loops.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20

Topic: Loops Objective: the student must learn how to work with loops Type of lessons: Lecture Interdisciplinary communication: English language

There may be a situation, when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first, followed by the second, and so on. to execute-выполнить; in general-в целом; several number of times-некоторое количество раз;
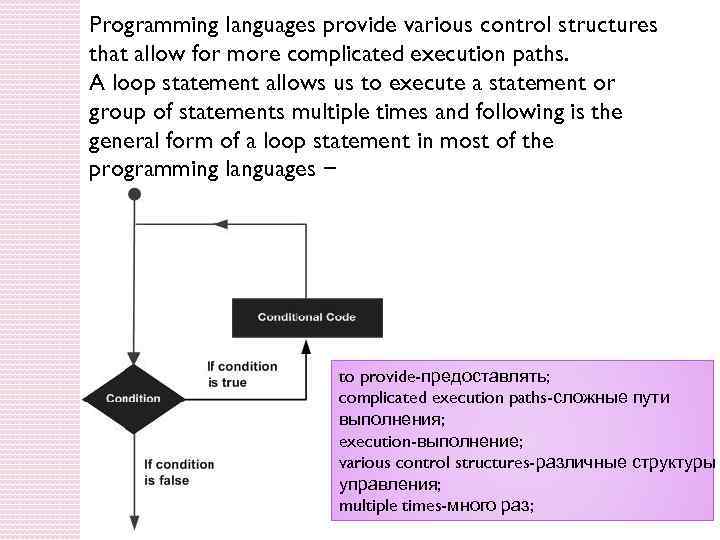
Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths. A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times and following is the general form of a loop statement in most of the programming languages − to provide-предоставлять; complicated execution paths-сложные пути выполнения; execution-выполнение; various control structures-различные структуры управления; multiple times-много раз;
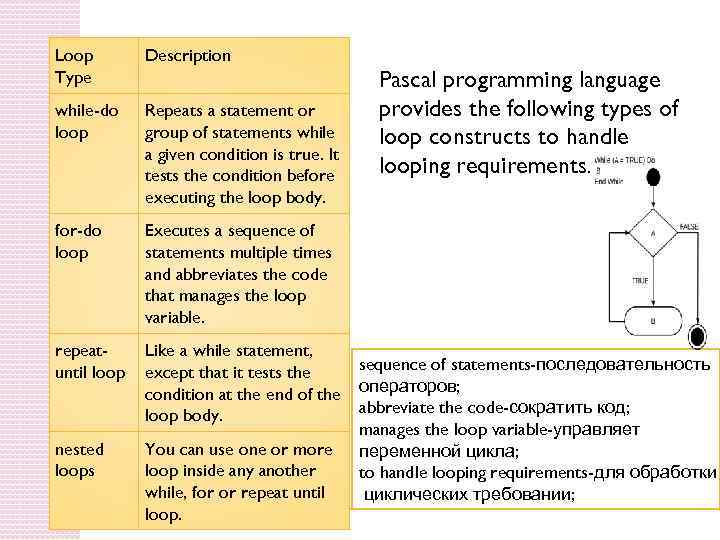
Loop Type Description while-do loop Repeats a statement or group of statements while a given condition is true. It tests the condition before executing the loop body. for-do loop Executes a sequence of statements multiple times and abbreviates the code that manages the loop variable. repeatuntil loop Like a while statement, except that it tests the condition at the end of the loop body. nested loops You can use one or more loop inside any another while, for or repeat until loop. Pascal programming language provides the following types of loop constructs to handle looping requirements. sequence of statements-последовательность операторов; abbreviate the code-сократить код; manages the loop variable-управляет переменной цикла; to handle looping requirements-для обработки циклических требовании;
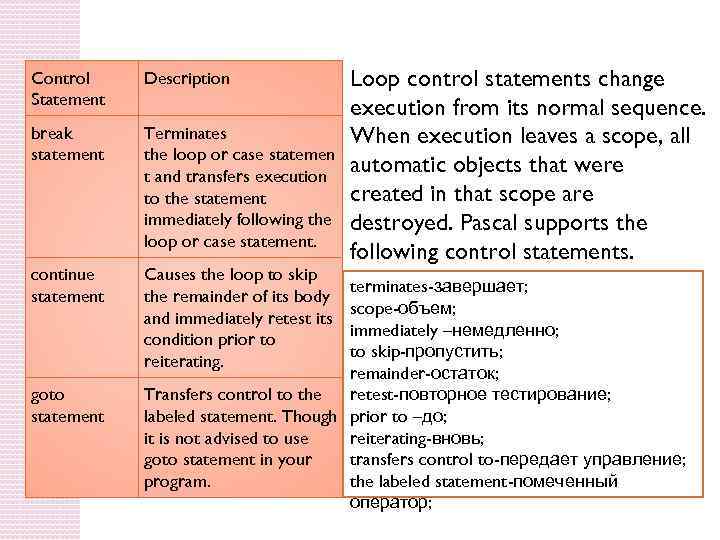
