4d9f9f54d624b965b19cd9939aab0cdb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 89

 Topics § § § Introduction Technologies in FMC with IP FMC with IMS FMC with SIP FMC with UMA
Topics § § § Introduction Technologies in FMC with IP FMC with IMS FMC with SIP FMC with UMA

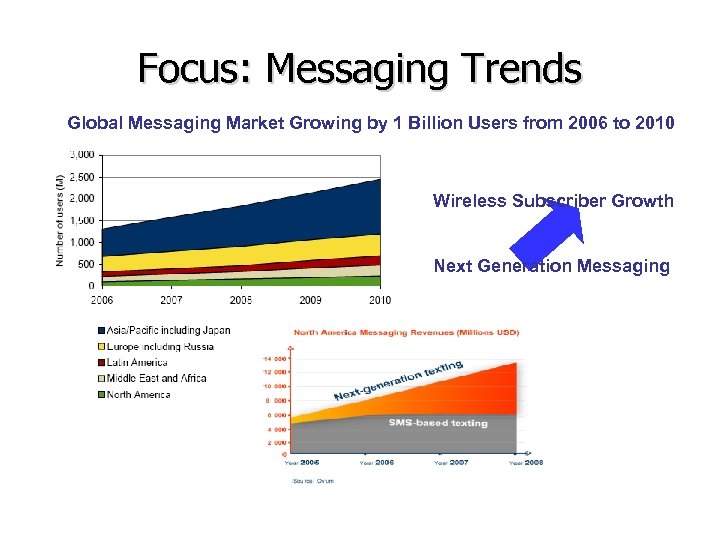 Focus: Messaging Trends Global Messaging Market Growing by 1 Billion Users from 2006 to 2010 Wireless Subscriber Growth Next Generation Messaging
Focus: Messaging Trends Global Messaging Market Growing by 1 Billion Users from 2006 to 2010 Wireless Subscriber Growth Next Generation Messaging
 Mobile Applications Have Come Long Way But This Is Just The Beginning…. ?
Mobile Applications Have Come Long Way But This Is Just The Beginning…. ?
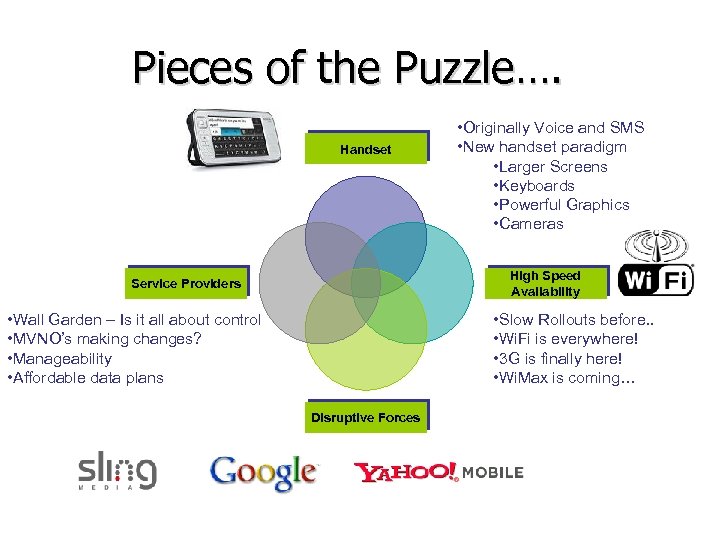 Pieces of the Puzzle…. Handset • Originally Voice and SMS • New handset paradigm • Larger Screens • Keyboards • Powerful Graphics • Cameras High Speed Availability Service Providers • Wall Garden – Is it all about control • MVNO’s making changes? • Manageability • Affordable data plans • Slow Rollouts before. . • Wi. Fi is everywhere! • 3 G is finally here! • Wi. Max is coming… Disruptive Forces
Pieces of the Puzzle…. Handset • Originally Voice and SMS • New handset paradigm • Larger Screens • Keyboards • Powerful Graphics • Cameras High Speed Availability Service Providers • Wall Garden – Is it all about control • MVNO’s making changes? • Manageability • Affordable data plans • Slow Rollouts before. . • Wi. Fi is everywhere! • 3 G is finally here! • Wi. Max is coming… Disruptive Forces
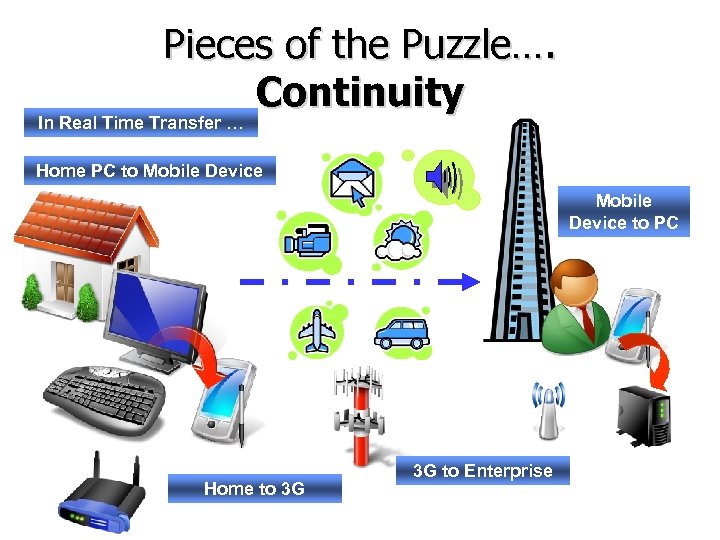 Pieces of the Puzzle…. Continuity In Real Time Transfer … Home PC to Mobile Device to PC Home to 3 G 3 G to Enterprise
Pieces of the Puzzle…. Continuity In Real Time Transfer … Home PC to Mobile Device to PC Home to 3 G 3 G to Enterprise
 So the Puzzle is coming together… Its no longer just a Phone! Lifestyle-enabled communicator and information device. 3 G Networks Carrier Rollout Smartphone Adoption Pre-IMS/IMS Cores Content Providers Video E-Mail Instant Messaging LBS PPT Social Networking Traffic Advertising
So the Puzzle is coming together… Its no longer just a Phone! Lifestyle-enabled communicator and information device. 3 G Networks Carrier Rollout Smartphone Adoption Pre-IMS/IMS Cores Content Providers Video E-Mail Instant Messaging LBS PPT Social Networking Traffic Advertising
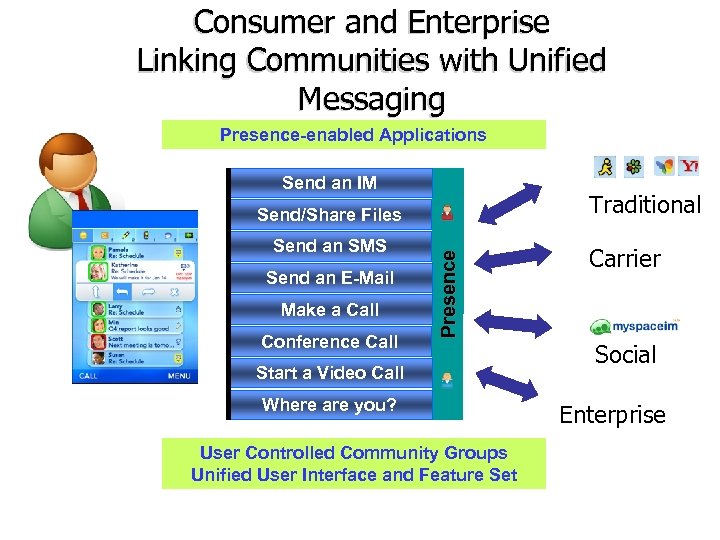 Consumer and Enterprise Linking Communities with Unified Messaging Presence-enabled Applications Send an IM Traditional Send an SMS Send an E-Mail Make a Call Conference Call Presence Send/Share Files Start a Video Call Where are you? User Controlled Community Groups Unified User Interface and Feature Set Carrier Social Enterprise
Consumer and Enterprise Linking Communities with Unified Messaging Presence-enabled Applications Send an IM Traditional Send an SMS Send an E-Mail Make a Call Conference Call Presence Send/Share Files Start a Video Call Where are you? User Controlled Community Groups Unified User Interface and Feature Set Carrier Social Enterprise
 Now that technology is arriving. . It’s all about user experience! Executive E-Mail Document Sharing Traffic Reports Flight Information. Mother Traffic Restaurants E-mail. . Student Challenges • Multiple Devices and Different Users • Multiple Applications – (Voice, VCC, IM, SMS ++) – How to unify • Multiple Access Technologies – (Wi-Fi, Wi-Max, CDMA, GSM, UMTS, DORA) Chat Games Music Video. .
Now that technology is arriving. . It’s all about user experience! Executive E-Mail Document Sharing Traffic Reports Flight Information. Mother Traffic Restaurants E-mail. . Student Challenges • Multiple Devices and Different Users • Multiple Applications – (Voice, VCC, IM, SMS ++) – How to unify • Multiple Access Technologies – (Wi-Fi, Wi-Max, CDMA, GSM, UMTS, DORA) Chat Games Music Video. .
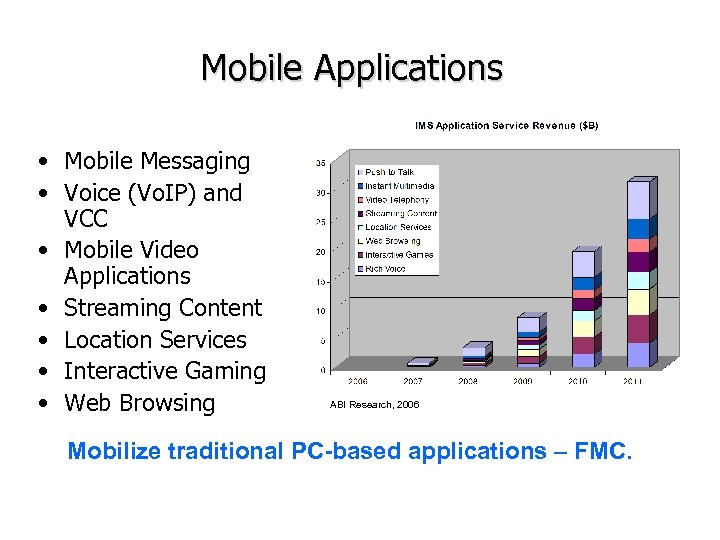 Mobile Applications • Mobile Messaging • Voice (Vo. IP) and VCC • Mobile Video Applications • Streaming Content • Location Services • Interactive Gaming • Web Browsing ABI Research, 2006 Mobilize traditional PC-based applications – FMC.
Mobile Applications • Mobile Messaging • Voice (Vo. IP) and VCC • Mobile Video Applications • Streaming Content • Location Services • Interactive Gaming • Web Browsing ABI Research, 2006 Mobilize traditional PC-based applications – FMC.
