b2ca00f7bdf30ecfd4f4f852c3f86f5b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

To Be Numerate …… Maths Information for Parents

Numeracy Project Goal “to be numerate is to have the ability and inclination to use mathematics effectively – at home, at work and in the community” Published in Curriculum Update 45:

Goals – We want our students to: n Develop multiple flexible thinking strategies Use mental strategies and confidently explain orally before written standard vertical forms n Use a range of strategies and make decisions about using the most effective strategy to work out any given problem. n Achieve and develop a positive attitude towards learning mathematics while enjoying the challenge of problem solving n

The Big Picture of Numeracy and Maths
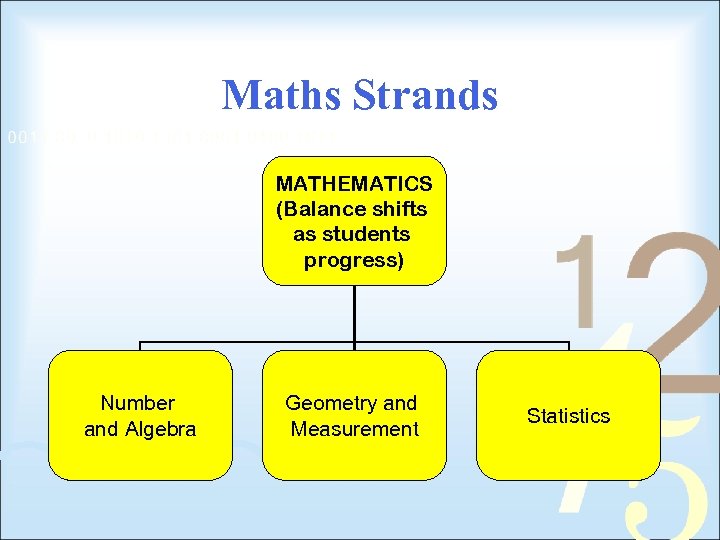
Maths Strands MATHEMATICS (Balance shifts as students progress) Number and Algebra Geometry and Measurement Statistics
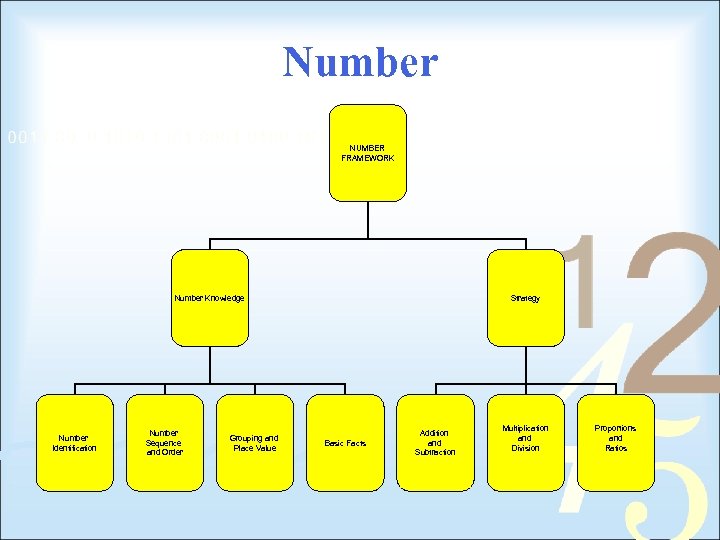
Number NUMBER FRAMEWORK Number Knowledge Number Identification Number Sequence and Order Grouping and Place Value Strategy Basic Facts Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Proportions and Ratios
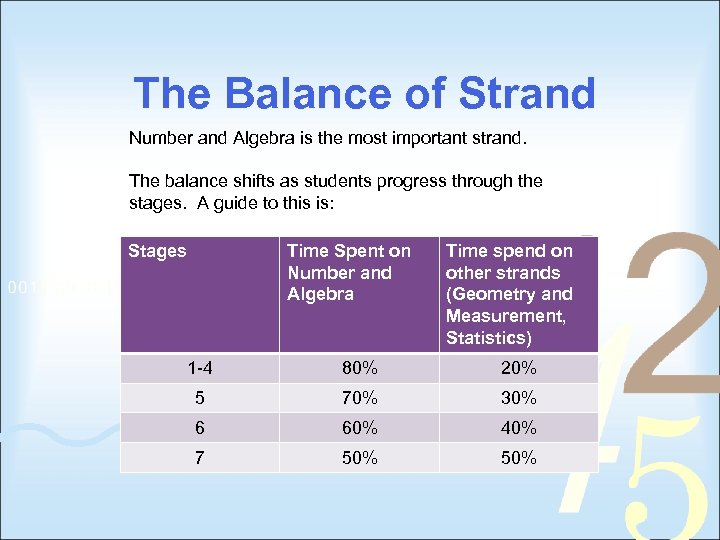
The Balance of Strand Number and Algebra is the most important strand. The balance shifts as students progress through the stages. A guide to this is: Stages Time Spent on Number and Algebra Time spend on other strands (Geometry and Measurement, Statistics) 1 -4 80% 20% 5 70% 30% 6 60% 40% 7 50%

