3e6a3c577b1ca7c232bbca0412061b50.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Tour I : Introduction to e-Business & e-Commerce E. Widodo e-

2 Objectives • Know the meaning and scope of e-Business & e. Commerce • Understand the benefits and barriers in its adoptions e-

3 “Computer science is no more about computers than astronomy is about telescopes” EW Dijkstra e-

Contents 4 • • e- Background e-Business management Terminology Significance B 2 B and B 2 C Drivers Barriers
5 e- What next will be?
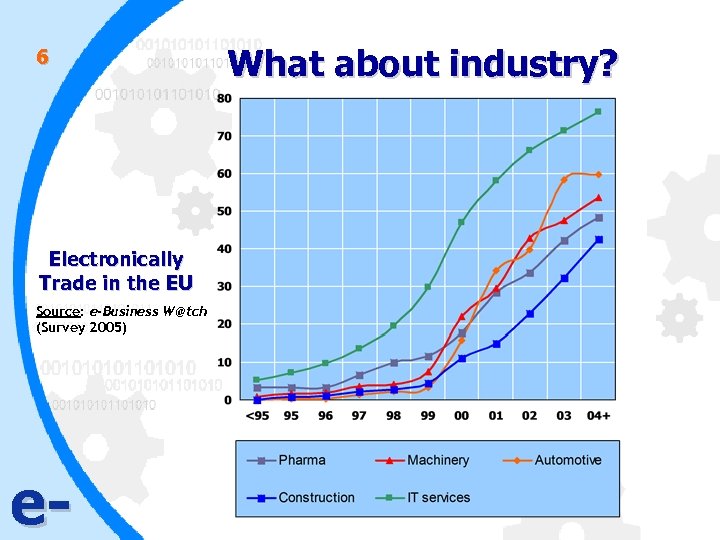
6 Electronically Trade in the EU Source: e-Business W@tch (Survey 2005) e- What about industry?
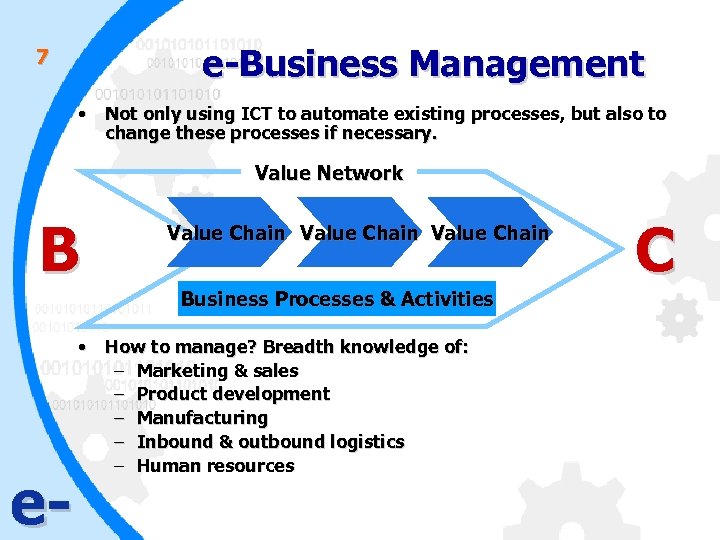
e-Business Management 7 • Not only using ICT to automate existing processes, but also to change these processes if necessary. Value Network B Value Chain Business Processes & Activities e- • How to manage? Breadth knowledge of: – Marketing & sales – Product development – Manufacturing – Inbound & outbound logistics – Human resources C

8 Management response should be • How should a electronic business strategy be developed? • To what extent we can use existing business processes and ICT strategy models? • What are the main changes that need to be made to the organization as part of implementation strategy? e-