 Cellular Network’s § § Wide coverage Large number of users Low speeds (in kbps) High deployment costs
Cellular Network’s § § Wide coverage Large number of users Low speeds (in kbps) High deployment costs
 Wired Networks § § High speeds High Bandwidth Low coverage Inexpensive to set up
Wired Networks § § High speeds High Bandwidth Low coverage Inexpensive to set up
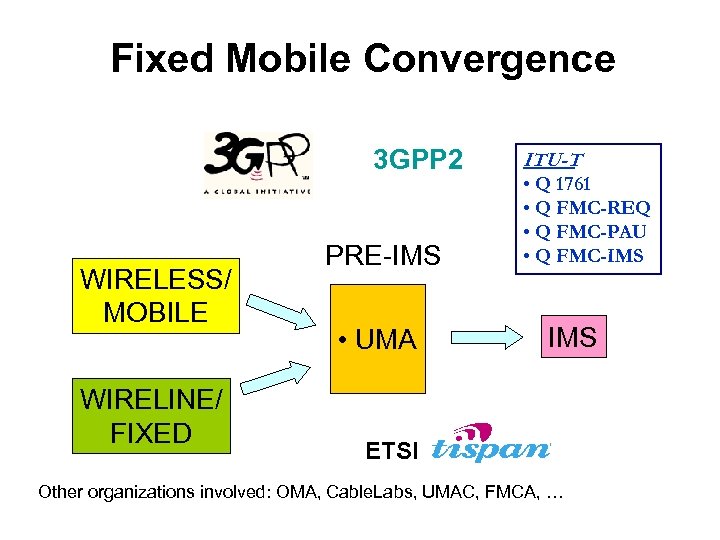 Fixed Mobile Convergence 3 GPP 2 WIRELESS/ MOBILE WIRELINE/ FIXED PRE-IMS • UMA ITU-T • Q 1761 • Q FMC-REQ • Q FMC-PAU • Q FMC-IMS ETSI Other organizations involved: OMA, Cable. Labs, UMAC, FMCA, …
Fixed Mobile Convergence 3 GPP 2 WIRELESS/ MOBILE WIRELINE/ FIXED PRE-IMS • UMA ITU-T • Q 1761 • Q FMC-REQ • Q FMC-PAU • Q FMC-IMS ETSI Other organizations involved: OMA, Cable. Labs, UMAC, FMCA, …
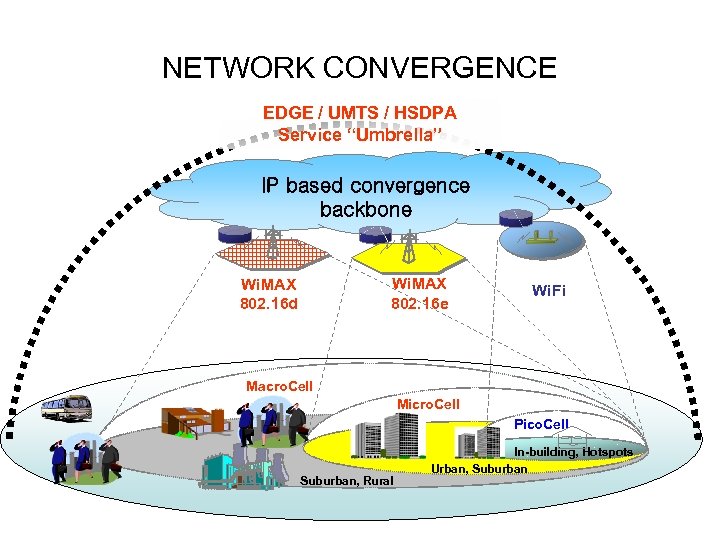 NETWORK CONVERGENCE EDGE / UMTS / HSDPA Service “Umbrella” IP based convergence backbone Wi. MAX 802. 16 d Wi. Fi Macro. Cell Micro. Cell Pico. Cell Suburban, Rural In-building, Hotspots Urban, Suburban
NETWORK CONVERGENCE EDGE / UMTS / HSDPA Service “Umbrella” IP based convergence backbone Wi. MAX 802. 16 d Wi. Fi Macro. Cell Micro. Cell Pico. Cell Suburban, Rural In-building, Hotspots Urban, Suburban
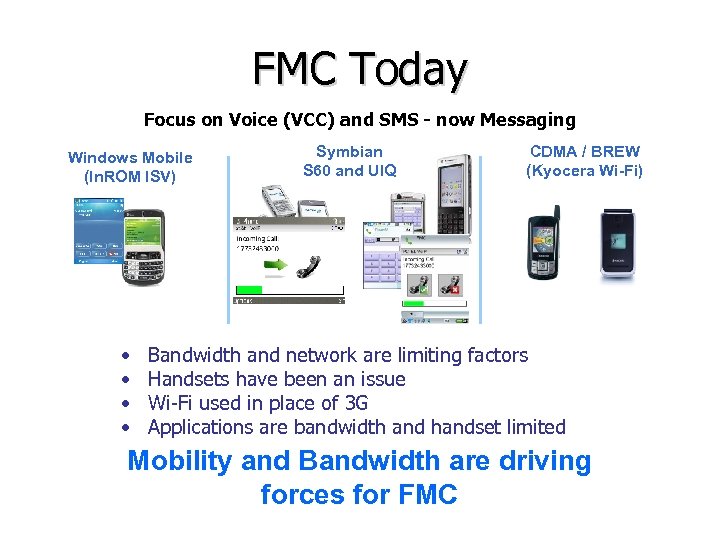 FMC Today Focus on Voice (VCC) and SMS - now Messaging Windows Mobile (In. ROM ISV) • • Symbian S 60 and UIQ CDMA / BREW (Kyocera Wi-Fi) Bandwidth and network are limiting factors Handsets have been an issue Wi-Fi used in place of 3 G Applications are bandwidth and handset limited Mobility and Bandwidth are driving forces for FMC
FMC Today Focus on Voice (VCC) and SMS - now Messaging Windows Mobile (In. ROM ISV) • • Symbian S 60 and UIQ CDMA / BREW (Kyocera Wi-Fi) Bandwidth and network are limiting factors Handsets have been an issue Wi-Fi used in place of 3 G Applications are bandwidth and handset limited Mobility and Bandwidth are driving forces for FMC
 Fixed Mobile Convergence § Way of connecting wireless to wireline infrastructure § The ultimate goal of convergence is to deliver seamless experience across multiple locations, multiple devices and multiple types of use (The Yankee group, Nov 2004)
Fixed Mobile Convergence § Way of connecting wireless to wireline infrastructure § The ultimate goal of convergence is to deliver seamless experience across multiple locations, multiple devices and multiple types of use (The Yankee group, Nov 2004)
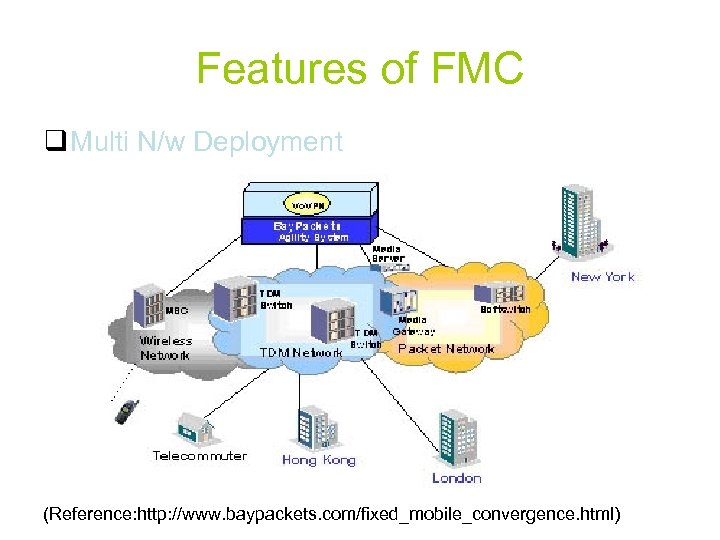 Features of FMC q Multi N/w Deployment (Reference: http: //www. baypackets. com/fixed_mobile_convergence. html)
Features of FMC q Multi N/w Deployment (Reference: http: //www. baypackets. com/fixed_mobile_convergence. html)
 Features of FMC § Unified Service of fixed and mobile n/w’s with one phone, one number and one bill § Seamless roaming between cellular, Wi-Fi, Wi. MAX and what ever wireless technology comes next. § More reliable mobile service with wider coverage at lower cost. Closer integration between public and enterprise phone networks. § Friendly user interfaces that makes it easy to make and manage calls (the user has a choice to select the type of network depending upon cost and convenience).
Features of FMC § Unified Service of fixed and mobile n/w’s with one phone, one number and one bill § Seamless roaming between cellular, Wi-Fi, Wi. MAX and what ever wireless technology comes next. § More reliable mobile service with wider coverage at lower cost. Closer integration between public and enterprise phone networks. § Friendly user interfaces that makes it easy to make and manage calls (the user has a choice to select the type of network depending upon cost and convenience).
 Features of FMC • Friendly user interface that makes it easy to make and manage calls (the user has a choice of N/w depending upon chose and convenience).
Features of FMC • Friendly user interface that makes it easy to make and manage calls (the user has a choice of N/w depending upon chose and convenience).
