802dd260940005d634c8f271ec60b49e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70
 Today • Review mortality & fertility • Age structure © T. M. Whitmore
Today • Review mortality & fertility • Age structure © T. M. Whitmore
 Questions? © T. M. Whitmore
Questions? © T. M. Whitmore
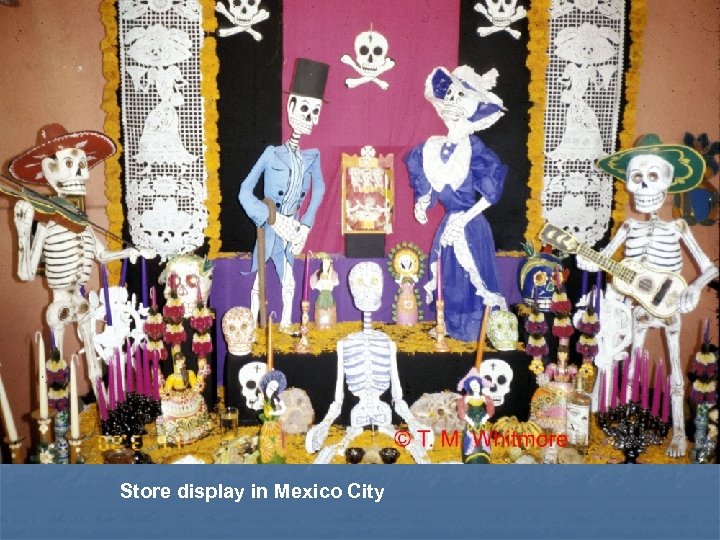 Store display in Mexico City
Store display in Mexico City
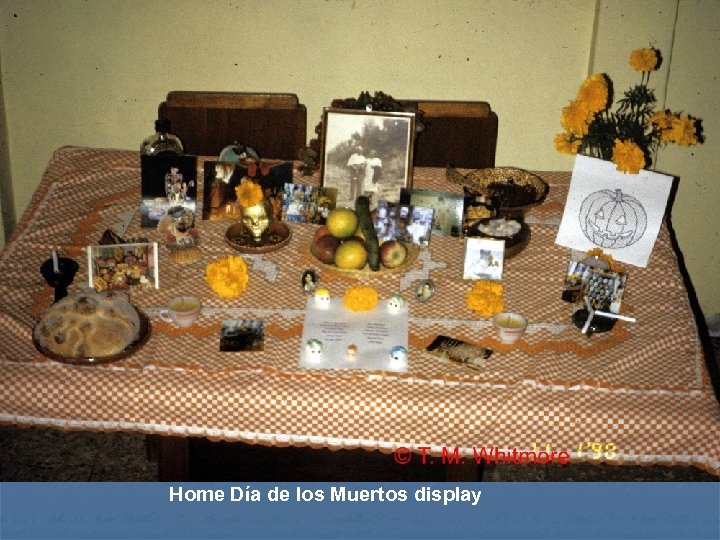 Home Día de los Muertos display
Home Día de los Muertos display
 Decorated graves in Guatemala
Decorated graves in Guatemala
 Decorated graves in Guatemala
Decorated graves in Guatemala
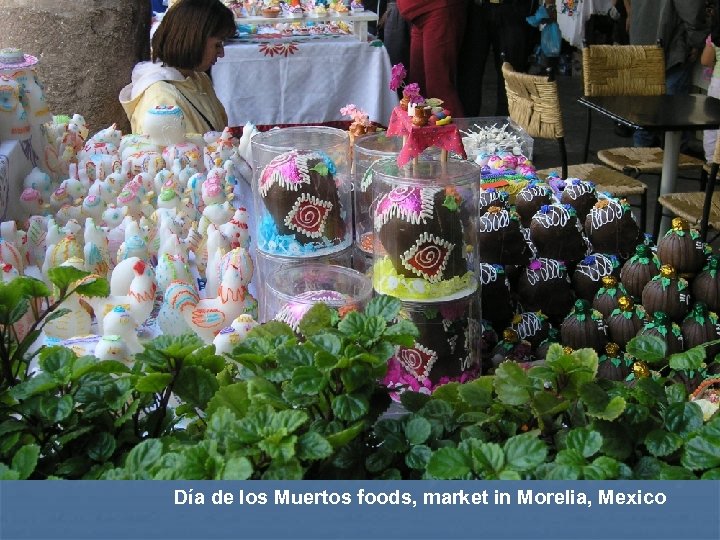
 Día de los Muertos foods, market in Morelia, Mexico
Día de los Muertos foods, market in Morelia, Mexico
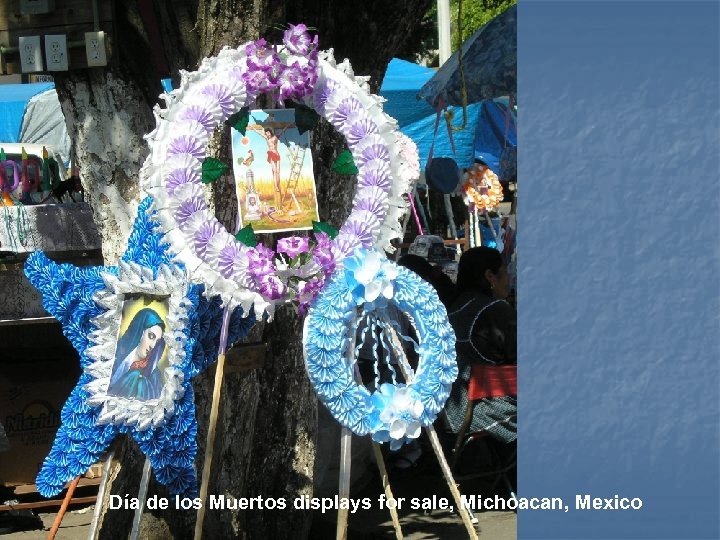 Día de los Muertos displays for sale, Michoacan, Mexico
Día de los Muertos displays for sale, Michoacan, Mexico
 Total Fertility Rate (TFR) • = Average total number of births to a • • woman in her lifetime (superior to CBR) ~ 2. 1 => parents only replacing themselves (called “replacement level fertility”) Øneed the extra 0. 1 due to childhood deaths LA ranges from: Ø~ 4 (Honduras, Guatemala, Haiti, Bolivia) Ø~2 (Costa Rica, Cuba, Uruguay) © T. M. Whitmore
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) • = Average total number of births to a • • woman in her lifetime (superior to CBR) ~ 2. 1 => parents only replacing themselves (called “replacement level fertility”) Øneed the extra 0. 1 due to childhood deaths LA ranges from: Ø~ 4 (Honduras, Guatemala, Haiti, Bolivia) Ø~2 (Costa Rica, Cuba, Uruguay) © T. M. Whitmore
 Death related (mortality) • Life expectancy at birth (Eo)= Average • • • projected span of life at the date LA Range: Ø> 75 ( Mexico, Costa Rica, Cuba, Chile) Ø< 70 (Guatemala, Nicaragua, Haiti, Bolivia) Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) Ø# deaths of infants (< 1 yr)/1000 live births in a given yr Range: > 30 (Guatemala, Honduras, Haiti, Bolivia); < 10 (Cuba, Chile, Costa Rica) Whitmore © T. M.
