ВМ англ лек матр визн.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Topic: Matrices and Determinants • • Literature: 1 , v. І, p. 72 -78, 2 , part І, p. 82 -137, 3 , p. 13 -33
Topic: Matrices and Determinants • • Literature: 1 , v. І, p. 72 -78, 2 , part І, p. 82 -137, 3 , p. 13 -33
 1. The definition of Matrix. The main notions. 2. The definitions of the Determinants of the second and third orders. 3. Properties of determinants. 4. Expanding of the determinant along the row or column.
1. The definition of Matrix. The main notions. 2. The definitions of the Determinants of the second and third orders. 3. Properties of determinants. 4. Expanding of the determinant along the row or column.
 5. Cramer’s rule. 6. The Matrix Method.
5. Cramer’s rule. 6. The Matrix Method.
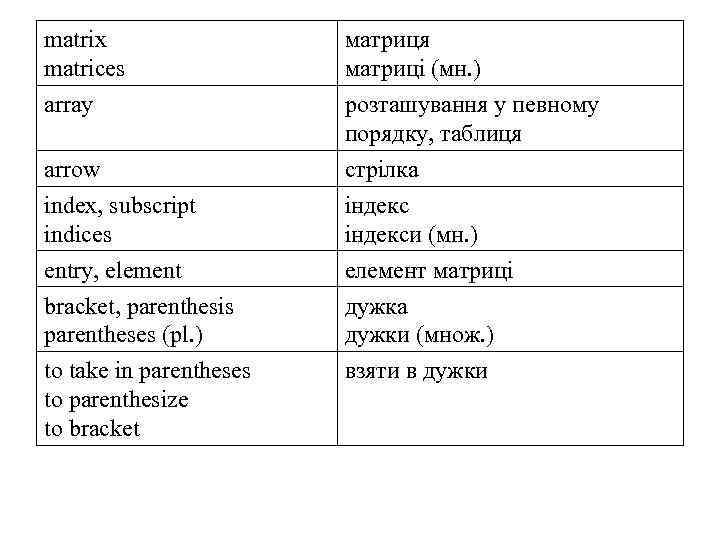 matrix matrices матриця матриці (мн. ) array розташування у певному порядку, таблиця arrow index, subscript indices стрілка індекси (мн. ) entry, element елемент матриці bracket, parenthesis parentheses (pl. ) to take in parentheses to parenthesize to bracket дужка дужки (множ. ) взяти в дужки
matrix matrices матриця матриці (мн. ) array розташування у певному порядку, таблиця arrow index, subscript indices стрілка індекси (мн. ) entry, element елемент матриці bracket, parenthesis parentheses (pl. ) to take in parentheses to parenthesize to bracket дужка дужки (множ. ) взяти в дужки