 Motivator FMC • Fixed Operator (with no Mobile assets) Perspective – Reverse the loss of voice-service minutes and revenue to mobile providers (MNVOs) – Reduce CAPEX and OPEX (harmonized network) – Offer new value-added Services – Reduce Churn, attract new customers, market “Brand” • Fixed Operator (with Mobile assets) Perspective – Reduce CAPEX and OPEX (harmonized network) – Offer new value-added Services -increase revenue • Mobile Operator Perspective – Reduce CAPEX and OPEX (harmonized network) – Offer new value-added Services` – Improve coverage (indoor /outdoor –Wi-Fi) • Cable Operator Perspective – Can offer a quadruple bundling of Vo. IP, video, mobility and broadband access services Source: 1. Adrian Scrase (ETSI), Mobile Fixed Convergence Progress with the Joint 3 GPP and ETSI TISPAN Initiative, 3 G World Congress, November 2005 2. Girish, Muckai (ARRIS), “Fixed Mobile Convergence for Cable Operators”, June 2006
Motivator FMC • Fixed Operator (with no Mobile assets) Perspective – Reverse the loss of voice-service minutes and revenue to mobile providers (MNVOs) – Reduce CAPEX and OPEX (harmonized network) – Offer new value-added Services – Reduce Churn, attract new customers, market “Brand” • Fixed Operator (with Mobile assets) Perspective – Reduce CAPEX and OPEX (harmonized network) – Offer new value-added Services -increase revenue • Mobile Operator Perspective – Reduce CAPEX and OPEX (harmonized network) – Offer new value-added Services` – Improve coverage (indoor /outdoor –Wi-Fi) • Cable Operator Perspective – Can offer a quadruple bundling of Vo. IP, video, mobility and broadband access services Source: 1. Adrian Scrase (ETSI), Mobile Fixed Convergence Progress with the Joint 3 GPP and ETSI TISPAN Initiative, 3 G World Congress, November 2005 2. Girish, Muckai (ARRIS), “Fixed Mobile Convergence for Cable Operators”, June 2006
 Objective FMC • • • Seamless services from the user perspective across the heterogeneous fixed (i. e. , PSTN, ISDN, PSDN, WAN/LAN/CATV, etc) and mobile networks should be guaranteed in FMC. Seamless service provisioning from the operator perspective across the heterogeneous fixed (i. e. , PSTN, ISDN, PSDN, WAN/LAN/CATV, etc) and mobile networks should be guaranteed in FMC. Generalized Mobility supporting should be supported in FMC (i. e. , terminal mobility, user mobility and session mobility). For a given scenario, different level mobility may be needed. Ubiquity of service availability. The end-users can enjoy virtually any application, from any location, on any device. All the services/application can be used by an end-user through any kind of access technology if that service has been subscribed and is supported by his/her terminal device. The service/application availability is only dependent on the user's subscription and capability of the terminals. Supporting multiple user identities and authentication/authorization mechanisms. Source: Draft of ITU-T FMC-REQ “FMC General Requirements“
Objective FMC • • • Seamless services from the user perspective across the heterogeneous fixed (i. e. , PSTN, ISDN, PSDN, WAN/LAN/CATV, etc) and mobile networks should be guaranteed in FMC. Seamless service provisioning from the operator perspective across the heterogeneous fixed (i. e. , PSTN, ISDN, PSDN, WAN/LAN/CATV, etc) and mobile networks should be guaranteed in FMC. Generalized Mobility supporting should be supported in FMC (i. e. , terminal mobility, user mobility and session mobility). For a given scenario, different level mobility may be needed. Ubiquity of service availability. The end-users can enjoy virtually any application, from any location, on any device. All the services/application can be used by an end-user through any kind of access technology if that service has been subscribed and is supported by his/her terminal device. The service/application availability is only dependent on the user's subscription and capability of the terminals. Supporting multiple user identities and authentication/authorization mechanisms. Source: Draft of ITU-T FMC-REQ “FMC General Requirements“
 So why don’t I give all my employees a mobile phone and be done with it? • Cost - mobile minutes are more expensive than landline minutes • Stranded Assets – I’ve invested in IP PBXs and IP desk phones and do not want those investments to go to waste • Lack of Integration - My deskbound employees don’t need a mobile phone, but I don’t want two islands of users (desk and mobile) Fixed Mobile Convergence – the seamless integration of mobility into business’s fixed infrastructure - addresses each of these concerns
So why don’t I give all my employees a mobile phone and be done with it? • Cost - mobile minutes are more expensive than landline minutes • Stranded Assets – I’ve invested in IP PBXs and IP desk phones and do not want those investments to go to waste • Lack of Integration - My deskbound employees don’t need a mobile phone, but I don’t want two islands of users (desk and mobile) Fixed Mobile Convergence – the seamless integration of mobility into business’s fixed infrastructure - addresses each of these concerns
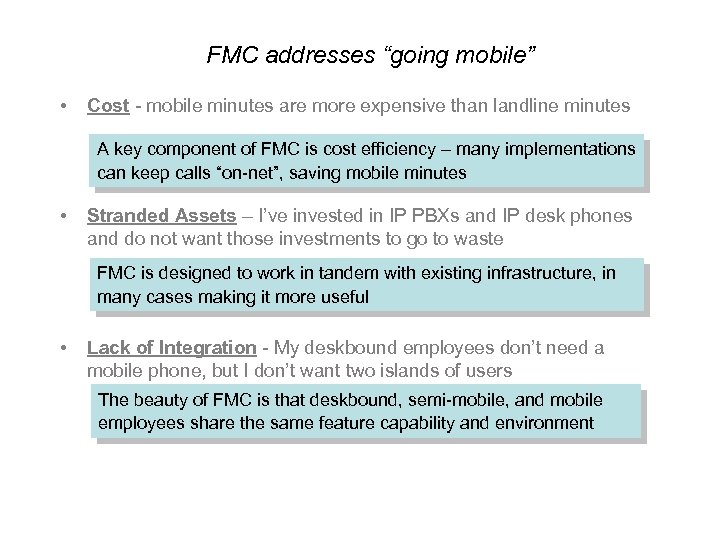 FMC addresses “going mobile” • Cost - mobile minutes are more expensive than landline minutes A key component of FMC is cost efficiency – many implementations can keep calls “on-net”, saving mobile minutes • Stranded Assets – I’ve invested in IP PBXs and IP desk phones and do not want those investments to go to waste FMC is designed to work in tandem with existing infrastructure, in many cases making it more useful • Lack of Integration - My deskbound employees don’t need a mobile phone, but I don’t want two islands of users The beauty of FMC is that deskbound, semi-mobile, and mobile employees share the same feature capability and environment
FMC addresses “going mobile” • Cost - mobile minutes are more expensive than landline minutes A key component of FMC is cost efficiency – many implementations can keep calls “on-net”, saving mobile minutes • Stranded Assets – I’ve invested in IP PBXs and IP desk phones and do not want those investments to go to waste FMC is designed to work in tandem with existing infrastructure, in many cases making it more useful • Lack of Integration - My deskbound employees don’t need a mobile phone, but I don’t want two islands of users The beauty of FMC is that deskbound, semi-mobile, and mobile employees share the same feature capability and environment

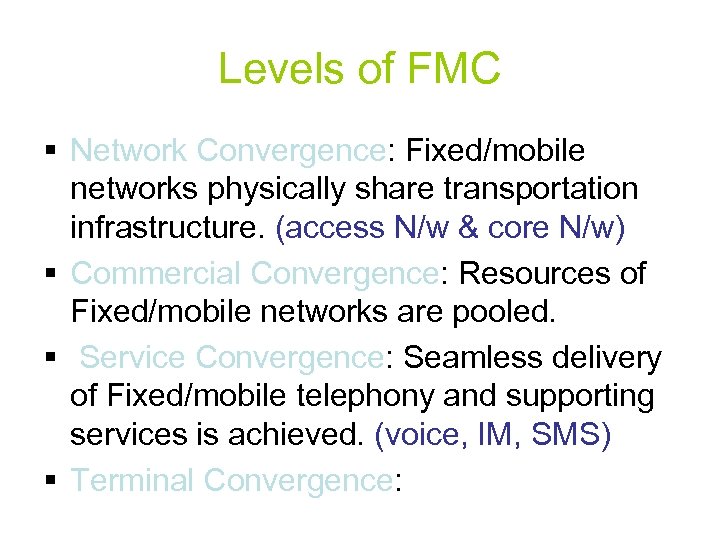 Levels of FMC § Network Convergence: Fixed/mobile networks physically share transportation infrastructure. (access N/w & core N/w) § Commercial Convergence: Resources of Fixed/mobile networks are pooled. § Service Convergence: Seamless delivery of Fixed/mobile telephony and supporting services is achieved. (voice, IM, SMS) § Terminal Convergence:
Levels of FMC § Network Convergence: Fixed/mobile networks physically share transportation infrastructure. (access N/w & core N/w) § Commercial Convergence: Resources of Fixed/mobile networks are pooled. § Service Convergence: Seamless delivery of Fixed/mobile telephony and supporting services is achieved. (voice, IM, SMS) § Terminal Convergence:
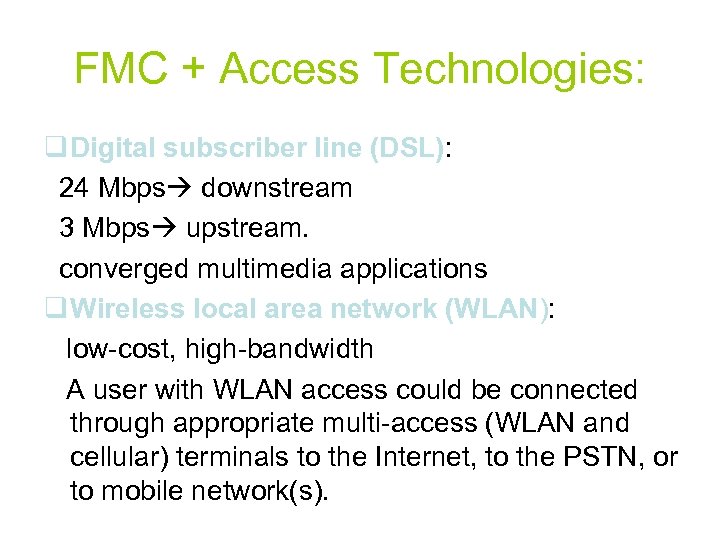 FMC + Access Technologies: q Digital subscriber line (DSL): 24 Mbps downstream 3 Mbps upstream. converged multimedia applications q Wireless local area network (WLAN): low-cost, high-bandwidth A user with WLAN access could be connected through appropriate multi-access (WLAN and cellular) terminals to the Internet, to the PSTN, or to mobile network(s).
FMC + Access Technologies: q Digital subscriber line (DSL): 24 Mbps downstream 3 Mbps upstream. converged multimedia applications q Wireless local area network (WLAN): low-cost, high-bandwidth A user with WLAN access could be connected through appropriate multi-access (WLAN and cellular) terminals to the Internet, to the PSTN, or to mobile network(s).
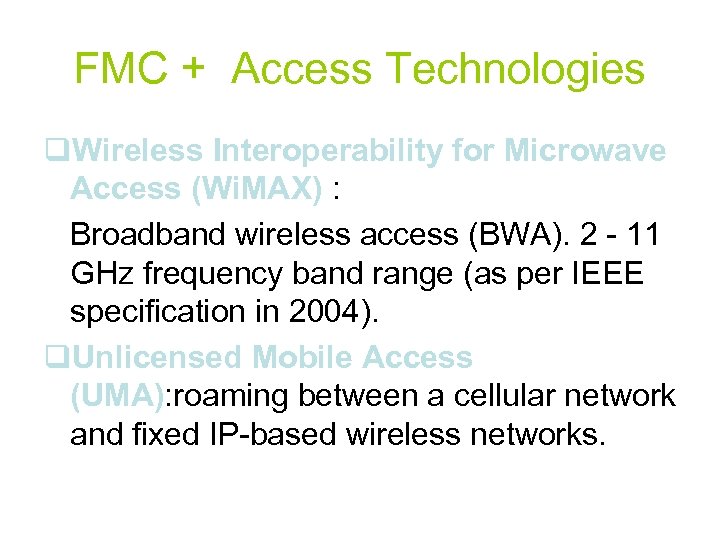 FMC + Access Technologies q. Wireless Interoperability for Microwave Access (Wi. MAX) : Broadband wireless access (BWA). 2 - 11 GHz frequency band range (as per IEEE specification in 2004). q. Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA): roaming between a cellular network and fixed IP-based wireless networks.
FMC + Access Technologies q. Wireless Interoperability for Microwave Access (Wi. MAX) : Broadband wireless access (BWA). 2 - 11 GHz frequency band range (as per IEEE specification in 2004). q. Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA): roaming between a cellular network and fixed IP-based wireless networks.
