b889f8bc1a9c7ad3e4b69e92eb0ba5a6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 1 Towards a New Set of Skills and Competencies beyond Knowledge Ryo Watanabe National Institute for Educational Policy Research (NIER) Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan 12 th July, 2010 KEDI-UNESCO Bangkok Joint Seminar Seoul, Republic of Korea
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 1 Towards a New Set of Skills and Competencies beyond Knowledge Ryo Watanabe National Institute for Educational Policy Research (NIER) Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan 12 th July, 2010 KEDI-UNESCO Bangkok Joint Seminar Seoul, Republic of Korea
 2 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Good Morning ! 안녕하세요?
2 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Good Morning ! 안녕하세요?
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 3 TODAY I. Changing World and Competencies for the 21 st Century II. International Benchmarking as a Global Standard III. Policy Levers in Asia and the Pacific: what we can do for things better
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 3 TODAY I. Changing World and Competencies for the 21 st Century II. International Benchmarking as a Global Standard III. Policy Levers in Asia and the Pacific: what we can do for things better
 4 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research I. Changing World and Competencies for the 21 st century
4 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research I. Changing World and Competencies for the 21 st century
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 5 Changing World - The challenges for assessments Ø Supporting governments to prepare students to… • Deal with more rapid change than ever before… … for jobs that have not yet been created… … using technologies that have not yet been invented… … to solve problems that we don’t yet know will arise
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 5 Changing World - The challenges for assessments Ø Supporting governments to prepare students to… • Deal with more rapid change than ever before… … for jobs that have not yet been created… … using technologies that have not yet been invented… … to solve problems that we don’t yet know will arise
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 6 Changing World - The challenges for assessments Ø Some trends are likely to continue… n Globalization n New technologies n Knowledge based economy n Competition
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 6 Changing World - The challenges for assessments Ø Some trends are likely to continue… n Globalization n New technologies n Knowledge based economy n Competition
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 7 Globalisation p Transnational human capital p Knowledge and skills as the basis for migration p Distance becomes irrelevant p Search for brain power
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 7 Globalisation p Transnational human capital p Knowledge and skills as the basis for migration p Distance becomes irrelevant p Search for brain power
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 8 Globalisation p Transnational human capital Brain circulation is where, not only products but people also move globally. The flows of knowledge workers are global.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 8 Globalisation p Transnational human capital Brain circulation is where, not only products but people also move globally. The flows of knowledge workers are global.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 9 Globalisation p Knowledge and skills as the basis for migration Many countries have knowledge and skill based criteria for migration. The total number of migrants around the world now surpasses 120 million - up from 75 million in 1965 - and continues to grow. (Peter Stalker, ILO, Workers without frontiers, 2000)
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 9 Globalisation p Knowledge and skills as the basis for migration Many countries have knowledge and skill based criteria for migration. The total number of migrants around the world now surpasses 120 million - up from 75 million in 1965 - and continues to grow. (Peter Stalker, ILO, Workers without frontiers, 2000)
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 10 Globalisation p Distance becomes irrelevant Already over 10 million people in Europe are engaged in e-work benefiting from flexibility in time and place of work. (Emergence Project, 2001, P. Bates, IES report 388, 2002) Employment could be in another country. This number could increase to 30 million people by 2010.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 10 Globalisation p Distance becomes irrelevant Already over 10 million people in Europe are engaged in e-work benefiting from flexibility in time and place of work. (Emergence Project, 2001, P. Bates, IES report 388, 2002) Employment could be in another country. This number could increase to 30 million people by 2010.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 11 Globalisation p Search for brain power Many industrialized countries rely on medical doctors and nurses trained elsewhere. 41% of doctors in NZ are foreign born.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 11 Globalisation p Search for brain power Many industrialized countries rely on medical doctors and nurses trained elsewhere. 41% of doctors in NZ are foreign born.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 12 New technologies p E-commerce p Computers on desks p Information retrieval is big business p Networking in daily life
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 12 New technologies p E-commerce p Computers on desks p Information retrieval is big business p Networking in daily life
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 13 New technologies p E-commerce Some services such as e-banking are cheaper than using the traditional service. E-commerce retail sales in the US is growing at a rate exceeding 25% a year.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 13 New technologies p E-commerce Some services such as e-banking are cheaper than using the traditional service. E-commerce retail sales in the US is growing at a rate exceeding 25% a year.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 14 New technologies p Computers on desks Fast changing technologies are creating new jobs or radically altering what workers need to know to perform existing jobs. The amount of technical information doubles every two years. Car mechanics could fix any car before. Now, they specialize in one make. In 1930, all the coded information for a GM car could be captured in 230 pages. Now a single car involves some 15000 pages of coded knowledge which workers will need to be able to access, manage, integrate and to evaluate. OECD 2007
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 14 New technologies p Computers on desks Fast changing technologies are creating new jobs or radically altering what workers need to know to perform existing jobs. The amount of technical information doubles every two years. Car mechanics could fix any car before. Now, they specialize in one make. In 1930, all the coded information for a GM car could be captured in 230 pages. Now a single car involves some 15000 pages of coded knowledge which workers will need to be able to access, manage, integrate and to evaluate. OECD 2007
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 15 New technologies p Information retrieval is big business The idea of “copyleft” ensures free access to information. Google had a turnover that rose 17 -fold in just four years to $1. 5 billion in 2005. In 2008 there were 2. 7 billion searches performed on Google each month.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 15 New technologies p Information retrieval is big business The idea of “copyleft” ensures free access to information. Google had a turnover that rose 17 -fold in just four years to $1. 5 billion in 2005. In 2008 there were 2. 7 billion searches performed on Google each month.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 16 New technologies p Networking in daily life The number of text messages sent daily exceeds the population of the planet.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 16 New technologies p Networking in daily life The number of text messages sent daily exceeds the population of the planet.
 17 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Knowledge based economy p Economy driven by knowledge p Increase in knowledge production p Knowledge work
17 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Knowledge based economy p Economy driven by knowledge p Increase in knowledge production p Knowledge work
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 18 Knowledge based economy p Economy driven by knowledge “It is an economy where knowledge is created, acquired, transmitted and used more effectively by individuals, enterprises, organizations and communities to promote economic and social development. ” (World Bank Institute, 2001).
