17b32681feabb097026e6605f583a97d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Towards Interoperable Healthcare Information Systems: The HL 7 Conformance Profile Approach Robert Snelick, Len Gebase, Lisa Carnahan National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Pete Rontey, U. S. Veterans Administration (VA) rsnelick@nist. gov http: //www. nist. gov/messagemaker

Outline n n n n Overview the HL 7 Standard HL 7 Message Structure Problems with the HL 7 Standard Using conformance profiles to improve interoperability Tools to support conformance profiles Conformance profiles in practice Summary
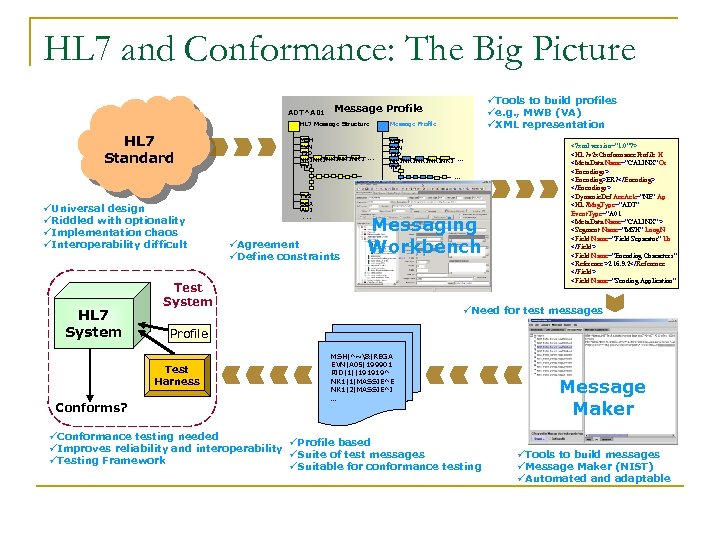
HL 7 and Conformance: The Big Picture ADT^A 01 üTools to build profiles üe. g. , MWB (VA) üXML representation Message Profile HL 7 Message Structure HL 7 Standard Message Profile MSH EVN PID NK 1 NK 1. . . PV 1 MSH EVN PID NK 1 NK 1. . . PV 1 . . . üUniversal design üRiddled with optionality üImplementation chaos üInteroperability difficult HL 7 System PV 2 OBX AL 1. . . üAgreement üDefine constraints Messaging Workbench Test System üNeed for test messages Profile Test Harness Conforms? PV 2 OBX AL 1 . . . <? xml version="1. 0"? > <HL 7 v 2 x. Conformance. Profile H <Meta. Data Name="CALINX" Or <Encodings> <Encoding>ER 7</Encoding> </Encodings> <Dynamic. Def Acc. Ack="NE" Ap <HL 7 Msg. Type=“ADT" Event. Type=“A 01 <Meta. Data Name="CALINX" > <Segment Name="MSH" Long. N <Field Name="Field Separator" Us </Field> <Field Name="Encoding Characters" <Reference>2. 16. 9. 2</Reference </Field> <Field Name="Sending Application" MSH|^~&|REGA EVN|A 05|199901 PID|1||191919^ NK 1|1|MASSIE^E NK 1|2|MASSIE^I … üConformance testing needed üProfile based üImproves reliability and interoperability üSuite of test messages üTesting Framework üSuitable for conformance testing Message Maker üTools to build messages üMessage Maker (NIST) üAutomated and adaptable
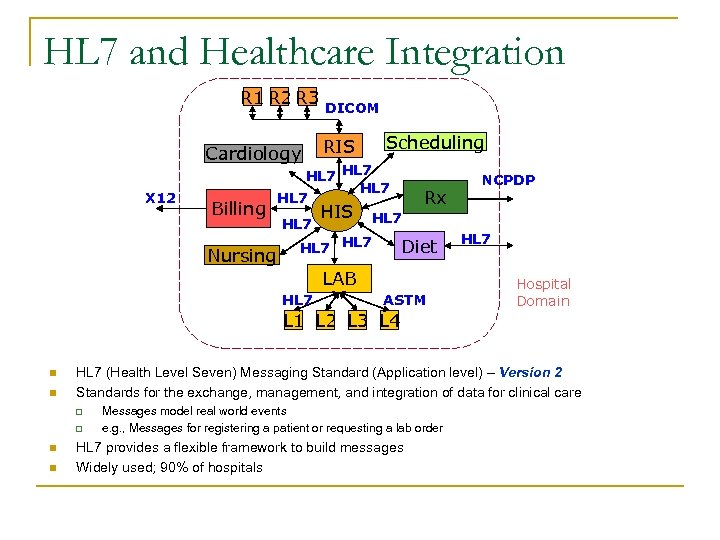
