71e041d3759c02e55b78b6e55289f0a0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Towards a European Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning Consultation Jens Bjornavold, European Commission, Directorate-General for Education and Culture
Towards a European Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning Consultation Jens Bjornavold, European Commission, Directorate-General for Education and Culture
 Functions of the EQF • Neutral reference point based on learning outcomes • Translation device for comparing qualifications • Facilitates credit transfer and quality assurance • Basis for sector qualification developments
Functions of the EQF • Neutral reference point based on learning outcomes • Translation device for comparing qualifications • Facilitates credit transfer and quality assurance • Basis for sector qualification developments
 The European Qualifications Framework • Builds on Bologna and Copenhagen processes • Covers all qualifications in lifelong learning • Meets a clearly expressed demand • Builds on work of a representative expert group Consultation on the basic form, not a final recommendation
The European Qualifications Framework • Builds on Bologna and Copenhagen processes • Covers all qualifications in lifelong learning • Meets a clearly expressed demand • Builds on work of a representative expert group Consultation on the basic form, not a final recommendation
 Lifelong Learning is important Social reasons • Inclusive communities • Active citizens • Equal opportunities Economic reasons • Lisbon • Jobs & growth • Innovation
Lifelong Learning is important Social reasons • Inclusive communities • Active citizens • Equal opportunities Economic reasons • Lisbon • Jobs & growth • Innovation
 The European Lifelong Learning Experience: Obstacles! • within and between countries • between education and training systems • to use of acquired skills • to new learning
The European Lifelong Learning Experience: Obstacles! • within and between countries • between education and training systems • to use of acquired skills • to new learning
 Strong political mandate • Member States & social partners support the development of a EQF • European Council have asked for adoption by the end of 2006
Strong political mandate • Member States & social partners support the development of a EQF • European Council have asked for adoption by the end of 2006
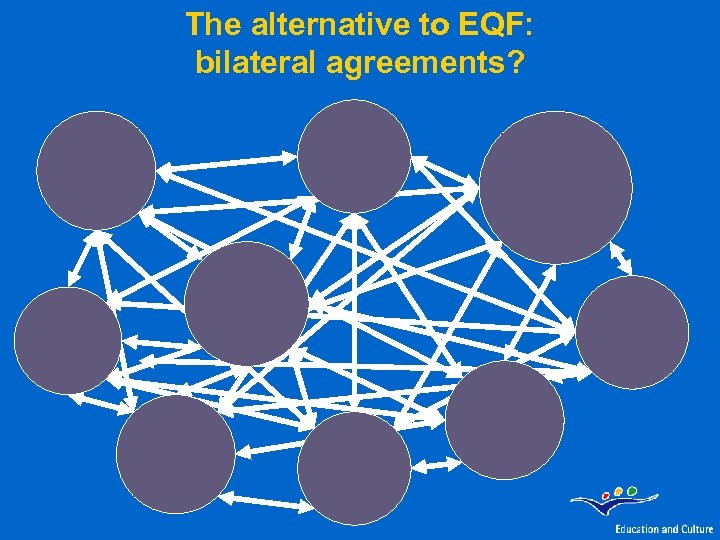 The alternative to EQF: bilateral agreements?
The alternative to EQF: bilateral agreements?
