Topic 1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Topic 1. General characteristics of mergers and acquisitions What are mergers and acquisitions? M&A market: waves and tendencies The objectives of M&A
Topic 1. General characteristics of mergers and acquisitions What are mergers and acquisitions? M&A market: waves and tendencies The objectives of M&A
 What are mergers and acquisitions? 2/14/2018 2
What are mergers and acquisitions? 2/14/2018 2
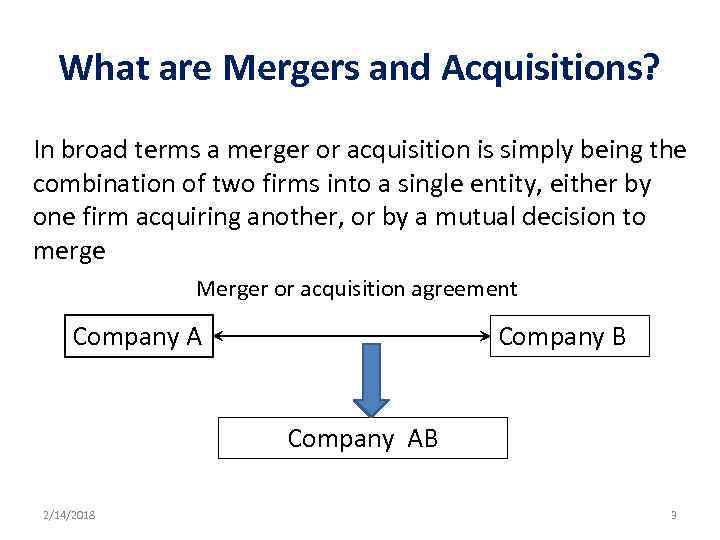 What are Mergers and Acquisitions? In broad terms a merger or acquisition is simply being the combination of two firms into a single entity, either by one firm acquiring another, or by a mutual decision to merge Merger or acquisition agreement Company A Company B Company AB 2/14/2018 3
What are Mergers and Acquisitions? In broad terms a merger or acquisition is simply being the combination of two firms into a single entity, either by one firm acquiring another, or by a mutual decision to merge Merger or acquisition agreement Company A Company B Company AB 2/14/2018 3
 A Merger • A merger (or consolidation) is an agreement between two companies to combine in to a single company. The merger has a friendly nature • The merger is completed by issuing new share certificates to the shareholders of both companies, so no external funds required. • A typical feature of a merger is that there is an agreement between the boards of the two companies on the terms of the merger. • The two companies exchange their shares for shares in the newly formed company. Often the identities of the original companies disappear. 2/14/2018 4
A Merger • A merger (or consolidation) is an agreement between two companies to combine in to a single company. The merger has a friendly nature • The merger is completed by issuing new share certificates to the shareholders of both companies, so no external funds required. • A typical feature of a merger is that there is an agreement between the boards of the two companies on the terms of the merger. • The two companies exchange their shares for shares in the newly formed company. Often the identities of the original companies disappear. 2/14/2018 4
 The scheme of a merger The decision, taken by management, is to be approved by shareholders of both the companies. In Russia it means that a qualified majority of shareholders (common shares) of both the companies should vote for the merger 2/14/2018 5
The scheme of a merger The decision, taken by management, is to be approved by shareholders of both the companies. In Russia it means that a qualified majority of shareholders (common shares) of both the companies should vote for the merger 2/14/2018 5
 An Acquisition (takeover) • An acquisition means the taking the corporate control upon one company (target, acquiring company) by the other one (bidding company, acquirer, raider) • The level of corporate control may vary from the full control (100% of shares) to an interest in the company (a reasonable deal of shares to have an impact) • The decision is also to be approved by the qualified majorities of both the companies 2/14/2018 6
An Acquisition (takeover) • An acquisition means the taking the corporate control upon one company (target, acquiring company) by the other one (bidding company, acquirer, raider) • The level of corporate control may vary from the full control (100% of shares) to an interest in the company (a reasonable deal of shares to have an impact) • The decision is also to be approved by the qualified majorities of both the companies 2/14/2018 6
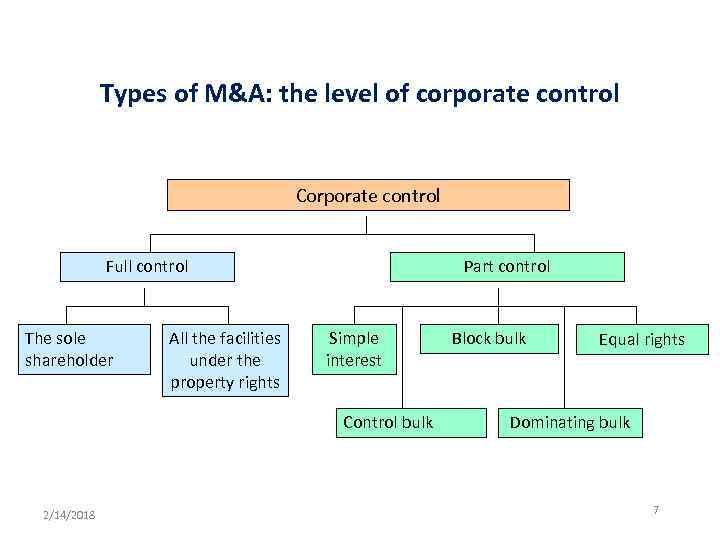 Types of M&A: the level of corporate control Corporate control Full control The sole shareholder All the facilities under the property rights Part control Simple interest Control bulk 2/14/2018 Block bulk Equal rights Dominating bulk 7