Death related (mortality) • Life expectancy at birth (Eo)= Average • • • projected span of life at the date LA Range: Ø> 75 ( Mexico, Costa Rica, Cuba, Chile) Ø< 70 (Guatemala, Nicaragua, Haiti, Bolivia) Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) Ø# deaths of infants (< 1 yr)/1000 live births in a given yr Range: > 30 (Guatemala, Honduras, Haiti, Bolivia); < 10 (Cuba, Chile, Costa Rica) Whitmore © T. M.
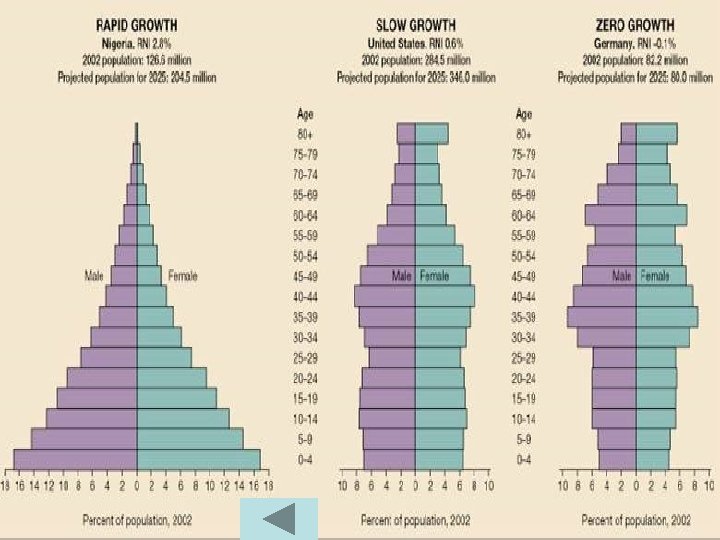
 Population age structure–youth (< 15) • World 29% • • ØLesser developed World 32% - 35% ØMore Developed World ~ 17% USA 20% Latin America 30% ØCentral America with Mexico 34% ØCaribbean 29% ØSouth America 29% Latin American extremes © T. M. Whitmore Consequences
Population age structure–youth (< 15) • World 29% • • ØLesser developed World 32% - 35% ØMore Developed World ~ 17% USA 20% Latin America 30% ØCentral America with Mexico 34% ØCaribbean 29% ØSouth America 29% Latin American extremes © T. M. Whitmore Consequences
 Population age structure - aged (> 65) • World 7% • • ØLesser developed World 5% ØMore developed 15% USA 12% Latin America 6% ØCentral America with Mexico 5% ØCaribbean 8% ØSouth America 6% Latin American extremes Consequences © T. M. Whitmore
Population age structure - aged (> 65) • World 7% • • ØLesser developed World 5% ØMore developed 15% USA 12% Latin America 6% ØCentral America with Mexico 5% ØCaribbean 8% ØSouth America 6% Latin American extremes Consequences © T. M. Whitmore
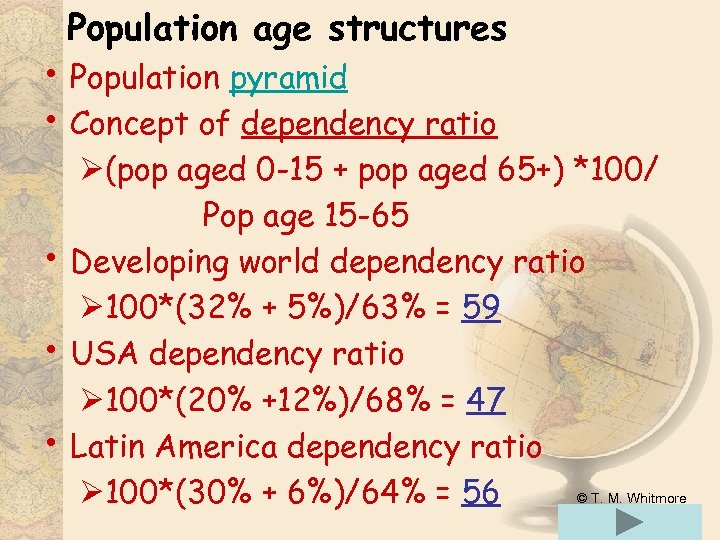 Population age structures • Population pyramid • Concept of dependency ratio • • • Ø(pop aged 0 -15 + pop aged 65+) *100/ Pop age 15 -65 Developing world dependency ratio Ø 100*(32% + 5%)/63% = 59 USA dependency ratio Ø 100*(20% +12%)/68% = 47 Latin America dependency ratio Ø 100*(30% + 6%)/64% = 56 © T. M. Whitmore
Population age structures • Population pyramid • Concept of dependency ratio • • • Ø(pop aged 0 -15 + pop aged 65+) *100/ Pop age 15 -65 Developing world dependency ratio Ø 100*(32% + 5%)/63% = 59 USA dependency ratio Ø 100*(20% +12%)/68% = 47 Latin America dependency ratio Ø 100*(30% + 6%)/64% = 56 © T. M. Whitmore
 © T. M. Whitmore
© T. M. Whitmore
 Geographic distribution of population • High density zones • Low density zones • ØSouth America’s “empty heart” ØArid N Mexico (save border) ØArid areas in S cone Key growth zones ØMedium and larger cities (most all population growth here) ØRural – Rural migration more a redistribution than real growth © T. M. Whitmore
Geographic distribution of population • High density zones • Low density zones • ØSouth America’s “empty heart” ØArid N Mexico (save border) ØArid areas in S cone Key growth zones ØMedium and larger cities (most all population growth here) ØRural – Rural migration more a redistribution than real growth © T. M. Whitmore
 Urbanization • Proportion of a country’s population living • • in cities ØWorld = 47% ØUSA = 79% ØLA = 76%! Extremes in LA Large city urbanization in LA (% in cities > 1 million) © T. M. Whitmore
Urbanization • Proportion of a country’s population living • • in cities ØWorld = 47% ØUSA = 79% ØLA = 76%! Extremes in LA Large city urbanization in LA (% in cities > 1 million) © T. M. Whitmore
 • Mega-cities • Urbanization II ØEmerging Megalopolis zones § Central Mexico § South Brazil triangle & Río de la Plata Concept of primacy ØSingle city in a country that dominates in pop, culture, economic development, etc. ØExamples: § Santo Domingo § Guatemala City § Mexico City © T. M. Whitmore § Lima
• Mega-cities • Urbanization II ØEmerging Megalopolis zones § Central Mexico § South Brazil triangle & Río de la Plata Concept of primacy ØSingle city in a country that dominates in pop, culture, economic development, etc. ØExamples: § Santo Domingo § Guatemala City § Mexico City © T. M. Whitmore § Lima
