Topic 3-stocks valuation-class 2,3-students.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 77
 Topic 3 Stocks Valuation
Topic 3 Stocks Valuation
 Topic 3 n n Factors that affect stock prices Stock valuation methods. Discounted dividend model Adjusting the dividend discount model. Multiples approach to stocks valuation
Topic 3 n n Factors that affect stock prices Stock valuation methods. Discounted dividend model Adjusting the dividend discount model. Multiples approach to stocks valuation
 Objectives n n n Understand how stock prices depend on future dividends and dividend growth Value stocks using the dividend growth model Explain and use multiples approach to stocks valuation
Objectives n n n Understand how stock prices depend on future dividends and dividend growth Value stocks using the dividend growth model Explain and use multiples approach to stocks valuation
 Сommon stocks n n n The common stockholders are the owners of the corporation’s equity Represent ownership Ownership implies control Do not have a specified maturity date and the firm is not obliged to pay dividends to shareholders Returns come from dividends and capital gains
Сommon stocks n n n The common stockholders are the owners of the corporation’s equity Represent ownership Ownership implies control Do not have a specified maturity date and the firm is not obliged to pay dividends to shareholders Returns come from dividends and capital gains
 Сommon stocks n n Stockholders have only limited liabilities Common stockholders are called the residual claimants of the firm. Why?
Сommon stocks n n Stockholders have only limited liabilities Common stockholders are called the residual claimants of the firm. Why?
 Preferred stocks n n n Hybrid securities: have characteristics of debt and equity Have face value, predetermined periodical (dividend) payments with priority over common stockholders If dividend is not paid, preferred stockholders may get voting rights
Preferred stocks n n n Hybrid securities: have characteristics of debt and equity Have face value, predetermined periodical (dividend) payments with priority over common stockholders If dividend is not paid, preferred stockholders may get voting rights
 Summary of companies: stocks, financials, ownership etc. http: //finance. yahoo. com General Electric http: //finance. yahoo. com/q? s=GE http: //www. rts. ru/en/
Summary of companies: stocks, financials, ownership etc. http: //finance. yahoo. com General Electric http: //finance. yahoo. com/q? s=GE http: //www. rts. ru/en/
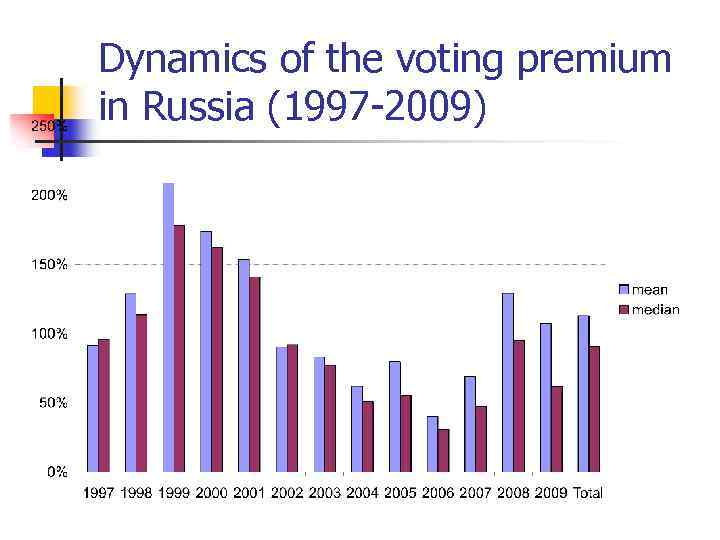 Dynamics of the voting premium in Russia (1997 -2009)
Dynamics of the voting premium in Russia (1997 -2009)
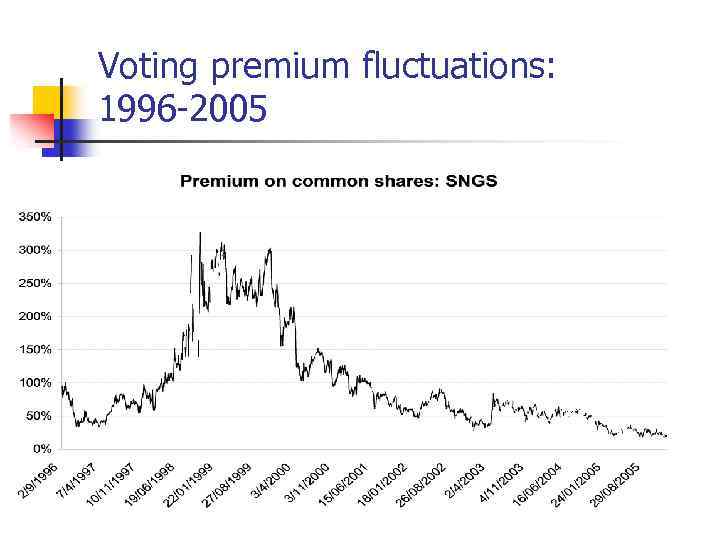 Voting premium fluctuations: 1996 -2005
Voting premium fluctuations: 1996 -2005
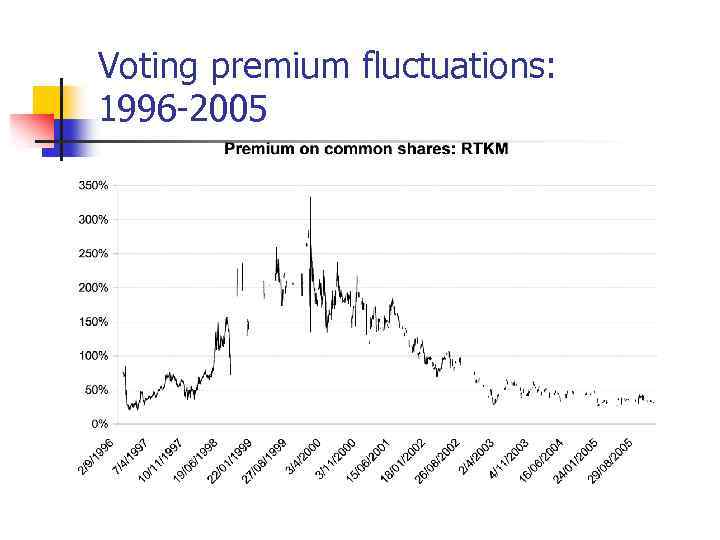 Voting premium fluctuations: 1996 -2005
Voting premium fluctuations: 1996 -2005
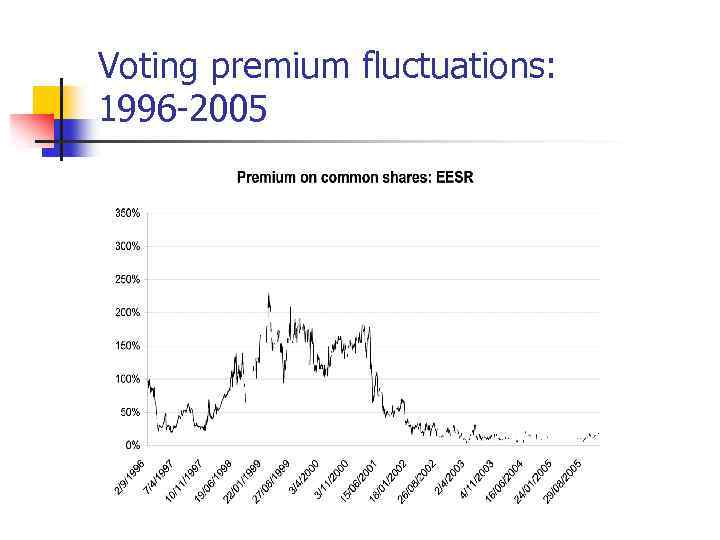 Voting premium fluctuations: 1996 -2005
Voting premium fluctuations: 1996 -2005
 Voting premium n How the size of the voting premium could be related to the level of shareholders legal protection in a country?
