ae31176507709d1b1e312a4202fe27ab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Topic 2: MODEL OF EARTH
Topic 2: MODEL OF EARTH
 Topic 2: Model of Earth Model- something that represents the properties or characteristics of something else. Ex: Scale- the ratio between the size of the model and the actual object. Ex:
Topic 2: Model of Earth Model- something that represents the properties or characteristics of something else. Ex: Scale- the ratio between the size of the model and the actual object. Ex:


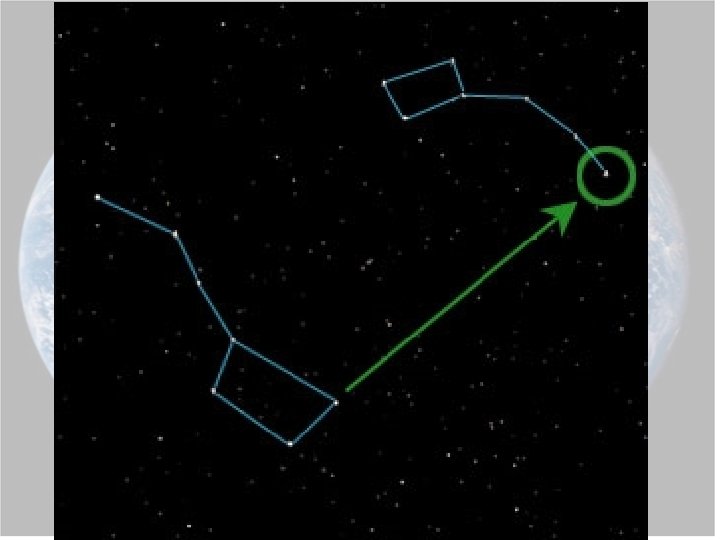



 Evidence For Shape of Earth 1. Ships mast example. 2. Altitude of polaris 3. Lunar Eclipse 4. *Pictures from space * Best form of evidence
Evidence For Shape of Earth 1. Ships mast example. 2. Altitude of polaris 3. Lunar Eclipse 4. *Pictures from space * Best form of evidence
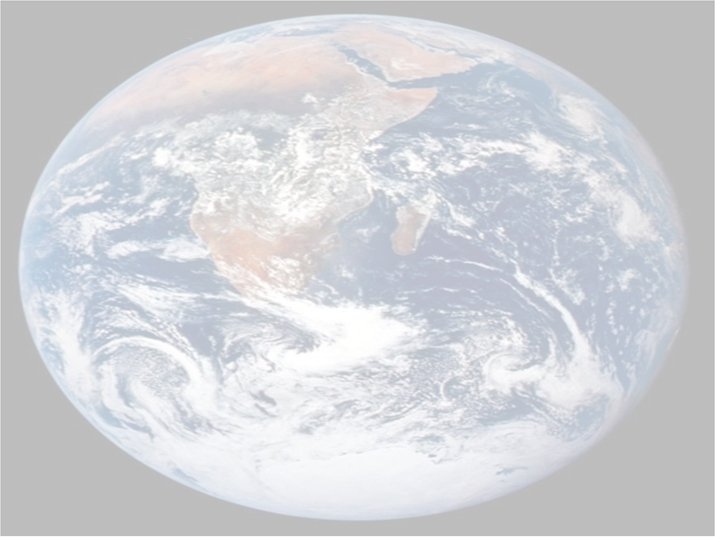
 Earths’ Shape True Shape Apparent Shape • Oblate Spheroid • “Slightly Squatty” • Equatorial diameter is greater than the polar diameter. • DIAGRAM • “Perfect sphere” • Models, pictures from space, scaled drawings
Earths’ Shape True Shape Apparent Shape • Oblate Spheroid • “Slightly Squatty” • Equatorial diameter is greater than the polar diameter. • DIAGRAM • “Perfect sphere” • Models, pictures from space, scaled drawings
 EARTH COMPONENTS Atmosphere- Thin layer of gases that surrounds Earth *!* See pages 1 & 14 in Reference Tables Hydrosphere- liquid water portion of Earths’ surface. 71% of Earths’ surface is covered by water. Lithosphere- solid outer portion of Earth. *!* See pages 1 & 10 in Reference Tables
EARTH COMPONENTS Atmosphere- Thin layer of gases that surrounds Earth *!* See pages 1 & 14 in Reference Tables Hydrosphere- liquid water portion of Earths’ surface. 71% of Earths’ surface is covered by water. Lithosphere- solid outer portion of Earth. *!* See pages 1 & 10 in Reference Tables

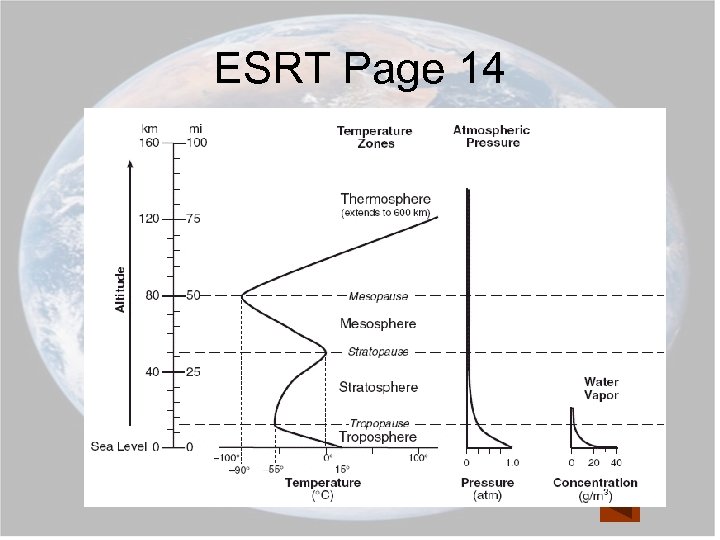 ESRT Page 14
ESRT Page 14


