79b716beac727093ae3e36955cac056a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 108
 TOXICOLOGY 3 Nadim J Lalani MD Special mention : Dr M. Beuhler Dr Mark Yarema Dr Vicas
TOXICOLOGY 3 Nadim J Lalani MD Special mention : Dr M. Beuhler Dr Mark Yarema Dr Vicas
 Name the General. Epilepsy or no?
Name the General. Epilepsy or no?
 Sun Tzu ? 722– 481 BC • heroic general of the King of Wu [544— 496 BC] • Author of “The Art of War” – Huge Influence on China – Adopted by Japanese Samurai – Studied by Napoleon • ? Existence of Sun Tzu – Based on anachronisms in text • Did not have seizures
Sun Tzu ? 722– 481 BC • heroic general of the King of Wu [544— 496 BC] • Author of “The Art of War” – Huge Influence on China – Adopted by Japanese Samurai – Studied by Napoleon • ? Existence of Sun Tzu – Based on anachronisms in text • Did not have seizures
 Julius Caesar 100– 44 BC • Was a priest at age 17 • Inspired by Alexander • Invented the 365 day calendar • Killed on March 15 44 BC “the Ides” • Never said “et tu Brutus” • four documented episodes of ? complex partial seizures
Julius Caesar 100– 44 BC • Was a priest at age 17 • Inspired by Alexander • Invented the 365 day calendar • Killed on March 15 44 BC “the Ides” • Never said “et tu Brutus” • four documented episodes of ? complex partial seizures
 Drug and Toxin Induced Seizures “The Generalised Version”
Drug and Toxin Induced Seizures “The Generalised Version”
 Outline • • Pathophysiology DDX ABCDEFP’s of DTS Cases – Bupropion – Diphenhydramine – Opioids – INH – Theophylline NO NO LIT TC HIU M A • Short snappers at any moment
Outline • • Pathophysiology DDX ABCDEFP’s of DTS Cases – Bupropion – Diphenhydramine – Opioids – INH – Theophylline NO NO LIT TC HIU M A • Short snappers at any moment
 Pathophysiology • Sz activity results from chaotic electrical discharge in the CNS • Disruption of normal structure – Congenital – acquired [mass/trauma] • Disruption of local metabolic milieu • Drugs/Toxins – metab/drugs/toxins/withdrawal result in changes in neurochemical pathways that “kindle” up a Sz
Pathophysiology • Sz activity results from chaotic electrical discharge in the CNS • Disruption of normal structure – Congenital – acquired [mass/trauma] • Disruption of local metabolic milieu • Drugs/Toxins – metab/drugs/toxins/withdrawal result in changes in neurochemical pathways that “kindle” up a Sz
 Neurochemical pathways • Balance exists between inhibitory and excitatory pathways • Main inhibitory neurotransmitters consist of – GABA – Glycine • Main excitatory neurotransmitter is glutamate
Neurochemical pathways • Balance exists between inhibitory and excitatory pathways • Main inhibitory neurotransmitters consist of – GABA – Glycine • Main excitatory neurotransmitter is glutamate
 Neurochemical p-ways : Inhibitors Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) • main inhibitory neurotransmitter of the CNS. • Stimulated GABA receptors chloride ion flux inhibit membrane depolarization • GABA antagonists/depletn of GABA incr membrane depolarization seizures
Neurochemical p-ways : Inhibitors Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) • main inhibitory neurotransmitter of the CNS. • Stimulated GABA receptors chloride ion flux inhibit membrane depolarization • GABA antagonists/depletn of GABA incr membrane depolarization seizures
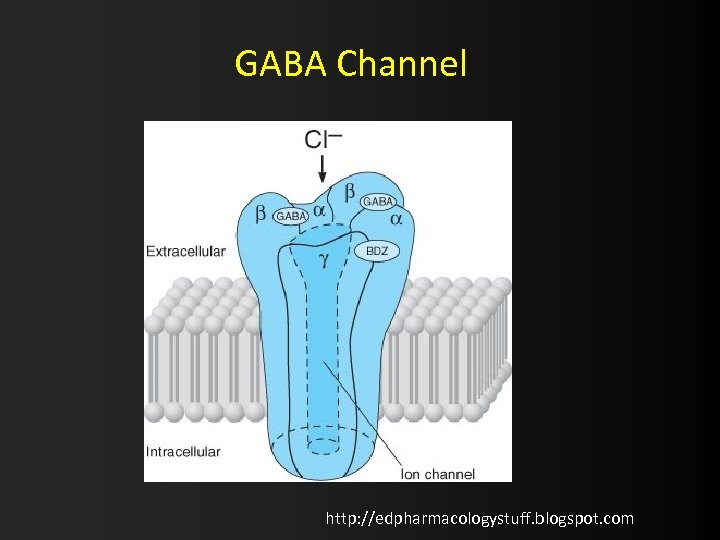 GABA Channel http: //edpharmacologystuff. blogspot. com
GABA Channel http: //edpharmacologystuff. blogspot. com
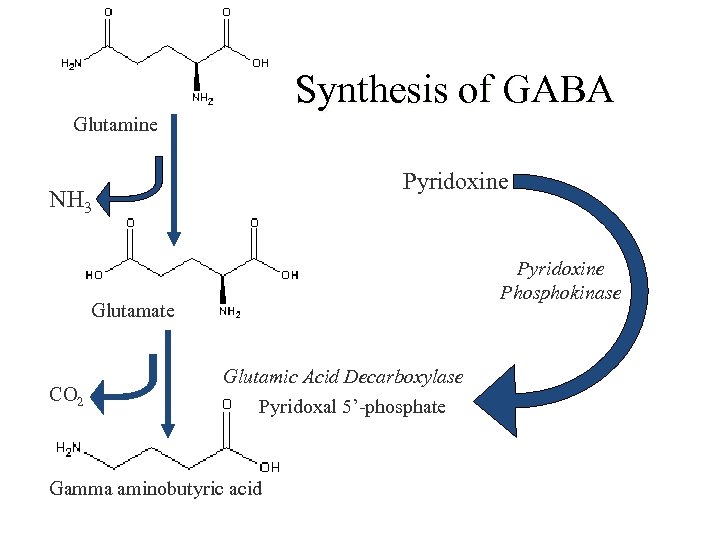 Synthesis of GABA Glutamine Pyridoxine NH 3 Pyridoxine Phosphokinase Glutamate CO 2 Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Gamma aminobutyric acid
Synthesis of GABA Glutamine Pyridoxine NH 3 Pyridoxine Phosphokinase Glutamate CO 2 Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Gamma aminobutyric acid
 • GABA is broken down by GABA transaminase this is exploited by the anticonvulsant Vigabatrin which inhibits GT • 3 -types of GABA rec (A [main one], B & C). • GABA B rec affected by GHB (drug of abuse) and Baclofen (antispasmodic) – in someone with Sz and a Baclofen pump think pump failure) • Anitbiotix that cause Sz do so through GABA antagonism
• GABA is broken down by GABA transaminase this is exploited by the anticonvulsant Vigabatrin which inhibits GT • 3 -types of GABA rec (A [main one], B & C). • GABA B rec affected by GHB (drug of abuse) and Baclofen (antispasmodic) – in someone with Sz and a Baclofen pump think pump failure) • Anitbiotix that cause Sz do so through GABA antagonism
 How Do Benzos Work? Barbituates?
How Do Benzos Work? Barbituates?
