9bee0ba15e069b675b1acad019e3b3d0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Towards ontology driven navigation of the lipid bibliosphere Chistopher J. O. Baker, Rajaraman Kanagasabai, Wee Tiong Ang, Anitha Veeramani, Hong-Sang Low, and Markus R. Wenk International Conference on Bioinformatics 2007 (In. Co. B 2007) 27 -31 August 2007

Motivation § Lipid research in 21 st century is in need of reliable & sensible integration of data from different sources. § Lipid nomenclature in biomedical literature is highly heterogeneous. § Semantic data integration is necessary for lipid research yet this is poorly achievable due to an absence of a single unified, consistent, and universally accepted lipid classification system.

Objective § Develop a system that can facilitate the navigation of the lipid bibliosphere using a standardized lipid vocabulary with precise semantics. § To make use of the expressivity of a w 3 c endorsed standard, the web ontology language (OWL) for representing lipid nomenclature & hierarchy.
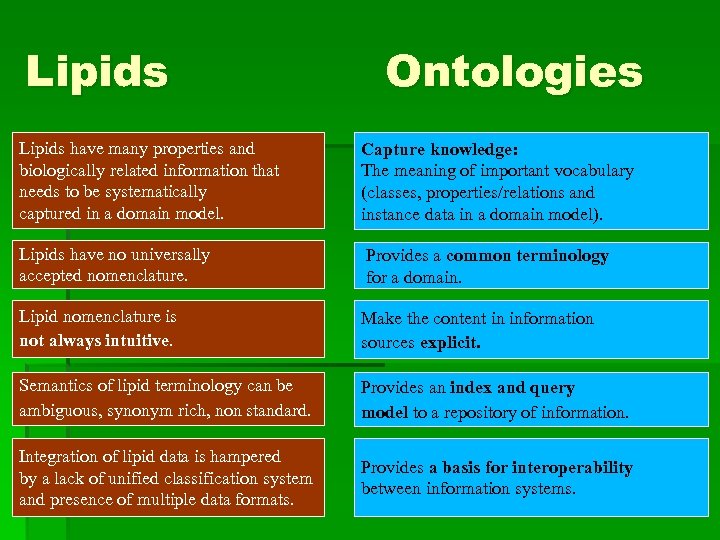