Types of M&A: the level of corporate control Corporate control Full control The sole shareholder All the facilities under the property rights Part control Simple interest Control bulk 2/14/2018 Block bulk Equal rights Dominating bulk 7
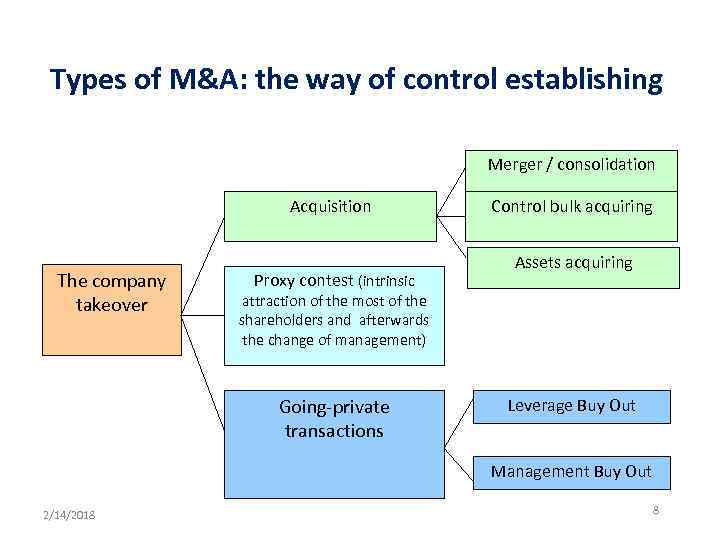 Types of M&A: the way of control establishing Merger / consolidation Acquisition The company takeover Proxy contest (intrinsic Control bulk acquiring Assets acquiring attraction of the most of the shareholders and afterwards the change of management) Going-private transactions Leverage Buy Out Management Buy Out 2/14/2018 8
Types of M&A: the way of control establishing Merger / consolidation Acquisition The company takeover Proxy contest (intrinsic Control bulk acquiring Assets acquiring attraction of the most of the shareholders and afterwards the change of management) Going-private transactions Leverage Buy Out Management Buy Out 2/14/2018 8
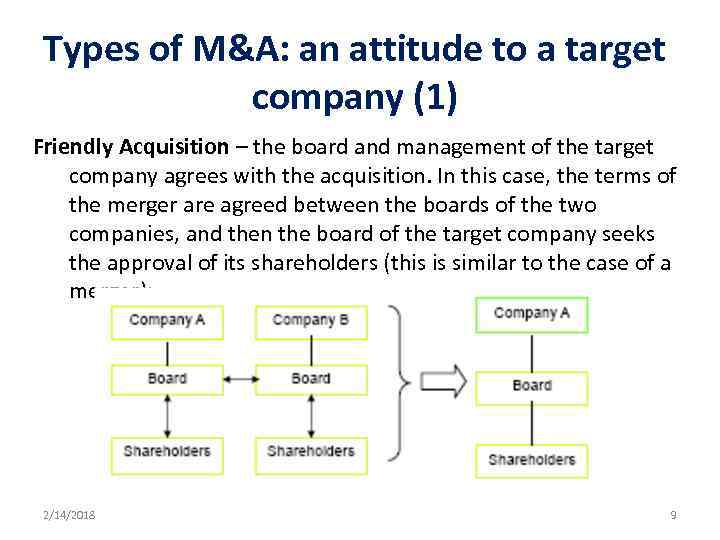 Types of M&A: an attitude to a target company (1) Friendly Acquisition – the board and management of the target company agrees with the acquisition. In this case, the terms of the merger are agreed between the boards of the two companies, and then the board of the target company seeks the approval of its shareholders (this is similar to the case of a merger): 2/14/2018 9
Types of M&A: an attitude to a target company (1) Friendly Acquisition – the board and management of the target company agrees with the acquisition. In this case, the terms of the merger are agreed between the boards of the two companies, and then the board of the target company seeks the approval of its shareholders (this is similar to the case of a merger): 2/14/2018 9
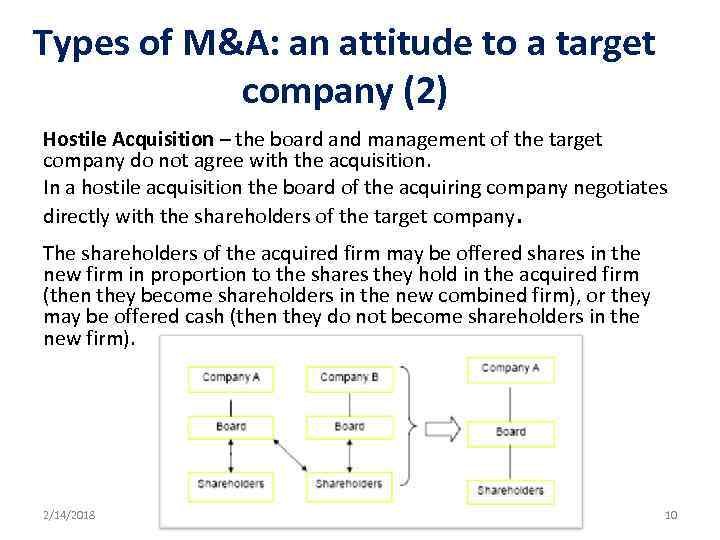 Types of M&A: an attitude to a target company (2) Hostile Acquisition – the board and management of the target company do not agree with the acquisition. In a hostile acquisition the board of the acquiring company negotiates directly with the shareholders of the target company. The shareholders of the acquired firm may be offered shares in the new firm in proportion to the shares they hold in the acquired firm (then they become shareholders in the new combined firm), or they may be offered cash (then they do not become shareholders in the new firm). 2/14/2018 10
Types of M&A: an attitude to a target company (2) Hostile Acquisition – the board and management of the target company do not agree with the acquisition. In a hostile acquisition the board of the acquiring company negotiates directly with the shareholders of the target company. The shareholders of the acquired firm may be offered shares in the new firm in proportion to the shares they hold in the acquired firm (then they become shareholders in the new combined firm), or they may be offered cash (then they do not become shareholders in the new firm). 2/14/2018 10
 Types of M&A: the business processes organization • The main type of M&A are: • Horizontal M&A ¨ These place between two companies in the same industry, at the same stage of production: For example, Daimler Benz and Chrysler; BP and Amoco. In Russia: Borlas and IBS, Rus. Al and Sib. AL • Vertical ¨ mergers These take place between two companies in the same industry, at different stages of production: For example, Rus. AL and Glencore, Vympelcom and Golden Telecom. • Conglomerate ¨ mergers These take place between two companies that are in unrelated industries: For example, AFK Systema and Detskyi Mir, Bazel and Rospechat. 2/14/2018 11