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 18 Knowledge based economy p Economy driven by knowledge “It is an economy where knowledge is created, acquired, transmitted and used more effectively by individuals, enterprises, organizations and communities to promote economic and social development. ” (World Bank Institute, 2001).
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 19 Knowledge based economy p Increase in knowledge production About 40 exabytes (4. 0 X 1019) will be generated this year – more than the previous 5000 years. More than 3000 books are published every day. A week of New York Times papers contains more information than a person in the 18 th century would see in a lifetime.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 19 Knowledge based economy p Increase in knowledge production About 40 exabytes (4. 0 X 1019) will be generated this year – more than the previous 5000 years. More than 3000 books are published every day. A week of New York Times papers contains more information than a person in the 18 th century would see in a lifetime.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 20 Knowledge based economy p Knowledge work Knowledge workers are those that use current knowledge in new ways or in new situations and those who generate new knowledge. A large number of workers also use more knowledge to do their jobs than they did before. All workers use more “higher order knowledge and skills” in the knowledge economy. Knowledge workers are now estimated to outnumber all other workers in North America by at least a four to one margin (Haag et al, 2006, pg. 4).
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 20 Knowledge based economy p Knowledge work Knowledge workers are those that use current knowledge in new ways or in new situations and those who generate new knowledge. A large number of workers also use more knowledge to do their jobs than they did before. All workers use more “higher order knowledge and skills” in the knowledge economy. Knowledge workers are now estimated to outnumber all other workers in North America by at least a four to one margin (Haag et al, 2006, pg. 4).
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 21 Competition p Competitive advantage of an educated workforce p Innovation and invention are people products p Importance of human capital
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 21 Competition p Competitive advantage of an educated workforce p Innovation and invention are people products p Importance of human capital
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 22 Competition p Competitive advantage of an educated workforce A highly competent workforce is adaptable and can compete on quality as well as price. There are significant external effects of human capital on the economy and major spill over effects in several countries.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 22 Competition p Competitive advantage of an educated workforce A highly competent workforce is adaptable and can compete on quality as well as price. There are significant external effects of human capital on the economy and major spill over effects in several countries.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 23 Competition p Innovation and invention are people products Without human capital, new economic growth through innovation/invention, increased productivity and improved technology penetration and application would not be possible. Increased knowledge is embedded in products and services which requires knowledgeable workers and consumers.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 23 Competition p Innovation and invention are people products Without human capital, new economic growth through innovation/invention, increased productivity and improved technology penetration and application would not be possible. Increased knowledge is embedded in products and services which requires knowledgeable workers and consumers.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 24 Competition p Importance of human capital In an environment of competition for knowledge assets and its global use, human capital is the key currency in the knowledge economy/society. Efficiency in knowledge processes results in shorter production cycles. In 1990, it took six years from concept to production in the automobile industry; Today, it takes two years. (World Bank, Lifelong learning and the global knowledge economy, 2003)
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 24 Competition p Importance of human capital In an environment of competition for knowledge assets and its global use, human capital is the key currency in the knowledge economy/society. Efficiency in knowledge processes results in shorter production cycles. In 1990, it took six years from concept to production in the automobile industry; Today, it takes two years. (World Bank, Lifelong learning and the global knowledge economy, 2003)
 25 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research itting ransm g for t dge ” catin owle “ Edu en kn giv
25 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research itting ransm g for t dge ” catin owle “ Edu en kn giv
 26 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research “ Ins ine ” scipl for di ting truc tine r rou ing fo ” hool “ Sc ures roced p
26 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research “ Ins ine ” scipl for di ting truc tine r rou ing fo ” hool “ Sc ures roced p
