516a013f1e2ded6c6e7ea6bf584d7a63.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Tips and tricks for using SAP Net. Weaver Business Intelligence 7. 0 as your Enterprise Data Warehouse Dr. Bjarne Berg © 2008 Wellesley Information Services. All rights reserved.
Tips and tricks for using SAP Net. Weaver Business Intelligence 7. 0 as your Enterprise Data Warehouse Dr. Bjarne Berg © 2008 Wellesley Information Services. All rights reserved.
 In This Session. . . We will explore 6 large-scale EDW implementations, and see how to apply lessons to your strategy and projects. Examine the difference between an evolutionary SAP Net. Weaver BI data warehouse architecture and a topdriven design method. Compare the results of using a data mart (bottom-up) approach to an EDW (top down) approach, and determine which approach best fits your requirements. Explore the ways in which new SAP Net. Weaver BI enhancements can support real-time data warehousing We will look at common EDW pitfalls and how to leverage the SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture in a large landscape using the Corporate Information Factory (CIF) 1
In This Session. . . We will explore 6 large-scale EDW implementations, and see how to apply lessons to your strategy and projects. Examine the difference between an evolutionary SAP Net. Weaver BI data warehouse architecture and a topdriven design method. Compare the results of using a data mart (bottom-up) approach to an EDW (top down) approach, and determine which approach best fits your requirements. Explore the ways in which new SAP Net. Weaver BI enhancements can support real-time data warehousing We will look at common EDW pitfalls and how to leverage the SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture in a large landscape using the Corporate Information Factory (CIF) 1
 What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 2
What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 2
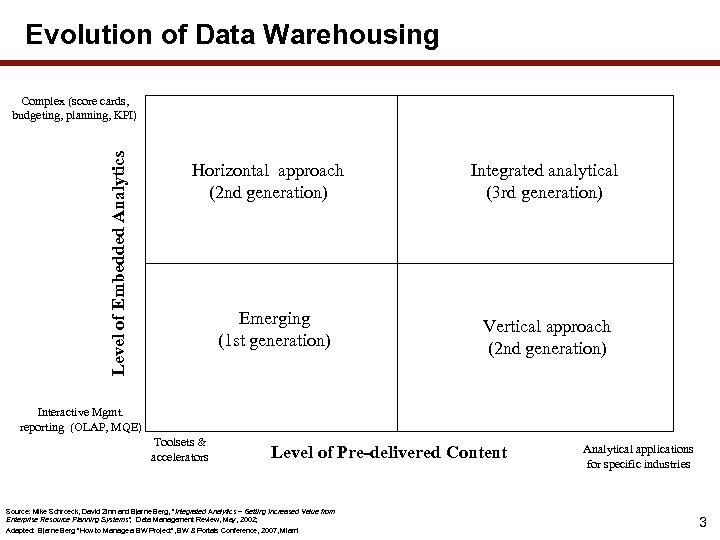 Evolution of Data Warehousing Level of Embedded Analytics Complex (score cards, budgeting, planning, KPI) Horizontal approach (2 nd generation) Integrated analytical (3 rd generation) Emerging (1 st generation) Vertical approach (2 nd generation) Interactive Mgmt. reporting (OLAP, MQE) Toolsets & accelerators Level of Pre-delivered Content Source: Mike Schroeck, David Zinn and Bjarne Berg, “Integrated Analytics – Getting Increased Value from Enterprise Resource Planning Systems”, Data Management Review, May, 2002; Adapted: Bjarne Berg “How to Manage a BW Project”, BW & Portals Conference, 2007, Miami Analytical applications for specific industries 3
Evolution of Data Warehousing Level of Embedded Analytics Complex (score cards, budgeting, planning, KPI) Horizontal approach (2 nd generation) Integrated analytical (3 rd generation) Emerging (1 st generation) Vertical approach (2 nd generation) Interactive Mgmt. reporting (OLAP, MQE) Toolsets & accelerators Level of Pre-delivered Content Source: Mike Schroeck, David Zinn and Bjarne Berg, “Integrated Analytics – Getting Increased Value from Enterprise Resource Planning Systems”, Data Management Review, May, 2002; Adapted: Bjarne Berg “How to Manage a BW Project”, BW & Portals Conference, 2007, Miami Analytical applications for specific industries 3
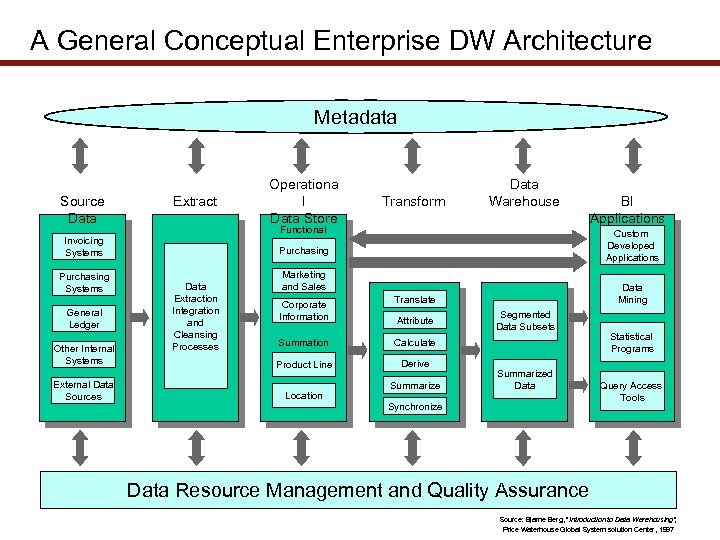 A General Conceptual Enterprise DW Architecture Metadata Source Data Extract General Ledger Other Internal Systems External Data Sources Transform Data Warehouse Functional Area Purchasing Invoicing Systems Purchasing Systems Operationa l Data Store Data Extraction Integration and Cleansing Processes Custom Developed Applications Marketing and Sales Corporate Information Data Mining Translate Attribute Summation Product Line Derive Segmented Data Subsets Calculate Location BI Applications Summarized Data Synchronize Statistical Programs Query Access Tools Data Resource Management and Quality Assurance Source: Bjarne Berg, “Introduction to Data Warehousing”, Price Waterhouse Global System solution Center, 1997
A General Conceptual Enterprise DW Architecture Metadata Source Data Extract General Ledger Other Internal Systems External Data Sources Transform Data Warehouse Functional Area Purchasing Invoicing Systems Purchasing Systems Operationa l Data Store Data Extraction Integration and Cleansing Processes Custom Developed Applications Marketing and Sales Corporate Information Data Mining Translate Attribute Summation Product Line Derive Segmented Data Subsets Calculate Location BI Applications Summarized Data Synchronize Statistical Programs Query Access Tools Data Resource Management and Quality Assurance Source: Bjarne Berg, “Introduction to Data Warehousing”, Price Waterhouse Global System solution Center, 1997
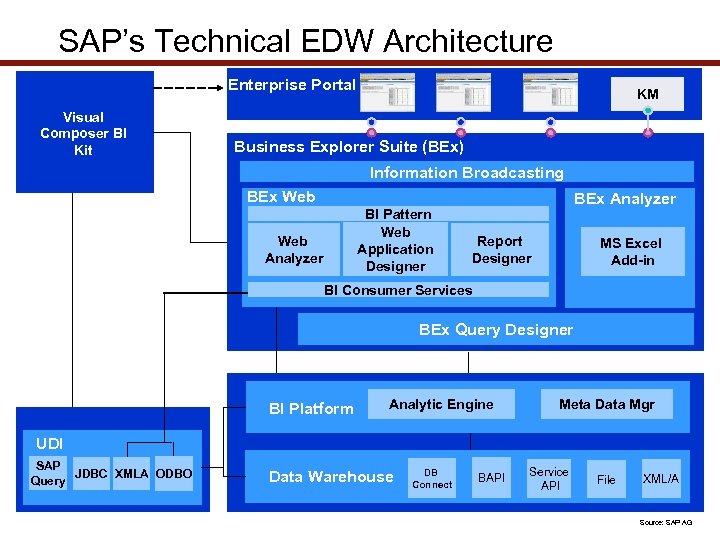 SAP’s Technical EDW Architecture Enterprise Portal Visual Composer BI Kit KM Business Explorer Suite (BEx) Information Broadcasting BEx Web BI Pattern Web Application Designer Web Analyzer BEx Analyzer Report Designer MS Excel Add-in BI Consumer Services BEx Query Designer BI Platform Analytic Engine Meta Data Mgr UDI SAP JDBC XMLA ODBO Query Data Warehouse DB Connect BAPI Service API File XML/A Source: SAP AG
SAP’s Technical EDW Architecture Enterprise Portal Visual Composer BI Kit KM Business Explorer Suite (BEx) Information Broadcasting BEx Web BI Pattern Web Application Designer Web Analyzer BEx Analyzer Report Designer MS Excel Add-in BI Consumer Services BEx Query Designer BI Platform Analytic Engine Meta Data Mgr UDI SAP JDBC XMLA ODBO Query Data Warehouse DB Connect BAPI Service API File XML/A Source: SAP AG
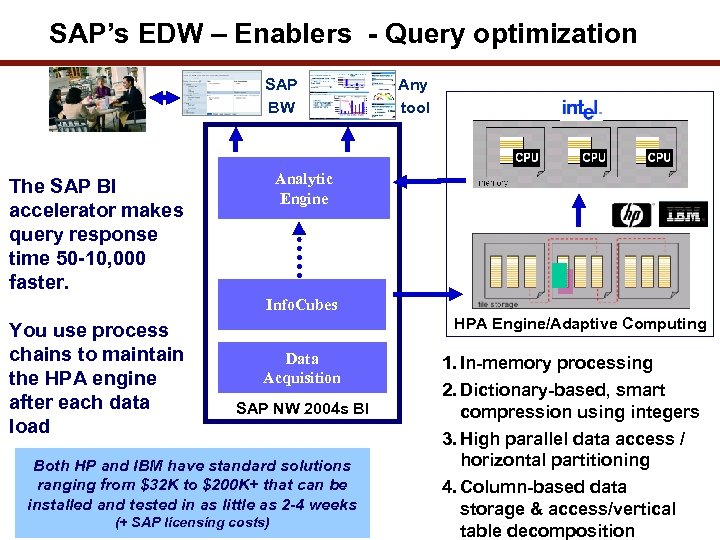 SAP’s EDW – Enablers - Query optimization SAP BW Any tool Analytic Engine The SAP BI accelerator makes query response time 50 -10, 000 faster. Info. Cubes You use process chains to maintain the HPA engine after each data load HPA Engine/Adaptive Computing Data Acquisition SAP NW 2004 s BI Both HP and IBM have standard solutions ranging from $32 K to $200 K+ that can be installed and tested in as little as 2 -4 weeks (+ SAP licensing costs) 1. In-memory processing 2. Dictionary-based, smart compression using integers 3. High parallel data access / horizontal partitioning 4. Column-based data storage & access/vertical 6 table decomposition