HL 7 and Healthcare Integration R 1 R 2 R 3 Cardiology X 12 Billing Nursing DICOM RIS Scheduling HL 7 HIS HL 7 Rx Diet LAB HL 7 ASTM L 1 L 2 L 3 L 4 n n q n HL 7 Hospital Domain HL 7 (Health Level Seven) Messaging Standard (Application level) – Version 2 Standards for the exchange, management, and integration of data for clinical care q n NCPDP Messages model real world events e. g. , Messages for registering a patient or requesting a lab order HL 7 provides a flexible framework to build messages Widely used; 90% of hospitals
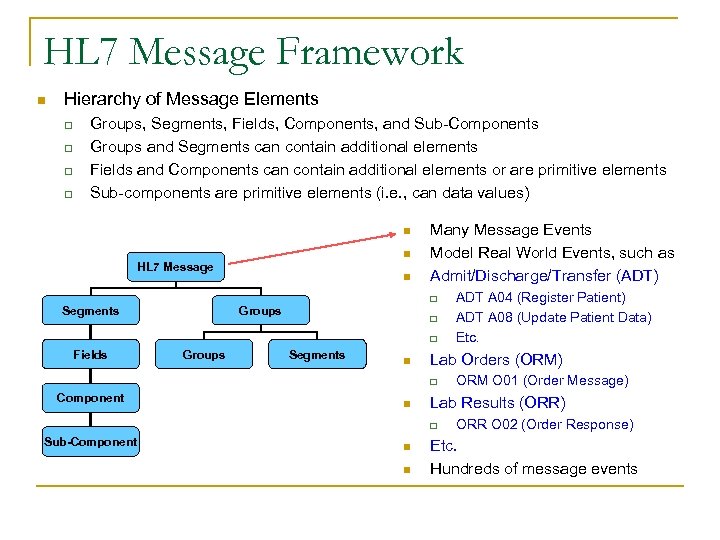
HL 7 Message Framework n Hierarchy of Message Elements q q Groups, Segments, Fields, Components, and Sub-Components Groups and Segments can contain additional elements Fields and Components can contain additional elements or are primitive elements Sub-components are primitive elements (i. e. , can data values) n n HL 7 Message n Many Message Events Model Real World Events, such as Admit/Discharge/Transfer (ADT) q Segments Groups q q Fields Groups Segments n Lab Orders (ORM) q Component n n n ORM O 01 (Order Message) Lab Results (ORR) q Sub-Component ADT A 04 (Register Patient) ADT A 08 (Update Patient Data) Etc. ORR O 02 (Order Response) Etc. Hundreds of message events
![Anatomy of an HL 7 Message MSH EVN PID [ PD 1 ] [{ Anatomy of an HL 7 Message MSH EVN PID [ PD 1 ] [{](https://present5.com/presentation/17b32681feabb097026e6605f583a97d/image-6.jpg)
Anatomy of an HL 7 Message MSH EVN PID [ PD 1 ] [{ ROL }] [{ NK 1 }] PV 1 [ PV 2 ] . . . [{ GT 1 } ] [{ IN 1 [ IN 2 ] [{ IN 3 }] [{ ROL }] }] [ ACC ] [ UB 1 ] [ UB 2 ] [ PDA ] LEN DT OPT 1 4 SI 2 20 3 ITEM# ELEMENT NAME O 00104 Set ID - PID CX B 00105 Patient ID 250 CX R Y 00106 Patient Identifier List 4 20 CX B Y 00107 Alternate Patient ID - PID 5 250 XPN R Y 00108 Patient Name 6 250 XPN O Y 00109 Mother’s Maiden Name 7 26 TS O 00110 Date/Time of Birth 8 1 IS O 00111 Administrative Sex 37 80 ST O 01541 Strain 38 ADT^A 04^ADT_A 01 SEQ RP/# PID Segment TBL# 250 CE O 01542 Production Class Code 0001 … 2 0429 Components: <family name (FN)> ^ <given name (ST)> ^ <second and further given names or initials thereof (ST)> ^ <suffix (e. g. , JR or III) (ST)> ^ <prefix (e. g. , DR) (ST)> ^ <degree (e. g. , MD) (IS)> ^ <name type code (ID) > ^ <name representation code (ID)> ^ <name context (CE)> ^ <name validity range (DR)> ^ <name assembly order (ID)> Subcomponents of family name: <surname (ST)> ^ <own surname prefix (ST)> ^ <own surname (ST)> ^ <surname prefix from partner/spouse (ST)> ^ <surname from partner/spouse (ST)> Subcomponents of name context: <identifier (ST)> & <text (ST)> & <name of coding system (IS)> & <alternate identifier (ST)> & <alternate text (ST)> & <name of alternate coding system (IS)> Subcomponents of name validity range: <date range start date/time (TS)> & <date range end date/time (TS)> HL 7 0001 - Admin Sex A Ambiguous F Female M Male U Unknown
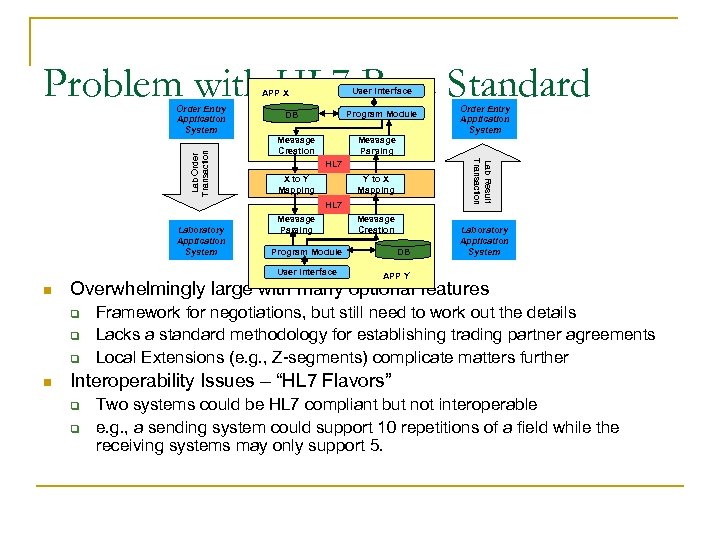
Problem with HL 7 Base Standard User Interface APP X Program Module DB Message Creation Message Parsing HL 7 X to Y Mapping Y to X Mapping HL 7 Laboratory Application System Message Parsing DB Laboratory Application System APP Y Overwhelmingly large with many optional features q q q n Message Creation Program Module User Interface n Order Entry Application System Lab Result Transaction Lab Order Transaction Order Entry Application System Framework for negotiations, but still need to work out the details Lacks a standard methodology for establishing trading partner agreements Local Extensions (e. g. , Z-segments) complicate matters further Interoperability Issues – “HL 7 Flavors” q q Two systems could be HL 7 compliant but not interoperable e. g. , a sending system could support 10 repetitions of a field while the receiving systems may only support 5.
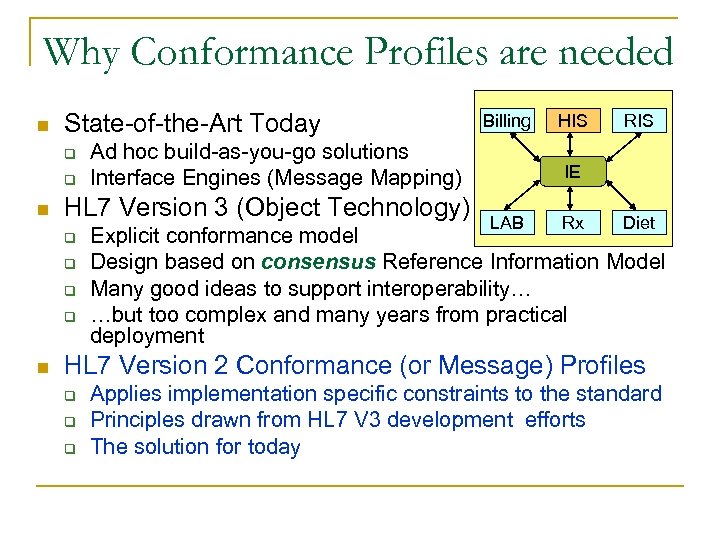
Why Conformance Profiles are needed n State-of-the-Art Today q q n q q q n Ad hoc build-as-you-go solutions Interface Engines (Message Mapping) HL 7 Version 3 (Object Technology) q Billing HIS RIS IE LAB Rx Diet Explicit conformance model Design based on consensus Reference Information Model Many good ideas to support interoperability… …but too complex and many years from practical deployment HL 7 Version 2 Conformance (or Message) Profiles q q q Applies implementation specific constraints to the standard Principles drawn from HL 7 V 3 development efforts The solution for today