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 27 Skills for the 21 st century Ø The great collaborators and orchestrators – The more complex the globalised world becomes, the more individuals and companies need various forms of co-ordination and management. Ø The great synthesisers – Conventionally, our approach to problems was breaking them down into manageable bits and pieces, today we create value by synthesising disparate bits together. Ø The great explainers – The more content we can search and access, the more important the filters and explainers become.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 27 Skills for the 21 st century Ø The great collaborators and orchestrators – The more complex the globalised world becomes, the more individuals and companies need various forms of co-ordination and management. Ø The great synthesisers – Conventionally, our approach to problems was breaking them down into manageable bits and pieces, today we create value by synthesising disparate bits together. Ø The great explainers – The more content we can search and access, the more important the filters and explainers become.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 28 Skills for the 21 st century Ø The great versatilists – Specialists generally have deep skills and narrow scope, giving them expertise that is recognised by peers but not valued outside their domain. – Generalists have broad scope but shallow skills. – Versatilists apply depth of skill to a progressively widening scope of situations and experiences, gaining new competencies, building relationships, and assuming new roles. – They are capable not only of constantly adapting but also of constantly learning and growing.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 28 Skills for the 21 st century Ø The great versatilists – Specialists generally have deep skills and narrow scope, giving them expertise that is recognised by peers but not valued outside their domain. – Generalists have broad scope but shallow skills. – Versatilists apply depth of skill to a progressively widening scope of situations and experiences, gaining new competencies, building relationships, and assuming new roles. – They are capable not only of constantly adapting but also of constantly learning and growing.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 29 Skills for the 21 st century Ø The great personalisers – A revival of interpersonal skills, skills that have atrhophied to some degree because of the industrial age and the Internet Ø The great localisers – Localising the global
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 29 Skills for the 21 st century Ø The great personalisers – A revival of interpersonal skills, skills that have atrhophied to some degree because of the industrial age and the Internet Ø The great localisers – Localising the global
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 30 Using “tools” interactively Three broad categories of key competencies Interacting in socially heterogeneous groups De. Se. Co Acting autonomously
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 30 Using “tools” interactively Three broad categories of key competencies Interacting in socially heterogeneous groups De. Se. Co Acting autonomously
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 31 Interacting in socially heterogeneous groups * Relating well to others; * Cooperating; and * Managing and resolving conflict
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 31 Interacting in socially heterogeneous groups * Relating well to others; * Cooperating; and * Managing and resolving conflict
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 32 Acting autonomously * Acting within the big picture or the larger context; * Forming and conducting life plans and personal projects; and * Defending and asserting one’s rights, interests, limits, and needs
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 32 Acting autonomously * Acting within the big picture or the larger context; * Forming and conducting life plans and personal projects; and * Defending and asserting one’s rights, interests, limits, and needs
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 33 Using “tools” interactively * Using language, symbols, and text interactively; * Using knowledge and information interactively; and * Using technology interactively
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 33 Using “tools” interactively * Using language, symbols, and text interactively; * Using knowledge and information interactively; and * Using technology interactively
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 34 A lot of projects to address skills and competencies required for the 21 st century have been launched as a global interest. One of the most recent efforts about defining 21 st century skills is “ATC 21 S”, namely the Assessment and Teaching of 21 st Century Skills project.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 34 A lot of projects to address skills and competencies required for the 21 st century have been launched as a global interest. One of the most recent efforts about defining 21 st century skills is “ATC 21 S”, namely the Assessment and Teaching of 21 st Century Skills project.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 35 ATC 21 S was created by Cisco, Intel and Microsoft and launched at the Learning and Technology World Forum 2009 in London. Five Working Groups This initiative is focused on defining those skills and developing ways to measure them using information technology. It will address the pedagogical implications and provide evidence on how the skills can best be developed in education.