 Concept of primacy • Single city in a country that dominates in pop, culture, economic development, etc. ØExamples: § Santo Domingo § Guatemala City § Mexico City § Lima © T. M. Whitmore
Concept of primacy • Single city in a country that dominates in pop, culture, economic development, etc. ØExamples: § Santo Domingo § Guatemala City § Mexico City § Lima © T. M. Whitmore




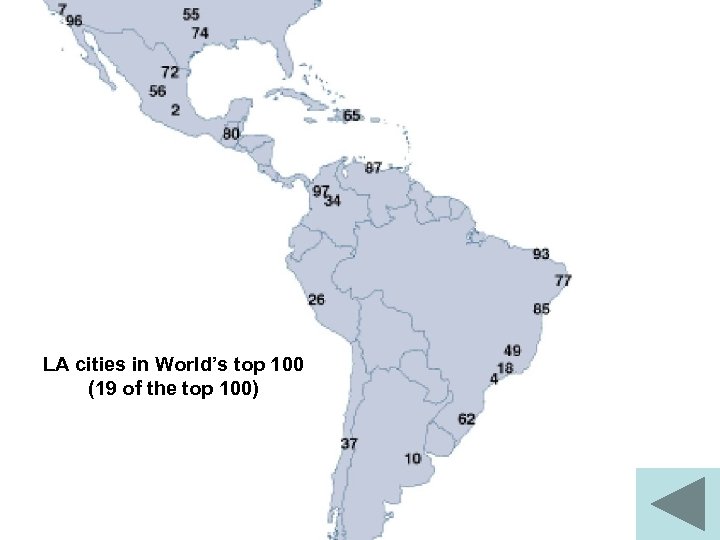 LA cities in World’s top 100 (19 of the top 100)
LA cities in World’s top 100 (19 of the top 100)
 Roots of urban growth • Demographic • • ØR—to—Urban migration ØNatural increase within the city Economic ØIndustrialization ØRural stagnation Organizations ØBanks and governments © T. M. Whitmore
Roots of urban growth • Demographic • • ØR—to—Urban migration ØNatural increase within the city Economic ØIndustrialization ØRural stagnation Organizations ØBanks and governments © T. M. Whitmore
 Benefits from urban growth • Efficient provision of social services • Cities are centers of information flow • • • and knowledge Concentrated (and better educated? ) labor pool Physical infrastructure often better Cities concentrate “human capital” Cities are a huge internal markets Easier linkages between industries Cities are often “better off” © T. M. Whitmore
Benefits from urban growth • Efficient provision of social services • Cities are centers of information flow • • • and knowledge Concentrated (and better educated? ) labor pool Physical infrastructure often better Cities concentrate “human capital” Cities are a huge internal markets Easier linkages between industries Cities are often “better off” © T. M. Whitmore
 Problems with urban growth I • Housing • ØFirst destination of poor migrants is the inner city slums ØElite often still in posh neighborhoods in inner city ØOften close juxtaposition of rich and poor Some planned attempts to deal with this © T. M. Whitmore
Problems with urban growth I • Housing • ØFirst destination of poor migrants is the inner city slums ØElite often still in posh neighborhoods in inner city ØOften close juxtaposition of rich and poor Some planned attempts to deal with this © T. M. Whitmore
 Problems with urban growth II • Self-help (often squatter) housing • ØMany names: Favelas (Brazil), colonias proletarias, cuidades perdidas, etc. Ø 2 nd destination of R migrant ØSeen as places of permanence Ø 25 -40% of total pop in some cities ØInitially settlements lack infrastructure ØA main characteristic is improvement New trends © T. M. Whitmore
Problems with urban growth II • Self-help (often squatter) housing • ØMany names: Favelas (Brazil), colonias proletarias, cuidades perdidas, etc. Ø 2 nd destination of R migrant ØSeen as places of permanence Ø 25 -40% of total pop in some cities ØInitially settlements lack infrastructure ØA main characteristic is improvement New trends © T. M. Whitmore
 Problems with urban growth III • Subsidy and Sink effects • Congestion • Pollution • Loss of urban open space • Poor provision of basic services • Export of problems • Poverty generally • Employment not always good © T. M. Whitmore
Problems with urban growth III • Subsidy and Sink effects • Congestion • Pollution • Loss of urban open space • Poor provision of basic services • Export of problems • Poverty generally • Employment not always good © T. M. Whitmore
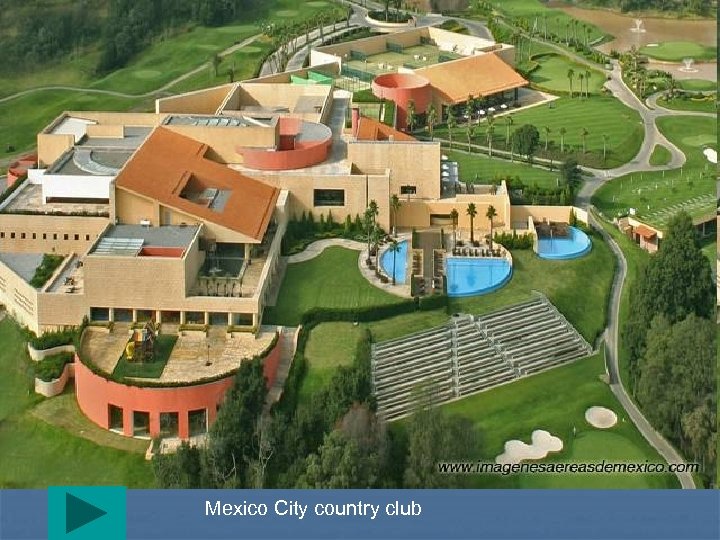 Mexico City country club
Mexico City country club
 Mexican stock exchange
Mexican stock exchange
 Elite housing, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
Elite housing, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
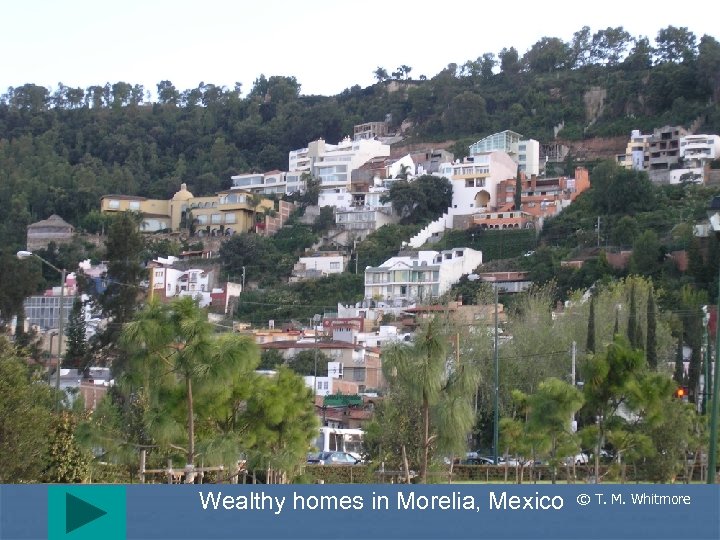 Wealthy homes in Morelia, Mexico © T. M. Whitmore
Wealthy homes in Morelia, Mexico © T. M. Whitmore
 Elite house Cuidad Juarez © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall
Elite house Cuidad Juarez © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall
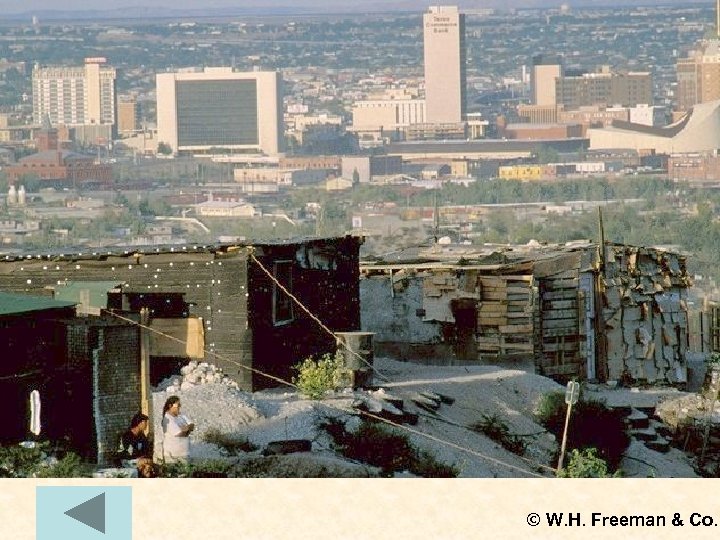 © W. H. Freeman & Co.