Lipids Ontologies Lipids have many properties and biologically related information that needs to be systematically captured in a domain model. Capture knowledge: The meaning of important vocabulary (classes, properties/relations and instance data in a domain model). Lipids have no universally accepted nomenclature. Provides a common terminology for a domain. Lipid nomenclature is not always intuitive. Make the content in information sources explicit. Semantics of lipid terminology can be ambiguous, synonym rich, non standard. Provides an index and query model to a repository of information. Integration of lipid data is hampered by a lack of unified classification system and presence of multiple data formats. Provides a basis for interoperability between information systems.
Lipid Ontology
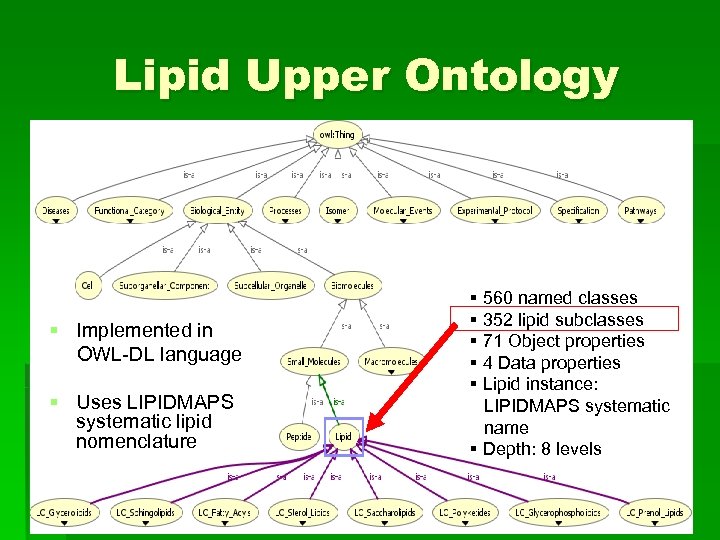
Lipid Upper Ontology § Implemented in OWL-DL language § Uses LIPIDMAPS systematic lipid nomenclature § 560 named classes § 352 lipid subclasses § 71 Object properties § 4 Data properties § Lipid instance: LIPIDMAPS systematic name § Depth: 8 levels
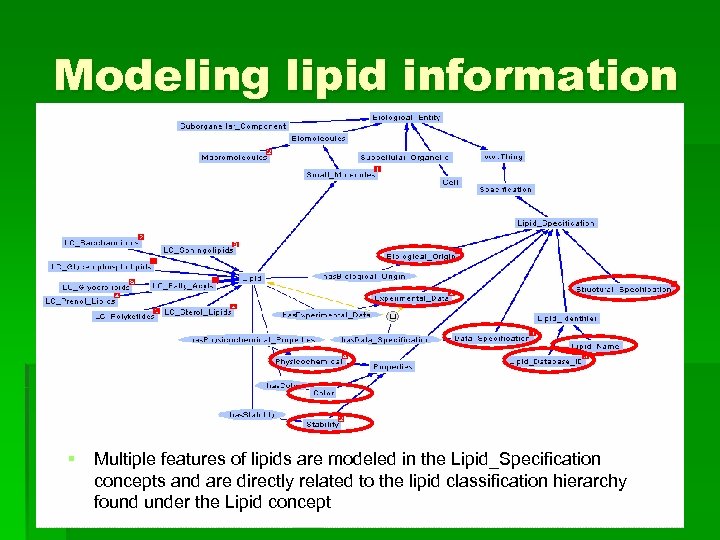
Modeling lipid information § Multiple features of lipids are modeled in the Lipid_Specification concepts and are directly related to the lipid classification hierarchy found under the Lipid concept
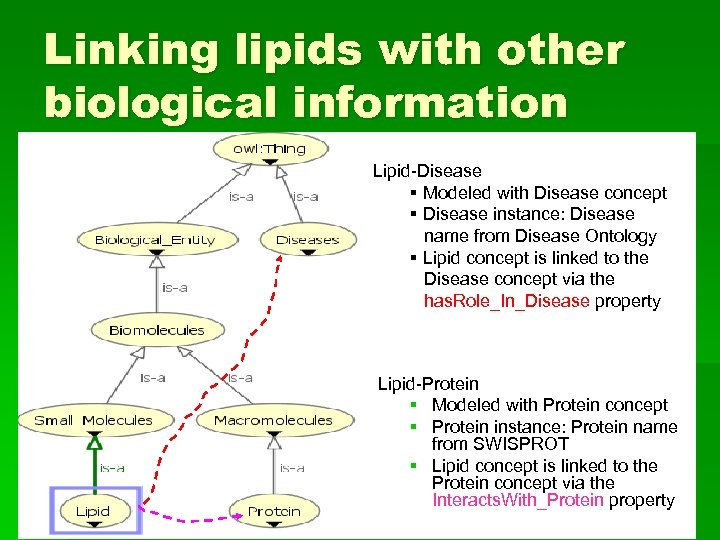
