1321c85fcf3b8bfd88621f5b62da3baa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Tracking the genetic legacy of past human populations through the grid UNIVERSITY OFENEVA G NICOLAS RAY & UNEP/GRID-EUROPE Swiss Grid Day, Bern, November 26 th 2009
Tracking the genetic legacy of past human populations through the grid UNIVERSITY OFENEVA G NICOLAS RAY & UNEP/GRID-EUROPE Swiss Grid Day, Bern, November 26 th 2009

![Human migrations [12, 000] [55, 000] Homo sapiens Adapted from Cavalli-Sforza & Feldman, 2003 Human migrations [12, 000] [55, 000] Homo sapiens Adapted from Cavalli-Sforza & Feldman, 2003](https://present5.com/presentation/1321c85fcf3b8bfd88621f5b62da3baa/image-3.jpg) Human migrations [12, 000] [55, 000] Homo sapiens Adapted from Cavalli-Sforza & Feldman, 2003
Human migrations [12, 000] [55, 000] Homo sapiens Adapted from Cavalli-Sforza & Feldman, 2003
 Why aiming at a good demographic model 1. Better understand human evolution • Origin of modern human (when, where, how many? ) • Relationship with other members of the Homo genus 2. Distinguish between the effect of demography and those of selection (biomedical applications)
Why aiming at a good demographic model 1. Better understand human evolution • Origin of modern human (when, where, how many? ) • Relationship with other members of the Homo genus 2. Distinguish between the effect of demography and those of selection (biomedical applications)
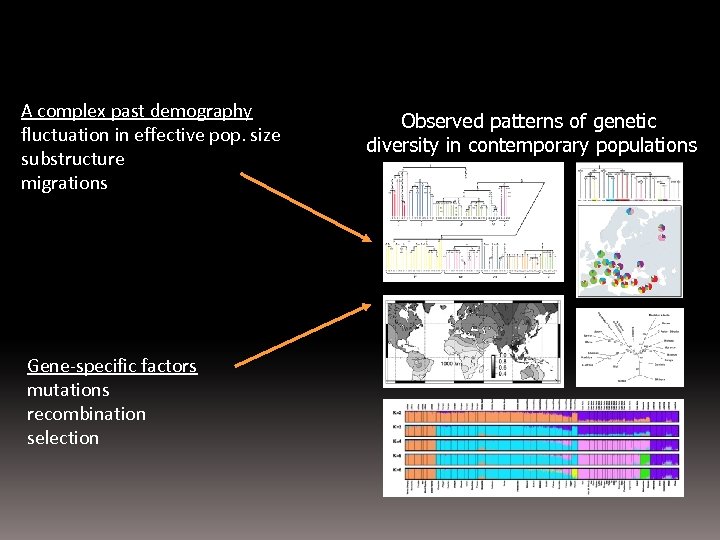 A complex past demography fluctuation in effective pop. size substructure migrations Gene-specific factors mutations recombination selection Observed patterns of genetic diversity in contemporary populations
A complex past demography fluctuation in effective pop. size substructure migrations Gene-specific factors mutations recombination selection Observed patterns of genetic diversity in contemporary populations