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 35 ATC 21 S was created by Cisco, Intel and Microsoft and launched at the Learning and Technology World Forum 2009 in London. Five Working Groups This initiative is focused on defining those skills and developing ways to measure them using information technology. It will address the pedagogical implications and provide evidence on how the skills can best be developed in education.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 36 Purpose of ATC 21 S ü Mobilise international educational, political and business communities to make the transformation of educational assessment and, hence, instructional practice a global priority; ü specify in measurable terms high-priority understanding and skills needed by productive and creative workers and citizens of the 21 st century; ü identify methodological and technological barriers to ICT-based assessment; ü develop and pilot new assessment methodologies; ü examine and recommend innovative ICT-enabled, classroom-based learning environments and formative assessments that support the development of 21 st century skills; ü examine the links between and the relevance of the 21 st century skills and the traditional outcome measures of school systems.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 36 Purpose of ATC 21 S ü Mobilise international educational, political and business communities to make the transformation of educational assessment and, hence, instructional practice a global priority; ü specify in measurable terms high-priority understanding and skills needed by productive and creative workers and citizens of the 21 st century; ü identify methodological and technological barriers to ICT-based assessment; ü develop and pilot new assessment methodologies; ü examine and recommend innovative ICT-enabled, classroom-based learning environments and formative assessments that support the development of 21 st century skills; ü examine the links between and the relevance of the 21 st century skills and the traditional outcome measures of school systems.
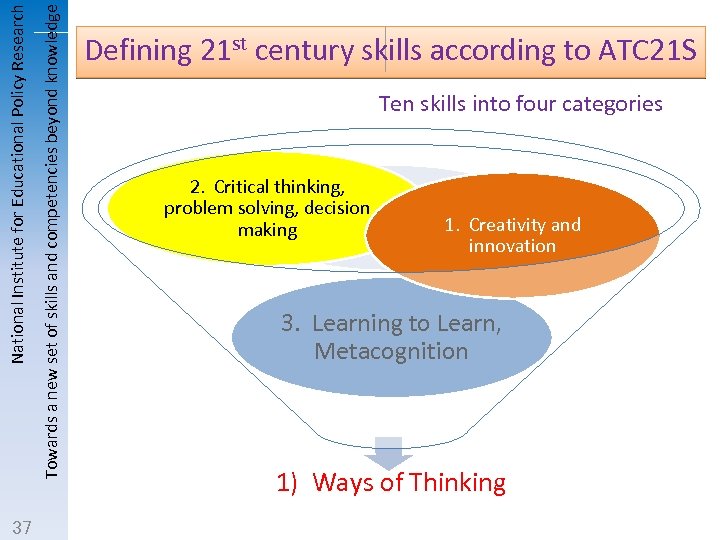 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 37 Defining 21 st century skills according to ATC 21 S Ten skills into four categories 2. Critical thinking, problem solving, decision making 1. Creativity and innovation 3. Learning to Learn, Metacognition 1) Ways of Thinking
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 37 Defining 21 st century skills according to ATC 21 S Ten skills into four categories 2. Critical thinking, problem solving, decision making 1. Creativity and innovation 3. Learning to Learn, Metacognition 1) Ways of Thinking
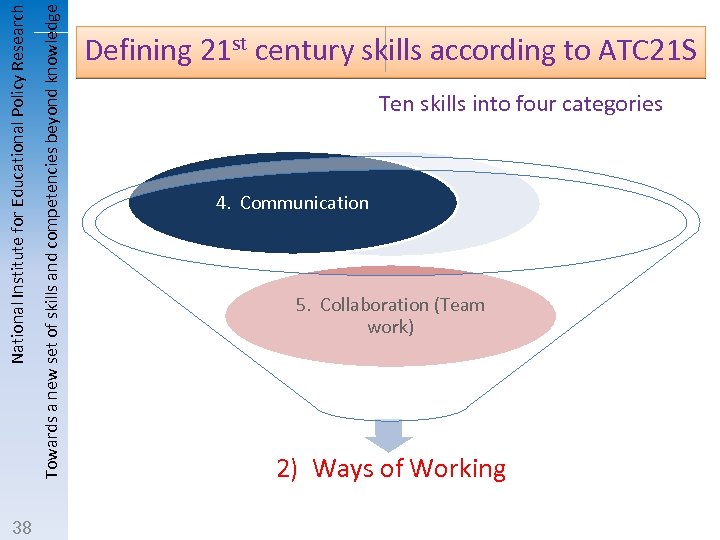 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 38 Defining 21 st century skills according to ATC 21 S Ten skills into four categories 4. Communication 5. Collaboration (Team work) 2) Ways of Working
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 38 Defining 21 st century skills according to ATC 21 S Ten skills into four categories 4. Communication 5. Collaboration (Team work) 2) Ways of Working
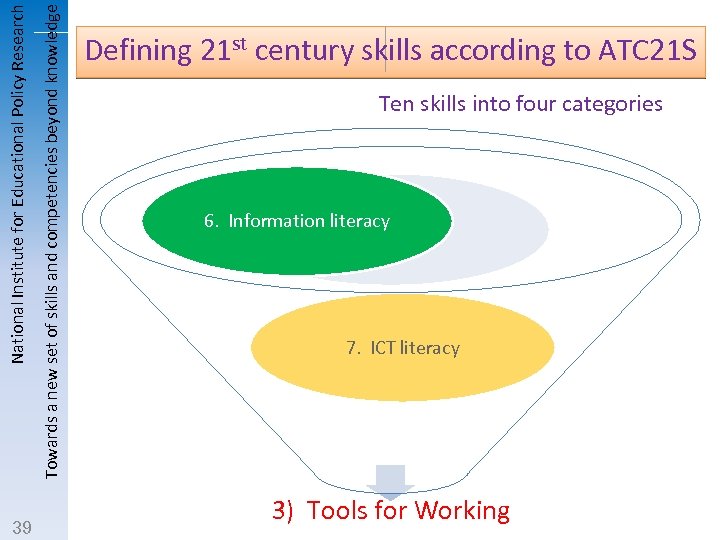 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 39 Defining 21 st century skills according to ATC 21 S Ten skills into four categories 6. Information literacy 7. ICT literacy 3) Tools for Working
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 39 Defining 21 st century skills according to ATC 21 S Ten skills into four categories 6. Information literacy 7. ICT literacy 3) Tools for Working
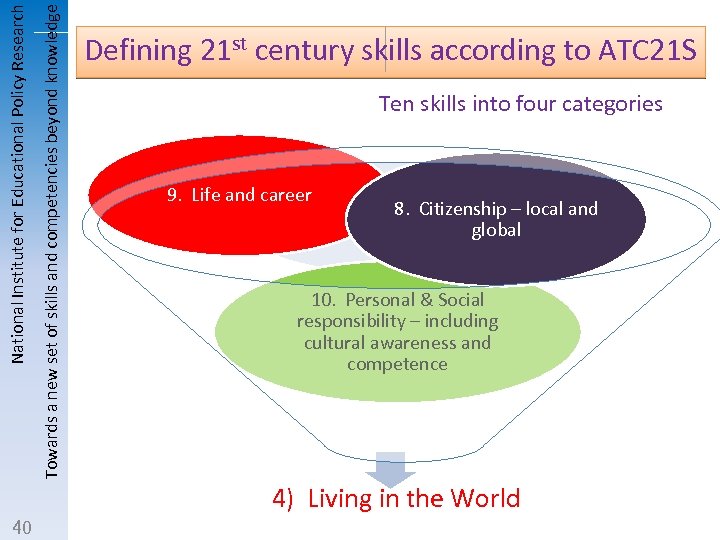 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Defining 21 st century skills according to ATC 21 S Ten skills into four categories 9. Life and career 8. Citizenship – local and global 10. Personal & Social responsibility – including cultural awareness and competence 4) Living in the World 40
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Defining 21 st century skills according to ATC 21 S Ten skills into four categories 9. Life and career 8. Citizenship – local and global 10. Personal & Social responsibility – including cultural awareness and competence 4) Living in the World 40
 41 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Sophisticated thinking Collaboration and communication skills Flexible problem solving
41 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Sophisticated thinking Collaboration and communication skills Flexible problem solving
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 42 Another international network also has undertaken collaborative effort to prepare students with 21 st century competencies and skills. Education Network (EDNET), which is part of APEC’S Human Resources Development Working Group was created at the 1 st APEC Education Ministers Meeting (AEMM) in Washington, DC in 1992 and has carried out education activities in APEC. EDNET activities support the priority areas set by the APEC Education Ministers. These priorities were established at the 4 th AEMM in Lima, Peru in June 2008.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 42 Another international network also has undertaken collaborative effort to prepare students with 21 st century competencies and skills. Education Network (EDNET), which is part of APEC’S Human Resources Development Working Group was created at the 1 st APEC Education Ministers Meeting (AEMM) in Washington, DC in 1992 and has carried out education activities in APEC. EDNET activities support the priority areas set by the APEC Education Ministers. These priorities were established at the 4 th AEMM in Lima, Peru in June 2008.