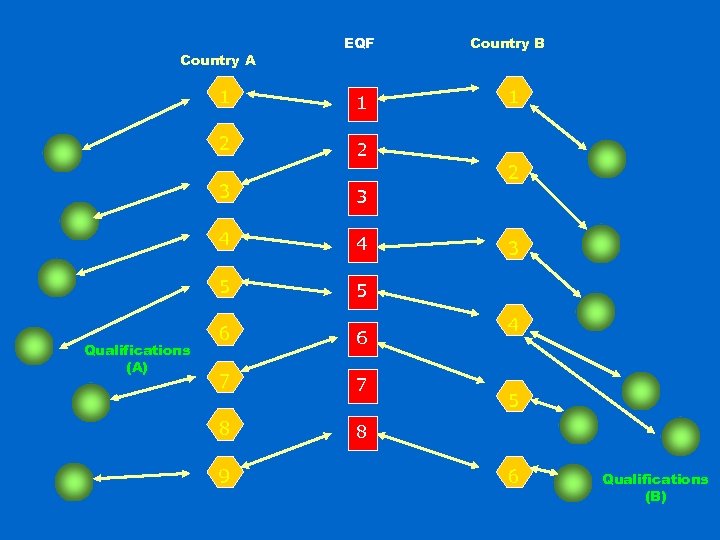 Country A EQF 1 1 2 2 1 2 3 3 4 4 5 Qualifications (A) Country B 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 3 4 5 6 Qualifications (B)
Country A EQF 1 1 2 2 1 2 3 3 4 4 5 Qualifications (A) Country B 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 3 4 5 6 Qualifications (B)
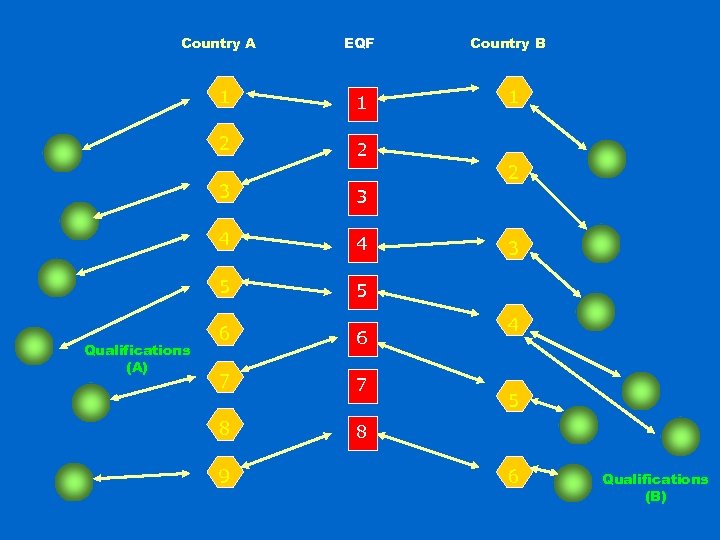 Country A EQF 1 1 2 2 1 2 3 3 4 4 5 Qualifications (A) Country B 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 3 4 5 6 Qualifications (B)
Country A EQF 1 1 2 2 1 2 3 3 4 4 5 Qualifications (A) Country B 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 3 4 5 6 Qualifications (B)
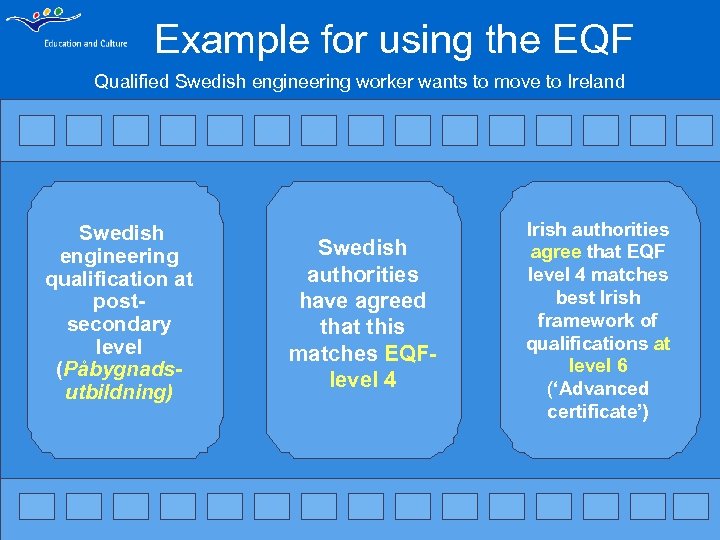 Example for using the EQF Qualified Swedish engineering worker wants to move to Ireland Swedish engineering qualification at postsecondary level (Påbygnadsutbildning) Swedish authorities have agreed that this matches EQFlevel 4 Irish authorities agree that EQF level 4 matches best Irish framework of qualifications at level 6 (‘Advanced certificate’)
Example for using the EQF Qualified Swedish engineering worker wants to move to Ireland Swedish engineering qualification at postsecondary level (Påbygnadsutbildning) Swedish authorities have agreed that this matches EQFlevel 4 Irish authorities agree that EQF level 4 matches best Irish framework of qualifications at level 6 (‘Advanced certificate’)
 A basis for co-operation • EQF implementation is voluntary • Entails no legal obligations on Member States or sectors • Fosters change by supporting and informing reform
A basis for co-operation • EQF implementation is voluntary • Entails no legal obligations on Member States or sectors • Fosters change by supporting and informing reform
 What EQF is NOT! • EQF no replacement for national/sectoral frameworks • EQF NOT about harmonisation • EQF CANNOT define new qualifications
