ce821908ccebdc9899b58fdbf7e17e05.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 To DP or not to DP, That is the Question? Dr Evans Tasmanian Institute of Agricultural Research University of Tasmania Australian Barley Biochemistry & Brewing Research Barley Malting Quality … from Grass to Glass.
To DP or not to DP, That is the Question? Dr Evans Tasmanian Institute of Agricultural Research University of Tasmania Australian Barley Biochemistry & Brewing Research Barley Malting Quality … from Grass to Glass.
 Starch is degraded by the four diastase enzymes
Starch is degraded by the four diastase enzymes
 Prediction of Fermentability in Commercial Malts
Prediction of Fermentability in Commercial Malts
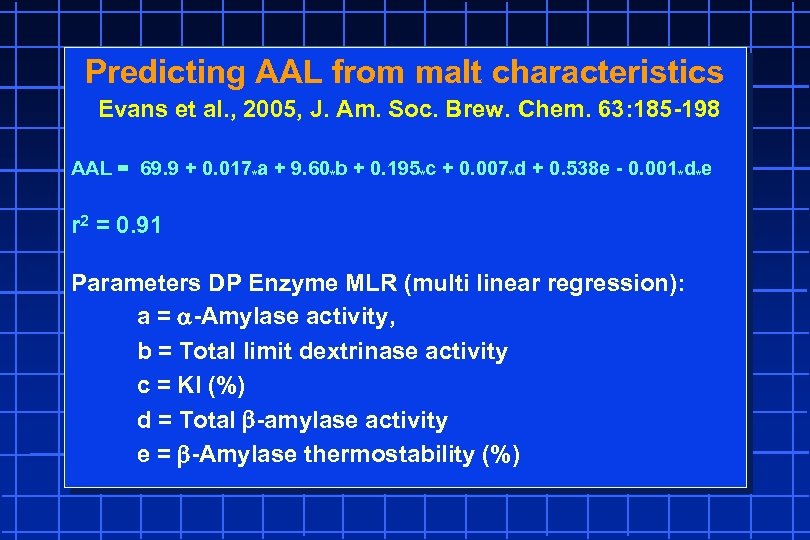 Predicting AAL from malt characteristics Evans et al. , 2005, J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 63: 185 -198 AAL = 69. 9 + 0. 017*a + 9. 60*b + 0. 195*c + 0. 007*d + 0. 538 e - 0. 001*d*e r 2 = 0. 91 Parameters DP Enzyme MLR (multi linear regression): a = a-Amylase activity, b = Total limit dextrinase activity c = KI (%) d = Total -amylase activity e = -Amylase thermostability (%)
Predicting AAL from malt characteristics Evans et al. , 2005, J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 63: 185 -198 AAL = 69. 9 + 0. 017*a + 9. 60*b + 0. 195*c + 0. 007*d + 0. 538 e - 0. 001*d*e r 2 = 0. 91 Parameters DP Enzyme MLR (multi linear regression): a = a-Amylase activity, b = Total limit dextrinase activity c = KI (%) d = Total -amylase activity e = -Amylase thermostability (%)
 Prediction (r 2) between DP enzymes and BEC data
Prediction (r 2) between DP enzymes and BEC data