Types of M&A: the business processes organization • The main type of M&A are: • Horizontal M&A ¨ These place between two companies in the same industry, at the same stage of production: For example, Daimler Benz and Chrysler; BP and Amoco. In Russia: Borlas and IBS, Rus. Al and Sib. AL • Vertical ¨ mergers These take place between two companies in the same industry, at different stages of production: For example, Rus. AL and Glencore, Vympelcom and Golden Telecom. • Conglomerate ¨ mergers These take place between two companies that are in unrelated industries: For example, AFK Systema and Detskyi Mir, Bazel and Rospechat. 2/14/2018 11
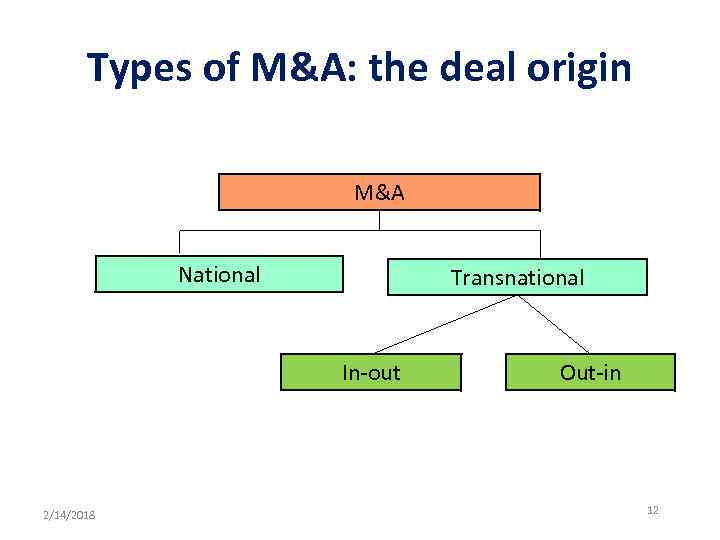 Types of M&A: the deal origin M&A National Transnational In-out 2/14/2018 Out-in 12
Types of M&A: the deal origin M&A National Transnational In-out 2/14/2018 Out-in 12
 Russian legislation • Strictly speaking, there is no the term as “mergers and acquisitions”. The term “reorganisation” is used which means such forms as: merger, joining, dividing, defining and change. 2/14/2018 13
Russian legislation • Strictly speaking, there is no the term as “mergers and acquisitions”. The term “reorganisation” is used which means such forms as: merger, joining, dividing, defining and change. 2/14/2018 13
 Слияния в российском законодательстве • Слиянием обществ признается возникновение нового общества путем передачи ему всех прав и обязанностей двух или нескольких обществ с прекращением последних. • Общества, участвующие в слиянии, заключают договор о слиянии, в котором определяются порядок и условия слияния, а также порядок конвертации акций каждого общества в акции нового общества. • Совет директоров (наблюдательный совет) общества выносит на решение общего собрания акционеров каждого общества, участвующего в слиянии, вопрос о реорганизации в форме слияния, об утверждении договора о слиянии, устава общества, создаваемого в результате слияния, и об утверждении передаточного акта. 2/14/2018 14
Слияния в российском законодательстве • Слиянием обществ признается возникновение нового общества путем передачи ему всех прав и обязанностей двух или нескольких обществ с прекращением последних. • Общества, участвующие в слиянии, заключают договор о слиянии, в котором определяются порядок и условия слияния, а также порядок конвертации акций каждого общества в акции нового общества. • Совет директоров (наблюдательный совет) общества выносит на решение общего собрания акционеров каждого общества, участвующего в слиянии, вопрос о реорганизации в форме слияния, об утверждении договора о слиянии, устава общества, создаваемого в результате слияния, и об утверждении передаточного акта. 2/14/2018 14
 Слияния в российском законодательстве (продолжение) • Образование органов вновь возникающего общества проводится на совместном общем собрании акционеров обществ, участвующих в слиянии. • Порядок голосования на совместном общем собрании акционеров может быть определен договором о слиянии обществ. • При слиянии обществ акции общества, принадлежащие другому обществу, участвующему в слиянии, а также собственные акции, принадлежащие участвующему в слиянии обществу, погашаются. • При слиянии обществ все права и обязанности каждого из них переходят к вновь возникшему обществу в соответствии с передаточным актом. 2/14/2018 15
Слияния в российском законодательстве (продолжение) • Образование органов вновь возникающего общества проводится на совместном общем собрании акционеров обществ, участвующих в слиянии. • Порядок голосования на совместном общем собрании акционеров может быть определен договором о слиянии обществ. • При слиянии обществ акции общества, принадлежащие другому обществу, участвующему в слиянии, а также собственные акции, принадлежащие участвующему в слиянии обществу, погашаются. • При слиянии обществ все права и обязанности каждого из них переходят к вновь возникшему обществу в соответствии с передаточным актом. 2/14/2018 15