![A complex demography [10, 000] [55, 000] demographic and spatial expansions population bottlenecks secondary A complex demography [10, 000] [55, 000] demographic and spatial expansions population bottlenecks secondary](https://present5.com/presentation/1321c85fcf3b8bfd88621f5b62da3baa/image-6.jpg) A complex demography [10, 000] [55, 000] demographic and spatial expansions population bottlenecks secondary contacts population isolation fast migration events Adapted from Cavalli-Sforza & Feldman, 2003
A complex demography [10, 000] [55, 000] demographic and spatial expansions population bottlenecks secondary contacts population isolation fast migration events Adapted from Cavalli-Sforza & Feldman, 2003
 SPLATCHE SPatia. L And Temporal Coalescences in Heterogeneous Environment (http: //cmpg. unibe. ch/software/splatche)
SPLATCHE SPatia. L And Temporal Coalescences in Heterogeneous Environment (http: //cmpg. unibe. ch/software/splatche)
 From environment to demography Carrying capacity low high Spatial resolution: 100 km
From environment to demography Carrying capacity low high Spatial resolution: 100 km
 From environment to demography Friction low high
From environment to demography Friction low high
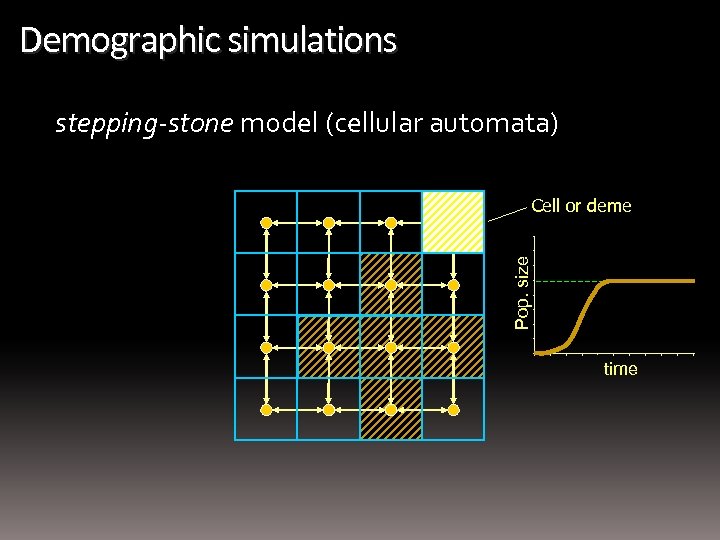 Demographic simulations stepping-stone model (cellular automata) Pop. size Cell or deme time
Demographic simulations stepping-stone model (cellular automata) Pop. size Cell or deme time
 Demography and spatial expansion Population density
Demography and spatial expansion Population density
 Genetic simulations
Genetic simulations
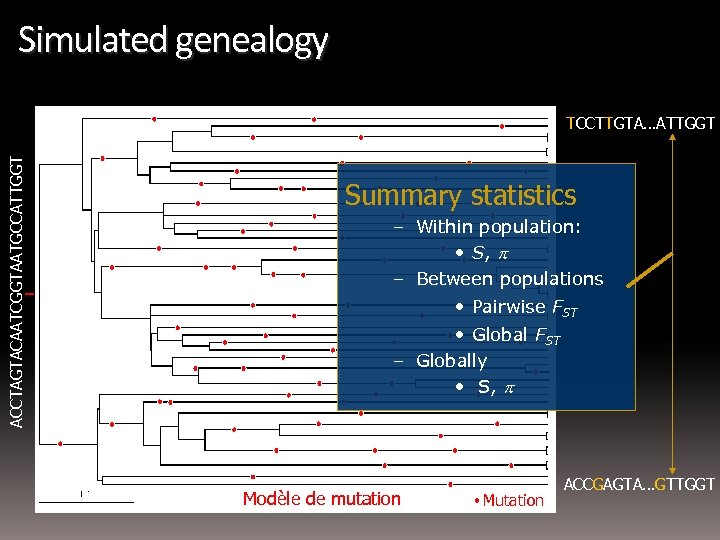 Simulated genealogy ACCTAGTACAATCGGTAATGCCATTGGT TCCTTGTA…ATTGGT Summary statistics – Within population: • S, p – Between populations • Pairwise FST • Global FST – Globally • S, p Modèle de mutation Mutation ACCGAGTA…GTTGGT
Simulated genealogy ACCTAGTACAATCGGTAATGCCATTGGT TCCTTGTA…ATTGGT Summary statistics – Within population: • S, p – Between populations • Pairwise FST • Global FST – Globally • S, p Modèle de mutation Mutation ACCGAGTA…GTTGGT