 FMC in Some Places Include § Multi Media Messaging Service (MMS) § WLAN with CDMA service § Integrated Portal Service
FMC in Some Places Include § Multi Media Messaging Service (MMS) § WLAN with CDMA service § Integrated Portal Service
 Multi Media Messaging Service (MMS) • MMS allows mobile phone users send and receive messages with formatted text graphics, photographs and audio –video clips. • With the integration of digital camera and mobile phone, MMS usage increases.
Multi Media Messaging Service (MMS) • MMS allows mobile phone users send and receive messages with formatted text graphics, photographs and audio –video clips. • With the integration of digital camera and mobile phone, MMS usage increases.
 WLAN with CDMA • In a zone where an access point is established, subscribes use WLAN service. When the subscribers are out of zone, they use CDMA. • High speed, low price from WLAN • Wide coverage from CDMA
WLAN with CDMA • In a zone where an access point is established, subscribes use WLAN service. When the subscribers are out of zone, they use CDMA. • High speed, low price from WLAN • Wide coverage from CDMA
 Integrated Portal Service • Integration of mobile and Web-based portals. • It provides aggregated content and services through a mobile Internet network.
Integrated Portal Service • Integration of mobile and Web-based portals. • It provides aggregated content and services through a mobile Internet network.

 Current Typical Solutions for FMC q. IP-PBX or soft-switch with mobile n/w interface q. IMS based coverage solution q. UMA Dual Mode solution
Current Typical Solutions for FMC q. IP-PBX or soft-switch with mobile n/w interface q. IMS based coverage solution q. UMA Dual Mode solution
 What is IP-PBX? ? ? • The Internet Protocol Private Branch e. Xchange (IP PBX) is telephone switching equipment that resides in a private business instead of the telephone company. • An IP PBX delivers employees dial-tone, the ability to conference, transfer, and dial other employees by extension number as well as many other features. (Virtual Private Network Services. . ) • Voice transmissions are sent via data packets over a data network instead of the traditional phone network • Least Routing of cellular. • 3 G ? ? ? (not applicable to 3 G)…
What is IP-PBX? ? ? • The Internet Protocol Private Branch e. Xchange (IP PBX) is telephone switching equipment that resides in a private business instead of the telephone company. • An IP PBX delivers employees dial-tone, the ability to conference, transfer, and dial other employees by extension number as well as many other features. (Virtual Private Network Services. . ) • Voice transmissions are sent via data packets over a data network instead of the traditional phone network • Least Routing of cellular. • 3 G ? ? ? (not applicable to 3 G)…
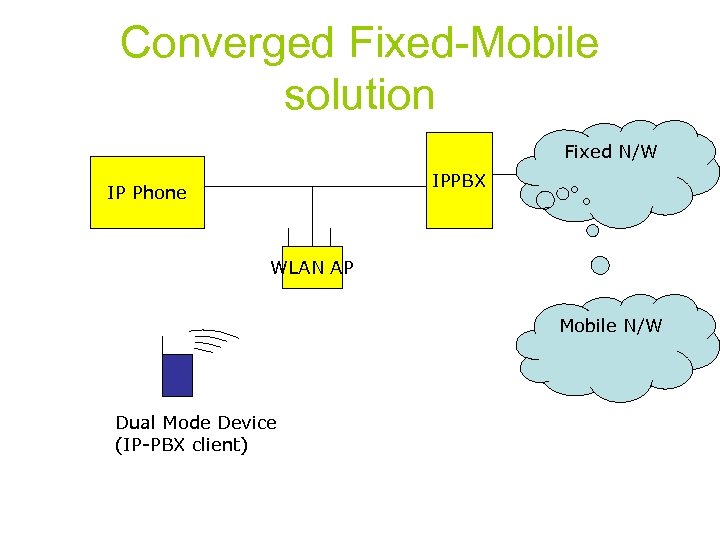 Converged Fixed-Mobile solution Fixed N/W IPPBX IP Phone WLAN AP Mobile N/W Dual Mode Device (IP-PBX client)
Converged Fixed-Mobile solution Fixed N/W IPPBX IP Phone WLAN AP Mobile N/W Dual Mode Device (IP-PBX client)
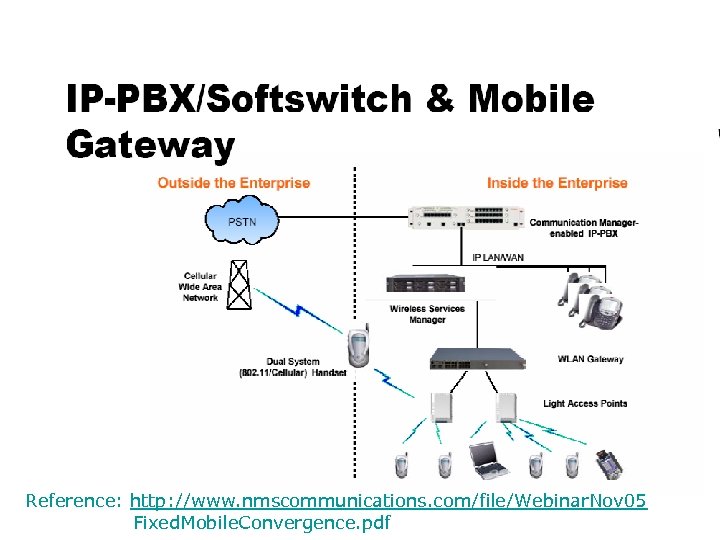 Reference: http: //www. nmscommunications. com/file/Webinar. Nov 05 Fixed. Mobile. Convergence. pdf
Reference: http: //www. nmscommunications. com/file/Webinar. Nov 05 Fixed. Mobile. Convergence. pdf
 • IP Enabled PBX functions on one device while on campus utilizing the WLA|N (802. 11 b/g) infrastructure. • Reduces on-campus and inter-campus calls. • Only with in campus • 3 G? ? (not applicable because IP-PBX does not support) (companies like Nokia, Avaya, Motorola use this technology).
• IP Enabled PBX functions on one device while on campus utilizing the WLA|N (802. 11 b/g) infrastructure. • Reduces on-campus and inter-campus calls. • Only with in campus • 3 G? ? (not applicable because IP-PBX does not support) (companies like Nokia, Avaya, Motorola use this technology).

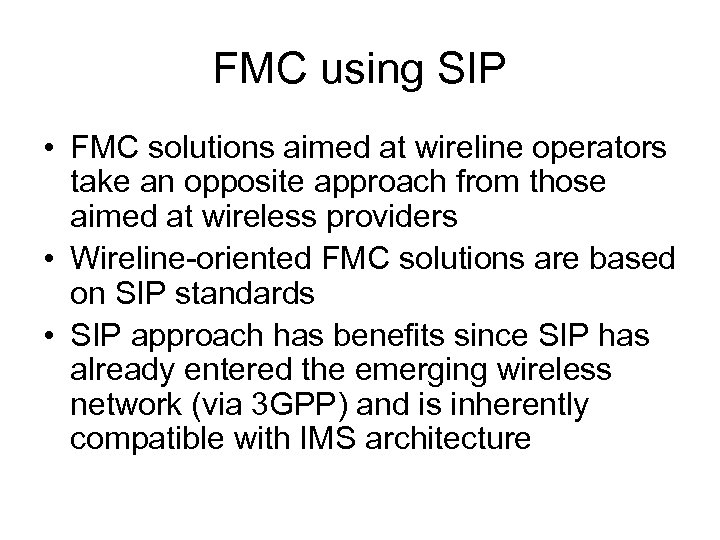 FMC using SIP • FMC solutions aimed at wireline operators take an opposite approach from those aimed at wireless providers • Wireline-oriented FMC solutions are based on SIP standards • SIP approach has benefits since SIP has already entered the emerging wireless network (via 3 GPP) and is inherently compatible with IMS architecture
FMC using SIP • FMC solutions aimed at wireline operators take an opposite approach from those aimed at wireless providers • Wireline-oriented FMC solutions are based on SIP standards • SIP approach has benefits since SIP has already entered the emerging wireless network (via 3 GPP) and is inherently compatible with IMS architecture
 INTRODUCTION to SIP • H. 323 protocol • Session initiation protocol • SIP considered to be a simpler, more flexible alternative to H. 323 with the ability to support advanced services.
INTRODUCTION to SIP • H. 323 protocol • Session initiation protocol • SIP considered to be a simpler, more flexible alternative to H. 323 with the ability to support advanced services.
 What is SIP § SIP or Session Initiation Protocol is an application-level control protocol for setting up, changing and terminating multimedia sessions between participants on IP data networks. § SIP is a text-based protocol, similar to HTTP and SMTP, for initiating interactive communication sessions between users. Such sessions include voice, video, chat, interactive games, and virtual reality.
What is SIP § SIP or Session Initiation Protocol is an application-level control protocol for setting up, changing and terminating multimedia sessions between participants on IP data networks. § SIP is a text-based protocol, similar to HTTP and SMTP, for initiating interactive communication sessions between users. Such sessions include voice, video, chat, interactive games, and virtual reality.