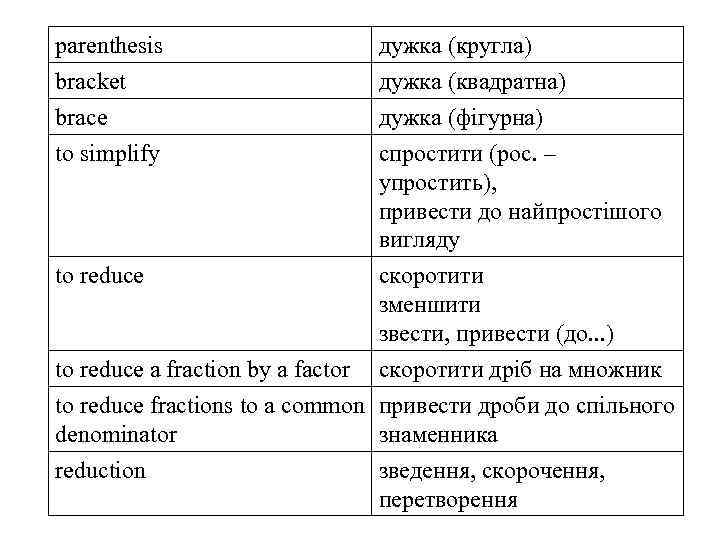 parenthesis дужка (кругла) bracket brace to simplify дужка (квадратна) дужка (фігурна) спростити (рос. – упростить), привести до найпростішого вигляду to reduce скоротити зменшити звести, привести (до. . . ) to reduce a fraction by a factor скоротити дріб на множник to reduce fractions to a common привести дроби до спільного denominator знаменника reduction зведення, скорочення, перетворення
parenthesis дужка (кругла) bracket brace to simplify дужка (квадратна) дужка (фігурна) спростити (рос. – упростить), привести до найпростішого вигляду to reduce скоротити зменшити звести, привести (до. . . ) to reduce a fraction by a factor скоротити дріб на множник to reduce fractions to a common привести дроби до спільного denominator знаменника reduction зведення, скорочення, перетворення
 row рядок column identity matrix invertible matrix стовпець одинична матриця оборотна матриця inverse matrix transpose of a matrix A обернена матриця, транспонована до матриці А скалярний добуток dot product
row рядок column identity matrix invertible matrix стовпець одинична матриця оборотна матриця inverse matrix transpose of a matrix A обернена матриця, транспонована до матриці А скалярний добуток dot product
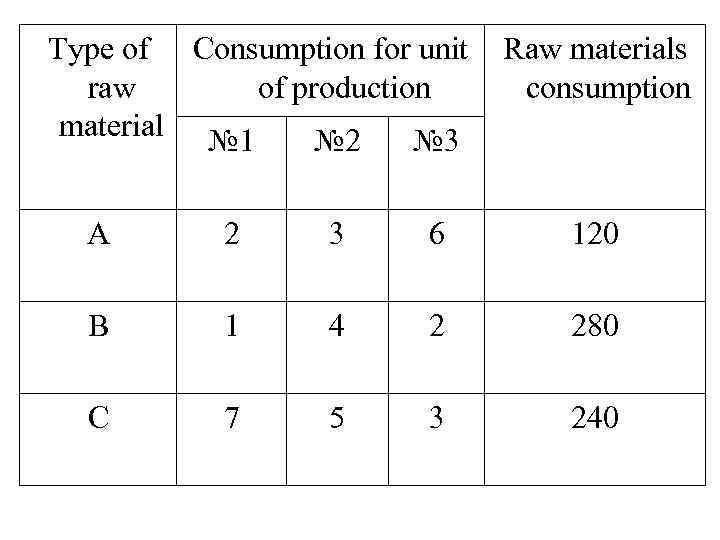 Type of Consumption for unit raw of production material № 1 № 2 № 3 Raw materials consumption A 2 3 6 120 B 1 4 2 280 C 7 5 3 240
Type of Consumption for unit raw of production material № 1 № 2 № 3 Raw materials consumption A 2 3 6 120 B 1 4 2 280 C 7 5 3 240
 Definition. A matrix is a rectangular array of elements.
