7e512162446c4568af96e9ef3f7f1a67.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 75
 Topics Electronic Commerce l Transaction Processing Systems l Enterprise Resource Planning l
Topics Electronic Commerce l Transaction Processing Systems l Enterprise Resource Planning l
 An Introduction to Electronic Commerce
An Introduction to Electronic Commerce
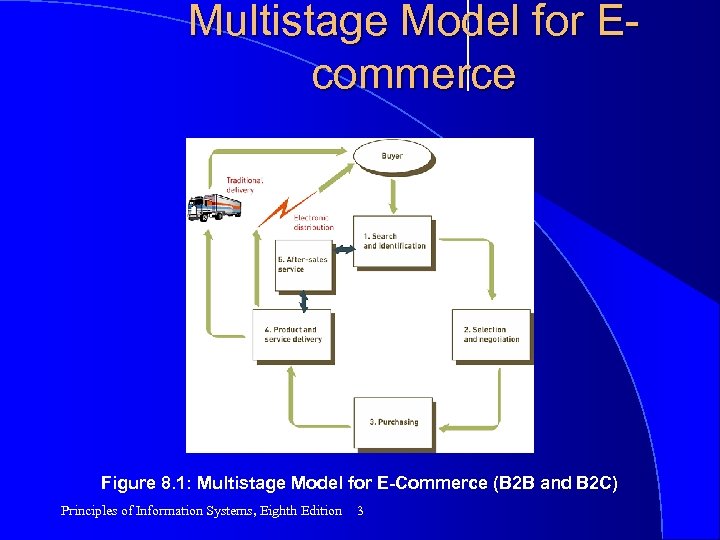 Multistage Model for Ecommerce Figure 8. 1: Multistage Model for E-Commerce (B 2 B and B 2 C) Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 3
Multistage Model for Ecommerce Figure 8. 1: Multistage Model for E-Commerce (B 2 B and B 2 C) Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 3
 E-Commerce Challenges Define strategy l Change distribution systems & work processes l Integrate web-based order processing with traditional systems l
E-Commerce Challenges Define strategy l Change distribution systems & work processes l Integrate web-based order processing with traditional systems l
 E-Commerce Challenges (continued) Figure 8. 3: Three Basic Components of a Successful E-Commerce Model Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 5
E-Commerce Challenges (continued) Figure 8. 3: Three Basic Components of a Successful E-Commerce Model Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 5
 Forms of E-Commerce Business to Business (B 2 B) l Business to Consumer (B 2 C) l
Forms of E-Commerce Business to Business (B 2 B) l Business to Consumer (B 2 C) l
 E-Commerce Applications
E-Commerce Applications
 Retail and Wholesale E-tailing: electronic retailing l Cybermalls l Wholesale e-commerce: B 2 B l
Retail and Wholesale E-tailing: electronic retailing l Cybermalls l Wholesale e-commerce: B 2 B l
 E-Commerce Challenges (continued) Figure 8. 4: Web-Based Order Processing Must Be Linked to Traditional Back-End Systems Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 9
E-Commerce Challenges (continued) Figure 8. 4: Web-Based Order Processing Must Be Linked to Traditional Back-End Systems Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 9
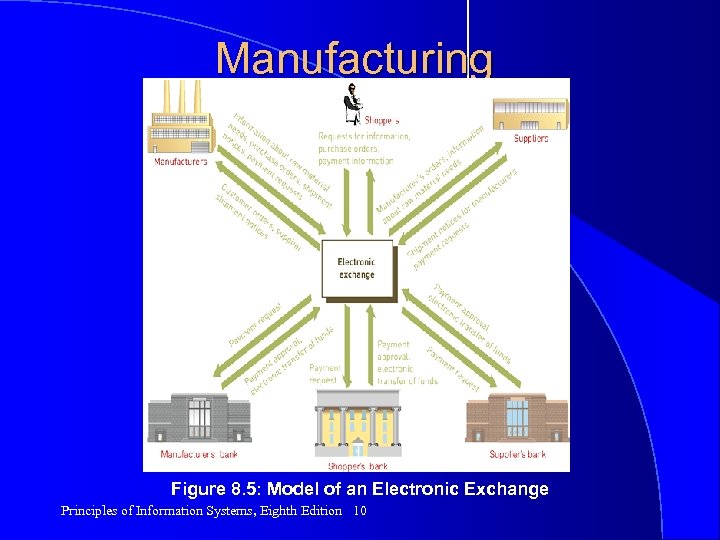 Manufacturing Figure 8. 5: Model of an Electronic Exchange Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 10
Manufacturing Figure 8. 5: Model of an Electronic Exchange Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 10
 Technology Infrastructure
Technology Infrastructure
 Required To Support Ecommerce and M-commerce (continued) Figure 8. 6: Key Technology Infrastructure Components Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 12
Required To Support Ecommerce and M-commerce (continued) Figure 8. 6: Key Technology Infrastructure Components Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 12
 Web Server Hardware l Server platform – Hardware – Operating system l Website hosting – Capital investment – Technical staff l Must run 24 -7 -365 to avoid disrupting business & losing customers
Web Server Hardware l Server platform – Hardware – Operating system l Website hosting – Capital investment – Technical staff l Must run 24 -7 -365 to avoid disrupting business & losing customers
 Web Server Software Security & identification l Encryption l Retrieving & sending web pages l Web site tracking l
Web Server Software Security & identification l Encryption l Retrieving & sending web pages l Web site tracking l
 E-Commerce Software Catalog management l Product configuration l Shopping cart l Transaction processing l Traffic data analysis l