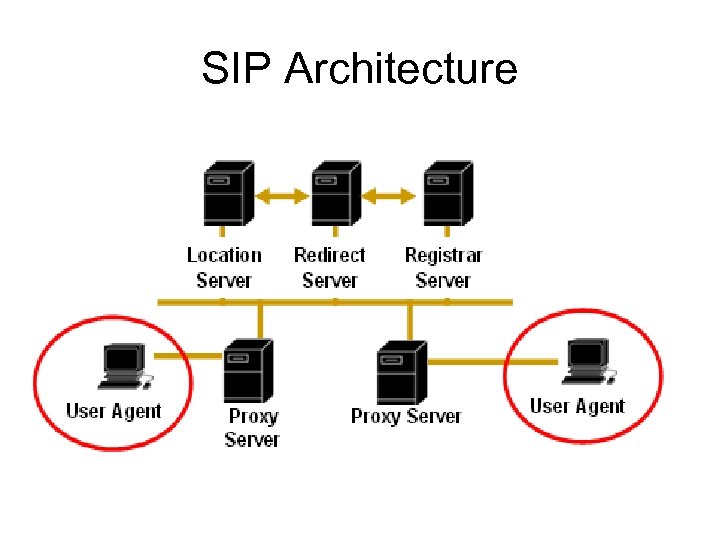 SIP Architecture
SIP Architecture
 SIP Entities • User Agent Client User Agent Server • Proxy Server • Redirect Server • Registrar Server
SIP Entities • User Agent Client User Agent Server • Proxy Server • Redirect Server • Registrar Server
 How SIP works • Long distance calls through the traditional telephony • Telephony system works via a cog and wheel setup • SIP refers to a protocol that allows computers to talk to each other without going through a central station. • SIP is typically offered in two formats, computer based and hardware based
How SIP works • Long distance calls through the traditional telephony • Telephony system works via a cog and wheel setup • SIP refers to a protocol that allows computers to talk to each other without going through a central station. • SIP is typically offered in two formats, computer based and hardware based
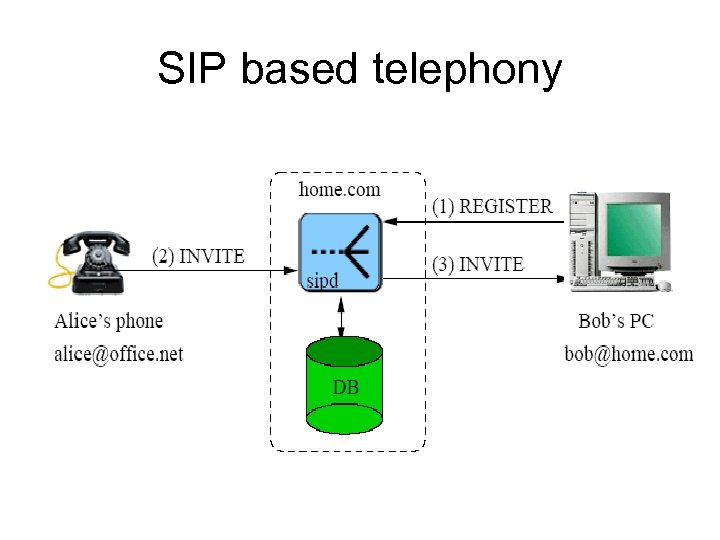 SIP based telephony
SIP based telephony
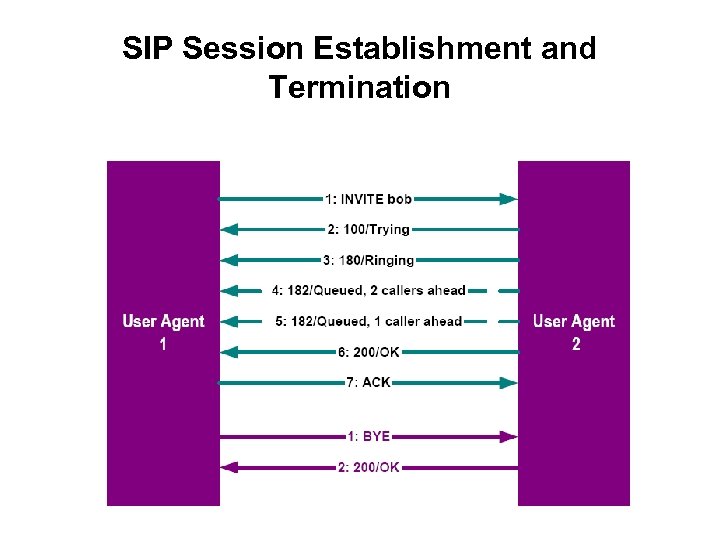 SIP Session Establishment and Termination
SIP Session Establishment and Termination
 Services that SIP can provide • • Call Hold Consultation Hold Unattended Transfer Call forward on Busy/No. Answer/Unconditiona § 3 -Way Conference • Find-Me • Incoming/Outgoing Call Screening • Call Waiting
Services that SIP can provide • • Call Hold Consultation Hold Unattended Transfer Call forward on Busy/No. Answer/Unconditiona § 3 -Way Conference • Find-Me • Incoming/Outgoing Call Screening • Call Waiting
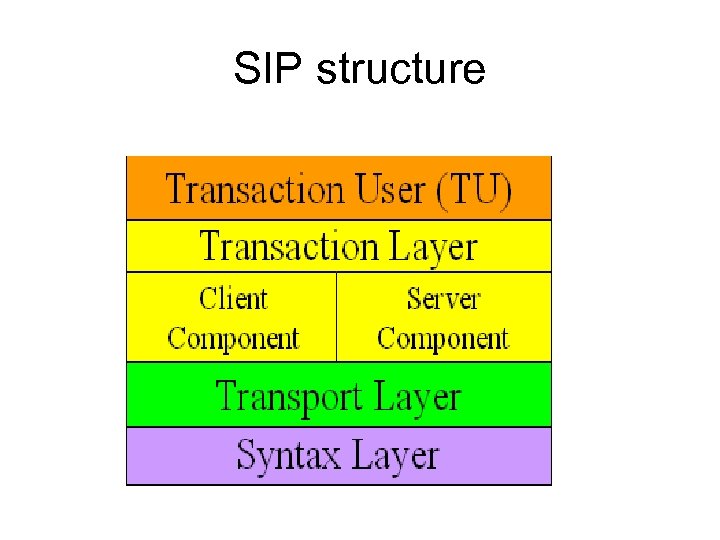 SIP structure
SIP structure
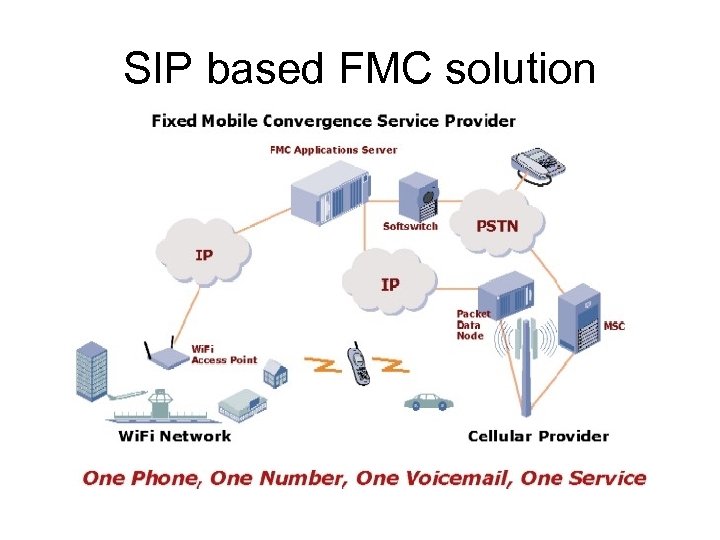 SIP based FMC solution
SIP based FMC solution
 SIP in FMC • FMC is likely to bring to reality the following scenarios hitherto considered impossible. – A cell phone user may start receiving calls on his SIP home phone when he enters his home, saving spectrum and charges for the ‘home roaming usage’. This kind of hand-off is both extremely non-intrusive and cost beneficial. – Enterprise subscribers may roam their mobile number into a business environment via one to many SIP devices. This may be offered by a service bureau as a managed service.
SIP in FMC • FMC is likely to bring to reality the following scenarios hitherto considered impossible. – A cell phone user may start receiving calls on his SIP home phone when he enters his home, saving spectrum and charges for the ‘home roaming usage’. This kind of hand-off is both extremely non-intrusive and cost beneficial. – Enterprise subscribers may roam their mobile number into a business environment via one to many SIP devices. This may be offered by a service bureau as a managed service.
 Contd… • Enterprise subscribers may roam their mobile numbers in their enterprise network via one to several SIP devices. This further establishes that none of the existing infrastructure will be rendered a waste. • Mobile subscribers may continue enjoying all enhanced services available on their home PLMN networks in any roaming network they are visiting and on their landline networks as well. • Mobile subscribers may seamlessly roam between locations with calls transparently following them irrespective of whether they are in a cable zone or a public Wi. Fi hot spot.
Contd… • Enterprise subscribers may roam their mobile numbers in their enterprise network via one to several SIP devices. This further establishes that none of the existing infrastructure will be rendered a waste. • Mobile subscribers may continue enjoying all enhanced services available on their home PLMN networks in any roaming network they are visiting and on their landline networks as well. • Mobile subscribers may seamlessly roam between locations with calls transparently following them irrespective of whether they are in a cable zone or a public Wi. Fi hot spot.
 SIP in IMS • The key technology behind IMS is the SIP protocol • Advantages of SIP – Simple – Extensible – Flexible – Familiar
SIP in IMS • The key technology behind IMS is the SIP protocol • Advantages of SIP – Simple – Extensible – Flexible – Familiar
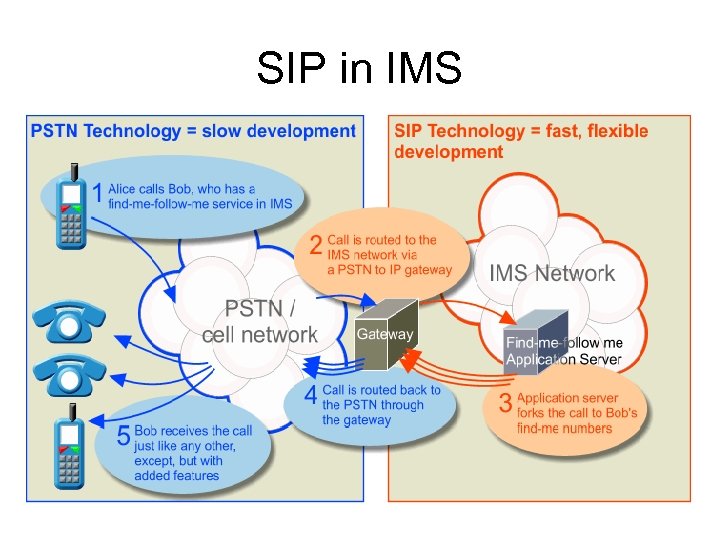 SIP in IMS
SIP in IMS

 Introduction to IMS • IMS stands for IP Multimedia Subsystem • IMS is a key enabler of Fixed-Mobile Convergence • IMS is an architecture that merges the applications and capabilities of the Internet with both wireless and wire line telephony, and promotes fixed/mobile convergence. • An IMS/SIP approach enables both voice and data applications to run over IP, rather than locking it into the mobile carriers' legacy networks.
Introduction to IMS • IMS stands for IP Multimedia Subsystem • IMS is a key enabler of Fixed-Mobile Convergence • IMS is an architecture that merges the applications and capabilities of the Internet with both wireless and wire line telephony, and promotes fixed/mobile convergence. • An IMS/SIP approach enables both voice and data applications to run over IP, rather than locking it into the mobile carriers' legacy networks.