Definition. A matrix is a rectangular array of elements.
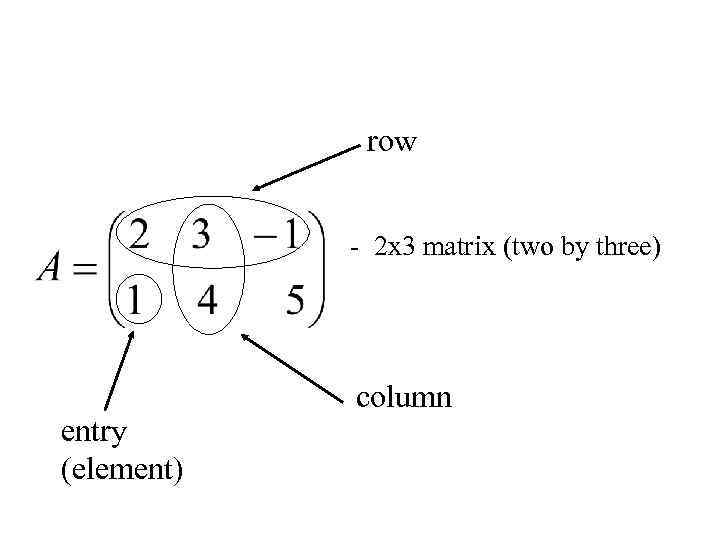 row - 2 x 3 matrix (two by three) entry (element) column
row - 2 x 3 matrix (two by three) entry (element) column
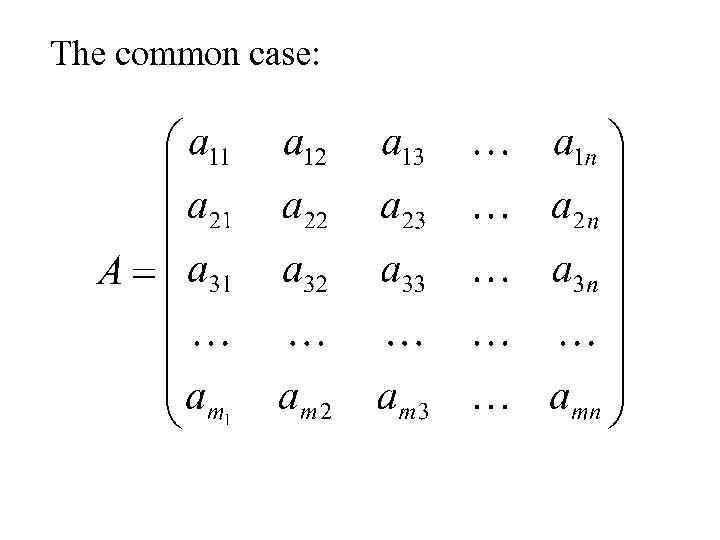 The common case:
The common case:
 The types of matrices 1) Matrix with one row is called a row vector, and a matrix with one column is called a column vector
The types of matrices 1) Matrix with one row is called a row vector, and a matrix with one column is called a column vector
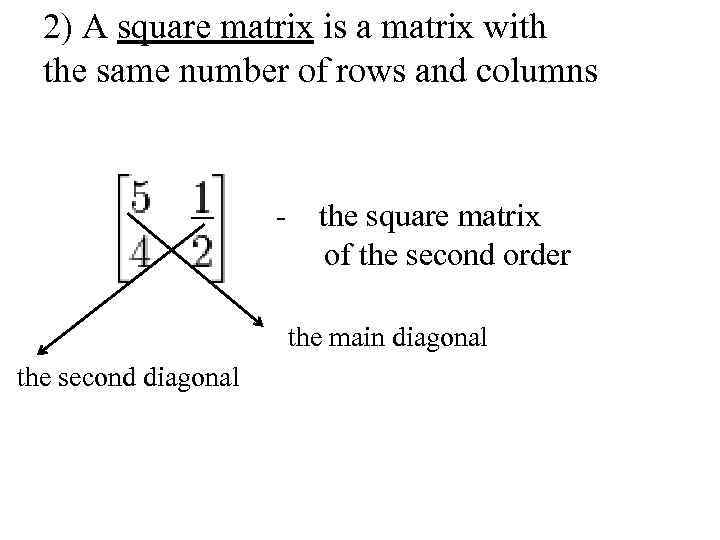 2) A square matrix is a matrix with the same number of rows and columns - the square matrix of the second order the main diagonal the second diagonal
2) A square matrix is a matrix with the same number of rows and columns - the square matrix of the second order the main diagonal the second diagonal
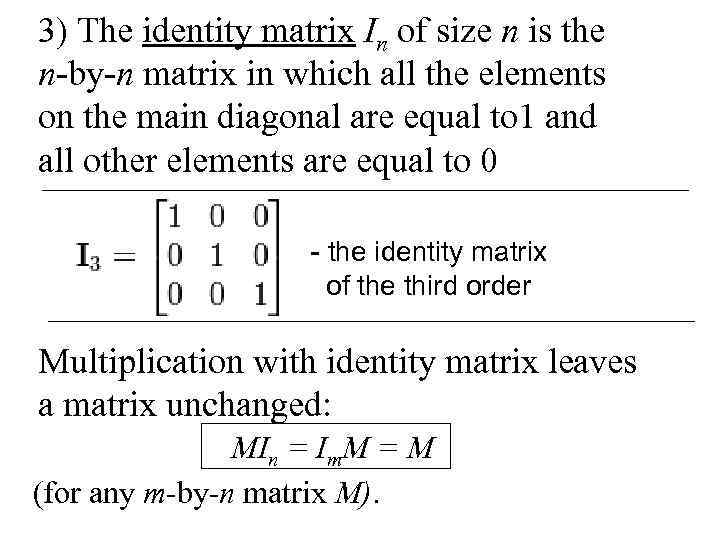 3) The identity matrix In of size n is the n-by-n matrix in which all the elements on the main diagonal are equal to 1 and all other elements are equal to 0 - the identity matrix of the third order Multiplication with identity matrix leaves a matrix unchanged: MIn = Im. M = M (for any m-by-n matrix M).
3) The identity matrix In of size n is the n-by-n matrix in which all the elements on the main diagonal are equal to 1 and all other elements are equal to 0 - the identity matrix of the third order Multiplication with identity matrix leaves a matrix unchanged: MIn = Im. M = M (for any m-by-n matrix M).