 Mechanism of Action • Benzodiazepines – At least two different binding sites – Increase GABA affinity for receptor – Increase frequency of channel opening – Inhibit adenosine uptake – Therefore Inhibits neuronal activity
Mechanism of Action • Benzodiazepines – At least two different binding sites – Increase GABA affinity for receptor – Increase frequency of channel opening – Inhibit adenosine uptake – Therefore Inhibits neuronal activity
 Mechanism of Action • Barbiturates – Increase duration of channel opening – At high concentrations, open Cl- channel directly – Will not require GABA presence to open channel – NB! Propofol also works by opening the Cl channel
Mechanism of Action • Barbiturates – Increase duration of channel opening – At high concentrations, open Cl- channel directly – Will not require GABA presence to open channel – NB! Propofol also works by opening the Cl channel
 Inhibitors ADENOSINE • Adenosine binds (A 1) receptors inhibit glutamate release anticonvulsant effect • A 1 antagonists increase seizure activity HISTAMINE • anticonvulsive properties via central H 1 receptor • Animal models Toxic doses of antihistamines Sz
Inhibitors ADENOSINE • Adenosine binds (A 1) receptors inhibit glutamate release anticonvulsant effect • A 1 antagonists increase seizure activity HISTAMINE • anticonvulsive properties via central H 1 receptor • Animal models Toxic doses of antihistamines Sz
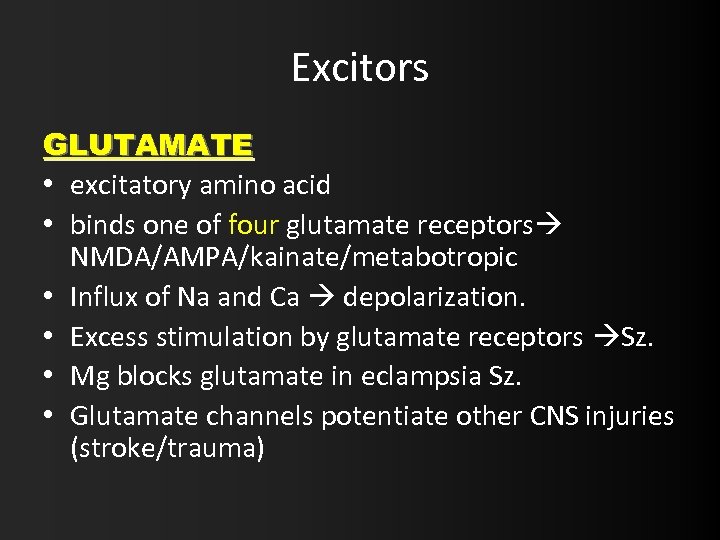 Excitors GLUTAMATE • excitatory amino acid • binds one of four glutamate receptors NMDA/AMPA/kainate/metabotropic • Influx of Na and Ca depolarization. • Excess stimulation by glutamate receptors Sz. • Mg blocks glutamate in eclampsia Sz. • Glutamate channels potentiate other CNS injuries (stroke/trauma)
Excitors GLUTAMATE • excitatory amino acid • binds one of four glutamate receptors NMDA/AMPA/kainate/metabotropic • Influx of Na and Ca depolarization. • Excess stimulation by glutamate receptors Sz. • Mg blocks glutamate in eclampsia Sz. • Glutamate channels potentiate other CNS injuries (stroke/trauma)
 NOREPINEPHRINE • Autonomic over stimulation can lead to Sz. • [e. g. ++ sympathetic outflow in Etoh withdrawal] ACETYLCHOLINE • ACh overstim can result in Sz [e. g. carbamates and organophosphates]
NOREPINEPHRINE • Autonomic over stimulation can lead to Sz. • [e. g. ++ sympathetic outflow in Etoh withdrawal] ACETYLCHOLINE • ACh overstim can result in Sz [e. g. carbamates and organophosphates]
 Others: GLYCINE • excitatory neurotransmitter in CNS • Binds to NMDA receptors Na influx • However, Postsynaptic receptors chloride influx inhibitory • Postsynaptic antagonists, [e. g. strychnine] cause seizure-like myoclonic activity.
Others: GLYCINE • excitatory neurotransmitter in CNS • Binds to NMDA receptors Na influx • However, Postsynaptic receptors chloride influx inhibitory • Postsynaptic antagonists, [e. g. strychnine] cause seizure-like myoclonic activity.
 Others SODIUM CHANNELS • Na channel blockers slow nerve transmission and hence should inhibit Sz. • However, in overdose, Lidocaine known to produce Sz by an unknown mechanism. • Same goes for other Na channel blockers e. g. carbamazepine (CMZ also antagonises adenosine Sz)
Others SODIUM CHANNELS • Na channel blockers slow nerve transmission and hence should inhibit Sz. • However, in overdose, Lidocaine known to produce Sz by an unknown mechanism. • Same goes for other Na channel blockers e. g. carbamazepine (CMZ also antagonises adenosine Sz)
 Match the following drug with the mechanism
Match the following drug with the mechanism
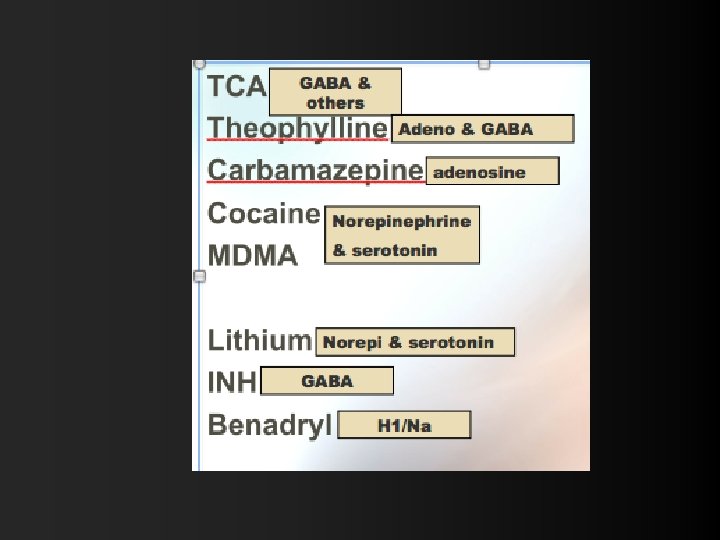
 TCA Theophylline Carbamazepine Cocaine MDMA Lithium INH Benadryl GABA Na-Chan 5 -HT Norepi NMDA H 1 Anticholinergic Adenosine
TCA Theophylline Carbamazepine Cocaine MDMA Lithium INH Benadryl GABA Na-Chan 5 -HT Norepi NMDA H 1 Anticholinergic Adenosine
 Name the General. Sz or no?
Name the General. Sz or no?
 Genghis Khan 1162– 1227 • Born Temüjin “iron” • Came to power in 1190 • Mongol Empire – Largest empire in hx. • Ruthless when crossed • Buried in secret grave • Did not have epilepsy
Genghis Khan 1162– 1227 • Born Temüjin “iron” • Came to power in 1190 • Mongol Empire – Largest empire in hx. • Ruthless when crossed • Buried in secret grave • Did not have epilepsy
 CASE • 40 yo M brought to ED with GTC Sz. Now comatose (may have ingested) • Approach?
CASE • 40 yo M brought to ED with GTC Sz. Now comatose (may have ingested) • Approach?
