e7b1e05ac425da6a5d3c6f425964840b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 TOPIC 6 INTRODUCTION TO NEAR FIELD COMMUNICATION (NFC) 近場通訊
TOPIC 6 INTRODUCTION TO NEAR FIELD COMMUNICATION (NFC) 近場通訊
 INTRODUCTION NFC is a short-range radio technology that enables communication between devices that either touch or are momentarily held close together. This non-contact technology enables users to perform contactless transactions, access digital content and connect electronic devices. 2
INTRODUCTION NFC is a short-range radio technology that enables communication between devices that either touch or are momentarily held close together. This non-contact technology enables users to perform contactless transactions, access digital content and connect electronic devices. 2
 INTRODUCTION NFC is an open-platform technology, which is being standardized in the NFC Forum formed by Nokia, Sony and Phillips in 2004. Based on and extends on RFID. It operates on 13. 56 MHz frequency, a license free allocation in the HF portion of the radio spectrum. Provides communication range up to 10 cm. Practical working distance of about 4 cm. Supports different data transmission rates such as 106 kbps, 212 kbps, and 424 kbps. 3
INTRODUCTION NFC is an open-platform technology, which is being standardized in the NFC Forum formed by Nokia, Sony and Phillips in 2004. Based on and extends on RFID. It operates on 13. 56 MHz frequency, a license free allocation in the HF portion of the radio spectrum. Provides communication range up to 10 cm. Practical working distance of about 4 cm. Supports different data transmission rates such as 106 kbps, 212 kbps, and 424 kbps. 3
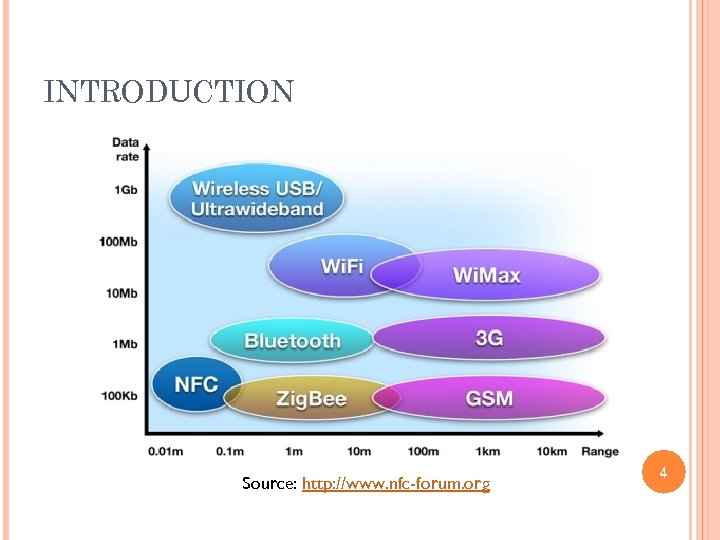 INTRODUCTION Source: http: //www. nfc-forum. org 4
INTRODUCTION Source: http: //www. nfc-forum. org 4
 NFC APPLICATIONS Service Initiation An NFC-enabled mobile phone taps against an NFC tag can receive information. Depending on the type of information read, the mobile phone may start a video stream, or open a web browser. One example is the smart poster, which could be promoting some kind of new product or service, or an event. ◦ http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 Rpc 3 u 8 m-ZY 5
NFC APPLICATIONS Service Initiation An NFC-enabled mobile phone taps against an NFC tag can receive information. Depending on the type of information read, the mobile phone may start a video stream, or open a web browser. One example is the smart poster, which could be promoting some kind of new product or service, or an event. ◦ http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=4 Rpc 3 u 8 m-ZY 5
 NFC APPLICATIONS Sharing NFC-enabled devices can share data through the peer-to-peer communication mode. For example, two NFC-enabled mobile phones can share business card information using NFC. Another example is when a user wants to print out photos in a digital camera. The user simply touches the device against the NFC-enabled printer, and a Bluetooth connection is established to transmit the digital photos from the device to be printed out on the printer. 6
