 Topic 8: Nucleic Acid Master Molecules
Topic 8: Nucleic Acid Master Molecules
 • They contain C, O, H, N and P. • They are the master molecules which control all life activities in the cell • There are two kind of nucleic acid; – DNA – RNA
• They contain C, O, H, N and P. • They are the master molecules which control all life activities in the cell • There are two kind of nucleic acid; – DNA – RNA
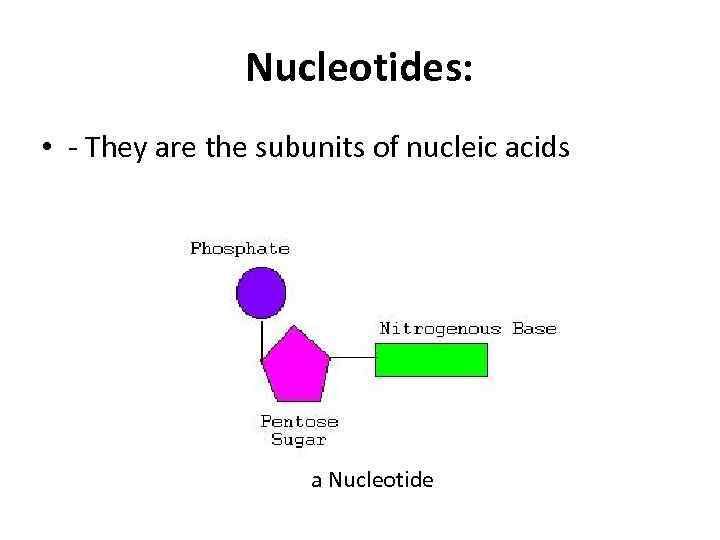 Nucleotides: • - They are the subunits of nucleic acids a Nucleotide
Nucleotides: • - They are the subunits of nucleic acids a Nucleotide
 Each nucleotide compose of a) Pentose Sugar: – Ribose in RNA – Deoxyribose in DNA b) Phosphate group: PO 4 c) Nitrogenous base: – Prymidines: Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil (single ring) – Purines: Adenine and Guanine (double ring)
Each nucleotide compose of a) Pentose Sugar: – Ribose in RNA – Deoxyribose in DNA b) Phosphate group: PO 4 c) Nitrogenous base: – Prymidines: Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil (single ring) – Purines: Adenine and Guanine (double ring)
 DNA (Deoxyribo. Nucleic Acid) Functions of DNA - Controls all metabolic activities - Stores genetic information - Transfer genetic information from one generation to the next
DNA (Deoxyribo. Nucleic Acid) Functions of DNA - Controls all metabolic activities - Stores genetic information - Transfer genetic information from one generation to the next