SAP’s EDW – Enablers - Query optimization SAP BW Any tool Analytic Engine The SAP BI accelerator makes query response time 50 -10, 000 faster. Info. Cubes You use process chains to maintain the HPA engine after each data load HPA Engine/Adaptive Computing Data Acquisition SAP NW 2004 s BI Both HP and IBM have standard solutions ranging from $32 K to $200 K+ that can be installed and tested in as little as 2 -4 weeks (+ SAP licensing costs) 1. In-memory processing 2. Dictionary-based, smart compression using integers 3. High parallel data access / horizontal partitioning 4. Column-based data storage & access/vertical 6 table decomposition
 SAP’s EDW Enablers - Remodeling Tool Box In NW 2004 s you get a new tool to add characteristics and key figures to your model. In older BW versions, if you forgot to include a field in your infocube, the rework was quite substantial and often involved reloading the infocube as well. NW 2004 s goes a long way to address the complaints that BW is a hard to maintain environment with ‘forever’ fixed Source: SAP AG, Richard Brown, Aug. 2006 7
SAP’s EDW Enablers - Remodeling Tool Box In NW 2004 s you get a new tool to add characteristics and key figures to your model. In older BW versions, if you forgot to include a field in your infocube, the rework was quite substantial and often involved reloading the infocube as well. NW 2004 s goes a long way to address the complaints that BW is a hard to maintain environment with ‘forever’ fixed Source: SAP AG, Richard Brown, Aug. 2006 7
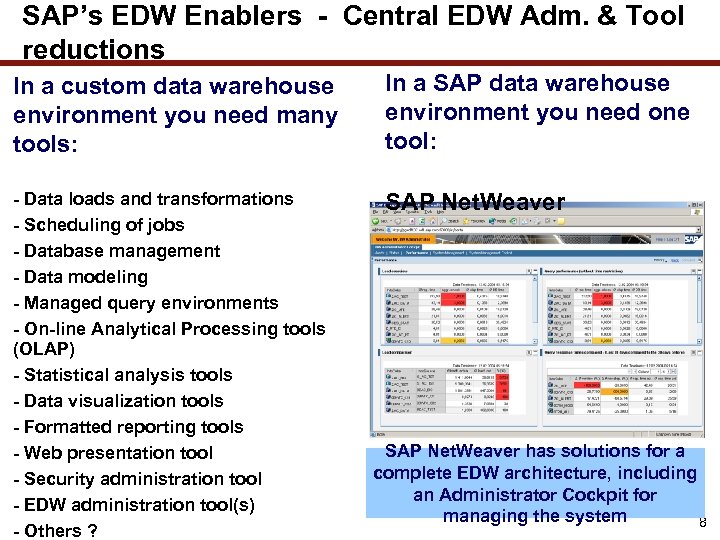 SAP’s EDW Enablers - Central EDW Adm. & Tool reductions In a custom data warehouse environment you need many tools: In a SAP data warehouse environment you need one tool: - Data loads and transformations - Scheduling of jobs - Database management - Data modeling - Managed query environments - On-line Analytical Processing tools (OLAP) - Statistical analysis tools - Data visualization tools - Formatted reporting tools - Web presentation tool - Security administration tool - EDW administration tool(s) - Others ? SAP Net. Weaver has solutions for a complete EDW architecture, including an Administrator Cockpit for managing the system 8
SAP’s EDW Enablers - Central EDW Adm. & Tool reductions In a custom data warehouse environment you need many tools: In a SAP data warehouse environment you need one tool: - Data loads and transformations - Scheduling of jobs - Database management - Data modeling - Managed query environments - On-line Analytical Processing tools (OLAP) - Statistical analysis tools - Data visualization tools - Formatted reporting tools - Web presentation tool - Security administration tool - EDW administration tool(s) - Others ? SAP Net. Weaver has solutions for a complete EDW architecture, including an Administrator Cockpit for managing the system 8
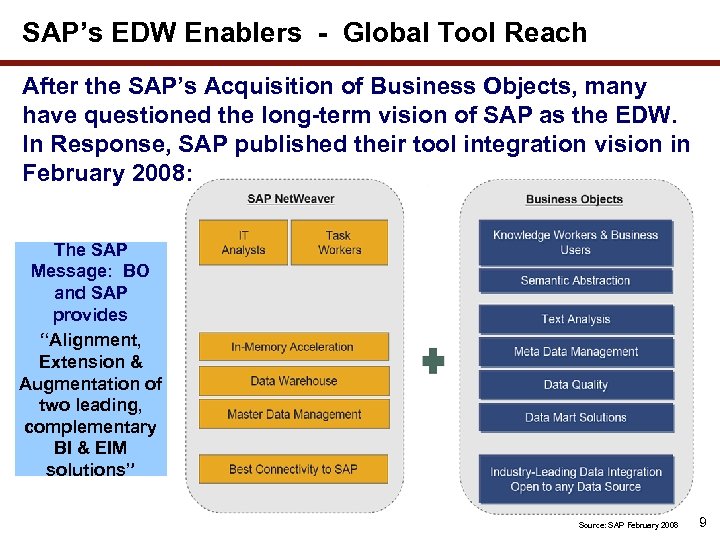 SAP’s EDW Enablers - Global Tool Reach After the SAP’s Acquisition of Business Objects, many have questioned the long-term vision of SAP as the EDW. In Response, SAP published their tool integration vision in February 2008: The SAP Message: BO and SAP provides “Alignment, Extension & Augmentation of two leading, complementary BI & EIM solutions” Source: SAP February 2008 9
SAP’s EDW Enablers - Global Tool Reach After the SAP’s Acquisition of Business Objects, many have questioned the long-term vision of SAP as the EDW. In Response, SAP published their tool integration vision in February 2008: The SAP Message: BO and SAP provides “Alignment, Extension & Augmentation of two leading, complementary BI & EIM solutions” Source: SAP February 2008 9
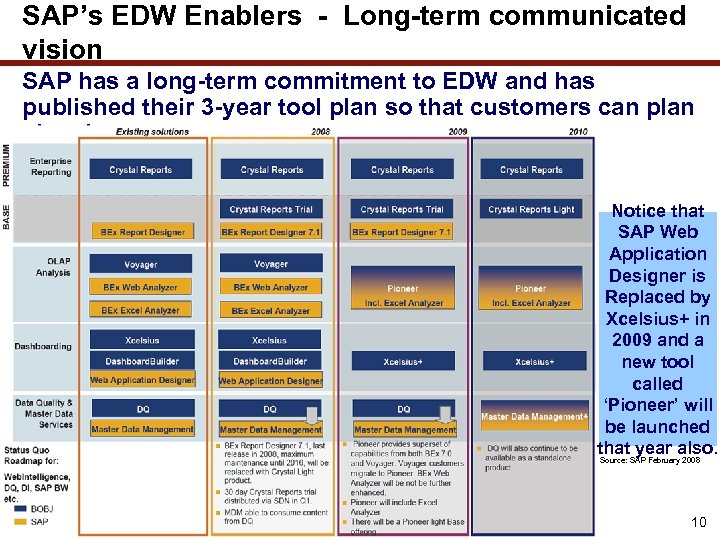 SAP’s EDW Enablers - Long-term communicated vision SAP has a long-term commitment to EDW and has published their 3 -year tool plan so that customers can plan ahead. Notice that SAP Web Application Designer is Replaced by Xcelsius+ in 2009 and a new tool called ‘Pioneer’ will be launched that. SAP Februaryalso. year 2008 Source: 10
SAP’s EDW Enablers - Long-term communicated vision SAP has a long-term commitment to EDW and has published their 3 -year tool plan so that customers can plan ahead. Notice that SAP Web Application Designer is Replaced by Xcelsius+ in 2009 and a new tool called ‘Pioneer’ will be launched that. SAP Februaryalso. year 2008 Source: 10
 What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 11
What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 11
 Design Vs. Evolution An organization has two fundamental choices: 1. Build a new well architected EDW Evolve the old EDW or reporting system 2. Both solutions are feasible, but organizations that selects an evolutionary approach should be selfaware and monitor undesirable addons and ‘workarounds”. Failure to break with the past can be detrimental to an EDW’s long-term 12
Design Vs. Evolution An organization has two fundamental choices: 1. Build a new well architected EDW Evolve the old EDW or reporting system 2. Both solutions are feasible, but organizations that selects an evolutionary approach should be selfaware and monitor undesirable addons and ‘workarounds”. Failure to break with the past can be detrimental to an EDW’s long-term 12
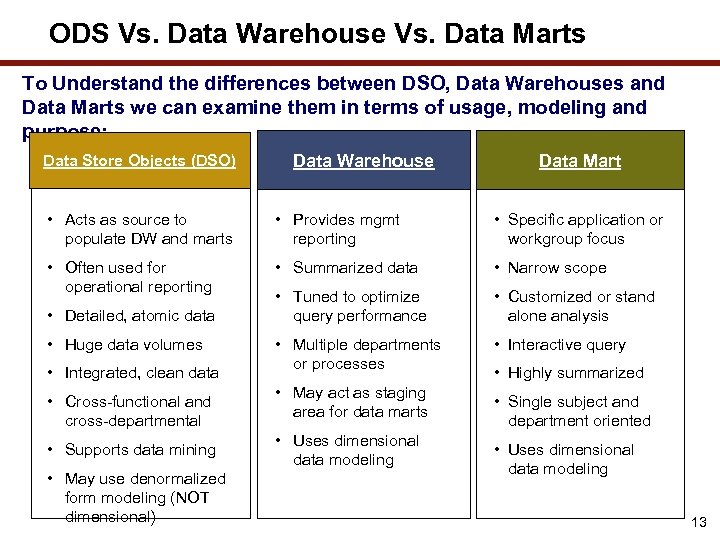 ODS Vs. Data Warehouse Vs. Data Marts To Understand the differences between DSO, Data Warehouses and Data Marts we can examine them in terms of usage, modeling and purpose: Data Store Objects (DSO) Data Warehouse Data Mart • Acts as source to populate DW and marts • Provides mgmt reporting • Specific application or workgroup focus • Often used for operational reporting • Summarized data • Narrow scope • Tuned to optimize query performance • Customized or stand alone analysis • Multiple departments or processes • Interactive query • Detailed, atomic data • Huge data volumes • Integrated, clean data • Cross-functional and cross-departmental • Supports data mining • May use denormalized form modeling (NOT dimensional) • May act as staging area for data marts • Uses dimensional data modeling • Highly summarized • Single subject and department oriented • Uses dimensional data modeling 13
