Product of enterprise and its quality.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 46
 Topic Product of enterprise and its quality 1
Topic Product of enterprise and its quality 1
 Plan of lection 1. Products of enterprise 2. Quality concept 2
Plan of lection 1. Products of enterprise 2. Quality concept 2
 1 3
1 3
 4
4
 Gross products include the total value of goods and services produced Ready to sell products — it is ready products, product parts and half-made products for selling; Sold products include ready to sell products and changes of leftovers of the prepared products on warehouse; The net products include salary fund with deductions on social insurance and normative income; Quasi- net products consist of depreciation and net products For the calculation of manufactured and sold products volume are used natural, quasi natural, cost, labour indexes 5
Gross products include the total value of goods and services produced Ready to sell products — it is ready products, product parts and half-made products for selling; Sold products include ready to sell products and changes of leftovers of the prepared products on warehouse; The net products include salary fund with deductions on social insurance and normative income; Quasi- net products consist of depreciation and net products For the calculation of manufactured and sold products volume are used natural, quasi natural, cost, labour indexes 5
 6
6
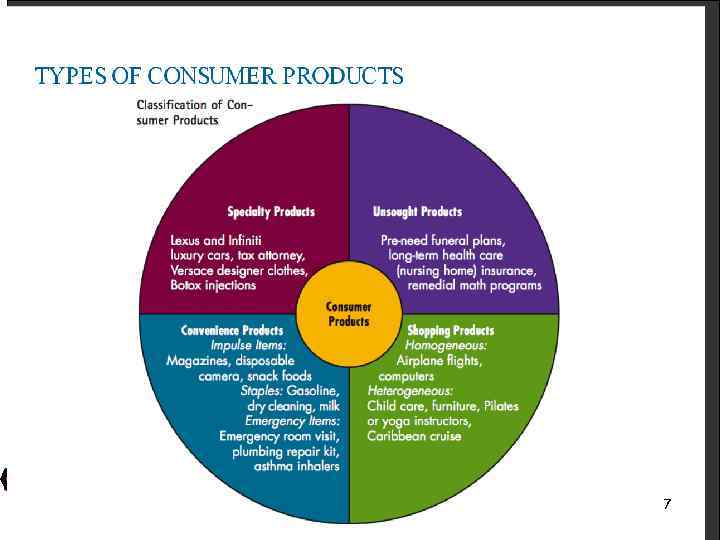 7
7
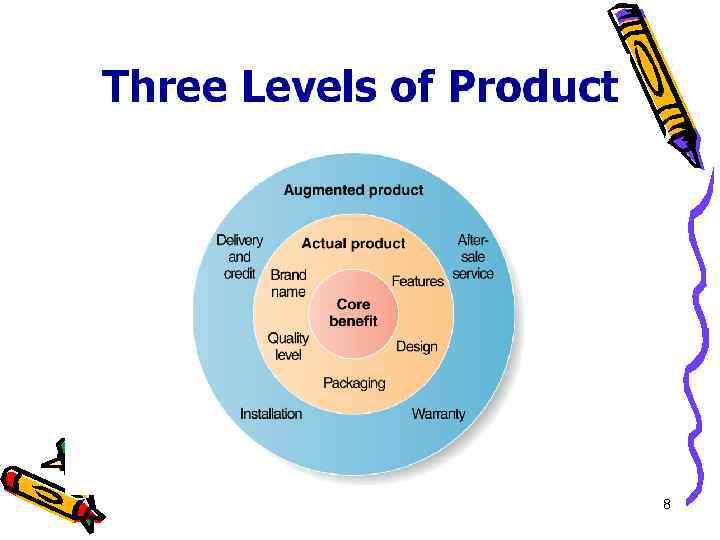 8
8
 9
9
 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
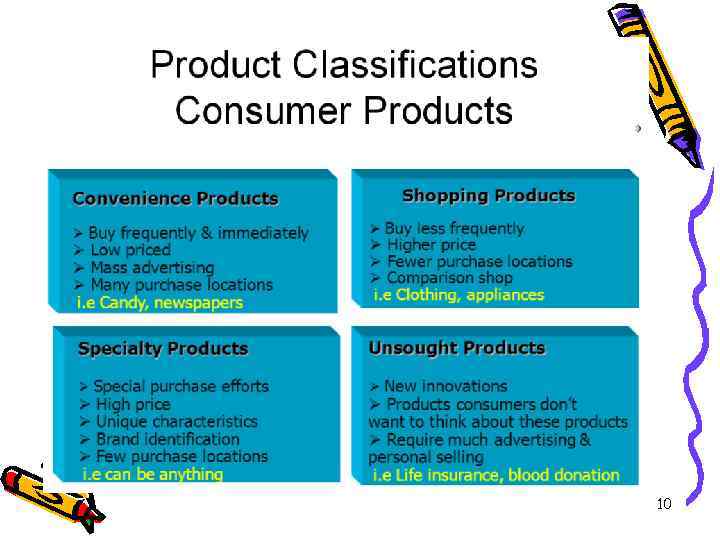
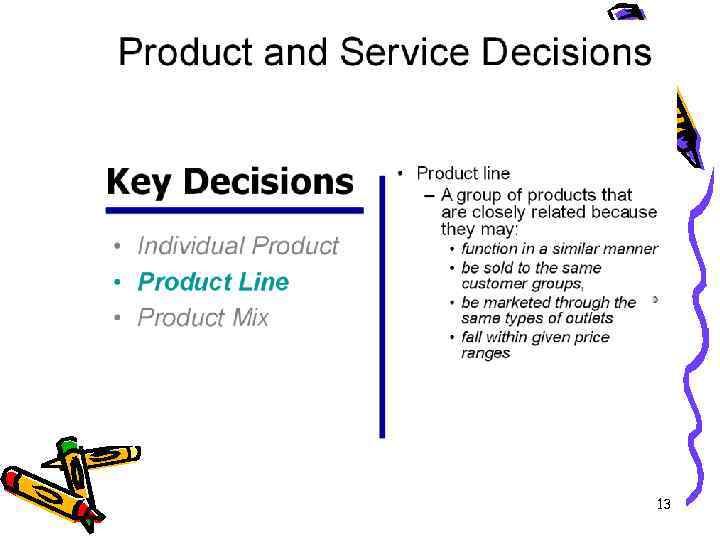
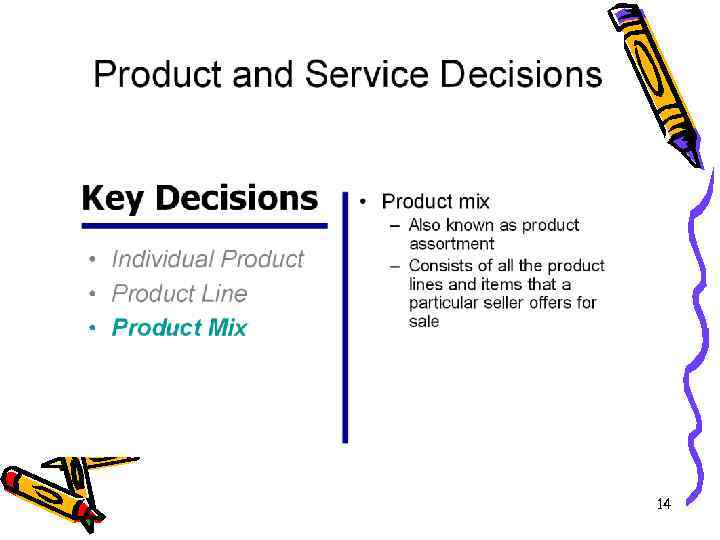
 Assortment of products — it is the list of the names, sorts, types of product in the set amount Nomenclature of products of enterprise — it is the list of planned types of product for manufacturing Assortment and nomenclature shape production program of the enterprise. 16
Assortment of products — it is the list of the names, sorts, types of product in the set amount Nomenclature of products of enterprise — it is the list of planned types of product for manufacturing Assortment and nomenclature shape production program of the enterprise. 16
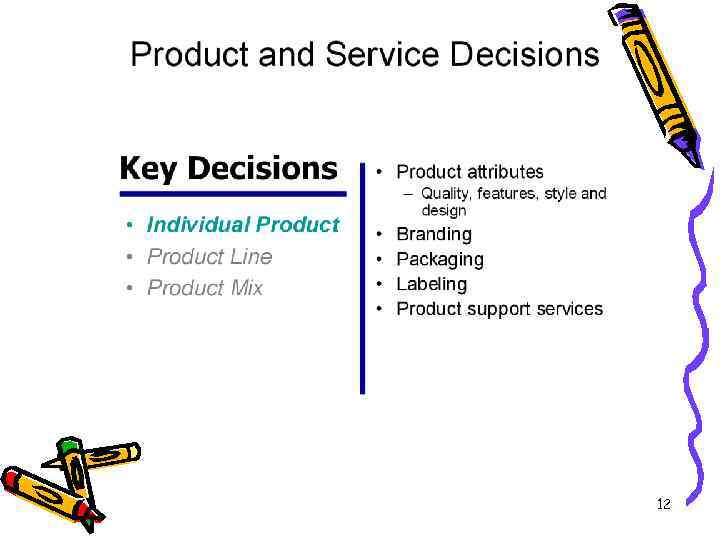
 The production program of enterprise represents volume of output of products The production program must be equal or less than production capacity Production capacity – maximum number of product that could be manufactured (determined by capacity of the main equipment) Gross, ready to sell and sold products are representing cost of the production program 17