E-Commerce Software Catalog management l Product configuration l Shopping cart l Transaction processing l Traffic data analysis l
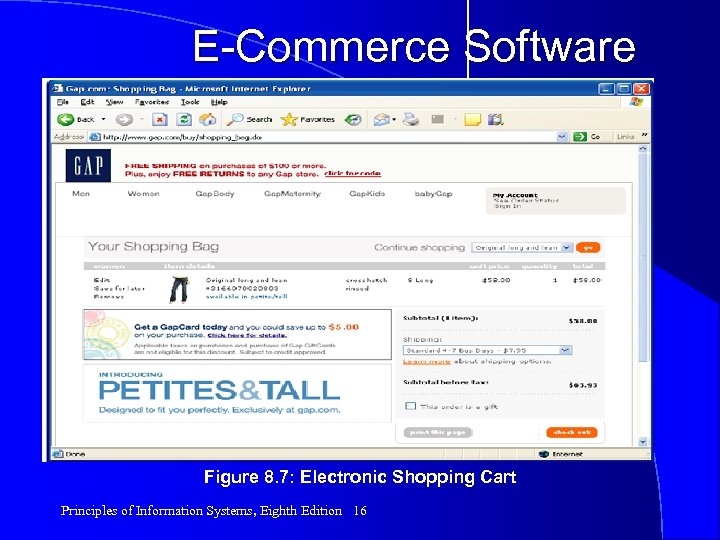 E-Commerce Software Figure 8. 7: Electronic Shopping Cart Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 16
E-Commerce Software Figure 8. 7: Electronic Shopping Cart Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 16
 Network Selection Cost l Availability l Reliability l Security l Redundancy l
Network Selection Cost l Availability l Reliability l Security l Redundancy l
 Electronic Payment Systems
Electronic Payment Systems
 Payment Security l Authentication – Digital certificate – Certificate authority (CA) l Encryption – Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Payment Security l Authentication – Digital certificate – Certificate authority (CA) l Encryption – Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
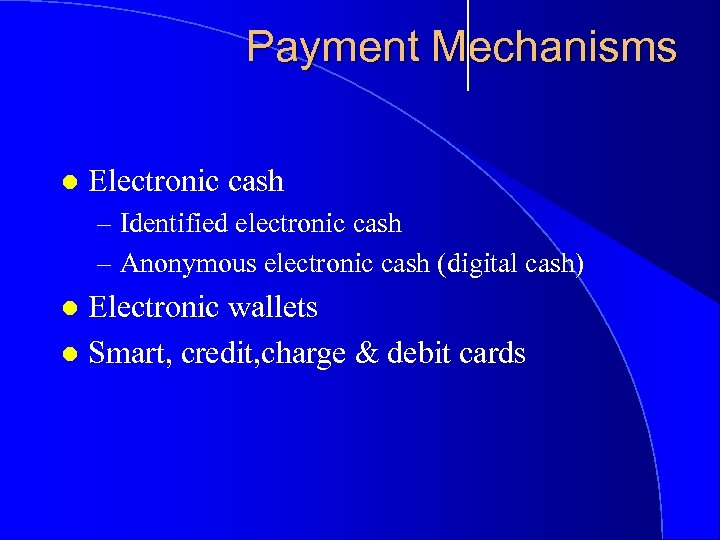 Payment Mechanisms l Electronic cash – Identified electronic cash – Anonymous electronic cash (digital cash) Electronic wallets l Smart, credit, charge & debit cards l
Payment Mechanisms l Electronic cash – Identified electronic cash – Anonymous electronic cash (digital cash) Electronic wallets l Smart, credit, charge & debit cards l
 Threats to E-Commerce
Threats to E-Commerce
 Threats to E-Commerce Security
Threats to E-Commerce Security
 Threats to E-Commerce Intellectual property l Fraud l – On-line auctions – Spam – Pyramid schemes – Investment fraud – Stock scams
Threats to E-Commerce Intellectual property l Fraud l – On-line auctions – Spam – Pyramid schemes – Investment fraud – Stock scams
 Threats to E-Commerce l Privacy – Online profiling – Clickstream data
Threats to E-Commerce l Privacy – Online profiling – Clickstream data
 TRUSTe Seal
TRUSTe Seal
 BBB Online Privacy Seal
BBB Online Privacy Seal
 How to Protect Your Privacy While Online
How to Protect Your Privacy While Online
 Strategies for Successful E-Commerce
Strategies for Successful E-Commerce
 Developing an Effective Web Presence Obtain information l Learn about products or services l Buy products or services l Check order status l Provide feedback or complaints l
Developing an Effective Web Presence Obtain information l Learn about products or services l Buy products or services l Check order status l Provide feedback or complaints l
 Putting Up a Web Site In-house development l Web site hosting companies l Storefront brokers l
Putting Up a Web Site In-house development l Web site hosting companies l Storefront brokers l
 Driving Traffic to Your Web Site Domain names l Meta tags l Traffic logs l
Driving Traffic to Your Web Site Domain names l Meta tags l Traffic logs l
 An Overview of Transaction Processing Systems
An Overview of Transaction Processing Systems
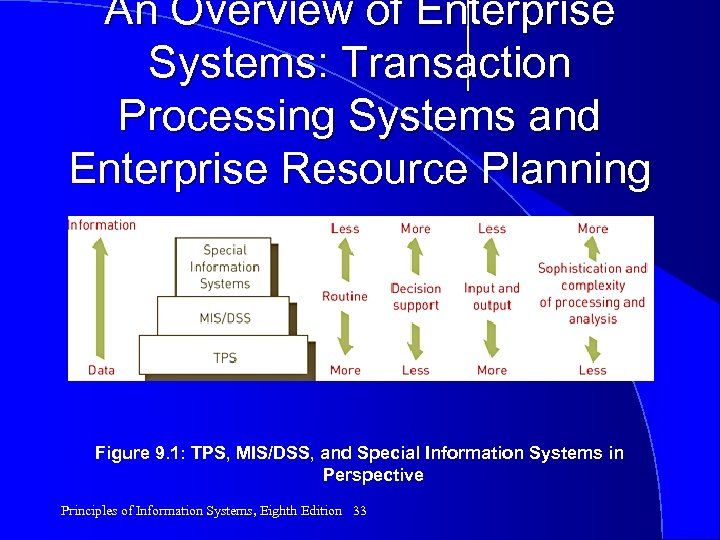 An Overview of Enterprise Systems: Transaction Processing Systems and Enterprise Resource Planning Figure 9. 1: TPS, MIS/DSS, and Special Information Systems in Perspective Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 33
An Overview of Enterprise Systems: Transaction Processing Systems and Enterprise Resource Planning Figure 9. 1: TPS, MIS/DSS, and Special Information Systems in Perspective Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 33
 Traditional Transaction Processing Methods & Objectives Batch l On-line l – Real-time – Online transaction processing (OLTP) l On-line entry with delayed processing