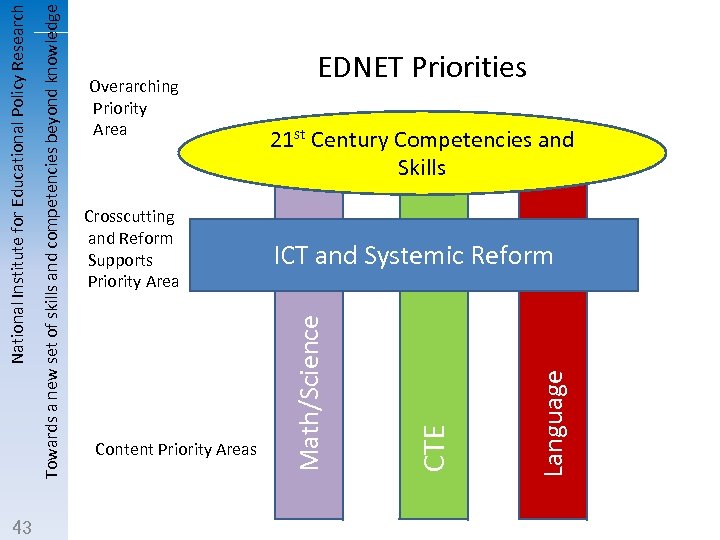 ICT and Systemic Reform Language Content Priority Areas 21 st Century Competencies and Skills CTE Crosscutting and Reform Supports Priority Area EDNET Priorities Math/Science Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 43 Overarching Priority Area
ICT and Systemic Reform Language Content Priority Areas 21 st Century Competencies and Skills CTE Crosscutting and Reform Supports Priority Area EDNET Priorities Math/Science Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 43 Overarching Priority Area
 44 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research II. International Benchmarking as a Global Standard
44 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research II. International Benchmarking as a Global Standard
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 45 How can international benchmarks help? Ø Comparative assessments of learning outcomes… • Can show what is possible in education and thus help optimise existing policies and to reflect on a more fundamental transformation of the paradigms and beliefs underlying current policies • Can help setting policy targets in terms of measurable goals achieved by other systems and help to establish trajectories for reform • Can assist with gauging the pace of educational progress and help reviewing the reality of educational delivery at the frontline • Can support the political economy of reform
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 45 How can international benchmarks help? Ø Comparative assessments of learning outcomes… • Can show what is possible in education and thus help optimise existing policies and to reflect on a more fundamental transformation of the paradigms and beliefs underlying current policies • Can help setting policy targets in terms of measurable goals achieved by other systems and help to establish trajectories for reform • Can assist with gauging the pace of educational progress and help reviewing the reality of educational delivery at the frontline • Can support the political economy of reform
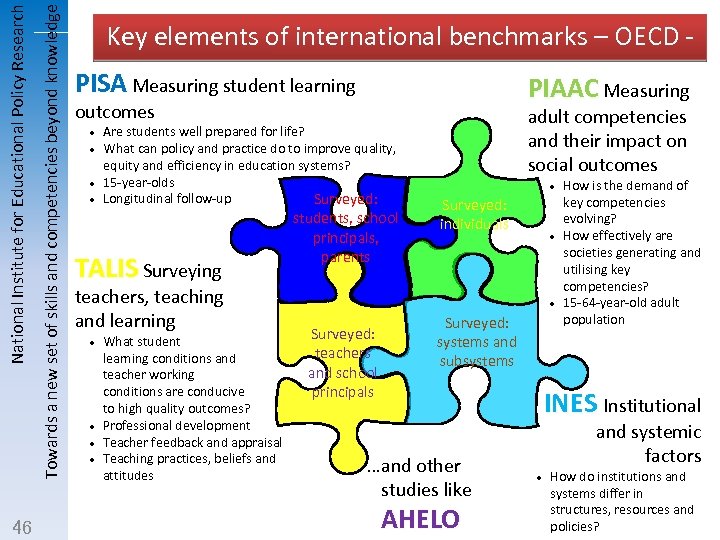 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 46 Key elements of international benchmarks – OECD PISA Measuring student learning PIAAC Measuring outcomes l l Are students well prepared for life? What can policy and practice do to improve quality, equity and efficiency in education systems? 15 -year-olds Longitudinal follow-up Surveyed: TALIS Surveying teachers, teaching and learning l l What student learning conditions and teacher working conditions are conducive to high quality outcomes? Professional development Teacher feedback and appraisal Teaching practices, beliefs and attitudes students, school principals, parents adult competencies and their impact on social outcomes l Surveyed: individuals l l Surveyed: teachers and school principals Surveyed: systems and subsystems …and other studies like AHELO How is the demand of key competencies evolving? How effectively are societies generating and utilising key competencies? 15 -64 -year-old adult population INES Institutional INES and systemic factors l How do institutions and systems differ in structures, resources and policies?
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 46 Key elements of international benchmarks – OECD PISA Measuring student learning PIAAC Measuring outcomes l l Are students well prepared for life? What can policy and practice do to improve quality, equity and efficiency in education systems? 15 -year-olds Longitudinal follow-up Surveyed: TALIS Surveying teachers, teaching and learning l l What student learning conditions and teacher working conditions are conducive to high quality outcomes? Professional development Teacher feedback and appraisal Teaching practices, beliefs and attitudes students, school principals, parents adult competencies and their impact on social outcomes l Surveyed: individuals l l Surveyed: teachers and school principals Surveyed: systems and subsystems …and other studies like AHELO How is the demand of key competencies evolving? How effectively are societies generating and utilising key competencies? 15 -64 -year-old adult population INES Institutional INES and systemic factors l How do institutions and systems differ in structures, resources and policies?
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 47 Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) A three-yearly global assessment of OECD that… … examines the performance of 15 -year-olds in key subject areas as well as a wider range of educational outcomes • Including students attitudes to learning and their learning behaviour … collects contextual data from… … students, parents, schools and systems… … in order to identify policy levers Coverage l Representative samples of between 3, 500 and 50, 000 15 year-old students drawn in each country l Most federal countries also draw state-level samples l PISA covers roughly 90% of the world economy
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 47 Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) A three-yearly global assessment of OECD that… … examines the performance of 15 -year-olds in key subject areas as well as a wider range of educational outcomes • Including students attitudes to learning and their learning behaviour … collects contextual data from… … students, parents, schools and systems… … in order to identify policy levers Coverage l Representative samples of between 3, 500 and 50, 000 15 year-old students drawn in each country l Most federal countries also draw state-level samples l PISA covers roughly 90% of the world economy
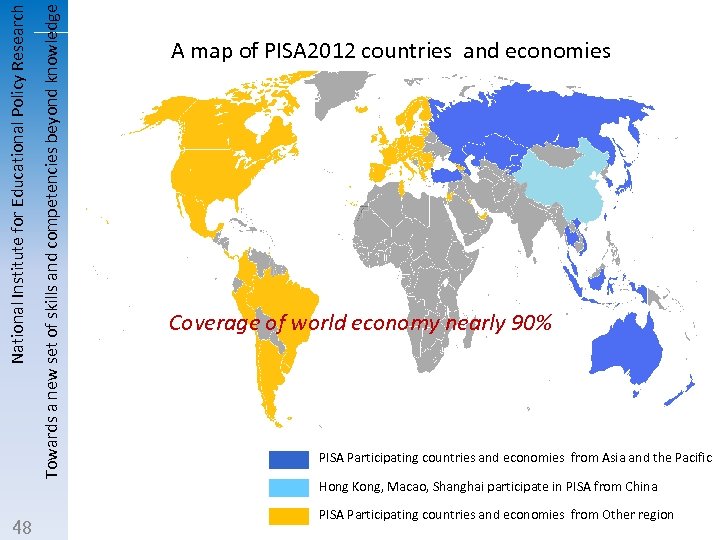 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 48 A map of PISA 2012 countries and economies Coverage of world economy nearly 90% PISA Participating countries and economies from Asia and the Pacific Hong Kong, Macao, Shanghai participate in PISA from China PISA Participating countries and economies from Other region
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 48 A map of PISA 2012 countries and economies Coverage of world economy nearly 90% PISA Participating countries and economies from Asia and the Pacific Hong Kong, Macao, Shanghai participate in PISA from China PISA Participating countries and economies from Other region