Linking lipids with other biological information Lipid-Disease § Modeled with Disease concept § Disease instance: Disease name from Disease Ontology § Lipid concept is linked to the Disease concept via the has. Role_In_Disease property Lipid-Protein § Modeled with Protein concept § Protein instance: Protein name from SWISPROT § Lipid concept is linked to the Protein concept via the Interacts. With_Protein property

A LIPID has many names • Phosphatidylcholine is an important component of the mucus layer in the large intestine. • The distribution of these pores was examined using 1, 2 -di-oleoyl-snglycero-3 -phosphocholine (DOPC) phospholipid vesicles under a standard fluorescent microscope. • Lecithin is usually used as a synonym for pure phosphatidylcholine, which is the major component isolated from egg yolk or soy beans. 2 -[[(2 R)-2, 3 di(octadecanoyloxy)propoxy]hydroxyphosphoryl]oxyethyltrimethylazanium
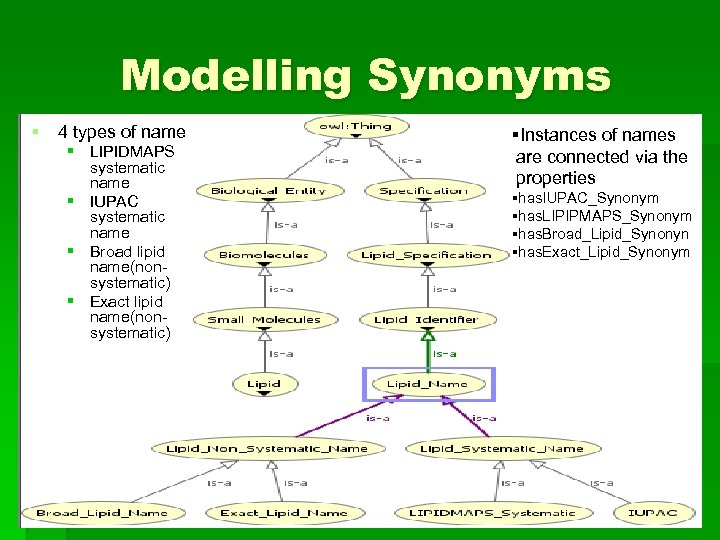
Modelling Synonyms § 4 types of name § LIPIDMAPS systematic name § IUPAC systematic name § Broad lipid name(nonsystematic) § Exact lipid name(nonsystematic) §Instances of names are connected via the properties §has. IUPAC_Synonym §has. LIPIPMAPS_Synonym §has. Broad_Lipid_Synonyn §has. Exact_Lipid_Synonym
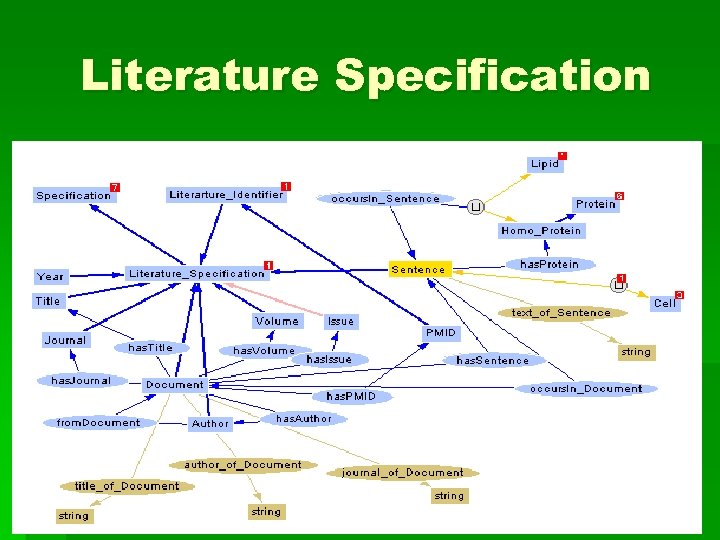