 DNA • - Found in nucleus of eukaryotic cells • - DNA base sequence is different between species but same between the cells of an organism • - DNA has double stranded helical Structure (Watson and Crick in 1953)
DNA • - Found in nucleus of eukaryotic cells • - DNA base sequence is different between species but same between the cells of an organism • - DNA has double stranded helical Structure (Watson and Crick in 1953)
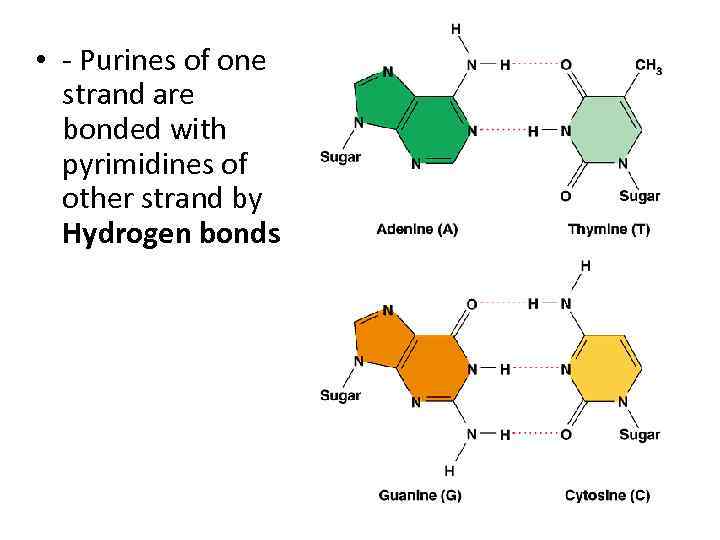 • - Purines of one strand are bonded with pyrimidines of other strand by Hydrogen bonds
• - Purines of one strand are bonded with pyrimidines of other strand by Hydrogen bonds
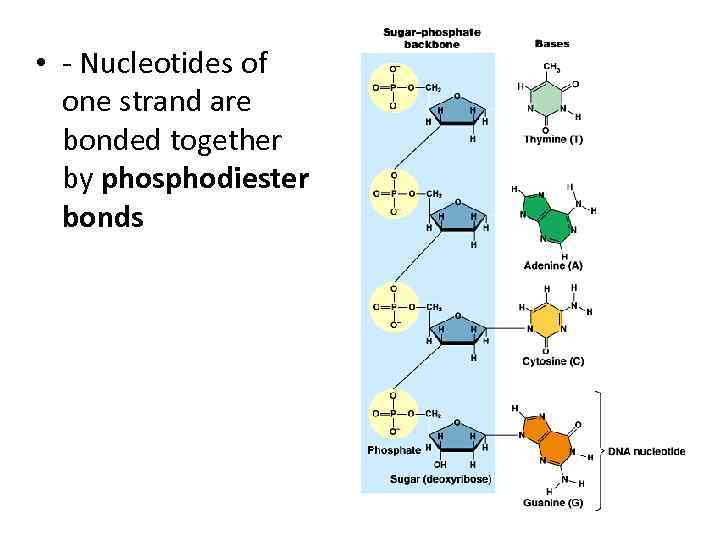 • - Nucleotides of one strand are bonded together by phosphodiester bonds
• - Nucleotides of one strand are bonded together by phosphodiester bonds
 RNA (Ribo. Nucleic Acid) • - They contain ribose sugar. • - Carry information within cell to perform protein synthesis • - synthesised from a strand of DNA by RNA polymerase enzyme • - has 3 types – m. RNA- t. RNA– r. RNA
RNA (Ribo. Nucleic Acid) • - They contain ribose sugar. • - Carry information within cell to perform protein synthesis • - synthesised from a strand of DNA by RNA polymerase enzyme • - has 3 types – m. RNA- t. RNA– r. RNA