 4) A square matrix A of order n is called invertible if there exists a matrix B such that AB=BA=In If B exists, it is called the inverse matrix of A, denoted A-1
4) A square matrix A of order n is called invertible if there exists a matrix B such that AB=BA=In If B exists, it is called the inverse matrix of A, denoted A-1
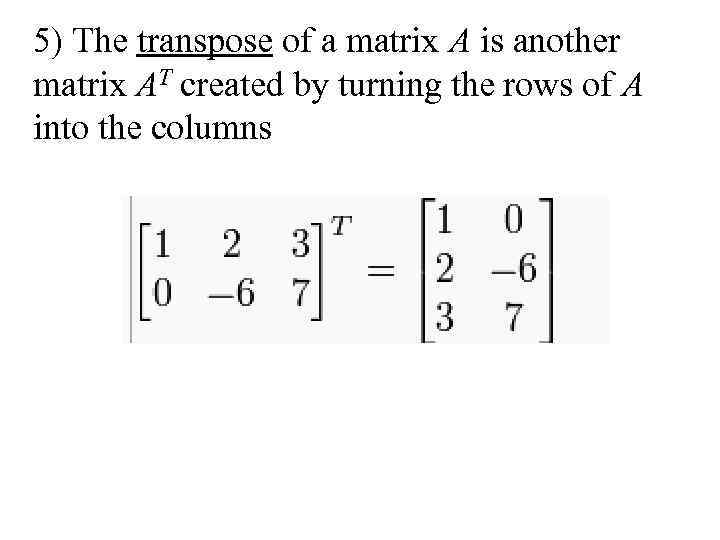 5) The transpose of a matrix A is another matrix AT created by turning the rows of A into the columns
5) The transpose of a matrix A is another matrix AT created by turning the rows of A into the columns
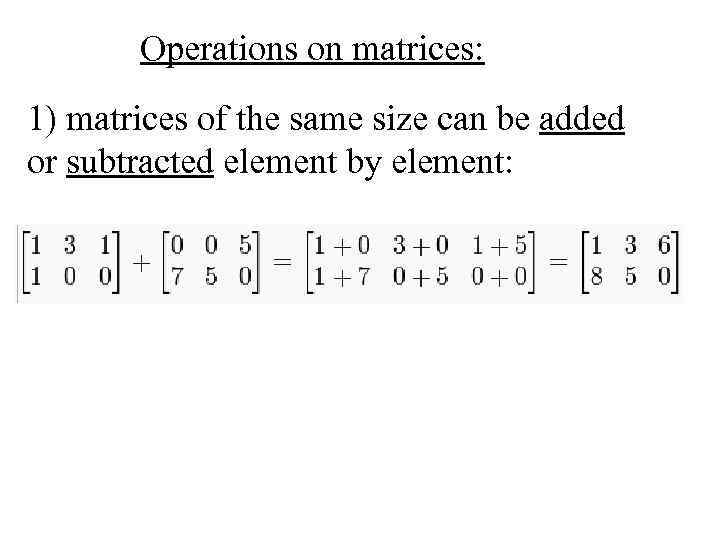 Operations on matrices: 1) matrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element:
Operations on matrices: 1) matrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element:
 2) The scalar multiplication of a matrix A and a number c is given by multiplying every entry of A by c:
2) The scalar multiplication of a matrix A and a number c is given by multiplying every entry of A by c:
 3) Two matrices can be multiplied only when the number of columns in the first equals the number of rows in the second. If A is an m-by-n matrix and B is n-by-k matrix, then their matrix product AB is the m-by-k matrix whose entries are given by dot product of the corresponding row of A and the corresponding column of B:
3) Two matrices can be multiplied only when the number of columns in the first equals the number of rows in the second. If A is an m-by-n matrix and B is n-by-k matrix, then their matrix product AB is the m-by-k matrix whose entries are given by dot product of the corresponding row of A and the corresponding column of B:
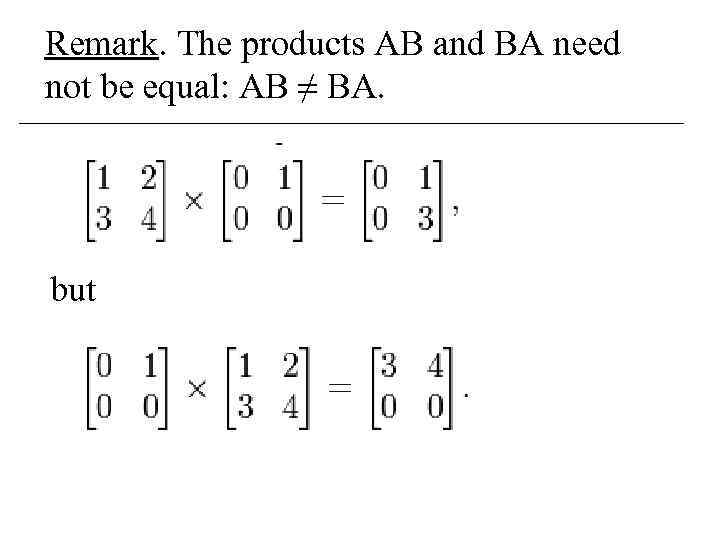 Remark. The products AB and BA need not be equal: AB ≠ BA. but
Remark. The products AB and BA need not be equal: AB ≠ BA. but
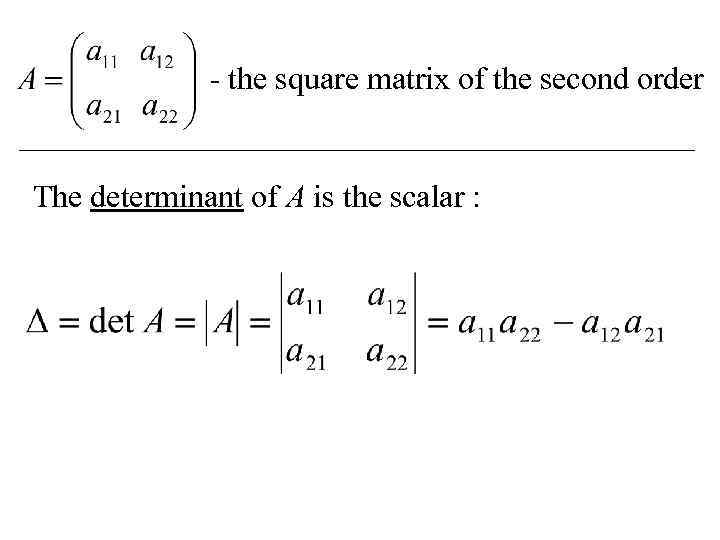 - the square matrix of the second order The determinant of A is the scalar :
- the square matrix of the second order The determinant of A is the scalar :
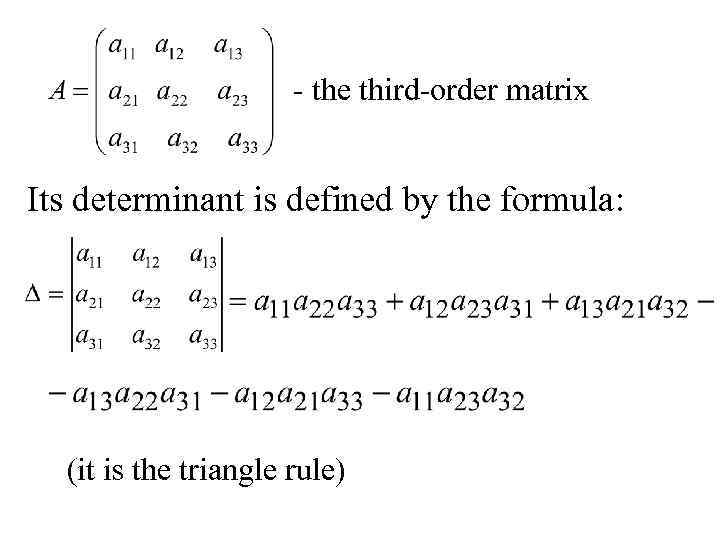 - the third-order matrix Its determinant is defined by the formula: (it is the triangle rule)
- the third-order matrix Its determinant is defined by the formula: (it is the triangle rule)
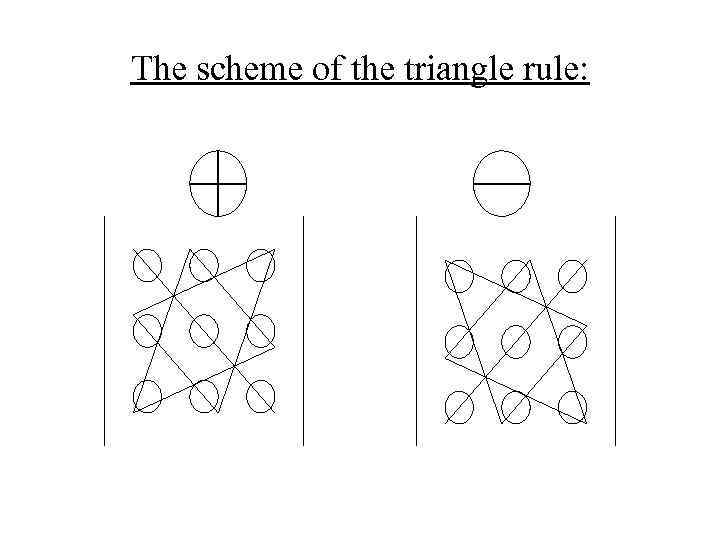 The scheme of the triangle rule:
The scheme of the triangle rule:
 The main properties of determinants 1) A matrix and its transpose have equal determinants. 2) If two rows of matrix are interchanged, the determinant changes sign. 3) If two rows of a matrix are equal, the determinant is zero. 4) The common factor of the row of the determinant can be taken outside this determinant.
The main properties of determinants 1) A matrix and its transpose have equal determinants. 2) If two rows of matrix are interchanged, the determinant changes sign. 3) If two rows of a matrix are equal, the determinant is zero. 4) The common factor of the row of the determinant can be taken outside this determinant.
 5) If the corresponding elements of two rows of the determinant are proportional, then the determinant is zero. 6) If a row of a matrix is zero, then the value of the determinants is zero.
5) If the corresponding elements of two rows of the determinant are proportional, then the determinant is zero. 6) If a row of a matrix is zero, then the value of the determinants is zero.