Literature Specification

Literature-driven, ontology-centric …. § Content Delivery Platform - Automated § § § Text Mining - Customized and Automated § § Domain Modeling / Customized / Rapid Prototype Knowledge Navigation / Ontology Interrogation Tools Interactive § § Regular Expressions, Named Entities, Relations, Co-reference Knowledge Engineering Ontology Creation § § Document delivery from Pubmed-PDF / USPTO-HTML Tools for conversion of docs to text-minable text Visual Query, Natural Language Interfaces Service platform for knowledge-intensive lipid navigation tasks
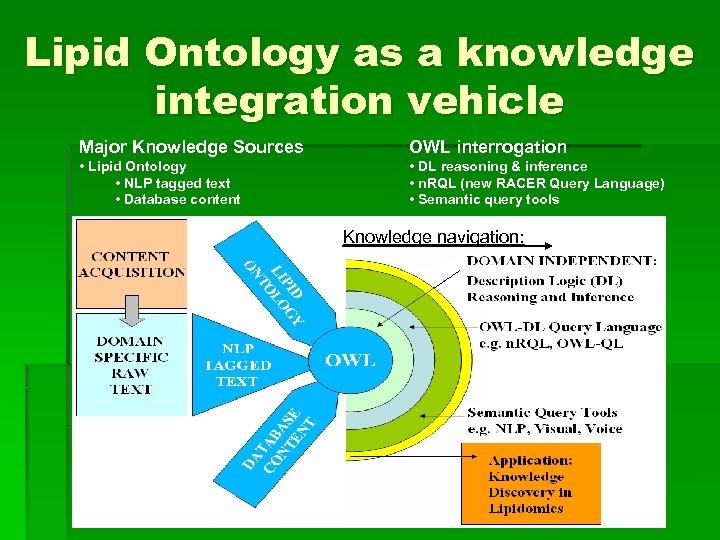
Lipid Ontology as a knowledge integration vehicle Major Knowledge Sources OWL interrogation • Lipid Ontology • NLP tagged text • Database content • DL reasoning & inference • n. RQL (new RACER Query Language) • Semantic query tools Knowledge navigation:
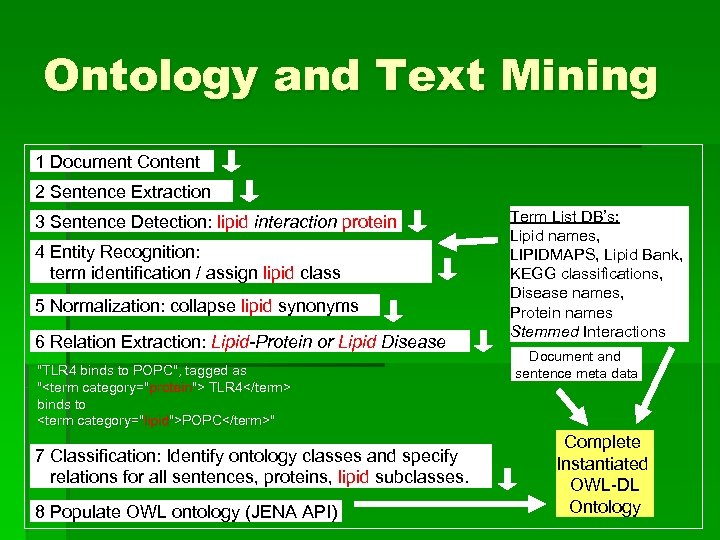
Ontology and Text Mining 1 Document Content 2 Sentence Extraction 3 Sentence Detection: lipid interaction protein 4 Entity Recognition: term identification / assign lipid class 5 Normalization: collapse lipid synonyms 6 Relation Extraction: Lipid-Protein or Lipid Disease "TLR 4 binds to POPC", tagged as "<term category="protein"> TLR 4</term> binds to <term category="lipid">POPC</term>" 7 Classification: Identify ontology classes and specify relations for all sentences, proteins, lipid subclasses. 