Control Statement Description break statement Terminates the loop or case statemen t and transfers execution to the statement immediately following the loop or case statement. continue statement Causes the loop to skip the remainder of its body and immediately retest its condition prior to reiterating. goto statement Loop control statements change execution from its normal sequence. When execution leaves a scope, all automatic objects that were created in that scope are destroyed. Pascal supports the following control statements. terminates-завершает; scope-объем; immediately –немедленно; to skip-пропустить; remainder-остаток; Transfers control to the retest-повторное тестирование; labeled statement. Though prior to –до; it is not advised to use reiterating-вновь; goto statement in your transfers control to-передает управление; program. the labeled statement-помеченный оператор;

While-do Loop A while-do loop statement in Pascal allows repetitive computations till some test condition is satisfied. In other words, it repeatedly executes a target statement as long as a given condition is true. The syntax of a while-do loop is − while (condition) do S; Where, condition is a Boolean or relational expression whose value would be true or false and S is a simple statement or group of statements within BEGIN. . . END block.
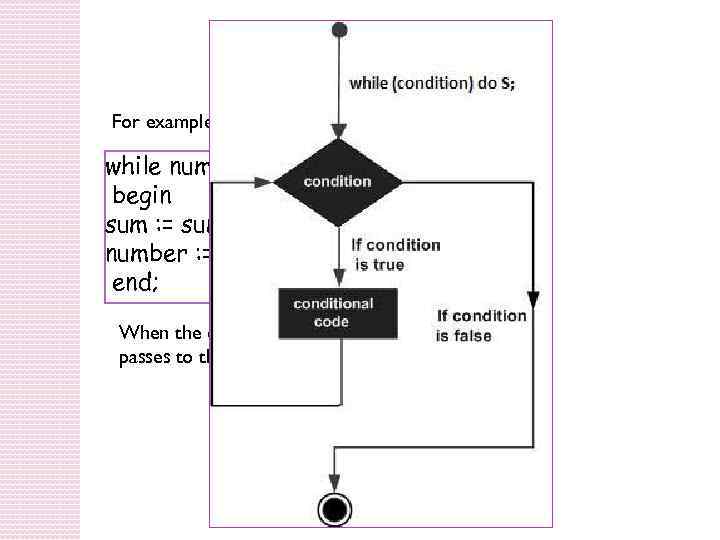
While-do Loop For example, while number>0 do begin sum : = sum + number; number : = number - 2; end; When the condition becomes false, program control passes to the line immediately following the loop.

While-do Loop Here, key point of the while loop is that the loop might not ever run. When the condition is tested and the result is false, the loop body will be skipped and the first statement after the while loop will be executed. Example: program while. Loop; var a: integer; begin a : = 10; while a < 20 do begin writeln('value of a: ', a); a : = a + 1; end.