 Commercial brewery fermentability variability explained by DP enzyme levels I
Commercial brewery fermentability variability explained by DP enzyme levels I
 Commercial brewery fermentability variability explained by DP enzyme levels II
Commercial brewery fermentability variability explained by DP enzyme levels II
 Variation in the levels of DP enzymes in Commercial malts
Variation in the levels of DP enzymes in Commercial malts
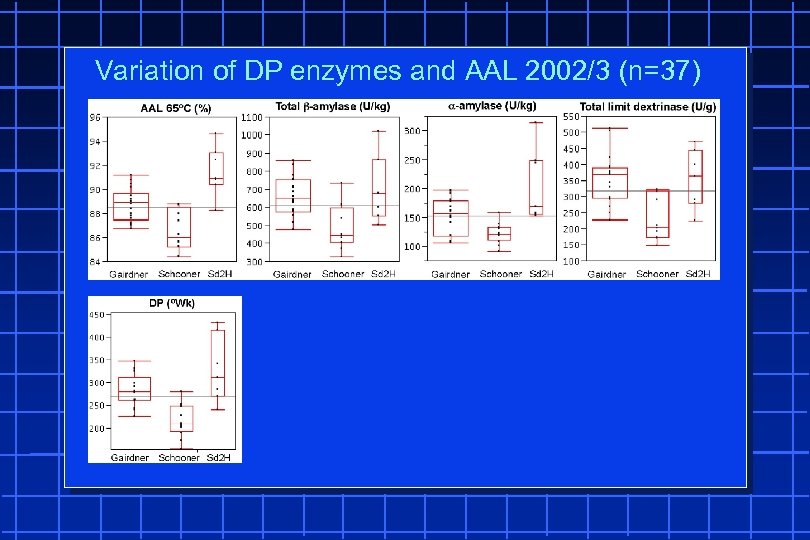 Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2002/3 (n=37)
Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2002/3 (n=37)
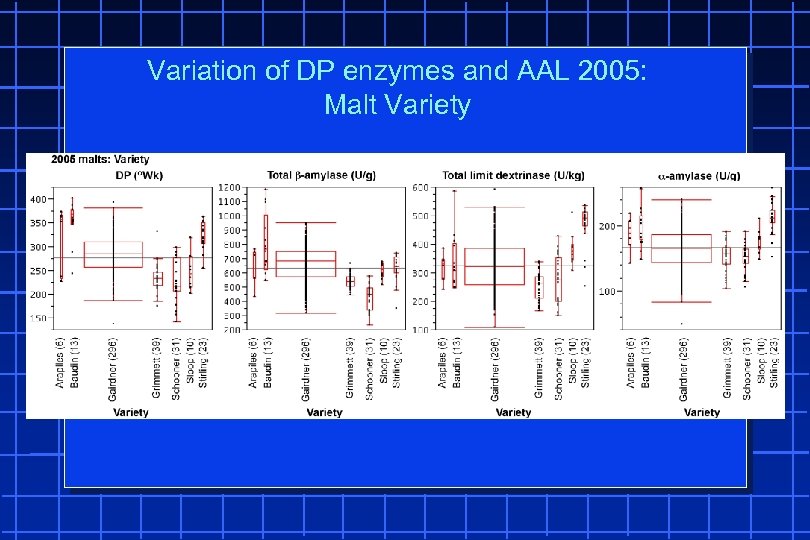 Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2005: Malt Variety
Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2005: Malt Variety
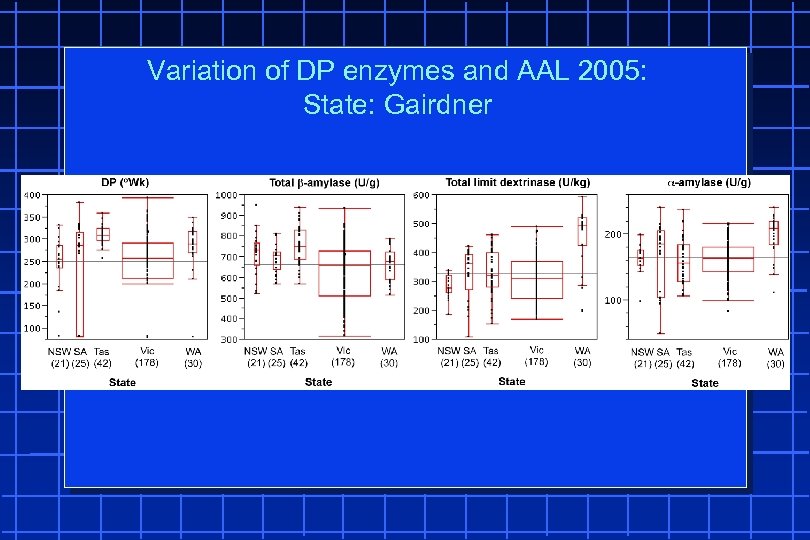 Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2005: State: Gairdner
Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2005: State: Gairdner
 Practical implications for delivering malt that satisfies brewers
Practical implications for delivering malt that satisfies brewers
 Considerations What best predicts wort fermentability? Prediction of malt fermentability performance based on: • -amylase thermostability and activity. • Level of a-amylase activity. • Limit dextrinase level. • Modification / KI. Is the DP malt specification redundant?
Considerations What best predicts wort fermentability? Prediction of malt fermentability performance based on: • -amylase thermostability and activity. • Level of a-amylase activity. • Limit dextrinase level. • Modification / KI. Is the DP malt specification redundant?