 ABCDEFP’S of D&T Sz A: Airway B: Breathing C: Circulation & Chemstrip D: Decontamination E: Elimination F: Find a cure P’s: Penes (benzodiaza…) Phenobarb (NO PHENYTOIN) Propofol Pyridoxine
ABCDEFP’S of D&T Sz A: Airway B: Breathing C: Circulation & Chemstrip D: Decontamination E: Elimination F: Find a cure P’s: Penes (benzodiaza…) Phenobarb (NO PHENYTOIN) Propofol Pyridoxine
 More on treatment: • • No trials best anticonvulsant Penes followed by Phenobarb 1 st and 2 nd line Ativan preferred (but can use midaz) Phenytoin not good for: – TCA / Etoh withdrawal – Worsens theophylline, LA’s and Lindane • Therefore not recommended
More on treatment: • • No trials best anticonvulsant Penes followed by Phenobarb 1 st and 2 nd line Ativan preferred (but can use midaz) Phenytoin not good for: – TCA / Etoh withdrawal – Worsens theophylline, LA’s and Lindane • Therefore not recommended
 More on Benzo’s: (know pharmacology of benzo’s for exams) Longest t 1/2 ? ativan (can also cause toxicity from its diluent propylene glycol) Active metabolites? Diazepam (can’t give IV in our region, but 10 -20 mg Po is great for Etoh withdrawal)
More on Benzo’s: (know pharmacology of benzo’s for exams) Longest t 1/2 ? ativan (can also cause toxicity from its diluent propylene glycol) Active metabolites? Diazepam (can’t give IV in our region, but 10 -20 mg Po is great for Etoh withdrawal)
 Charcoal Not good for? “PHAILS” Phosphates/ potassium Hydrocarbons Acids/alkalis Iron Lithium (can use kayexelate) Solvents/ “syanide”
Charcoal Not good for? “PHAILS” Phosphates/ potassium Hydrocarbons Acids/alkalis Iron Lithium (can use kayexelate) Solvents/ “syanide”
 Dialyzable overdoses? SMELT Salycilates Methanol Ethlene Glycol Lithium Theophylline
Dialyzable overdoses? SMELT Salycilates Methanol Ethlene Glycol Lithium Theophylline
 HX & P/E pointers • Always suspect intoxication – Foraging / Food ingestions – Psych hx • Use all potential historians • Look for toxidromes: – Sympath cocaine/amphet/withdrawal • Beware mimickers • Note other injuries (head) rhabdo • Know DDx for Sz in general –?
HX & P/E pointers • Always suspect intoxication – Foraging / Food ingestions – Psych hx • Use all potential historians • Look for toxidromes: – Sympath cocaine/amphet/withdrawal • Beware mimickers • Note other injuries (head) rhabdo • Know DDx for Sz in general –?
 Secondary Seizures: I N T R A C R A N I A L “IS IT MEATh? ” • I intracranial Hemorrhage [Sub/epidural, arachnoid, parenchymal] • S structural Ab. N [Vascular, mass, congenital, degenerative] • I infection [mening, enceph, abscess] • T trauma
Secondary Seizures: I N T R A C R A N I A L “IS IT MEATh? ” • I intracranial Hemorrhage [Sub/epidural, arachnoid, parenchymal] • S structural Ab. N [Vascular, mass, congenital, degenerative] • I infection [mening, enceph, abscess] • T trauma
 E X T R A C R A N I A L • M metabolic [hypo/hyper Glycemia, hypo/hyper Na, hyperosm, uremia, hepatic, , hypo. Ca++, Hypo. Mg++] • E eclampsia • A anoxia/ischemia [cardiac arrest, severe hypox] • T toxins/Drugs – [Cocaine, lidocaine, anti. D, w/drawal, theophylline] • h htn encephalopathy
E X T R A C R A N I A L • M metabolic [hypo/hyper Glycemia, hypo/hyper Na, hyperosm, uremia, hepatic, , hypo. Ca++, Hypo. Mg++] • E eclampsia • A anoxia/ischemia [cardiac arrest, severe hypox] • T toxins/Drugs – [Cocaine, lidocaine, anti. D, w/drawal, theophylline] • h htn encephalopathy
 ? OTIS CAMPBELL
? OTIS CAMPBELL
 §The "town drunk" in The Andy Griffith Show in the 60’s §known to go on regular binges, then lock himself in the town jail until he sobered up. (He had a key to the jail ) §When sober enough, Otis would occasionally be deputized, when needed to fight minor crimewaves in the town. §Otis would often see something genuinely bizarre but attribute it to being drunk.
§The "town drunk" in The Andy Griffith Show in the 60’s §known to go on regular binges, then lock himself in the town jail until he sobered up. (He had a key to the jail ) §When sober enough, Otis would occasionally be deputized, when needed to fight minor crimewaves in the town. §Otis would often see something genuinely bizarre but attribute it to being drunk.
 OTIS CAMPBELL Opioids (darvon &c) carbamazepine Antidepressants (bupropion) Envenomations, ephedra
OTIS CAMPBELL Opioids (darvon &c) carbamazepine Antidepressants (bupropion) Envenomations, ephedra
 CASE • Teenager found agitated/combative and tremulous at home • Last seen 3 hours earlier was well. EMS found an empty pill bottle which they lost • En route sinus tach, but developed N/V then a GTC seizure • o/e: Still seizing (now 10 mins) • Approach?
CASE • Teenager found agitated/combative and tremulous at home • Last seen 3 hours earlier was well. EMS found an empty pill bottle which they lost • En route sinus tach, but developed N/V then a GTC seizure • o/e: Still seizing (now 10 mins) • Approach?
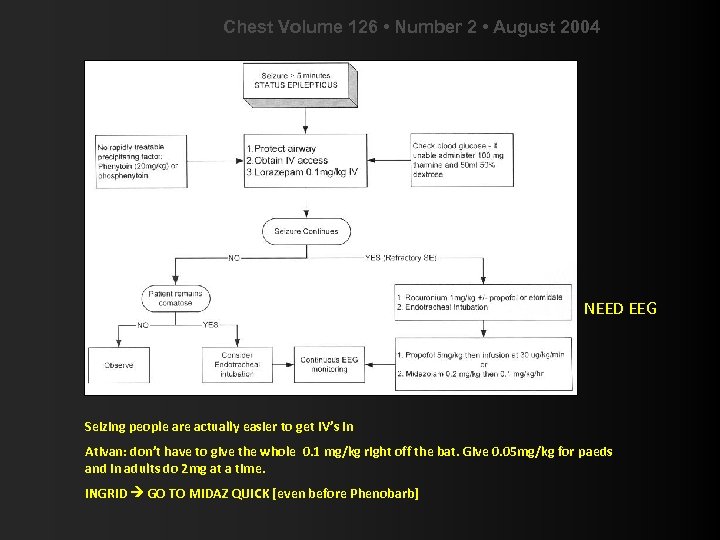 Chest Volume 126 • Number 2 • August 2004 NEED EEG Seizing people are actually easier to get IV’s in Ativan: don’t have to give the whole 0. 1 mg/kg right off the bat. Give 0. 05 mg/kg for paeds and in adults do 2 mg at a time. INGRID GO TO MIDAZ QUICK [even before Phenobarb]
Chest Volume 126 • Number 2 • August 2004 NEED EEG Seizing people are actually easier to get IV’s in Ativan: don’t have to give the whole 0. 1 mg/kg right off the bat. Give 0. 05 mg/kg for paeds and in adults do 2 mg at a time. INGRID GO TO MIDAZ QUICK [even before Phenobarb]
 Airway IV, O 2, Monitor, BW, glu Dextrose 25 -50 g IV Consider Thiamine 100 mg IV, Mg 1 -2 g. IV Lorazepam 2 mg/min IV up to 0. 1 mg/kg Can Load with 4 mg IV or Diazepam] Phenobarb 20 mg/kg at 5 -75 mg/min IV Propofol Pyridoxine 5 g Others (propofol/pentobarb) Adapted from: Lowenstein DH Status Epilepticus NEJM 338(14): 970 1998
Airway IV, O 2, Monitor, BW, glu Dextrose 25 -50 g IV Consider Thiamine 100 mg IV, Mg 1 -2 g. IV Lorazepam 2 mg/min IV up to 0. 1 mg/kg Can Load with 4 mg IV or Diazepam] Phenobarb 20 mg/kg at 5 -75 mg/min IV Propofol Pyridoxine 5 g Others (propofol/pentobarb) Adapted from: Lowenstein DH Status Epilepticus NEJM 338(14): 970 1998
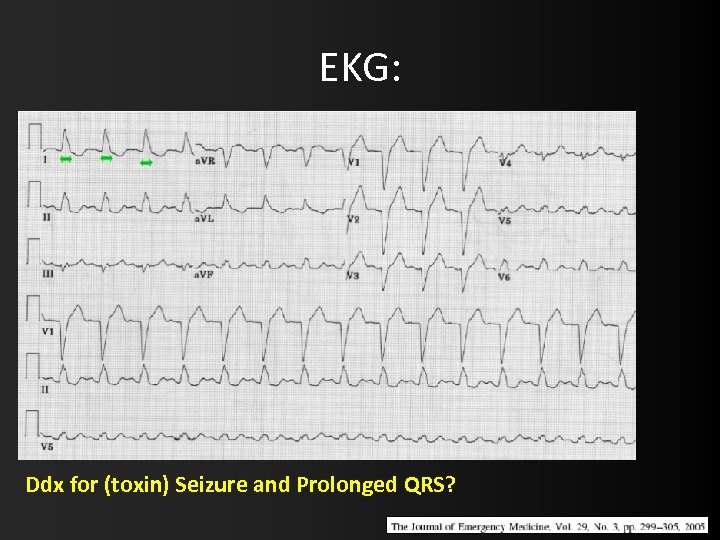 EKG: Ddx for (toxin) Seizure and Prolonged QRS?