Voting premium n How the size of the voting premium could be related to the level of shareholders legal protection in a country?
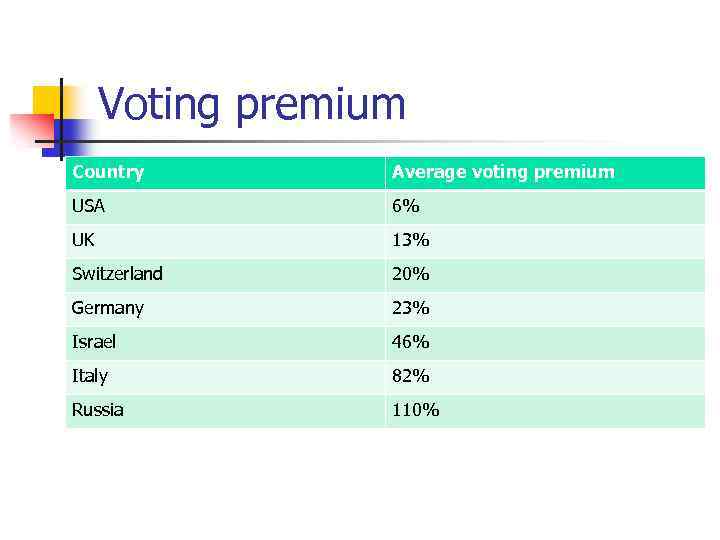 Voting premium Country Average voting premium USA 6% UK 13% Switzerland 20% Germany 23% Israel 46% Italy 82% Russia 110%
Voting premium Country Average voting premium USA 6% UK 13% Switzerland 20% Germany 23% Israel 46% Italy 82% Russia 110%
 Stocks valuation vs. debt securities valuation n n 2 forms of shareholder’s income: dividends and capital gains. Income stream is uncertain, expected. Expected income is considered as infinite. So investor should forecast the investment period and plan to sell a stock at the end of this period at forecasted future price. It is hard to choose a market required rate of return as a discount rate.
Stocks valuation vs. debt securities valuation n n 2 forms of shareholder’s income: dividends and capital gains. Income stream is uncertain, expected. Expected income is considered as infinite. So investor should forecast the investment period and plan to sell a stock at the end of this period at forecasted future price. It is hard to choose a market required rate of return as a discount rate.
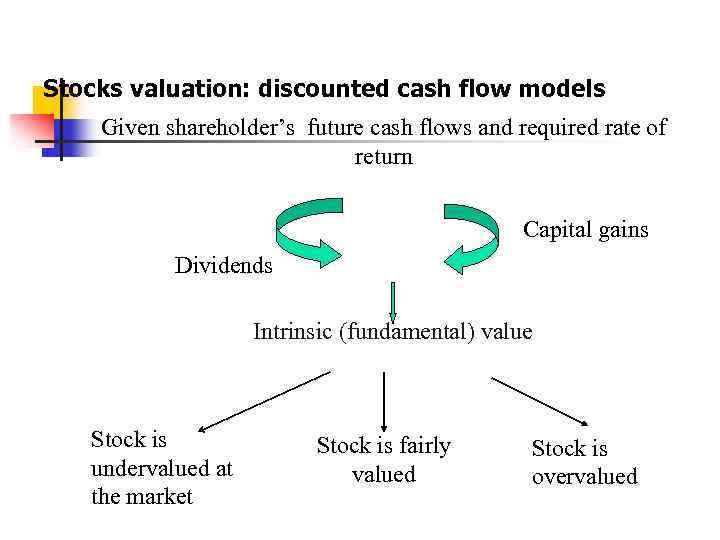 Stocks valuation: discounted cash flow models Given shareholder’s future cash flows and required rate of return Capital gains Dividends Intrinsic (fundamental) value Stock is undervalued at the market Stock is fairly valued Stock is overvalued
Stocks valuation: discounted cash flow models Given shareholder’s future cash flows and required rate of return Capital gains Dividends Intrinsic (fundamental) value Stock is undervalued at the market Stock is fairly valued Stock is overvalued
 Market price and intrinsic value: the difference n n n The stock price is the current market price and is observed for publicly traded companies Intrinsic (“true”) value cannot be observed and must be estimated. Market equilibrium occurs when the stock’s price equals its intrinsic value.
Market price and intrinsic value: the difference n n n The stock price is the current market price and is observed for publicly traded companies Intrinsic (“true”) value cannot be observed and must be estimated. Market equilibrium occurs when the stock’s price equals its intrinsic value.
 Intrinsic value use n How intrinsic value is used in managerial decisions? • Investors decide whether to buy stocks (undervalued) or sell stocks (overvalued) • Managers care about the fair value of their company while deciding to issue stocks, repurchase stocks etc.
Intrinsic value use n How intrinsic value is used in managerial decisions? • Investors decide whether to buy stocks (undervalued) or sell stocks (overvalued) • Managers care about the fair value of their company while deciding to issue stocks, repurchase stocks etc.