 a) Messenger RNA (m. RNA) • - Carry information from DNA to ribosomes • - Transcription: copying of genetic information from DNA to m. RNA • Codon: is the triplet of nucleotides on m. RNA
a) Messenger RNA (m. RNA) • - Carry information from DNA to ribosomes • - Transcription: copying of genetic information from DNA to m. RNA • Codon: is the triplet of nucleotides on m. RNA
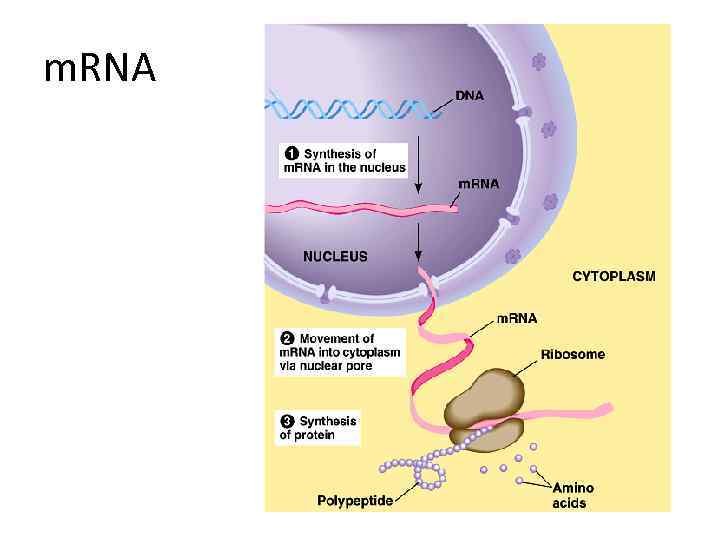 m. RNA
m. RNA
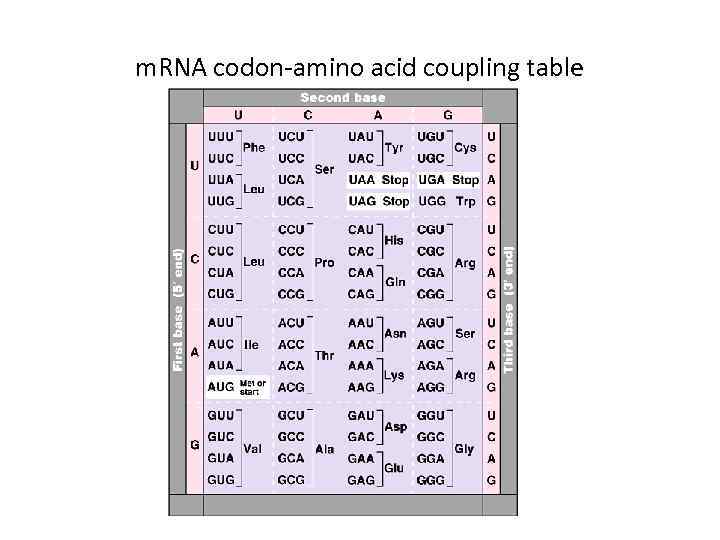 m. RNA codon-amino acid coupling table
m. RNA codon-amino acid coupling table
 b) Transfer RNA (t. RNA): • - Carry amino acids from cytoplasm to ribosomes • - There are 61 kind of t. RNA for 20 kind of aa. • - Anticodon: A part of t. RNA that complementary to its codon
b) Transfer RNA (t. RNA): • - Carry amino acids from cytoplasm to ribosomes • - There are 61 kind of t. RNA for 20 kind of aa. • - Anticodon: A part of t. RNA that complementary to its codon
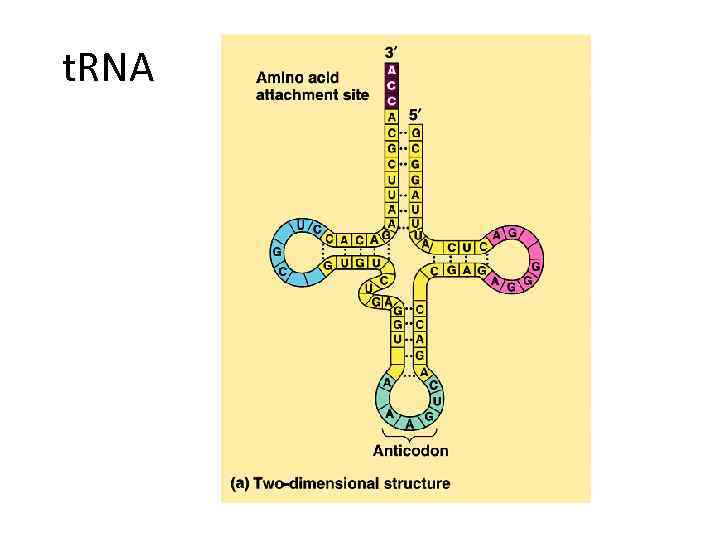 t. RNA
t. RNA
 c) Ribosomal RNA (r. RNA): • - Compose of ribosome with proteins • - Ribosomes are the centres of protein synthesis • - Translation: producing polypeptides according to sequence of m. RNA in ribosomes
c) Ribosomal RNA (r. RNA): • - Compose of ribosome with proteins • - Ribosomes are the centres of protein synthesis • - Translation: producing polypeptides according to sequence of m. RNA in ribosomes