 Finding Location • Coordinate system- grid system of lines for determining location. • Examples:
Finding Location • Coordinate system- grid system of lines for determining location. • Examples:
 Latitude and Longitude Latitude Longitude § Angular distance north or south of the equator. § Maximum latitude=90 o § Angular distance East or west of the Prime Meridian § Maximum longitude =180 o § Latitude = altitude of Polaris! § Longitude is calculated using the difference in local solar time and time at the prime meridian.
Latitude and Longitude Latitude Longitude § Angular distance north or south of the equator. § Maximum latitude=90 o § Angular distance East or west of the Prime Meridian § Maximum longitude =180 o § Latitude = altitude of Polaris! § Longitude is calculated using the difference in local solar time and time at the prime meridian.
 Finding Longitude: Example: An observer measures the local solar time as 3 pm. The time at the prime meridian is noon. What is the observers longitude?
Finding Longitude: Example: An observer measures the local solar time as 3 pm. The time at the prime meridian is noon. What is the observers longitude?

 Practice • What is the Latitude and Longitude of the southern-most point of Australia? • What Continent is found at 40 o. S and 60 o. W?
Practice • What is the Latitude and Longitude of the southern-most point of Australia? • What Continent is found at 40 o. S and 60 o. W?
 Altitude of Polaris: Diagram:
Altitude of Polaris: Diagram:
 Practice • If the time at the Prime Meridian is 4 pm and Local Solar Time is 12 noon, what is the observers longitude?
Practice • If the time at the Prime Meridian is 4 pm and Local Solar Time is 12 noon, what is the observers longitude?
 Practice: • What would the approximate altitude of Polaris be for an observer located in Watertown New York?
Practice: • What would the approximate altitude of Polaris be for an observer located in Watertown New York?
 Practice: • What city in New York State is located at 43 o 5’ N and 79 o 0’W?