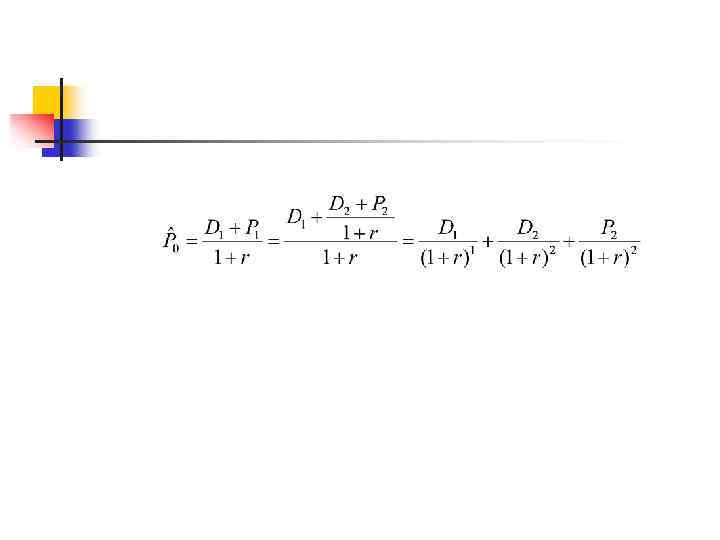
 Value of the stock is a present value of future cash flows generated Example. Investor buys a stock today assuming to resell it one year from now at $70. Dividend expected to be paid in one year is $10. If required rate of return is 25%, how much investor is ready to pay for the stock today? That is, what is the PV of future cash flows generated by the investor?
Value of the stock is a present value of future cash flows generated Example. Investor buys a stock today assuming to resell it one year from now at $70. Dividend expected to be paid in one year is $10. If required rate of return is 25%, how much investor is ready to pay for the stock today? That is, what is the PV of future cash flows generated by the investor?
 $64 – price, that investor is going to pay for the stock today. That is:
$64 – price, that investor is going to pay for the stock today. That is:

 Stocks valuation: discounted dividends and selling price
Stocks valuation: discounted dividends and selling price
 What if we postpone selling the stock for uncertain period? If we postpone selling the stock for uncertain time in the future, present value of the cash flow from this selling is zero.
What if we postpone selling the stock for uncertain period? If we postpone selling the stock for uncertain time in the future, present value of the cash flow from this selling is zero.
 Thus a current value of the stock could be calculated as a present value of dividends, started for the payment in year 1 and to be paid infinitely.
Thus a current value of the stock could be calculated as a present value of dividends, started for the payment in year 1 and to be paid infinitely.
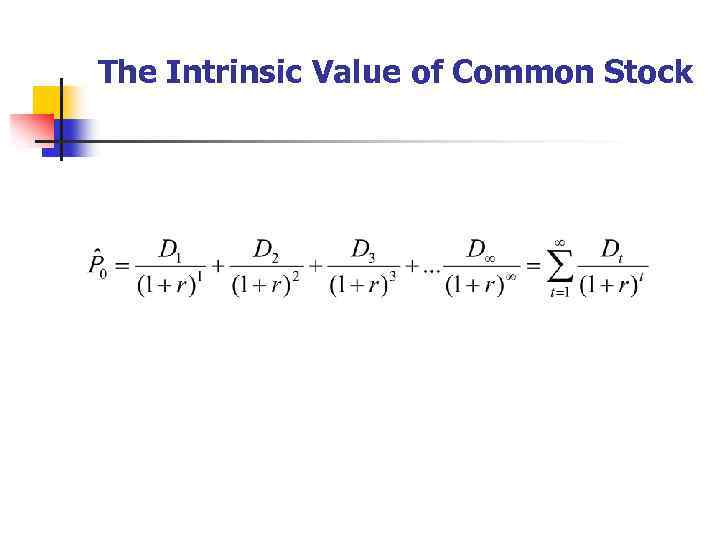 The Intrinsic Value of Common Stock
The Intrinsic Value of Common Stock
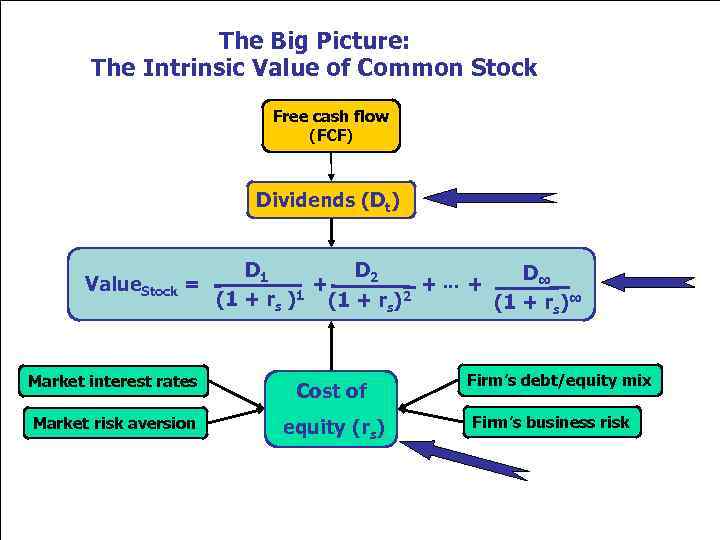 The Big Picture: The Intrinsic Value of Common Stock Free cash flow (FCF) Dividends (Dt) Value. Stock = D 2 D 1 D∞ + +. . . + (1 + rs )1 (1 + rs)2 (1 + rs)∞ Market interest rates Cost of Market risk aversion equity (rs) Firm’s debt/equity mix Firm’s business risk
The Big Picture: The Intrinsic Value of Common Stock Free cash flow (FCF) Dividends (Dt) Value. Stock = D 2 D 1 D∞ + +. . . + (1 + rs )1 (1 + rs)2 (1 + rs)∞ Market interest rates Cost of Market risk aversion equity (rs) Firm’s debt/equity mix Firm’s business risk
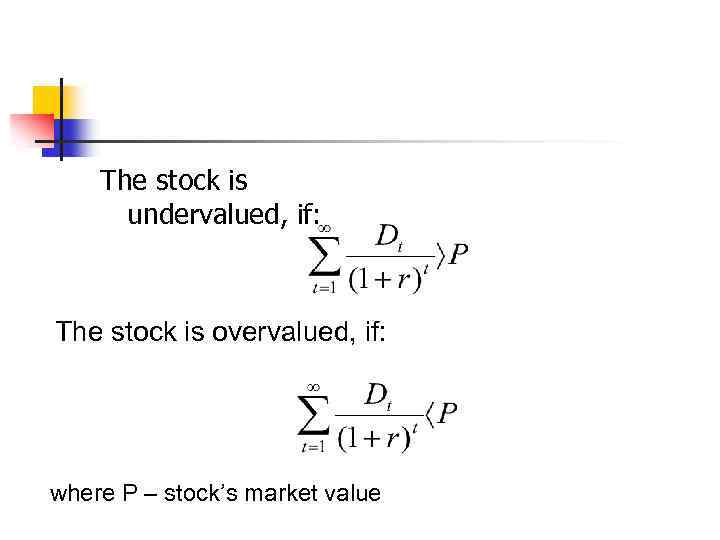 The stock is undervalued, if: The stock is overvalued, if: where P – stock’s market value