ODS Vs. Data Warehouse Vs. Data Marts To Understand the differences between DSO, Data Warehouses and Data Marts we can examine them in terms of usage, modeling and purpose: Data Store Objects (DSO) Data Warehouse Data Mart • Acts as source to populate DW and marts • Provides mgmt reporting • Specific application or workgroup focus • Often used for operational reporting • Summarized data • Narrow scope • Tuned to optimize query performance • Customized or stand alone analysis • Multiple departments or processes • Interactive query • Detailed, atomic data • Huge data volumes • Integrated, clean data • Cross-functional and cross-departmental • Supports data mining • May use denormalized form modeling (NOT dimensional) • May act as staging area for data marts • Uses dimensional data modeling • Highly summarized • Single subject and department oriented • Uses dimensional data modeling 13
 Data Warehouse Vs. Data Marts - Implementation Sequence There are several alternatives for an iterative approach to implementing the various storage structures, based upon organizational needs. The various structures can be enterprise or departmentally focused. They can be built first, middle, or last. They can be standalone or combined. The important point is to have a concept of the long term vision of the data warehouse project and how each type of structure is to be used. A) ODS first: Start by building an enterprise data warehouse from a subject area perspective and then gradually move subsets of data to data marts. This approach may take a longer time to implement. B) Data mart first: Start by building data marts to get data out to users quickly. This approach may encounter difficulties in integrating data from an enterprise perspective. 14 C) Data marts first within the framework or vision of an ODS: Start
Data Warehouse Vs. Data Marts - Implementation Sequence There are several alternatives for an iterative approach to implementing the various storage structures, based upon organizational needs. The various structures can be enterprise or departmentally focused. They can be built first, middle, or last. They can be standalone or combined. The important point is to have a concept of the long term vision of the data warehouse project and how each type of structure is to be used. A) ODS first: Start by building an enterprise data warehouse from a subject area perspective and then gradually move subsets of data to data marts. This approach may take a longer time to implement. B) Data mart first: Start by building data marts to get data out to users quickly. This approach may encounter difficulties in integrating data from an enterprise perspective. 14 C) Data marts first within the framework or vision of an ODS: Start
 Advantages of building the data marts first There is a significant trend in the industry today toward building data marts first, then consolidating “backwards” to create the data warehouse and operational data store. There are several advantages to this approach: A) Allows faster implementation The average data mart may take 2 -3 months to implement; the average EDW evolves over many iteration and may take years to mature. Several marts can be started in parallel. B) Reduces political liability through alignment with a specific business need. The mart can deliver value to the organization in a much shorter period of time and can focus on a specific business function or problem. The business sponsors will see faster results and can affirm their decisions with benefit analysis and feedback. This is important to maintaining interest and adequate funding levels for the program. This is in contrast to the time and complexity of building 15
Advantages of building the data marts first There is a significant trend in the industry today toward building data marts first, then consolidating “backwards” to create the data warehouse and operational data store. There are several advantages to this approach: A) Allows faster implementation The average data mart may take 2 -3 months to implement; the average EDW evolves over many iteration and may take years to mature. Several marts can be started in parallel. B) Reduces political liability through alignment with a specific business need. The mart can deliver value to the organization in a much shorter period of time and can focus on a specific business function or problem. The business sponsors will see faster results and can affirm their decisions with benefit analysis and feedback. This is important to maintaining interest and adequate funding levels for the program. This is in contrast to the time and complexity of building 15
 Advantages of building the data marts first (continued) C) Limits risk while learning how to implement data warehouse. Building very large databases of several Terabytes is inherently complex. Backup and recovery systems may require specialized hardware and software. Complex tuning may be necessary to achieve satisfactory query performance levels. Identifying and defining data from many different sources creates opportunities for users and sponsoring departments to disagree. The ultimate business goals may be overshadowed by the technical and political difficulties of building the large warehouse. Starting small with a data mart, experimenting, and using the implementation as a learning experience, will reduce the risk and may actually result in a higher quality deliverable. D) Costs less than an EDW. Initially, the economics of smaller scale hardware, software, and 16
Advantages of building the data marts first (continued) C) Limits risk while learning how to implement data warehouse. Building very large databases of several Terabytes is inherently complex. Backup and recovery systems may require specialized hardware and software. Complex tuning may be necessary to achieve satisfactory query performance levels. Identifying and defining data from many different sources creates opportunities for users and sponsoring departments to disagree. The ultimate business goals may be overshadowed by the technical and political difficulties of building the large warehouse. Starting small with a data mart, experimenting, and using the implementation as a learning experience, will reduce the risk and may actually result in a higher quality deliverable. D) Costs less than an EDW. Initially, the economics of smaller scale hardware, software, and 16