The production program of enterprise represents volume of output of products The production program must be equal or less than production capacity Production capacity – maximum number of product that could be manufactured (determined by capacity of the main equipment) Gross, ready to sell and sold products are representing cost of the production program 17
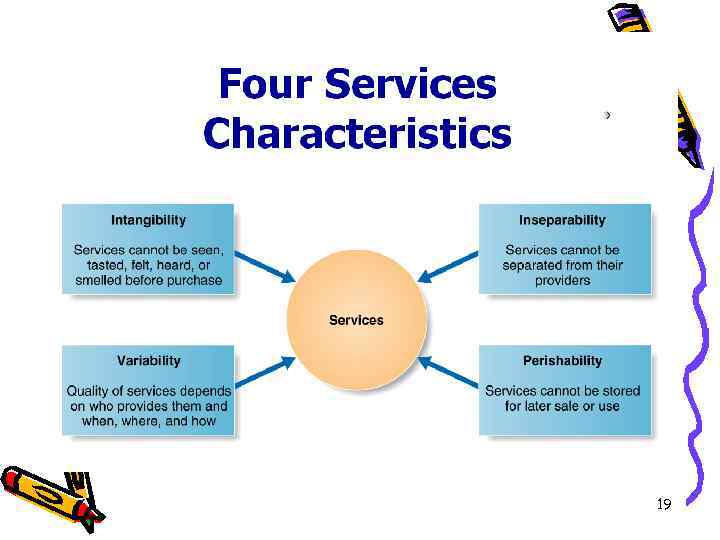
 Differences Between Services and Goods • • • Information Asymmetry Intangible Inventory Customer Contact Response Time Labor Intensity 18
Differences Between Services and Goods • • • Information Asymmetry Intangible Inventory Customer Contact Response Time Labor Intensity 18
 19
19
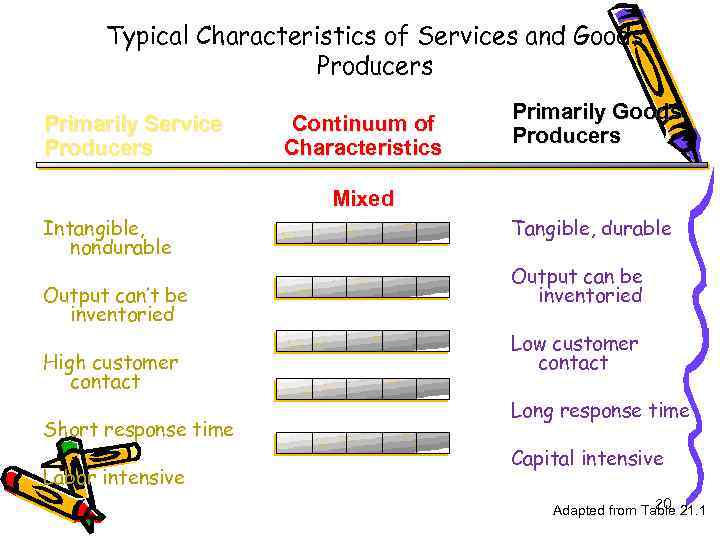 Typical Characteristics of Services and Goods Producers Primarily Service Producers Continuum of Characteristics Primarily Goods Producers Mixed Intangible, nondurable Output can’t be inventoried High customer contact Short response time Labor intensive Tangible, durable Output can be inventoried Low customer contact Long response time Capital intensive 20 Adapted from Table 21. 1
Typical Characteristics of Services and Goods Producers Primarily Service Producers Continuum of Characteristics Primarily Goods Producers Mixed Intangible, nondurable Output can’t be inventoried High customer contact Short response time Labor intensive Tangible, durable Output can be inventoried Low customer contact Long response time Capital intensive 20 Adapted from Table 21. 1
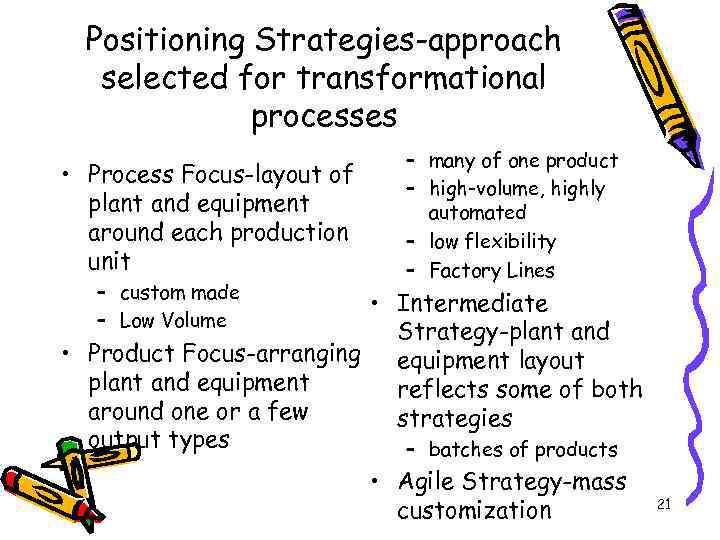 Positioning Strategies-approach selected for transformational processes • Process Focus-layout of plant and equipment around each production unit – custom made – Low Volume – many of one product – high-volume, highly automated – low flexibility – Factory Lines • Intermediate Strategy-plant and • Product Focus-arranging equipment layout plant and equipment reflects some of both around one or a few strategies output types – batches of products • Agile Strategy-mass customization 21
Positioning Strategies-approach selected for transformational processes • Process Focus-layout of plant and equipment around each production unit – custom made – Low Volume – many of one product – high-volume, highly automated – low flexibility – Factory Lines • Intermediate Strategy-plant and • Product Focus-arranging equipment layout plant and equipment reflects some of both around one or a few strategies output types – batches of products • Agile Strategy-mass customization 21