The NZ Numeracy Framework • Each Numeracy Stage highlights key knowledge and strategy that a child should know. • Strong knowledge is essential for students to broaden their strategies across a full range of numbers. Creates new knowledge through use Strategy Knowledge Provides the foundation for strategies

Knowledge and Strategy • Knowledge – • • Number Identification Number Sequence and Order Grouping and Place Value Basic Facts • Strategy – Three domains • Addition and Subtraction • Multiplication and Division • Ratios and Proportions
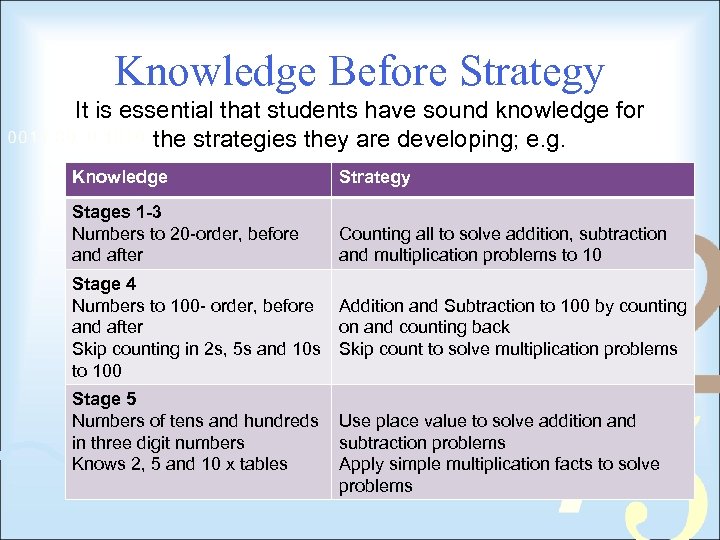
Knowledge Before Strategy It is essential that students have sound knowledge for the strategies they are developing; e. g. Knowledge Strategy Stages 1 -3 Numbers to 20 -order, before and after Counting all to solve addition, subtraction and multiplication problems to 10 Stage 4 Numbers to 100 - order, before Addition and Subtraction to 100 by counting and after on and counting back Skip counting in 2 s, 5 s and 10 s Skip count to solve multiplication problems to 100 Stage 5 Numbers of tens and hundreds in three digit numbers Knows 2, 5 and 10 x tables Use place value to solve addition and subtraction problems Apply simple multiplication facts to solve problems

Developmental Stage Progression The New Zealand Number Framework
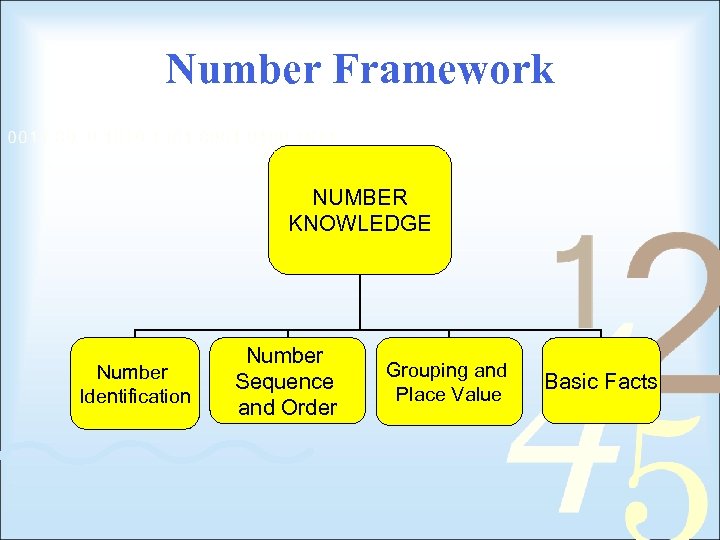
Number Framework NUMBER KNOWLEDGE Number Identification Number Sequence and Order Grouping and Place Value Basic Facts
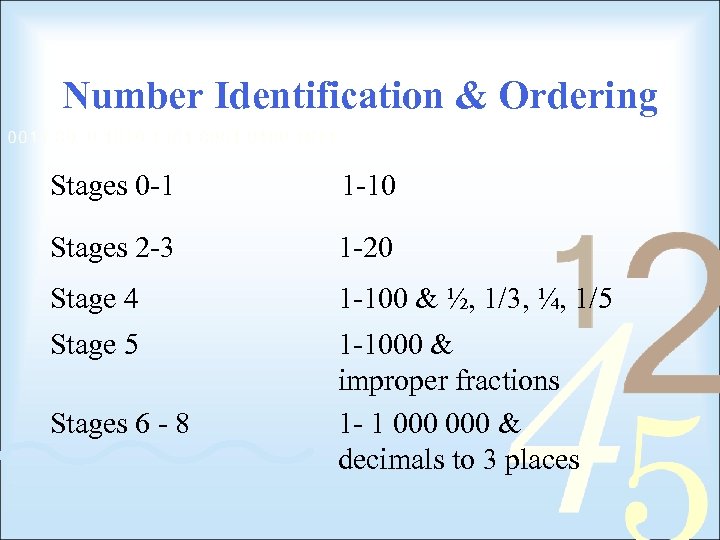
Number Identification & Ordering Stages 0 -1 1 -10 Stages 2 -3 1 -20 Stage 4 1 -100 & ½, 1/3, ¼, 1/5 Stage 5 1 -1000 & improper fractions 1 - 1 000 & decimals to 3 places Stages 6 - 8