NFC APPLICATIONS Sharing NFC-enabled devices can share data through the peer-to-peer communication mode. For example, two NFC-enabled mobile phones can share business card information using NFC. Another example is when a user wants to print out photos in a digital camera. The user simply touches the device against the NFC-enabled printer, and a Bluetooth connection is established to transmit the digital photos from the device to be printed out on the printer. 6
 NFC APPLICATIONS Payment and Ticketing Banks and mobile network operators are very interested in putting payment and ticketing applications on NFC-enabled mobile phones. Research conducted by Visa International found that 89 per cent of those who tried phonebased transactions preferred its convenience to alternative payment methods. 7
NFC APPLICATIONS Payment and Ticketing Banks and mobile network operators are very interested in putting payment and ticketing applications on NFC-enabled mobile phones. Research conducted by Visa International found that 89 per cent of those who tried phonebased transactions preferred its convenience to alternative payment methods. 7
 NFC APPLICATIONS Source: http: //www. nfc-forum. org More NFC use cases by visiting: http: //www. youtube. com/user/NFCForum 8
NFC APPLICATIONS Source: http: //www. nfc-forum. org More NFC use cases by visiting: http: //www. youtube. com/user/NFCForum 8
 TAG AND READER For two devices to communicate using NFC, one device must have an NFC reader/writer and one must have an NFC tag. Tag Thin device contains an antenna and a small amount of memory. It is a passive device, powered by a magnetic field. Memory types: read only, rewritable, or writable once Memory NFC Tag Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 9
TAG AND READER For two devices to communicate using NFC, one device must have an NFC reader/writer and one must have an NFC tag. Tag Thin device contains an antenna and a small amount of memory. It is a passive device, powered by a magnetic field. Memory types: read only, rewritable, or writable once Memory NFC Tag Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 9
 TAG AND READER Reader It is an active device that generates radio signals to communicate with the tags. The reader powers the passive device when the two are engaged in the passive mode of communication. Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 10
TAG AND READER Reader It is an active device that generates radio signals to communicate with the tags. The reader powers the passive device when the two are engaged in the passive mode of communication. Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 10