EKG: Ddx for (toxin) Seizure and Prolonged QRS?
 Ddx Seizure with QRS
Ddx Seizure with QRS
 Which antidepressants make you seize?
Which antidepressants make you seize?
 • • • TCA’s Venlafaxine (Effexor) Bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) Lithium Citalopram
• • • TCA’s Venlafaxine (Effexor) Bupropion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) Lithium Citalopram
 BUPROPION (Wellbutrin) • Wellbutrin, Wellbutrin SR, Zyban • Monocyclic antidepressant structurally similar to amphetamines • Inhibits uptake of norepi and dopamine • QRS effects because of cardiac sodium channel blockade Journal of Toxicology: Clinical Toxicology v 36. n 6 (Oct 1998): pp 595 (4).
BUPROPION (Wellbutrin) • Wellbutrin, Wellbutrin SR, Zyban • Monocyclic antidepressant structurally similar to amphetamines • Inhibits uptake of norepi and dopamine • QRS effects because of cardiac sodium channel blockade Journal of Toxicology: Clinical Toxicology v 36. n 6 (Oct 1998): pp 595 (4).
 Pharmacokinetics • Metabolized in liver 3 active metabolites: – Hydroxybupropion, threohydrobupropion – & erythrohydrobupropion. • half-life: – Bupropion & hydroxybupropion 20 h – Other metabs 35 h. • Seizure dose: 30 g or more • False + urine amphetamines screen
Pharmacokinetics • Metabolized in liver 3 active metabolites: – Hydroxybupropion, threohydrobupropion – & erythrohydrobupropion. • half-life: – Bupropion & hydroxybupropion 20 h – Other metabs 35 h. • Seizure dose: 30 g or more • False + urine amphetamines screen
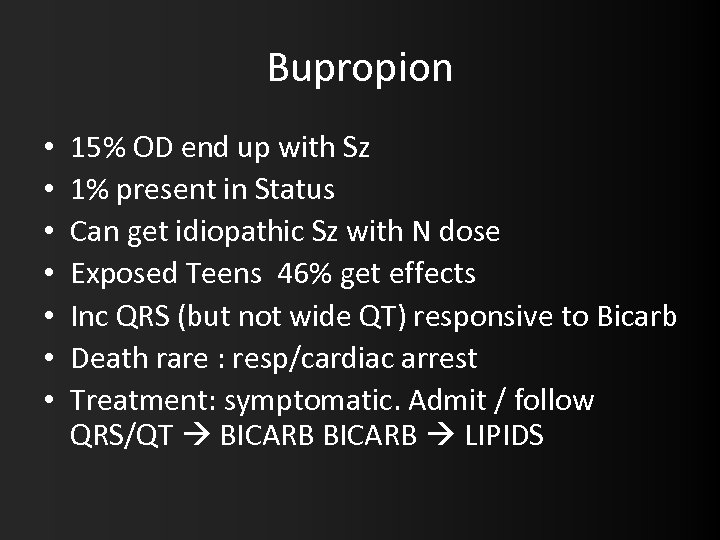 Bupropion • • 15% OD end up with Sz 1% present in Status Can get idiopathic Sz with N dose Exposed Teens 46% get effects Inc QRS (but not wide QT) responsive to Bicarb Death rare : resp/cardiac arrest Treatment: symptomatic. Admit / follow QRS/QT BICARB LIPIDS
Bupropion • • 15% OD end up with Sz 1% present in Status Can get idiopathic Sz with N dose Exposed Teens 46% get effects Inc QRS (but not wide QT) responsive to Bicarb Death rare : resp/cardiac arrest Treatment: symptomatic. Admit / follow QRS/QT BICARB LIPIDS
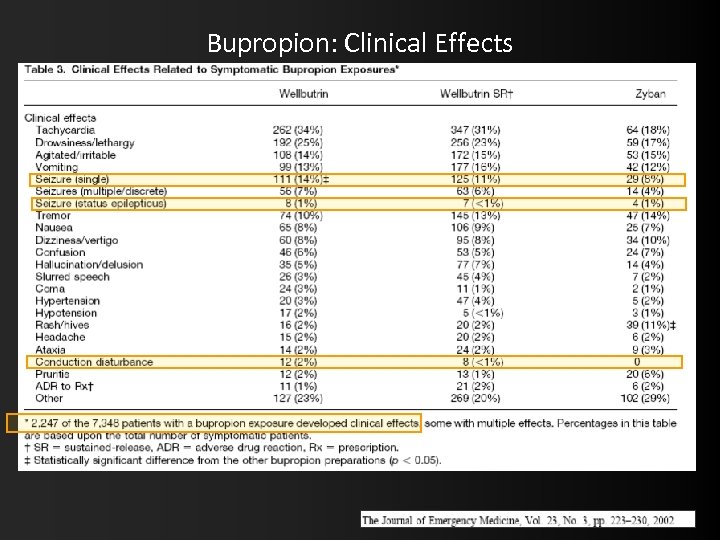 Bupropion: Clinical Effects
Bupropion: Clinical Effects
 Name the General. Sz or no?
Name the General. Sz or no?
 Hannibal 247– 183 BC • Born in Carthage • 218 BC crossed the Pyrenes attacked Rome. • Genius of strategy – Romans copied – “Snake Bombs” • No record of epilepsy
Hannibal 247– 183 BC • Born in Carthage • 218 BC crossed the Pyrenes attacked Rome. • Genius of strategy – Romans copied – “Snake Bombs” • No record of epilepsy
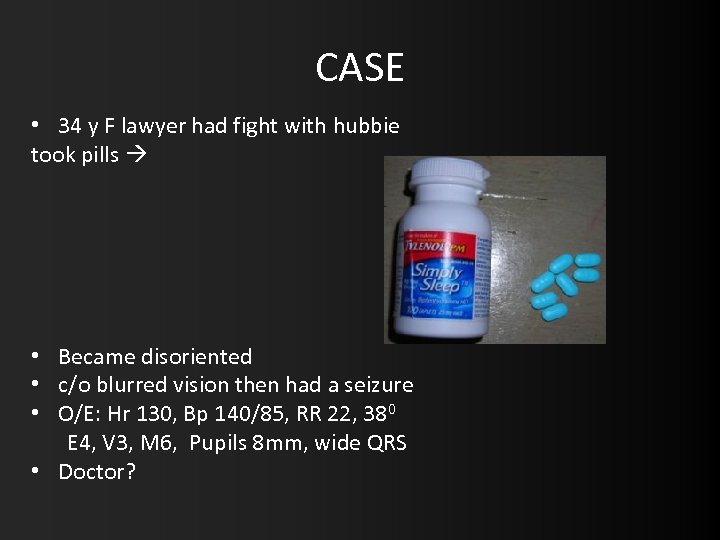 CASE • 34 y F lawyer had fight with hubbie took pills • Became disoriented • c/o blurred vision then had a seizure • O/E: Hr 130, Bp 140/85, RR 22, 380 E 4, V 3, M 6, Pupils 8 mm, wide QRS • Doctor?