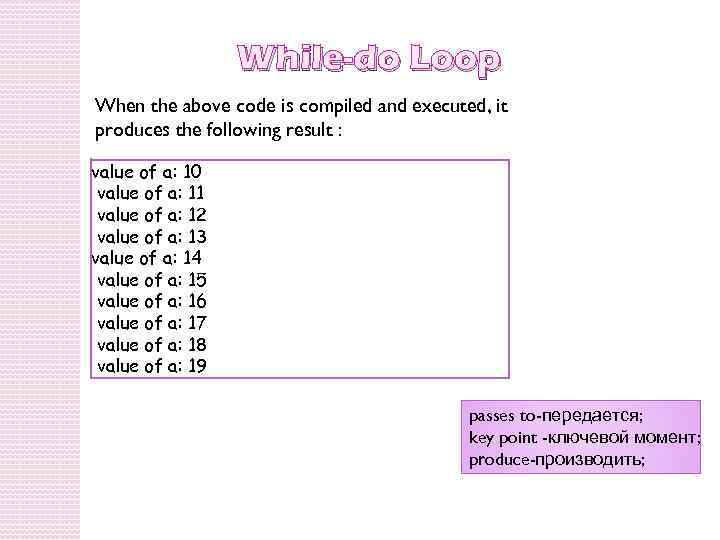
While-do Loop When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result : value of a: 10 value of a: 11 value of a: 12 value of a: 13 value of a: 14 value of a: 15 value of a: 16 value of a: 17 value of a: 18 value of a: 19 passes to-передается; key point -ключевой момент; produce-производить;
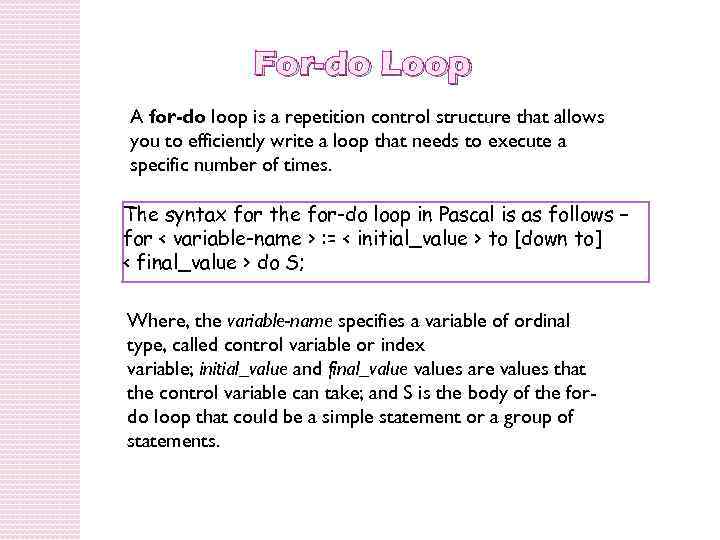
For-do Loop A for-do loop is a repetition control structure that allows you to efficiently write a loop that needs to execute a specific number of times. The syntax for the for-do loop in Pascal is as follows − for < variable-name > : = < initial_value > to [down to] < final_value > do S; Where, the variable-name specifies a variable of ordinal type, called control variable or index variable; initial_value and final_values are values that the control variable can take; and S is the body of the fordo loop that could be a simple statement or a group of statements.
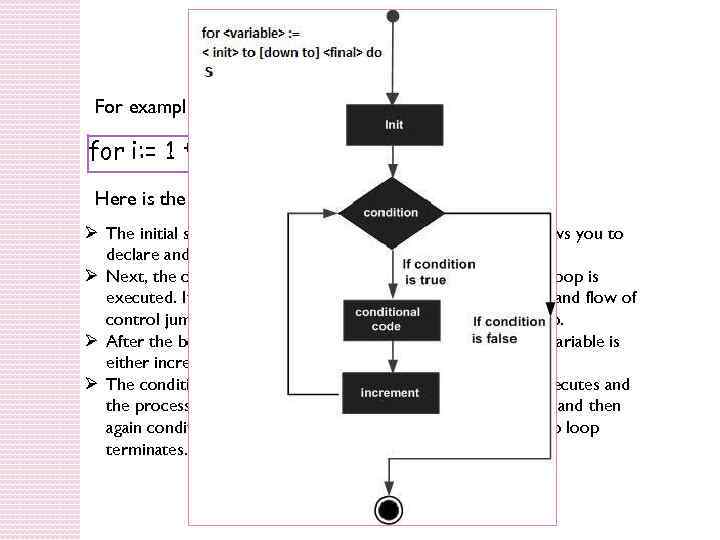
For-do Loop For example, for i: = 1 to 10 do writeln(i); Here is the flow of control in a for-do loop − Ø The initial step is executed first, and only once. This step allows you to declare and initialize any loop control variables. Ø Next, the condition is evaluated. If it is true, the body of the loop is executed. If it is false, the body of the loop does not execute and flow of control jumps to the next statement just after the for-do loop. Ø After the body of the for-do loop executes, the value of the variable is either increased or decreased. Ø The condition is now evaluated again. If it is true, the loop executes and the process repeats itself (body of loop, then increment step, and then again condition). After the condition becomes false, the for-do loop terminates.