Practice: • What city in New York State is located at 43 o 5’ N and 79 o 0’W?

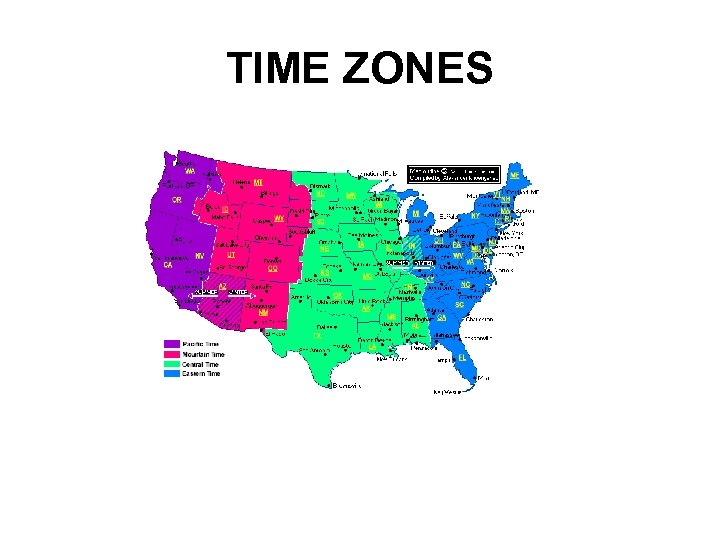 TIME ZONES
TIME ZONES

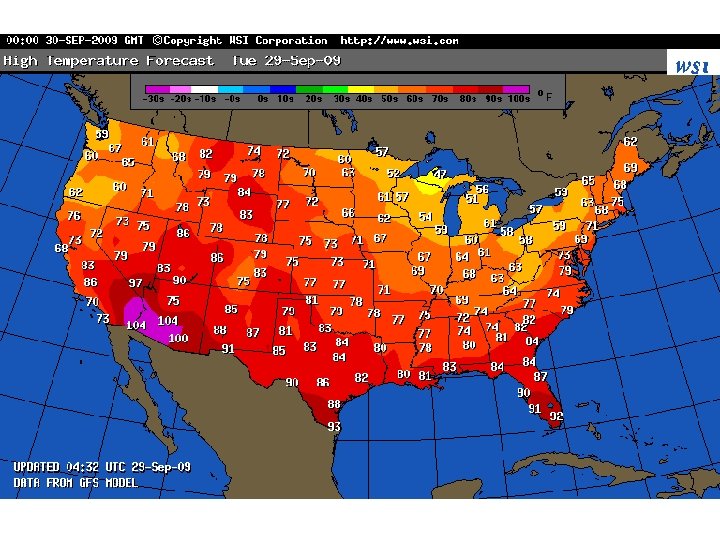
 Field Mapping Field- any area that has a measurable value of a given quantity at every point. Examples: temperature, magnetic, gravitational, elevation. Isolines- lines that connect points of equal field value.
Field Mapping Field- any area that has a measurable value of a given quantity at every point. Examples: temperature, magnetic, gravitational, elevation. Isolines- lines that connect points of equal field value.