 Layered Approach • Access Network – Transport ( Connectivity) layer • Core Network – Control Layer – Service Layer
Layered Approach • Access Network – Transport ( Connectivity) layer • Core Network – Control Layer – Service Layer
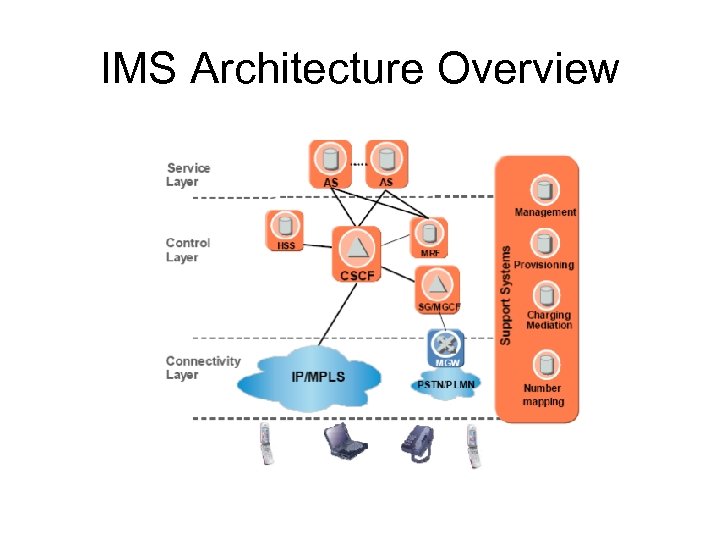 IMS Architecture Overview
IMS Architecture Overview
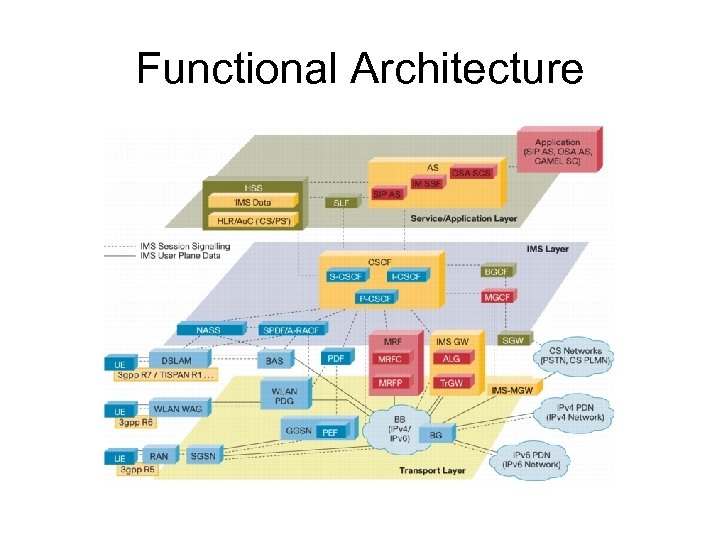 Functional Architecture
Functional Architecture
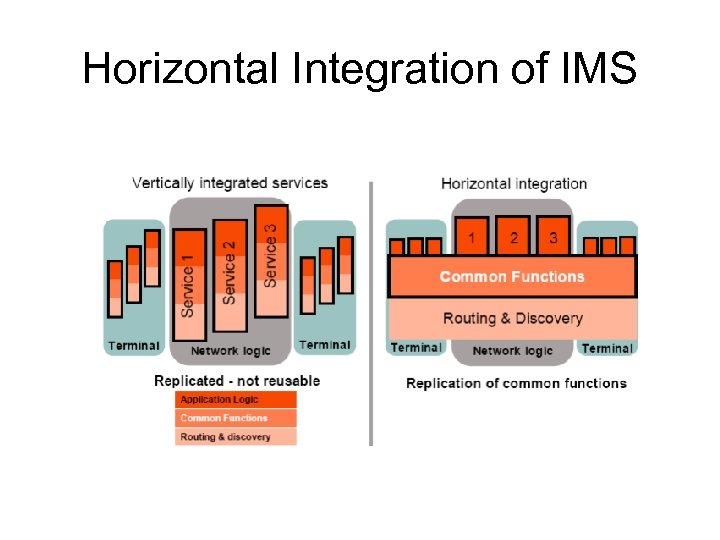 Horizontal Integration of IMS
Horizontal Integration of IMS
 Advantages of Horizontal Integration • Service Enablers and common functions can be reused for multiple operations • Operations competence required is more generic • Helps to provide interoperability and reaming and other such functions more economically to the consumer
Advantages of Horizontal Integration • Service Enablers and common functions can be reused for multiple operations • Operations competence required is more generic • Helps to provide interoperability and reaming and other such functions more economically to the consumer
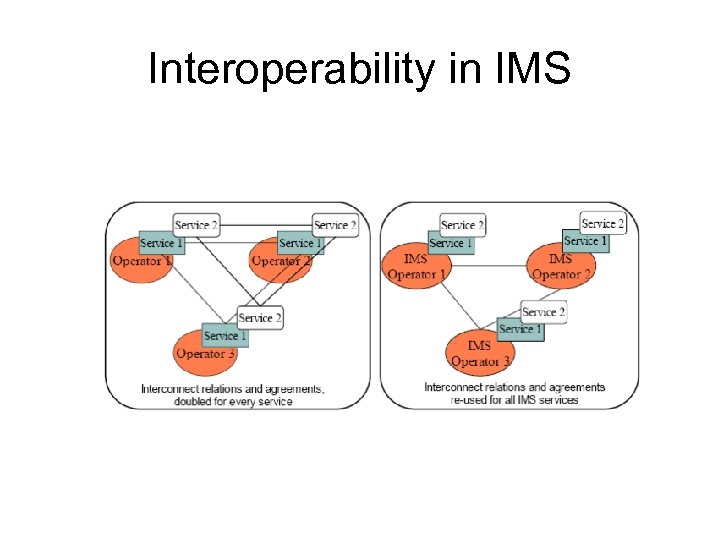 Interoperability in IMS
Interoperability in IMS
 Advantages over Existing Systems • The core network is independent of a particular access technology ( GSM, WCDMA, CDMA and also WLAN) • Integrated mobility for all network applications • Easier migration of applications from fixed to mobile users • Faster deployment of new services based on standardized architecture
Advantages over Existing Systems • The core network is independent of a particular access technology ( GSM, WCDMA, CDMA and also WLAN) • Integrated mobility for all network applications • Easier migration of applications from fixed to mobile users • Faster deployment of new services based on standardized architecture
 Advantages over Existing Systems • New applications such as presence information, videoconferencing, Push to talk over cellular (POC), multiparty gaming, community services and content sharing. • Evolution to combinational services, for example by combining instant messaging and voice • User profiles are stored in a central location
Advantages over Existing Systems • New applications such as presence information, videoconferencing, Push to talk over cellular (POC), multiparty gaming, community services and content sharing. • Evolution to combinational services, for example by combining instant messaging and voice • User profiles are stored in a central location
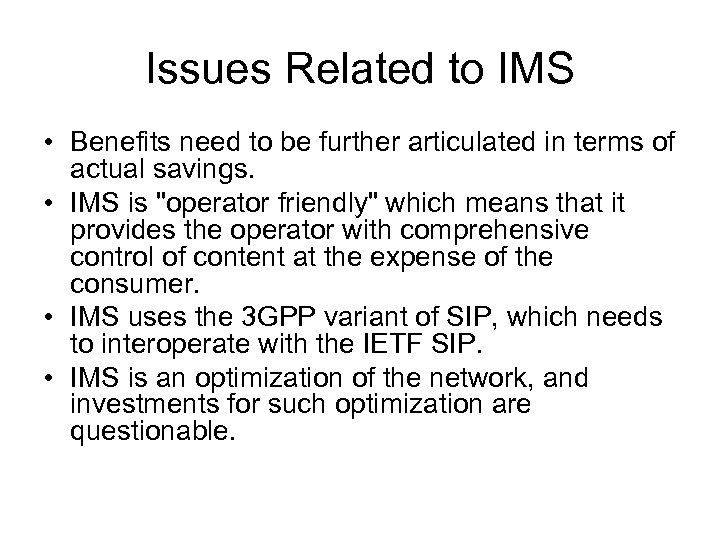 Issues Related to IMS • Benefits need to be further articulated in terms of actual savings. • IMS is "operator friendly" which means that it provides the operator with comprehensive control of content at the expense of the consumer. • IMS uses the 3 GPP variant of SIP, which needs to interoperate with the IETF SIP. • IMS is an optimization of the network, and investments for such optimization are questionable.
Issues Related to IMS • Benefits need to be further articulated in terms of actual savings. • IMS is "operator friendly" which means that it provides the operator with comprehensive control of content at the expense of the consumer. • IMS uses the 3 GPP variant of SIP, which needs to interoperate with the IETF SIP. • IMS is an optimization of the network, and investments for such optimization are questionable.
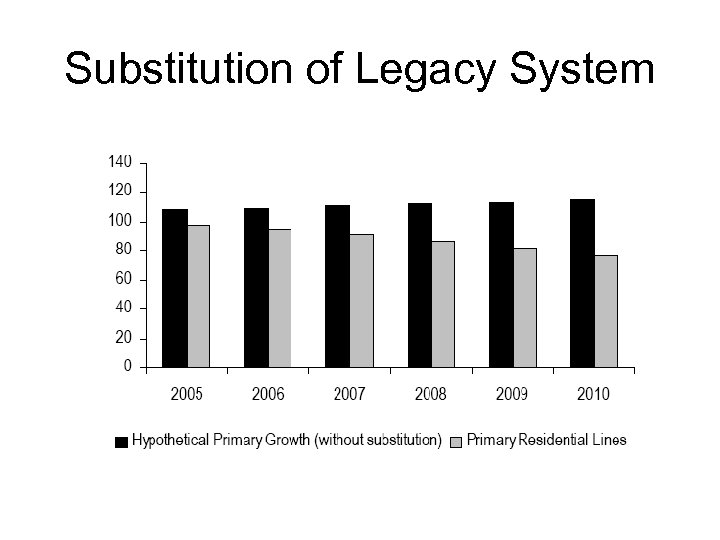 Substitution of Legacy System
Substitution of Legacy System
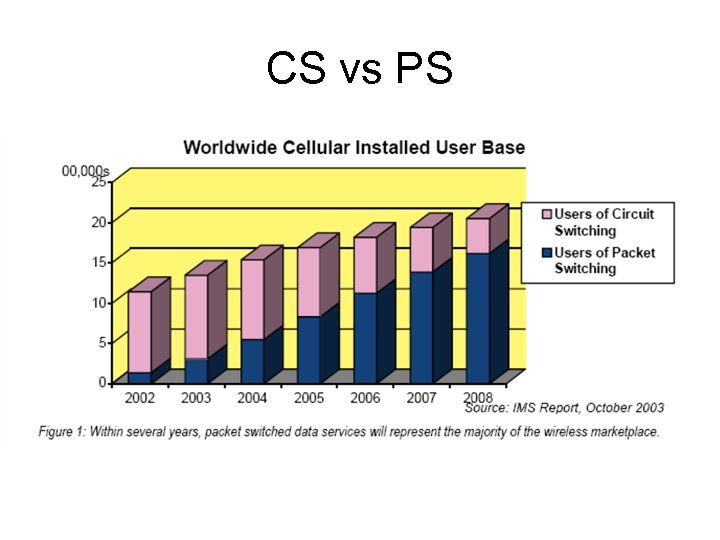 CS vs PS
CS vs PS

 What is UMA? Unlicensed Mobile Access §Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) technology provides access to GSM and GPRS mobile services over unlicensed spectrum technologies, including Bluetooth and 802. 11. § It establishes a standard for seamless hand -off and roaming between a cellular network and fixed IP-based wireless networks.
What is UMA? Unlicensed Mobile Access §Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) technology provides access to GSM and GPRS mobile services over unlicensed spectrum technologies, including Bluetooth and 802. 11. § It establishes a standard for seamless hand -off and roaming between a cellular network and fixed IP-based wireless networks.
 UMA • UMA lets mobile operators deliver voice, data and IMS/SIP(IP Multi media Subsystem /Session Initiated Protocol) applications to mobile phones on Wi-Fi access network using dual-mode mobile handsets. • In order to promote the widespread adoption of UMA technology, a number of leading companies within the wireless industry have jointly developed a set of open specifications.