Traditional Transaction Processing Methods & Objectives Batch l On-line l – Real-time – Online transaction processing (OLTP) l On-line entry with delayed processing
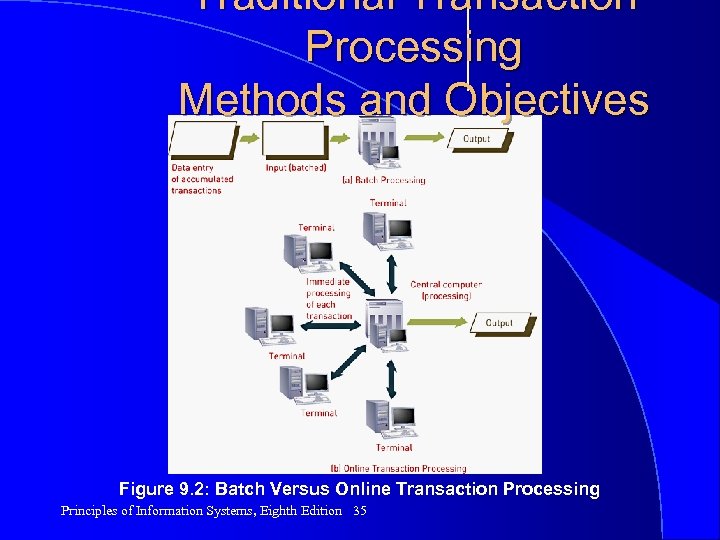 Traditional Transaction Processing Methods and Objectives Figure 9. 2: Batch Versus Online Transaction Processing Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 35
Traditional Transaction Processing Methods and Objectives Figure 9. 2: Batch Versus Online Transaction Processing Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 35
 Objectives of a Transaction Processing System Process data generated for and about transactions. l Maintain a high degree of accuracy and integrity. l Produce timely documents & reports l
Objectives of a Transaction Processing System Process data generated for and about transactions. l Maintain a high degree of accuracy and integrity. l Produce timely documents & reports l
 Objectives of a Transaction Processing System Increase labor efficiency l Help provide improved service l Help build and maintain customer loyalty l Achieve competitive advantage l
Objectives of a Transaction Processing System Increase labor efficiency l Help provide improved service l Help build and maintain customer loyalty l Achieve competitive advantage l
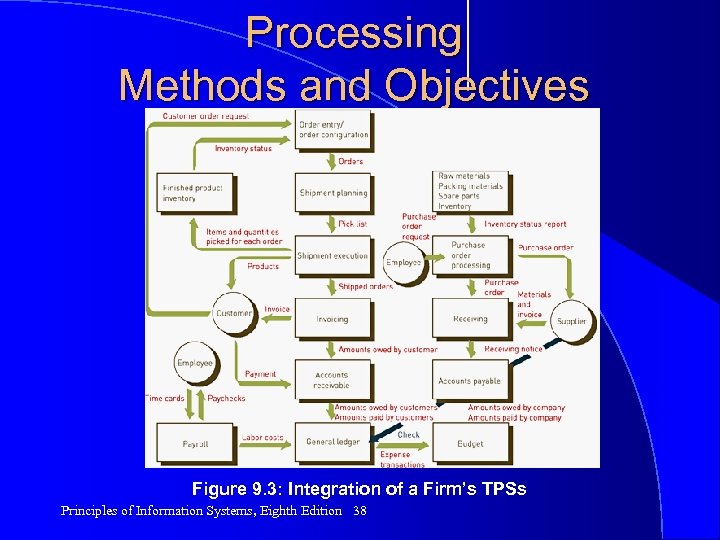 Processing Methods and Objectives (continued) Figure 9. 3: Integration of a Firm’s TPSs Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 38
Processing Methods and Objectives (continued) Figure 9. 3: Integration of a Firm’s TPSs Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 38
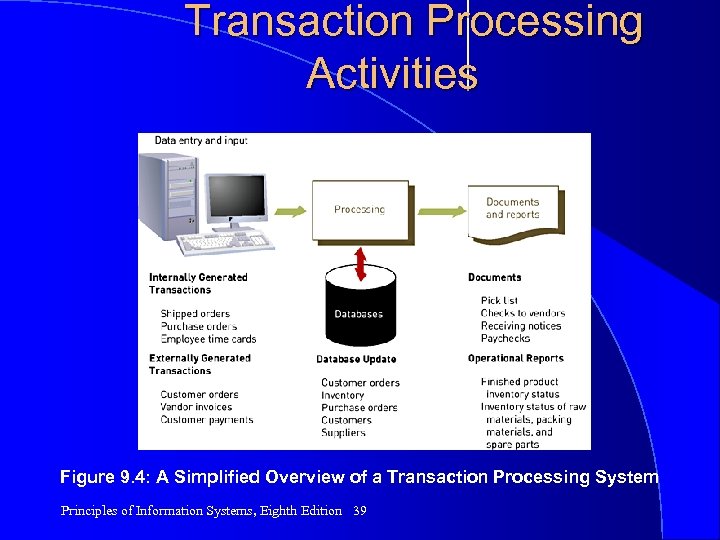 Transaction Processing Activities Figure 9. 4: A Simplified Overview of a Transaction Processing System Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 39
Transaction Processing Activities Figure 9. 4: A Simplified Overview of a Transaction Processing System Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 39
 Control & Management Issues Business resumption planning l Disaster recovery l – Backups – Hot sites – Cold sites l Backups
Control & Management Issues Business resumption planning l Disaster recovery l – Backups – Hot sites – Cold sites l Backups
 Transaction Processing Audit – Does the system meet its business requirements? – Are there procedures and controls? – Are the procedures & controls properly used?
Transaction Processing Audit – Does the system meet its business requirements? – Are there procedures and controls? – Are the procedures & controls properly used?
 Traditional Transaction Processing Applications
Traditional Transaction Processing Applications
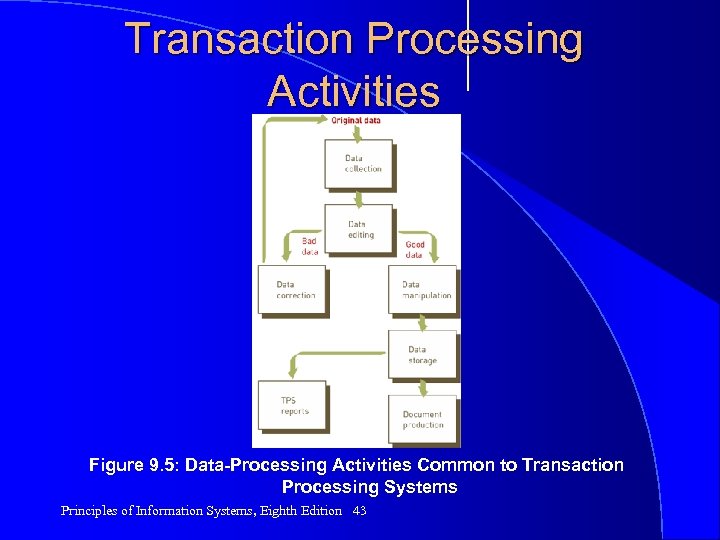 Transaction Processing Activities Figure 9. 5: Data-Processing Activities Common to Transaction Processing Systems Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 43
Transaction Processing Activities Figure 9. 5: Data-Processing Activities Common to Transaction Processing Systems Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 43
 Data Collection Capturing and gathering all data necessary to complete the processing of transactions l Data collection can be: l – Manual – Automated via special input devices (such as scanners, point-of-sale devices, and terminals) l Data should be: – Collected at source Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition – Recorded accurately, in a timely fashion 44