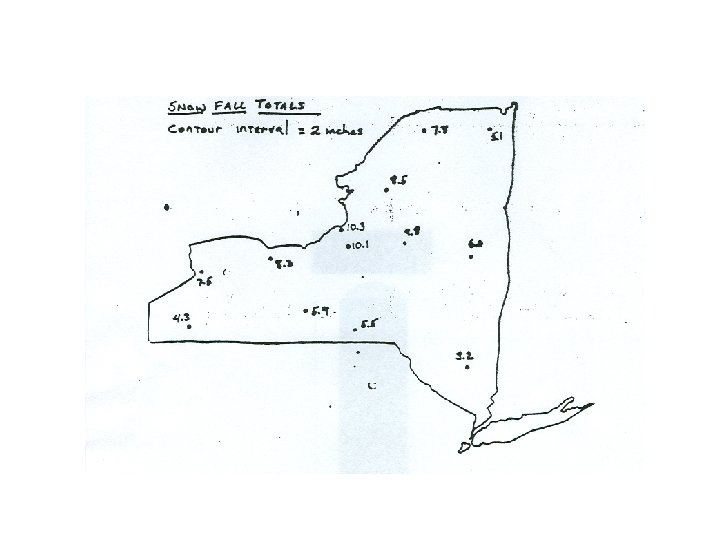
 Rules for Drawing Isolines: 1. Never cross or touch. (why? ) 2. Tend to run parallel 3. Must end at the edge of the map or form a loop 4. “Smooth Curves”
Rules for Drawing Isolines: 1. Never cross or touch. (why? ) 2. Tend to run parallel 3. Must end at the edge of the map or form a loop 4. “Smooth Curves”

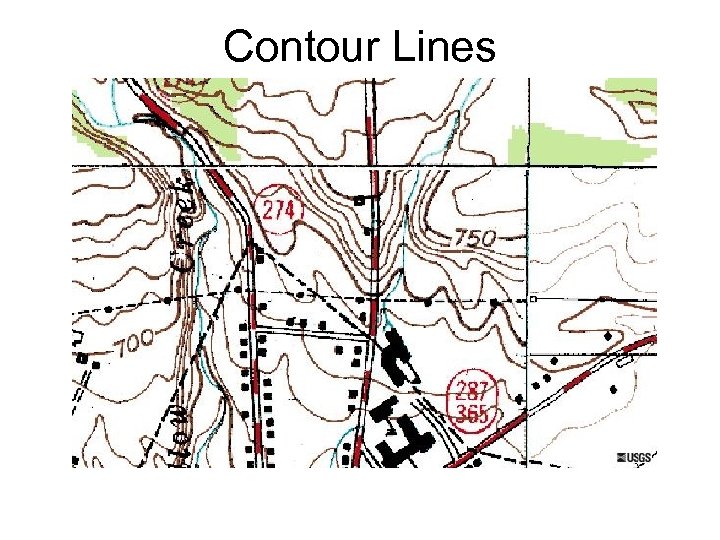 Contour Lines
Contour Lines
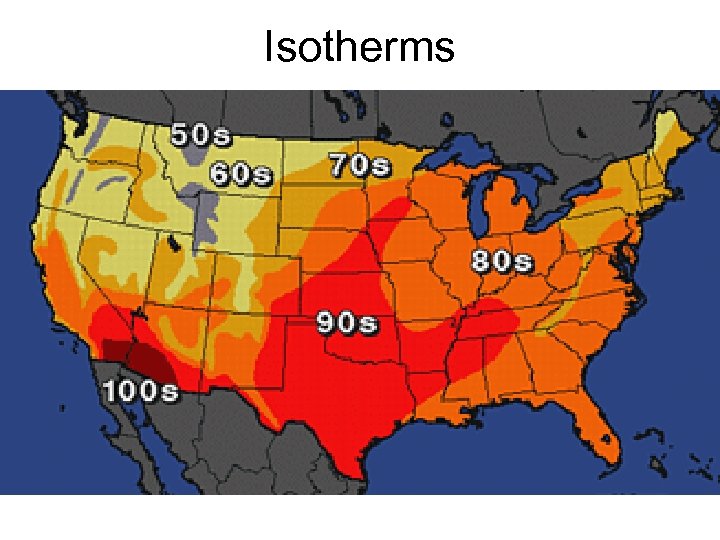 Isotherms