 Flexibility • Product Flexibility-speed with which products are created, ability to customize, ability to modify products for special needs • Volume Flexibility-ability to respond to sudden changes in demand, change from small to full scale • Process Flexibility-ability to manufacture a variety of goods in a short time, adjust to product mix over time, ability to accommodate changes in raw materials 22
Flexibility • Product Flexibility-speed with which products are created, ability to customize, ability to modify products for special needs • Volume Flexibility-ability to respond to sudden changes in demand, change from small to full scale • Process Flexibility-ability to manufacture a variety of goods in a short time, adjust to product mix over time, ability to accommodate changes in raw materials 22
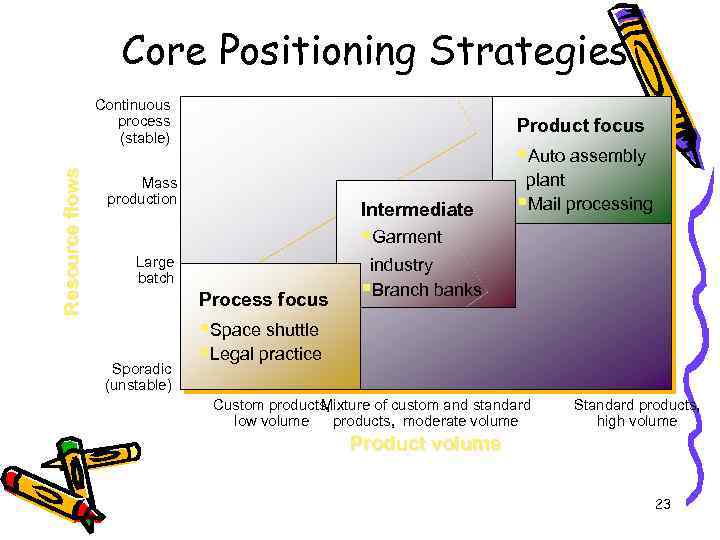 Core Positioning Strategies Resource flows Continuous process (stable) Product focus §Auto assembly Mass production Intermediate plant §Mail processing §Garment Large batch Process focus Sporadic (unstable) industry §Branch banks §Space shuttle §Legal practice Custom products, Mixture of custom and standard low volume products, moderate volume Standard products, high volume Product volume 23
Core Positioning Strategies Resource flows Continuous process (stable) Product focus §Auto assembly Mass production Intermediate plant §Mail processing §Garment Large batch Process focus Sporadic (unstable) industry §Branch banks §Space shuttle §Legal practice Custom products, Mixture of custom and standard low volume products, moderate volume Standard products, high volume Product volume 23
 Improving Responsiveness to Customers – Without customers, organizations cease to exist. • Non-profit and for-profit firms all have customers. • Managers need to identify who the customer is and their needs. – What do customers want? Usually customers prefer: • A lower price to a higher price. • High quality over low quality. • Fast service over slow service. – Also good after sale support. • Many features over few features. • Products tailored to their specific needs. 24
Improving Responsiveness to Customers – Without customers, organizations cease to exist. • Non-profit and for-profit firms all have customers. • Managers need to identify who the customer is and their needs. – What do customers want? Usually customers prefer: • A lower price to a higher price. • High quality over low quality. • Fast service over slow service. – Also good after sale support. • Many features over few features. • Products tailored to their specific needs. 24