 NFC COMMUNICATION MODES Active Mode The target and the initiator devices have power supplies and both devices generate their own radio signal to transmit data. Passive Mode The initiator device generates radio signals and the target device is powered by this electromagnetic field. The target device responds to the initiator by modulating the existing electromagnetic field. 11
NFC COMMUNICATION MODES Active Mode The target and the initiator devices have power supplies and both devices generate their own radio signal to transmit data. Passive Mode The initiator device generates radio signals and the target device is powered by this electromagnetic field. The target device responds to the initiator by modulating the existing electromagnetic field. 11
 NFC OPERATING MODES Read/write The NFC-enabled phone can read or write data to any of the supported tag types in a standard NFC data format. Peer-to-peer Two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data. For example, you can share Bluetooth or Wi-Fi link setup parameters to initiate a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi link. Card Emulation An NFC-enabled phone acts as a tag or contactless card for existing readers. 12
NFC OPERATING MODES Read/write The NFC-enabled phone can read or write data to any of the supported tag types in a standard NFC data format. Peer-to-peer Two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data. For example, you can share Bluetooth or Wi-Fi link setup parameters to initiate a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi link. Card Emulation An NFC-enabled phone acts as a tag or contactless card for existing readers. 12
 NFC OPERATING MODES Card Emulation Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 13
NFC OPERATING MODES Card Emulation Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 13
 NFC TAG TYPES NFC tags can be used in applications such as posters, where small amounts of data can be stored and transferred to active NFC devices. The stored data on the NFC tag may contain any form of data such as a URL, a phone number, or calendar information. To ensure interoperability between different NFC tag providers and NFC device manufacturers, the NFC Forum has defined four tag types. 14
NFC TAG TYPES NFC tags can be used in applications such as posters, where small amounts of data can be stored and transferred to active NFC devices. The stored data on the NFC tag may contain any form of data such as a URL, a phone number, or calendar information. To ensure interoperability between different NFC tag providers and NFC device manufacturers, the NFC Forum has defined four tag types. 14
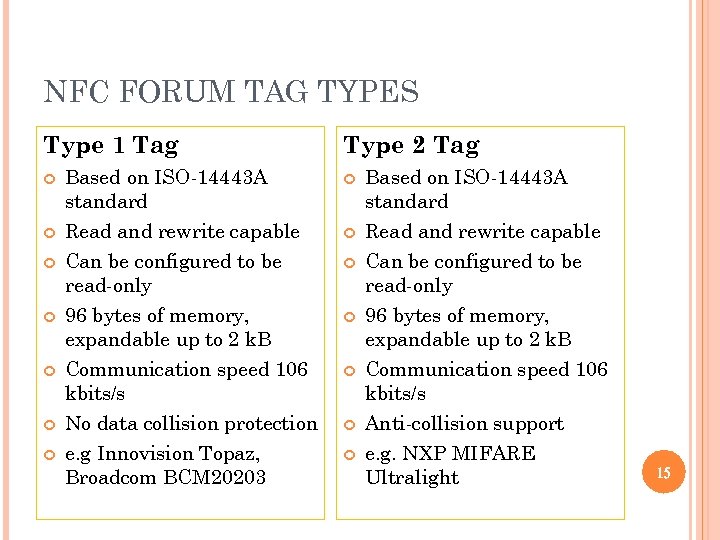 NFC FORUM TAG TYPES Type 1 Tag Based on ISO-14443 A standard Read and rewrite capable Can be configured to be read-only 96 bytes of memory, expandable up to 2 k. B Communication speed 106 kbits/s No data collision protection e. g Innovision Topaz, Broadcom BCM 20203 Type 2 Tag Based on ISO-14443 A standard Read and rewrite capable Can be configured to be read-only 96 bytes of memory, expandable up to 2 k. B Communication speed 106 kbits/s Anti-collision support e. g. NXP MIFARE Ultralight 15