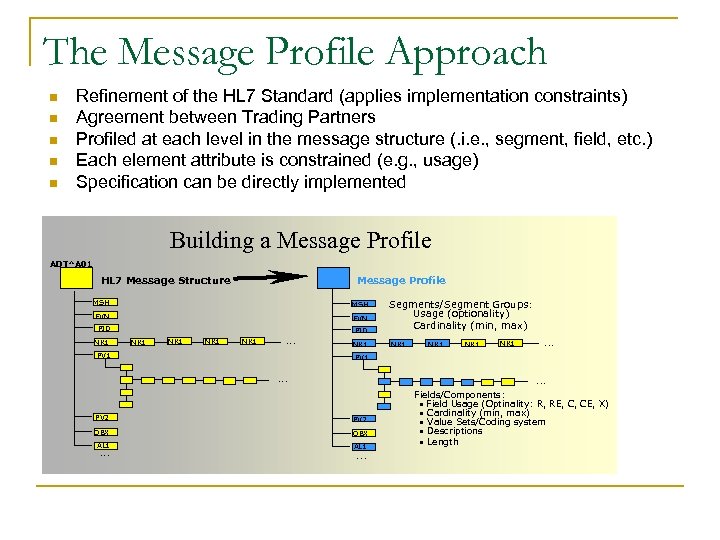
The Message Profile Approach n n n Refinement of the HL 7 Standard (applies implementation constraints) Agreement between Trading Partners Profiled at each level in the message structure (. i. e. , segment, field, etc. ) Each element attribute is constrained (e. g. , usage) Specification can be directly implemented Building a Message Profile ADT^A 01 Message Profile HL 7 Message Structure MSH EVN PID NK 1 NK 1 NK 1 . . . PV 2 OBX AL 1 . . . Segments/Segment Groups: Usage (optionality) Cardinality (min, max) . . . Fields/Components: • Field Usage (Optinality: R, RE, C, CE, X) • Cardinality (min, max) • Value Sets/Coding system • Descriptions • Length
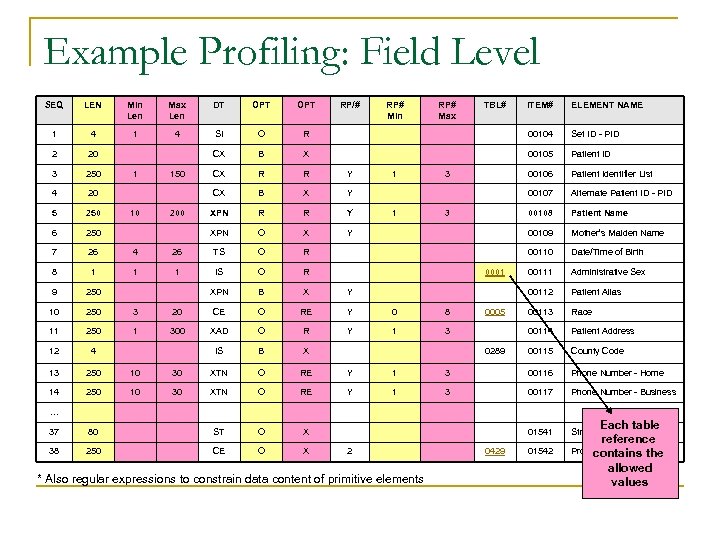
Example Profiling: Field Level SEQ LEN Min Len Max Len DT OPT 1 4 SI O 2 20 CX 3 250 4 20 5 250 6 250 ELEMENT NAME R 00104 Set ID - PID B X 00105 Patient ID CX R R Y 00106 Patient Identifier List B X Y 00107 Alternate Patient ID - PID XPN R R Y 00108 Patient Name XPN 7 26 4 8 1 1 9 250 O X Y 00109 Mother’s Maiden Name 26 TS O R 00110 Date/Time of Birth 1 IS O R 00111 Administrative Sex XPN 10 250 3 11 250 1 12 4 B X Y 00112 Patient Alias 20 CE O RE Y 0 8 00113 Race 300 XAD O R Y 1 3 00114 Patient Address IS 13 250 10 14 250 10 10 ITEM# CX 1 B X 00115 County Code 30 XTN O RE Y 1 3 00116 Phone Number - Home 30 XTN O RE Y 1 3 00117 Phone Number - Business 01541 Strain 150 200 RP/# RP# Min 1 1 RP# Max TBL# 3 3 0001 0005 0289 … 37 80 ST O X 38 250 CE O X 2 * Also regular expressions to constrain data content of primitive elements 0429 01542 Each table reference Production Class Code contains the allowed values
Benefits of Conformance Profiles n n Agreement between trading partners Eliminates the potential ambiguities that the standard allows as implementation alternatives Provides a better way to conduct and document interface negotiations Standardized XML representation q q q n n Profile Registries n Reuse n Comparison Enables interoperability among tools Automated message validation Automated message generation Can expose vendors’ value added product features Provides a clear method to document localizations Facilitates conformance and interoperability testing