Data Collection Capturing and gathering all data necessary to complete the processing of transactions l Data collection can be: l – Manual – Automated via special input devices (such as scanners, point-of-sale devices, and terminals) l Data should be: – Collected at source Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition – Recorded accurately, in a timely fashion 44
 Data Editing Checking data for validity and completeness to detect any problems l Examples l – Quantity and cost data must be numeric – Names must be alphabetic – Verification that codes associated with an individual transaction are present in a database containing valid codes Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 45
Data Editing Checking data for validity and completeness to detect any problems l Examples l – Quantity and cost data must be numeric – Names must be alphabetic – Verification that codes associated with an individual transaction are present in a database containing valid codes Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 45
 Data Correction Reentering data that was not typed or scanned properly l If invalid data is detected, system should provide error messages l – Error messages must specify the problem so proper corrections can be made l Software tools can be used to identify bad data – Example: Business Objects IQEdition Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Insight 46
Data Correction Reentering data that was not typed or scanned properly l If invalid data is detected, system should provide error messages l – Error messages must specify the problem so proper corrections can be made l Software tools can be used to identify bad data – Example: Business Objects IQEdition Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Insight 46
 Data Manipulation Performing calculations and other data transformations related to business transactions l Can include the following: l – Classifying data – Sorting data into categories – Performing calculations – Summarizing results Principles Information Systems, Eighth Edition – Storing data inofthe organization’s database for 47
Data Manipulation Performing calculations and other data transformations related to business transactions l Can include the following: l – Classifying data – Sorting data into categories – Performing calculations – Summarizing results Principles Information Systems, Eighth Edition – Storing data inofthe organization’s database for 47
 Data Storage Updating one or more databases with new transactions l After being updated, this data can be further processed and manipulated by other systems l Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 48
Data Storage Updating one or more databases with new transactions l After being updated, this data can be further processed and manipulated by other systems l Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 48
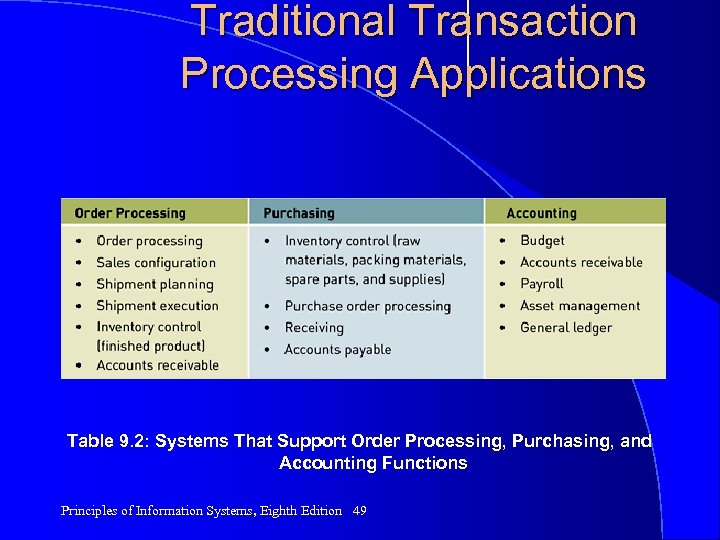 Traditional Transaction Processing Applications Table 9. 2: Systems That Support Order Processing, Purchasing, and Accounting Functions Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 49
Traditional Transaction Processing Applications Table 9. 2: Systems That Support Order Processing, Purchasing, and Accounting Functions Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 49
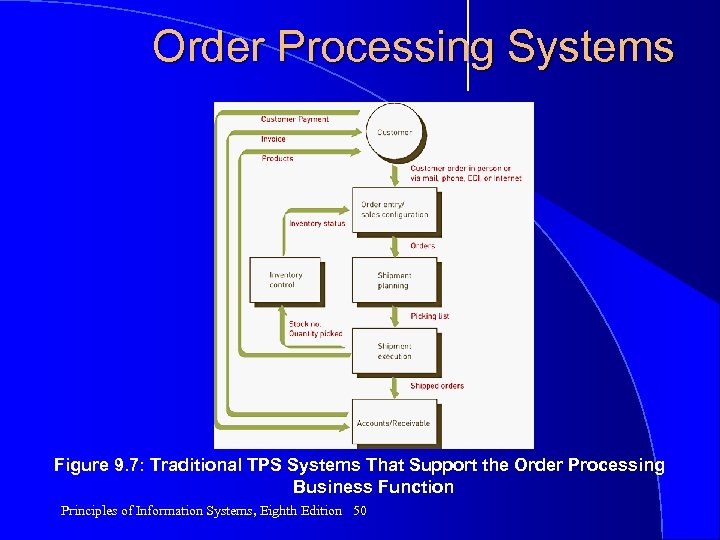 Order Processing Systems Figure 9. 7: Traditional TPS Systems That Support the Order Processing Business Function Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 50
Order Processing Systems Figure 9. 7: Traditional TPS Systems That Support the Order Processing Business Function Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 50