Grouping and Place Value Stages 1 - 3 within 5, within 10, patterns to 10. Stage 4 groupings with 10 and 20, number of tens in decades Stage 5 groupings within 100, groups of 10 s, 100 s & 1000 s in 4 digit numbers Stages 6 groupings within 1000, groupings of 2, 3, 5 and 10 in 100, groupings of 2, 3, 5, & 10 in 4 digit numbers (& remainders) tenths and hundredths in decimals to (2 places) Stages 7 groupings of all numbers up to 10 in 100 (& remainders) groupings of 10 s, 100 s &1000 s in (up to) 7 digit numbers equivalent fractions

Basic Facts Stages 1 - 3 addition and subtraction facts to 5, doubles to 10 Stage 4 addition and subtraction facts to 10, doubles to 20, ten and facts, multiples of ten that add to 100 Stage 5 addition facts to 20, subtraction facts to 10, 2 x, 5 x and 10 x timetables, hundreds that add to 1000 Stages 6 addition & subtraction facts to 20 multiplication facts up to 10 x (& some corresponding division facts) multiplication facts with 10 s, 100 s & 1000 s Stages 7/8 division facts up to 10 x tables conversions (fractions/decimal/percentage) factors, common multiples, divisibility rules & square roots

How is maths taught differently now?
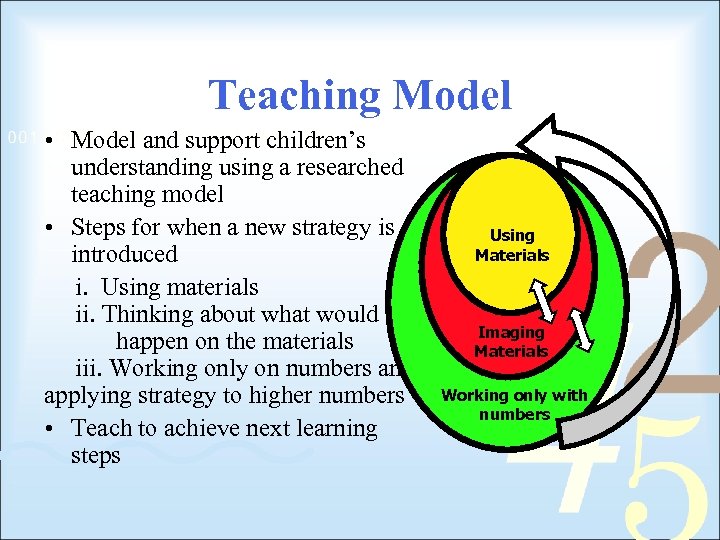
Teaching Model • Model and support children’s understanding using a researched teaching model • Steps for when a new strategy is introduced i. Using materials ii. Thinking about what would happen on the materials iii. Working only on numbers and applying strategy to higher numbers • Teach to achieve next learning steps Using Materials Imaging Materials Working only with numbers