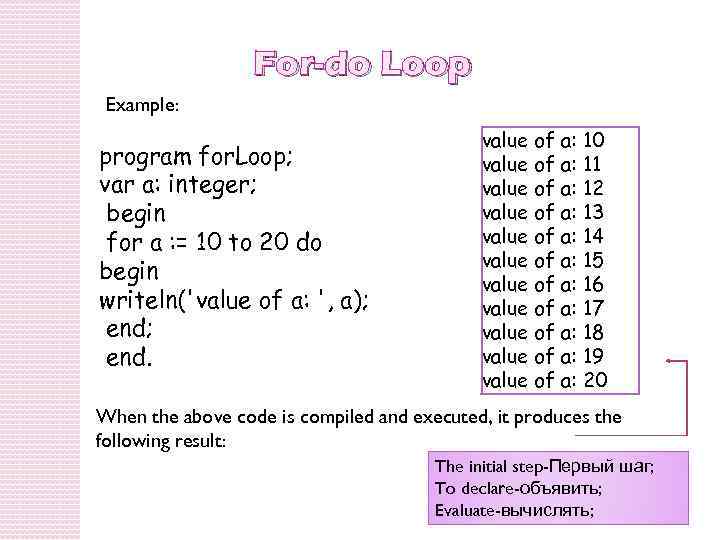
For-do Loop Example: program for. Loop; var a: integer; begin for a : = 10 to 20 do begin writeln('value of a: ', a); end. value of a: 10 value of a: 11 value of a: 12 value of a: 13 value of a: 14 value of a: 15 value of a: 16 value of a: 17 value of a: 18 value of a: 19 value of a: 20 When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result: The initial step-Первый шаг; To declare-объявить; Evaluate-вычислять;

Repeat-Until Loop Unlike for and while loops, which test the loop condition at the top of the loop, the repeat. . . until loop in Pascal checks its condition at the bottom of the loop. A “repeat. . . Until” loop is similar to a while loop, except that a “repeat. . . Until” loop is guaranteed to execute at least one time. Syntax: repeat S 1; S 2; . . . Sn; until condition;
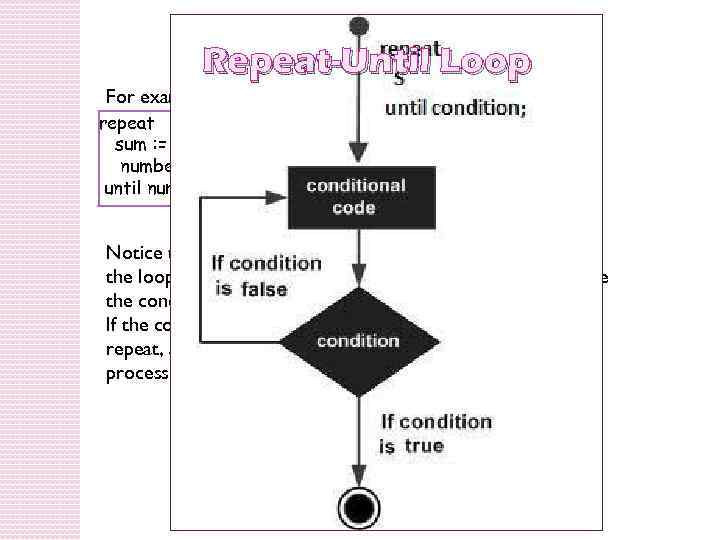
Repeat-Until Loop For example, repeat sum : = sum + number; number : = number - 2; until number = 0; Notice that the conditional expression appears at the end of the loop, so the statement(s) in the loop execute once before the condition is tested. If the condition is false, the flow of control jumps back up to repeat, and the statement(s) in the loop execute again. This process repeats until the given condition becomes true.