8 Populate OWL ontology (JENA API) Term List DB’s: Lipid names, LIPIDMAPS, Lipid Bank, KEGG classifications, Disease names, Protein names Stemmed Interactions Document and sentence meta data Complete Instantiated OWL-DL Ontology
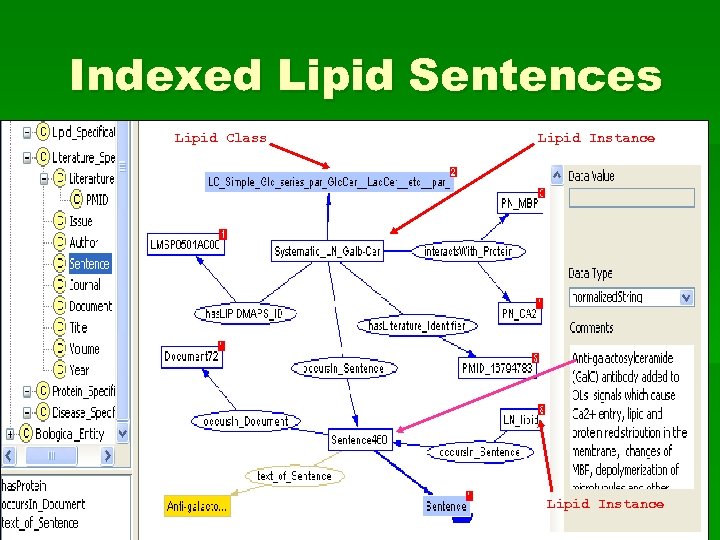
Indexed Lipid Sentences Lipid Class Lipid Instance
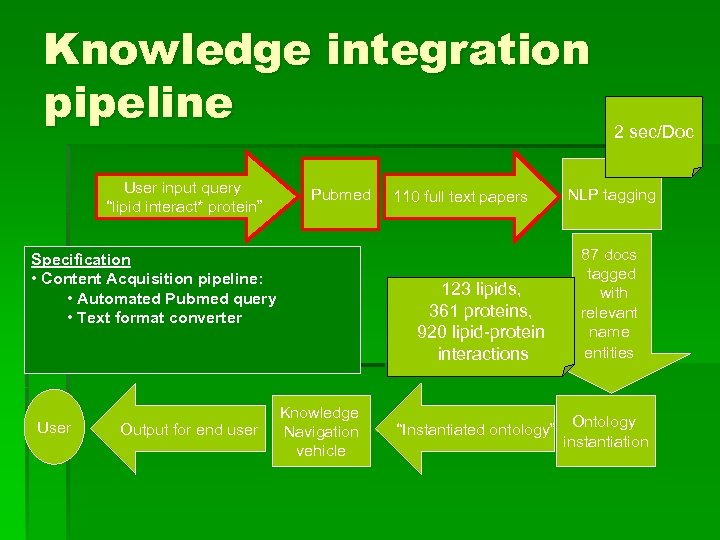
Knowledge integration pipeline User input query “lipid interact* protein” Pubmed Specification • Content Acquisition pipeline: • Automated Pubmed query • Text format converter User Output for end user 110 full text papers 123 lipids, 361 proteins, 920 lipid-protein interactions Knowledge Navigation vehicle “Instantiated ontology” 2 sec/Doc NLP tagging 87 docs tagged with relevant name entities Ontology instantiation
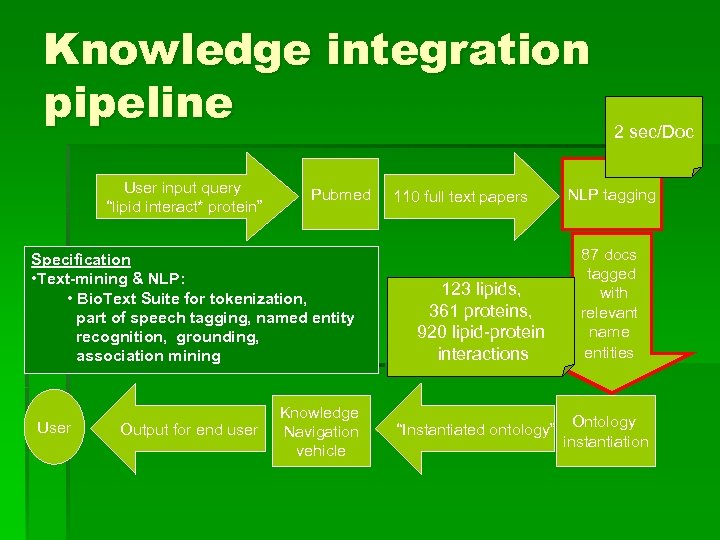
Knowledge integration pipeline User input query “lipid interact* protein” Pubmed Specification • Text-mining & NLP: • Bio. Text Suite for tokenization, part of speech tagging, named entity recognition, grounding, association mining User Output for