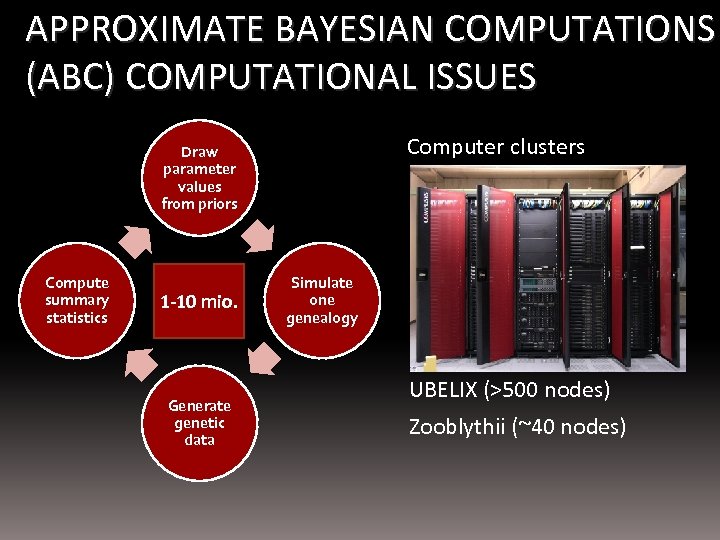 APPROXIMATE BAYESIAN COMPUTATIONS (ABC) COMPUTATIONAL ISSUES Computer clusters Draw parameter values from priors Compute summary statistics 1 -10 mio. Generate genetic data Simulate one genealogy UBELIX (>500 nodes) Zooblythii (~40 nodes)
APPROXIMATE BAYESIAN COMPUTATIONS (ABC) COMPUTATIONAL ISSUES Computer clusters Draw parameter values from priors Compute summary statistics 1 -10 mio. Generate genetic data Simulate one genealogy UBELIX (>500 nodes) Zooblythii (~40 nodes)
 Computational issues A fully spatially-explicit model using 500 loci in 800 individuals: 10 CPU-years Adding long-distance dispersal: 20 CPU-years
Computational issues A fully spatially-explicit model using 500 loci in 800 individuals: 10 CPU-years Adding long-distance dispersal: 20 CPU-years
 SPLATCHE on the grid early 2005: joined the Biomed VO of the EGEE project mid 2005: tested on GILDA test bed, and deployed on the Grid since mid 2006: production mode and optimization
SPLATCHE on the grid early 2005: joined the Biomed VO of the EGEE project mid 2005: tested on GILDA test bed, and deployed on the Grid since mid 2006: production mode and optimization
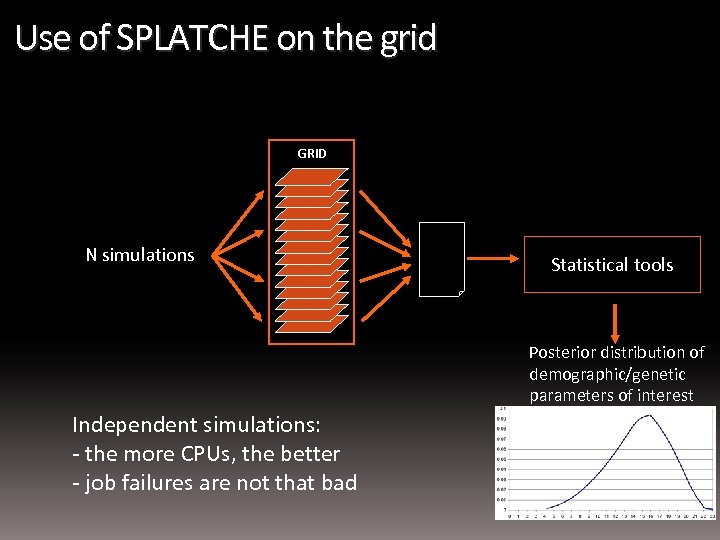 Use of SPLATCHE on the grid GRID N simulations Statistical tools Posterior distribution of demographic/genetic parameters of interest Independent simulations: - the more CPUs, the better - job failures are not that bad
Use of SPLATCHE on the grid GRID N simulations Statistical tools Posterior distribution of demographic/genetic parameters of interest Independent simulations: - the more CPUs, the better - job failures are not that bad
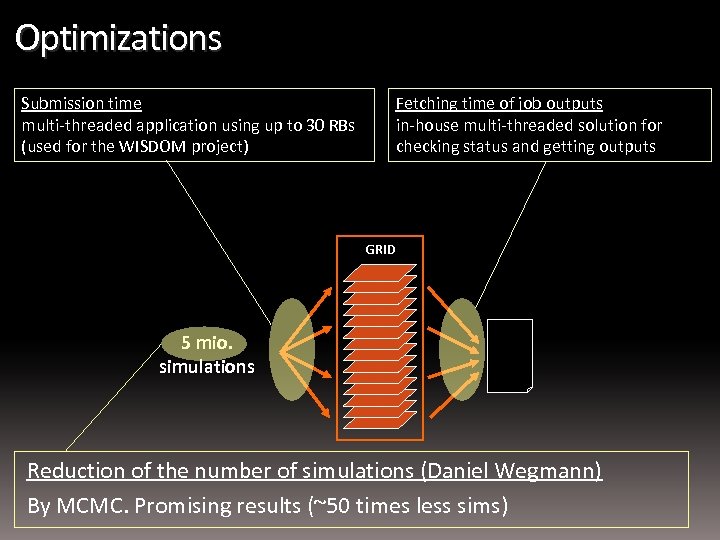 Optimizations Submission time multi-threaded application using up to 30 RBs (used for the WISDOM project) Fetching time of job outputs in-house multi-threaded solution for checking status and getting outputs GRID 5 mio. simulations Reduction of the number of simulations (Daniel Wegmann) By MCMC. Promising results (~50 times less sims)