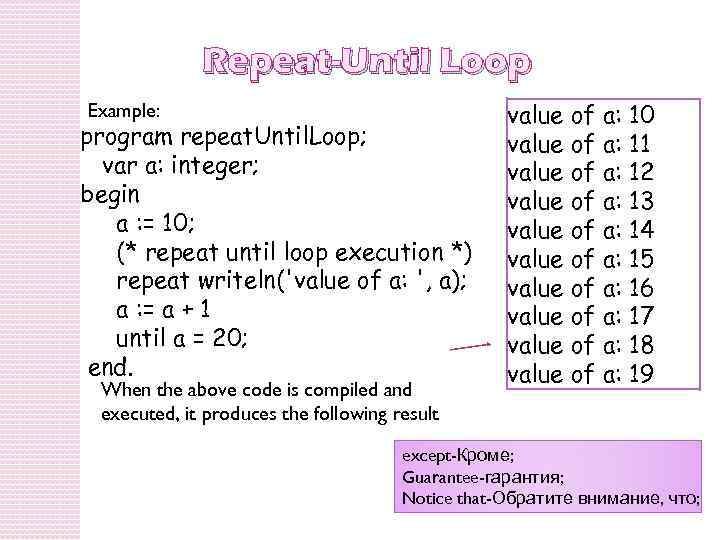
Repeat-Until Loop Example: program repeat. Until. Loop; var a: integer; begin a : = 10; (* repeat until loop execution *) repeat writeln('value of a: ', a); a : = a + 1 until a = 20; end. When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result value of a: 10 value of a: 11 value of a: 12 value of a: 13 value of a: 14 value of a: 15 value of a: 16 value of a: 17 value of a: 18 value of a: 19 except-Кроме; Guarantee-гарантия; Notice that-Обратите внимание, что;
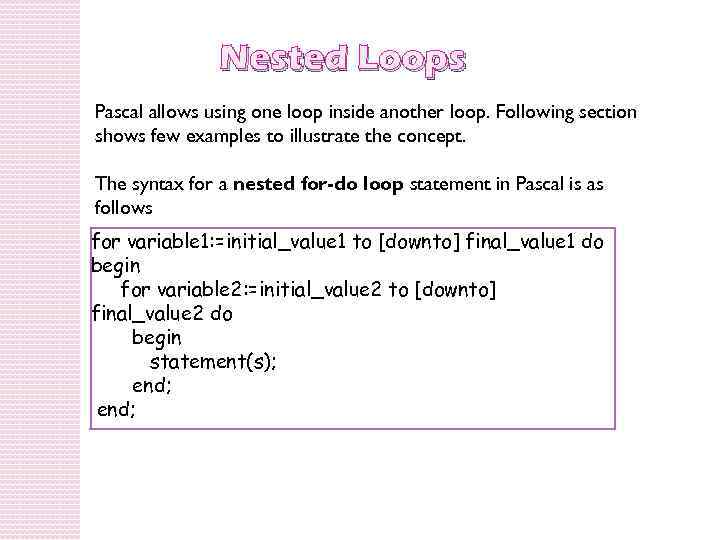
Nested Loops Pascal allows using one loop inside another loop. Following section shows few examples to illustrate the concept. The syntax for a nested for-do loop statement in Pascal is as follows for variable 1: =initial_value 1 to [downto] final_value 1 do begin for variable 2: =initial_value 2 to [downto] final_value 2 do begin statement(s); end;
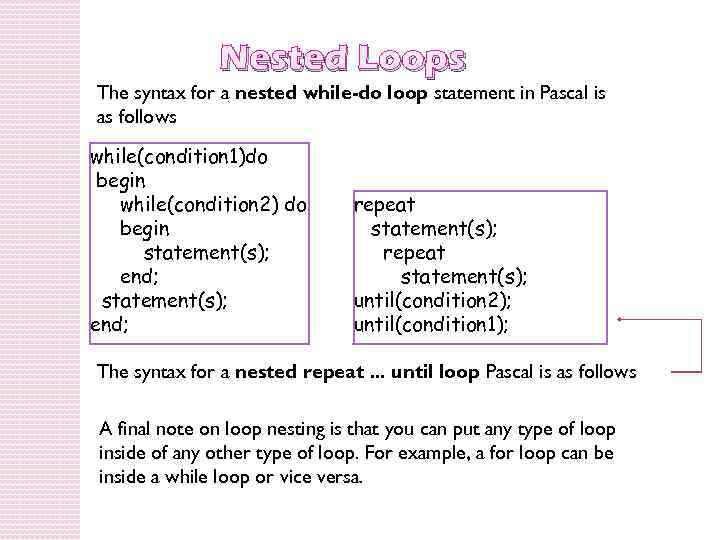
Nested Loops The syntax for a nested while-do loop statement in Pascal is as follows while(condition 1)do begin while(condition 2) do begin statement(s); end; repeat statement(s); until(condition 2); until(condition 1); The syntax for a nested repeat. . . until loop Pascal is as follows A final note on loop nesting is that you can put any type of loop inside of any other type of loop. For example, a for loop can be inside a while loop or vice versa.