CASE • 34 y F lawyer had fight with hubbie took pills • Became disoriented • c/o blurred vision then had a seizure • O/E: Hr 130, Bp 140/85, RR 22, 380 E 4, V 3, M 6, Pupils 8 mm, wide QRS • Doctor?
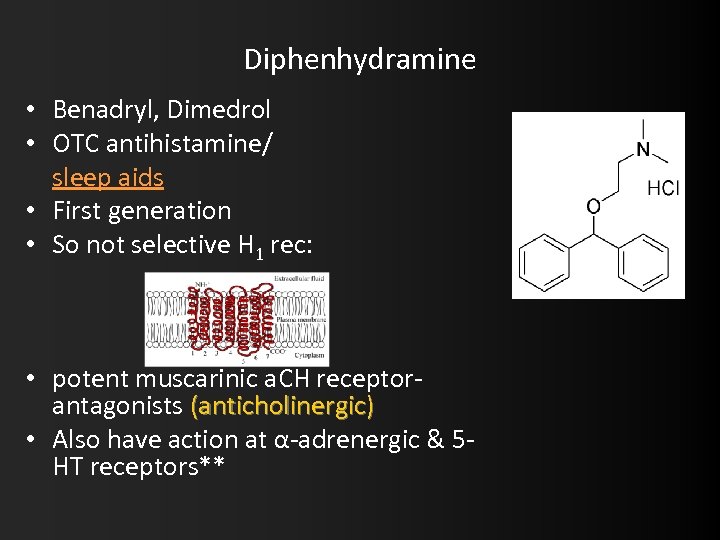 Diphenhydramine • Benadryl, Dimedrol • OTC antihistamine/ sleep aids • First generation • So not selective H 1 rec: • potent muscarinic a. CH receptorantagonists (anticholinergic) • Also have action at α-adrenergic & 5 HT receptors**
Diphenhydramine • Benadryl, Dimedrol • OTC antihistamine/ sleep aids • First generation • So not selective H 1 rec: • potent muscarinic a. CH receptorantagonists (anticholinergic) • Also have action at α-adrenergic & 5 HT receptors**
 Diphenhydramine • Drug of abuse for hallucinogenic properties • 55% of fatal antihistamine OD’s are benadryl
Diphenhydramine • Drug of abuse for hallucinogenic properties • 55% of fatal antihistamine OD’s are benadryl
 Pharmacology Half life 2. 5 hours 90% protein-bound Cleared by Cyt P 450 Readily crosses bbb where anti-a. CH affect visual and auditory cortex • Renally excreted • Asian descent “fast acetylators” less effects • Autoinduction of metabolism chronic use enhances it’s own clearance • •
Pharmacology Half life 2. 5 hours 90% protein-bound Cleared by Cyt P 450 Readily crosses bbb where anti-a. CH affect visual and auditory cortex • Renally excreted • Asian descent “fast acetylators” less effects • Autoinduction of metabolism chronic use enhances it’s own clearance • •
 clinical • CNS: limbic system & hippocampus confusion & temporary amnesia. • Autonomic NS: – NMJ ataxia & EPS – sympathetic post-ganglionic junctions – urinary retention / ileus – pupil dilation – tachycardia – dry skin and mucous membranes. • “Mad as a hatter, dry as a bone, blind as a bat, red as a beet, hot as a hare…”
clinical • CNS: limbic system & hippocampus confusion & temporary amnesia. • Autonomic NS: – NMJ ataxia & EPS – sympathetic post-ganglionic junctions – urinary retention / ileus – pupil dilation – tachycardia – dry skin and mucous membranes. • “Mad as a hatter, dry as a bone, blind as a bat, red as a beet, hot as a hare…”
 Clinical Summary • • • Antimuscarinic Anticholinergic toxidrome Anti-Serotonin Sedation Block Na channel Wide QRS/QT Anti H 1 + Anti – ac. H Seizures High doses K+ channel blocking effect
Clinical Summary • • • Antimuscarinic Anticholinergic toxidrome Anti-Serotonin Sedation Block Na channel Wide QRS/QT Anti H 1 + Anti – ac. H Seizures High doses K+ channel blocking effect
 Management • • • ABCDEFP’s Physostigmine? The only indication: KNOWN ingestion Give one dose can clear up delerium long enough to get a better hx from the pt. Problem physostigmine usually clears quicker than toxin so pts revert back to toxidromic state Multi-dose associated with bradyrhythmias have atropine by the bedside! • If you don’t know for SURE don’t use – Used to be given as cocktail and that’s when people ran into problems – Can precipitate Sz / cholinergic symptoms. – Asystole with cyclic antidepressant poisoning. • Does Bicarb work for QRS? – Yes – use it. Helps with Na channel blockade and rhabdo
Management • • • ABCDEFP’s Physostigmine? The only indication: KNOWN ingestion Give one dose can clear up delerium long enough to get a better hx from the pt. Problem physostigmine usually clears quicker than toxin so pts revert back to toxidromic state Multi-dose associated with bradyrhythmias have atropine by the bedside! • If you don’t know for SURE don’t use – Used to be given as cocktail and that’s when people ran into problems – Can precipitate Sz / cholinergic symptoms. – Asystole with cyclic antidepressant poisoning. • Does Bicarb work for QRS? – Yes – use it. Helps with Na channel blockade and rhabdo
 Case • • • 16 yo rushed into ED by step-dad. Found her in room Breathing slow, blue in face Had been surfing net …something about a “cocktail” O/E: HR 50, SBP 70, RR 6, Wide QRS Pinpoint pupils GCS E 1, V 1, M 4 Cyanotic Starts to seize … DOCTOR?
Case • • • 16 yo rushed into ED by step-dad. Found her in room Breathing slow, blue in face Had been surfing net …something about a “cocktail” O/E: HR 50, SBP 70, RR 6, Wide QRS Pinpoint pupils GCS E 1, V 1, M 4 Cyanotic Starts to seize … DOCTOR?
 OPIOIDS • Evidence of opium use as early as 1500 BCE • Opium is extract from poppy plant Papaver somniferum • Extracts (alkaloids) from opium are called opiates morphine, codeine & papaverine • Semi synthetic “opioids” heroin, naloxone & oxycodone • Synthetics Methadone & fentanyl • Morphine purified in 1804 • 1898 Bayer created a semi synthetic morphine as antiptussive. Anyone? – Heroin!
OPIOIDS • Evidence of opium use as early as 1500 BCE • Opium is extract from poppy plant Papaver somniferum • Extracts (alkaloids) from opium are called opiates morphine, codeine & papaverine • Semi synthetic “opioids” heroin, naloxone & oxycodone • Synthetics Methadone & fentanyl • Morphine purified in 1804 • 1898 Bayer created a semi synthetic morphine as antiptussive. Anyone? – Heroin!