 Присоединения • Под присоединением общества понимается прекращение деятельности одного или нескольких обществ с передачей всех их прав и обязанностей другому. • Присоединяемое общество и общество, к которому осуществляется присоединение, заключают договор о присоединении, в котором определяются порядок и условия присоединения, а также порядок конвертации акций присоединяемого общества в акции общества, к которому осуществляется присоединение. • Совет директоров (наблюдательный совет) каждого общества выносит на решение общего собрания акционеров своего общества, участвующего в присоединении, вопрос о реорганизации в форме присоединения и об утверждении договора о присоединении. • Совет директоров (наблюдательный совет) присоединяемого общества выносит на решение общего собрания акционеров вопрос об утверждении передаточного акта. 2/14/2018 16
Присоединения • Под присоединением общества понимается прекращение деятельности одного или нескольких обществ с передачей всех их прав и обязанностей другому. • Присоединяемое общество и общество, к которому осуществляется присоединение, заключают договор о присоединении, в котором определяются порядок и условия присоединения, а также порядок конвертации акций присоединяемого общества в акции общества, к которому осуществляется присоединение. • Совет директоров (наблюдательный совет) каждого общества выносит на решение общего собрания акционеров своего общества, участвующего в присоединении, вопрос о реорганизации в форме присоединения и об утверждении договора о присоединении. • Совет директоров (наблюдательный совет) присоединяемого общества выносит на решение общего собрания акционеров вопрос об утверждении передаточного акта. 2/14/2018 16
 Присоединения (продолжение) • Совместное общее собрание акционеров указанных обществ принимает решение о внесении изменений и дополнений в устав и в случае необходимости по иным вопросам. • Порядок голосования на совместном общем собрании акционеров определяется договором о присоединении. • При присоединении общества акции присоединяемого общества, принадлежащие обществу, к которому осуществляется присоединение, а также собственные акции, принадлежащие присоединяемому обществу, погашаются. • При присоединении одного общества к другому к последнему переходят все права и обязанности присоединяемого общества в соответствии с передаточным актом. 2/14/2018 17
Присоединения (продолжение) • Совместное общее собрание акционеров указанных обществ принимает решение о внесении изменений и дополнений в устав и в случае необходимости по иным вопросам. • Порядок голосования на совместном общем собрании акционеров определяется договором о присоединении. • При присоединении общества акции присоединяемого общества, принадлежащие обществу, к которому осуществляется присоединение, а также собственные акции, принадлежащие присоединяемому обществу, погашаются. • При присоединении одного общества к другому к последнему переходят все права и обязанности присоединяемого общества в соответствии с передаточным актом. 2/14/2018 17
 Критерии отнесения сделок к категории M&A в российском законодательстве • Объектом сделки является пакет акций (доля) компании или целостный имущественный комплекс • Объект сделки представляет собой действующий бизнес, не является пустой «оболочкой» • Объектом сделки или одним из ее участников является российское предприятие или юридическое лицо • Размер проданного пакета (доли) превышает 25% • Сделка осуществлена без участия государственных органов (приватизационные сделки не рассматриваются) • сделка привела к смене собственника актива (не является формальной передачей юридических прав от одного лица другому внутри холдинга) 2/14/2018 18