 Major Risks of building the Data Marts first Data marts do not replace data warehouses. The data mart is not the next step in data warehouse evolution. It must be planned and implemented as part of the overall architectural vision. To be effective, you must maintain centralized control of data distribution to the mart in order to support the enterprise’s overarching warehouse goals of data quality, consolidation, and sharing. Data marts also increase the complexity of the data There are some great risks of succumbing to political warehouse environment with multiple extract, transform, pressures. and transfer routines. Business units that demand a quick hit and a stovepipe implementation of data marts may only serve to undermine the best laid plans for an integrated and durable data warehousing program. 17
Major Risks of building the Data Marts first Data marts do not replace data warehouses. The data mart is not the next step in data warehouse evolution. It must be planned and implemented as part of the overall architectural vision. To be effective, you must maintain centralized control of data distribution to the mart in order to support the enterprise’s overarching warehouse goals of data quality, consolidation, and sharing. Data marts also increase the complexity of the data There are some great risks of succumbing to political warehouse environment with multiple extract, transform, pressures. and transfer routines. Business units that demand a quick hit and a stovepipe implementation of data marts may only serve to undermine the best laid plans for an integrated and durable data warehousing program. 17
 Risks of building the data marts first If the IT department agrees to a bottom-up EDW, a strictly application specific approach, they may end up with multiple data marts that can not be integrated into a larger EDW/ODS view and which can not support analysis across different marts. The bottom line is plan and build a reusable data and technical foundation (technology standards, data modeling principles, and integrated databases). The Gartner Group estimates that resources required to manage a disjointed data mart environment are three times greater than an integrated data warehouse architecture. 18
Risks of building the data marts first If the IT department agrees to a bottom-up EDW, a strictly application specific approach, they may end up with multiple data marts that can not be integrated into a larger EDW/ODS view and which can not support analysis across different marts. The bottom line is plan and build a reusable data and technical foundation (technology standards, data modeling principles, and integrated databases). The Gartner Group estimates that resources required to manage a disjointed data mart environment are three times greater than an integrated data warehouse architecture. 18
 SAP’s Vision of Data Marts If you insist on building data marts, you can also use SAP’s newly acquired “Rapid Marts” tool from Business Objects. Built with Data Integrator, SAP Rapid Marts are ready-made data marts for SAP. It has “pre-built data flows, business logic, and schema that understand the SAP meta-data”. SAP Rapids Marts also include content that is immediately consumable by business users and can be deployed independent from an EDW implementation. It supports data profiling and cleansing and can be “the first step toward a holistic EIM program or global EDW strategy”. In a prototype environment it can also provide early understanding of data quality Source: SAP, Feb 2008 SAP has now inherited a tool for Data Marts that is independent from the SAP Net. Weaver Platform 19
SAP’s Vision of Data Marts If you insist on building data marts, you can also use SAP’s newly acquired “Rapid Marts” tool from Business Objects. Built with Data Integrator, SAP Rapid Marts are ready-made data marts for SAP. It has “pre-built data flows, business logic, and schema that understand the SAP meta-data”. SAP Rapids Marts also include content that is immediately consumable by business users and can be deployed independent from an EDW implementation. It supports data profiling and cleansing and can be “the first step toward a holistic EIM program or global EDW strategy”. In a prototype environment it can also provide early understanding of data quality Source: SAP, Feb 2008 SAP has now inherited a tool for Data Marts that is independent from the SAP Net. Weaver Platform 19
 What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 20
What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 20
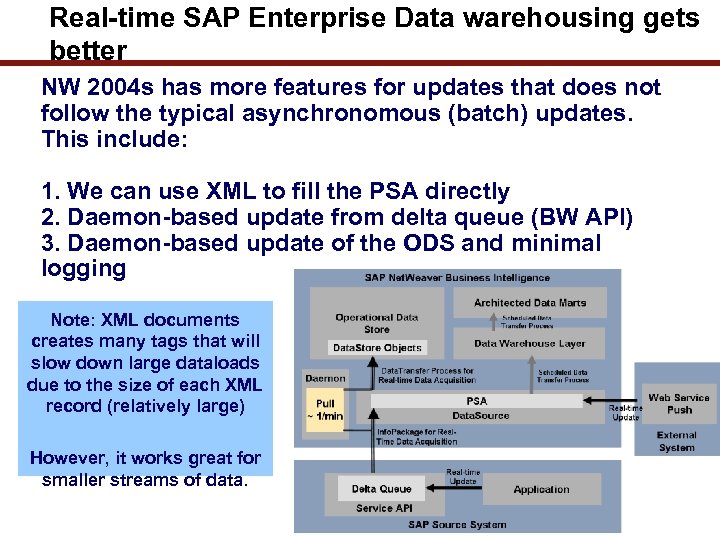 Real-time SAP Enterprise Data warehousing gets better NW 2004 s has more features for updates that does not follow the typical asynchronomous (batch) updates. This include: 1. We can use XML to fill the PSA directly 2. Daemon-based update from delta queue (BW API) 3. Daemon-based update of the ODS and minimal logging Note: XML documents creates many tags that will slow down large dataloads due to the size of each XML record (relatively large) However, it works great for smaller streams of data. 21
Real-time SAP Enterprise Data warehousing gets better NW 2004 s has more features for updates that does not follow the typical asynchronomous (batch) updates. This include: 1. We can use XML to fill the PSA directly 2. Daemon-based update from delta queue (BW API) 3. Daemon-based update of the ODS and minimal logging Note: XML documents creates many tags that will slow down large dataloads due to the size of each XML record (relatively large) However, it works great for smaller streams of data. 21