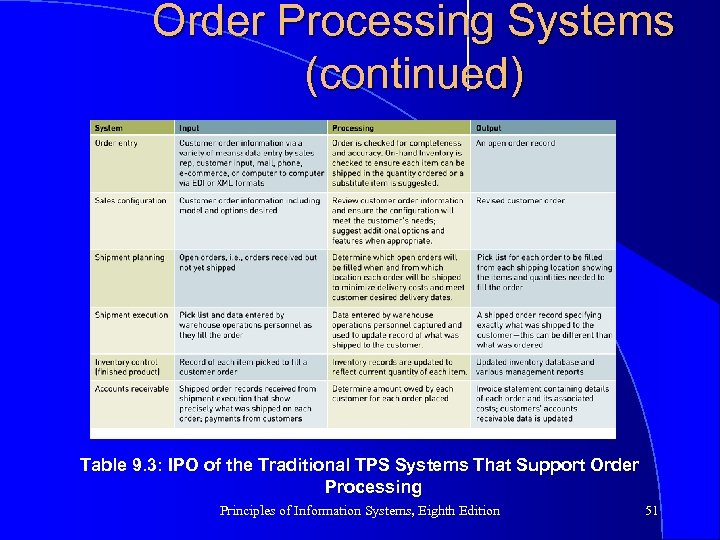 Order Processing Systems (continued) Table 9. 3: IPO of the Traditional TPS Systems That Support Order Processing Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 51
Order Processing Systems (continued) Table 9. 3: IPO of the Traditional TPS Systems That Support Order Processing Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 51
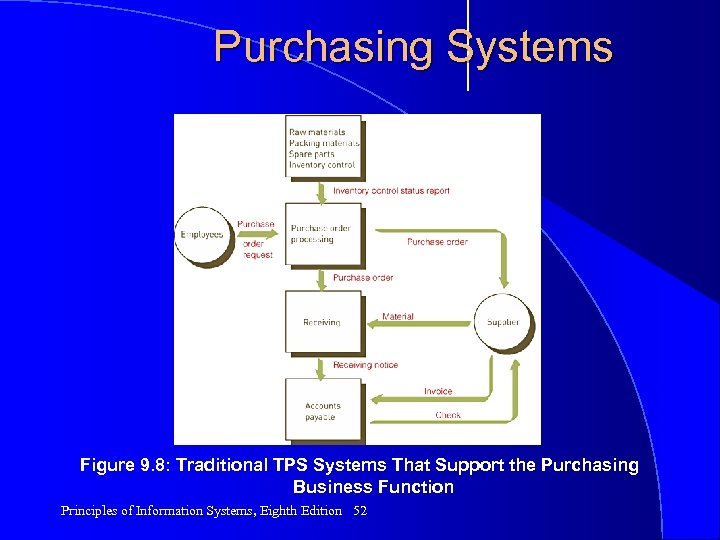 Purchasing Systems Figure 9. 8: Traditional TPS Systems That Support the Purchasing Business Function Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 52
Purchasing Systems Figure 9. 8: Traditional TPS Systems That Support the Purchasing Business Function Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 52
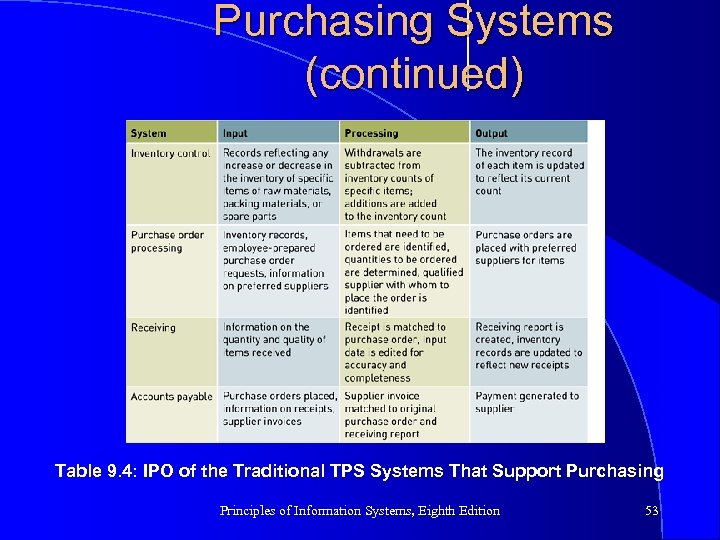 Purchasing Systems (continued) Table 9. 4: IPO of the Traditional TPS Systems That Support Purchasing Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 53
Purchasing Systems (continued) Table 9. 4: IPO of the Traditional TPS Systems That Support Purchasing Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 53
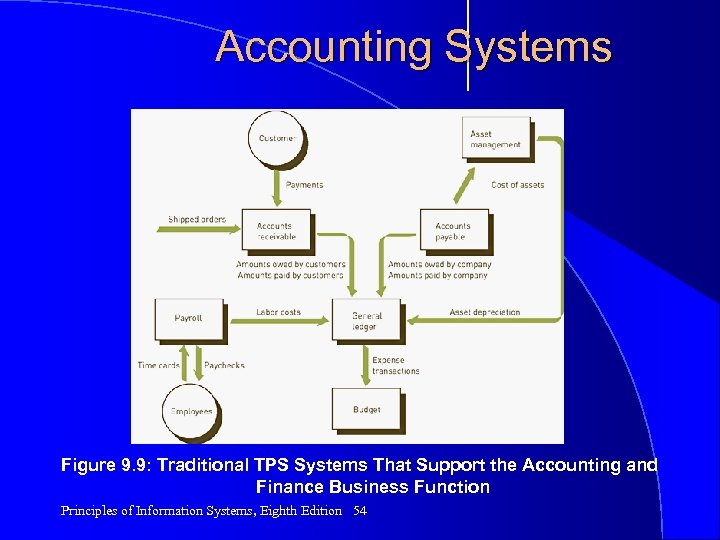 Accounting Systems Figure 9. 9: Traditional TPS Systems That Support the Accounting and Finance Business Function Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 54
Accounting Systems Figure 9. 9: Traditional TPS Systems That Support the Accounting and Finance Business Function Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 54
 Accounting Systems (continued) Table 9. 5: IPO of the Traditional TPS Systems That Support Accounting Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 55
Accounting Systems (continued) Table 9. 5: IPO of the Traditional TPS Systems That Support Accounting Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 55
 Enterprise Resource Planning
Enterprise Resource Planning
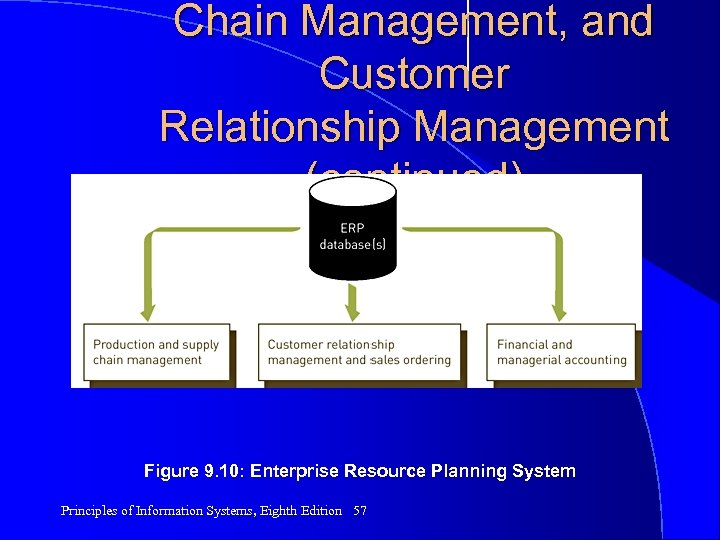 Chain Management, and Customer Relationship Management (continued) Figure 9. 10: Enterprise Resource Planning System Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 57
Chain Management, and Customer Relationship Management (continued) Figure 9. 10: Enterprise Resource Planning System Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 57
 Advantages of ERP Eliminates costly, inflexible legacy systems l Improved technology infrastructure l Improved work processes l Increased data access for decision making l
Advantages of ERP Eliminates costly, inflexible legacy systems l Improved technology infrastructure l Improved work processes l Increased data access for decision making l
 Disadvantages of ERP l l Expense & time Radical change Integrating with other systems One vendor risks
Disadvantages of ERP l l Expense & time Radical change Integrating with other systems One vendor risks
 Disadvantages of ERP Systems l Tips for avoiding failed ERP implementations – Assign a full-time project manager – Appoint an experienced, independent resource to oversee project and validate system performance – Allow sufficient time for transition – Spend substantial time and money for training – Define metrics to assess progress and identify Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 60 risks
Disadvantages of ERP Systems l Tips for avoiding failed ERP implementations – Assign a full-time project manager – Appoint an experienced, independent resource to oversee project and validate system performance – Allow sufficient time for transition – Spend substantial time and money for training – Define metrics to assess progress and identify Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 60 risks