Критерии отнесения сделок к категории M&A в российском законодательстве • Объектом сделки является пакет акций (доля) компании или целостный имущественный комплекс • Объект сделки представляет собой действующий бизнес, не является пустой «оболочкой» • Объектом сделки или одним из ее участников является российское предприятие или юридическое лицо • Размер проданного пакета (доли) превышает 25% • Сделка осуществлена без участия государственных органов (приватизационные сделки не рассматриваются) • сделка привела к смене собственника актива (не является формальной передачей юридических прав от одного лица другому внутри холдинга) 2/14/2018 18
 M&A market: waves and tendencies 2/14/2018 19
M&A market: waves and tendencies 2/14/2018 19
 M&A waves First wave (mostly horizontal) - 1897 – 1904 th Second wave (mostly vertical) - 1916 – 1929 th “Conglomerate” wave - 1965 – 1970 th Fourth wave – 1980 th (hostile takeovers) Fifth wave (transnational) – second half of 1990 th • Sixth wave (financial) - 2003 -2008 • Now we may observe the rise of the seventh wave • • • 2/14/2018 20
M&A waves First wave (mostly horizontal) - 1897 – 1904 th Second wave (mostly vertical) - 1916 – 1929 th “Conglomerate” wave - 1965 – 1970 th Fourth wave – 1980 th (hostile takeovers) Fifth wave (transnational) – second half of 1990 th • Sixth wave (financial) - 2003 -2008 • Now we may observe the rise of the seventh wave • • • 2/14/2018 20
 M&A in Russia • 1993 -1998 – privatization processes and “voucher -based” deals. Classic methods are very rare • 1999 -2002 – hostile takeovers with very specific features • Since 2003 – markets consolidation in most of the spheres, classic approaches development 2/14/2018 21
M&A in Russia • 1993 -1998 – privatization processes and “voucher -based” deals. Classic methods are very rare • 1999 -2002 – hostile takeovers with very specific features • Since 2003 – markets consolidation in most of the spheres, classic approaches development 2/14/2018 21
 The reasons for the market growth in Russia • High rates of economy growth • Integration of Russian economy into the world community • The problem of the low efficiency and thus – of low competitiveness • The favorable situation with world prices on raw resources • The need on the business “lightening” • Others… 2/14/2018 22
The reasons for the market growth in Russia • High rates of economy growth • Integration of Russian economy into the world community • The problem of the low efficiency and thus – of low competitiveness • The favorable situation with world prices on raw resources • The need on the business “lightening” • Others… 2/14/2018 22
 Russian М&A market, 2011 • • • Total deals - 1070 (exceeds the 2010 indicator at 20% The total value of deals – $ 90, 3 bn The average deal value - $ 100, 4 mln (21% higher than in 2009) The number of deals with the value > $ 100 mln – 110 The contribution to the Russian GDP – 5% (as at pre-crisis period) • The share of МВО deals was 2, 6% in the whole bulk (1, 1 % of the total value) • 32% of the total value and 20% of the total quantity are the deals in ICT and oil processing and oil-based chemistry • 41% of total value and 18% of total quantity are the deals of diversification 2/14/2018 23
Russian М&A market, 2011 • • • Total deals - 1070 (exceeds the 2010 indicator at 20% The total value of deals – $ 90, 3 bn The average deal value - $ 100, 4 mln (21% higher than in 2009) The number of deals with the value > $ 100 mln – 110 The contribution to the Russian GDP – 5% (as at pre-crisis period) • The share of МВО deals was 2, 6% in the whole bulk (1, 1 % of the total value) • 32% of the total value and 20% of the total quantity are the deals in ICT and oil processing and oil-based chemistry • 41% of total value and 18% of total quantity are the deals of diversification 2/14/2018 23
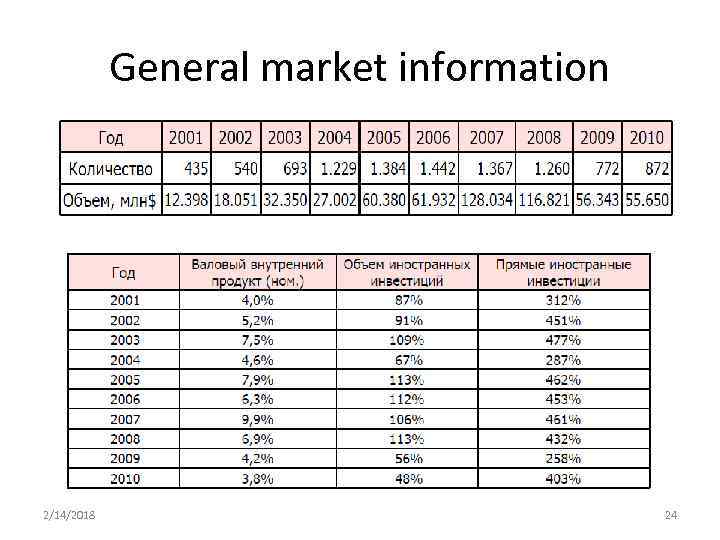 General market information 2/14/2018 24
General market information 2/14/2018 24
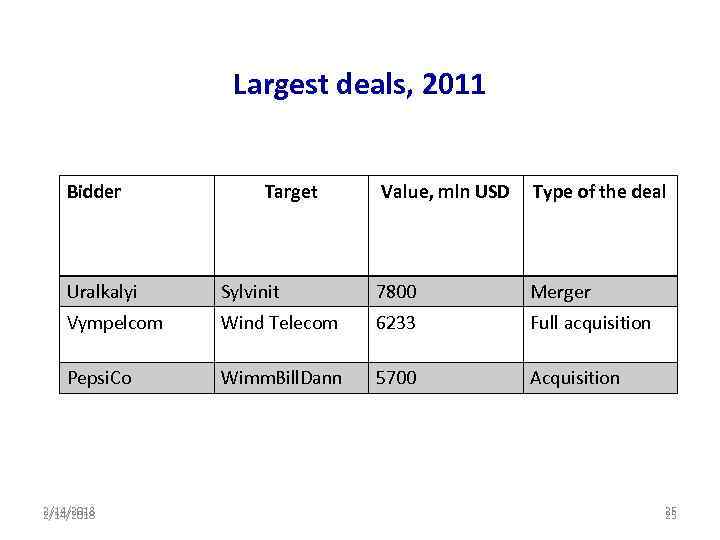 Largest deals, 2011 Bidder Target Value, mln USD Type of the deal Uralkalyi Sylvinit 7800 Merger Vympelcom Wind Telecom 6233 Full acquisition Pepsi. Co Wimm. Bill. Dann 5700 Acquisition 2/14/2018 25 25