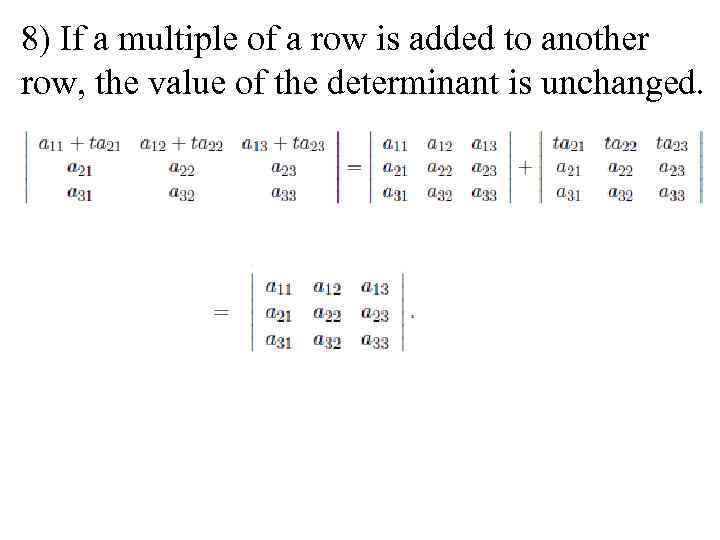 8) If a multiple of a row is added to another row, the value of the determinant is unchanged.
8) If a multiple of a row is added to another row, the value of the determinant is unchanged.
 The determinant of the third order: Delete the first row and the first column of this determinant. We get the determinant of the second order, which is called the minor of the element a 11. It is denoted by M 11.
The determinant of the third order: Delete the first row and the first column of this determinant. We get the determinant of the second order, which is called the minor of the element a 11. It is denoted by M 11.
 Definition. The cofactor of the element equals the minor of this element with the corresponding sign from the chess- board pattern of signs:
Definition. The cofactor of the element equals the minor of this element with the corresponding sign from the chess- board pattern of signs:
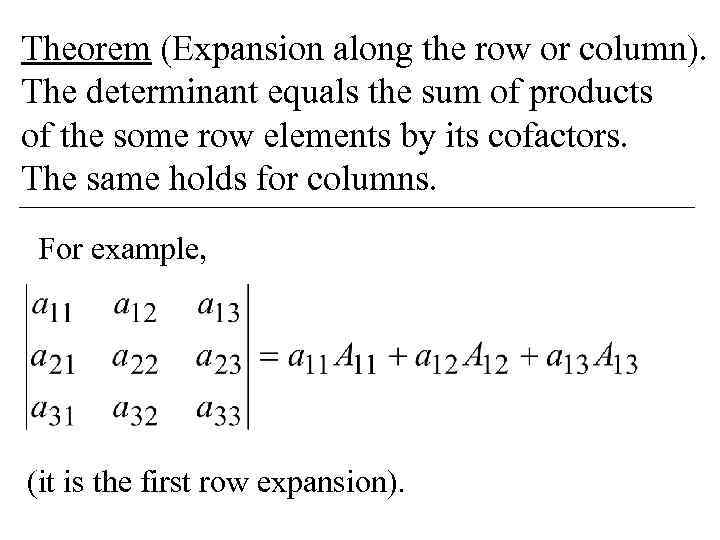 Theorem (Expansion along the row or column). The determinant equals the sum of products of the some row elements by its cofactors. The same holds for columns. For example, (it is the first row expansion).
Theorem (Expansion along the row or column). The determinant equals the sum of products of the some row elements by its cofactors. The same holds for columns. For example, (it is the first row expansion).
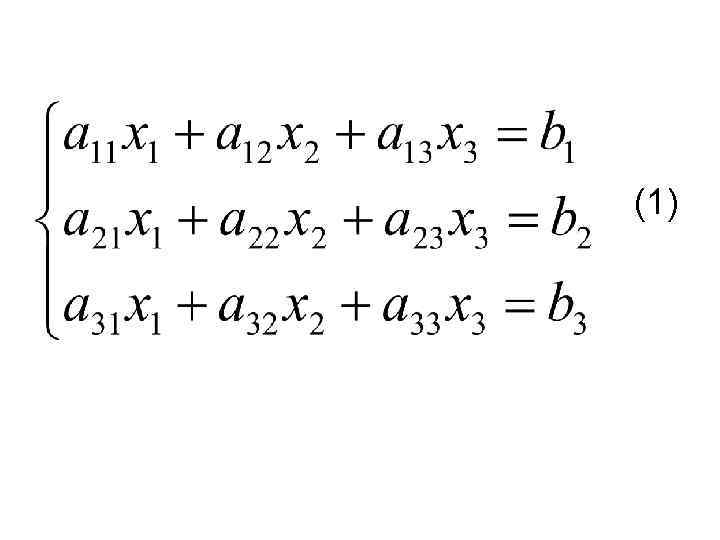 (1)
(1)
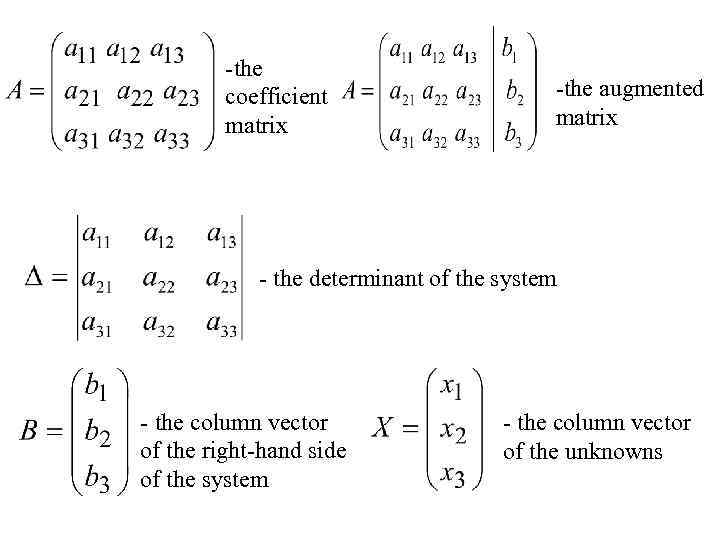 -the coefficient matrix -the augmented matrix - the determinant of the system - the column vector of the right-hand side of the system - the column vector of the unknowns
-the coefficient matrix -the augmented matrix - the determinant of the system - the column vector of the right-hand side of the system - the column vector of the unknowns