UMA • UMA lets mobile operators deliver voice, data and IMS/SIP(IP Multi media Subsystem /Session Initiated Protocol) applications to mobile phones on Wi-Fi access network using dual-mode mobile handsets. • In order to promote the widespread adoption of UMA technology, a number of leading companies within the wireless industry have jointly developed a set of open specifications.
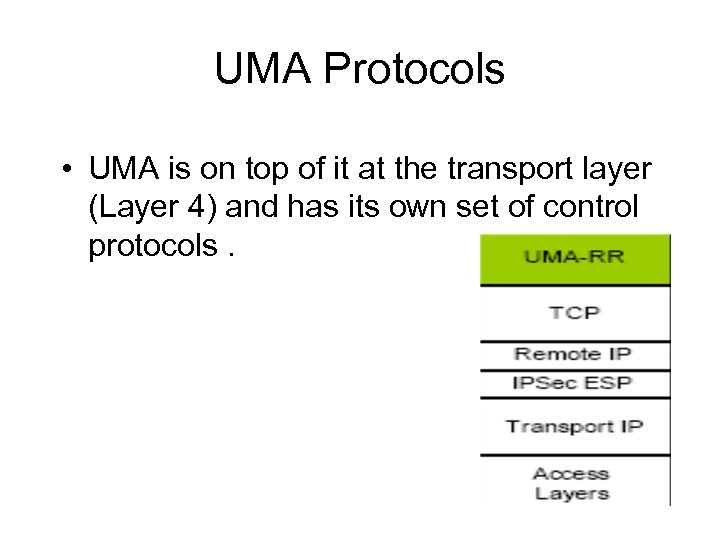 UMA Protocols • UMA is on top of it at the transport layer (Layer 4) and has its own set of control protocols.
UMA Protocols • UMA is on top of it at the transport layer (Layer 4) and has its own set of control protocols.
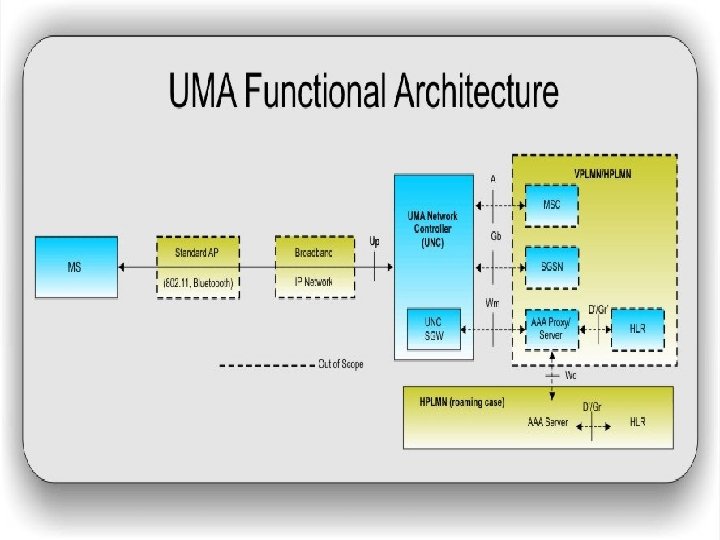
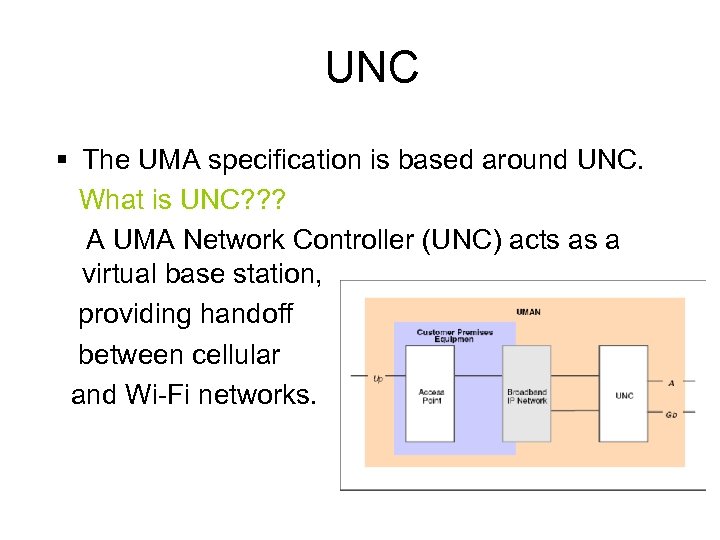 UNC § The UMA specification is based around UNC. What is UNC? ? ? A UMA Network Controller (UNC) acts as a virtual base station, providing handoff between cellular and Wi-Fi networks.
UNC § The UMA specification is based around UNC. What is UNC? ? ? A UMA Network Controller (UNC) acts as a virtual base station, providing handoff between cellular and Wi-Fi networks.
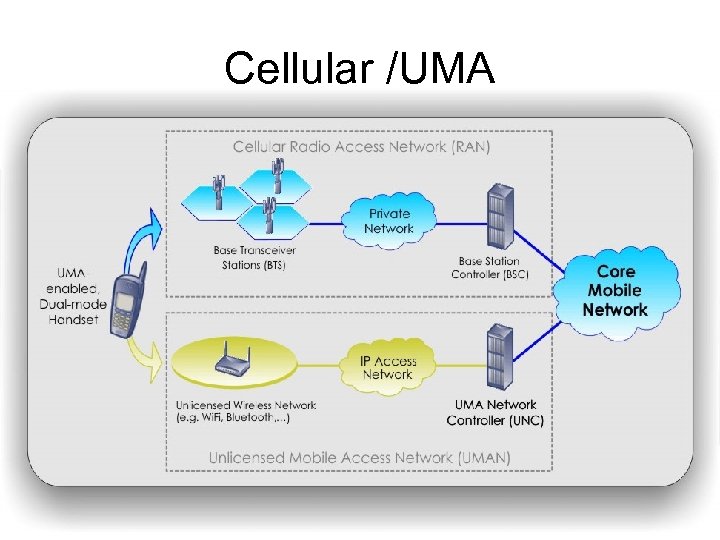 Cellular /UMA
Cellular /UMA
 How UMA Technology Works • A mobile subscriber with a UMA-enabled, dual-mode handset moves within range of an unlicensed wireless network to which the handset is allowed to connect. • Upon connecting, the handset contacts the UMA Network Controller (UNC) over the broadband IP access network to be authenticated and authorized to access GSM voice and GPRS data services via the unlicensed wireless network.
How UMA Technology Works • A mobile subscriber with a UMA-enabled, dual-mode handset moves within range of an unlicensed wireless network to which the handset is allowed to connect. • Upon connecting, the handset contacts the UMA Network Controller (UNC) over the broadband IP access network to be authenticated and authorized to access GSM voice and GPRS data services via the unlicensed wireless network.
 (Contd. . ) • If approved, the subscriber’s current location information stored in the core network is updated, and from that point on all mobile voice and data traffic is routed to the handset via the Unlicensed Mobile Access Network (UMAN) rather than the cellular radio access network (RAN).
(Contd. . ) • If approved, the subscriber’s current location information stored in the core network is updated, and from that point on all mobile voice and data traffic is routed to the handset via the Unlicensed Mobile Access Network (UMAN) rather than the cellular radio access network (RAN).
 Roaming • When a UMA-enabled subscriber moves outside the range of an unlicensed wireless network to which they are connected, the UNC and handset facilitate roaming back to the licensed outdoor network. This roaming process is completely transparent to the subscriber.
Roaming • When a UMA-enabled subscriber moves outside the range of an unlicensed wireless network to which they are connected, the UNC and handset facilitate roaming back to the licensed outdoor network. This roaming process is completely transparent to the subscriber.
 Handover § Handover in: The mobile station moves from macro network to a UMAN. § Handover out: The mobile station moves from UMAN to macro network. § Handover UMA: The mobile station moves with in a UMAN or from UMAN to UMAN.
Handover § Handover in: The mobile station moves from macro network to a UMAN. § Handover out: The mobile station moves from UMAN to macro network. § Handover UMA: The mobile station moves with in a UMAN or from UMAN to UMAN.
 Handoff Specifications q Subject to mode selection, UMA shall support seamless handover in and handover out , provided the following conditions are true: § The mobile station stays within the limits of service (pedestrian state of motion) § The mobile station remains during the time of handover within the coverage of both the networks. § UMA shall manage bandwidth during handover between macro network and UMAN.
Handoff Specifications q Subject to mode selection, UMA shall support seamless handover in and handover out , provided the following conditions are true: § The mobile station stays within the limits of service (pedestrian state of motion) § The mobile station remains during the time of handover within the coverage of both the networks. § UMA shall manage bandwidth during handover between macro network and UMAN.
 Security in UMA Different security mechanism operate at different levels: • MS to AP – UMA does not mandate any security mechanism, but can coexist with those available, such WPA, WPA 2, or WEP. • MS to UNC – The UNC includes a security gateway that provides mutual authentication and encryption for the traffic across the WLAN and the broadband connection. • MS to core mobile network – The encryption and authentication methods used by the MS when using the GERAN are also used to protect UMA connections. • MS to application server – An additional end-to-end data application mechanism (for example, HTTPS) may be used if needed.
Security in UMA Different security mechanism operate at different levels: • MS to AP – UMA does not mandate any security mechanism, but can coexist with those available, such WPA, WPA 2, or WEP. • MS to UNC – The UNC includes a security gateway that provides mutual authentication and encryption for the traffic across the WLAN and the broadband connection. • MS to core mobile network – The encryption and authentication methods used by the MS when using the GERAN are also used to protect UMA connections. • MS to application server – An additional end-to-end data application mechanism (for example, HTTPS) may be used if needed.
 Advantages Availability & Pricing § UMA could be used to provide better inbuilding coverage for customers who don't get a good cellular signal in some areas, including basements. § It enables service providers to deliver voice at a lower cost when handsets are within range of an unlicensed wireless network.
Advantages Availability & Pricing § UMA could be used to provide better inbuilding coverage for customers who don't get a good cellular signal in some areas, including basements. § It enables service providers to deliver voice at a lower cost when handsets are within range of an unlicensed wireless network.