 Production and Supply Chain Management l ERP production plan process: draws on the information available in the ERP system database – Sales forecasting: estimates future customer demand – Sales and operations plan: takes demand current inventory levels to determine production for future demands – Demand management: develops master Principles of Information production schedule Systems, Eighth Edition 61
Production and Supply Chain Management l ERP production plan process: draws on the information available in the ERP system database – Sales forecasting: estimates future customer demand – Sales and operations plan: takes demand current inventory levels to determine production for future demands – Demand management: develops master Principles of Information production schedule Systems, Eighth Edition 61
 Production and Supply Chain Management (continued) l ERP production plan process (continued) – Detailed scheduling: schedules production run for each product and from one product to the next – Materials requirement planning: determines amount and timing of raw material orders with suppliers – Purchasing: purchases raw materials and transmits to qualified suppliers Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 62 – Production: plans details of running and staffing
Production and Supply Chain Management (continued) l ERP production plan process (continued) – Detailed scheduling: schedules production run for each product and from one product to the next – Materials requirement planning: determines amount and timing of raw material orders with suppliers – Purchasing: purchases raw materials and transmits to qualified suppliers Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 62 – Production: plans details of running and staffing
 Customer Relationship Management and Sales Ordering l Customer relationship management (CRM) system: helps a company manage all aspects of customer encounters, including: – Marketing and advertising – Sales – Customer service after the sale – Programs to retain loyal customers Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 63
Customer Relationship Management and Sales Ordering l Customer relationship management (CRM) system: helps a company manage all aspects of customer encounters, including: – Marketing and advertising – Sales – Customer service after the sale – Programs to retain loyal customers Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 63
 Customer Relationship Management and Sales Ordering Figure 9. 11: Customer Relationship Management System Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 64
Customer Relationship Management and Sales Ordering Figure 9. 11: Customer Relationship Management System Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 64
 Customer Relationship Management and Sales Ordering l Sales ordering: set of activities that must be performed to capture a customer sales order, including the following: – Recording items to be purchased – Setting sales price – Recording order quantity – Determining total cost of the order including delivery costs – Confirming customer’s available credit Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 65
