c44c88f07d62e581dff20654c2117ded.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

TORELANCE LEVEL OF DIFFERENT CABBAGE VARIETIES TO BLACK ROT BY: MUNENE DAVID M. A 22/0081/2009 SUPERVISOR: PROF. DANIEL MUKUNYA

Introduction Cabbage is the most valued and the most used vegetable in the world Of all the crucifers, cabbages are the most affected by black rot caused by a bacteria Xanthomonas campestris pv campestris Different seed companies have breed for resistant varieties (F 1) but farmers are still suffering losses related to black rot This means there is a need to evaluate the most resistant variety that can minimize losses encountered by the farmers around Kabete
Problem statement and justification Despite breeders effort to breed for resistant varieties of cabbage, black rot disease has remained to be a threat in most parts of the world, especially in small scale Production(21 MT/ Ha) has remained much lower than the yield potential (26 -75 MT/Ha depending on variety) despite high demand, good market prices and health benefits associated with cabbages Infected cabbages are also prone to other pathogens leading to high storage losses This is as result of break down of resistant gene following the continued mutation of the bacteria over time

OBJECTIVES General objective; Evaluation of the most tolerant cabbage varieties against black rot commonly grown in Kenya Specific objective; Determine the incidence of black rot in different cabbage varieties

Materials Four cabbage varieties. Riana, Fanaka F 1, Pructor F 1, Queen F 1 1 kg DAP 2 kg CAN pesticides 70% alcohol(100 ml) 3% Sodium hypochlorite (50 ml) Sterile distilled water Empty Petri dishes 12 plates of nutrient agar Wire loop Spirit lamp 12 universal bottles Clean distilled water Teat pipette/ dropper

Methodology Ø Ø Ø Ø Planting and establishment of cabbages in the field Collection of young black rot infected cabbage material from the field station for bacterial isolation in the laboratory Isolation of bacteria using aseptic method Sub-culturing of bacteria to produce clean pure colonies Serial dilution to achieve different numbers of colony forming units(c. f. u) Bacterial inoculation to cabbage plants Data collection

Reference Bacteriology exercise book, fourth year, isolation of bacteria http: //go. warwick. ac. uk/wrap Edward J. Sikora, Extension Plant Pathologist, Professor, Entomology and Plant Pathology, Auburn University International Rules for Seed Testing Annexe to Chapter 7: Seed Health Testing Methods HCDA ( Horticulture Crop Development Authority), 2007 Report http: //dx. doi. org/10. 1094/PDIS-94 -3 -0298 Massomo SMS, Mabagala RB, Swai IS, Hockenhull J, Mortensen CN. “Evaluation of varietal resistance in cabbage against the black rot pathogen, Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Tanzania. ” Crop Protection 23, 4(2004): 315 -325. Chupp C. “Black rot of cabbage. ” Manual of Vegetable Plant Diseases. New Delhi, India : Discovery Publishing House, 2006. p. 132 -133 Williams PH. "Black rot: a continuing threat to world crucifers. " Plant Disease 64. 8 (1980): 736 -742. "Black rot of cabbage and other crucifers. " Integrated Pest Management. University of Illinois Extension. Dec 1999.
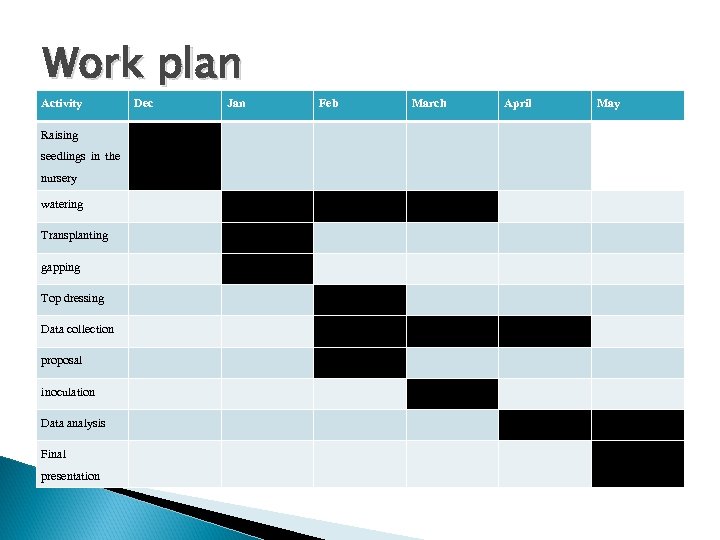
Work plan Activity Raising seedlings in the nursery watering Transplanting gapping Top dressing Data collection proposal inoculation Data analysis Final presentation Dec Jan Feb March April May

THANK YOU FOR YOUR AUDIENCE
c44c88f07d62e581dff20654c2117ded.ppt