The stock is undervalued, if: The stock is overvalued, if: where P – stock’s market value
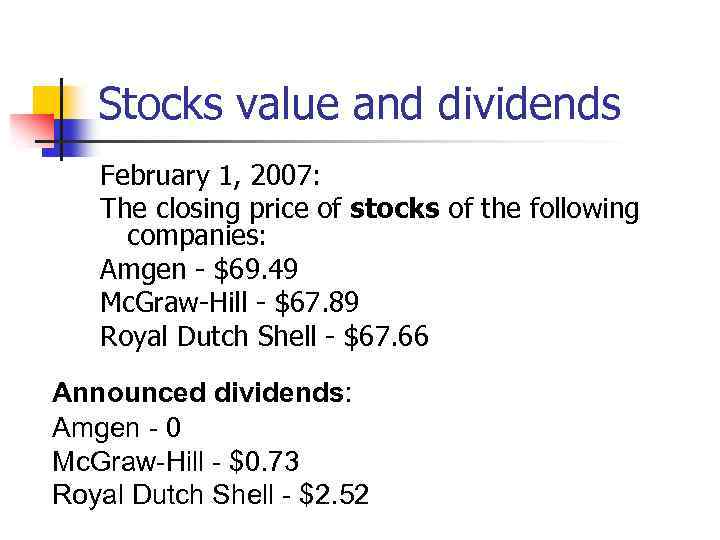 Stocks value and dividends February 1, 2007: The closing price of stocks of the following companies: Amgen - $69. 49 Mc. Graw-Hill - $67. 89 Royal Dutch Shell - $67. 66 Announced dividends: Amgen - 0 Mc. Graw-Hill - $0. 73 Royal Dutch Shell - $2. 52
Stocks value and dividends February 1, 2007: The closing price of stocks of the following companies: Amgen - $69. 49 Mc. Graw-Hill - $67. 89 Royal Dutch Shell - $67. 66 Announced dividends: Amgen - 0 Mc. Graw-Hill - $0. 73 Royal Dutch Shell - $2. 52
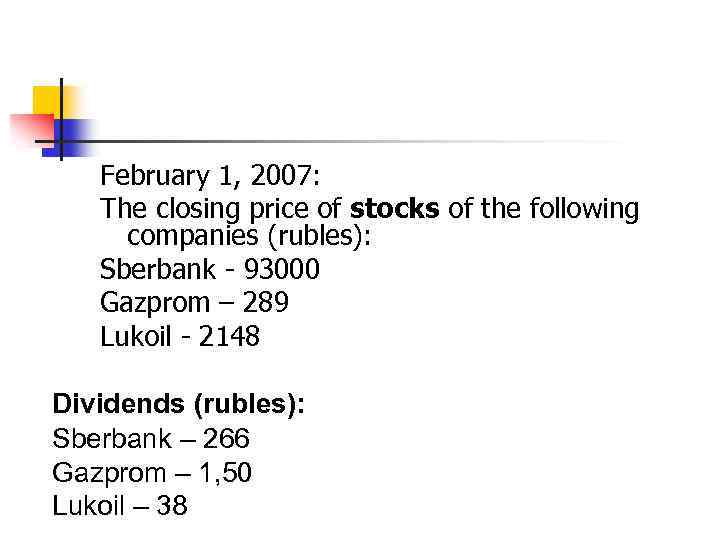 February 1, 2007: The closing price of stocks of the following companies (rubles): Sberbank - 93000 Gazprom – 289 Lukoil - 2148 Dividends (rubles): Sberbank – 266 Gazprom – 1, 50 Lukoil – 38
February 1, 2007: The closing price of stocks of the following companies (rubles): Sberbank - 93000 Gazprom – 289 Lukoil - 2148 Dividends (rubles): Sberbank – 266 Gazprom – 1, 50 Lukoil – 38
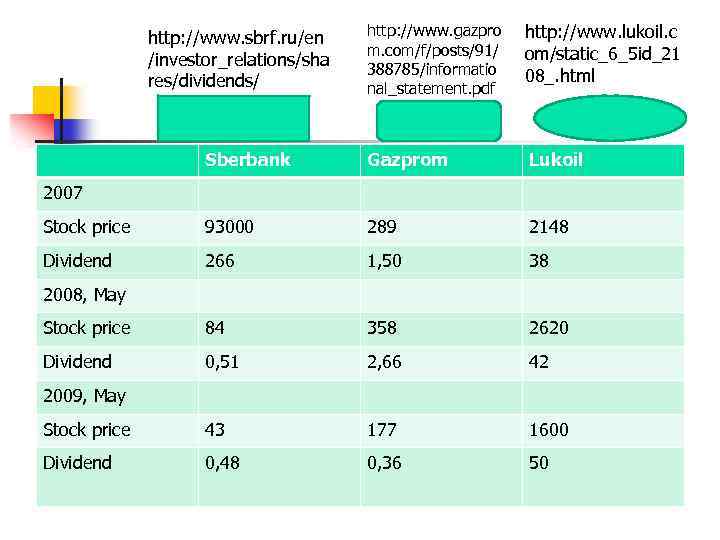 http: //www. gazpro m. com/f/posts/91/ 388785/informatio nal_statement. pdf http: //www. lukoil. c om/static_6_5 id_21 08_. html Sberbank Gazprom Lukoil Stock price 93000 289 2148 Dividend 266 1, 50 38 Stock price 84 358 2620 Dividend 0, 51 2, 66 42 Stock price 43 177 1600 Dividend 0, 48 0, 36 50 http: //www. sbrf. ru/en /investor_relations/sha res/dividends/ 2007 2008, May 2009, May
http: //www. gazpro m. com/f/posts/91/ 388785/informatio nal_statement. pdf http: //www. lukoil. c om/static_6_5 id_21 08_. html Sberbank Gazprom Lukoil Stock price 93000 289 2148 Dividend 266 1, 50 38 Stock price 84 358 2620 Dividend 0, 51 2, 66 42 Stock price 43 177 1600 Dividend 0, 48 0, 36 50 http: //www. sbrf. ru/en /investor_relations/sha res/dividends/ 2007 2008, May 2009, May
 n n What should be the stock value of companies that don’t pay any dividends? Do such companies exist? New hi tech comp which invest everything for development, But some div are expected farther No. There are companies that don’t pay dividends for a certain period of time. Otherwise the value of investments in these companies should be zero.
n n What should be the stock value of companies that don’t pay any dividends? Do such companies exist? New hi tech comp which invest everything for development, But some div are expected farther No. There are companies that don’t pay dividends for a certain period of time. Otherwise the value of investments in these companies should be zero.