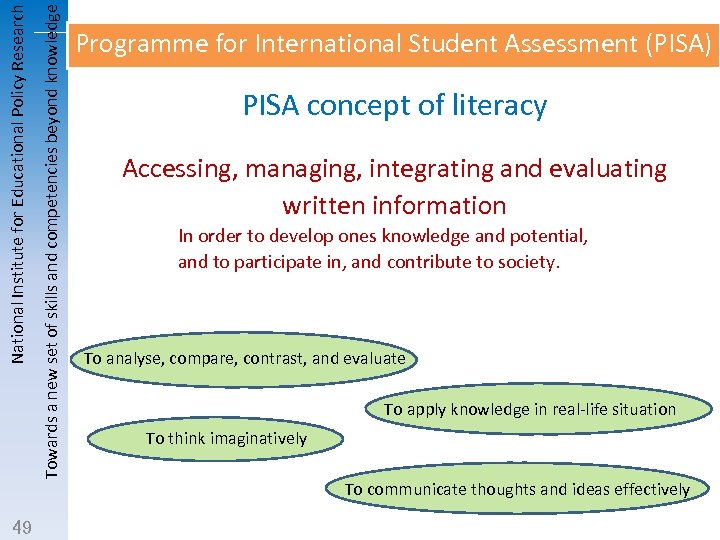 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 49 Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) PISA concept of literacy Accessing, managing, integrating and evaluating written information In order to develop ones knowledge and potential, and to participate in, and contribute to society. To analyse, compare, contrast, and evaluate To apply knowledge in real-life situation To think imaginatively To communicate thoughts and ideas effectively
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 49 Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) PISA concept of literacy Accessing, managing, integrating and evaluating written information In order to develop ones knowledge and potential, and to participate in, and contribute to society. To analyse, compare, contrast, and evaluate To apply knowledge in real-life situation To think imaginatively To communicate thoughts and ideas effectively
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 50 Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) ……conducted every four years by IEA … assesses achievement in countries and collects information about the educational contexts for learning mathematics and science at the Fourth and Eighth Grades … uses the curriculum broadly defined • intended curriculum specified by countries • implemented curriculum actually taught • achieved curriculum – what students have learned ……involved in TIMSS 2007 about 36 countries at the fourth grade and about 48 countries at the eighth grade l
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 50 Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS) ……conducted every four years by IEA … assesses achievement in countries and collects information about the educational contexts for learning mathematics and science at the Fourth and Eighth Grades … uses the curriculum broadly defined • intended curriculum specified by countries • implemented curriculum actually taught • achieved curriculum – what students have learned ……involved in TIMSS 2007 about 36 countries at the fourth grade and about 48 countries at the eighth grade l
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 51 What is PIAAC? Programme for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies • New initiative of the OECD to assess key cognitive and workplace skills and competencies of adults ( 16 - 65 years old) • Multi-cycle program with first assessment to be conducted in 2011, frequency yet to be determined (5 or 10 years, likely the latter) • Benchmarking adult competencies to a global standard, as 27 countries are on board (including all G-7 countries) • Successor to IALS (1994) and ALL (2003)
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 51 What is PIAAC? Programme for the International Assessment of Adult Competencies • New initiative of the OECD to assess key cognitive and workplace skills and competencies of adults ( 16 - 65 years old) • Multi-cycle program with first assessment to be conducted in 2011, frequency yet to be determined (5 or 10 years, likely the latter) • Benchmarking adult competencies to a global standard, as 27 countries are on board (including all G-7 countries) • Successor to IALS (1994) and ALL (2003)
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 52 What competencies will be assessed in PIAAC? Directly Assessed Competencies • Literacy and Numeracy - Updated instrument, computer-based test • Problem Solving in a Technology-Rich Environment – New competency to be measured to reflect current and future labour market requirements Generic Job Skills • Job Requirements Approach (JRA) – Generic skills used at work, adding a labour-demand perspective to an international survey of competencies for the first time
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 52 What competencies will be assessed in PIAAC? Directly Assessed Competencies • Literacy and Numeracy - Updated instrument, computer-based test • Problem Solving in a Technology-Rich Environment – New competency to be measured to reflect current and future labour market requirements Generic Job Skills • Job Requirements Approach (JRA) – Generic skills used at work, adding a labour-demand perspective to an international survey of competencies for the first time
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowgedge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 53 Value of PIAAC for Participating Countries • Offers international comparability: benchmarking against 27 countries • Contains an assessment of literacy in the information age including digital technology and communication tools • Provides essential insights in the nature of labour demand, through indirect assessment of generic skills used in jobs such as computer use, communication, teamwork and management • Provides a rich evidence base for policy-relevant analysis and intervention strategies based on: – Scaled ability measures of competence as opposed to credentials – Complete and nuanced picture of the stock of human capital (labour supply) – Utilization of skills in jobs (labour demand), getting closer to covering the full set of essential skills – Rich set of socio-demographic and economic characteristics of adults
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowgedge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 53 Value of PIAAC for Participating Countries • Offers international comparability: benchmarking against 27 countries • Contains an assessment of literacy in the information age including digital technology and communication tools • Provides essential insights in the nature of labour demand, through indirect assessment of generic skills used in jobs such as computer use, communication, teamwork and management • Provides a rich evidence base for policy-relevant analysis and intervention strategies based on: – Scaled ability measures of competence as opposed to credentials – Complete and nuanced picture of the stock of human capital (labour supply) – Utilization of skills in jobs (labour demand), getting closer to covering the full set of essential skills – Rich set of socio-demographic and economic characteristics of adults
