formats etc. ). 23

Metadata access: Top-level metadata • The methodologies used can be accessed via the metadata functionalities of OECD. STAT (red “i”), both metadata for the top-level (general methodology for the whole theme) and detailed level as well (e. g. detailed information about matching ratios by country). 24
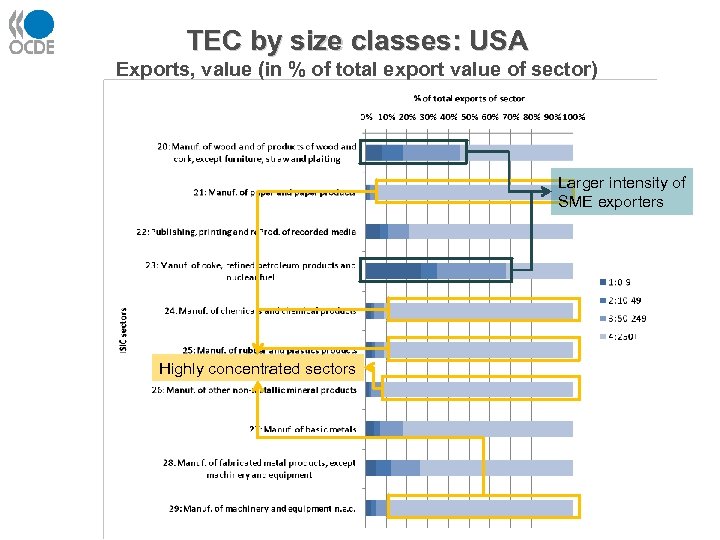
TEC by size classes: USA Exports, value (in % of total export value of sector) Larger intensity of SME exporters Highly concentrated sectors 25
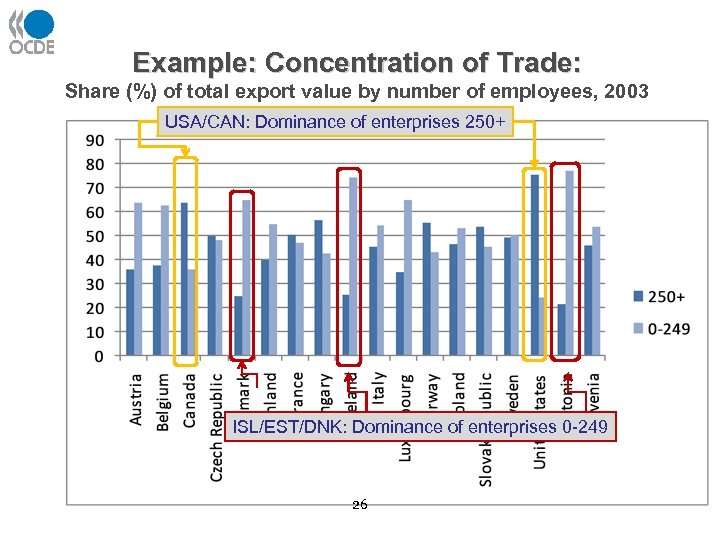
Example: Concentration of Trade: Share (%) of total export value by number of employees, 2003 USA/CAN: Dominance of enterprises 250+ ISL/EST/DNK: Dominance of enterprises 0 -249 26
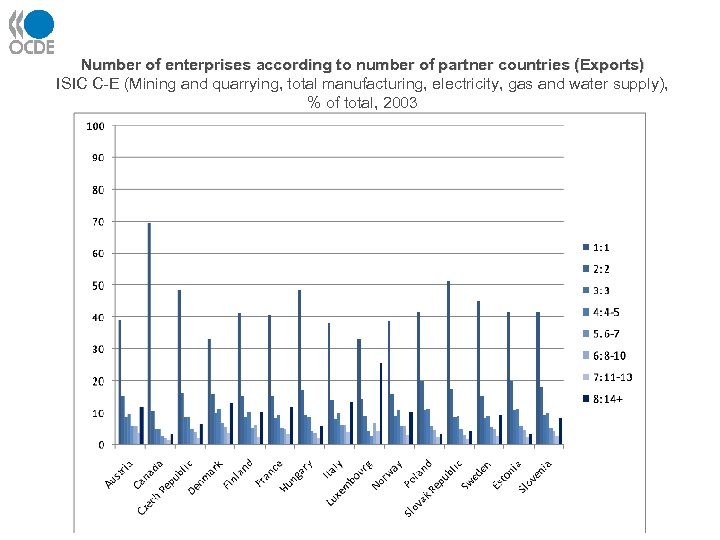
Number of enterprises according to number of partner countries (Exports) ISIC C-E (Mining and quarrying, total manufacturing, electricity, gas and water supply), % of total, 2003 27
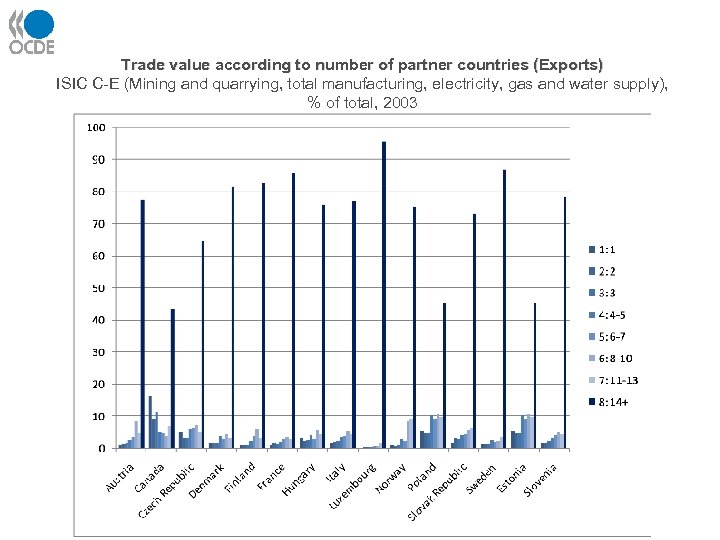
Trade value according to number of partner countries (Exports) ISIC C-E (Mining and quarrying, total manufacturing, electricity, gas and water supply), % of total, 2003 28