Isotherms
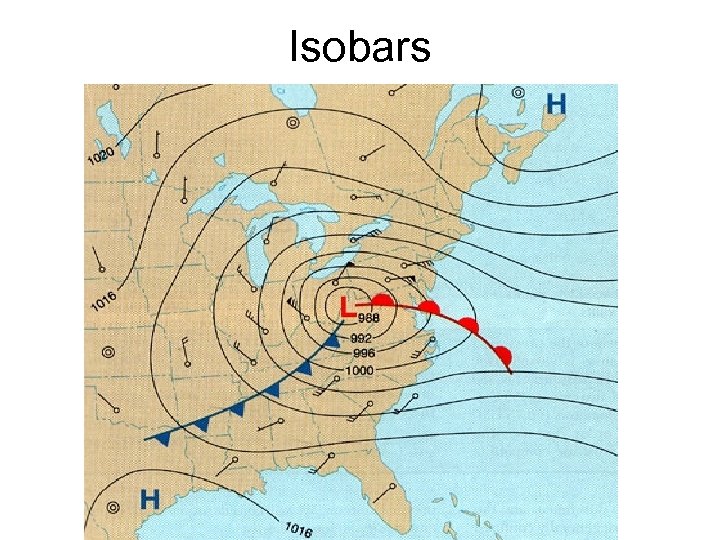 Isobars
Isobars
 Types of Isolines: • Isotherms • Isobars • Contour lines-
Types of Isolines: • Isotherms • Isobars • Contour lines-
 Interval- difference in field value between isolines. Ex: Gradient = Change in Field Value Distance Ex:
Interval- difference in field value between isolines. Ex: Gradient = Change in Field Value Distance Ex:
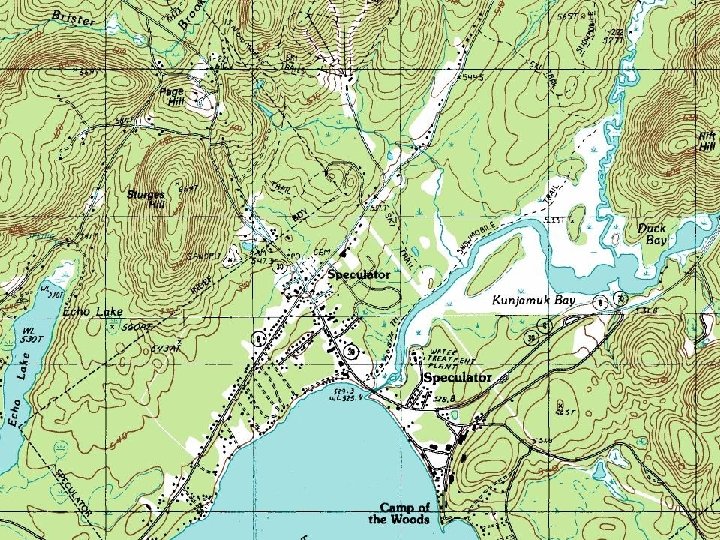