![Opioid pharmacology • Readily absorbed [any method] • Bind 3 types of G-protein receptors: Opioid pharmacology • Readily absorbed [any method] • Bind 3 types of G-protein receptors:](https://present5.com/presentation/79b716beac727093ae3e36955cac056a/image-60.jpg) Opioid pharmacology • Readily absorbed [any method] • Bind 3 types of G-protein receptors: – μ (mu), κ (kappa), and δ (delta) • mu widespread in CNS. Controls resp / pain / euphoria / GI motility • kappa & delta mostly spinal cord
Opioid pharmacology • Readily absorbed [any method] • Bind 3 types of G-protein receptors: – μ (mu), κ (kappa), and δ (delta) • mu widespread in CNS. Controls resp / pain / euphoria / GI motility • kappa & delta mostly spinal cord
 Opioids • Bound recs inhibit presynaptic NT release. • Cleared by liver (glucoronidation) • Toxidrome: ALOC, Resp depression, hypotension and miosis (constricted pupils) • However certain ones can infact cause seizures: – Propoxyphene – Meperidine – Tramodol – pentazocine
Opioids • Bound recs inhibit presynaptic NT release. • Cleared by liver (glucoronidation) • Toxidrome: ALOC, Resp depression, hypotension and miosis (constricted pupils) • However certain ones can infact cause seizures: – Propoxyphene – Meperidine – Tramodol – pentazocine
 Propoxyphene • Darvon = Propoxyphene (racemic mix) • Dextropropoxyphene: r-isomer usually found in combinations Darvocet (with APAP) Darvon Compound-65 (with ASA & caffeine) • Both drugs have narrow therapeutic index
Propoxyphene • Darvon = Propoxyphene (racemic mix) • Dextropropoxyphene: r-isomer usually found in combinations Darvocet (with APAP) Darvon Compound-65 (with ASA & caffeine) • Both drugs have narrow therapeutic index
 pharmacology • • • Peak levels 2 h Propoxyphene t 1/2 of 6 - 12 h Metabolite norpropoxyphene 30 - 36 h Max dose is 360 mg/day Potent anti- Na channel effects prolonged QRS Seizures
pharmacology • • • Peak levels 2 h Propoxyphene t 1/2 of 6 - 12 h Metabolite norpropoxyphene 30 - 36 h Max dose is 360 mg/day Potent anti- Na channel effects prolonged QRS Seizures
 clinical • Behave like TCA’s – Hypotension – Cardiac effects – ALOC – Seizures in 10% of OD • Management: – ABCEFP’s – Bicarb
clinical • Behave like TCA’s – Hypotension – Cardiac effects – ALOC – Seizures in 10% of OD • Management: – ABCEFP’s – Bicarb
 Tramadol • Ultram® Ultracet®. • Weak Mu opiod activity • Inhibits: norepi reuptake Seratonin reuptake • Also modulates GABA
Tramadol • Ultram® Ultracet®. • Weak Mu opiod activity • Inhibits: norepi reuptake Seratonin reuptake • Also modulates GABA
 pharmacology • Hepatic metab via the cyt P 450 isozyme CYP 2 D 6 5 metabolites. • M 1 metabolite more active at mu rec • t 1/2 6 h • 8% of OD will have seizure
pharmacology • Hepatic metab via the cyt P 450 isozyme CYP 2 D 6 5 metabolites. • M 1 metabolite more active at mu rec • t 1/2 6 h • 8% of OD will have seizure
 Meperidine • Acts at mu receptor • Anticholinergic • Na – channels • Some serotonin effects • Postulated less spasmodic activity NB! Don’t ever signover a patient on demerol without noting how much they’ve had or placing a maximum dose 300 mg!!!
Meperidine • Acts at mu receptor • Anticholinergic • Na – channels • Some serotonin effects • Postulated less spasmodic activity NB! Don’t ever signover a patient on demerol without noting how much they’ve had or placing a maximum dose 300 mg!!!
 pharmacology • v. lipid soluble so fast onset • 70% protein bound • t 1/2: 4 h • Metabolized by liver normeperidine • Normeperidine toxic • Build up leads to agitation, myoclonus, seizures Risk factors: • IV (instead of PO) • > 300 mg/d • Renal failure What else should you know about before giving Meperidine?
pharmacology • v. lipid soluble so fast onset • 70% protein bound • t 1/2: 4 h • Metabolized by liver normeperidine • Normeperidine toxic • Build up leads to agitation, myoclonus, seizures Risk factors: • IV (instead of PO) • > 300 mg/d • Renal failure What else should you know about before giving Meperidine?
 pentazocine • • • Talwin Synthetic opioid 2004 Mcgill Study Red heads require less! T 1/2: 2. 5 h Cleared by liver Also a proconvulsant
pentazocine • • • Talwin Synthetic opioid 2004 Mcgill Study Red heads require less! T 1/2: 2. 5 h Cleared by liver Also a proconvulsant
 Why don’t you use Narcan for known OD of Tramadol and Demerol?
Why don’t you use Narcan for known OD of Tramadol and Demerol?
 • Known to precipitate Sz with Tramadol and Meperidine
• Known to precipitate Sz with Tramadol and Meperidine
 General? Seizures or no?
General? Seizures or no?
 Alexander the Great 356– 323 BC • • • Mentored by Aristotle Became King at 20 Huge empire Didn’t have seizures Death at 33 Septic + using Hellebore: – Veratrine Na channel poison
Alexander the Great 356– 323 BC • • • Mentored by Aristotle Became King at 20 Huge empire Didn’t have seizures Death at 33 Septic + using Hellebore: – Veratrine Na channel poison
 CASE • 26 yo M found in NE Calgary (Rundle to be exact) seizing • Brought in by EMS: • o/e GTC sz • Doctor? • Further Hx: being treated for depression and TB
CASE • 26 yo M found in NE Calgary (Rundle to be exact) seizing • Brought in by EMS: • o/e GTC sz • Doctor? • Further Hx: being treated for depression and TB
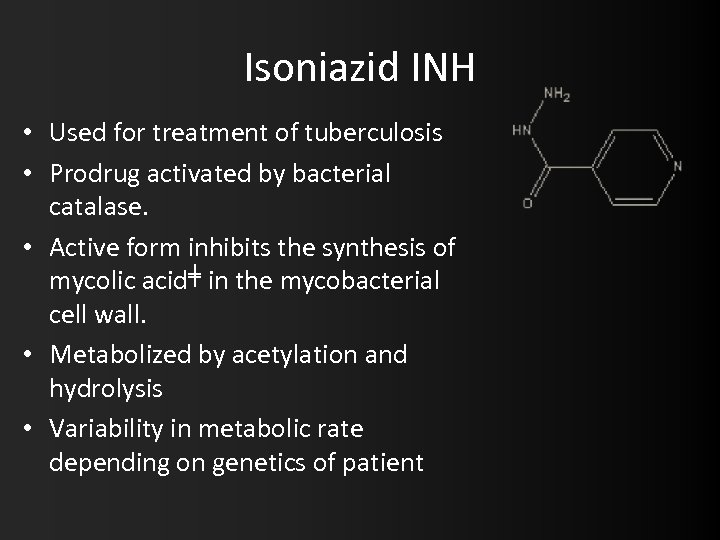 Isoniazid INH • Used for treatment of tuberculosis • Prodrug activated by bacterial catalase. • Active form inhibits the synthesis of mycolic acid╪ in the mycobacterial cell wall. • Metabolized by acetylation and hydrolysis • Variability in metabolic rate depending on genetics of patient
Isoniazid INH • Used for treatment of tuberculosis • Prodrug activated by bacterial catalase. • Active form inhibits the synthesis of mycolic acid╪ in the mycobacterial cell wall. • Metabolized by acetylation and hydrolysis • Variability in metabolic rate depending on genetics of patient