Optimizations Submission time multi-threaded application using up to 30 RBs (used for the WISDOM project) Fetching time of job outputs in-house multi-threaded solution for checking status and getting outputs GRID 5 mio. simulations Reduction of the number of simulations (Daniel Wegmann) By MCMC. Promising results (~50 times less sims)
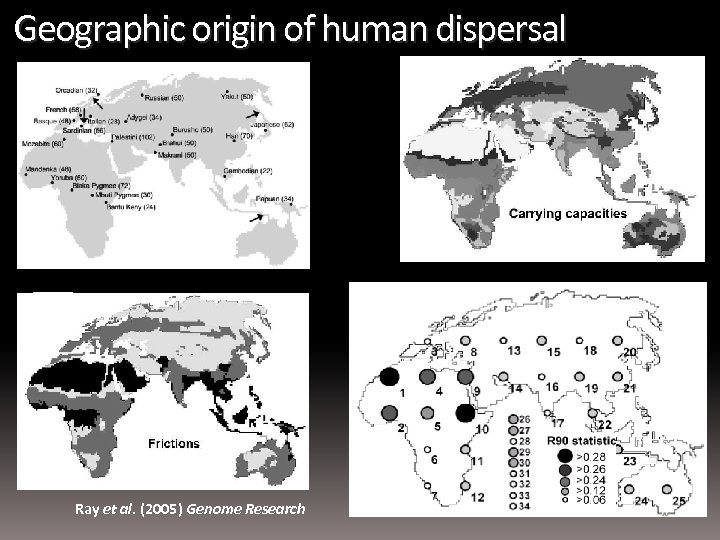 Geographic origin of human dispersal Ray et al. (2005) Genome Research
Geographic origin of human dispersal Ray et al. (2005) Genome Research
 Interactions among populations Interaction between modern humans and Neanderthals in Europe Currat & Excoffier (2004), PLo. S Biol.
Interactions among populations Interaction between modern humans and Neanderthals in Europe Currat & Excoffier (2004), PLo. S Biol.
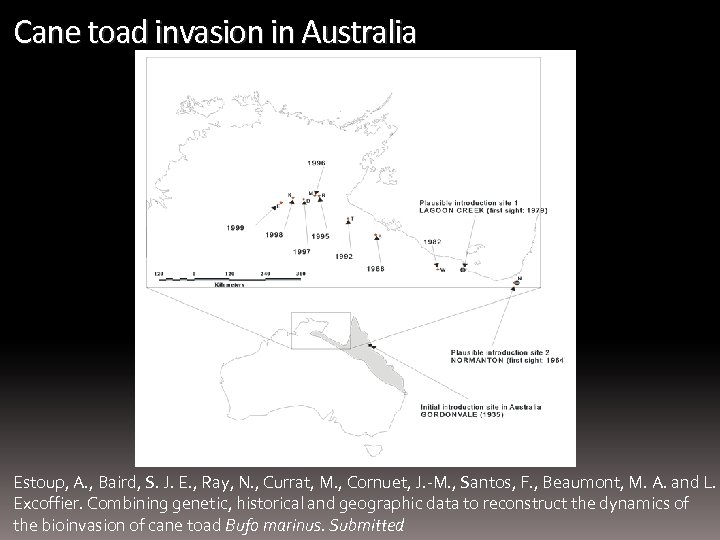 Cane toad invasion in Australia Estoup, A. , Baird, S. J. E. , Ray, N. , Currat, M. , Cornuet, J. -M. , Santos, F. , Beaumont, M. A. and L. Excoffier. Combining genetic, historical and geographic data to reconstruct the dynamics of the bioinvasion of cane toad Bufo marinus. Submitted
Cane toad invasion in Australia Estoup, A. , Baird, S. J. E. , Ray, N. , Currat, M. , Cornuet, J. -M. , Santos, F. , Beaumont, M. A. and L. Excoffier. Combining genetic, historical and geographic data to reconstruct the dynamics of the bioinvasion of cane toad Bufo marinus. Submitted
 Take-home message A good human demographic model is important Realistic spatially-explicit approaches are essential The grid is key for sufficient exploration of parameter space User support and connections outside one’s discipline is crucial
Take-home message A good human demographic model is important Realistic spatially-explicit approaches are essential The grid is key for sufficient exploration of parameter space User support and connections outside one’s discipline is crucial
 THANK YOU !
THANK YOU !