 Limitations of Real-time SAP Enterprise Data warehousing There are some limitations depending on the version of SAP BI/BW you use. For versions 3. 5 and higher, there are few limitations and they include: § You can only use real-time to load ODSs or PSA § A “normal” delta update and a real-time update cannot happen at the same time for the same Data. Source and/or ODS § For data targets that subsequently store the real-timesupported ODS objects, real time data transfer cannot be used § Info. Packages that use real-time updates cannot be associated. Using SAP Exchange Infrastructure or Process Chains Consider with Info. Package Groups (SAP-XI) to generate the XML documents from non-SAP Systems. This can help build a corporate data hub center that can reduce the number of custom interfaces in the organization 22
Limitations of Real-time SAP Enterprise Data warehousing There are some limitations depending on the version of SAP BI/BW you use. For versions 3. 5 and higher, there are few limitations and they include: § You can only use real-time to load ODSs or PSA § A “normal” delta update and a real-time update cannot happen at the same time for the same Data. Source and/or ODS § For data targets that subsequently store the real-timesupported ODS objects, real time data transfer cannot be used § Info. Packages that use real-time updates cannot be associated. Using SAP Exchange Infrastructure or Process Chains Consider with Info. Package Groups (SAP-XI) to generate the XML documents from non-SAP Systems. This can help build a corporate data hub center that can reduce the number of custom interfaces in the organization 22
 What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 23
What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 23
 Common EDW Mistakes – Not Using Standard SAP Solutions In the 1950 s, you could buy a standard Sears house for $2, 065 and pay $935 more to have it implemented on your own land The customer’s who selected to buy the standard house were either “extremely happy” or “totally disappointed”. When Sears examined why, they found a strong correlation between level of modifications to the home and SAP Net. Weaver You buyunhappiness for its pre-built content and connections to other SAP applications. The more you add to the standard solutions, the harder it will become to 24
Common EDW Mistakes – Not Using Standard SAP Solutions In the 1950 s, you could buy a standard Sears house for $2, 065 and pay $935 more to have it implemented on your own land The customer’s who selected to buy the standard house were either “extremely happy” or “totally disappointed”. When Sears examined why, they found a strong correlation between level of modifications to the home and SAP Net. Weaver You buyunhappiness for its pre-built content and connections to other SAP applications. The more you add to the standard solutions, the harder it will become to 24
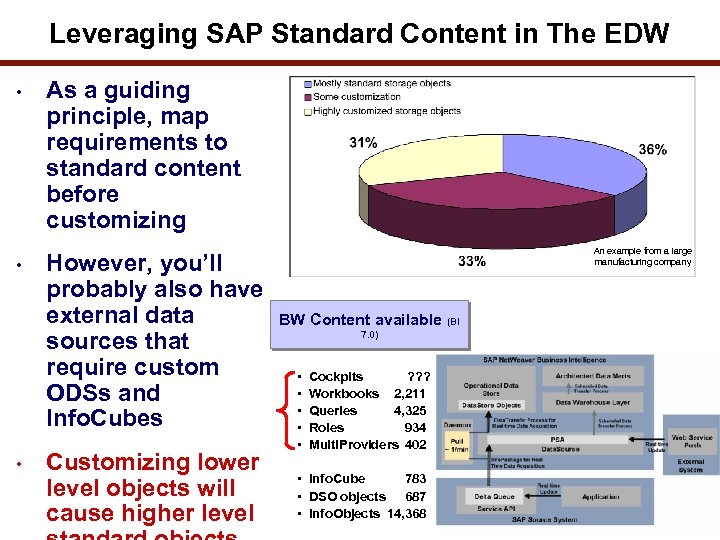 Leveraging SAP Standard Content in The EDW • • • As a guiding principle, map requirements to standard content before customizing However, you’ll probably also have external data sources that require custom ODSs and Info. Cubes Customizing lower level objects will cause higher level An example from a large manufacturing company BW Content available (BI 7. 0) • • • Cockpits ? ? ? Workbooks 2, 211 Queries 4, 325 Roles 934 Multi. Providers 402 • Info. Cube 783 • DSO objects 687 • Info. Objects 14, 368 25
Leveraging SAP Standard Content in The EDW • • • As a guiding principle, map requirements to standard content before customizing However, you’ll probably also have external data sources that require custom ODSs and Info. Cubes Customizing lower level objects will cause higher level An example from a large manufacturing company BW Content available (BI 7. 0) • • • Cockpits ? ? ? Workbooks 2, 211 Queries 4, 325 Roles 934 Multi. Providers 402 • Info. Cube 783 • DSO objects 687 • Info. Objects 14, 368 25
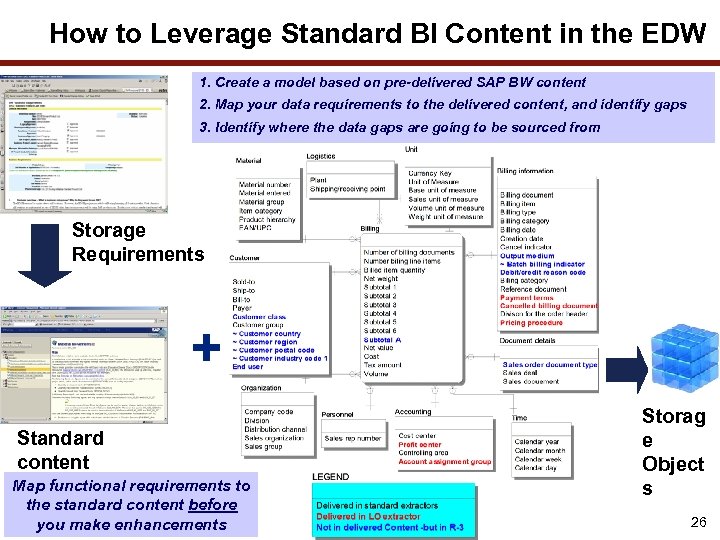 How to Leverage Standard BI Content in the EDW 1. Create a model based on pre-delivered SAP BW content 2. Map your data requirements to the delivered content, and identify gaps 3. Identify where the data gaps are going to be sourced from Storage Requirements + Standard content Map functional requirements to the standard content before you make enhancements Storag e Object s 26
How to Leverage Standard BI Content in the EDW 1. Create a model based on pre-delivered SAP BW content 2. Map your data requirements to the delivered content, and identify gaps 3. Identify where the data gaps are going to be sourced from Storage Requirements + Standard content Map functional requirements to the standard content before you make enhancements Storag e Object s 26
 Common EDW Mistakes – No Tailored Approach BOTTOM-UP APPROACH CHANGE CONTINUE TOP-DOWN APPROACH Build a global data warehouse for the company, and proceed sourcing data from old legacy systems driven from a top-down approach. Focus on a bottom-up approach where the BW project will prioritize supporting and delivering local BW solutions, thereby setting the actual establishment of the global Data Warehouse as secondary, BUT not forgotten. Each organization has different corporate cultures and considerations. The Top-down approach is preferred in centralized organizations, and the bottom-up is preferred in decentralized organizations. Pick one approach 27
Common EDW Mistakes – No Tailored Approach BOTTOM-UP APPROACH CHANGE CONTINUE TOP-DOWN APPROACH Build a global data warehouse for the company, and proceed sourcing data from old legacy systems driven from a top-down approach. Focus on a bottom-up approach where the BW project will prioritize supporting and delivering local BW solutions, thereby setting the actual establishment of the global Data Warehouse as secondary, BUT not forgotten. Each organization has different corporate cultures and considerations. The Top-down approach is preferred in centralized organizations, and the bottom-up is preferred in decentralized organizations. Pick one approach 27
 Common EDW Mistakes – loose data standards Some Many organizations place little value on enforcing data standards. This include Info. Object, DSO and Info. Cube naming standards. It also include naming conventions for queries and Info. Areas. As a result, these organizations often have a ‘mess’ where it is hard to understand what is available without researching every field and data store. It may also lead to problems integrating data with different data types and data lengths due to lack of enforcement 0 FIA Develop your data standard and have an architect enforce them throughout the lifetime of the EDW. R_O 0 5 X 0 C_K 01 0 SD_C 03 SUDHIRC 99 Vchar 2(15) AA Z 0986 Query ry Jims Que Ch ar(1 8) 28