Using Equipment The use of equipment is essential when developing new strategies Bridging to Ten Happy Hundreds
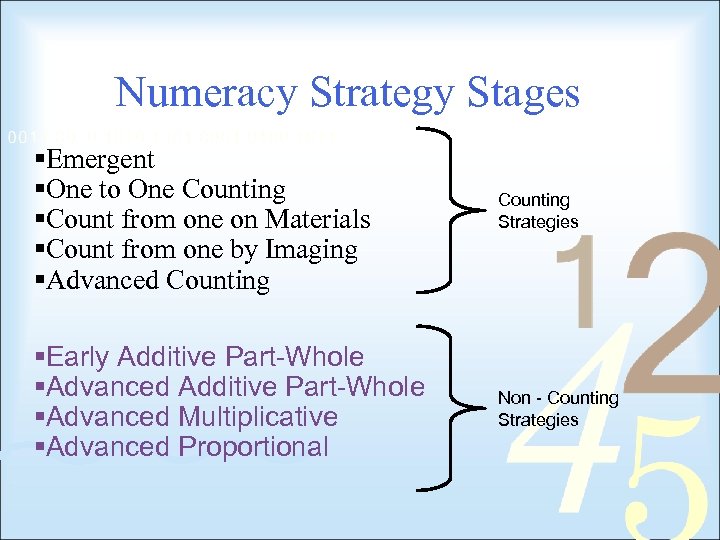
Numeracy Strategy Stages §Emergent §One to One Counting §Count from one on Materials §Count from one by Imaging §Advanced Counting Strategies §Early Additive Part-Whole §Advanced Multiplicative §Advanced Proportional Non - Counting Strategies

Examples of Strategies for each Stage

Emergent Stage 0 Can you get me 7 counters from the pile please? 1, 2, 3, 5, 8. . . ? The child can not consistently count a collection of objects.

One to One Counting Stage 1 Can you get me 7 counters from the pile please? 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 The child can count a set of objects up to ten but can’t join and separate sets like 4+3=

Count From One on Materials Stage 2 There are 4 counters and another 3 counters. How many are there altogether? 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 The child solves the problem by using their fingers or other materials and counts from one.

Count From One By Imaging Stage 3 There are 4 counters and another 3 counters. How many are there altogether? Counts in head 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 67 The child counts all the objects from one by imaging visual patterns of the objects in their mind.
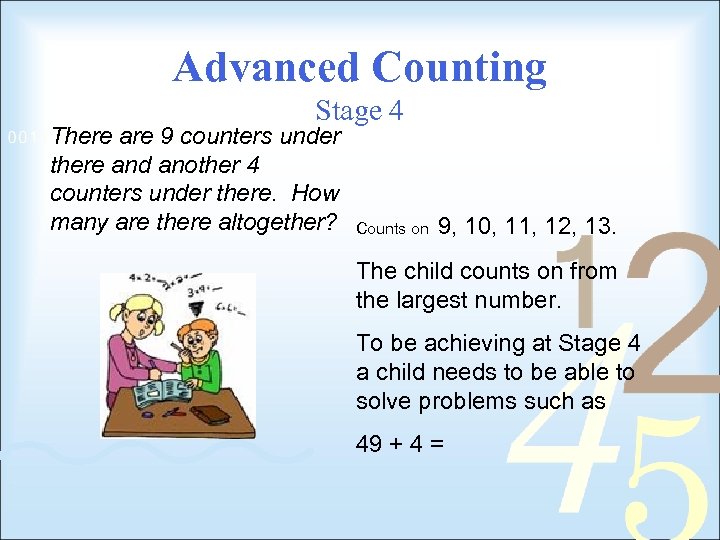
Advanced Counting Stage 4 There are 9 counters under there and another 4 counters under there. How many are there altogether? Counts on 9, 10, 11, 12, 13. The child counts on from the largest number. To be achieving at Stage 4 a child needs to be able to solve problems such as 49 + 4 =

Early Part-Whole Stage 5 (Early Stage 5) There are 9 counters under there and another 6 counters under there. How many are there altogether? Take one off the 6 and put it on the 9 it =10 so 10 + 5 = 15 The child uses simple strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems mentally
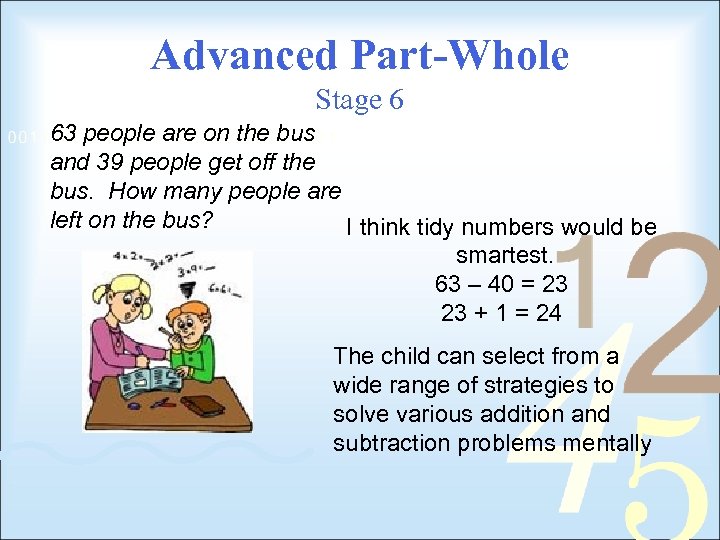
Advanced Part-Whole Stage 6 63 people are on the bus and 39 people get off the bus. How many people are left on the bus? I think tidy numbers would be smartest. 63 – 40 = 23 23 + 1 = 24 The child can select from a wide range of strategies to solve various addition and subtraction problems mentally