 2 Quality-how well a product does what the customer expects or Quality - the extent to which a product or service is able to meet customer needs and expectations. • Internal View-within the organization • External View-value customers expect • Value-the relationship between quality and price 25
2 Quality-how well a product does what the customer expects or Quality - the extent to which a product or service is able to meet customer needs and expectations. • Internal View-within the organization • External View-value customers expect • Value-the relationship between quality and price 25
 Quality of products — it is collection of properties of product, which determine its ability to satisfy the certain necessities of users on purpose The individual indexes of quality characterize certain feature of good. Complex indexes is used for evaluation of all quality aspects of the products Quality Management System - totality of bodies and objects of management, interacting with logistical and information tools during quality control 26
Quality of products — it is collection of properties of product, which determine its ability to satisfy the certain necessities of users on purpose The individual indexes of quality characterize certain feature of good. Complex indexes is used for evaluation of all quality aspects of the products Quality Management System - totality of bodies and objects of management, interacting with logistical and information tools during quality control 26
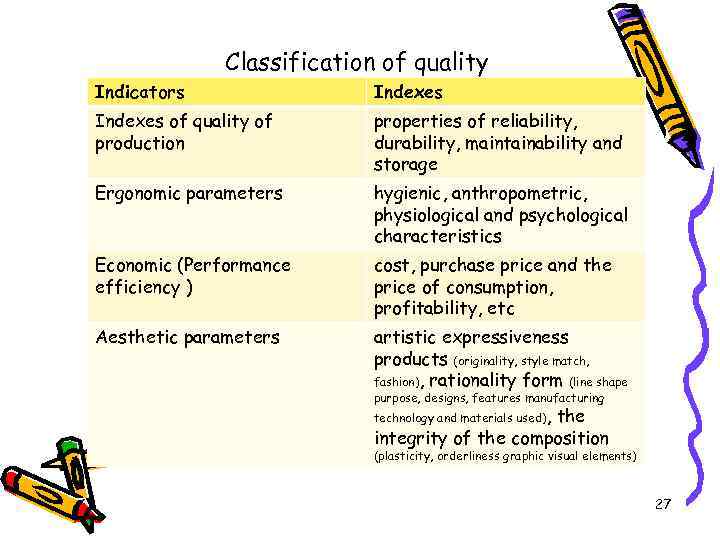 Classification of quality Indicators Indexes of quality of production properties of reliability, durability, maintainability and storage Ergonomic parameters hygienic, anthropometric, physiological and psychological characteristics Economic (Performance efficiency ) cost, purchase price and the price of consumption, profitability, etc Aesthetic parameters artistic expressiveness products (originality, style match, fashion), rationality form (line shape purpose, designs, features manufacturing technology and materials used), the integrity of the composition (plasticity, orderliness graphic visual elements) 27