Common EDW Mistakes – loose data standards Some Many organizations place little value on enforcing data standards. This include Info. Object, DSO and Info. Cube naming standards. It also include naming conventions for queries and Info. Areas. As a result, these organizations often have a ‘mess’ where it is hard to understand what is available without researching every field and data store. It may also lead to problems integrating data with different data types and data lengths due to lack of enforcement 0 FIA Develop your data standard and have an architect enforce them throughout the lifetime of the EDW. R_O 0 5 X 0 C_K 01 0 SD_C 03 SUDHIRC 99 Vchar 2(15) AA Z 0986 Query ry Jims Que Ch ar(1 8) 28
 Common EDW Mistakes – Lack of environment management Some organization have a hard-time to say “No” to the business community. As a result, their architecture often looks like mix-andmatch of systems that was acquired to put out “urgent needs”. In these organizations, multiple portals are common and EDWs are like marriages between IT and Business. You have to work at it constantly, give it attention, and be faithful to the solution. 29
Common EDW Mistakes – Lack of environment management Some organization have a hard-time to say “No” to the business community. As a result, their architecture often looks like mix-andmatch of systems that was acquired to put out “urgent needs”. In these organizations, multiple portals are common and EDWs are like marriages between IT and Business. You have to work at it constantly, give it attention, and be faithful to the solution. 29
 Common EDW Mistakes – lack of transport controls Most companies have strong change management of their R/3 systems. However, it is common that the same organizations have very loose approval processes for their BI systems. BI is becoming a mission critical system for most organizations and the same processes placed on the R/3 system should be applied to a production BI system. Don’t allow quick-fixes and untested service packs and notes to be applied to the production box without adequate testing. BWQ is not for window dressing!! If you want a stable BI system, you have to enforce testing and controls 30
Common EDW Mistakes – lack of transport controls Most companies have strong change management of their R/3 systems. However, it is common that the same organizations have very loose approval processes for their BI systems. BI is becoming a mission critical system for most organizations and the same processes placed on the R/3 system should be applied to a production BI system. Don’t allow quick-fixes and untested service packs and notes to be applied to the production box without adequate testing. BWQ is not for window dressing!! If you want a stable BI system, you have to enforce testing and controls 30
 Common EDW Mistakes – Poor Performance When you build an enterprise data warehouse, you should plan for at least 10 -15% of your project time for performance testing and tuning. Click-stream analysis have shown the 50% of your casual audience will hit the refresh button or navigate away from your web site if the reports take more than 7 seconds. If your query takes more then 20 seconds to run, you have major problems. Get substantial amount of memory for caching and make sure your have a fast network and hardware resources. #1 complaint of EDW is lack of performance. Consider BIA as part of your infrastructure 31
Common EDW Mistakes – Poor Performance When you build an enterprise data warehouse, you should plan for at least 10 -15% of your project time for performance testing and tuning. Click-stream analysis have shown the 50% of your casual audience will hit the refresh button or navigate away from your web site if the reports take more than 7 seconds. If your query takes more then 20 seconds to run, you have major problems. Get substantial amount of memory for caching and make sure your have a fast network and hardware resources. #1 complaint of EDW is lack of performance. Consider BIA as part of your infrastructure 31
 What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 32
What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 32
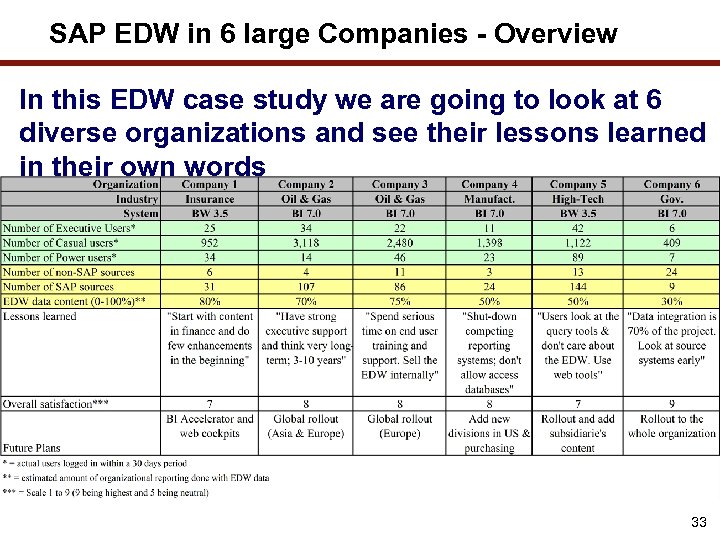 SAP EDW in 6 large Companies - Overview In this EDW case study we are going to look at 6 diverse organizations and see their lessons learned in their own words 33
SAP EDW in 6 large Companies - Overview In this EDW case study we are going to look at 6 diverse organizations and see their lessons learned in their own words 33
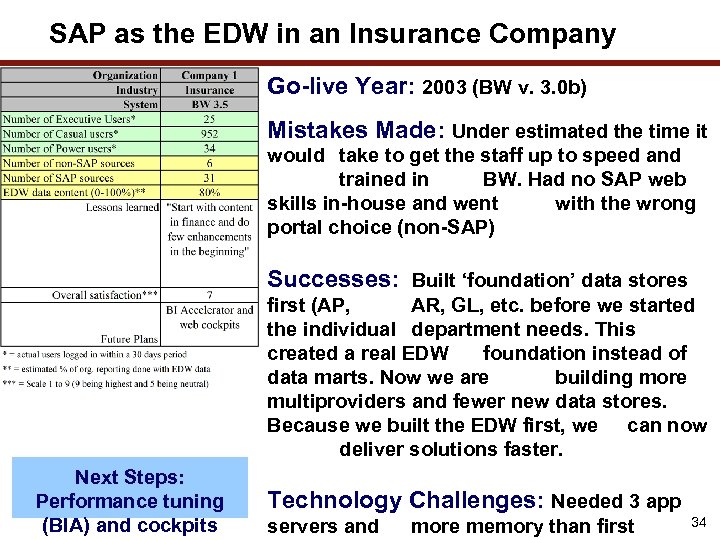 SAP as the EDW in an Insurance Company Go-live Year: 2003 (BW v. 3. 0 b) Mistakes Made: Under estimated the time it would take to get the staff up to speed and trained in BW. Had no SAP web skills in-house and went with the wrong portal choice (non-SAP) Successes: Built ‘foundation’ data stores first (AP, AR, GL, etc. before we started the individual department needs. This created a real EDW foundation instead of data marts. Now we are building more multiproviders and fewer new data stores. Because we built the EDW first, we can now deliver solutions faster. Next Steps: Performance tuning (BIA) and cockpits Technology Challenges: Needed 3 app servers and more memory than first 34
SAP as the EDW in an Insurance Company Go-live Year: 2003 (BW v. 3. 0 b) Mistakes Made: Under estimated the time it would take to get the staff up to speed and trained in BW. Had no SAP web skills in-house and went with the wrong portal choice (non-SAP) Successes: Built ‘foundation’ data stores first (AP, AR, GL, etc. before we started the individual department needs. This created a real EDW foundation instead of data marts. Now we are building more multiproviders and fewer new data stores. Because we built the EDW first, we can now deliver solutions faster. Next Steps: Performance tuning (BIA) and cockpits Technology Challenges: Needed 3 app servers and more memory than first 34