 Theorem (Cramer’s rule). The system (1) has a unique solution if Δ≠ 0, namely
Theorem (Cramer’s rule). The system (1) has a unique solution if Δ≠ 0, namely
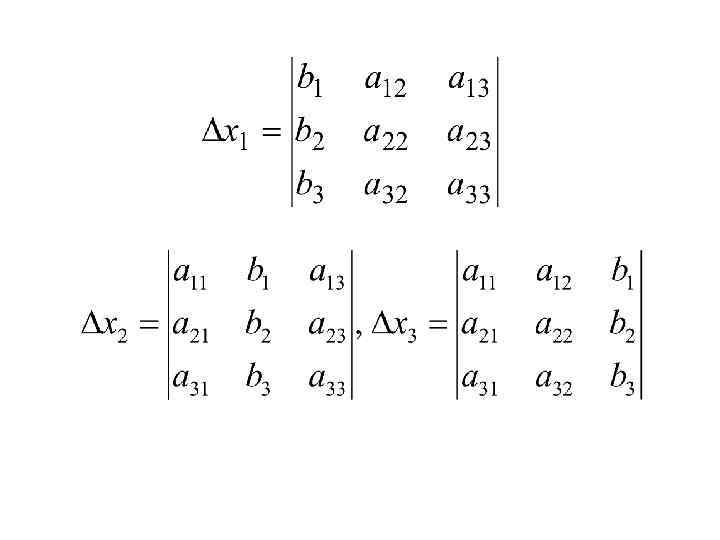
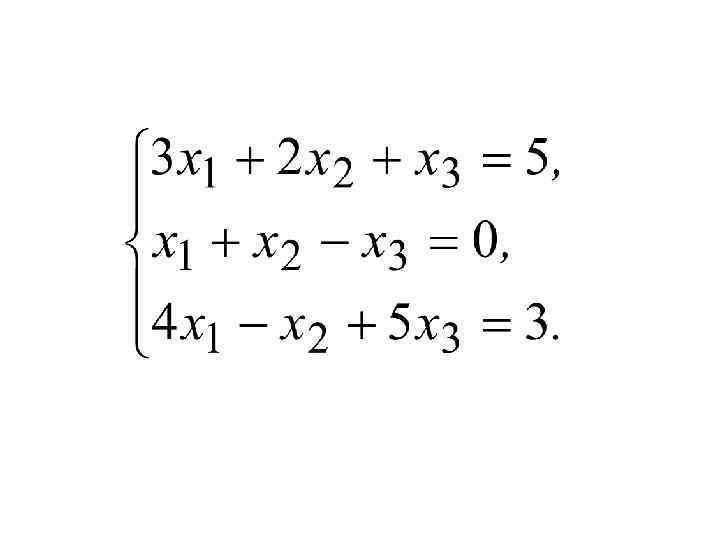
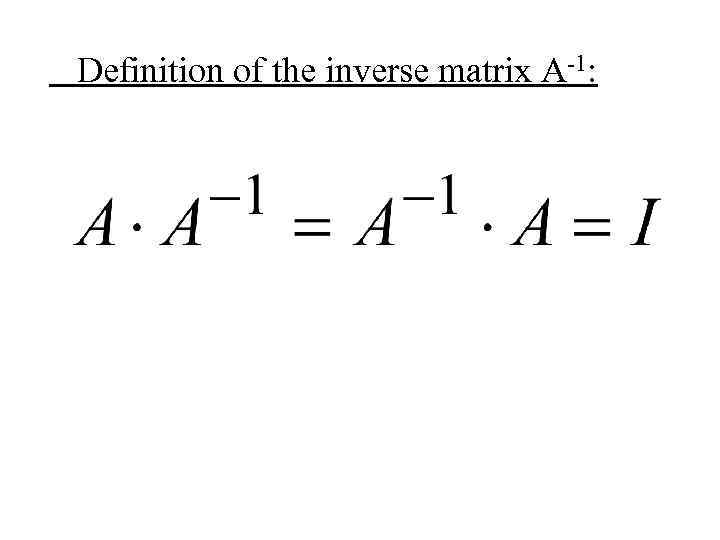 Definition of the inverse matrix A-1:
Definition of the inverse matrix A-1:
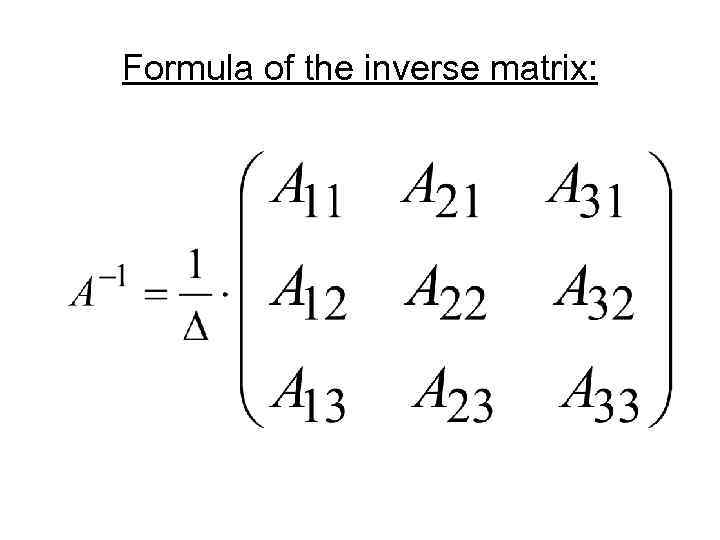 Formula of the inverse matrix:
Formula of the inverse matrix:
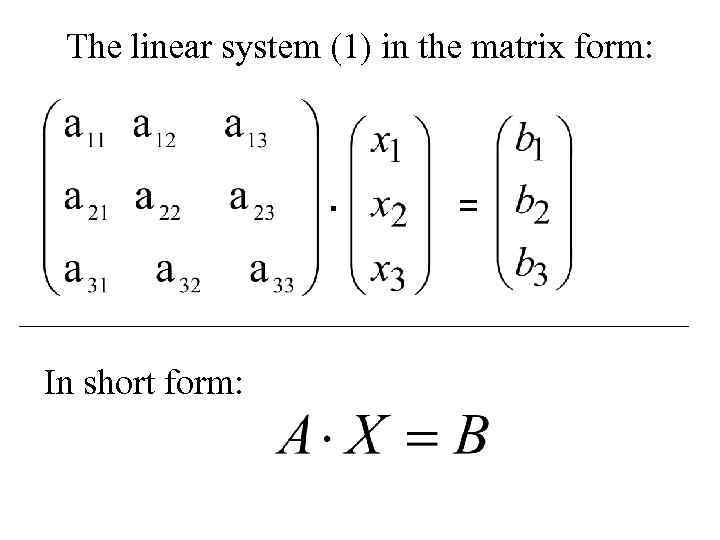 The linear system (1) in the matrix form: · In short form: =
The linear system (1) in the matrix form: · In short form: =
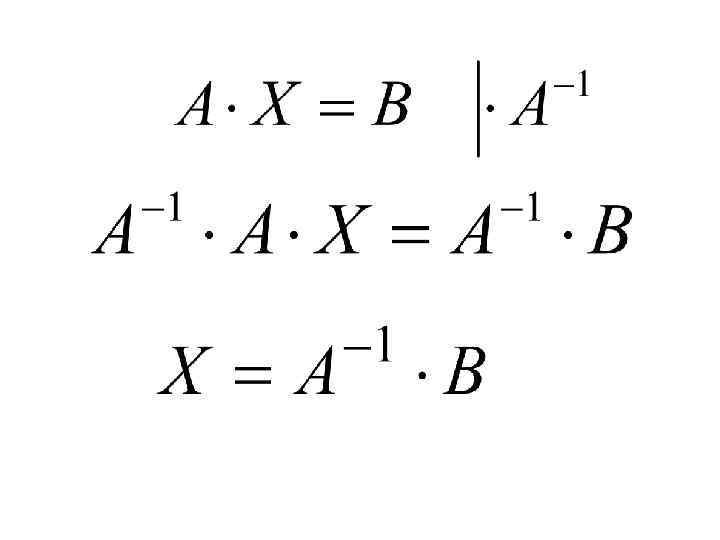
 Matrix method: If Δ≠ 0 for the system (1), then it has a unique solution, which can be found by the formula
Matrix method: If Δ≠ 0 for the system (1), then it has a unique solution, which can be found by the formula