Classification of quality Indicators Indexes of quality of production properties of reliability, durability, maintainability and storage Ergonomic parameters hygienic, anthropometric, physiological and psychological characteristics Economic (Performance efficiency ) cost, purchase price and the price of consumption, profitability, etc Aesthetic parameters artistic expressiveness products (originality, style match, fashion), rationality form (line shape purpose, designs, features manufacturing technology and materials used), the integrity of the composition (plasticity, orderliness graphic visual elements) 27
 Classification of quality (cont’d) Indicators Indexes Indicators relevant to the manufacturability specific complexity, materials, energy production and maintenance product cycle maintenance and repairs, etc Indicators of standardization and unification applicability coefficient, coefficient of repeatability, coefficient of unification of product or group of products Patent legal parameters characterizing the degree of patent protection Environmental indicators content of contaminants released into the environment, the release of harmful particles, gases and radiation levels that do not exceed the maximum allowable concentration 28
Classification of quality (cont’d) Indicators Indexes Indicators relevant to the manufacturability specific complexity, materials, energy production and maintenance product cycle maintenance and repairs, etc Indicators of standardization and unification applicability coefficient, coefficient of repeatability, coefficient of unification of product or group of products Patent legal parameters characterizing the degree of patent protection Environmental indicators content of contaminants released into the environment, the release of harmful particles, gases and radiation levels that do not exceed the maximum allowable concentration 28
 Reliability shows feature of product continuously remain operational for some time for certain, expressed in time to failure, failure rate. Durability – property of products to remain operational until the boundary condition at the installed system maintenance and repairs. Individual cases indicators of durability is the average lifespan. Maintainability - property of products to adapt it to prevention and detection of the causes of failure, damage and eliminate their consequences through repairs and maintenance. 29
Reliability shows feature of product continuously remain operational for some time for certain, expressed in time to failure, failure rate. Durability – property of products to remain operational until the boundary condition at the installed system maintenance and repairs. Individual cases indicators of durability is the average lifespan. Maintainability - property of products to adapt it to prevention and detection of the causes of failure, damage and eliminate their consequences through repairs and maintenance. 29