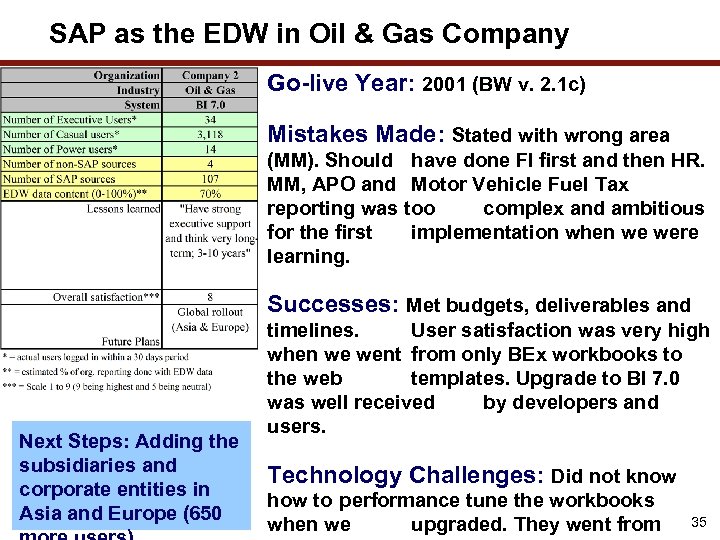 SAP as the EDW in Oil & Gas Company Go-live Year: 2001 (BW v. 2. 1 c) Mistakes Made: Stated with wrong area (MM). Should have done FI first and then HR. MM, APO and Motor Vehicle Fuel Tax reporting was too complex and ambitious for the first implementation when we were learning. Successes: Met budgets, deliverables and Next Steps: Adding the subsidiaries and corporate entities in Asia and Europe (650 timelines. User satisfaction was very high when we went from only BEx workbooks to the web templates. Upgrade to BI 7. 0 was well received by developers and users. Technology Challenges: Did not know how to performance tune the workbooks when we upgraded. They went from 35
SAP as the EDW in Oil & Gas Company Go-live Year: 2001 (BW v. 2. 1 c) Mistakes Made: Stated with wrong area (MM). Should have done FI first and then HR. MM, APO and Motor Vehicle Fuel Tax reporting was too complex and ambitious for the first implementation when we were learning. Successes: Met budgets, deliverables and Next Steps: Adding the subsidiaries and corporate entities in Asia and Europe (650 timelines. User satisfaction was very high when we went from only BEx workbooks to the web templates. Upgrade to BI 7. 0 was well received by developers and users. Technology Challenges: Did not know how to performance tune the workbooks when we upgraded. They went from 35
 SAP as the EDW in another Oil & Gas Company Go-live Year: 2000 (BW v. 2. 0 b) Mistakes Made: No formal commitment to the EDW, that evolved over time (3 years). Did not have the top C-level commitment until 2003 and had to do a lot of rework to accommodate the new global vision. Successes: We are 8 years into the EDW and it has been adapted as the core platform for global HR, finance and sales reporting. We have most divisions on the system and have retired six legacy reporting environments. Technology Challenges: Needed more Next Steps: Adding European training and rollout (2 more R/3 HW than originally planned. Performance was a real problem until 2006 when we started using the 36 Broadcaster and cached some reports
SAP as the EDW in another Oil & Gas Company Go-live Year: 2000 (BW v. 2. 0 b) Mistakes Made: No formal commitment to the EDW, that evolved over time (3 years). Did not have the top C-level commitment until 2003 and had to do a lot of rework to accommodate the new global vision. Successes: We are 8 years into the EDW and it has been adapted as the core platform for global HR, finance and sales reporting. We have most divisions on the system and have retired six legacy reporting environments. Technology Challenges: Needed more Next Steps: Adding European training and rollout (2 more R/3 HW than originally planned. Performance was a real problem until 2006 when we started using the 36 Broadcaster and cached some reports
 SAP as the EDW in a Manufacturing Company Go-live Year: 1999 (BW v. 1. 2 b) Mistakes Made: Started too early with too ambitious scope. BW was not ready for EDW in 1999. Not until version 3. 0 b (2002) did we get a real ODS and could realize our earlier ideas of the EDW. Successes: We kept the scope small and manageable, and had good consultants. The turnover rate on the project team has been low and the system was allowed to mature without business disruptions. We have consolidated three reporting groups into one and saved hundred of thousands of dollars in licenses each year. Next Steps: Add more functionality (purchasing) and rollout to purchasing Technology Challenges: Data integration was the hardest. We had to spend most of our project time on masterdata mapping & 37 consolidation.
SAP as the EDW in a Manufacturing Company Go-live Year: 1999 (BW v. 1. 2 b) Mistakes Made: Started too early with too ambitious scope. BW was not ready for EDW in 1999. Not until version 3. 0 b (2002) did we get a real ODS and could realize our earlier ideas of the EDW. Successes: We kept the scope small and manageable, and had good consultants. The turnover rate on the project team has been low and the system was allowed to mature without business disruptions. We have consolidated three reporting groups into one and saved hundred of thousands of dollars in licenses each year. Next Steps: Add more functionality (purchasing) and rollout to purchasing Technology Challenges: Data integration was the hardest. We had to spend most of our project time on masterdata mapping & 37 consolidation.
 SAP as the EDW in a High-Tech Company Go-live Year: 2003 (BW v. 3. 1 c) Mistakes Made: User interface was not prioritized high enough. Executives and casual users hated BEx workbooks. We had to relauch the EDW in 2006 with a new web interface. Successes: After the relaunch we have had success with user adaptation and have a functional steering committee and CFO sponsorship. Closing the financial books have gone from 5 days to 3. Technology Challenges: Was unsure on Next Steps: Add 2 more acquired companies to SAP R/3 and BI. how to interface our existing portal with SAP BI content (SSO). Security setup was hard and advise was too divergent. Process chains ran very slow until we 38
SAP as the EDW in a High-Tech Company Go-live Year: 2003 (BW v. 3. 1 c) Mistakes Made: User interface was not prioritized high enough. Executives and casual users hated BEx workbooks. We had to relauch the EDW in 2006 with a new web interface. Successes: After the relaunch we have had success with user adaptation and have a functional steering committee and CFO sponsorship. Closing the financial books have gone from 5 days to 3. Technology Challenges: Was unsure on Next Steps: Add 2 more acquired companies to SAP R/3 and BI. how to interface our existing portal with SAP BI content (SSO). Security setup was hard and advise was too divergent. Process chains ran very slow until we 38