9 e- Important terminologies • e-Business: all electronically mediated information exchanges, within an organization &/ with external stakeholders supporting the range of business processes. • e-Commerce: <<only with external stakeholder>> ditto. • Value chain: a model for analysis how supply chain activities can add value to products or services. • Value network: link between organization and its strategic and non strategic partners that forms its value.
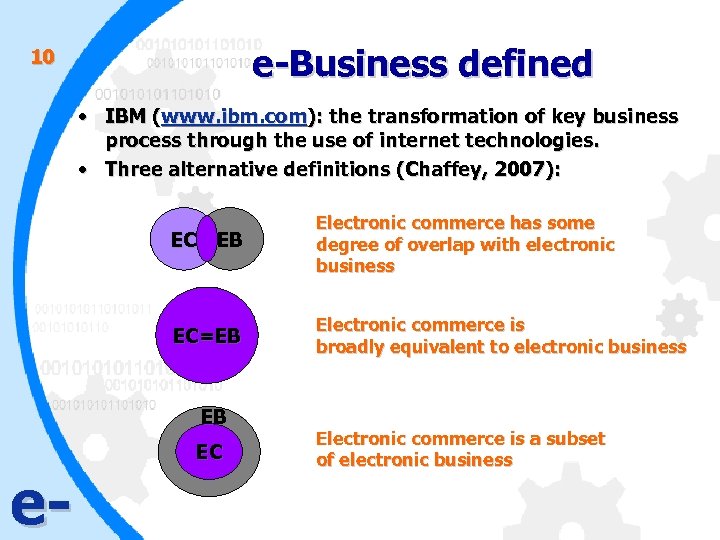
e-Business defined 10 • IBM (www. ibm. com): the transformation of key business process through the use of internet technologies. • Three alternative definitions (Chaffey, 2007): EC EB Electronic commerce has some degree of overlap with electronic business EC=EB Electronic commerce is broadly equivalent to electronic business EB e- EC Electronic commerce is a subset of electronic business
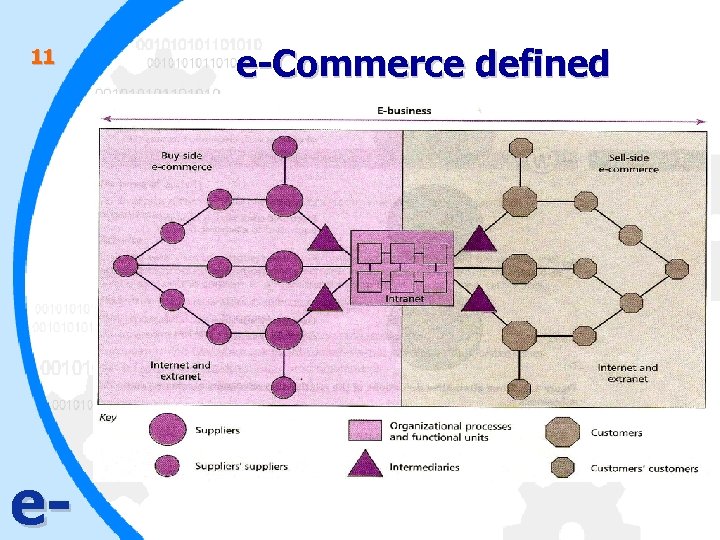
11 e- e-Commerce defined

12 e-Commerce defined • Includes non-financial transactions (not only imaging www. amazon. com ) such as customer request. • Different perspective by Kalakota & Whinston 1997: – Communication perspective: delivery of information, products/services payment by e-means. – Business process perspective: application of ICT towards the automation of business transactions & workflows. – Service perspective: enabling cost cutting and increasing in speed and quality of service delivery. – Online perspective: buying & selling of products & information online. e-

13 How significant? • 1 of 5 people walks into department store in America to buy an electrical appliances will purchase online. • 3 of 4 Americans start shopping for new cars online but eventually most end up buying them from traditional dealers. • 50% of 60 millions consumers in Europe who have an internet connection bought products offline after having investigated prices and details online. e-