Advanced Multiplicative Stage 7 There are 28 fruit trees in each row of the orchard. There are 6 rows. How many trees are there Tidy Numbers would be a smart altogether? strategy. 30 x 6 = 180 – (2 x 6) = 168 The child can select from a wide range of strategies to solve various multiplication and division problems mentally.

Advanced Proportional Stage 8 You can make 9 mittens from 15 balls of wool. How many mittens can you make from 10 balls of wool? The child sees that 9: 15 are both multiples of 3. They simplify by ÷ 3 and get a ratio of 3: 5 ? : 10 =6 The child can select from a wide range of strategies to solve challenging problems involving, decimals, fraction percentages and ratios.

Assessing what children know n Teachers use a variety of tasks (informal and formal) to form our Overall Teacher Judgements (OTJs) n Group according to a child’s strategy stage using the New Zealand Number Framework n Encourage children to self assess (reflect) know and own their next learning steps. (Personalised Learning)

National Standards • Maths illustrations • JAM
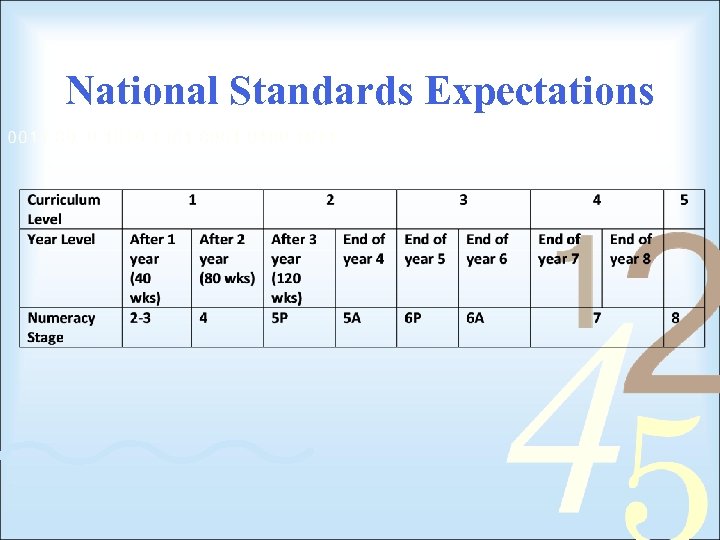
National Standards Expectations