© W. H. Freeman & Co.
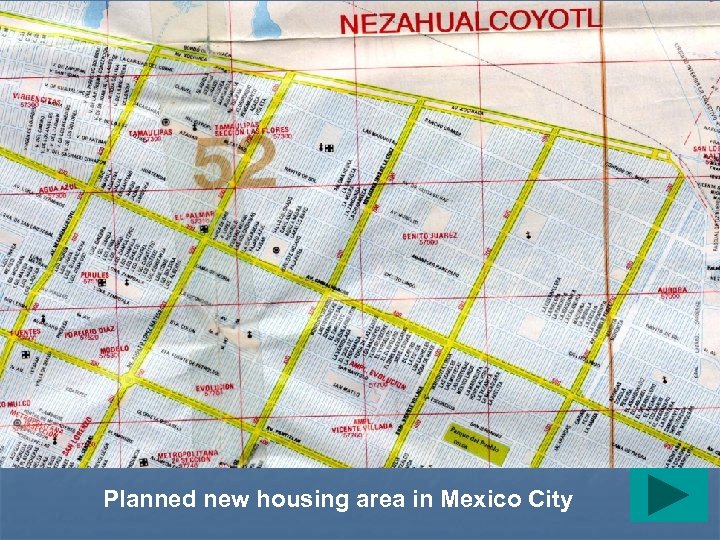 Planned new housing area in Mexico City
Planned new housing area in Mexico City
 Nezahualcoyotl: Planned housing area in Mexico City
Nezahualcoyotl: Planned housing area in Mexico City
 Nezahualcoyotl - 3 millon people
Nezahualcoyotl - 3 millon people
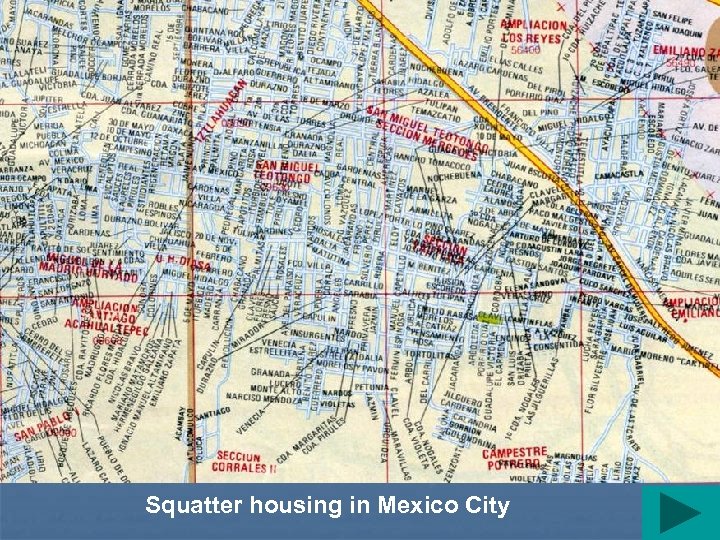 Squatter housing in Mexico City
Squatter housing in Mexico City
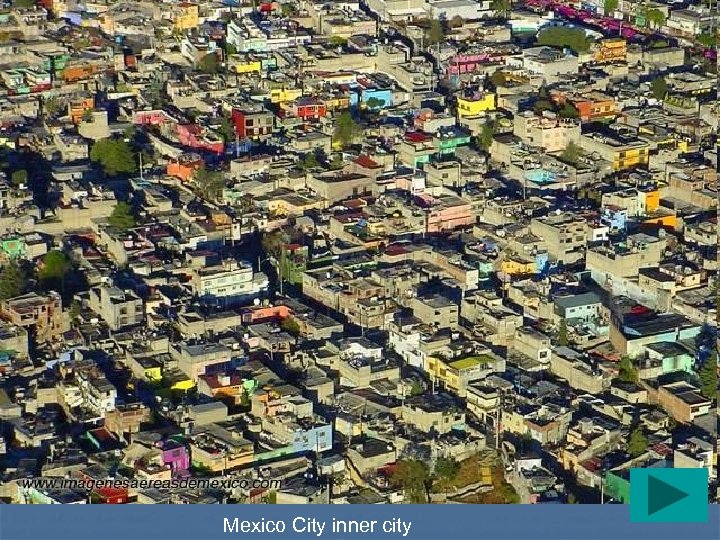 Mexico City inner city
Mexico City inner city
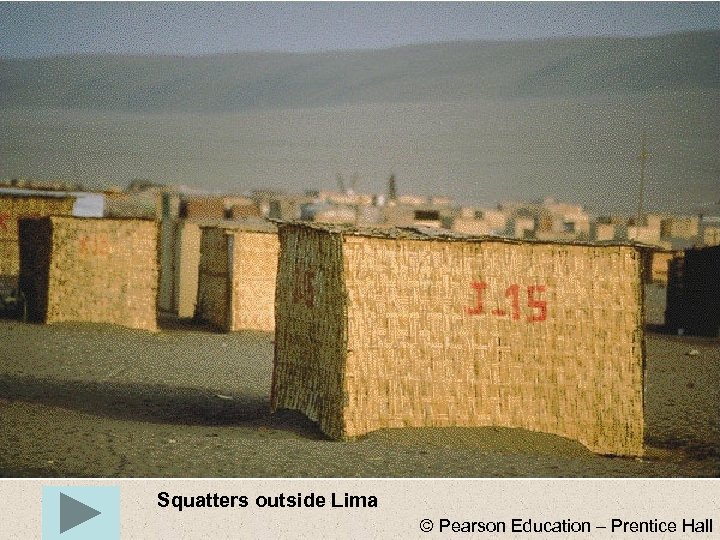 Squatters outside Lima © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall
Squatters outside Lima © Pearson Education – Prentice Hall
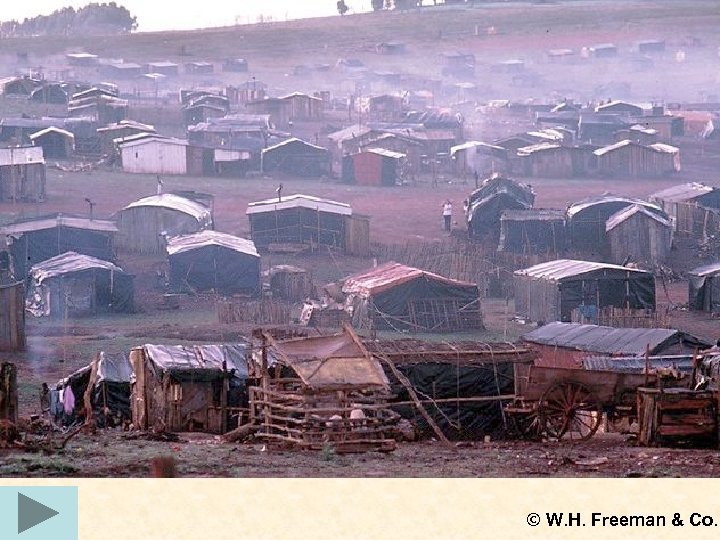 © W. H. Freeman & Co.