What EQF is NOT! • EQF no replacement for national/sectoral frameworks • EQF NOT about harmonisation • EQF CANNOT define new qualifications
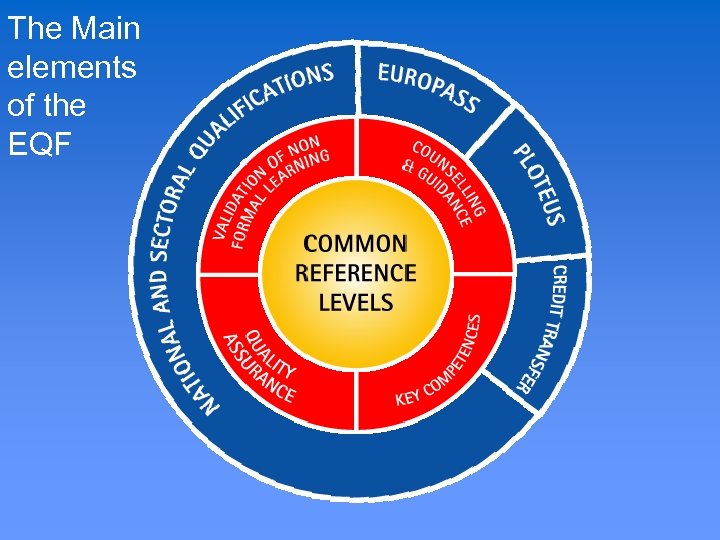 The Main elements of the EQF
The Main elements of the EQF
 The Core of the EQF 8 Common Reference Levels
The Core of the EQF 8 Common Reference Levels
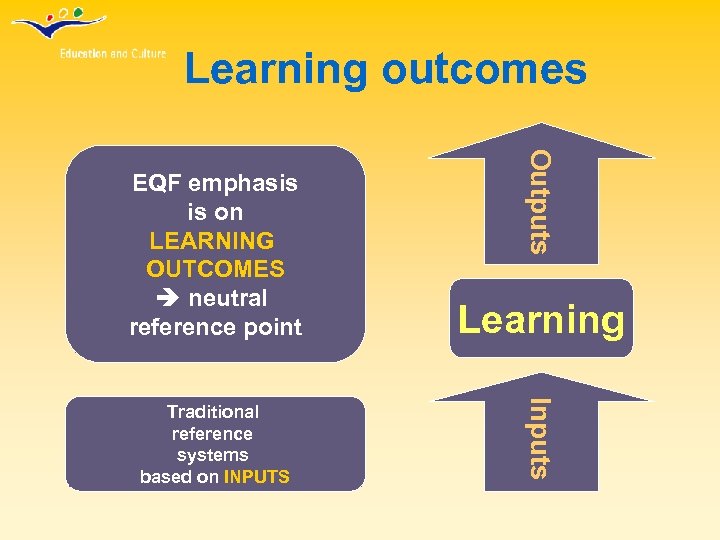 Learning outcomes Learning Traditional reference systems based on INPUTS Inputs Outputs EQF emphasis is on LEARNING OUTCOMES neutral reference point
Learning outcomes Learning Traditional reference systems based on INPUTS Inputs Outputs EQF emphasis is on LEARNING OUTCOMES neutral reference point
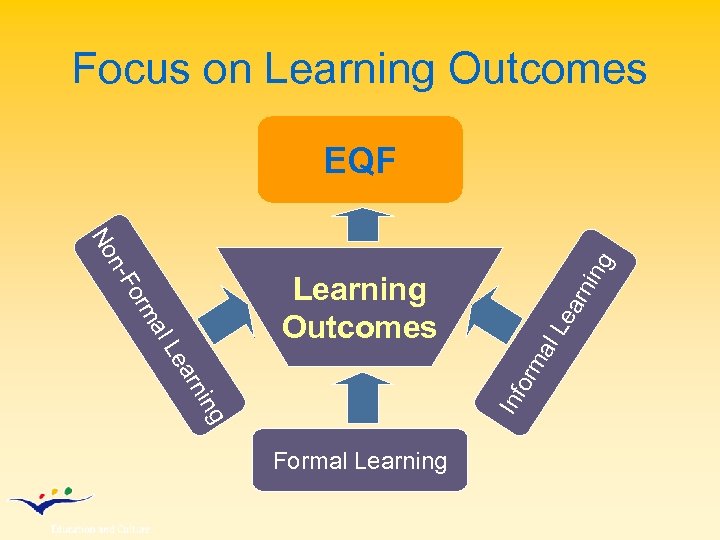 Focus on Learning Outcomes EQF arn ing Le al orm ing Inf arn orm Le al n-F No Learning Outcomes Formal Learning
Focus on Learning Outcomes EQF arn ing Le al orm ing Inf arn orm Le al n-F No Learning Outcomes Formal Learning
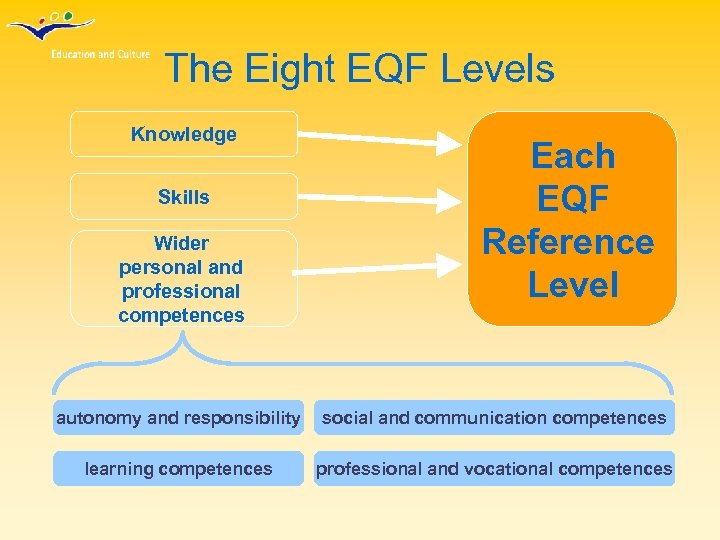 The Eight EQF Levels Knowledge Skills Wider personal and professional competences Each EQF Reference Level autonomy and responsibility social and communication competences learning competences professional and vocational competences
The Eight EQF Levels Knowledge Skills Wider personal and professional competences Each EQF Reference Level autonomy and responsibility social and communication competences learning competences professional and vocational competences
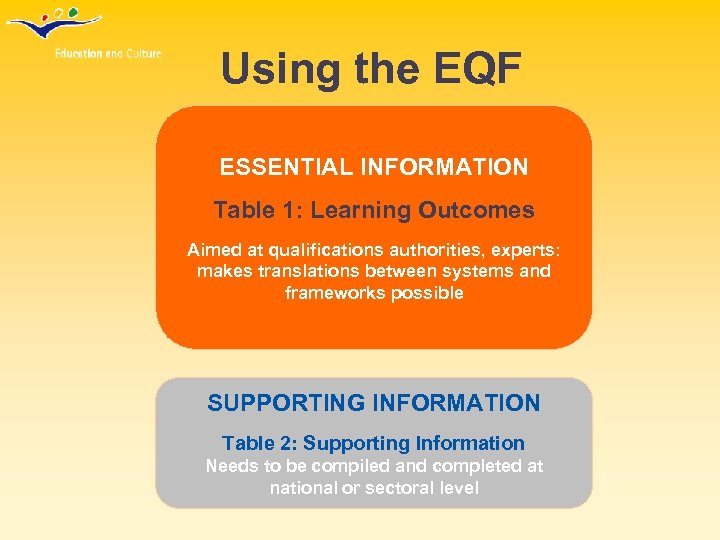 Using the EQF ESSENTIAL INFORMATION Table 1: Learning Outcomes Aimed at qualifications authorities, experts: makes translations between systems and frameworks possible SUPPORTING INFORMATION Table 2: Supporting Information Needs to be compiled and completed at national or sectoral level