Tools to Support Conformance Profiles n Profile Builder q n Test Generation q n VA Messaging Workbench (MWB) NIST Message Maker Test Administration and Analysis q q NIST Testing Framework NIST Web Services n q Message Generation and Message Validation VA MWB Validation Server

Messaging Workbench (MWB) n n n n Created by Pete Rontey at the U. S. Veterans Administration (VA) Productivity tool to build message profiles Incorporates all HL 7 Version 2. x artifacts as MWB libraries Reverse engineering from sample message Multiple reports (profile, tables, etc. ) Multiple reports formats (html, xml, etc. ) Supports localizations
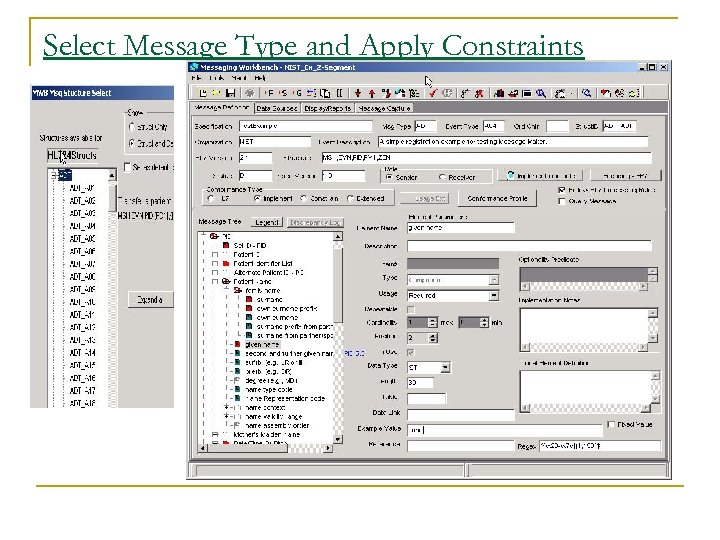
Select Message Type and Apply Constraints
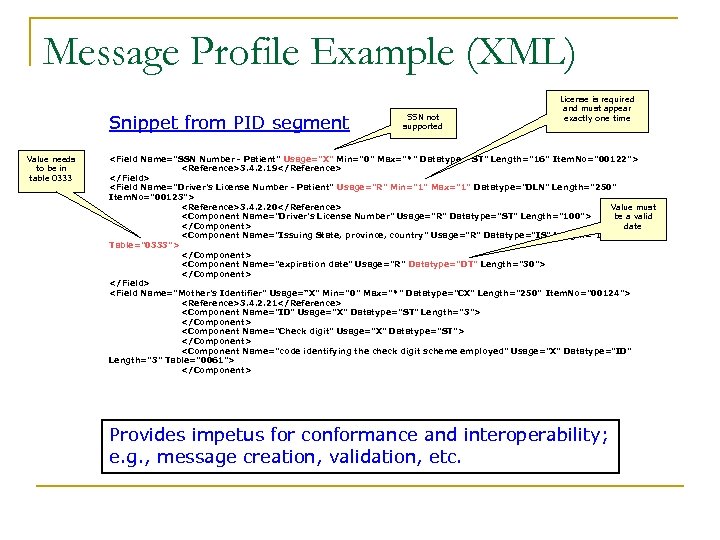
Message Profile Example (XML) Snippet from PID segment Value needs to be in table 0333 SSN not supported License is required and must appear exactly one time <Field Name="SSN Number - Patient" Usage="X" Min="0" Max="*" Datatype="ST" Length="16" Item. No="00122"> <Reference>3. 4. 2. 19</Reference> </Field> <Field Name="Driver's License Number - Patient" Usage="R" Min="1" Max="1" Datatype="DLN" Length="250" Item. No="00123"> <Reference>3. 4. 2. 20</Reference> Value must be a valid <Component Name="Driver's License Number" Usage="R" Datatype="ST" Length="100"> date </Component> <Component Name="Issuing State, province, country" Usage="R" Datatype="IS" Length="10" Table="0333"> </Component> <Component Name="expiration date" Usage="R" Datatype="DT" Length="30"> </Component> </Field> <Field Name="Mother's Identifier" Usage=“X" Min="0" Max="*" Datatype="CX" Length="250" Item. No="00124"> <Reference>3. 4. 2. 21</Reference> <Component Name="ID" Usage="X" Datatype="ST" Length="3"> </Component> <Component Name="Check digit" Usage="X" Datatype="ST"> </Component> <Component Name="code identifying the check digit scheme employed" Usage="X" Datatype="ID" Length="3" Table="0061"> </Component> Provides impetus for conformance and interoperability; e. g. , message creation, validation, etc.