 Considerations If so, what are the implications in the quality lab? Discontinue DP evaluation? Analyses to be done: • -amylase thermostability specific to variety. • KI already routinely measured. New lab tests to be implemented: • -Amylase activity - Betamyl®. • a-Amylase activity - Ceralpha®. • Limit dextrinase - Limit Dextri. Zyme®.
Considerations If so, what are the implications in the quality lab? Discontinue DP evaluation? Analyses to be done: • -amylase thermostability specific to variety. • KI already routinely measured. New lab tests to be implemented: • -Amylase activity - Betamyl®. • a-Amylase activity - Ceralpha®. • Limit dextrinase - Limit Dextri. Zyme®.
 Maltster & brewer advantages? • More accurate description of malt quality. • Malt blending to balance DP enzyme levels. • Greater malt consistency and predictability. • Reduced surprises in brew house. • Warn brewers if malt not in spec • Better targeted selection by barley breeders.
Maltster & brewer advantages? • More accurate description of malt quality. • Malt blending to balance DP enzyme levels. • Greater malt consistency and predictability. • Reduced surprises in brew house. • Warn brewers if malt not in spec • Better targeted selection by barley breeders.
 A future malt description
A future malt description
 Commercial Implementation? Opportunities to deliver better barley and malt: • Environment - Can we predict barley quality of regions-silos-farms? • Marketer/grain handler - Can barley be segregated - delivered to maltster or OS buyer. • Maltster - Can maltsters ameliorate variation in barley supplied? • Brewer - Information to adjust process for malt quality • Breeder - Select genes for targeted market.
Commercial Implementation? Opportunities to deliver better barley and malt: • Environment - Can we predict barley quality of regions-silos-farms? • Marketer/grain handler - Can barley be segregated - delivered to maltster or OS buyer. • Maltster - Can maltsters ameliorate variation in barley supplied? • Brewer - Information to adjust process for malt quality • Breeder - Select genes for targeted market.
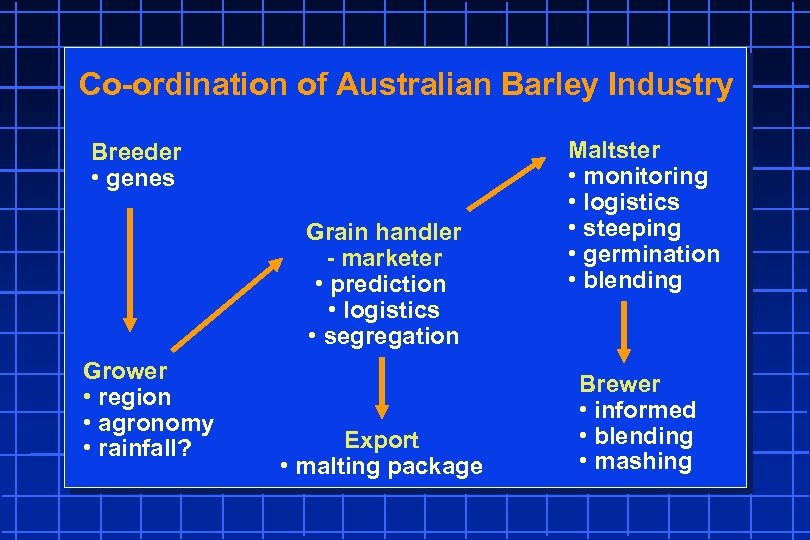 Co-ordination of Australian Barley Industry Breeder • genes Grain handler - marketer • prediction • logistics • segregation Grower • region • agronomy • rainfall? Export • malting package Maltster • monitoring • logistics • steeping • germination • blending Brewer • informed • blending • mashing
Co-ordination of Australian Barley Industry Breeder • genes Grain handler - marketer • prediction • logistics • segregation Grower • region • agronomy • rainfall? Export • malting package Maltster • monitoring • logistics • steeping • germination • blending Brewer • informed • blending • mashing
 New Australian malt varieties The new generation of malt varieties have very high levels of fermentability. Good for starch adjunct brewing. Varieties: • Baudin: Sd 1 -amylase, VERY high DP enzyme levels. • Flagship: Sd 2 H -amylase, high DP enzyme levels. • Buloke: Sd 2 H -amylase, high DP enzyme levels. Need variety/s with low/intermediate fermentability? • Look after domestic brewers requirements. • Allow blending to temper the fermentability of the above.