NFC FORUM TAG TYPES Type 1 Tag Based on ISO-14443 A standard Read and rewrite capable Can be configured to be read-only 96 bytes of memory, expandable up to 2 k. B Communication speed 106 kbits/s No data collision protection e. g Innovision Topaz, Broadcom BCM 20203 Type 2 Tag Based on ISO-14443 A standard Read and rewrite capable Can be configured to be read-only 96 bytes of memory, expandable up to 2 k. B Communication speed 106 kbits/s Anti-collision support e. g. NXP MIFARE Ultralight 15
 NFC FORUM TAG TYPES Type 3 Tag Based on the Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) X 6319 -4 Preconfigured: read and rewritable or read-only Variable memory: up to 1 MB per service Communication speeds: 212 or 424 kbits/s Anti-collision support e. g. Sony Feli. Ca Type 4 Tag Based on ISO-14443 A standard Preconfigured: read and rewritable or read-only Variable memory: up to 32 k. B per service Communication speeds: 106, 212, or 424 kbits/s Anti-collision support e. g. NXP DESFire, Smart. MX-JCOP 16
NFC FORUM TAG TYPES Type 3 Tag Based on the Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS) X 6319 -4 Preconfigured: read and rewritable or read-only Variable memory: up to 1 MB per service Communication speeds: 212 or 424 kbits/s Anti-collision support e. g. Sony Feli. Ca Type 4 Tag Based on ISO-14443 A standard Preconfigured: read and rewritable or read-only Variable memory: up to 32 k. B per service Communication speeds: 106, 212, or 424 kbits/s Anti-collision support e. g. NXP DESFire, Smart. MX-JCOP 16
 NXP-SPECIFIC TAG TYPE Type MIFARE Classic Tag (Proprietary tag type defined by NXP Semiconductors) Based on ISO-14443 A standard Read and rewrite capable Can be configure to be read-only Variable memory 192/768/3584 bytes Communication speed 106 kbits/s Source (2010): http: //nfctimes. com Anticollision support e. g NXP MIFARE Classic 1 K, MIFARE Classic 4 K, and Classic Mini 17
NXP-SPECIFIC TAG TYPE Type MIFARE Classic Tag (Proprietary tag type defined by NXP Semiconductors) Based on ISO-14443 A standard Read and rewrite capable Can be configure to be read-only Variable memory 192/768/3584 bytes Communication speed 106 kbits/s Source (2010): http: //nfctimes. com Anticollision support e. g NXP MIFARE Classic 1 K, MIFARE Classic 4 K, and Classic Mini 17
 SECURE ELEMENT IN NFC DEVICE Embedded in mobile phone, SIM based, removable secure element (SD Card). Source: http: //www. nfc-forum. org/ 18
SECURE ELEMENT IN NFC DEVICE Embedded in mobile phone, SIM based, removable secure element (SD Card). Source: http: //www. nfc-forum. org/ 18
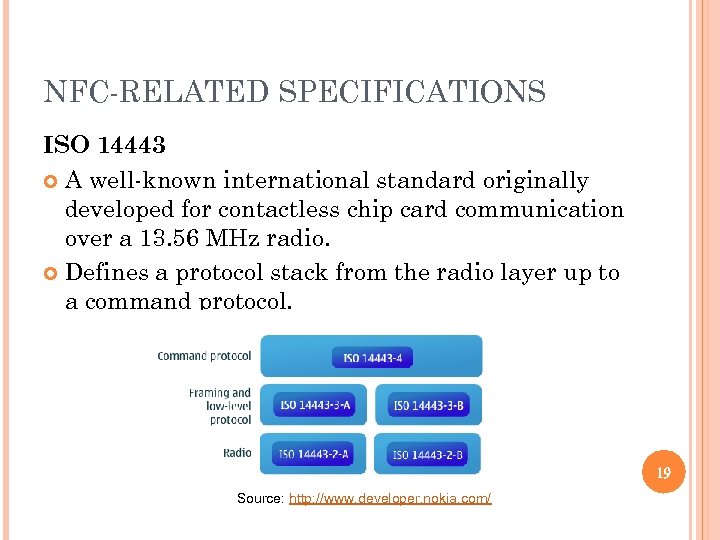 NFC-RELATED SPECIFICATIONS ISO 14443 A well-known international standard originally developed for contactless chip card communication over a 13. 56 MHz radio. Defines a protocol stack from the radio layer up to a command protocol. 19 Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/