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 54 What is TALIS? Teaching and Learning International Survey • OECD international survey to focus on the learning environment and the working conditions of teachers in schools • An opportunity for teachers and school principals to give their input into education analysis and policy development in some key policy areas • The first TALIS main survey conducted in 24 countries in Oct. /Nov. 2007 (southern hemisphere) and Feb. /Mar. 2008 (northern hemisphere) • The initial report published in June 2009
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 54 What is TALIS? Teaching and Learning International Survey • OECD international survey to focus on the learning environment and the working conditions of teachers in schools • An opportunity for teachers and school principals to give their input into education analysis and policy development in some key policy areas • The first TALIS main survey conducted in 24 countries in Oct. /Nov. 2007 (southern hemisphere) and Feb. /Mar. 2008 (northern hemisphere) • The initial report published in June 2009
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 55 Who is surveyed in TALIS? • The first round of TALIS surveyed teachers of lower secondary education and the principals of the schools in which they work. • Within participating countries, schools as well as teachers within schools, were randomly selected to take part in TALIS. For each country – except for smaller countries – some 200 schools and 20 teachers within each of these schools were sampled. • Separate questionnaires for teachers and principals were developed by an international expert group and were discussed throughout their development with teacher representative bodies, in particular the Trade Union Advisory Committee (TUAC) at the OECD. • Each questionnaire took about 45 minutes to complete. The TALIS survey could also be completed on line and the structure of the questionnaires was adapted for computer use.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 55 Who is surveyed in TALIS? • The first round of TALIS surveyed teachers of lower secondary education and the principals of the schools in which they work. • Within participating countries, schools as well as teachers within schools, were randomly selected to take part in TALIS. For each country – except for smaller countries – some 200 schools and 20 teachers within each of these schools were sampled. • Separate questionnaires for teachers and principals were developed by an international expert group and were discussed throughout their development with teacher representative bodies, in particular the Trade Union Advisory Committee (TUAC) at the OECD. • Each questionnaire took about 45 minutes to complete. The TALIS survey could also be completed on line and the structure of the questionnaires was adapted for computer use.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 56 Issues examined in TALIS • The leadership and management of schools- the roles adopted by school leaders, given increasing accountability and devolution of educational authority and the impact this has on the learning environment in schools and the work of teachers. • The appraisal of teachers’ work in schools and the form and nature of the feedback they receive, as well as the use of outcomes from these processes to reward and develop teachers. Linked to this, the professional development that teachers undertake and how this is connected to appraisal systems, how it is supported by school leaders and how it impacts on classroom practices. • The profiles of countries with regard to teaching practices, activities, beliefs and attitudes, and how these vary according to teacher background characteristics.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 56 Issues examined in TALIS • The leadership and management of schools- the roles adopted by school leaders, given increasing accountability and devolution of educational authority and the impact this has on the learning environment in schools and the work of teachers. • The appraisal of teachers’ work in schools and the form and nature of the feedback they receive, as well as the use of outcomes from these processes to reward and develop teachers. Linked to this, the professional development that teachers undertake and how this is connected to appraisal systems, how it is supported by school leaders and how it impacts on classroom practices. • The profiles of countries with regard to teaching practices, activities, beliefs and attitudes, and how these vary according to teacher background characteristics.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 57 What is AHELO? Feasibility Study for the International Assessment of Higher Education Learning Outcomes • Born out of discussions at the 2006 OECD Ministerial Conference in Athens • Not a university ranking, but a grand-breaking initiative to assess leaning outcomes on HE facing to rapid changes of job market. • Seeking to identify and measure as many factors as possible influencing HE, with the emphasis on teaching and learning. • HE students in over fifteen countries will take part in a feasibility study.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 57 What is AHELO? Feasibility Study for the International Assessment of Higher Education Learning Outcomes • Born out of discussions at the 2006 OECD Ministerial Conference in Athens • Not a university ranking, but a grand-breaking initiative to assess leaning outcomes on HE facing to rapid changes of job market. • Seeking to identify and measure as many factors as possible influencing HE, with the emphasis on teaching and learning. • HE students in over fifteen countries will take part in a feasibility study.
 58 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research III. Policy Levers in Asia and the Pacific : what we can do for things better
58 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research III. Policy Levers in Asia and the Pacific : what we can do for things better
