e02627fff0184cd8a5f7e0277ac7ba0f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Tips for USMLE Step 1 Presentation by: Joe Walsh For educational purposes only

Test Format • 350 questions – 7 sections of 50 questions at 1 hr each (one section does NOT count). • 8 hrs total time. 45 min of break to distribute. – Add 15 min to break if you skip tutorial (recommended). – Finishing a section early adds remaining time to break. • Register by Dec & ideally schedule for mid-June. – Need 3 -4 mos of hardcore study time. – Register online at www. nbme. org - schedule 3 mos elgibility – Eligibility period with NBME, Scheduling Permit with prometric.

Types of Questions

Factual Questions Example Question 1 What are the calcium-dependent proteins responsible for cell-to-cell junctional adhesion? A. Cadherins B. Collagens C. Integrins D. Connexins E. Occludins

Factual Questions Example Question 1 What are the calcium-dependent proteins responsible for cell-to-cell junctional adhesion? A. Cadherins B. Collagens C. Integrins D. Connexins E. Occludins
Factual Q’s with a Trick Example Question 2 A 34 -year-old Brazilian housewife from Rio de Janeiro complained of a cutaneous ulcer on the left forearm and palpable subcutaneous nodules. Her illness had begun as a small pimple about 2 months prior to presentation. On physical exam she presented with a 10 mm ulcer on her left forearm and subcutaneous nodules ascending linearly towards the axilla. Mycological cultures yield Sporothrix schenkii. What do you prescribe as treatment? A. Mebendazole B. Actinomycin C. Teraconazole D. Itraconazole E. Nystatin

Factual Q’s with a Trick Example Question 2 A 34 -year-old Brazilian housewife from Rio de Janeiro complained of a cutaneous ulcer on the left forearm and palpable subcutaneous nodules. Her illness had begun as a small pimple about 2 months prior to presentation. On physical exam she presented with a 10 mm ulcer on her left forearm and subcutaneous nodules ascending linearly towards the axilla. Mycological cultures yield Sporothrix schenkii. What do you prescribe as treatment? A. Mebendazole B. Actinomycin C. Teraconazole D. Itraconazole (Potassium Iodide) E. Nystatin

Reasoning Questions Example Question 3 A 32 -year-old woman with type 1 diabetes mellitus had progressive renal failure over the past 2 years. She has not yet started dialysis. Examination shows no abnormalities. Her hemoglobin concentration is 9 g/d. L, hematocrit is 28%, and mean corpuscular volume is 94 µm 3. A blood smear shows normochromic, normocytic cells. Which of the following is the most likely cause? A. Acute blood loss B. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia C. Erythrocyte enzyme deficiency D. Erythropoietin deficiency E. Immunohemolysis F. Microangiopathic hemolysis G. Polycythemia vera H. Sickle cell disease I. Sideroblastic anemia J. b-Thalassemia trait

Reasoning Questions Example Question 3 A 32 -year-old woman with type 1 diabetes mellitus had progressive renal failure over the past 2 years. She has not yet started dialysis. Examination shows no abnormalities. Her hemoglobin concentration is 9 g/d. L, hematocrit is 28%, and mean corpuscular volume is 94 µm 3. A blood smear shows normochromic, normocytic cells. Which of the following is the most likely cause? A. Acute blood loss B. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia C. Erythrocyte enzyme deficiency D. Erythropoietin deficiency E. Immunohemolysis F. Microangiopathic hemolysis G. Polycythemia vera H. Sickle cell disease I. Sideroblastic anemia J. b-Thalassemia trait

Reasoning Questions Example Question 4 A 68 -year-old male with a history of type 2 diabetes and peripheral vascular disease develops abdominal pain from bowel ischemia. Exploratory laparotomy revealed a 4 -cm region of necrotic colon, which was subsequently resected. Where was this ischemic region most likely located? A. Ascending colon B. Hepatic flexure C. Splenic flexure D. Descending colon E. Sigmoid colon

Reasoning Questions Example Question 4 A 68 -year-old male with a history of type 2 diabetes and peripheral vascular disease develops abdominal pain from bowel ischemia. Exploratory laparotomy revealed a 4 -cm region of necrotic colon, which was subsequently resected. Where was this ischemic region most likely located? A. Ascending colon B. Hepatic flexure C. Splenic flexure D. Descending colon E. Sigmoid colon