NIST Testing Services n n n n n Message Management Profile Validation Message Generation Encoding Transformation Logging HL 7 Actors (Simulations) Communication Test Framework Provided as a set of Java APIs which can be used to develop applications, web services, and web applications
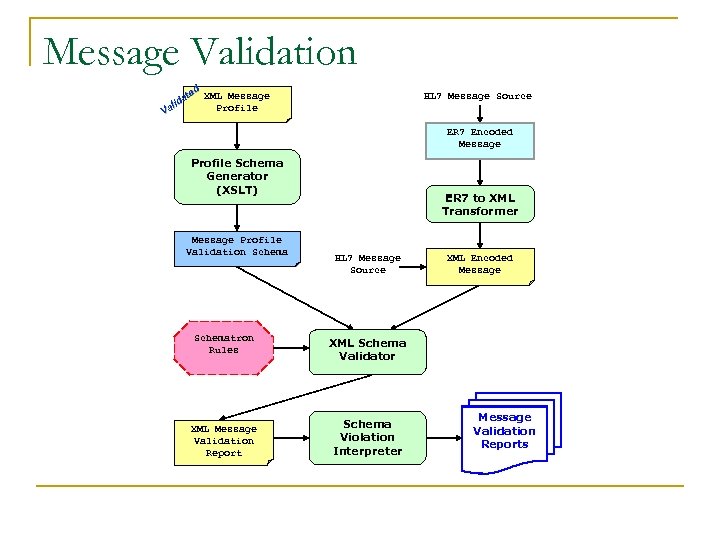
Message Validation ed at XML Message id l Profile Va HL 7 Message Source ER 7 Encoded Message Profile Schema Generator (XSLT) Message Profile Validation Schema ER 7 to XML Transformer HL 7 Message Source Schematron Rules XML Schema Validator XML Message Validation Report Schema Violation Interpreter XML Encoded Message Validation Reports
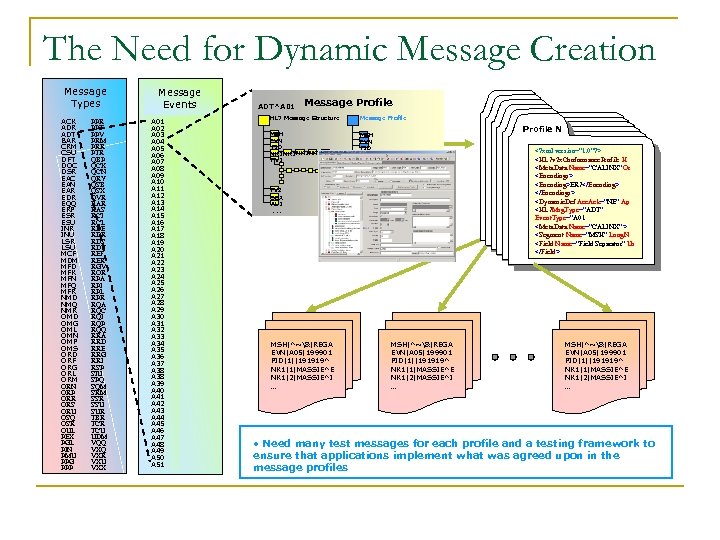
The Need for Dynamic Message Creation Message Types ACK ADR ADT BAR CRM CSU DFT DOC DSR EAC EAN EAR EDR EQQ ERP ESR ESU INR INU LSR LSU MCF MDM MFD MFK MFN MFQ MFR NMD NMQ NMR OMD OMG OML OMN OMP OMS ORD ORF ORG ORL ORM ORN ORP ORR ORS ORU OSQ OSR OUL PEX PGL PIN PMU PPG PPP PPR PPT PPV PRM PRR PTR QBP QCK QCN QRY QSB QSX QVR RAS RCI RCL RDE RDR RDS RDY REF RER RGV ROR RPA RPI RPL RPR RQA RQC RQI RQP RQQ RRA RRD RRE RRG RRI RSP SIU SPQ SQM SRM SSR SSU SUR TBR TCU UDM VQQ VXR VXU VXX Message Events A 01 A 02 A 03 A 04 A 05 A 06 A 07 A 08 A 09 A 10 A 11 A 12 A 13 A 14 A 15 A 16 A 17 A 18 A 19 A 20 A 21 A 22 A 23 A 24 A 25 A 26 A 27 A 28 A 29 A 30 A 31 A 32 A 33 A 34 A 35 A 36 A 37 A 38 A 39 A 40 A 41 A 42 A 43 A 44 A 45 A 46 A 47 A 48 A 49 A 50 A 51 ADT^A 01 Message Profile HL 7 Message Structure Message Profile MSH EVN PID NK 1 NK 1. . . PV 1 MSH EVN PID NK 1 NK 1. . . PV 1 . . . PV 2 OBX AL 1. . . Profile N Message Profile § explicitly defines § § Message defines explicitly Profile Message Profile explicitly defines message <? xml version="1. 