 Isoniazid • N half-life is 3 h • Fast acetylators have half-life of 1 hour • More toxic effects with slow acetylators
Isoniazid • N half-life is 3 h • Fast acetylators have half-life of 1 hour • More toxic effects with slow acetylators
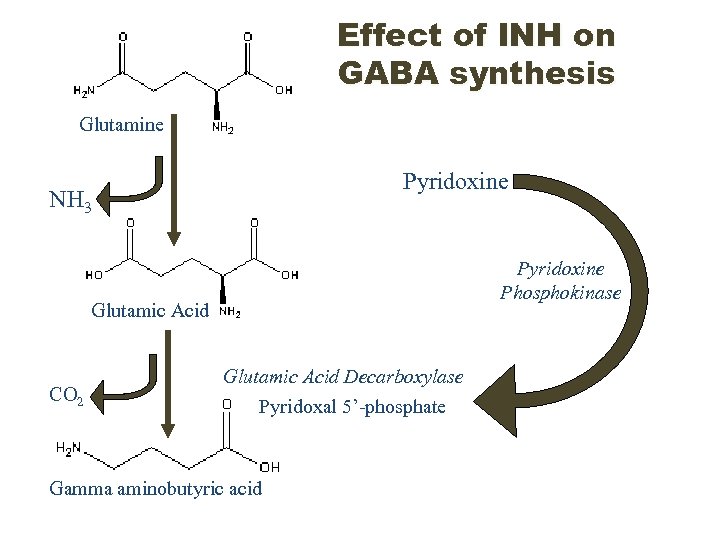 Effect of INH on GABA synthesis Glutamine Pyridoxine NH 3 Pyridoxine Phosphokinase Glutamic Acid CO 2 Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Gamma aminobutyric acid
Effect of INH on GABA synthesis Glutamine Pyridoxine NH 3 Pyridoxine Phosphokinase Glutamic Acid CO 2 Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Gamma aminobutyric acid
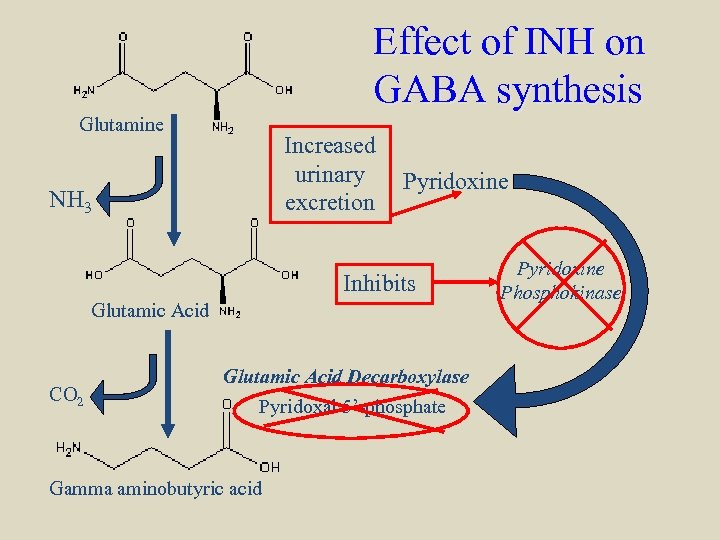 Effect of INH on GABA synthesis Glutamine Increased urinary excretion NH 3 Pyridoxine Inhibits Glutamic Acid CO 2 Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Gamma aminobutyric acid Pyridoxine Phosphokinase
Effect of INH on GABA synthesis Glutamine Increased urinary excretion NH 3 Pyridoxine Inhibits Glutamic Acid CO 2 Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Gamma aminobutyric acid Pyridoxine Phosphokinase
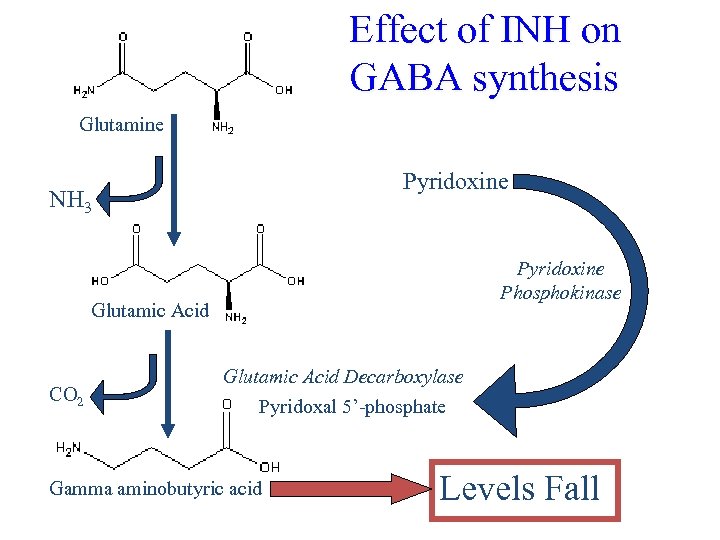 Effect of INH on GABA synthesis Glutamine Pyridoxine NH 3 Pyridoxine Phosphokinase Glutamic Acid CO 2 Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Gamma aminobutyric acid Levels Fall
Effect of INH on GABA synthesis Glutamine Pyridoxine NH 3 Pyridoxine Phosphokinase Glutamic Acid CO 2 Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Gamma aminobutyric acid Levels Fall
 Isoniazid Overdose Clinically: • Nausea/Vomiting/ataxia/mydraisis • Triad of Severe Metabolic Acidosis Coma Seizures
Isoniazid Overdose Clinically: • Nausea/Vomiting/ataxia/mydraisis • Triad of Severe Metabolic Acidosis Coma Seizures
 Why severe lactic acidosis? • INH inhibits NAD Lactate buildup
Why severe lactic acidosis? • INH inhibits NAD Lactate buildup
 Isoniazid Management • ABCD (charcoal) EF • “Penes” or phenobarb? – Need GABA for “penes” to work • P Pyridoxine • If don’t know amount of INH: Give 5 grams IV • Otherwise 1 g for each g INH (may get transient base deficit w/ >5 g) Problem hospital often don’t have enough … so go to local supplement store and buy vit b 6 and put down NG!!!
Isoniazid Management • ABCD (charcoal) EF • “Penes” or phenobarb? – Need GABA for “penes” to work • P Pyridoxine • If don’t know amount of INH: Give 5 grams IV • Otherwise 1 g for each g INH (may get transient base deficit w/ >5 g) Problem hospital often don’t have enough … so go to local supplement store and buy vit b 6 and put down NG!!!
 Ddx Status Epilepticus?
Ddx Status Epilepticus?
 • • Hypoglycemia INH TCA CO Theophylline Gyrometra Wellbutrin Other process bleed/tumor
• • Hypoglycemia INH TCA CO Theophylline Gyrometra Wellbutrin Other process bleed/tumor
 CASE • 68 yo M via EMS. Got cough and so was taking old asthma medication • c/o profound N/V • EMS: HR 150, BP 90 systolic, began to seize • Doctor? • Additional hx – was taking theophylline
CASE • 68 yo M via EMS. Got cough and so was taking old asthma medication • c/o profound N/V • EMS: HR 150, BP 90 systolic, began to seize • Doctor? • Additional hx – was taking theophylline
 Theophylline • Is a methylxanthine – Caffeine in same group • Extracted from tea leaves • Used for treatment of COPD and asthma b/c relaxes sm. muscle • Inhibits phosphodiesterase enzymes increase in intracellular c. AMP;
Theophylline • Is a methylxanthine – Caffeine in same group • Extracted from tea leaves • Used for treatment of COPD and asthma b/c relaxes sm. muscle • Inhibits phosphodiesterase enzymes increase in intracellular c. AMP;
 Mechanism of Action • Theophylline (& caffeine): adenosine A 1 & A 2 receptor antagonists • Peripherally release of catecholamines • Catecholamine responses made worse by blocking of A 1 receptors • Cause vasoconstriction of the cerebral vasculature by A 2 antagonism result ? SEIZure
Mechanism of Action • Theophylline (& caffeine): adenosine A 1 & A 2 receptor antagonists • Peripherally release of catecholamines • Catecholamine responses made worse by blocking of A 1 receptors • Cause vasoconstriction of the cerebral vasculature by A 2 antagonism result ? SEIZure
 Pharmacology • • • 50% protein-bound Metabolized by liver Cyt P 450 T 1/2: 6 h V. narrow therapeutic range Seizures related to: 1) Chronicity chronic OD worse 2) Age >60 do worse 3) Levels > 250 mmol/L (chronic) 550 mmol/L (acute)
Pharmacology • • • 50% protein-bound Metabolized by liver Cyt P 450 T 1/2: 6 h V. narrow therapeutic range Seizures related to: 1) Chronicity chronic OD worse 2) Age >60 do worse 3) Levels > 250 mmol/L (chronic) 550 mmol/L (acute)
 Theophylline • In overdose is very dangerous – Causes seizures (27%) – Tachydysrhythmias (75%) – Hypotension – Hypokalemia (25%)
Theophylline • In overdose is very dangerous – Causes seizures (27%) – Tachydysrhythmias (75%) – Hypotension – Hypokalemia (25%)
 Theophylline management: ABC D: Multi dose charcoal effective E don’t forget dialysis Otherapies? P Pyridoxine as theophylline has some anti. GABA effects • P propanolol? . Case reports of esmolol use despite hypotension • • •
Theophylline management: ABC D: Multi dose charcoal effective E don’t forget dialysis Otherapies? P Pyridoxine as theophylline has some anti. GABA effects • P propanolol? . Case reports of esmolol use despite hypotension • • •
 Indications for multi-dose charcoal? “Think! Several Doses o. Ph Charcoal!” • Theophylline • Salicylates • Dapsone • Phenobarb • Carbamazepine
Indications for multi-dose charcoal? “Think! Several Doses o. Ph Charcoal!” • Theophylline • Salicylates • Dapsone • Phenobarb • Carbamazepine
 Seizures or no?