© W. H. Freeman & Co.
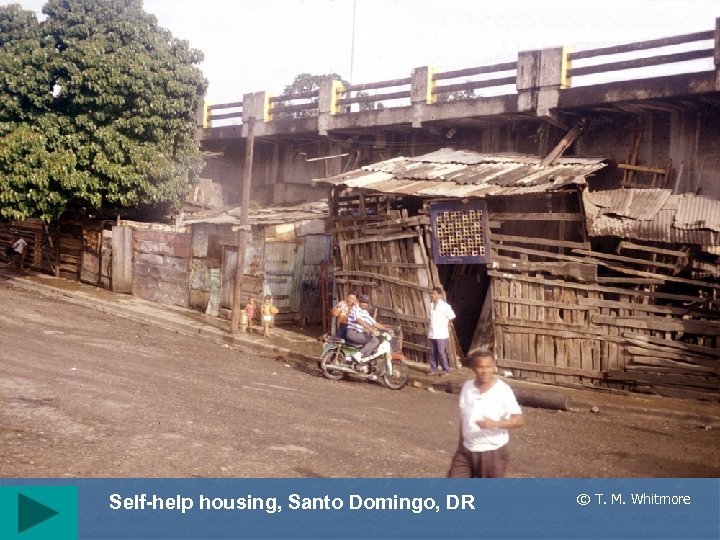 Self-help housing, Santo Domingo, DR © T. M. Whitmore
Self-help housing, Santo Domingo, DR © T. M. Whitmore
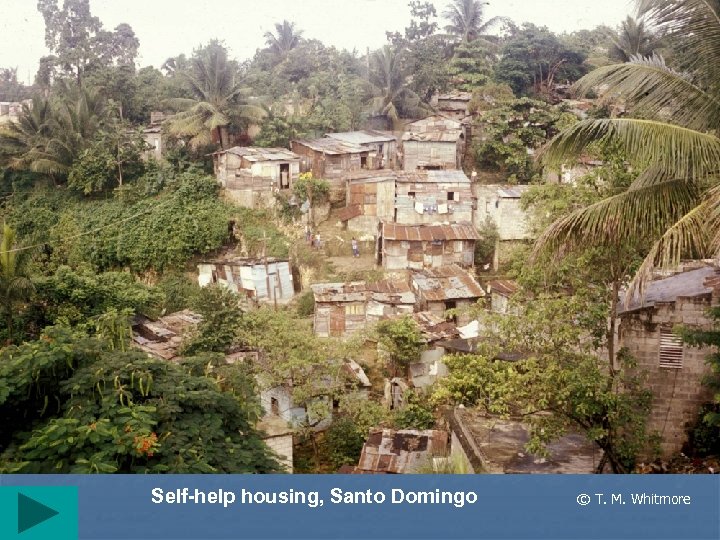 Self-help housing, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
Self-help housing, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
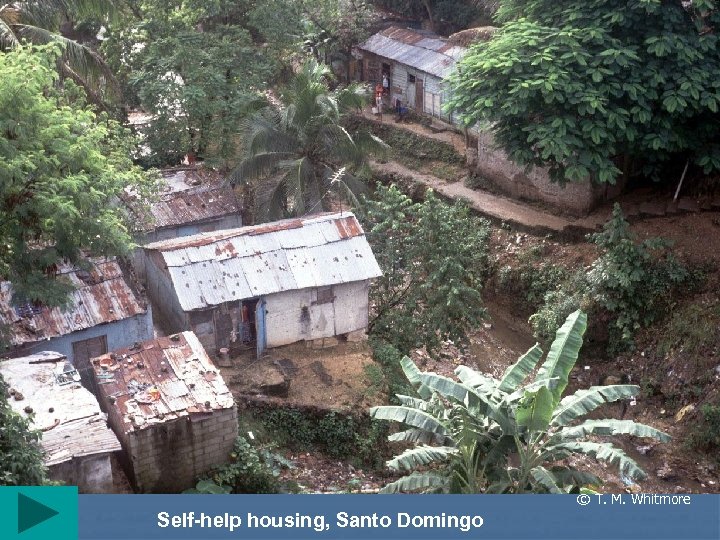 © T. M. Whitmore Self-help housing, Santo Domingo
© T. M. Whitmore Self-help housing, Santo Domingo
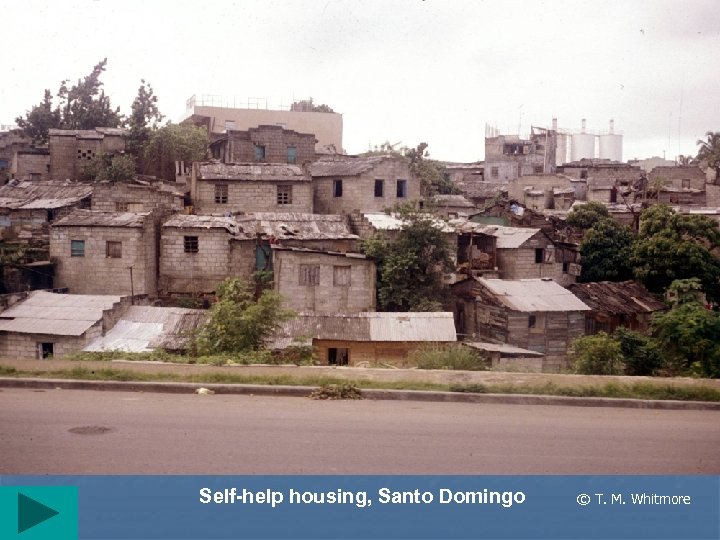 Self-help housing, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
Self-help housing, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
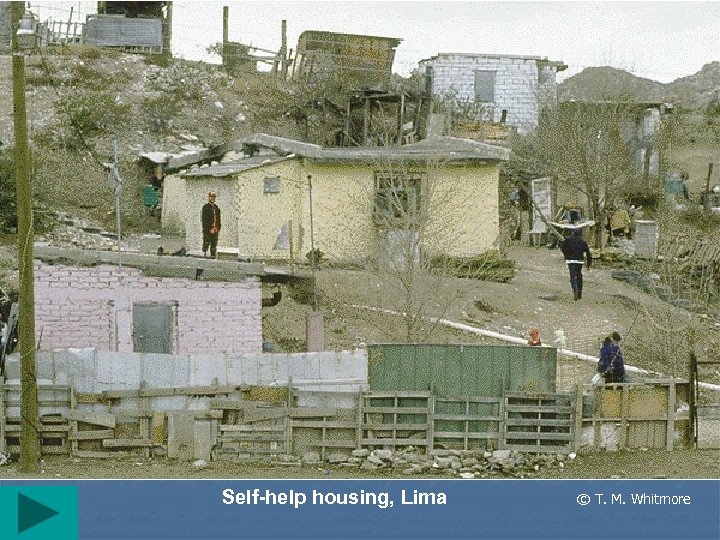 Self-help housing, Lima © T. M. Whitmore