 ! Why the sale price of the stock could be ignored while valuing the stock with a dividend discount model?
! Why the sale price of the stock could be ignored while valuing the stock with a dividend discount model?
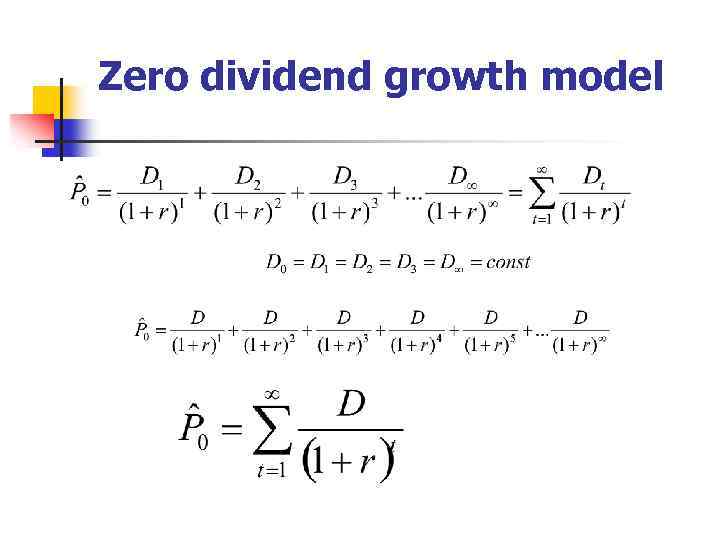 Zero dividend growth model
Zero dividend growth model
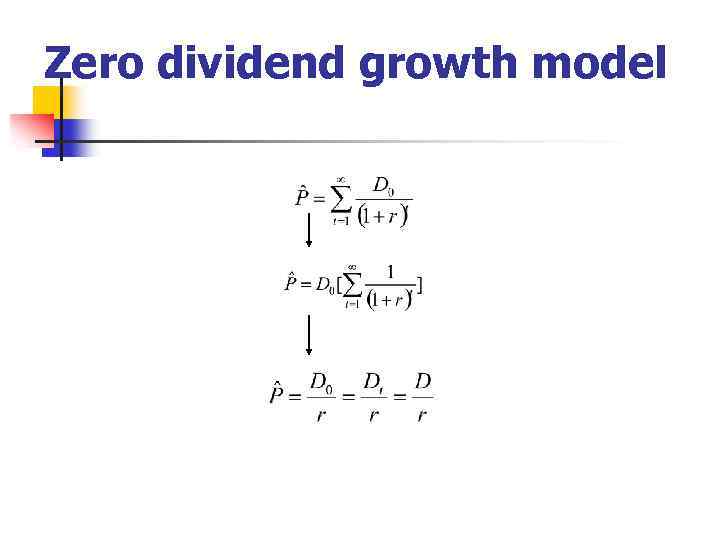 Zero dividend growth model
Zero dividend growth model
 Example. n If the dividend policy of the company implies annual dividend payments of $10 constantly, what should be the stock’s price with required rate of return of 20%?
Example. n If the dividend policy of the company implies annual dividend payments of $10 constantly, what should be the stock’s price with required rate of return of 20%?
 Dividend constant growth model
Dividend constant growth model
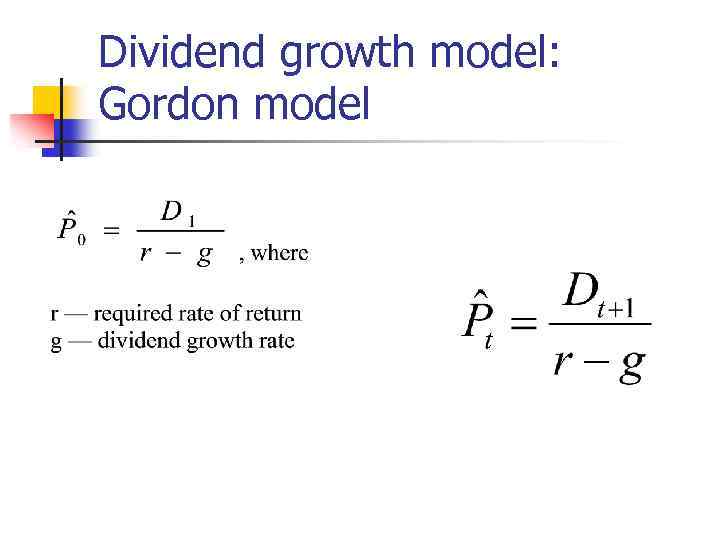 Dividend growth model: Gordon model
Dividend growth model: Gordon model
 Constant-growth dividend discount model
Constant-growth dividend discount model
 Constant-growth dividend discount model
Constant-growth dividend discount model
 Example. What should be the stock price in 5 years, if the last dividend was $2. 30, dividend growth rate is 5%, required rate of return is 13%? 2. 93*1. 05/(0. 13 -0. 05)=38
Example. What should be the stock price in 5 years, if the last dividend was $2. 30, dividend growth rate is 5%, required rate of return is 13%? 2. 93*1. 05/(0. 13 -0. 05)=38
 Exercise: declining growth n n The company’s ore reserves are being depleted, so its sales are falling, and costs are rising. As a result, the company’s earnings and dividends are declining at the constant rate of 4% per year. If D 0=$5, r=15%, what is the value of the stock? =5*(1 -(-0, 04))/0, 15 -(-0, 04)=4, 8/0, 19=25, 26
Exercise: declining growth n n The company’s ore reserves are being depleted, so its sales are falling, and costs are rising. As a result, the company’s earnings and dividends are declining at the constant rate of 4% per year. If D 0=$5, r=15%, what is the value of the stock? =5*(1 -(-0, 04))/0, 15 -(-0, 04)=4, 8/0, 19=25, 26
 Dividend growth model ! The model assumes, that the stock price will grow at the same constant rate, as a dividend. That is if the cash flow from investment grows at the constant rate, then the value of investment grows at the same rate. What if the dividend growth rate is higher then the required rate of return? We can not apply Gordon’s model ( в знаменателе отриц цифра)