 Contour Mapping Topographic map- Used to show the topography (shape) of the land. • Lines connect points of equal elevation. Ex: !*! See page 24 in the Review Book
Contour Mapping Topographic map- Used to show the topography (shape) of the land. • Lines connect points of equal elevation. Ex: !*! See page 24 in the Review Book
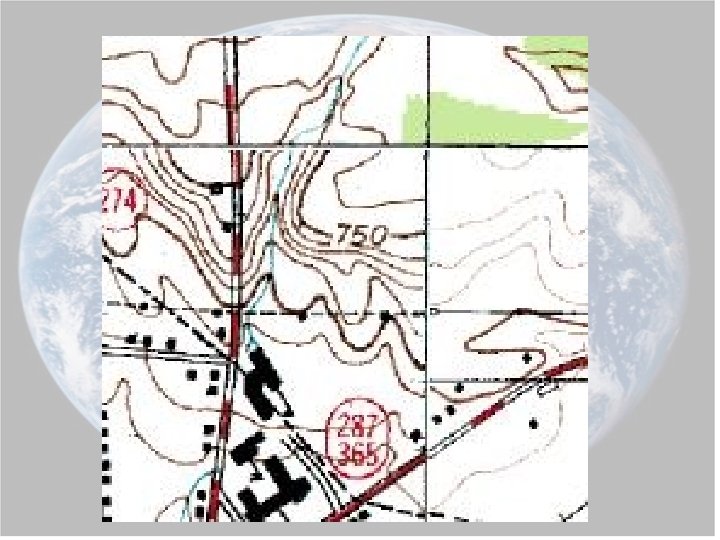
 Rules for Topo Maps 1. The closer the contour lines the steeper the slope. Ex:
Rules for Topo Maps 1. The closer the contour lines the steeper the slope. Ex:
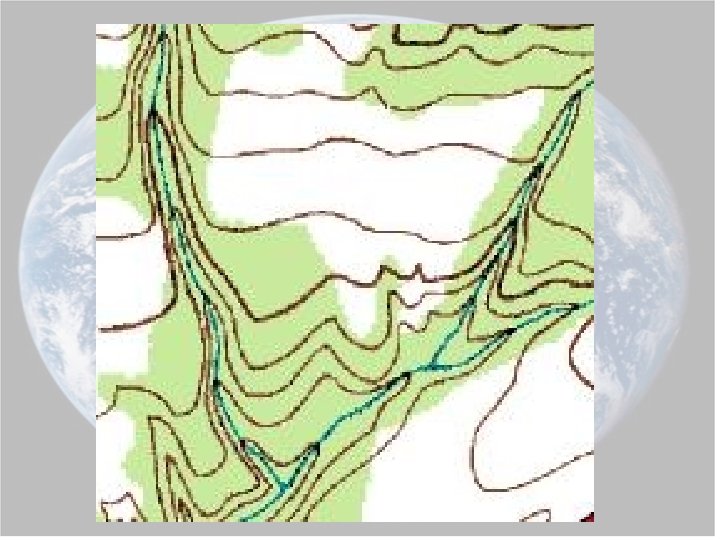
 2. The V’s in the contour lines that form where they cross a stream point in the opposite direction that the stream flows. Ex:
2. The V’s in the contour lines that form where they cross a stream point in the opposite direction that the stream flows. Ex:
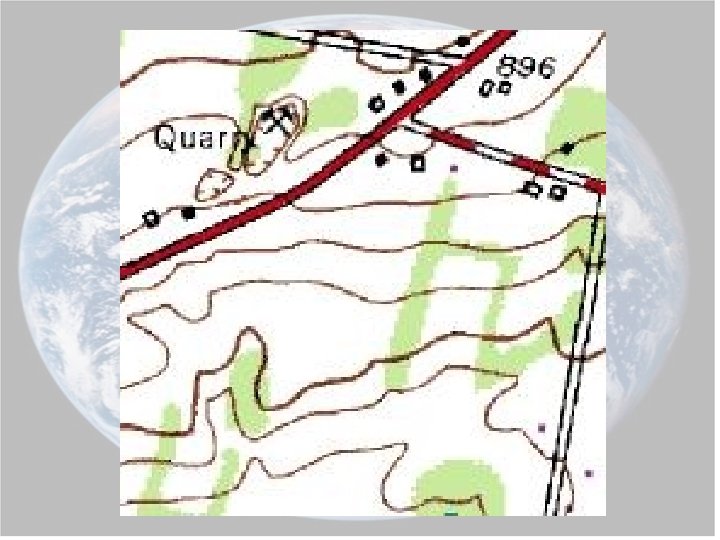
 3. Hachures are used to show depressions in the topography. Ex:
3. Hachures are used to show depressions in the topography. Ex:


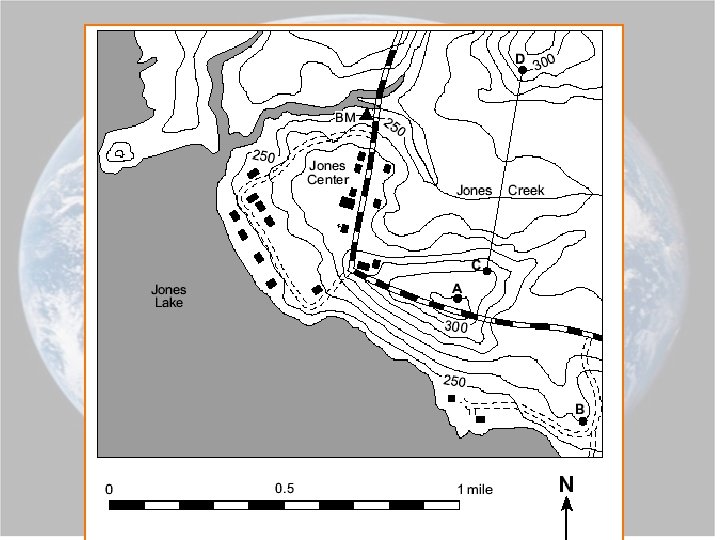 PROFILES:
PROFILES:
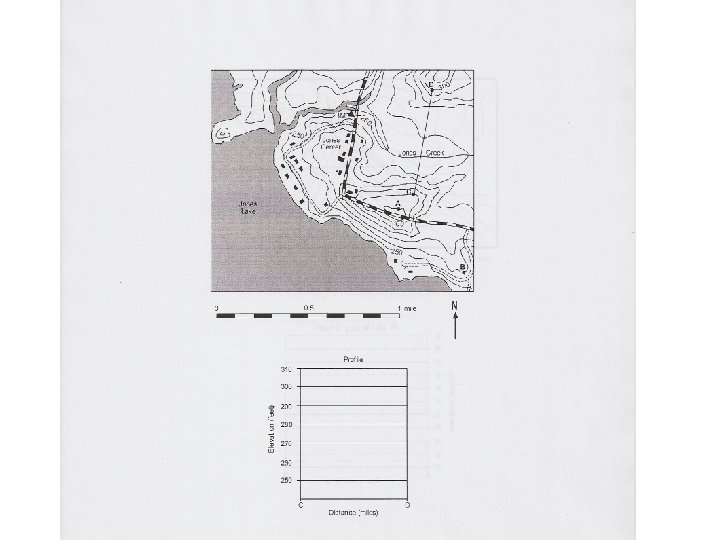

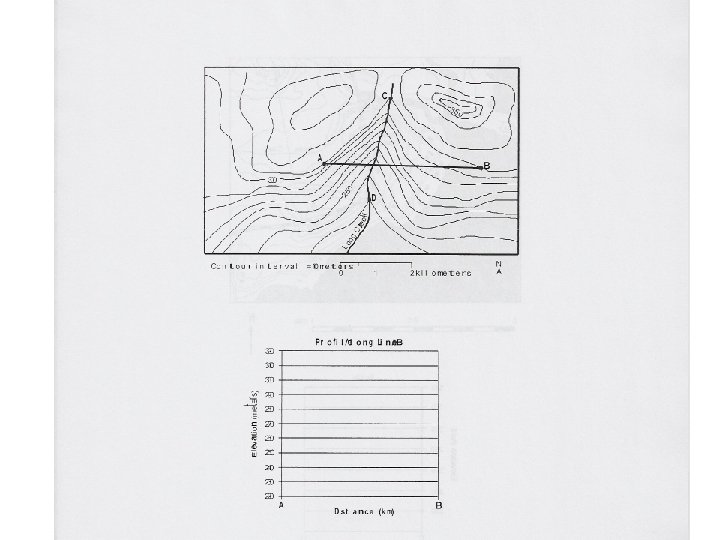
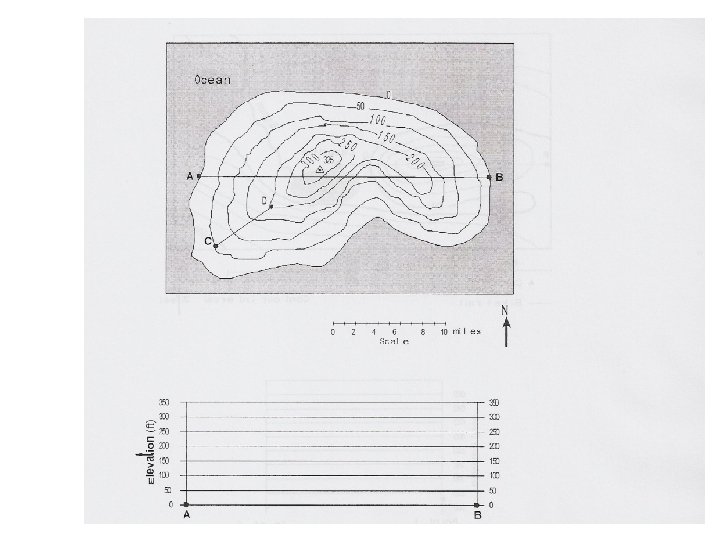
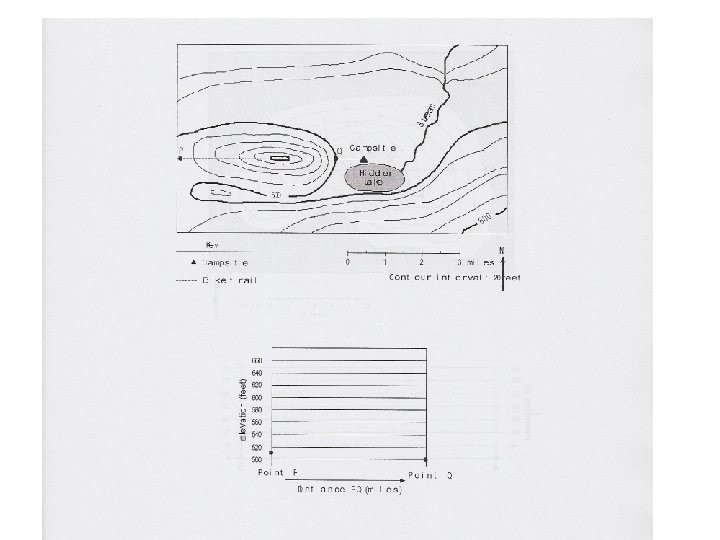
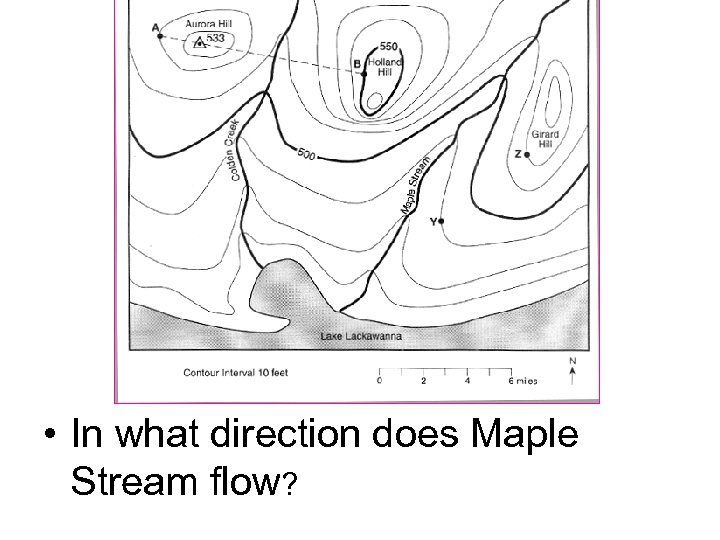 • In what direction does Maple Stream flow?
• In what direction does Maple Stream flow?