0"? > components § explicitly defines at message components at H <HL 7 v 2 x. Conformance. Profile message components each § explicitly defines at Or level <Meta. Data Name="CALINX" message each level components at § implementable level § § each <Encodings> implementable each level <Encoding>ER 7</Encoding> implementable specification § § implementable specification </Encodings> specification § still sites defined. Acc. Ack="NE" Ap their <Dynamic. Def § § specification still sites defined their specification still sites defined own§ profiles (many) their <HL 7 Msg. Type=“ADT" still sites defined own§ profiles (many) their own still sites(many) their profiles defined Event. Type=“A 01 § nature profilesbeast of the (many) § § own <Meta. Data Name="CALINX" > nature profiles (many) own of the beast nature of the beast <Segment § § nature of. Name="MSH" Long. N nature of the beast <Field Name="Field Separator" Us </Field> MSH|^~&|REGA EVN|A 05|199901 PID|1||191919^ NK 1|1|MASSIE^E NK 1|2|MASSIE^I … • Need many test messages for each profile and a testing framework to ensure that applications implement what was agreed upon in the message profiles
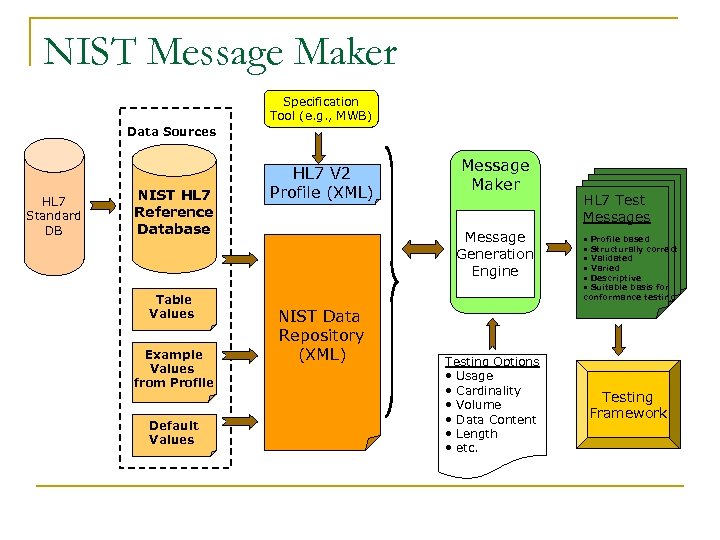
NIST Message Maker Specification Tool (e. g. , MWB) Data Sources HL 7 Standard DB NIST HL 7 Reference Database Table Values Example Values from Profile Default Values HL 7 V 2 Profile (XML) Message Maker Message Generation Engine NIST Data Repository (XML) Testing Options • Usage • Cardinality • Volume • Data Content • Length • etc. HL 7 Test Messages • • • Profile based Structurally correct Validated Varied Descriptive Suitable basis for conformance testing Testing Framework
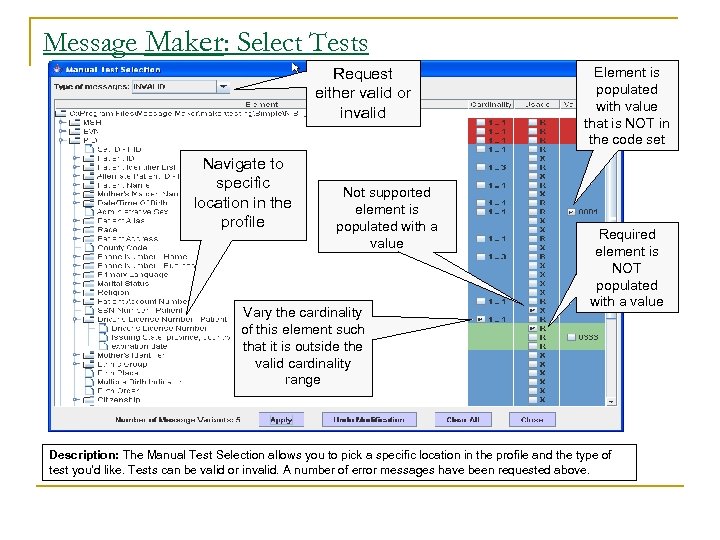
Message Maker: Select Tests Request either valid or invalid Navigate to specific location in the profile Not supported element is populated with a value Vary the cardinality of this element such that it is outside the valid cardinality range Element is populated with value that is NOT in the code set Required element is NOT populated with a value Description: The Manual Test Selection allows you to pick a specific location in the profile and the type of test you’d like. Tests can be valid or invalid. A number of error messages have been requested above.