NFC-RELATED SPECIFICATIONS ISO 14443 A well-known international standard originally developed for contactless chip card communication over a 13. 56 MHz radio. Defines a protocol stack from the radio layer up to a command protocol. 19 Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/
 NFC-RELATED SPECIFICATIONS NFCIP-1 Peer-to-peer communication defined in the Near Field Communication — Interface and Protocol Specification, NFCIP-1. Also known as ISO 18092 and ECMA-340. Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 20
NFC-RELATED SPECIFICATIONS NFCIP-1 Peer-to-peer communication defined in the Near Field Communication — Interface and Protocol Specification, NFCIP-1. Also known as ISO 18092 and ECMA-340. Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 20
 NFC DATA EXCHANGE FORMAT To enable interoperability when transferring data to and from tags and between NFC devices, the NFC Forum has specified a common data format known as the NFC Data Exchange Format (NDEF). NDEF is exchanged in messages that consist of a sequence of records. Each record carries a payload. The payload contents can be of type URL, MIME media, or an NFC-specific data type. For NFC-specific data types, the payload contents must be defined in an NFC Record Type Definition (RTD) file. 21
NFC DATA EXCHANGE FORMAT To enable interoperability when transferring data to and from tags and between NFC devices, the NFC Forum has specified a common data format known as the NFC Data Exchange Format (NDEF). NDEF is exchanged in messages that consist of a sequence of records. Each record carries a payload. The payload contents can be of type URL, MIME media, or an NFC-specific data type. For NFC-specific data types, the payload contents must be defined in an NFC Record Type Definition (RTD) file. 21
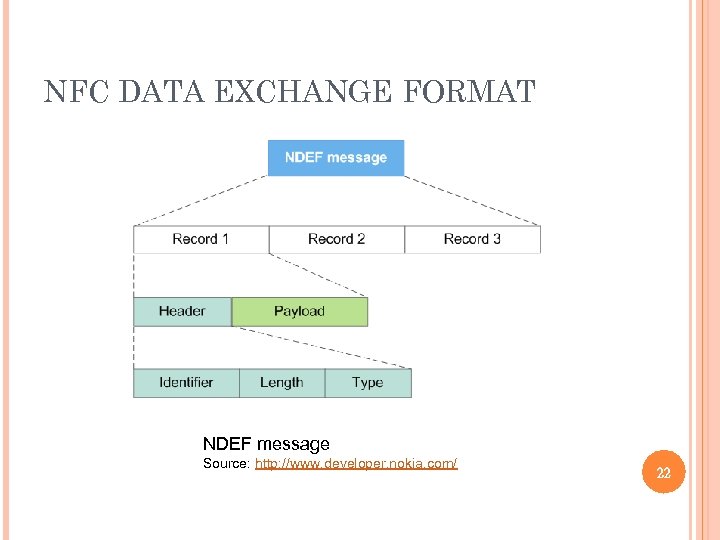 NFC DATA EXCHANGE FORMAT NDEF message Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 22
NFC DATA EXCHANGE FORMAT NDEF message Source: http: //www. developer. nokia. com/ 22
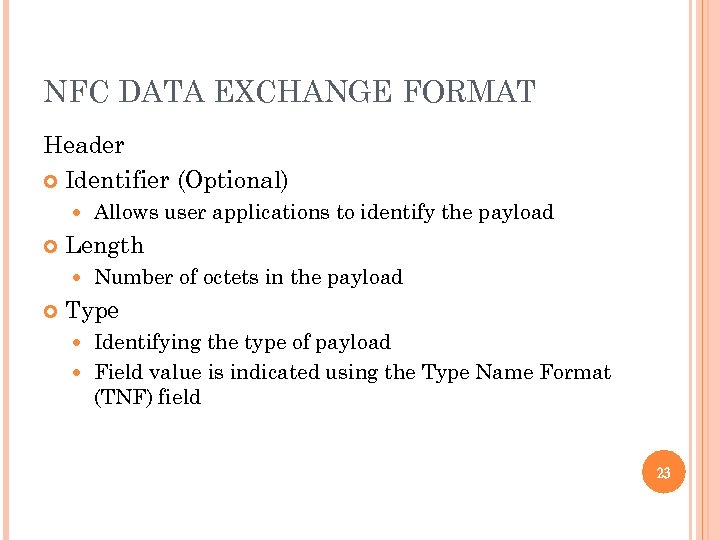 NFC DATA EXCHANGE FORMAT Header Identifier (Optional) Length Allows user applications to identify the payload Number of octets in the payload Type Identifying the type of payload Field value is indicated using the Type Name Format (TNF) field 23
NFC DATA EXCHANGE FORMAT Header Identifier (Optional) Length Allows user applications to identify the payload Number of octets in the payload Type Identifying the type of payload Field value is indicated using the Type Name Format (TNF) field 23
 NFC DATA EXCHANGE FORMAT Payload One of a variety of different types: URL, MIME media, or NFC-specific data type. For NFC-specific data types the payload contents must be defined in an NFC Record Type Definition file, RTD. 24
NFC DATA EXCHANGE FORMAT Payload One of a variety of different types: URL, MIME media, or NFC-specific data type. For NFC-specific data types the payload contents must be defined in an NFC Record Type Definition file, RTD. 24