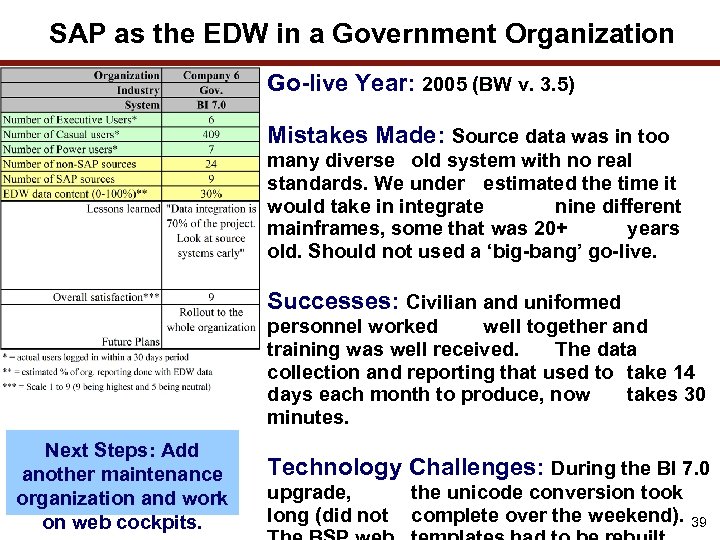 SAP as the EDW in a Government Organization Go-live Year: 2005 (BW v. 3. 5) Mistakes Made: Source data was in too many diverse old system with no real standards. We under estimated the time it would take in integrate nine different mainframes, some that was 20+ years old. Should not used a ‘big-bang’ go-live. Successes: Civilian and uniformed personnel worked well together and training was well received. The data collection and reporting that used to take 14 days each month to produce, now takes 30 minutes. Next Steps: Add another maintenance organization and work on web cockpits. Technology Challenges: During the BI 7. 0 upgrade, long (did not the unicode conversion took complete over the weekend). 39
SAP as the EDW in a Government Organization Go-live Year: 2005 (BW v. 3. 5) Mistakes Made: Source data was in too many diverse old system with no real standards. We under estimated the time it would take in integrate nine different mainframes, some that was 20+ years old. Should not used a ‘big-bang’ go-live. Successes: Civilian and uniformed personnel worked well together and training was well received. The data collection and reporting that used to take 14 days each month to produce, now takes 30 minutes. Next Steps: Add another maintenance organization and work on web cockpits. Technology Challenges: During the BI 7. 0 upgrade, long (did not the unicode conversion took complete over the weekend). 39
 What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 40
What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 40
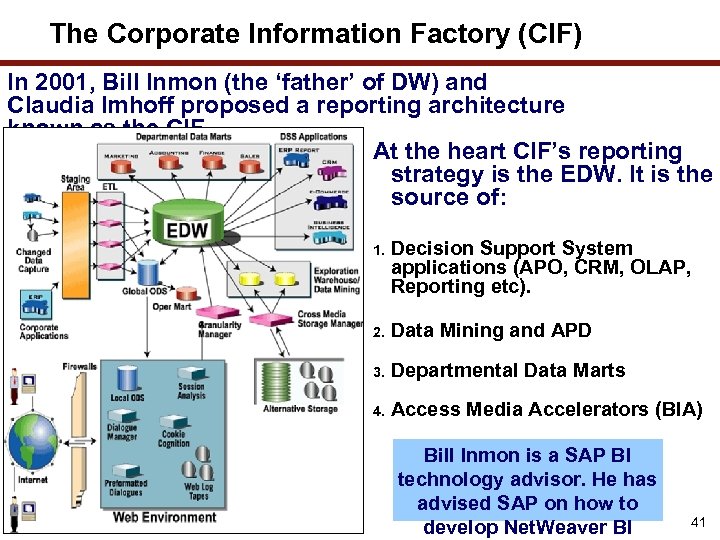 The Corporate Information Factory (CIF) In 2001, Bill Inmon (the ‘father’ of DW) and Claudia Imhoff proposed a reporting architecture known as the CIF. At the heart CIF’s reporting strategy is the EDW. It is the source of: 1. Decision Support System applications (APO, CRM, OLAP, Reporting etc). 2. Data Mining and APD 3. Departmental Data Marts 4. Access Media Accelerators (BIA) Bill Inmon is a SAP BI technology advisor. He has advised SAP on how to develop Net. Weaver BI 41
The Corporate Information Factory (CIF) In 2001, Bill Inmon (the ‘father’ of DW) and Claudia Imhoff proposed a reporting architecture known as the CIF. At the heart CIF’s reporting strategy is the EDW. It is the source of: 1. Decision Support System applications (APO, CRM, OLAP, Reporting etc). 2. Data Mining and APD 3. Departmental Data Marts 4. Access Media Accelerators (BIA) Bill Inmon is a SAP BI technology advisor. He has advised SAP on how to develop Net. Weaver BI 41
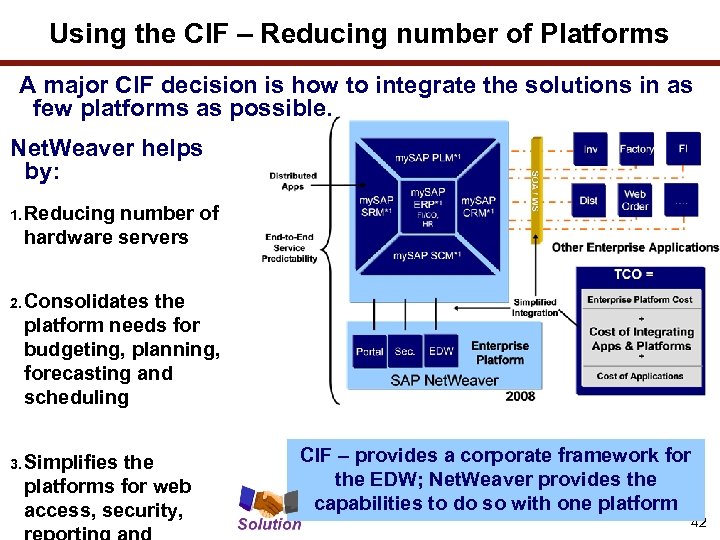 Using the CIF – Reducing number of Platforms A major CIF decision is how to integrate the solutions in as few platforms as possible. Net. Weaver helps by: 1. Reducing number of hardware servers 2. Consolidates the platform needs for budgeting, planning, forecasting and scheduling 3. Simplifies the platforms for web access, security, CIF – provides a corporate framework for the EDW; Net. Weaver provides the capabilities to do so with one platform 42
Using the CIF – Reducing number of Platforms A major CIF decision is how to integrate the solutions in as few platforms as possible. Net. Weaver helps by: 1. Reducing number of hardware servers 2. Consolidates the platform needs for budgeting, planning, forecasting and scheduling 3. Simplifies the platforms for web access, security, CIF – provides a corporate framework for the EDW; Net. Weaver provides the capabilities to do so with one platform 42
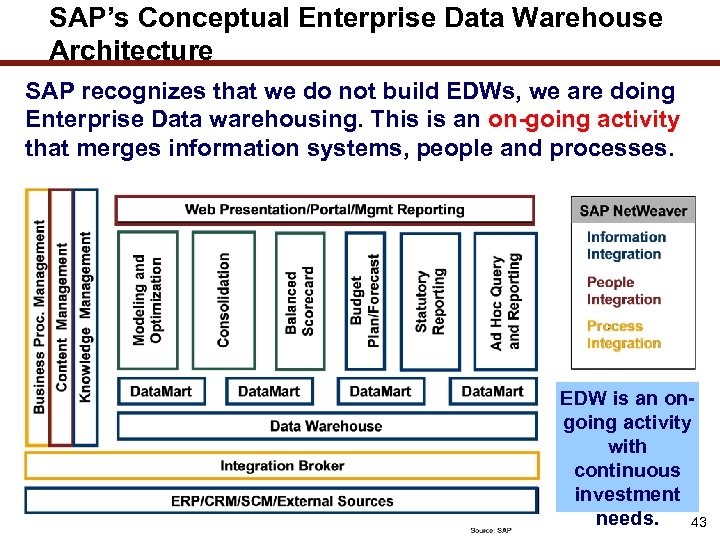 SAP’s Conceptual Enterprise Data Warehouse Architecture SAP recognizes that we do not build EDWs, we are doing Enterprise Data warehousing. This is an on-going activity that merges information systems, people and processes. EDW is an ongoing activity with continuous investment needs. 43
SAP’s Conceptual Enterprise Data Warehouse Architecture SAP recognizes that we do not build EDWs, we are doing Enterprise Data warehousing. This is an on-going activity that merges information systems, people and processes. EDW is an ongoing activity with continuous investment needs. 43
 What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 44
What We’ll Cover … • Difference between evolutionary DW architecture and a design • Data marts vs. Data warehouses • Real-time Data warehousing • The many mistakes of EDWs • Successes and failures of six large-scale SAP BIEDWs • SAP Net. Weaver BI architecture & Corporate Info. Factory (CIF) • Wrap-up 44
 Resources COMERIT (Presentations, articles and accellerators) www. comerit. net Enterprise Wide Data Warehousing with SAP BW https: //www. sdn. sap. com/irj/sdn/go/portal/prtroot/docs/li brary/uuid/5586 d 290 -0201 -0010 -b 19 e-a 8 b 8 b 91207 b 8 Enterprise Data. Warehousing – SAP Help http: //help. sap. com/saphelp_nw 70/helpdata/en/29/d 9144 236 bcda 2 ce 10000000 a 1550 b 0/frameset. htm 45
Resources COMERIT (Presentations, articles and accellerators) www. comerit. net Enterprise Wide Data Warehousing with SAP BW https: //www. sdn. sap. com/irj/sdn/go/portal/prtroot/docs/li brary/uuid/5586 d 290 -0201 -0010 -b 19 e-a 8 b 8 b 91207 b 8 Enterprise Data. Warehousing – SAP Help http: //help. sap. com/saphelp_nw 70/helpdata/en/29/d 9144 236 bcda 2 ce 10000000 a 1550 b 0/frameset. htm 45
 7 Key Points to Take Home • Plan Your Target EDW Architecture before you start the project. • Enforce Standards and pick the right tools for the job • SAP BI is no longer “leading” or “bleeding” edge and is used extensively as the EDW for large organizations • If you are still on BI 3. 5: Upgrade! • SAP BI has many new tools that will enhance the frontend for end users. Your EDW will need them • Critical to EDW success: reduce number of competing reporting system very quickly • Hire an EDW Technical Architect if you have not already. 46
7 Key Points to Take Home • Plan Your Target EDW Architecture before you start the project. • Enforce Standards and pick the right tools for the job • SAP BI is no longer “leading” or “bleeding” edge and is used extensively as the EDW for large organizations • If you are still on BI 3. 5: Upgrade! • SAP BI has many new tools that will enhance the frontend for end users. Your EDW will need them • Critical to EDW success: reduce number of competing reporting system very quickly • Hire an EDW Technical Architect if you have not already. 46
 Your Turn! How to contact me: Dr. Bjarne Berg bberg@comerit. net 47
Your Turn! How to contact me: Dr. Bjarne Berg bberg@comerit. net 47