National Standards are based on all areas of the Maths Curriculum • Number and Algebra - Knowledge -Addition/ Subtraction -Multiplication and Division -Ratios and Proportions (Fractions) -Patterning (Algebra) • Geometry and Measurement • Statistics
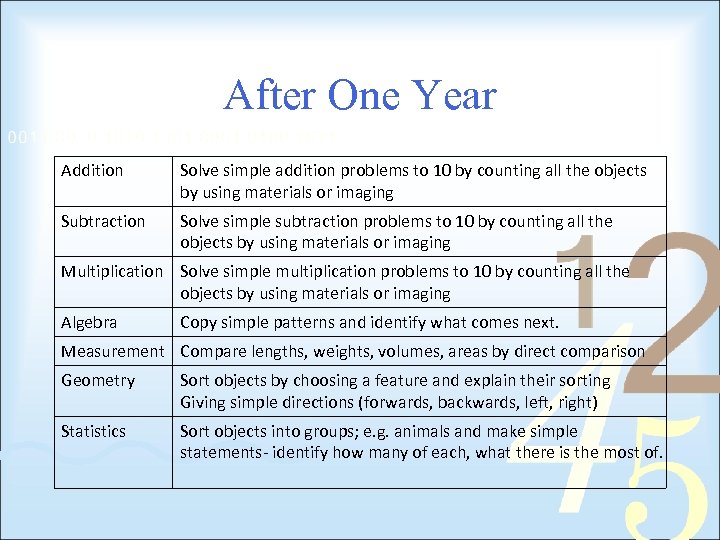
After One Year Addition Solve simple addition problems to 10 by counting all the objects by using materials or imaging Subtraction Solve simple subtraction problems to 10 by counting all the objects by using materials or imaging Multiplication Solve simple multiplication problems to 10 by counting all the objects by using materials or imaging Algebra Copy simple patterns and identify what comes next. Measurement Compare lengths, weights, volumes, areas by direct comparison Geometry Sort objects by choosing a feature and explain their sorting Giving simple directions (forwards, backwards, left, right) Statistics Sort objects into groups; e. g. animals and make simple statements- identify how many of each, what there is the most of.
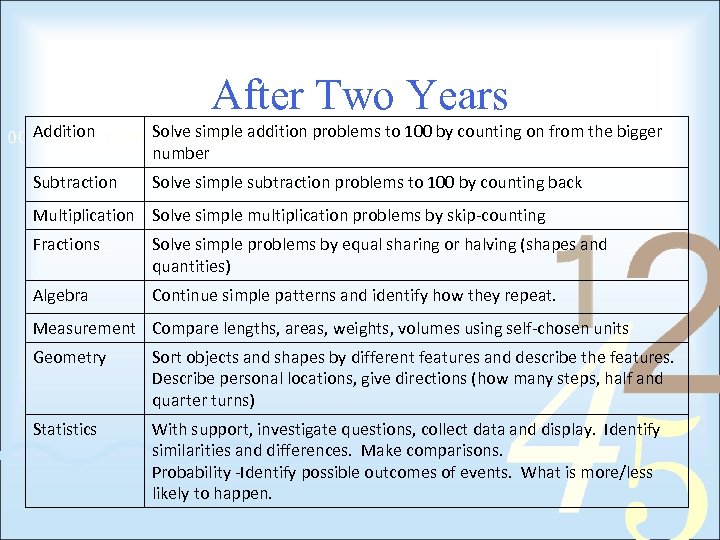
After Two Years Addition Solve simple addition problems to 100 by counting on from the bigger number Subtraction Solve simple subtraction problems to 100 by counting back Multiplication Solve simple multiplication problems by skip-counting Fractions Solve simple problems by equal sharing or halving (shapes and quantities) Algebra Continue simple patterns and identify how they repeat. Measurement Compare lengths, areas, weights, volumes using self-chosen units Geometry Sort objects and shapes by different features and describe the features. Describe personal locations, give directions (how many steps, half and quarter turns) Statistics With support, investigate questions, collect data and display. Identify similarities and differences. Make comparisons. Probability -Identify possible outcomes of events. What is more/less likely to happen.
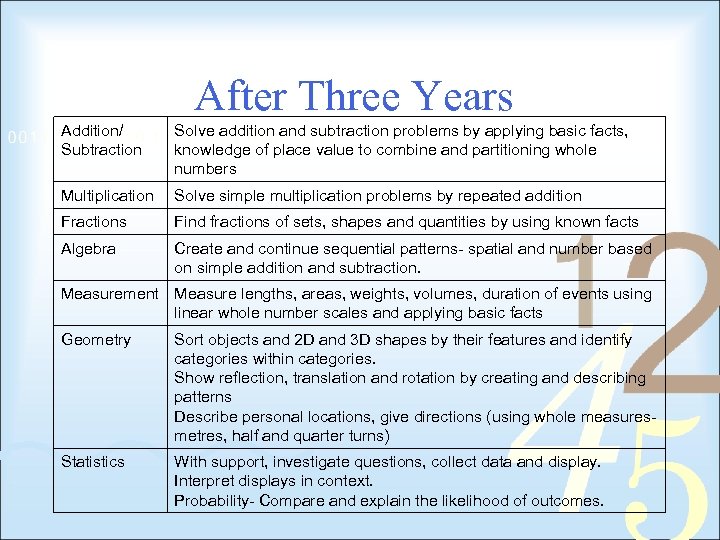
After Three Years Addition/ Subtraction Solve addition and subtraction problems by applying basic facts, knowledge of place value to combine and partitioning whole numbers Multiplication Solve simple multiplication problems by repeated addition Fractions Find fractions of sets, shapes and quantities by using known facts Algebra Create and continue sequential patterns- spatial and number based on simple addition and subtraction. Measurement Measure lengths, areas, weights, volumes, duration of events using linear whole number scales and applying basic facts Geometry Sort objects and 2 D and 3 D shapes by their features and identify categories within categories. Show reflection, translation and rotation by creating and describing patterns Describe personal locations, give directions (using whole measuresmetres, half and quarter turns) Statistics With support, investigate questions, collect data and display. Interpret displays in context. Probability- Compare and explain the likelihood of outcomes.
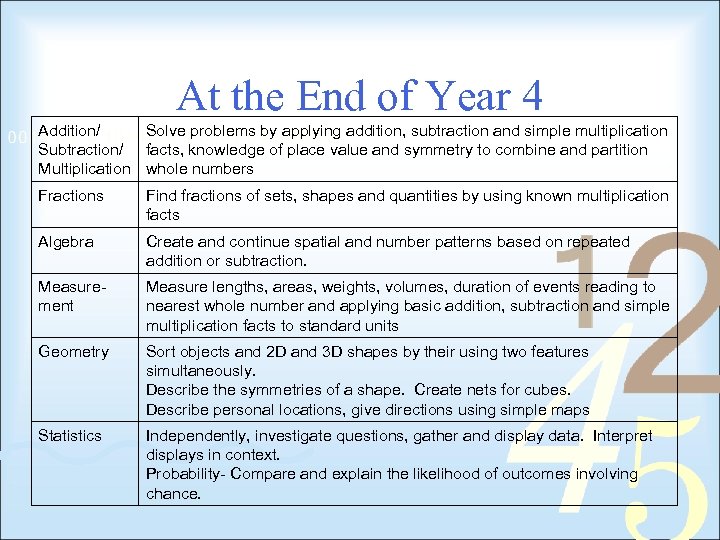