Dividend growth model ! The model assumes, that the stock price will grow at the same constant rate, as a dividend. That is if the cash flow from investment grows at the constant rate, then the value of investment grows at the same rate. What if the dividend growth rate is higher then the required rate of return? We can not apply Gordon’s model ( в знаменателе отриц цифра)
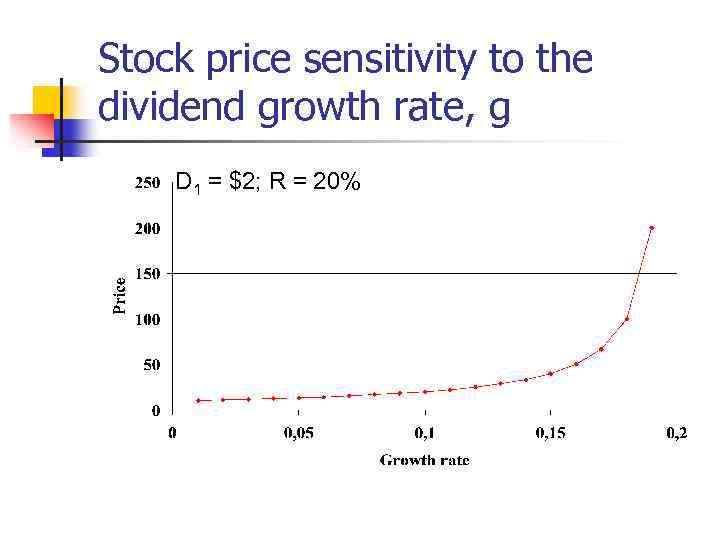 Stock price sensitivity to the dividend growth rate, g D 1 = $2; R = 20%
Stock price sensitivity to the dividend growth rate, g D 1 = $2; R = 20%
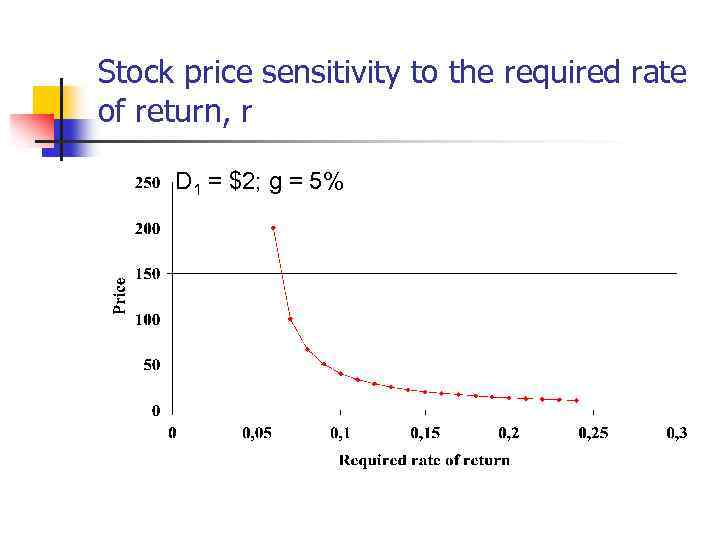 Stock price sensitivity to the required rate of return, r D 1 = $2; g = 5%
Stock price sensitivity to the required rate of return, r D 1 = $2; g = 5%
 Dividend constant growth model ! The expected dividends are growing, but the present value of each dividend payment is declining, because the dividend growth rate is less than the discount rate. ! Although the model assumes infinite time periods, most of the stock value is based on dividends during a finite time period.
Dividend constant growth model ! The expected dividends are growing, but the present value of each dividend payment is declining, because the dividend growth rate is less than the discount rate. ! Although the model assumes infinite time periods, most of the stock value is based on dividends during a finite time period.
 Problems associated with stocks valuation Dividends forecast Required rate of return estimation
Problems associated with stocks valuation Dividends forecast Required rate of return estimation
 Non-constant growth dividend discount model 1. 2. 3. Dividends are forecasted for the certain period till Т (D 1, D 2, D 3, … Dt). The moment Т is forecasted. It is expected that after the moment Т dividends will grow at a constant rate g.
Non-constant growth dividend discount model 1. 2. 3. Dividends are forecasted for the certain period till Т (D 1, D 2, D 3, … Dt). The moment Т is forecasted. It is expected that after the moment Т dividends will grow at a constant rate g.
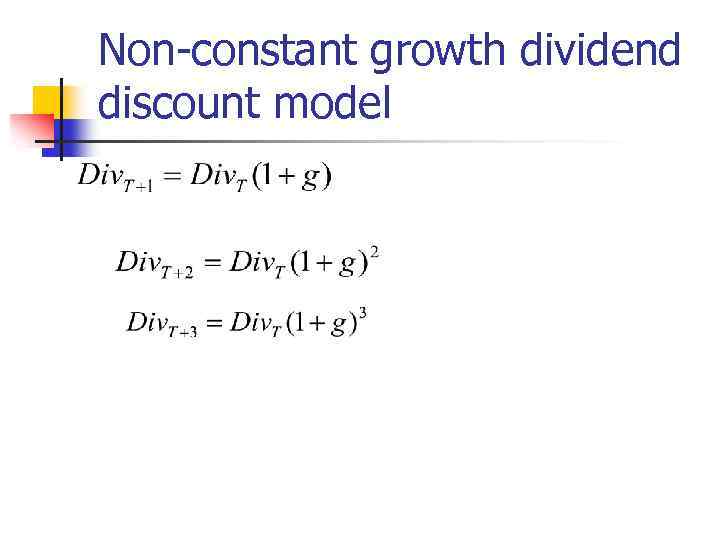 Non-constant growth dividend discount model
Non-constant growth dividend discount model
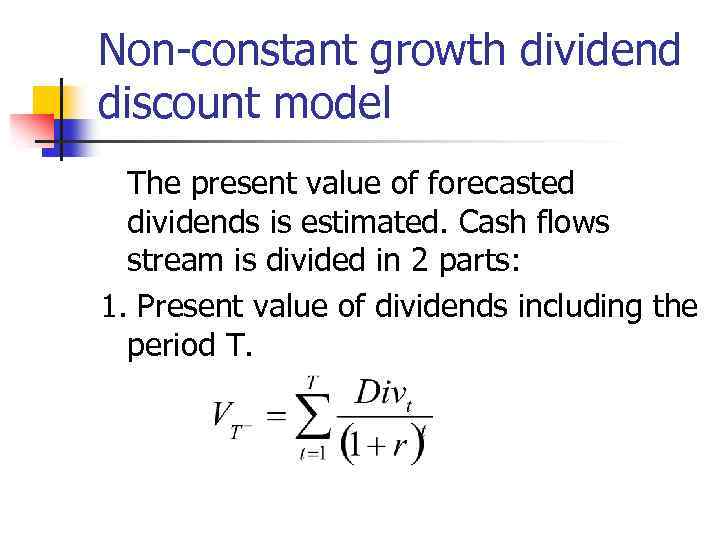 Non-constant growth dividend discount model The present value of forecasted dividends is estimated. Cash flows stream is divided in 2 parts: 1. Present value of dividends including the period Т.