Self-help housing, Lima © T. M. Whitmore
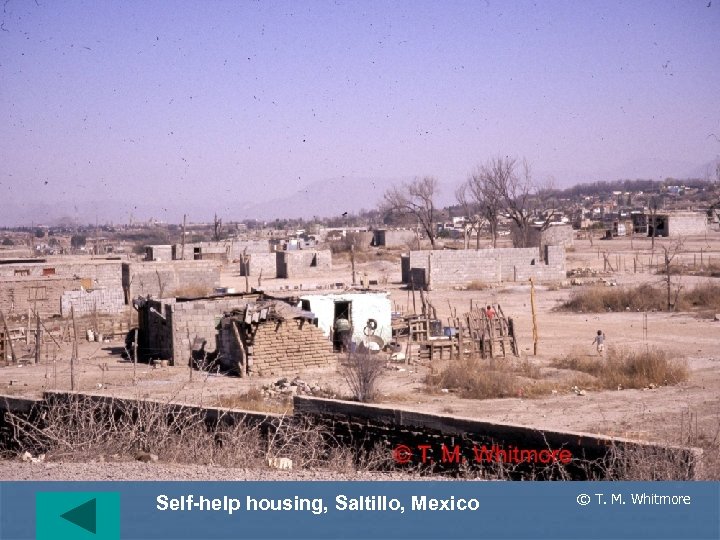 Self-help housing, Saltillo, Mexico © T. M. Whitmore
Self-help housing, Saltillo, Mexico © T. M. Whitmore
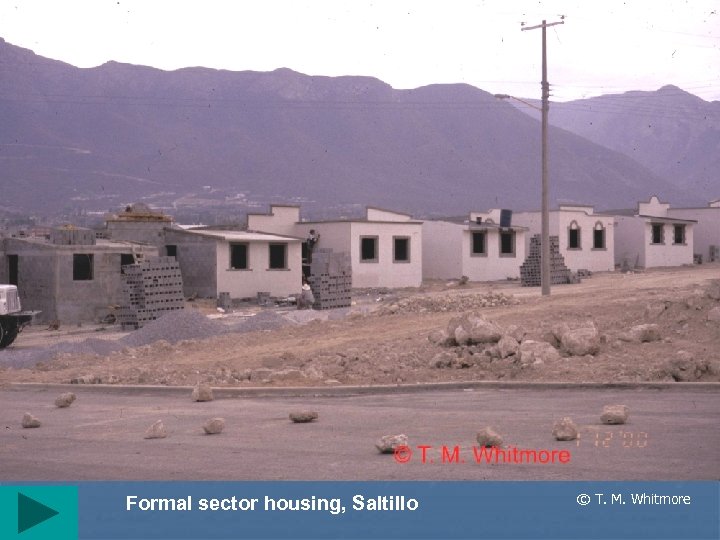 Formal sector housing, Saltillo © T. M. Whitmore
Formal sector housing, Saltillo © T. M. Whitmore
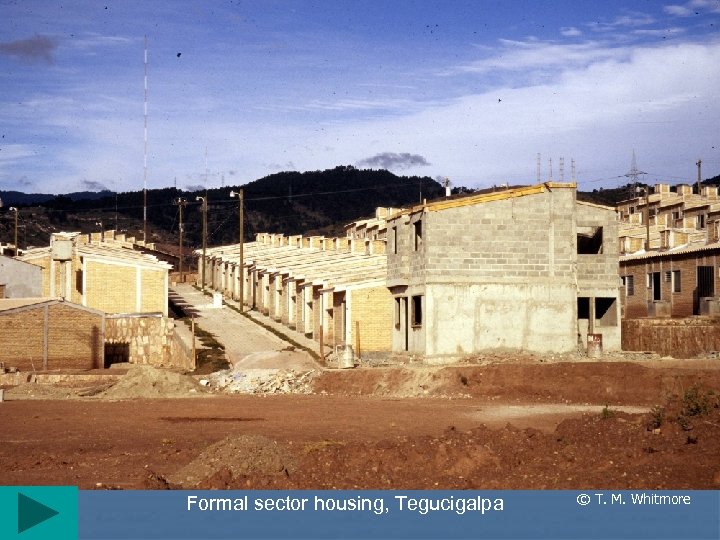 Formal sector housing, Tegucigalpa © T. M. Whitmore
Formal sector housing, Tegucigalpa © T. M. Whitmore
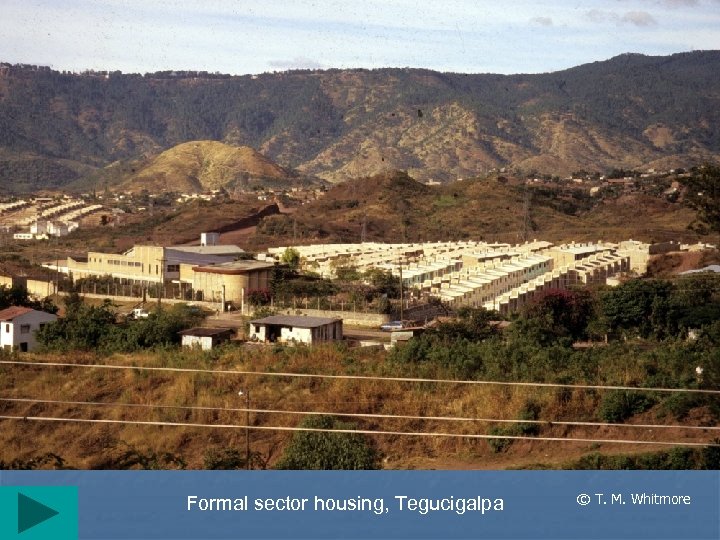 Formal sector housing, Tegucigalpa © T. M. Whitmore
Formal sector housing, Tegucigalpa © T. M. Whitmore
 300+ low income homes in Ixtapaluca, Mexico Entire complex has > 10, 000!
300+ low income homes in Ixtapaluca, Mexico Entire complex has > 10, 000!