 Certification of products — it is the procedure of recognition of the conformity of products, quality systems, quality management systems, environmental quality systems and staff to the requirements defined by the legislation In Ukraine direct guidance on the state system of certification is carries out by the State Committee of Ukraine for Technical Regulation and Consumer Policy Organizational basis of certification is presented by the network of state test centers in Ukraine, one of which is located in our University 30
Certification of products — it is the procedure of recognition of the conformity of products, quality systems, quality management systems, environmental quality systems and staff to the requirements defined by the legislation In Ukraine direct guidance on the state system of certification is carries out by the State Committee of Ukraine for Technical Regulation and Consumer Policy Organizational basis of certification is presented by the network of state test centers in Ukraine, one of which is located in our University 30
 A certificate of quality of products is a document which certifies the level of quality of products (in Ukraine it is called certificate of conformity) 31
A certificate of quality of products is a document which certifies the level of quality of products (in Ukraine it is called certificate of conformity) 31
 Controlling For Quality And Productivity • Quality – The extent to which a product or service is able to meet customer needs and expectations. • Customer’s needs are the basic standard for measuring quality • High quality does not have to mean high price. • ISO 14000 and 9000 – The quality standards of the International Standards Organization. 32
Controlling For Quality And Productivity • Quality – The extent to which a product or service is able to meet customer needs and expectations. • Customer’s needs are the basic standard for measuring quality • High quality does not have to mean high price. • ISO 14000 and 9000 – The quality standards of the International Standards Organization. 32
 Methods of providing of quality of products: • Economic (profitability) • Administrative (law) • Social (pressure of people) 33
Methods of providing of quality of products: • Economic (profitability) • Administrative (law) • Social (pressure of people) 33