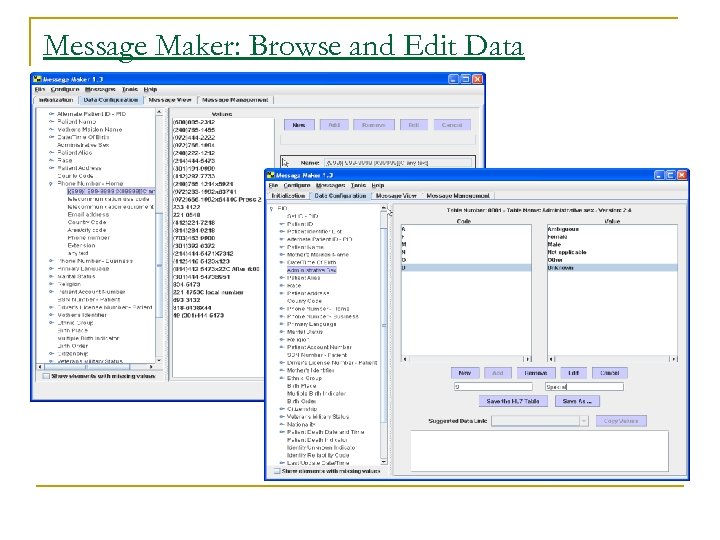
Message Maker: Browse and Edit Data
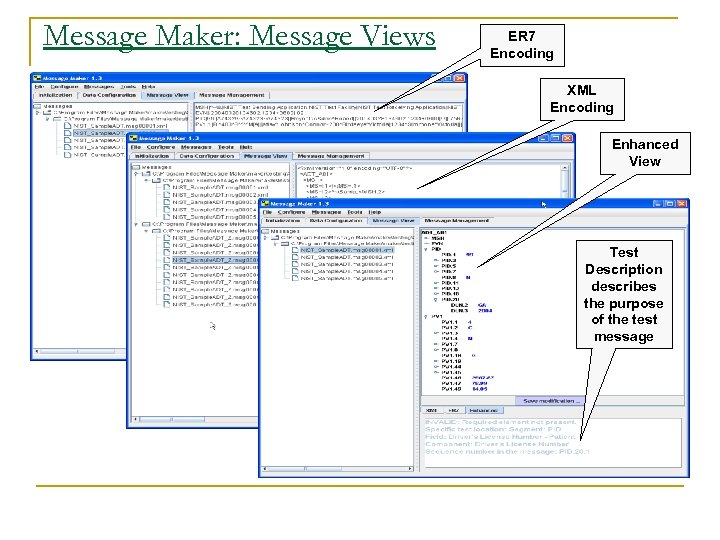
Message Maker: Message Views ER 7 Encoding XML Encoding Enhanced View Test Description describes the purpose of the test message
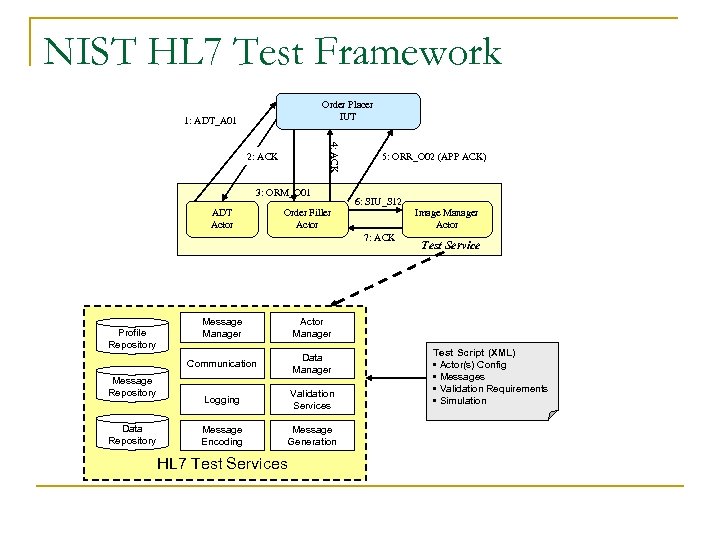
NIST HL 7 Test Framework Order Placer IUT 1: ADT_A 01 4: ACK 2: ACK 3: ORM_O 01 ADT Actor Order Filler Actor 5: ORR_O 02 (APP ACK) 6: SIU_S 12 7: ACK Message Repository Data Repository Message Manager Data Manager Logging Validation Services Message Encoding Message Generation Test Service Actor Manager Communication Profile Repository Image Manager Actor HL 7 Test Services Test Script (XML) • Actor(s) Config • Messages • Validation Requirements • Simulation
Conformance Profiles in Practice n n Adoption of conformance profiles is gaining momentum Example Installations q q n n U. S. Veterans Administration IHE: Integrating the Healthcare Enterprises ELINCS: The EHR-Lab Interoperability and connectivity specification HITSP: Healthcare Information Technology Standards Panel Anticipated increase usage adoption as latest versions of HL 7 make it into implementations (conformance added in HL 7 Version 2. 5) Support from vendors increasing
Summary n n n Data exchange among healthcare systems is problematic due to inadequate messaging standards Conformance profile approach provides a roadmap Approach: q q Incorporate and refine conformance concepts into standards Provide tools that support the conformance concepts n n q n Profile Builder Message Generation Profile and Message Validation Testing Framework and Support Utilities Work with industry to demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of the methodology with use case example implementations supported by organizations such as IHE and HITSP End result is improved interoperability of healthcare information systems
17b32681feabb097026e6605f583a97d.ppt