Ethics Questions Example Question 5 A 46 -year-old male presents to the emergency room with tearing pain in his chest radiating towards his back and blood pressure 84/40. He is pale and diaphoretic but remains conscious. He tells you that he is a Jehovah’s witness and refuses to receive any blood products before or during surgery. What do you tell the patient? A. “Your request is against my ethics, and I feel that I must find another doctor for you who is willing to comply with your request. ” B. “I insist that you receive a blood transfusion because otherwise you will probably die. ” C. “We will only use blood products as absolutely necessary to save your life. ” D. “We will comply with your request because your condition does not appear life-threatening. ”

Ethics Questions Example Question 5 A 46 -year-old male presents to the emergency room with tearing pain in his chest radiating towards his back and blood pressure 84/40. He is pale and diaphoretic but remains conscious. He tells you that he is a Jehovah’s witness and refuses to receive any blood products before or during surgery. What do you tell the patient? A. “Your request is against my ethics, and I feel that I must find another doctor for you who is willing to comply with your request. ” B. “I insist that you receive a blood transfusion because otherwise you will probably die. ” C. “We will only use blood products as absolutely necessary to save your life. ” D. “We will comply with your request because your condition does not appear life-threatening. ”

Ethics Questions -Do NOT use common sense for these. -Learn medicolegal rules (Hi-Yield or BRS Behavioral Science). -Don’t take into account “sounding mean”.
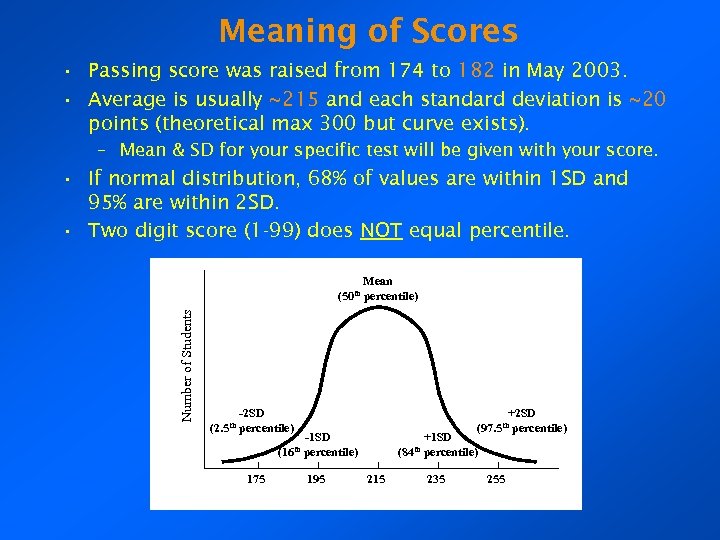
Meaning of Scores • Passing score was raised from 174 to 182 in May 2003. • Average is usually ~215 and each standard deviation is ~20 points (theoretical max 300 but curve exists). – Mean & SD for your specific test will be given with your score. • If normal distribution, 68% of values are within 1 SD and 95% are within 2 SD. • Two digit score (1 -99) does NOT equal percentile. Number of Students Mean (50 th percentile) -2 SD (2. 5 th percentile) +2 SD (97. 5 th percentile) -1 SD (16 th percentile) 175 195 +1 SD (84 th percentile) 215 235 255
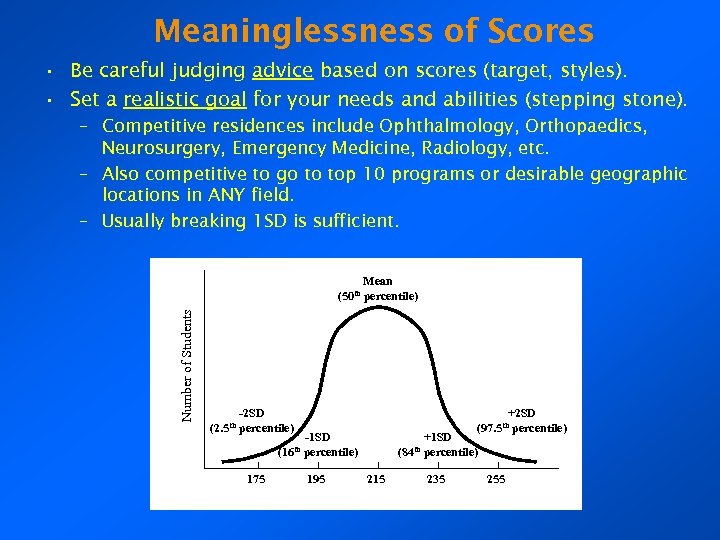
Meaninglessness of Scores • Be careful judging advice based on scores (target, styles). • Set a realistic goal for your needs and abilities (stepping stone). – Competitive residences include Ophthalmology, Orthopaedics, Neurosurgery, Emergency Medicine, Radiology, etc. – Also competitive to go to top 10 programs or desirable geographic locations in ANY field. – Usually breaking 1 SD is sufficient. Number of Students Mean (50 th percentile) -2 SD (2. 5 th percentile) +2 SD (97. 5 th percentile) -1 SD (16 th percentile) 175 195 +1 SD (84 th percentile) 215 235 255