end user Knowledge Navigation vehicle 110 full text papers 123 lipids, 361 proteins, 920 lipid-protein interactions “Instantiated ontology” 2 sec/Doc NLP tagging 87 docs tagged with relevant name entities Ontology instantiation
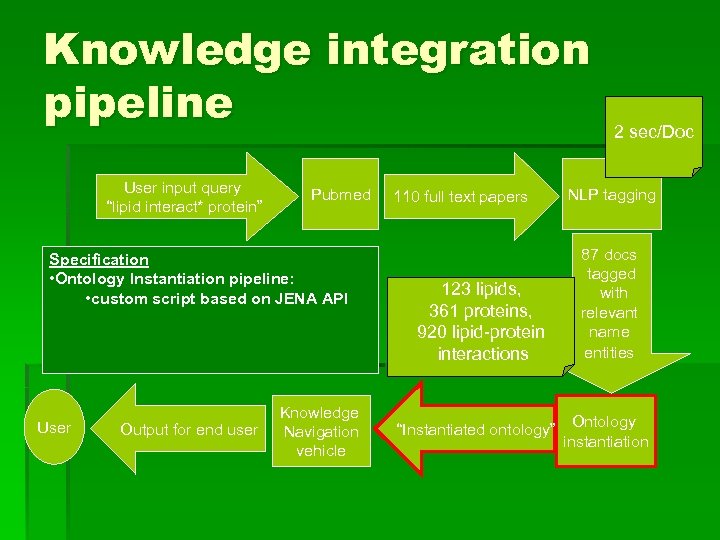
Knowledge integration pipeline User input query “lipid interact* protein” Pubmed Specification • Ontology Instantiation pipeline: • custom script based on JENA API User Output for end user Knowledge Navigation vehicle 110 full text papers 123 lipids, 361 proteins, 920 lipid-protein interactions “Instantiated ontology” 2 sec/Doc NLP tagging 87 docs tagged with relevant name entities Ontology instantiation
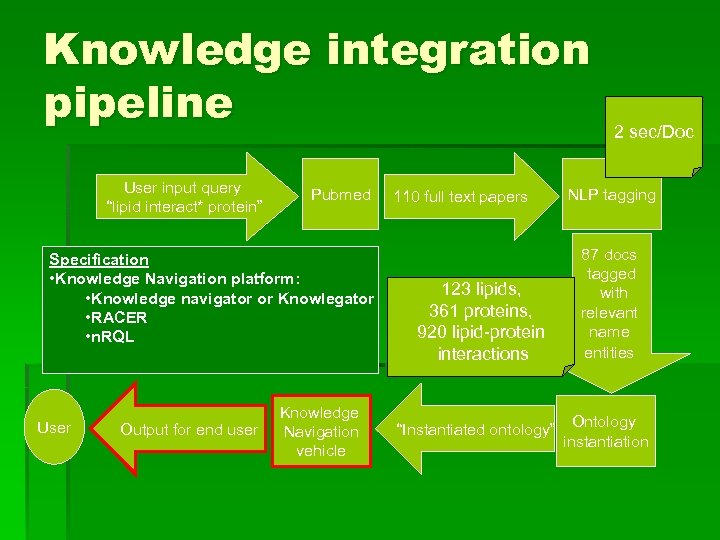
Knowledge integration pipeline User input query “lipid interact* protein” Pubmed Specification • Knowledge Navigation platform: • Knowledge navigator or Knowlegator • RACER • n. RQL User Output for end user Knowledge Navigation vehicle 110 full text papers 123 lipids, 361 proteins, 920 lipid-protein interactions “Instantiated ontology” 2 sec/Doc NLP tagging 87 docs tagged with relevant name entities Ontology instantiation
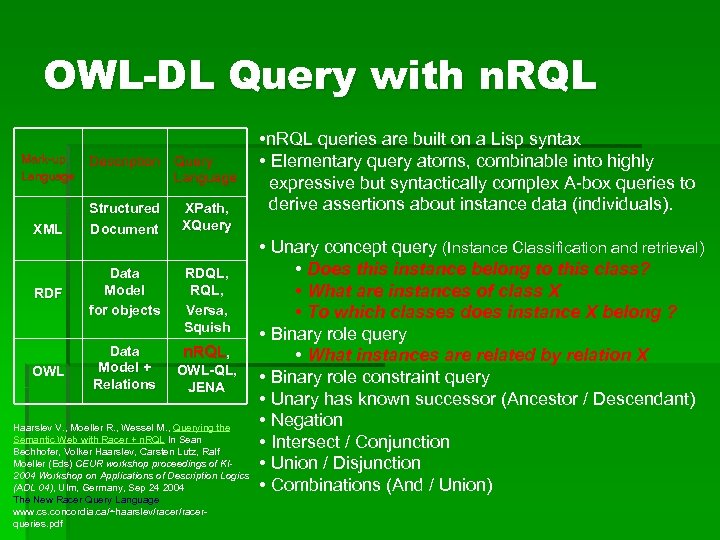