Using the EQF ESSENTIAL INFORMATION Table 1: Learning Outcomes Aimed at qualifications authorities, experts: makes translations between systems and frameworks possible SUPPORTING INFORMATION Table 2: Supporting Information Needs to be compiled and completed at national or sectoral level
 Common Guiding Principles
Common Guiding Principles
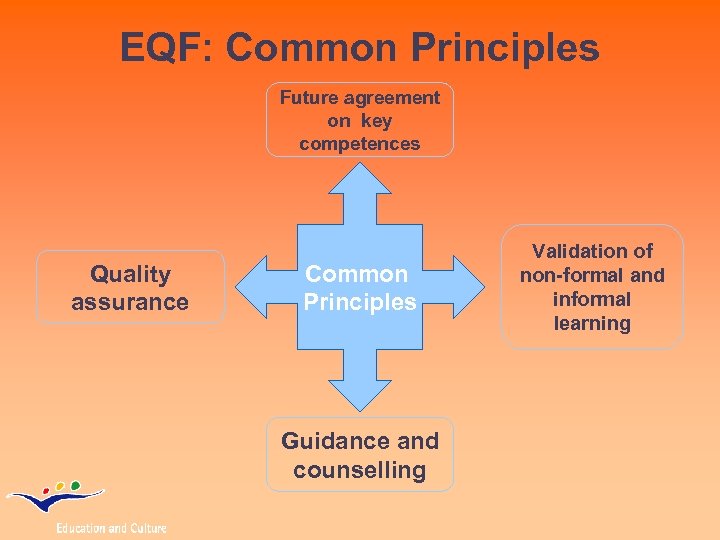 EQF: Common Principles Future agreement on key competences Quality assurance Common Principles Guidance and counselling Validation of non-formal and informal learning
EQF: Common Principles Future agreement on key competences Quality assurance Common Principles Guidance and counselling Validation of non-formal and informal learning
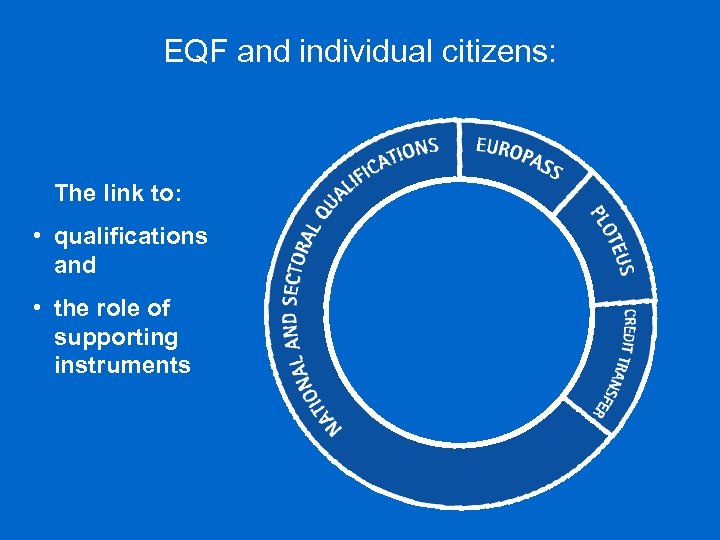 EQF and individual citizens: The link to: • qualifications and • the role of supporting instruments
EQF and individual citizens: The link to: • qualifications and • the role of supporting instruments
 Credit transfer and accumulation system Goal: to create an integrated credit transfer system at European level, meeting the needs of vocational and academic institutions Note: A separate Commission consultation is taking place on credit transfer
Credit transfer and accumulation system Goal: to create an integrated credit transfer system at European level, meeting the needs of vocational and academic institutions Note: A separate Commission consultation is taking place on credit transfer
 Linking qualifications to the EQF: the role of national authorities • Commitments to link national qualifications to EQF • Long term reform process • Learning outcome-based qualifications • National Framework of Qualifications?
Linking qualifications to the EQF: the role of national authorities • Commitments to link national qualifications to EQF • Long term reform process • Learning outcome-based qualifications • National Framework of Qualifications?