Customer Relationship Management and Sales Ordering l Sales ordering: set of activities that must be performed to capture a customer sales order, including the following: – Recording items to be purchased – Setting sales price – Recording order quantity – Determining total cost of the order including delivery costs – Confirming customer’s available credit Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 65
 Financial and Managerial Accounting l General ledger: main accounting record of a business – Assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses, and equity l ERP system – Captures transactions entered by workers in all functional areas of the business – Creates associated general ledger record to track the financial impact of the transaction Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 66
Financial and Managerial Accounting l General ledger: main accounting record of a business – Assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses, and equity l ERP system – Captures transactions entered by workers in all functional areas of the business – Creates associated general ledger record to track the financial impact of the transaction Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 66
 Financial and Managerial Accounting (continued) l Financial accounting – Captures and records all transactions that affect a company’s financial state – Uses these documented transactions to prepare financial statements to external decision makers l Managerial accounting – Provides data to enable the firm’s managers to make decisions about current and future operations, and develop overall business Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 67 strategies
Financial and Managerial Accounting (continued) l Financial accounting – Captures and records all transactions that affect a company’s financial state – Uses these documented transactions to prepare financial statements to external decision makers l Managerial accounting – Provides data to enable the firm’s managers to make decisions about current and future operations, and develop overall business Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 67 strategies
 Hosted Software Model for Enterprise Software l Hosted software model offers many benefits to small to medium businesses – No need to make a major financial investment – No need to employ a full-time IT person – Reduced hardware costs and costs associated with maintaining an appropriate computer environment l Some large companies are also experimenting of Information Systems, Eighth Edition with hosted software Principles 68
Hosted Software Model for Enterprise Software l Hosted software model offers many benefits to small to medium businesses – No need to make a major financial investment – No need to employ a full-time IT person – Reduced hardware costs and costs associated with maintaining an appropriate computer environment l Some large companies are also experimenting of Information Systems, Eighth Edition with hosted software Principles 68
 International Issues Associated with Enterprise Systems l Challenges that must be met by an enterprise system of a multinational company include: – Different languages and cultures – Disparities in IS infrastructure – Varying laws and customs rules – Multiple currencies l ERP software vendors help meet these challenges. Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 69
International Issues Associated with Enterprise Systems l Challenges that must be met by an enterprise system of a multinational company include: – Different languages and cultures – Disparities in IS infrastructure – Varying laws and customs rules – Multiple currencies l ERP software vendors help meet these challenges. Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 69