New Australian malt varieties The new generation of malt varieties have very high levels of fermentability. Good for starch adjunct brewing. Varieties: • Baudin: Sd 1 -amylase, VERY high DP enzyme levels. • Flagship: Sd 2 H -amylase, high DP enzyme levels. • Buloke: Sd 2 H -amylase, high DP enzyme levels. Need variety/s with low/intermediate fermentability? • Look after domestic brewers requirements. • Allow blending to temper the fermentability of the above.
 Advice for Concept Adoption 1. Confidential + Potential competitive advantage internal - external. - Customers in ie China will not gain full value from concept. - Probably will not remain confidential very long. 2. Pre-competitive (release some of the information) + Gain full value from concepts adoption. + Confirm Australia now has world leading malting varieties. + Australia first to use (apply first in domestic industry). + Improvement associated with Australian industry (Volvo principle). ~ systems for batch selection and malting package confidential. - competitors able to adopt part of the concept.
Advice for Concept Adoption 1. Confidential + Potential competitive advantage internal - external. - Customers in ie China will not gain full value from concept. - Probably will not remain confidential very long. 2. Pre-competitive (release some of the information) + Gain full value from concepts adoption. + Confirm Australia now has world leading malting varieties. + Australia first to use (apply first in domestic industry). + Improvement associated with Australian industry (Volvo principle). ~ systems for batch selection and malting package confidential. - competitors able to adopt part of the concept.
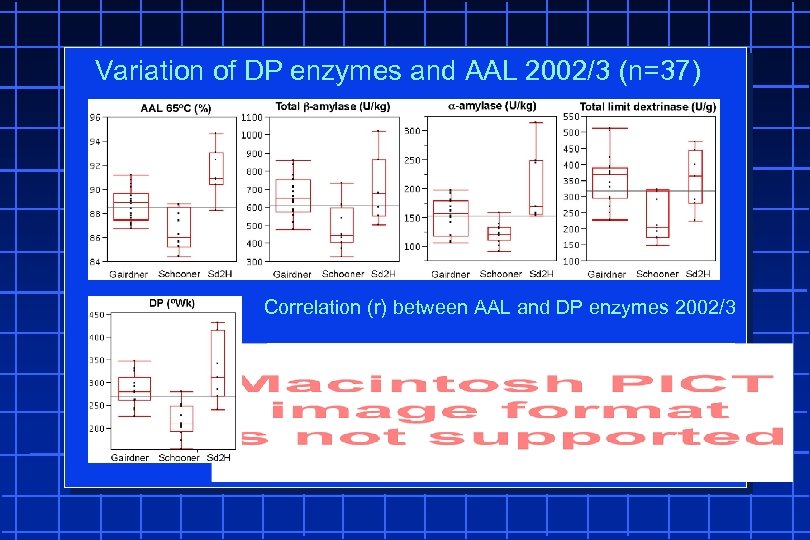 Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2002/3 (n=37) Correlation (r) between AAL and DP enzymes 2002/3
Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2002/3 (n=37) Correlation (r) between AAL and DP enzymes 2002/3
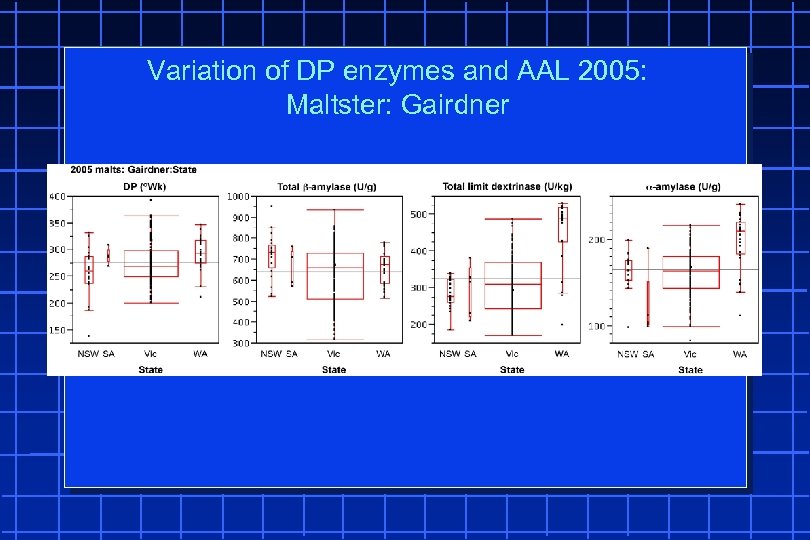 Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2005: Maltster: Gairdner
Variation of DP enzymes and AAL 2005: Maltster: Gairdner