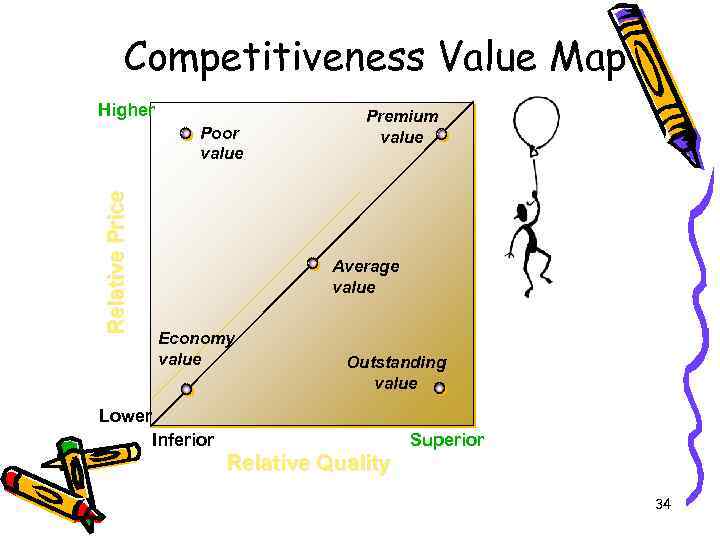 Competitiveness Value Map Higher Relative Price Poor value Premium value Average value Economy value Outstanding value Lower Inferior Superior Relative Quality 34
Competitiveness Value Map Higher Relative Price Poor value Premium value Average value Economy value Outstanding value Lower Inferior Superior Relative Quality 34
 Price v. Attributes – Firms offering high quality, fast service and other customer desires, often must raise price. – Customers must tradeoff price for attributes. – Operations management tries to push the price/attribute curve to the right with better production. • Provides more attributes at the same cost. – By enhancing the price/attribute relationship, the firm can increase its competitive position. 35
Price v. Attributes – Firms offering high quality, fast service and other customer desires, often must raise price. – Customers must tradeoff price for attributes. – Operations management tries to push the price/attribute curve to the right with better production. • Provides more attributes at the same cost. – By enhancing the price/attribute relationship, the firm can increase its competitive position. 35
 Customer Responsive Production Systems – An output’s attributes is determined by the production system. • Firms must strike a balance between cost and attributes – Improving Quality: can apply to firms producing goods and services. • A firm that provides higher quality than others at the same price is more responsive to customers. • Higher quality can also lead to better efficiency. – Lowers waste levels and operating costs. 36
Customer Responsive Production Systems – An output’s attributes is determined by the production system. • Firms must strike a balance between cost and attributes – Improving Quality: can apply to firms producing goods and services. • A firm that provides higher quality than others at the same price is more responsive to customers. • Higher quality can also lead to better efficiency. – Lowers waste levels and operating costs. 36
 Methods of Quality Control • Acceptance Sampling (Expert) – a method of monitoring product quality that requires the inspection of only a small portion of the produced items. 37
Methods of Quality Control • Acceptance Sampling (Expert) – a method of monitoring product quality that requires the inspection of only a small portion of the produced items. 37
 Controlling For Quality And Productivity • Total Quality Management (TQM) – A specific organization-wide program that integrates all the functions and related processes of a business such that they are all aimed at maximizing customer satisfaction through ongoing improvements. – Also called: Continuous improvement, Zero defects, Six-Sigma, and Kaizen (Japan) 38