Largest deals, 2011 Bidder Target Value, mln USD Type of the deal Uralkalyi Sylvinit 7800 Merger Vympelcom Wind Telecom 6233 Full acquisition Pepsi. Co Wimm. Bill. Dann 5700 Acquisition 2/14/2018 25 25
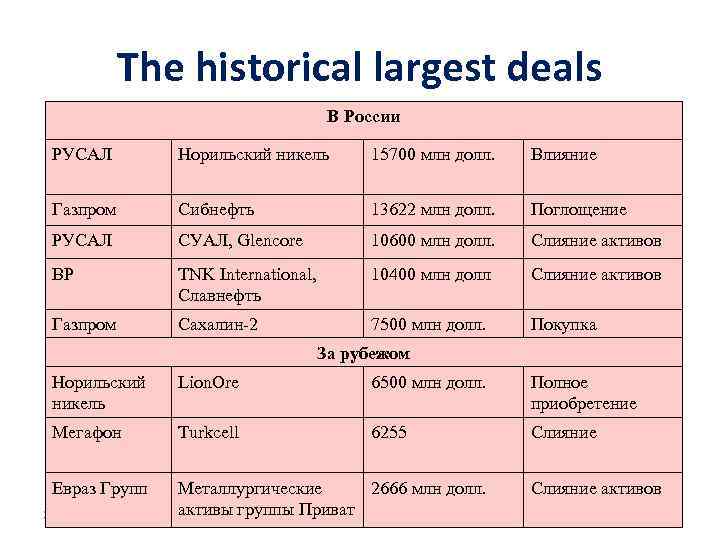 The historical largest deals В России РУСАЛ Норильский никель 15700 млн долл. Влияние Газпром Сибнефть 13622 млн долл. Поглощение РУСАЛ СУАЛ, Glencore 10600 млн долл. Слияние активов ВР TNK International, Славнефть 10400 млн долл Слияние активов Газпром Сахалин-2 7500 млн долл. Покупка За рубежом Норильский никель Lion. Ore 6500 млн долл. Полное приобретение Мегафон Turkcell 6255 Слияние Евраз Групп Металлургические 2666 млн долл. активы группы Приват 2/14/2018 Слияние активов 26
The historical largest deals В России РУСАЛ Норильский никель 15700 млн долл. Влияние Газпром Сибнефть 13622 млн долл. Поглощение РУСАЛ СУАЛ, Glencore 10600 млн долл. Слияние активов ВР TNK International, Славнефть 10400 млн долл Слияние активов Газпром Сахалин-2 7500 млн долл. Покупка За рубежом Норильский никель Lion. Ore 6500 млн долл. Полное приобретение Мегафон Turkcell 6255 Слияние Евраз Групп Металлургические 2666 млн долл. активы группы Приват 2/14/2018 Слияние активов 26
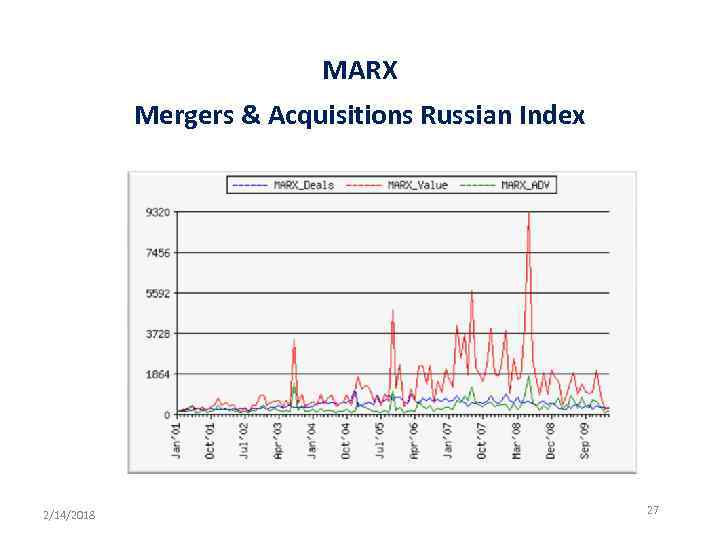 MARX Mergers & Acquisitions Russian Index 2/14/2018 27
MARX Mergers & Acquisitions Russian Index 2/14/2018 27
 The specifics of the Russian M&A market 1. The dominance of horizontal deals 2. The sectoral differences in M&A strategies 3. The stable leadership of some industries (oil and gas extracting, processing and transportation; energy production and distribution; metallurgy; ICT; food processing) 4. The modest share of MBO deals and other modern modes of dealing 5. The large-scale prevailing of hostile takeovers with very specific instruments especially to medium-sized enterprises 6. The government and local authorities intervention 2/14/2018 28
The specifics of the Russian M&A market 1. The dominance of horizontal deals 2. The sectoral differences in M&A strategies 3. The stable leadership of some industries (oil and gas extracting, processing and transportation; energy production and distribution; metallurgy; ICT; food processing) 4. The modest share of MBO deals and other modern modes of dealing 5. The large-scale prevailing of hostile takeovers with very specific instruments especially to medium-sized enterprises 6. The government and local authorities intervention 2/14/2018 28
 The objectives of M&A 2/14/2018 29
The objectives of M&A 2/14/2018 29
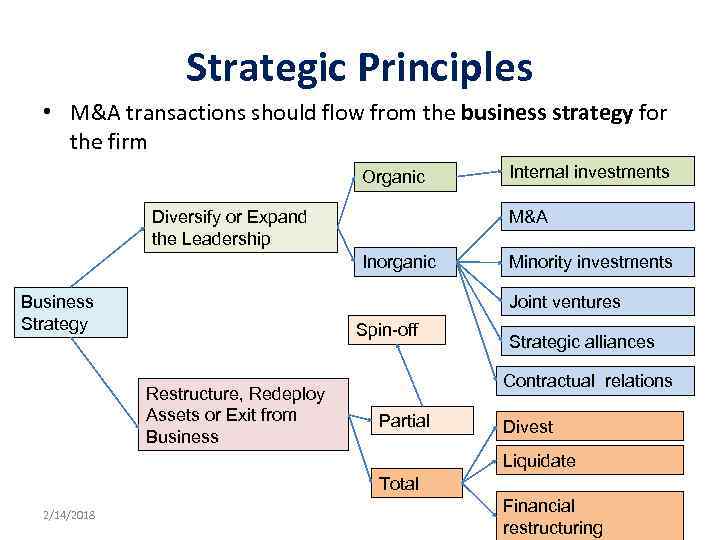 Strategic Principles • M&A transactions should flow from the business strategy for the firm Organic Diversify or Expand the Leadership M&A Inorganic Business Strategy Internal investments Minority investments Joint ventures Spin-off Restructure, Redeploy Assets or Exit from Business Strategic alliances Contractual relations Partial Divest Liquidate Total 2/14/2018 Financial restructuring 30
Strategic Principles • M&A transactions should flow from the business strategy for the firm Organic Diversify or Expand the Leadership M&A Inorganic Business Strategy Internal investments Minority investments Joint ventures Spin-off Restructure, Redeploy Assets or Exit from Business Strategic alliances Contractual relations Partial Divest Liquidate Total 2/14/2018 Financial restructuring 30
 5 main reasons why firms pursue inorganic growth 1. Maturing product line 2. Regulatory and antitrust limits 3. Value creation through horizontal and vertical integration 4. Acquisition of resources and capabilities 5. Value creation through diversification 2/14/2018 31
5 main reasons why firms pursue inorganic growth 1. Maturing product line 2. Regulatory and antitrust limits 3. Value creation through horizontal and vertical integration 4. Acquisition of resources and capabilities 5. Value creation through diversification 2/14/2018 31