OWL-DL Query with n. RQL Mark-up Language Description Query Language Structured Document XPath, XQuery RDF Data Model for objects RDQL, RQL, Versa, Squish n. RQL, OWL Data Model + Relations XML OWL-QL, JENA Haarslev V. , Moeller R. , Wessel M. , Querying the Semantic Web with Racer + n. RQL In Sean Bechhofer, Volker Haarslev, Carsten Lutz, Ralf Moeller (Eds) CEUR workshop proceedings of KI 2004 Workshop on Applications of Description Logics (ADL 04), Ulm, Germany, Sep 24 2004 The New Racer Query Language www. cs. concordia. ca/~haarslev/racerqueries. pdf • n. RQL queries are built on a Lisp syntax • Elementary query atoms, combinable into highly expressive but syntactically complex A-box queries to derive assertions about instance data (individuals). • Unary concept query (Instance Classification and retrieval) • Does this instance belong to this class? • What are instances of class X • To which classes does instance X belong ? • Binary role query • What instances are related by relation X • Binary role constraint query • Unary has known successor (Ancestor / Descendant) • Negation • Intersect / Conjunction • Union / Disjunction • Combinations (And / Union)
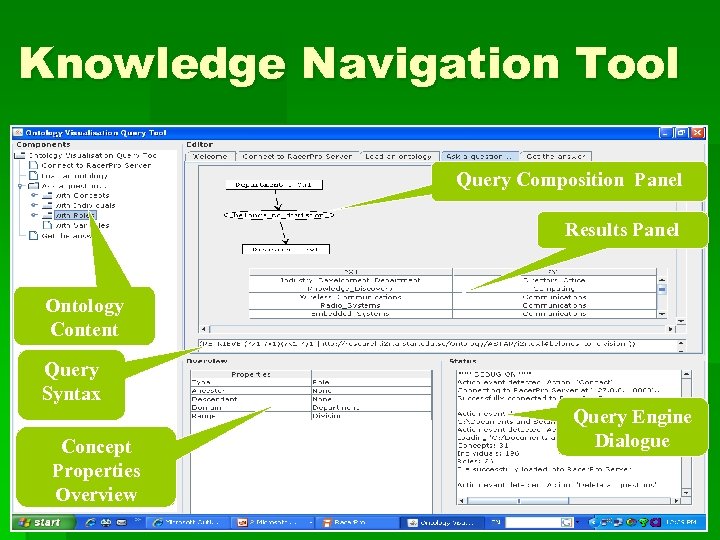
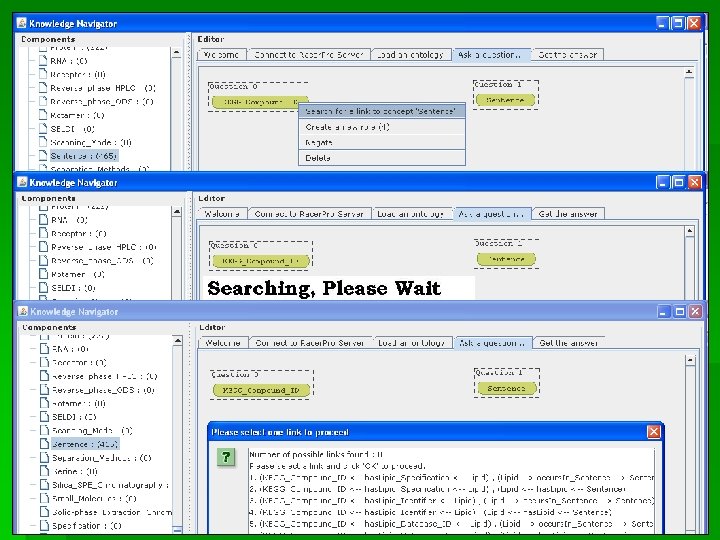
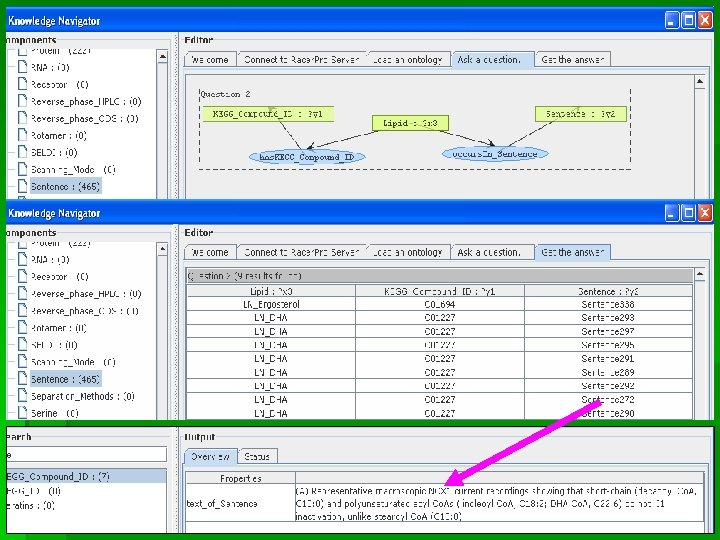