Seizures or no?
 Napoleon I 1769– 1821 • Coup in 1799 • Studied “Art of War” • Brilliant military strategist – Semaphore system – Espionage – Moving artillery • Purported to have had seizures • Drop attacks vs syncope
Napoleon I 1769– 1821 • Coup in 1799 • Studied “Art of War” • Brilliant military strategist – Semaphore system – Espionage – Moving artillery • Purported to have had seizures • Drop attacks vs syncope
 4 indications for pyridoxine?
4 indications for pyridoxine?
 • INH • Theophylline • Ethylene Glycol • Gyromitra
• INH • Theophylline • Ethylene Glycol • Gyromitra
 Name the poison +
Name the poison +
 Strychnine Poisoning: WHAT: bitter, white, powder alkaloid derived from the seeds of the tree Strychnos nux-vomica. introduced in the 16 th century as a rodenticide, until recently it was used as a respiratory, circulatory and digestive stimulant no longer used in any pharmaceutical products, but is still used as a rodenticide. Strychnine is also found as an adulterant in street drugs such as amphetamines, heroin and cocaine
Strychnine Poisoning: WHAT: bitter, white, powder alkaloid derived from the seeds of the tree Strychnos nux-vomica. introduced in the 16 th century as a rodenticide, until recently it was used as a respiratory, circulatory and digestive stimulant no longer used in any pharmaceutical products, but is still used as a rodenticide. Strychnine is also found as an adulterant in street drugs such as amphetamines, heroin and cocaine
![PATHOPHYS: • Lethal dose 50 mg [15 mg paeds] • T 1/2 10 -15 PATHOPHYS: • Lethal dose 50 mg [15 mg paeds] • T 1/2 10 -15](https://present5.com/presentation/79b716beac727093ae3e36955cac056a/image-98.jpg) PATHOPHYS: • Lethal dose 50 mg [15 mg paeds] • T 1/2 10 -15 h • Readily absorbed from MM’s/intact skin • Antagonises post-synaptic glycine receptors muscles over stimulated • rhabdo, • lactic acidosis • Eventually die of resp compromise
PATHOPHYS: • Lethal dose 50 mg [15 mg paeds] • T 1/2 10 -15 h • Readily absorbed from MM’s/intact skin • Antagonises post-synaptic glycine receptors muscles over stimulated • rhabdo, • lactic acidosis • Eventually die of resp compromise
 CLINICALLY: • features occur from 15 to 30 minutes after ingestion • muscular spasms and twitches can progress to painful generalized convulsions (patients remain awake as CNS NMDAglycine receptors not affected) • Risus sardonicus? • hypersensitivity to stimuli. • HTN, Tacchy, cyanosis
CLINICALLY: • features occur from 15 to 30 minutes after ingestion • muscular spasms and twitches can progress to painful generalized convulsions (patients remain awake as CNS NMDAglycine receptors not affected) • Risus sardonicus? • hypersensitivity to stimuli. • HTN, Tacchy, cyanosis
 Mgmt: ABC’s – may have to intubate/paralyse IV, O 2, Monitor Decontaminate with charcoal [if ingested] Benzos Avoid stimulation Treat hyperkalemia/rhabdo/hyperthermia
Mgmt: ABC’s – may have to intubate/paralyse IV, O 2, Monitor Decontaminate with charcoal [if ingested] Benzos Avoid stimulation Treat hyperkalemia/rhabdo/hyperthermia
 The End
The End
 SEIZURES Dr Vicas Is this a toxin-induced seizure? Or Is this toxin known to cause seizures ? And If seizures occur, what is the outcome ?
SEIZURES Dr Vicas Is this a toxin-induced seizure? Or Is this toxin known to cause seizures ? And If seizures occur, what is the outcome ?
 TOXIN-INDUCED SEIZURES OUTCOME • Catastrophic event – cyclic antidepressants – theophylline • Expected short-lived effect – diphenhydramine • Refractory to conventional therapy – INH • Mistaken for seizures – myoclonic jerks – dystonic reactions – strychnine
TOXIN-INDUCED SEIZURES OUTCOME • Catastrophic event – cyclic antidepressants – theophylline • Expected short-lived effect – diphenhydramine • Refractory to conventional therapy – INH • Mistaken for seizures – myoclonic jerks – dystonic reactions – strychnine
 ** knowledge of this led to discovery of SSRI’s notably prozac ╪ Mycolic acids in cell walls Mycobacterium tuberculosis increased resistance to chemical damage & antibiotics allow bacterium to grow inside macrophages. ¥
** knowledge of this led to discovery of SSRI’s notably prozac ╪ Mycolic acids in cell walls Mycobacterium tuberculosis increased resistance to chemical damage & antibiotics allow bacterium to grow inside macrophages. ¥
 REFERENCES
REFERENCES


 Patti A. Paris. ECG conduction delays associated with massive bupropion overdose. Journal of Toxicology: Clinical Toxicology v 36. n 6 (Oct 1998): pp 595 (4). David J Mc. Cann. Toxicity, Antihistamine http: //www. emedicine. com/emerg/topic 38. htm Greg Hymel. Toxicity, Theophylline http: //www. emedicine. com/EMERG/topic 577. htm Michael Seneff et al , Acute theophylline toxicity and the use of esmolol to reverse cardiovascular instability. Annals of Emergency Medicine Volume 19, Issue 6 , June 1990, Pages 671 -673 Kempf J. Rusterholtz T. Ber C. Gayol S. Jaeger A. Haemodynamic study as guideline for the use of beta blockers in acute theophylline poisoning. Intensive Care Medicine. 22(6): 585 -7, 1996 Jun.
Patti A. Paris. ECG conduction delays associated with massive bupropion overdose. Journal of Toxicology: Clinical Toxicology v 36. n 6 (Oct 1998): pp 595 (4). David J Mc. Cann. Toxicity, Antihistamine http: //www. emedicine. com/emerg/topic 38. htm Greg Hymel. Toxicity, Theophylline http: //www. emedicine. com/EMERG/topic 577. htm Michael Seneff et al , Acute theophylline toxicity and the use of esmolol to reverse cardiovascular instability. Annals of Emergency Medicine Volume 19, Issue 6 , June 1990, Pages 671 -673 Kempf J. Rusterholtz T. Ber C. Gayol S. Jaeger A. Haemodynamic study as guideline for the use of beta blockers in acute theophylline poisoning. Intensive Care Medicine. 22(6): 585 -7, 1996 Jun.