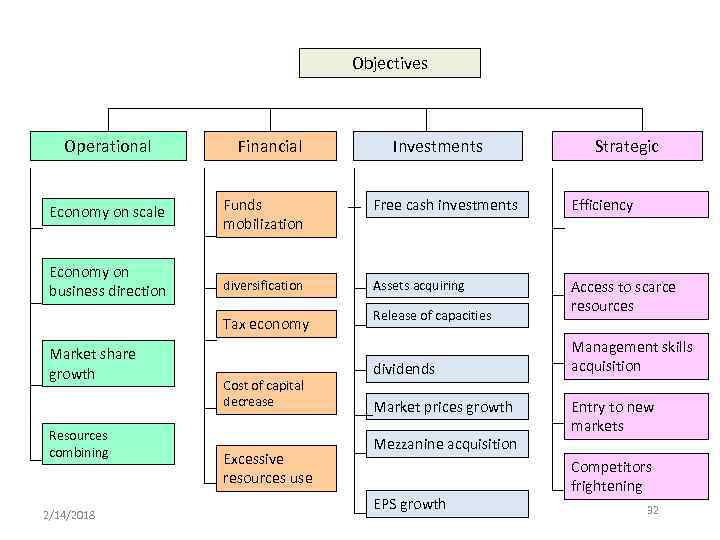 Objectives Operational Financial Investments Strategic Economy on scale Funds mobilization Free cash investments Efficiency Economy on business direction diversification Assets acquiring Access to scarce resources Tax economy Market share growth Resources combining 2/14/2018 Cost of capital decrease Excessive resources use Release of capacities dividends Market prices growth Mezzanine acquisition EPS growth Management skills acquisition Entry to new markets Competitors frightening 32
Objectives Operational Financial Investments Strategic Economy on scale Funds mobilization Free cash investments Efficiency Economy on business direction diversification Assets acquiring Access to scarce resources Tax economy Market share growth Resources combining 2/14/2018 Cost of capital decrease Excessive resources use Release of capacities dividends Market prices growth Mezzanine acquisition EPS growth Management skills acquisition Entry to new markets Competitors frightening 32
 Why Engage in M&A? • Theories as to why firms merge: • Synergy theory: firms merge because the value of the new, combined, firm is greater than the sum of the two individual firms. • Undervaluation theory: Firms merge because one firm is undervalued. • Agency theory: Firms merge to resolve conflicts between shareholders and managers. • Market power theory: Firms merge to increase market share and thus profit. • Diversification theory: Firms merge to reduce business risk. • Growth theory: firms merge in increase earnings growth. 2/14/2018 33
Why Engage in M&A? • Theories as to why firms merge: • Synergy theory: firms merge because the value of the new, combined, firm is greater than the sum of the two individual firms. • Undervaluation theory: Firms merge because one firm is undervalued. • Agency theory: Firms merge to resolve conflicts between shareholders and managers. • Market power theory: Firms merge to increase market share and thus profit. • Diversification theory: Firms merge to reduce business risk. • Growth theory: firms merge in increase earnings growth. 2/14/2018 33
 Why Merge: Synergy Theory • The synergy theory • Firms merge because the value of the combined firm is greater than the sum of the values of the individual firms. The shareholders of the two firms will potentially benefit because they are able to share the increase in value that results from the merger. • These synergies are of two types: • Operating synergies occur when a merger between two firms reduces the average cost of production. • Financial synergies occur when a merger between two companies reduces the average cost of financing the firms’ activities 2/14/2018 34
Why Merge: Synergy Theory • The synergy theory • Firms merge because the value of the combined firm is greater than the sum of the values of the individual firms. The shareholders of the two firms will potentially benefit because they are able to share the increase in value that results from the merger. • These synergies are of two types: • Operating synergies occur when a merger between two firms reduces the average cost of production. • Financial synergies occur when a merger between two companies reduces the average cost of financing the firms’ activities 2/14/2018 34
 Why Merge: Undervaluation theory • The undervaluation theory says that firms merge because one firm is undervalued, MV(A)
Why Merge: Undervaluation theory • The undervaluation theory says that firms merge because one firm is undervalued, MV(A)