Controlling For Quality And Productivity • Total Quality Management (TQM) – A specific organization-wide program that integrates all the functions and related processes of a business such that they are all aimed at maximizing customer satisfaction through ongoing improvements. – Also called: Continuous improvement, Zero defects, Six-Sigma, and Kaizen (Japan) 38
 39
39
 Total Versus Traditional Quality Total Quality Management Traditional Quality Control n Quality is a strategic issue n Quality is a tactical issue n Plan for quality n Screen for quality n n Quality is everybody’s responsibility Strive for zero defects Quality means conformance to requirements that meet or exceed customers’ expectations Scrap and reworking are only a small part of the costs of nonconformance n Quality is the responsibility of the quality control department n Some mistakes are inevitable n Quality means inspection n Scrap and reworking are the major costs of poor quality 40
Total Versus Traditional Quality Total Quality Management Traditional Quality Control n Quality is a strategic issue n Quality is a tactical issue n Plan for quality n Screen for quality n n Quality is everybody’s responsibility Strive for zero defects Quality means conformance to requirements that meet or exceed customers’ expectations Scrap and reworking are only a small part of the costs of nonconformance n Quality is the responsibility of the quality control department n Some mistakes are inevitable n Quality means inspection n Scrap and reworking are the major costs of poor quality 40
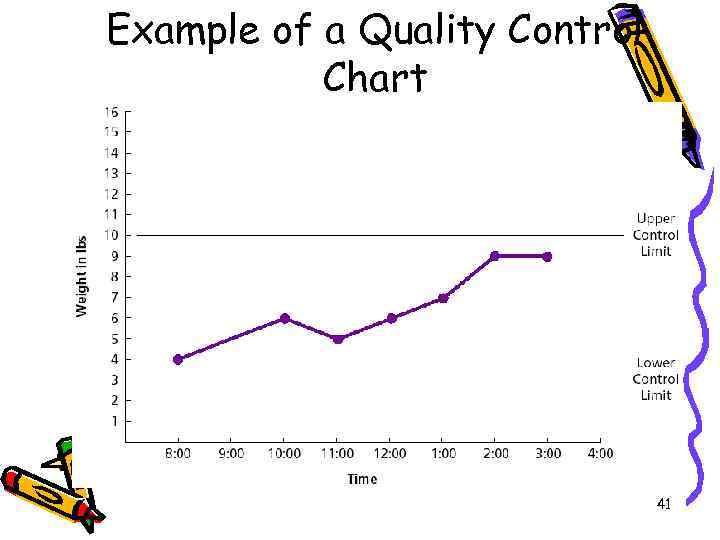 Example of a Quality Control Chart 41
Example of a Quality Control Chart 41
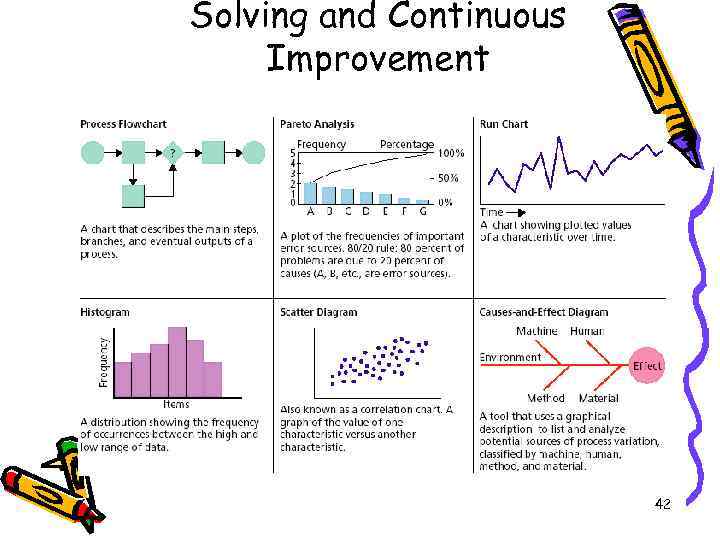 Solving and Continuous Improvement 42
Solving and Continuous Improvement 42
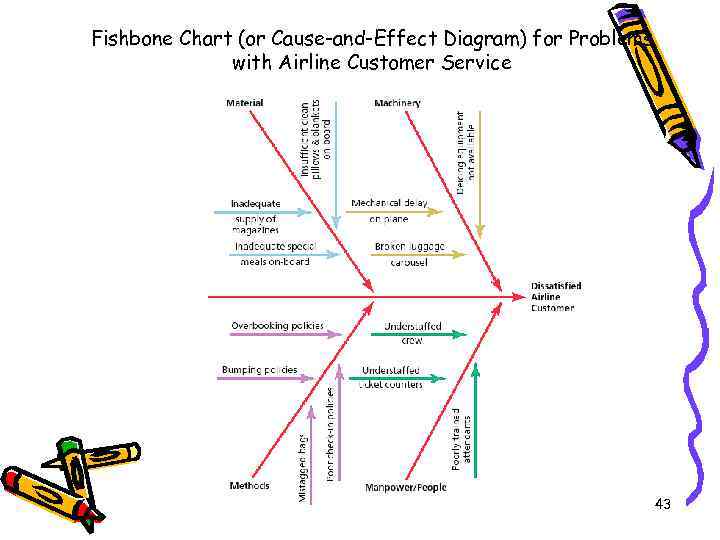 Fishbone Chart (or Cause-and-Effect Diagram) for Problems with Airline Customer Service 43
Fishbone Chart (or Cause-and-Effect Diagram) for Problems with Airline Customer Service 43
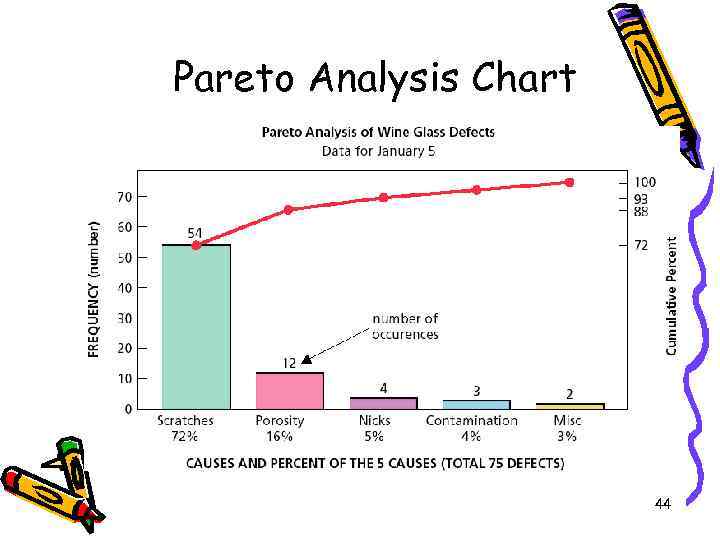 Pareto Analysis Chart 44
Pareto Analysis Chart 44
 A concept "technical level of products" is narrower than concept "quality of products" 45
A concept "technical level of products" is narrower than concept "quality of products" 45
 Thank you for your attention! 46
Thank you for your attention! 46