Knowledge Navigation Tool Query Composition Panel Results Panel Ontology Content Query Syntax Concept Properties Overview Query Engine Dialogue
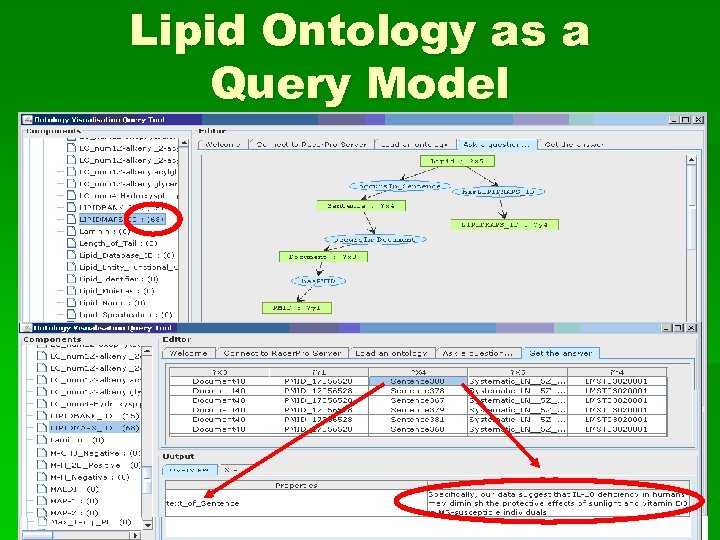
Lipid Ontology as a Query Model
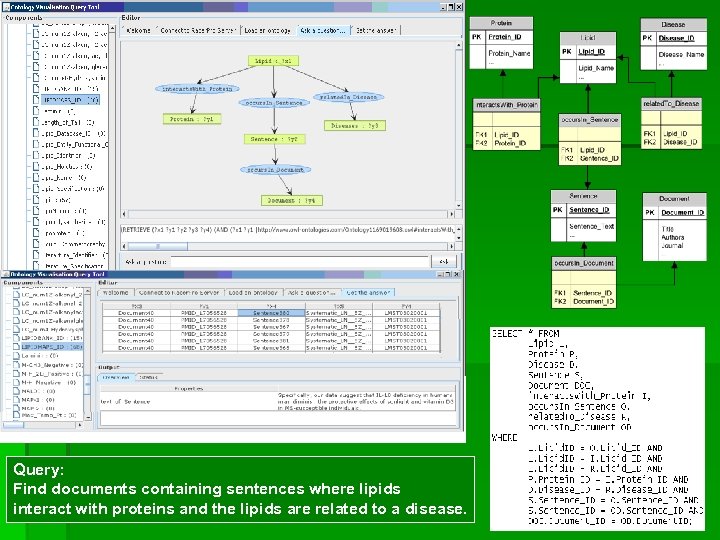
Query: Find documents containing sentences where lipids interact with proteins and the lipids are related to a disease.

Summary § We build a lipid ontology in the Web Ontology Language (OWL) to represent the LIPIDMAPS classification hierarchy. § The ontology model resolves nomenclature inconsistencies by grounding lipid synonyms to a individual lipid names. § We report a document delivery system that in conjunction with a lipid specific text mining platform instantiates lipid sentences into the lipid ontology. § We facilitate navigation of lipid literature using a drag ‘n’ drop visual query composer which poses description logic queries to the OWL-DL ontology. § Lipid – disease and Lipid - protein statements in the lipid literature can be readily queried and made easily available to lipid researchers.

Acknowledgement § A*STAR – Agency for Science and Technology, Singapore Government. § National University of Singapore, Graduate Student Travel Grant.
9bee0ba15e069b675b1acad019e3b3d0.ppt