At the End of Year 4 Addition/ Solve problems by applying addition, subtraction and simple multiplication Subtraction/ facts, knowledge of place value and symmetry to combine and partition Multiplication whole numbers Fractions Find fractions of sets, shapes and quantities by using known multiplication facts Algebra Create and continue spatial and number patterns based on repeated addition or subtraction. Measurement Measure lengths, areas, weights, volumes, duration of events reading to nearest whole number and applying basic addition, subtraction and simple multiplication facts to standard units Geometry Sort objects and 2 D and 3 D shapes by their using two features simultaneously. Describe the symmetries of a shape. Create nets for cubes. Describe personal locations, give directions using simple maps Statistics Independently, investigate questions, gather and display data. Interpret displays in context. Probability- Compare and explain the likelihood of outcomes involving chance.
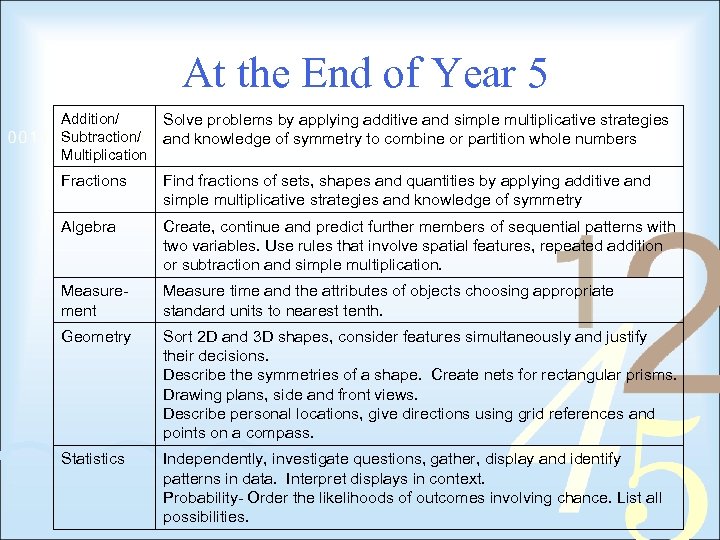
At the End of Year 5 Addition/ Subtraction/ Multiplication Solve problems by applying additive and simple multiplicative strategies and knowledge of symmetry to combine or partition whole numbers Fractions Find fractions of sets, shapes and quantities by applying additive and simple multiplicative strategies and knowledge of symmetry Algebra Create, continue and predict further members of sequential patterns with two variables. Use rules that involve spatial features, repeated addition or subtraction and simple multiplication. Measurement Measure time and the attributes of objects choosing appropriate standard units to nearest tenth. Geometry Sort 2 D and 3 D shapes, consider features simultaneously and justify their decisions. Describe the symmetries of a shape. Create nets for rectangular prisms. Drawing plans, side and front views. Describe personal locations, give directions using grid references and points on a compass. Statistics Independently, investigate questions, gather, display and identify patterns in data. Interpret displays in context. Probability- Order the likelihoods of outcomes involving chance. List all possibilities.
At the End of Year 6 Addition/ Subtraction/ Multiplication Solve problems by applying additive and simple multiplicative strategies (including mixed operations) to combine or partition whole numbers Fractions Find fractions of sets, shapes and quantities by applying additive and simple multiplicative strategies Algebra Describe spatial number patterns using tables and graphs, rules that involve spatial features, repeated addition, subtraction and simple multiplication. Measurement Measure time and the attributes of objects choosing appropriate standard units. Geometry Sort 2 D and 3 D shapes, consider features simultaneously and justify their decisions. Describe the symmetries of a shape. Draw or make objects given their plan, side and front views. Describe personal locations, give directions using grid references, turns and points on a compass. Statistics Independently, investigate questions, gather or access multivariate data. Interpret displays in context. Probability- Order the likelihoods of outcomes involving chance.

