b271017021f9803af8b6f36057d2a26a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Total Quality Management: an Organizational Perspective By: Dr. Tarik Al Sulimani Chairman, Information Systems Department College, CS & IS December 22, 2008 1

Introduction Complexity of the business today due to : • Fierce competition • Economy • Technology • Lack of natural resources in many developing nations, therefore more focus on survival • New and changing Management concepts. 2

The Challenges-Contd. • Blazing drive for Quality all over the world • Implementing Quality Improvement approaches in a multicultural environments • More focus on quick profits rather than quality products & services • Use of traditional practices • Lack of support for change 3

Total Quality Management “Total Quality Management is performance leadership in meeting customer requirements by doing the right things the first time. ” • “A cooperative form of doing business that relies on the talents and capabilities of labor and management, using teamwork, to continuously improve quality, economy, and productivity, to satisfy the customer” 4

The Quality Revolution • Focus on quality approaches: *The Quality Circles *Japanese manufacturing industry has used TQ for decades to pioneer its domination of key international markets *The US “bought back” TQ in the late 70 s and 80 s *Deming, Juran, Crosby, and Hammer *Business Process Reengineering *Six Sigma and others. 5

Pillars of the House of Total Quality • • Customers satisfaction Continuous improvement Speaking with facts Everyone to participate/Team work • Customer Delight!!! 6
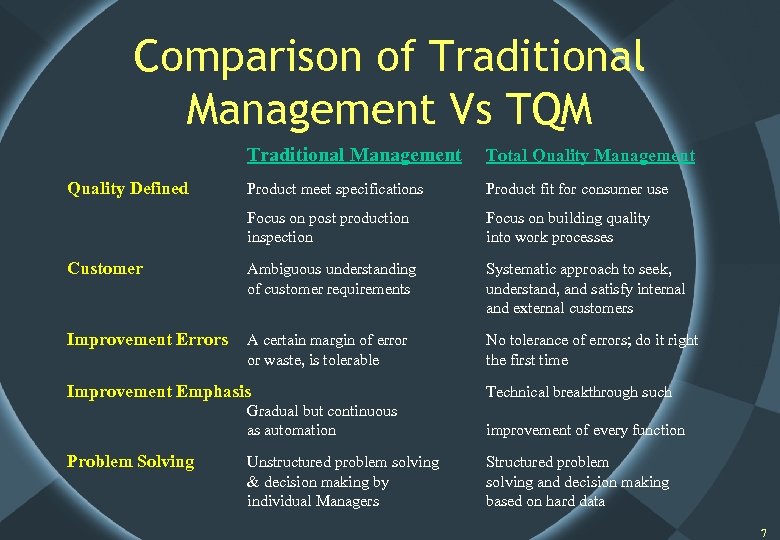
Comparison of Traditional Management Vs TQM Traditional Management Total Quality Management Product meet specifications Product fit for consumer use Focus on post production inspection Focus on building quality into work processes Customer Ambiguous understanding of customer requirements Systematic approach to seek, understand, and satisfy internal and external customers Improvement Errors A certain margin of error or waste, is tolerable No tolerance of errors; do it right the first time Quality Defined Improvement Emphasis Technical breakthrough such Gradual but continuous as automation Problem Solving improvement of every function Unstructured problem solving & decision making by individual Managers Structured problem solving and decision making based on hard data 7

Preparation for the Change: The KSA Quality Journey • • Organizations adopting to change Development of skilled national manpower High dependence on foreign workers Limited availability of job openings in the public sector • Meeting customer’s demands/provision of high quality products & services. 8

Preparation for the Change: The KSA Quality Journey • • • Expatriates and skilled labor from all over the world Focus on education for everyone Economic independence through diversification Expansion of exports Use of national resources as key sources of income Narrow the gap between themselves and other developed nations. 9

Quality Vs Education If it works for Nations If it works in Organizations Can Quality be One Size Fits All? 10

Are Universities and Organizations the Same? • Is Education really a service? • Do universities have customers like other businesses? • Do university customers express their dissatisfaction? • Can the techniques and tools of quality and productivity be transplanted successfully from industries to schools/universities? 11

New Trends of Education • Increased need for Quality knowledge of Science & Technology to provide highly talented population • The university of today must focus on quality education to prepare new generations for challenges ahead • The gap between universities and industries is quite large in some nations which must be bridged. 12

Marching Through the 21 st Century • No matter how good our schools/universities are, they must be ready to meet the rapidly changing world • Education must be committed to creating a climate that is evidenced by the following: – A commitment to helping students succeed to the very best of their ability – Development and enhancement of educational standards which assures that students are mastering needed knowledge and skills. 13

Using the Quality Process to Evaluate Universities • Measure student’s satisfaction as related to the quality of education getting and key student services • Determine satisfaction of faculty members • Assess staff perceptions and the organization as a whole • Measure the public image of students to improve learning • Track progress of students after graduation. 14

Common Ground Rules for Quality in Education • Establishment of educational standards ensuring that every student leaves the university with demonstrated abilities to perform at the highest levels • Demonstration of a new sprit of caring for students and fellow educators • Communication with students/parents to reach the hopes we have for the future of our students • Collaboration with business, industry, and the community, since their support is crucial to the success of our endeavors. 15

Common Ground Rules for Quality in Education-Contd. • Focus on the process which has created bureaucracies rather than on people who are involved • Recognition that professors play major roles in quality & productivity initiatives while assuming greater roles in university management functions. 16

Disadvantages of Implementing Quality in Local Organizations • Lack of awareness about the importance of Quality • Limited specialist in the field • Lack of support from people and management • Strong interests in making quick profits and less focus on improvements • Lack of policies and procedures • Lack of long-term objectives 17

Pluses of Implementing Quality in Local Organizations • • Use of religion as a way of life High level of education among the people Young workforce Strong national economy from available resources helps in shaping the way organizations operate • Attractiveness of to foreign workers. 18

Changes Required for Key Improvements in Universities • Management and teaching philosophies that focus on defined measures of excellence and quality improvements • Goals that meet or exceed the expectations of internal and external customers (students, employees, parents, and industries) • Customer satisfaction systems and organizational climate that prevent errors or mistakes • Decisions based on inputs from those closes to the students, using data obtained from research, not guesswork. 19
Obstacles of Implementing TQM in Universities • Centralization in educational decision making in some institutions • Unavailability of qualified educators and specialists in the field of Quality in general and TQM in particular at university levels • Weaknesses in the structure of IS (non availability of data) and its dependence on traditional experience. 20

Implementation Plan • Establish a vision for the future • Increase awareness about the importance of Quality to organizations • Invite and encourage researchers to work on Quality projects • Create more societies for Quality in the region • Create a culture where people see Quality as a way of life. 21

Implementation Plan-Contd. • Involve Management in the process of change • Create Quality Improvement Teams to enhance processes • Provide training and education to all. . 22

Conclusion • Challenges of 21 st century on our organizations today • Change to new styles of Management practices • Increase the awareness about the importance of Quality and customer satisfaction • Need to create a culture within our organizations to promote quality, cost saving and improvement approaches • Think about future competition and survival as long term goals • Extreme focus on people (our assets!!) as our internal customers. 23

THANK YOU 24
b271017021f9803af8b6f36057d2a26a.ppt