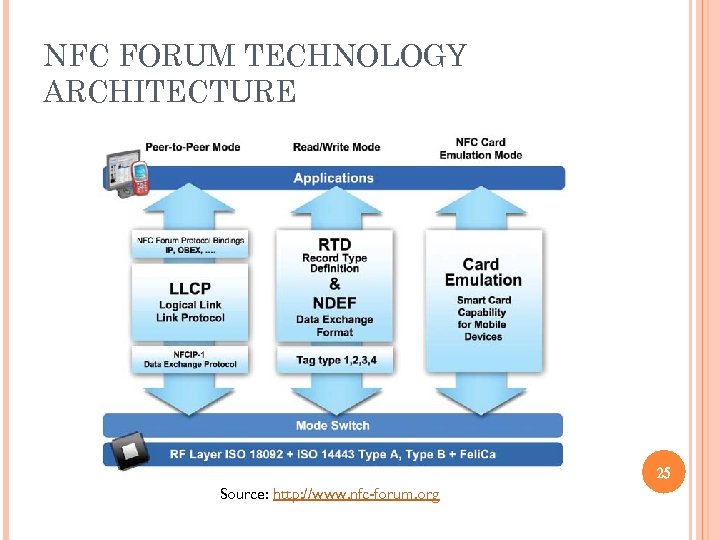 NFC FORUM TECHNOLOGY ARCHITECTURE 25 Source: http: //www. nfc-forum. org
NFC FORUM TECHNOLOGY ARCHITECTURE 25 Source: http: //www. nfc-forum. org
 NFC THREATS Eavesdropping When two devices communicate via NFC they use RF signals to talk to each other. An attacker can use an antenna to receive the transmitted signals. Data modification The attacker aiming to arrange for the receiving device to receive data that has been manipulated in some form. This form of attack is theoretically possible for some bits under different coding schemes. 26
NFC THREATS Eavesdropping When two devices communicate via NFC they use RF signals to talk to each other. An attacker can use an antenna to receive the transmitted signals. Data modification The attacker aiming to arrange for the receiving device to receive data that has been manipulated in some form. This form of attack is theoretically possible for some bits under different coding schemes. 26
 NFC THREATS Data corruption A form of denial of service attack. The attacker disturbs the communications by sending data or even blocking he channel so that the legitimate data is corrupted. Man-in-middle attack For the attack to be succeeded the two original parties must not know that there is an interceptor between them. It is particularly difficult to achieve a man-inthe-middle attack on an NFC link. 27
NFC THREATS Data corruption A form of denial of service attack. The attacker disturbs the communications by sending data or even blocking he channel so that the legitimate data is corrupted. Man-in-middle attack For the attack to be succeeded the two original parties must not know that there is an interceptor between them. It is particularly difficult to achieve a man-inthe-middle attack on an NFC link. 27
 ATTACKS ON NFC Relay Attack The attacker has to forward the request of the reader to the victim and relay back its answer to the reader in real time. Shown by Lishoy Francism, it can be practically implemented using only two NFC-enabled mobile phones. Attacker 28 Source: http: //eprint. iacr. org/2011/618
ATTACKS ON NFC Relay Attack The attacker has to forward the request of the reader to the victim and relay back its answer to the reader in real time. Shown by Lishoy Francism, it can be practically implemented using only two NFC-enabled mobile phones. Attacker 28 Source: http: //eprint. iacr. org/2011/618
 ATTACKS ON NFC MIFARE Classic Tag Attack Published by a paper “A Practical Attack on the MIFARE Classic”. Using the vulnerability of CRYPTO-1 (48 -bit symmetric key cryptography) stream cipher. The algorithm to generate a nonce is weak. Recover the keystream, read all memory blocks of the card. 29
ATTACKS ON NFC MIFARE Classic Tag Attack Published by a paper “A Practical Attack on the MIFARE Classic”. Using the vulnerability of CRYPTO-1 (48 -bit symmetric key cryptography) stream cipher. The algorithm to generate a nonce is weak. Recover the keystream, read all memory blocks of the card. 29