 Linking qualifications to the EQF: the role of sectoral stakeholders • Invite sectors to link sectoral qualifications to EQF • Facilitate sectoral developments • Facilitate link between national and sectoral qualifications • Decentralisation and self-certification
Linking qualifications to the EQF: the role of sectoral stakeholders • Invite sectors to link sectoral qualifications to EQF • Facilitate sectoral developments • Facilitate link between national and sectoral qualifications • Decentralisation and self-certification
 Consultation Europe-wide consultation process from July to November 2005: • 32 countries in ‘Education and Training 2010’ • Bologna follow-up group • European Social Partner organisations • Education and training NGO’s • Industry & sector organisations
Consultation Europe-wide consultation process from July to November 2005: • 32 countries in ‘Education and Training 2010’ • Bologna follow-up group • European Social Partner organisations • Education and training NGO’s • Industry & sector organisations
 Consultation — Results • Input to drafting of Council and EP Recommendation in Spring 2006 • Integrated Lifelong Learning Programme — support?
Consultation — Results • Input to drafting of Council and EP Recommendation in Spring 2006 • Integrated Lifelong Learning Programme — support?
 Summary • 8 common reference levels (learning outcomes) • Common principles support EQF levels and provide guidelines for cooperation • A range of tools and instruments for individuals (e. g. credit transfer and accumulation) • Commitment from national and sectoral bodies
Summary • 8 common reference levels (learning outcomes) • Common principles support EQF levels and provide guidelines for cooperation • A range of tools and instruments for individuals (e. g. credit transfer and accumulation) • Commitment from national and sectoral bodies