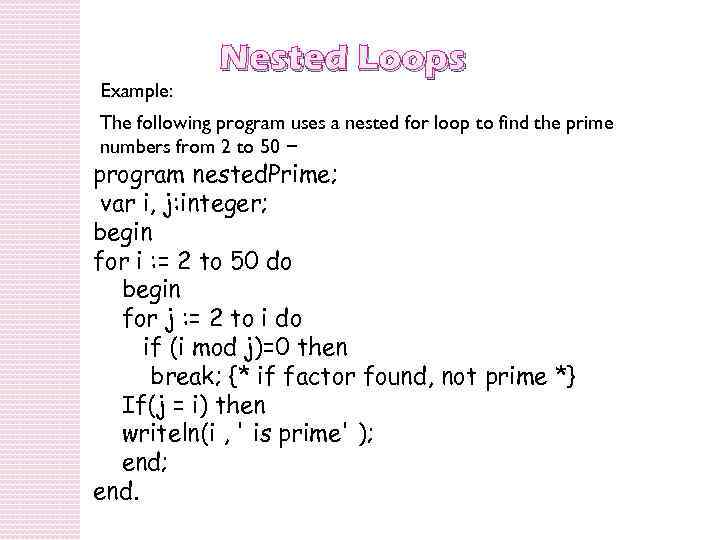
Example: Nested Loops The following program uses a nested for loop to find the prime numbers from 2 to 50 − program nested. Prime; var i, j: integer; begin for i : = 2 to 50 do begin for j : = 2 to i do if (i mod j)=0 then break; {* if factor found, not prime *} If(j = i) then writeln(i , ' is prime' ); end.
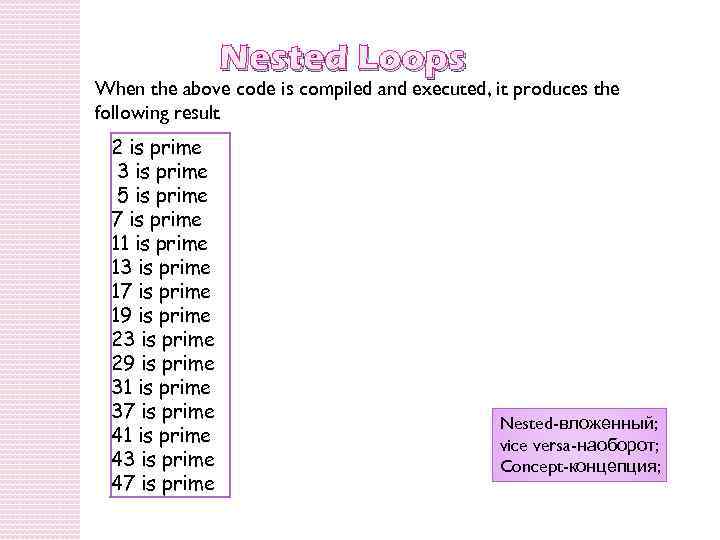
Nested Loops When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result 2 is prime 3 is prime 5 is prime 7 is prime 11 is prime 13 is prime 17 is prime 19 is prime 23 is prime 29 is prime 31 is prime 37 is prime 41 is prime 43 is prime 47 is prime Nested-вложенный; vice versa-наоборот; Concept-концепция;

Thanks for you attention!
loops.pptx