Non-constant growth dividend discount model The present value of forecasted dividends is estimated. Cash flows stream is divided in 2 parts: 1. Present value of dividends including the period Т.
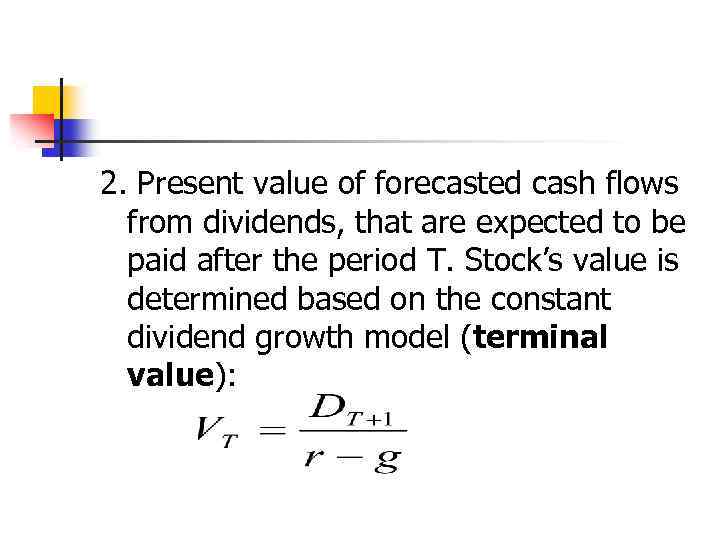 2. Present value of forecasted cash flows from dividends, that are expected to be paid after the period Т. Stock’s value is determined based on the constant dividend growth model (terminal value):
2. Present value of forecasted cash flows from dividends, that are expected to be paid after the period Т. Stock’s value is determined based on the constant dividend growth model (terminal value):
 Example. Company is planning to increase dividends on its stocks for 20% the next year, for 15% 2 years from now. After that dividends will grow at 5% annually. The last dividend paid was $1, required rate of return is 20%. What is the stock’s fair value? div: 1*1, 2=1, 2*1, 15=1, 26*1, 05=1, 449/(2 -0, 05)=9, 66 1, 2+1, 38/1, 2^2+9, 66/1, 2^2=8, 67
Example. Company is planning to increase dividends on its stocks for 20% the next year, for 15% 2 years from now. After that dividends will grow at 5% annually. The last dividend paid was $1, required rate of return is 20%. What is the stock’s fair value? div: 1*1, 2=1, 2*1, 15=1, 26*1, 05=1, 449/(2 -0, 05)=9, 66 1, 2+1, 38/1, 2^2+9, 66/1, 2^2=8, 67
 Stock price, dividends and earnings n Is the stock price based on short-term or long-term growth? Long-term growth – the most of the stock value (see previous example) is attributable to long-term cash flows.
Stock price, dividends and earnings n Is the stock price based on short-term or long-term growth? Long-term growth – the most of the stock value (see previous example) is attributable to long-term cash flows.
 Stock price, dividends and earnings n If most of a stock’s value is due to longterm cash flows, why do so many managers focus on quarterly earnings? - Quarterly earnings could bear information on future prospects of the company - Compensation packages could be based on these performance results
Stock price, dividends and earnings n If most of a stock’s value is due to longterm cash flows, why do so many managers focus on quarterly earnings? - Quarterly earnings could bear information on future prospects of the company - Compensation packages could be based on these performance results
 Exercise: Non-constant dividend growth model In-class exercise 3. 2 -build a model
Exercise: Non-constant dividend growth model In-class exercise 3. 2 -build a model
 Preferred stocks valuation Preferred stock’s value is estimated as an ordinary perpetuity:
Preferred stocks valuation Preferred stock’s value is estimated as an ordinary perpetuity:
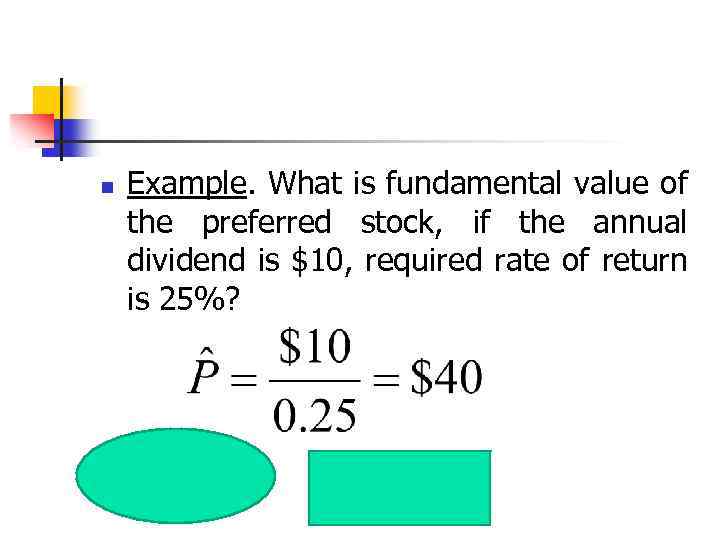 n Example. What is fundamental value of the preferred stock, if the annual dividend is $10, required rate of return is 25%?
n Example. What is fundamental value of the preferred stock, if the annual dividend is $10, required rate of return is 25%?
 Return on investments in stocks Dividend yield (current yield) , where d - dividend P – current stock price
Return on investments in stocks Dividend yield (current yield) , where d - dividend P – current stock price
 Return on investments in stocks Capital gains yield
Return on investments in stocks Capital gains yield
 Return on investments in stocks di – dividend payments in i-year P 0 – the purchase price Pt – the selling price (market price in year t) Т – number of years of holding shares
Return on investments in stocks di – dividend payments in i-year P 0 – the purchase price Pt – the selling price (market price in year t) Т – number of years of holding shares
 Example Investor holds the stock for 3 years. Dividend for year 1 is $30, for year 2 = $20, for year 3 = $25. What is the return on investment for the holding period, if investor bought the stock for $150, and sold it in 3 years for $250?
Example Investor holds the stock for 3 years. Dividend for year 1 is $30, for year 2 = $20, for year 3 = $25. What is the return on investment for the holding period, if investor bought the stock for $150, and sold it in 3 years for $250?