14 How significant? • $24 billion-worth of trade was done in 2004 on e. Bay. • In January 2004, 83. 5 m people, or just over half of the US’s internet users, visited either e. Bay or Amazon. • It now hosts virtual “shop fronts” for some 150, 000 stores worldwide. e-
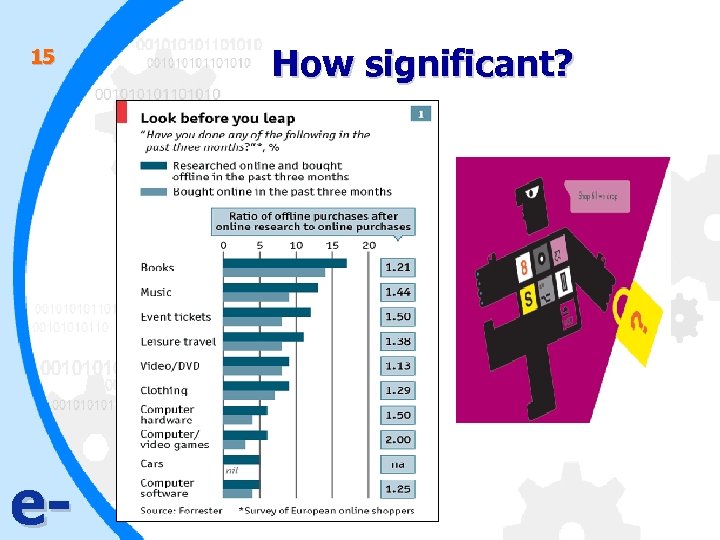
15 e- How significant?
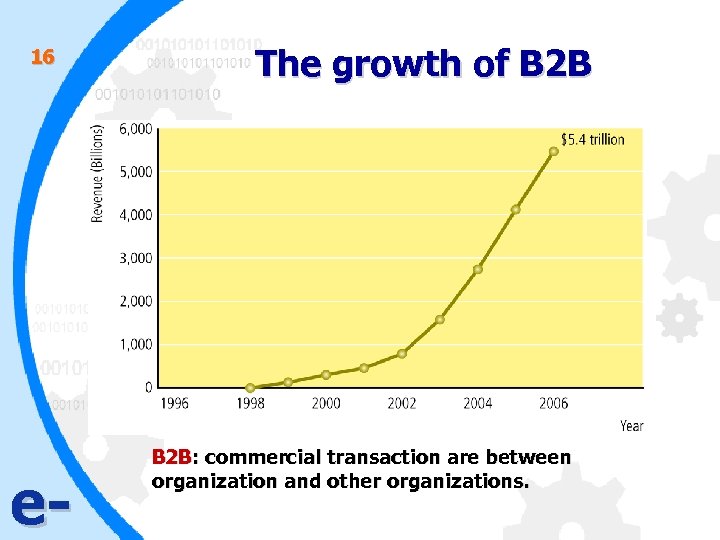
16 e- The growth of B 2 B: commercial transaction are between organization and other organizations.
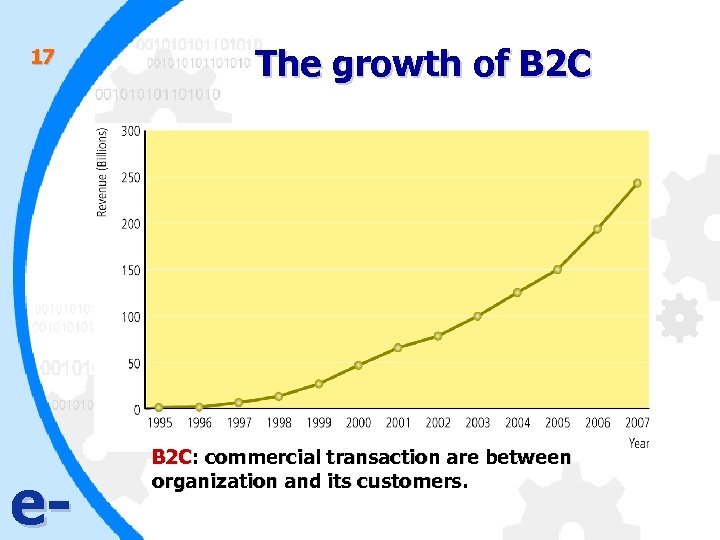
17 e- The growth of B 2 C: commercial transaction are between organization and its customers.

18 e- Drivers • Tangible drivers: – Increasing sales increasing revenue from: • New customer, new market • Existing customer (repeat selling) • Existing customer (cross selling) – Marketing cost reduction from: • Customer service & marketing communication • Online sales – Supply-chain cost reduction from: • Level of inventory • Supplier competitiveness • Lead time – Administrative cost reduction from routine business processes.

19 Drivers • Intangible drivers: – Corporate & brand image – Rapid & responsive marketing communication – Improving customer service (feedback for customer needs) – Learning for the future – Ability to evaluate partners e-
20 Barriers • A survey from DTI, 2000 using 5 scale, 5=strongly agree, 1=strongly disagree: – e-commerce is not relevant to the business (3. 6) – No tangible benefit (3. 51) – Technology cost is too high (3. 5) – Concern about confidentiality (3. 22) – Concern about fraud (3. 11) e-

1 st week souvenir 21 Task 1: Please find two (2) Indonesian e-business and e-commerce implementers. To what extent you state whether they are e-business or ecommerce implementers? e-
3e6a3c577b1ca7c232bbca0412061b50.ppt