How do we cater for individual learning needs in Maths? • Using a variety of assessments and analyse data • Grouping and teaching according to learning needs • Individual Learning Goals • Cross grouping in the middle and senior classes • Personalised Learning Programmes

How can parents help? Developing a child’s knowledge is a key to their success and development in mathematics This is the perfect area for you to help and support your child at home Knowledge lists for each stage and activities are on our school website Encourage your child to spend 10 minutes a day or 3 x 20 minutes a week on Mathletics

Knowledge Building These activities can be used at all levels – just use different range of numbers for different levels n Counting (cars, shells on beach, pegs, run around the house, how many steps you walk, count backwards, start from different numbers, skip counting groups of objects; e. g. pairs of shoes ) n Numbers before and after (Letter boxes, say a number, use a number line, use number cards, write a number down, ladder game, keyboard numbers, using dice) n Identifying numbers (Letter boxes, number plates, speed signs, how many km to go, number cards, combine numbers, odometers, metres) n Ordering numbers (Number cards, write some numbers down, cut up calendars)

Knowledge Building cont. . n Knowing Groups of ten (Using ten frames, using fingers, abacus, ice- block sticks) n Recalling Doubles and Halves (ten frames, fingers, flashcards) n Basic addition & subtraction facts to 5, then 10, then 20 (Buttons, ten frames, fingers, flashcards, number boggle, playing cards)
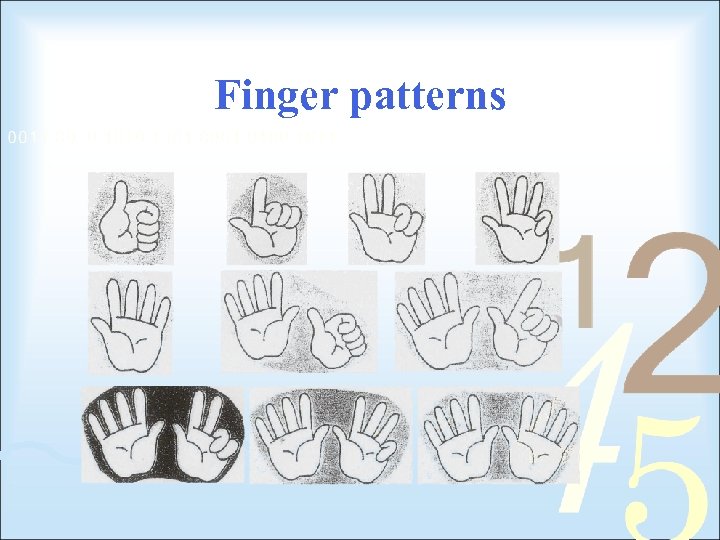
Finger patterns

The Reality? To become a Part-Whole thinker (stage 5 plus) children need automatic recall of… Facts to Ten (addition and subtraction) n Doubles Facts n Ten and …. 10 + 6 = 16 n Groups of ten (Place Value) To become a Multiplicative thinker (stage 7) children need automatic recall of … n n n All of the above The times tables

It may surprise you to know…. Algorithms are okay but only when… n A student shows an understanding of how they work e. g. 73 - 59 involves renaming 73 as 60+13 n A student reaches end of Stage 6 It is an effective method for the problem posed. e. g. Try working out this out as an algorithm 10004 or 199 - 9998 + 99 n n n They also know other strategies they can use They are achieving at Stage 6

It may surprise you… n In Stage 1 -4: We focus on learning our addition and subtraction facts to 10 n At Stage 3 -4: We focus on developing understanding of multiplication and division (not learning the multiplication & division facts) n At Stage 5 Students learn addition facts to 20 & subtraction facts to 10 2 x, 5 x and 10 x multiplication facts n

Support Material • www. nzmaths. co. nz/families – Video, Maths at Our House (cooking, maps, shopping, newspapers) – Number Knowledge Activities (games, activities and flashcards) School Website: Knowledge Lists Knowledge activities • Student-led conferences/reports: It will identify you child’s next learning step.
b2ca00f7bdf30ecfd4f4f852c3f86f5b.ppt