 Why Merge: The Agency Theory ¨ The agency theory says that firms merge to resolve the conflicts of interest that exist between shareholders and managers. ¨ The managers of a firm may act in such a way that reduces the value of the firm. ¨ In an efficient market, the market value of a firm will reflect the consequences of the managers’ actions: ¨ ¨ Firms with bad management will generally be cheaper than those with good management. This will increase the probability that the firms with bad management are acquired by other firms. The managers of a firm know that if the firm is acquired by another firm, they may lose their jobs; this should ensure that they will act in the interests of their shareholders. ¨ M&A serves to keep managers acting in the interests of their 2/14/2018 shareholders 36
Why Merge: The Agency Theory ¨ The agency theory says that firms merge to resolve the conflicts of interest that exist between shareholders and managers. ¨ The managers of a firm may act in such a way that reduces the value of the firm. ¨ In an efficient market, the market value of a firm will reflect the consequences of the managers’ actions: ¨ ¨ Firms with bad management will generally be cheaper than those with good management. This will increase the probability that the firms with bad management are acquired by other firms. The managers of a firm know that if the firm is acquired by another firm, they may lose their jobs; this should ensure that they will act in the interests of their shareholders. ¨ M&A serves to keep managers acting in the interests of their 2/14/2018 shareholders 36
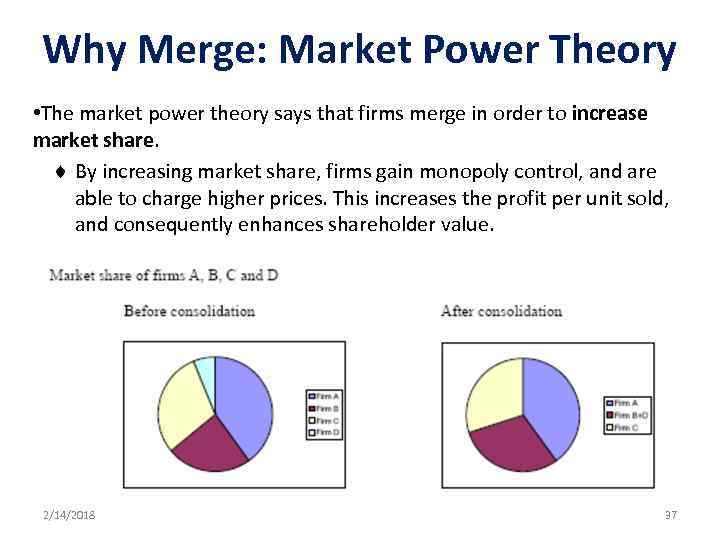 Why Merge: Market Power Theory • The market power theory says that firms merge in order to increase market share. ¨ By increasing market share, firms gain monopoly control, and are able to charge higher prices. This increases the profit per unit sold, and consequently enhances shareholder value. 2/14/2018 37
Why Merge: Market Power Theory • The market power theory says that firms merge in order to increase market share. ¨ By increasing market share, firms gain monopoly control, and are able to charge higher prices. This increases the profit per unit sold, and consequently enhances shareholder value. 2/14/2018 37
 Why Merge: Diversification Theory • The diversification theory says that firms merge to reduce business risk through diversification of the firm’s activities. This would be particularly true of conglomerate mergers. ¨ However, shareholders can diversify risk much more cheaply than firms simply by buying shares in the two companies. ¨ Alternatively other stakeholders in the firm (such as managers and employees) may not be able to diversify risk as easily as shareholders and so merging may be optimal for them. ¨ Bondholders, will also benefit from diversification, since it will reduce the probability of bankruptcy. 2/14/2018 38
Why Merge: Diversification Theory • The diversification theory says that firms merge to reduce business risk through diversification of the firm’s activities. This would be particularly true of conglomerate mergers. ¨ However, shareholders can diversify risk much more cheaply than firms simply by buying shares in the two companies. ¨ Alternatively other stakeholders in the firm (such as managers and employees) may not be able to diversify risk as easily as shareholders and so merging may be optimal for them. ¨ Bondholders, will also benefit from diversification, since it will reduce the probability of bankruptcy. 2/14/2018 38
 Why merge: specific motives • The managers’ power increase • The defense • Too big to fail 2/14/2018 39
Why merge: specific motives • The managers’ power increase • The defense • Too big to fail 2/14/2018 39
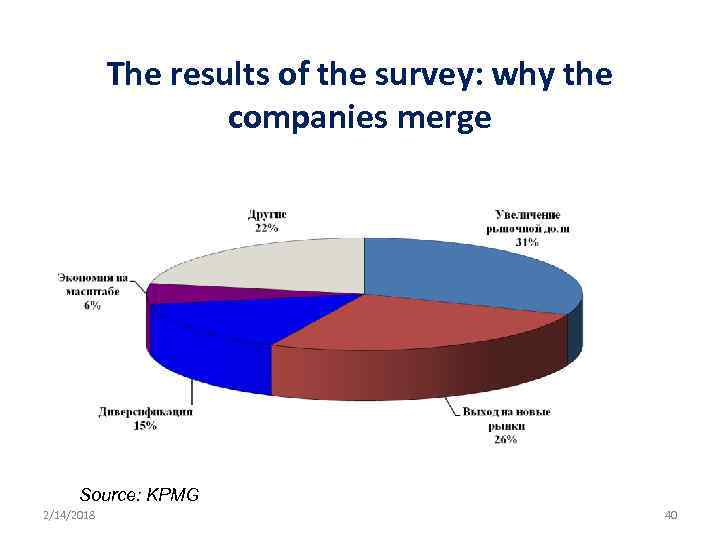 The results of the survey: why the companies merge Source: KPMG 2/14/2018 40
The results of the survey: why the companies merge Source: KPMG 2/14/2018 40
 Thank you for your attention! 2/14/2018 41
Thank you for your attention! 2/14/2018 41