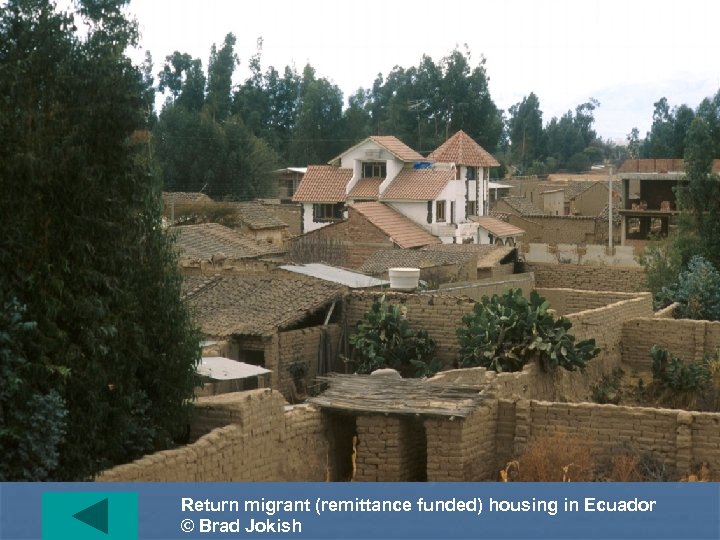 Return migrant (remittance funded) housing in Ecuador © Brad Jokish
Return migrant (remittance funded) housing in Ecuador © Brad Jokish
 Mexico City on a rare clear day
Mexico City on a rare clear day
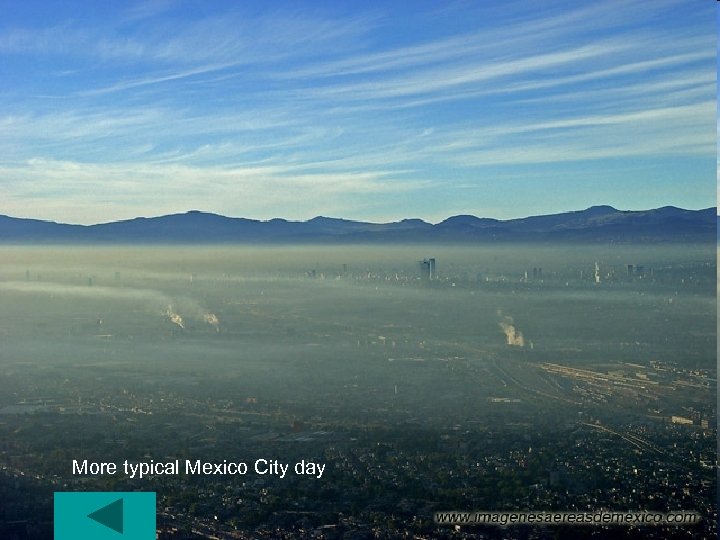 More typical Mexico City day
More typical Mexico City day
 Urban water, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
Urban water, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
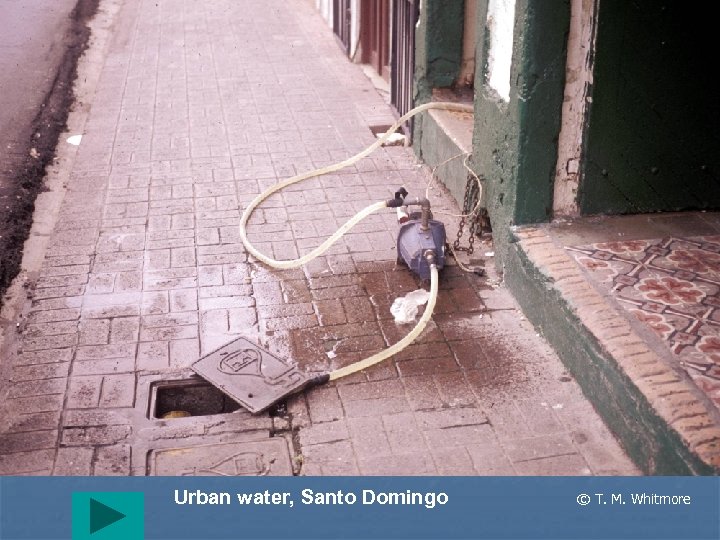 Urban water, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
Urban water, Santo Domingo © T. M. Whitmore
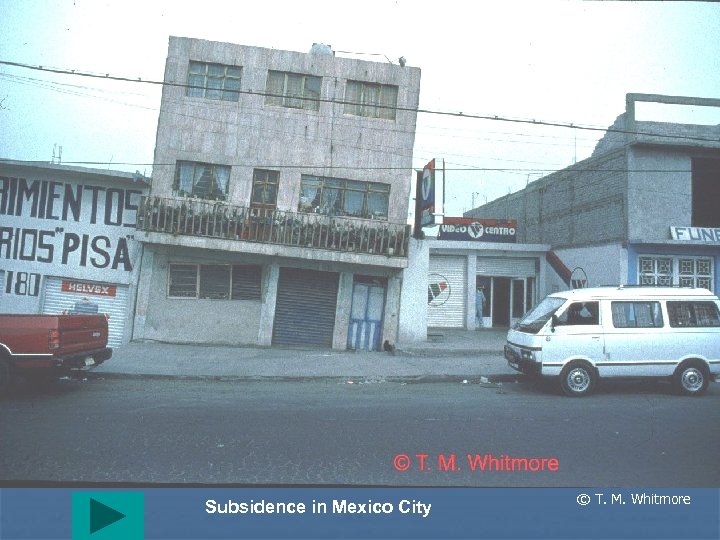 Subsidence in Mexico City © T. M. Whitmore
Subsidence in Mexico City © T. M. Whitmore
 Subsidence in Mexico City © T. M. Whitmore
Subsidence in Mexico City © T. M. Whitmore
 The urban economy • Dual system ØFormal § corporate, government, commerce, and major businesses § Minority of jobs? ØInformal § services, local assembly and repair shops, family-run micro-businesses; day labor, domestics, etc. § Majority of jobs? © T. M. Whitmore