 Different Languages and Cultures Multinational companies sometimes roll out standard IS applications for all to use l To meet the needs of business partners and employees operating in other parts of the world, standard applications sometimes require extensive and costly customization l Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 70
Different Languages and Cultures Multinational companies sometimes roll out standard IS applications for all to use l To meet the needs of business partners and employees operating in other parts of the world, standard applications sometimes require extensive and costly customization l Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 70
 Disparities in Information System Infrastructure Lack of a robust or a common information infrastructure can create problems l Many countries’ telecommunications services are controlled by a central government or operated as a monopoly l – No incentives to provide fast and inexpensive customer service Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 71
Disparities in Information System Infrastructure Lack of a robust or a common information infrastructure can create problems l Many countries’ telecommunications services are controlled by a central government or operated as a monopoly l – No incentives to provide fast and inexpensive customer service Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 71
 Varying Laws and Customs Rules Numerous laws can affect collection and dissemination of data l Examples l – Labor laws in some countries prohibit recording of worker performance data – Some countries have laws limiting the transborder flow of data linked to individuals l Trade custom rules between nations – North American Free Systems, Eighth Edition Principles of Information Trade Agreement 72
Varying Laws and Customs Rules Numerous laws can affect collection and dissemination of data l Examples l – Labor laws in some countries prohibit recording of worker performance data – Some countries have laws limiting the transborder flow of data linked to individuals l Trade custom rules between nations – North American Free Systems, Eighth Edition Principles of Information Trade Agreement 72
 Multiple Currencies Enterprise system of multinational companies must conduct transactions in multiple currencies l Systems must: l – Be current with foreign currency exchange rates – Handle reporting and other transactions – Issue vendor payments and customer statements – Record retail store payments – Generate. Principles of Information Systems, in the currency of 73 financial reports Eighth Edition
Multiple Currencies Enterprise system of multinational companies must conduct transactions in multiple currencies l Systems must: l – Be current with foreign currency exchange rates – Handle reporting and other transactions – Issue vendor payments and customer statements – Record retail store payments – Generate. Principles of Information Systems, in the currency of 73 financial reports Eighth Edition
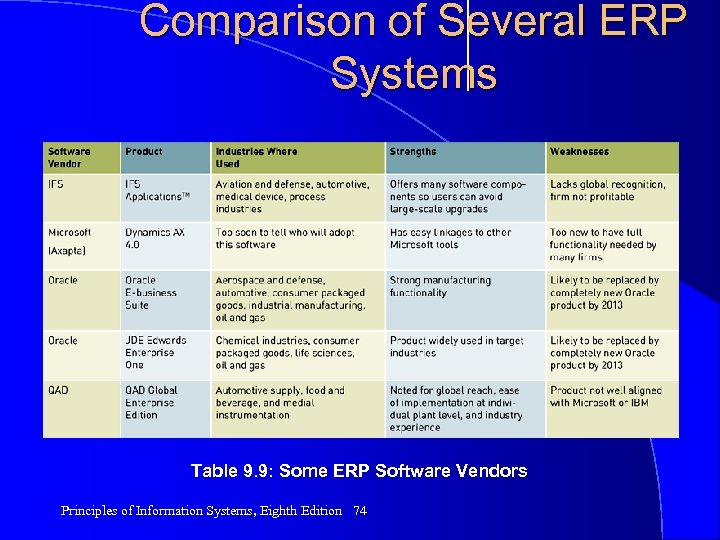 Comparison of Several ERP Systems Table 9. 9: Some ERP Software Vendors Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 74
Comparison of Several ERP Systems Table 9. 9: Some ERP Software Vendors Principles of Information Systems, Eighth Edition 74
 Questions (? )
Questions (? )