 Issues § If a customer doesn't have a wireless network already in the house, a wireless access point would be needed in addition to a broadband link. § The most expensive and technologically challenging component of UMA solution is the Wi-Fi and cellular handset, because of battery-life limitations, cost, and size. § UMA cannot guarantee the quality of a voice call or the throughput of a data connection and traffic prioritization with Qo. S can significantly improve performance, especially in a residential environment where traffic is likely to be less heavy than in the enterprise. http: //www. arcchart. com/blueprint/show. asp? id=368
Issues § If a customer doesn't have a wireless network already in the house, a wireless access point would be needed in addition to a broadband link. § The most expensive and technologically challenging component of UMA solution is the Wi-Fi and cellular handset, because of battery-life limitations, cost, and size. § UMA cannot guarantee the quality of a voice call or the throughput of a data connection and traffic prioritization with Qo. S can significantly improve performance, especially in a residential environment where traffic is likely to be less heavy than in the enterprise. http: //www. arcchart. com/blueprint/show. asp? id=368
 Pre-IMS Solution – UMA or Mobile/WLAN Convergence Implementations • • WLAN/GPRS “Handover” by Nokia WLAN/GSM Vo. IP terminal announced by Motorola NTT Do. Co. Mo: FOMA – Wi. Fi 1) BT “Fusion”: GSM – Wi. Fi 1) France Telecom “Business Anywhere”: GPRS-Wi. Fi 1) O 2 Germany “surf@home”: UMTS-Wi. Fi 1) Korean KT & KTF “One. Phone”: CDMA – Bluetooth 2) Dual Phone, by Deutche Telekom’s T-Com 3) Sources: 1. Gianluca Zaffiro (Telecom Italia), Convergent Data and Voice Solutions - Data and Voice Solutions Evolution towards an integrated IP Architecture, 3 G World Congress, November 2005 2. Dr. Hoon HAN (KTF), Vision for Korea’s wireless/ICT Industry - New opportunities and directions, 3 G World Congress, November 2005 3. International Herald Tribune, 5 September 2005
Pre-IMS Solution – UMA or Mobile/WLAN Convergence Implementations • • WLAN/GPRS “Handover” by Nokia WLAN/GSM Vo. IP terminal announced by Motorola NTT Do. Co. Mo: FOMA – Wi. Fi 1) BT “Fusion”: GSM – Wi. Fi 1) France Telecom “Business Anywhere”: GPRS-Wi. Fi 1) O 2 Germany “surf@home”: UMTS-Wi. Fi 1) Korean KT & KTF “One. Phone”: CDMA – Bluetooth 2) Dual Phone, by Deutche Telekom’s T-Com 3) Sources: 1. Gianluca Zaffiro (Telecom Italia), Convergent Data and Voice Solutions - Data and Voice Solutions Evolution towards an integrated IP Architecture, 3 G World Congress, November 2005 2. Dr. Hoon HAN (KTF), Vision for Korea’s wireless/ICT Industry - New opportunities and directions, 3 G World Congress, November 2005 3. International Herald Tribune, 5 September 2005
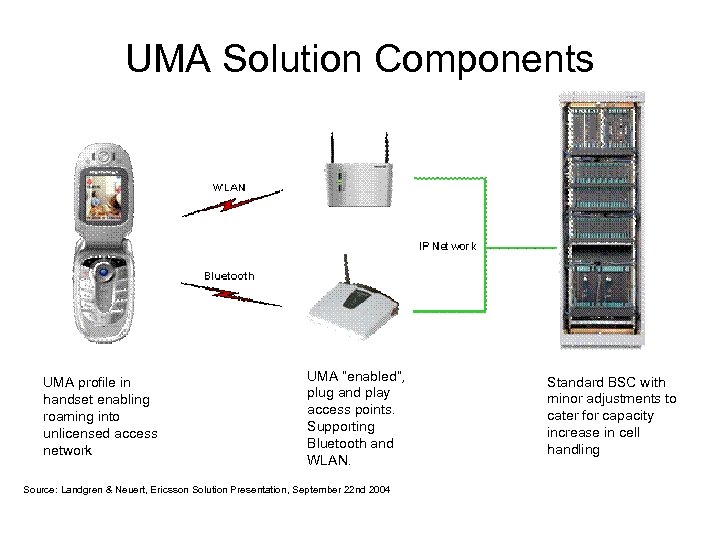 UMA Solution Components UMA profile in handset enabling roaming into unlicensed access network UMA “enabled”, plug and play access points. Supporting Bluetooth and WLAN. Source: Landgren & Neuert, Ericsson Solution Presentation, September 22 nd 2004 Standard BSC with minor adjustments to cater for capacity increase in cell handling
UMA Solution Components UMA profile in handset enabling roaming into unlicensed access network UMA “enabled”, plug and play access points. Supporting Bluetooth and WLAN. Source: Landgren & Neuert, Ericsson Solution Presentation, September 22 nd 2004 Standard BSC with minor adjustments to cater for capacity increase in cell handling
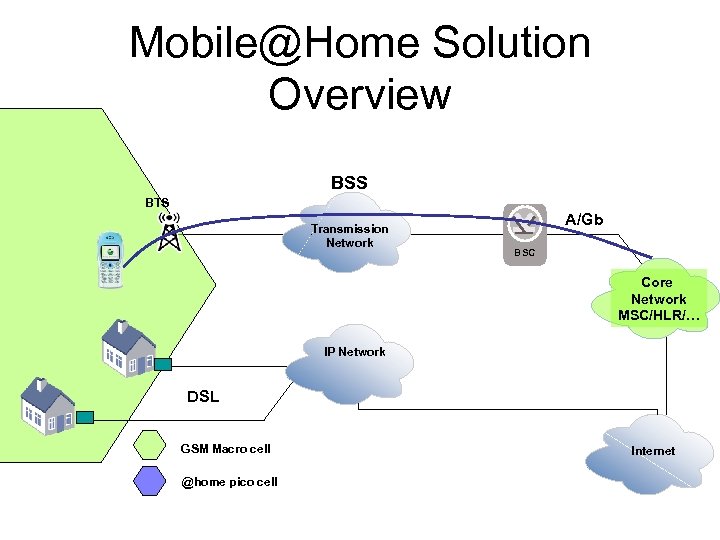 Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… IP Network DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… IP Network DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
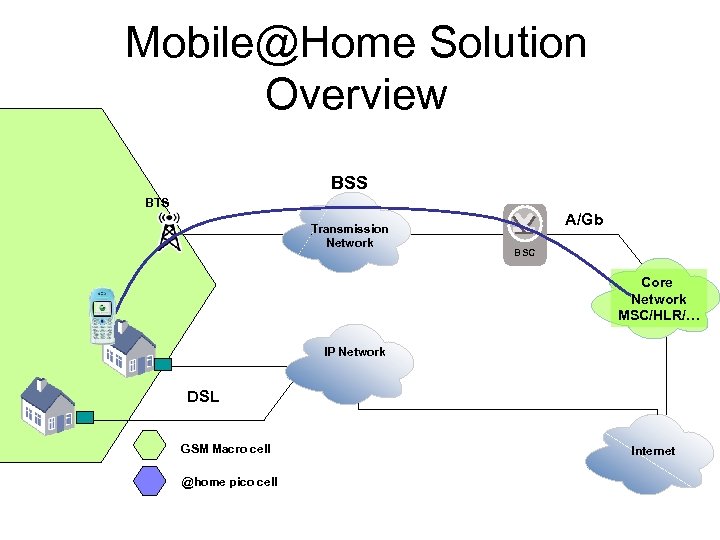 Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… IP Network DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… IP Network DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
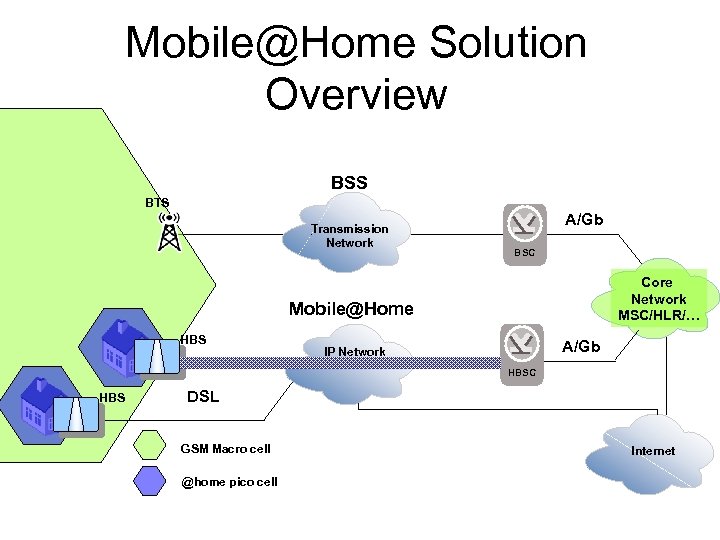 Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… Mobile@Home HBS A/Gb IP Network HBSC HBS DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… Mobile@Home HBS A/Gb IP Network HBSC HBS DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
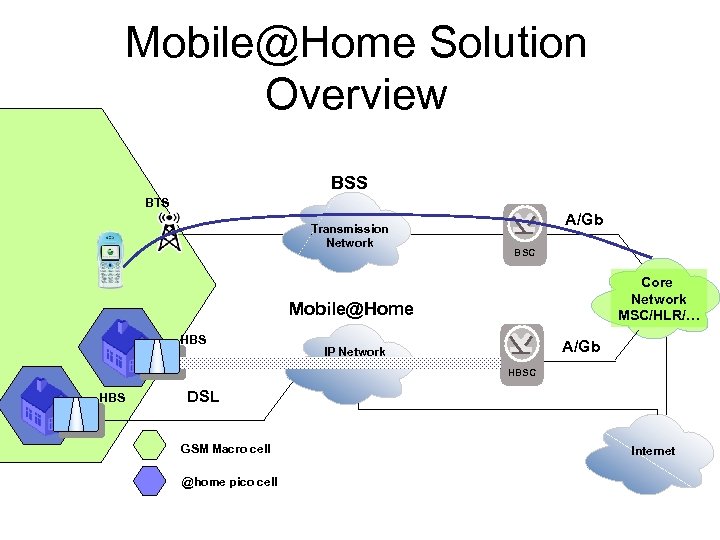 Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… Mobile@Home HBS A/Gb IP Network HBSC HBS DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… Mobile@Home HBS A/Gb IP Network HBSC HBS DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
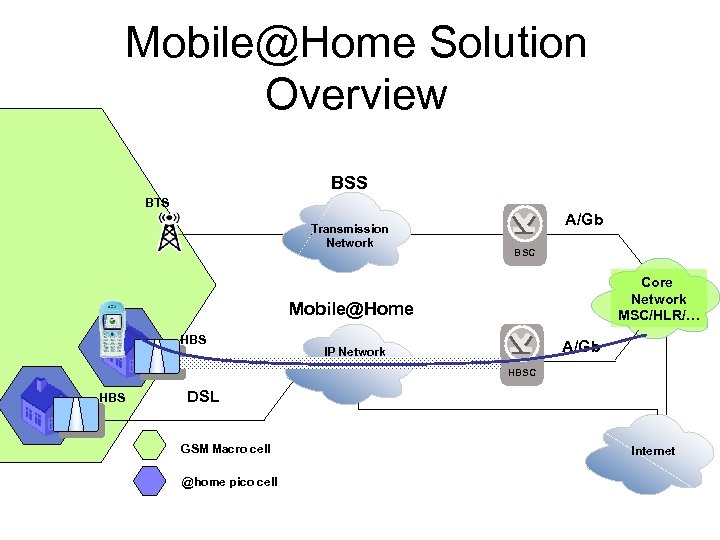 Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… Mobile@Home HBS A/Gb IP Network HBSC HBS DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet
Mobile@Home Solution Overview BSS BTS Transmission Network A/Gb BSC Core Network MSC/HLR/… Mobile@Home HBS A/Gb IP Network HBSC HBS DSL GSM Macro cell @home pico cell Internet