The urban economy • Dual system ØFormal § corporate, government, commerce, and major businesses § Minority of jobs? ØInformal § services, local assembly and repair shops, family-run micro-businesses; day labor, domestics, etc. § Majority of jobs? © T. M. Whitmore
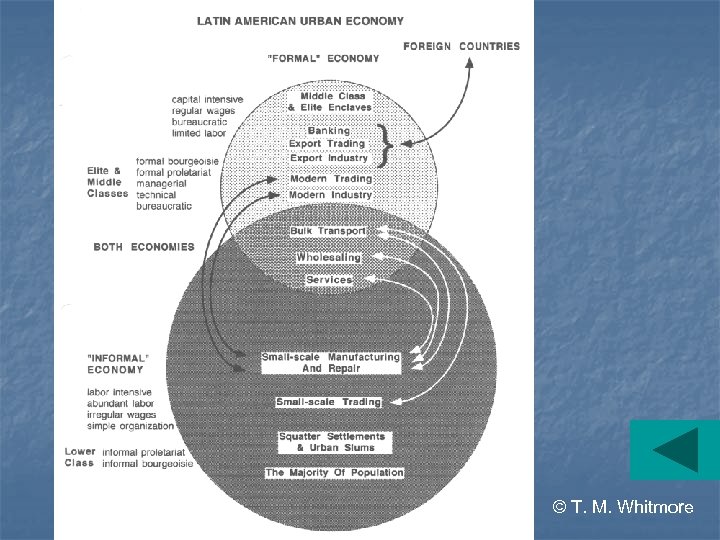 © T. M. Whitmore
© T. M. Whitmore
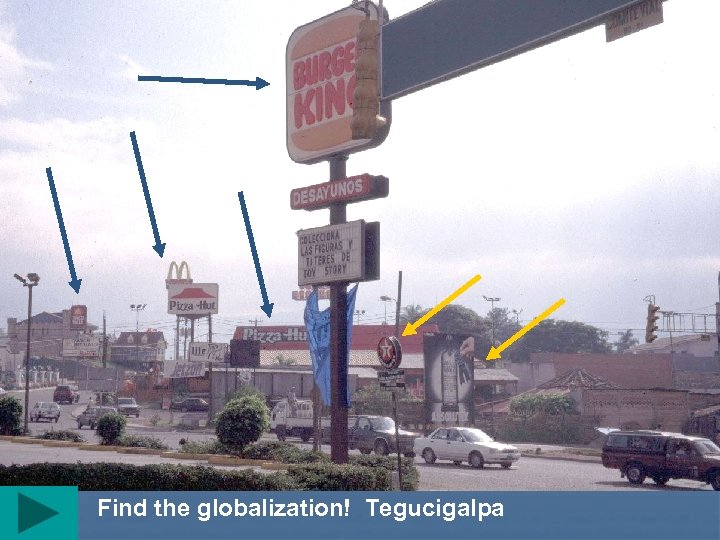 Find the globalization! Tegucigalpa
Find the globalization! Tegucigalpa
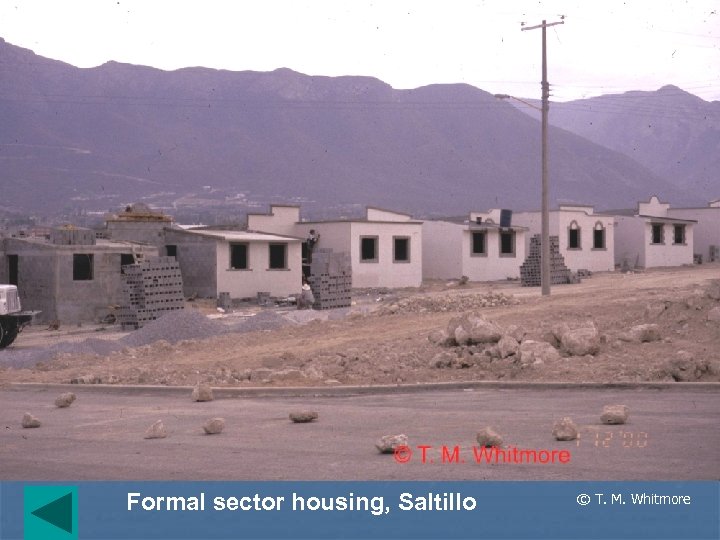 Formal sector housing, Saltillo © T. M. Whitmore
Formal sector housing, Saltillo © T. M. Whitmore
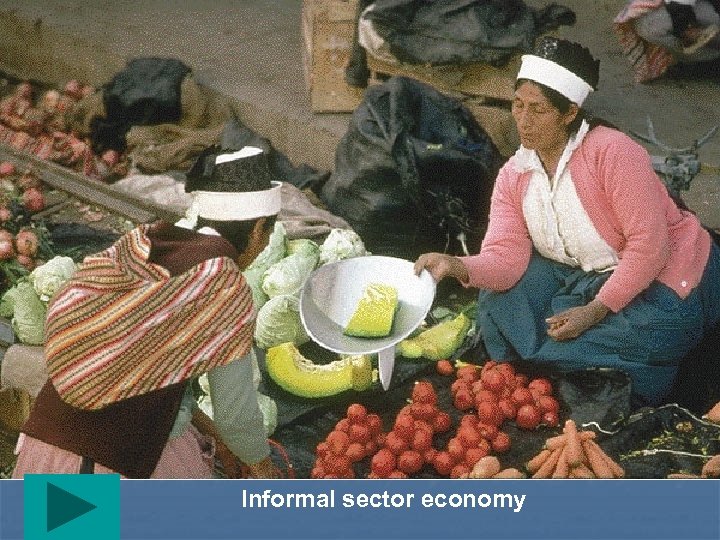 Informal sector economy
Informal sector economy
 © T. M. Whitmore
© T. M. Whitmore
 © T. M. Whitmore
© T. M. Whitmore
 © T. M. Whitmore
© T. M. Whitmore
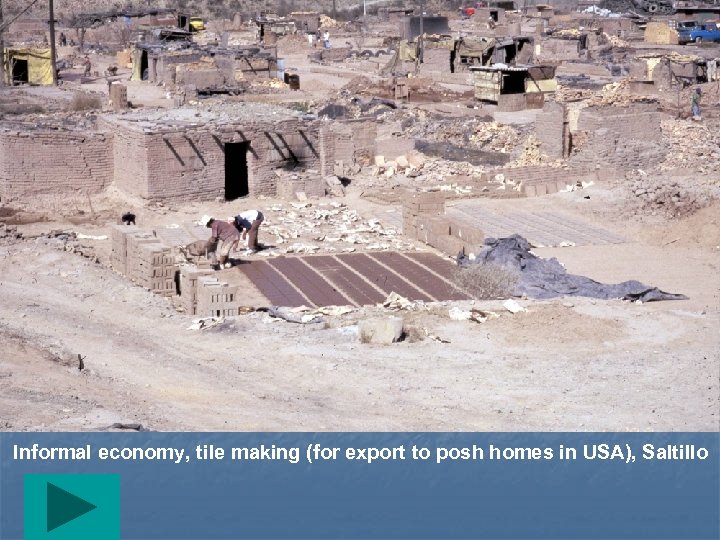 Informal economy, tile making (for export to posh homes in USA), Saltillo
Informal economy, tile making (for export to posh homes in USA), Saltillo
 Informal economy, tile making (for export to posh homes in USA), Saltillo
Informal economy, tile making (for export to posh homes in USA), Saltillo
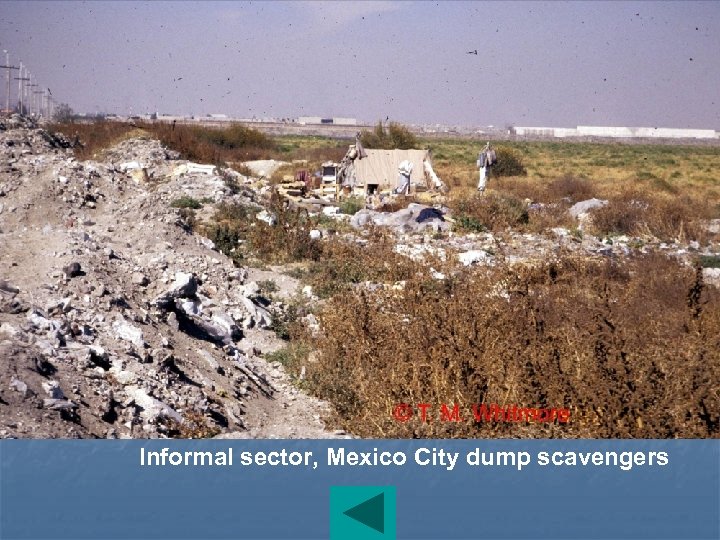 Informal sector, Mexico City dump scavengers
Informal sector, Mexico City dump scavengers