Creating a Goal • Different studying strategies based on goals: – Passing the test (master core high-yield info) – Breaking 1 SD (high-yield plus know some low-yield) – Breaking 2 SD (high-yield plus lots of low-yield info) • Risky if you create an unrealistic goal.

Creating a Goal • How do you know what goal you can achieve? • Honoring classes is sometimes unrelated. – People who did well in classes may do poorly on Step 1 and vice versa. – Luck component (many different test versions; different score distributions & curves)

Diagnostic Exams • Free Kaplan diagnostic test (% correct x 3) = Starting point – Can realistically increase score by 10% raw score max (or 30 points max) each month. • NBME diagnostic test 1 -2 mos before test (evaluate progress & effectiveness of study plan). – Adjust studying in final month based on diagnostic. – Only use First Aid or other general source in final week. • Check-out testing site (can walk around inside). • COMMON SENSE: Sleeping & Eating (physical = mental)

Kaplan or NOT? Boxers or Briefs?

DEPENDS!!

KAPLAN or not • Pros: – – – Keeps you on track Extrinsic motivation Proven record Skilled teachers Geared towards achieving a good score • Cons: – – Expensive Not unique or individual preparation Geared towards passing or 1 SD Stifling towards additional independent study

General Study Strategy Content Questions

General Study Strategy • Choose books for content review – – Format your comfortable with/used in M 2 classes High yield without extraneous info Class notes NOT BEST SOURCE Don’t spend too much time on anatomy, Biochem, Behav. Sc. – Emphasize ACTIVE reading - Ask questions to reinforce what you’ve learned • Gradually work questions into study plan – Start w/ 1 block of 50 q and inc q week – Read explanations carefully - write down wrong answers – Constantly reassess strengths and weaknesses

GENERAL SOURCES -Don’t write in First Aid until last 2 -3 mos. -Read multiple times -Use as starting point for content review

Content Review • Consensus “must read” books – Micro Ridiculously Simple – Constanzo BRS or Physio text – BRS Path – Pathophysiology for Boards and Wards – Pharm Cards

Question Review • Kaplan Q-Bank – 2000+ questions: excellent stratification by subject, organ system, etc. . • NMS question book • Blackwell’s free test online • NBME tests(2) • Robbins question book

-Board Simulator Series (BSS): organized by Organ Systems. -5 books of questions & explanations, four-and-a-half tests per book. -Reading explanations is more painful than doing the questions. -90% of those who start BSS never finish (too painful).

Specific Books Used ANATOMY: Hi-Yield Gross Anatomy BEHAV SCI/PSYCHOPATH: Hi-Yield Behav Sci BIOCHEMISTRY: BRS Biochem(didn’t like HY) EMBRYOLOGY: Hi-Yield HISTOLOGY: Hi-Yield (nothing is needed) IMMUNOLOGY: Hi-Yield (nothing is needed) NEUROANATOMY: Hi-Yield, Ridiculously Simple (BRS = too detailed) MICROBIOLOGY: Ridiculously Simple, Micro Cards PATHOLOGY: BRS, Pathophysiology for B & W PHARMACOLOGY: Lippincott’s, Pharm Cards PHYSIOLOGY: Costanzo Text AUDIO SOURCES: Goljan, Gold Standard

WEEK/DAY OF TEST ADVICE • Week of: – Get up early and be active during day – Go over first aid slowly one last time – Review pictures, notes, wrong answers • Day of: – Pack lunch, bring layers(cold test center) • After: – Run, don’t walk, to pub
e02627fff0184cd8a5f7e0277ac7ba0f.ppt