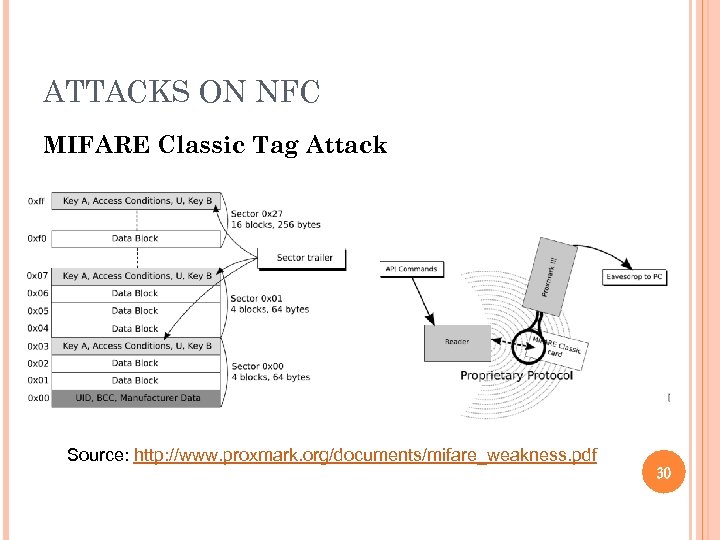 ATTACKS ON NFC MIFARE Classic Tag Attack Source: http: //www. proxmark. org/documents/mifare_weakness. pdf 30
ATTACKS ON NFC MIFARE Classic Tag Attack Source: http: //www. proxmark. org/documents/mifare_weakness. pdf 30
 COUNTERMEASURES Prevention of eavesdropping and data modification Using Faraday cage/sleeve. A secure channel is established with symmetric key like 3 DES (56/112/168 bits) or AES (128/192/256 bits). Prevention of relay attack Two-factor authentication (e. g. PIN/password in addition to card) Distance bounding protocols (distance checking) More: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=EKks 3 vfiy 6 Q 31
COUNTERMEASURES Prevention of eavesdropping and data modification Using Faraday cage/sleeve. A secure channel is established with symmetric key like 3 DES (56/112/168 bits) or AES (128/192/256 bits). Prevention of relay attack Two-factor authentication (e. g. PIN/password in addition to card) Distance bounding protocols (distance checking) More: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=EKks 3 vfiy 6 Q 31
 COUNTERMEASURES Prevent of attacks on MIFARE classic Additional encryption on the card and transaction counters. To enable the back office to detect a fraudulent card, and put it on a blacklist. Source: http: //www. scmp. com/article/631075/octopus-card-not-vulnerable-hackingsystem-operator-says 32
COUNTERMEASURES Prevent of attacks on MIFARE classic Additional encryption on the card and transaction counters. To enable the back office to detect a fraudulent card, and put it on a blacklist. Source: http: //www. scmp. com/article/631075/octopus-card-not-vulnerable-hackingsystem-operator-says 32
 REFERENCES (1) NFC Forum http: //www. nfc-forum. org/aboutnfc/ (2) Nokia Developer - NFC Document l http: //www. developer. nokia. com/Develop/NFC/Documen tation/ (3) NFC World l http: //www. nfcworld. com/nfc-devices/nokia-6131 -nfc/ (4) Near. Field. Communication. org l http: //www. nearfieldcommunication. org/nfcsecurity. html (5) How NFC phones can steal your credit card info l http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=EKks 3 vfiy 6 Q (6) MIFARE Hack l http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=NW 3 RGb. QTLh. E l 33
REFERENCES (1) NFC Forum http: //www. nfc-forum. org/aboutnfc/ (2) Nokia Developer - NFC Document l http: //www. developer. nokia. com/Develop/NFC/Documen tation/ (3) NFC World l http: //www. nfcworld. com/nfc-devices/nokia-6131 -nfc/ (4) Near. Field. Communication. org l http: //www. nearfieldcommunication. org/nfcsecurity. html (5) How NFC phones can steal your credit card info l http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=EKks 3 vfiy 6 Q (6) MIFARE Hack l http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=NW 3 RGb. QTLh. E l 33