 Using dividend growth model for return estimation
Using dividend growth model for return estimation
 Example Investor bought the stock for 70 rub. , received a dividend of 5% of market value. What is the expected annual return, if dividends are expected to grow annually at 3%? 3, 5/70 +0, 03=0, 08
Example Investor bought the stock for 70 rub. , received a dividend of 5% of market value. What is the expected annual return, if dividends are expected to grow annually at 3%? 3, 5/70 +0, 03=0, 08
 Example. n Assume, the stock is sold for $10. 50. The dividend just paid is $1 and expected to grow at the rate of 5% annually. What is the required return? Div Yeild+Capital gains What is the dividend yield? 1*1, 05/10, 5=10% What is the capital gains yield? 5% n 1*1, 05/10, 5 +0, 05=15 n n
Example. n Assume, the stock is sold for $10. 50. The dividend just paid is $1 and expected to grow at the rate of 5% annually. What is the required return? Div Yeild+Capital gains What is the dividend yield? 1*1, 05/10, 5=10% What is the capital gains yield? 5% n 1*1, 05/10, 5 +0, 05=15 n n
 Wal-Mart Stores stocks http: //finance. yahoo. com/q? s=WMT
Wal-Mart Stores stocks http: //finance. yahoo. com/q? s=WMT
 Wal-Mart Stores stocks October 14, 2011 Explain: Shares of Wal-Mart Stores (WMT) have a 2. 65% dividend yield, based on last night’s closing stock price of $55. 02. The stock has technical support in the $52 price area. If the shares can firm up, we see overhead resistance around the $57 -$58 price levels.
Wal-Mart Stores stocks October 14, 2011 Explain: Shares of Wal-Mart Stores (WMT) have a 2. 65% dividend yield, based on last night’s closing stock price of $55. 02. The stock has technical support in the $52 price area. If the shares can firm up, we see overhead resistance around the $57 -$58 price levels.
 S&P Stock Index
S&P Stock Index
 Exercise: return on stocks investment In-class exercise 3. 2 -build a model
Exercise: return on stocks investment In-class exercise 3. 2 -build a model
 In-class exercise Agarwal Technologies was founded 10 years ago. It has been profitable for the last 5 years, but it has needed all of its earnings to support growth and thus has never paid a dividend. Management has indicated that it plans to pay a $0. 25 dividend 3 years from today, then to increase it at a relatively rapid rate for 2 years, and then to increase it at a constant rate of 8. 00% thereafter. Management's forecast of the future dividend stream, along with the forecasted growth rates, is shown below. Assuming a required return of 11. 00%, what is your estimate of the stock's current value? Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Growth rate. NA NA 50. 00% 25. 00% 8. 00% Dividends$0. 000 $0. 250 $0. 375 $0. 469 $0. 506 n
In-class exercise Agarwal Technologies was founded 10 years ago. It has been profitable for the last 5 years, but it has needed all of its earnings to support growth and thus has never paid a dividend. Management has indicated that it plans to pay a $0. 25 dividend 3 years from today, then to increase it at a relatively rapid rate for 2 years, and then to increase it at a constant rate of 8. 00% thereafter. Management's forecast of the future dividend stream, along with the forecasted growth rates, is shown below. Assuming a required return of 11. 00%, what is your estimate of the stock's current value? Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Growth rate. NA NA 50. 00% 25. 00% 8. 00% Dividends$0. 000 $0. 250 $0. 375 $0. 469 $0. 506 n
 Home exercise n Problems 7 -17, 7 -18 of the BE (p. 299).
Home exercise n Problems 7 -17, 7 -18 of the BE (p. 299).
 Multiples approach. P/E ratio Price of the share/Earnings per share (previous year’s earnings or expected earnings) Valuation per share = (expected earnings of firm per share) * (mean industry P/E ratio) Future earnings is an important determinant of a firm’s value
Multiples approach. P/E ratio Price of the share/Earnings per share (previous year’s earnings or expected earnings) Valuation per share = (expected earnings of firm per share) * (mean industry P/E ratio) Future earnings is an important determinant of a firm’s value
 P/E ratio n Example. Consider a firm that is expected to generate earnings of $3 per share next year. If the mean ratio of share price to expected earnings of competitors in the same industry is 15, then the valuation of the firm’s shares is: Valuation per share = (expected earnings of firm per share) * (Mean industry P/E ratio) = $3 * 15 = $45
P/E ratio n Example. Consider a firm that is expected to generate earnings of $3 per share next year. If the mean ratio of share price to expected earnings of competitors in the same industry is 15, then the valuation of the firm’s shares is: Valuation per share = (expected earnings of firm per share) * (Mean industry P/E ratio) = $3 * 15 = $45
 Limitations of the P/E method n The P/E method may result in an inaccurate valuation for a firm if errors are made in forecasting the firm’s future earnings or in choosing the industry composite used to derive the P/E ratio.
Limitations of the P/E method n The P/E method may result in an inaccurate valuation for a firm if errors are made in forecasting the firm’s future earnings or in choosing the industry composite used to derive the P/E ratio.
 Price-to-book ratio Average: 1 -3 (100 to 300%)
Price-to-book ratio Average: 1 -3 (100 to 300%)
 Book value per share http: //finance. yahoo. com/q? s=XRX
Book value per share http: //finance. yahoo. com/q? s=XRX

 Free cash flow model For companies that do not pay dividends, a more suitable valuation may be the free cash flow model, which is based on the present value of future cash flows: 1. Estimate the free cash flows that will result from operations. 2. Find the present value of FCFs. 3. Subtract existing liabilities to determine the value of the firm equity. 4. Divide the value of the firm equity by the number of shares to derive a value per share. Limitation of the model: Difficulty of obtaining an accurate estimate of long-term free cash flows.
Free cash flow model For companies that do not pay dividends, a more suitable valuation may be the free cash flow model, which is based on the present value of future cash flows: 1. Estimate the free cash flows that will result from operations. 2. Find the present value of FCFs. 3. Subtract existing liabilities to determine the value of the firm equity. 4. Divide the value of the firm equity by the number of shares to derive a value per share. Limitation of the model: Difficulty of obtaining an accurate estimate of long-term free cash flows.
 Resources on the Web finance. yahoo. com www. nasdaq. com money. cnn. com www. dividenddiscountmodel. com www. fool. com/school/earningsbasedvaluations. htm http: //www. dividendstocksonline. com
Resources on the Web finance. yahoo. com www. nasdaq. com money. cnn. com www. dividenddiscountmodel. com www. fool. com/school/earningsbasedvaluations. htm http: //www. dividendstocksonline. com