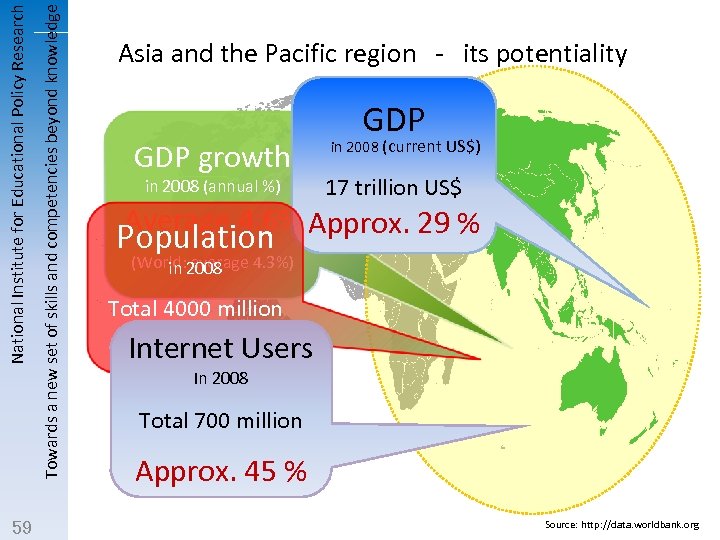 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 59 Asia and the Pacific region - its potentiality GDP growth in 2008 (current US$) in 2008 (annual %) 17 trillion US$ Average 4. 6% Approx. 29 % Population (World: average 4. 3%) in 2008 Total 4000 million Approx. 60 % Internet Users In 2008 Total 700 million Approx. 45 % Source: http: //data. worldbank. org
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 59 Asia and the Pacific region - its potentiality GDP growth in 2008 (current US$) in 2008 (annual %) 17 trillion US$ Average 4. 6% Approx. 29 % Population (World: average 4. 3%) in 2008 Total 4000 million Approx. 60 % Internet Users In 2008 Total 700 million Approx. 45 % Source: http: //data. worldbank. org
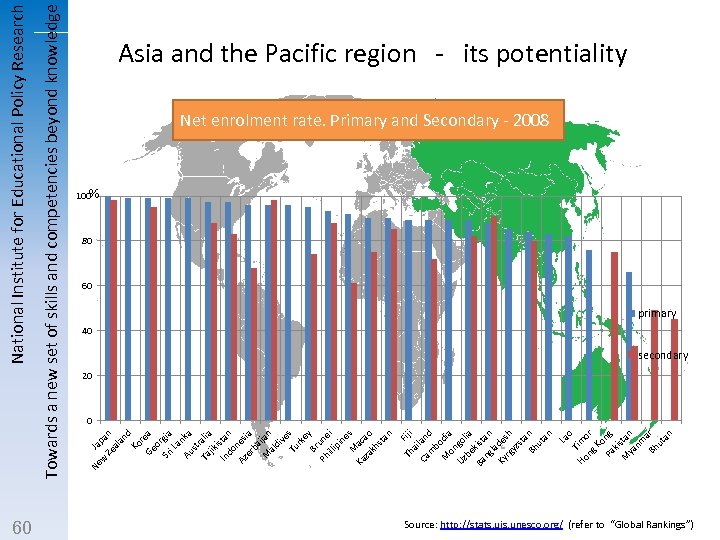 60 Th Fiji ai Ca lan m d bo M dia on Uz gol be ia Ba kist ng an la Ky des rg h yz st a Bh n ut an La o Ti Ho m ng or K o Pa ng kis M tan ya nm a Bh r ut an Ja p Ze an al an d Ko re Ge a or Sr gia i L an Au ka st r Ta alia jik i In stan do Az nes er ia ba M ijan al di ve Tu s rk e Br y un Ph illi ei pi ne M s Ka ac za ao kh st an w Ne Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Asia and the Pacific region - its potentiality Net enrolment rate. Primary and Secondary - 2008 % 100 80 60 primary 40 secondary 20 0 Source: http: //stats. uis. unesco. org/ (refer to “Global Rankings”)
60 Th Fiji ai Ca lan m d bo M dia on Uz gol be ia Ba kist ng an la Ky des rg h yz st a Bh n ut an La o Ti Ho m ng or K o Pa ng kis M tan ya nm a Bh r ut an Ja p Ze an al an d Ko re Ge a or Sr gia i L an Au ka st r Ta alia jik i In stan do Az nes er ia ba M ijan al di ve Tu s rk e Br y un Ph illi ei pi ne M s Ka ac za ao kh st an w Ne Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Asia and the Pacific region - its potentiality Net enrolment rate. Primary and Secondary - 2008 % 100 80 60 primary 40 secondary 20 0 Source: http: //stats. uis. unesco. org/ (refer to “Global Rankings”)
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Our goal : achieving 21 century skills and competencies Country A 61 Country B Country C Country D Country E Country F Country G Country H
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Our goal : achieving 21 century skills and competencies Country A 61 Country B Country C Country D Country E Country F Country G Country H
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 62 Why is international benchmark important? Ø Many education systems are improving by their own national standards, but present standing points are different among them. Today the world’s best education systems are not simply improved by national standards. Ø International benchmarks can help us to look at the pace of educational reforms and give useful hints/ideas how to further improve. Ø Not only country A, or country B, C…. . but all our countries need to strive for developing 21 century skills and competencies as our common goal.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 62 Why is international benchmark important? Ø Many education systems are improving by their own national standards, but present standing points are different among them. Today the world’s best education systems are not simply improved by national standards. Ø International benchmarks can help us to look at the pace of educational reforms and give useful hints/ideas how to further improve. Ø Not only country A, or country B, C…. . but all our countries need to strive for developing 21 century skills and competencies as our common goal.
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 63 What do educational benchmarks show us? n. Progress Concerns about skill barriers to economic growth, productivity growth and rates of technological innovation • One additional year of education equals to between 3 and 6% of GDP • Rising college-level qualifications seem generally not to have led to an “inflation” of the labour-market value of qualifications (in all but three of the 20 countries with available data, the earnings benefit increased between 1997 and 2003, in Germany, Italy and Hungary by between 20% and 40%) n. Fairness Concerns about the role of skills in creating social inequity in economic outcomes Both average and distribution of skill matter to long-term growth n. Value for money Concerns about the demand for, and efficiency and effectiveness of, investments in public goods
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 63 What do educational benchmarks show us? n. Progress Concerns about skill barriers to economic growth, productivity growth and rates of technological innovation • One additional year of education equals to between 3 and 6% of GDP • Rising college-level qualifications seem generally not to have led to an “inflation” of the labour-market value of qualifications (in all but three of the 20 countries with available data, the earnings benefit increased between 1997 and 2003, in Germany, Italy and Hungary by between 20% and 40%) n. Fairness Concerns about the role of skills in creating social inequity in economic outcomes Both average and distribution of skill matter to long-term growth n. Value for money Concerns about the demand for, and efficiency and effectiveness of, investments in public goods
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 64 Asia and the Pacific Policy levers lead us to the success. Improved performance has huge impact for nations as a whole.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 64 Asia and the Pacific Policy levers lead us to the success. Improved performance has huge impact for nations as a whole.
 65 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Sustainable reforms towards new goals
65 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Sustainable reforms towards new goals
 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 66 I am grateful to Andreas Schleicher, Advisor to the OECD Secretary -General on Education Policy for his useful information.
Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research 66 I am grateful to Andreas Schleicher, Advisor to the OECD Secretary -General on Education Policy for his useful information.
 67 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Thank you ! 감사합니다. Mt. Fuji
67 Towards a new set of skills and competencies beyond knowledge National Institute for Educational Policy Research Thank you ! 감사합니다. Mt. Fuji