Trade by Enterprise Characteristics • • • challenges Extend range of participating OECD countries outside the EU Extend to some EEP countries From fixed indicators to more flexible “micro-type” indicators database Add pertinent new indicators Promote, as a general rule, better integration (or at least compatibility) of trade and business registers 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 29

Part II: Globalisation Indicators • Part of OECDs “Economic Globalisation Indicators” (EGI) and the related Handbook • Grouped together under the “Globalisation” theme in OECD. Stat • Contents is growing, at present it includes – Activity of Multinationals (more details under cluster 3) – FDI – Trade Indicators – Trade by Enterprise Characteristics (TEC) 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 30

Trade is one chapter of EGI 2009 Besides the other chapters on FDI, Multinationals, FATS etc. , FDI MNEs EGI 2008 Trade 31 Others. .

Economic Globalisation Indicators: a standard approach and presentation • One page of analysis • With standard lay-out containing sources used and links to Websites in a shaded box at the bottom • An explanatory box for non-specialists, explaining – – What the indicator measures The formular Factors to be taken into account when interpreting results General strenghts and limitations of the indicator shown • A standardized graphical presentation – Covering OECD countries plus Accession countries and Enhanced Engagement countries (30+5+5= up to 40 countries) wherever possible – Easy to understand interpret 32
Online: Globalisation Indicators 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 33

The list of trade indicators (red box) • • • Trade as % of GDP Trade Balance as % of GDP World Export Market Shares World Exp. Market Sh. by Type of Goods Geographical Distribution of Export Shares in OECD, Accession c. and Enhanced Engagement countries Geographical Distribution of Export Shares in Services Import Penetration of G & S Merchandise Trade with China and Hong Kong, China Merchandise Trade with the Rset of World Intra-Industry Trade High-Tech Merchandise Trade Sensitivity of Trade flows to Price and Income Changes 34

…They do tell a story… • Globalisation affected countries very differently • Winners and loosers • But "grouping patterns" emerge • Heterogeneity of trends and impact on countries • No “one fits all” strategy, rather tailored analysis and approaches • Requiring cross-cutting approach for statistics and indicators development 35

Globalisation Indicators challenges • Issue OECDs “Economic Globalisation Indicators” (EGI) publication in 2009 • Update and complete the underlying Handbook(HEGI) • Complete OECDs “Globalisation Cube” with data from other OECD Directorates • More outcomes indicators, less output-oriented data • Impact measures and links, but incompatible frameworks limit scope • Promote Register Integration, national enterprise IDs, Multi-national Enterprises as statistical unit (Wiesbaden City Group) • Can FDI and FATS be brought more into line? 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 36
Trade Indicators www. oecd. org/std/its/tradeindicators 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 37

Radar chart: access via www. oecd. org/std/its/tradeindicators 38
Trade Indicators 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 39

Trade Indicators • 10 Macro Indicators, country profiles, interactive radar charts and pivot tables (next slide) • Micro Indicators (RCA, Export market share, trade balance, export performance, Herfindhal Index) for – 100 HS product categories – 6 ICT categories – 80 SITC categories – 27 ISIC categories – 12 TIS categories 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 40

1. Trade (Goods and Services) as % of GDP Central & East European countries become increasingly integrated into world economy 41

…and average growth 2000 - 2006 42

2. OECD Trade Balances as % of GDP 43

3. World Export Market Shares (G&S) – average annual growth 2000 -2006 44
Trade Indicators challenges • Complete and extend coverage while preserving standard methodological approach used • Add new dimensions through integration of new indicators (for instance, I-O and trade, trade and value added, subject-specific additions) • Incorporate innovative graphic tools for visualising complex relationships over time • Promote availability using new Web-based tools (e. g. RSS feeds) 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 45

Thank you for your attention! Andreas. lindner@oecd. org 19 May 2009 WTO Data Day, 18 -19 May 2009 46
9b25cb2ad4ecc1fc38021972740b22a0.ppt