2205de39fa92adc1f25bf90489be35c0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 Tinea Pedis Natural History & Clinical Trials Joseph Porres, M. D. , Ph. D. Medical Officer, DDDDP 1
Tinea Pedis Natural History & Clinical Trials Joseph Porres, M. D. , Ph. D. Medical Officer, DDDDP 1
 Part I: Natural History • Tinea pedis subtypes • Causative organisms • Dermatomycosis syndrome • Predisposing factors • Complicating factors & Complications • Epidemiology & recurrence • Diagnosis • Treatment 2
Part I: Natural History • Tinea pedis subtypes • Causative organisms • Dermatomycosis syndrome • Predisposing factors • Complicating factors & Complications • Epidemiology & recurrence • Diagnosis • Treatment 2
 Tinea Pedis Subtypes • Interdigital: pruritus, erythema, scaling, fissuring, maceration • Plantar: - Moccasin: scaling, pruritus, erythema - Vesicobullous: pruritus, vesicles, scaling, erythema • Combinations of interdigital and plantar • Athlete’s foot is the layman’s term and can be found in reference to any of these forms 3
Tinea Pedis Subtypes • Interdigital: pruritus, erythema, scaling, fissuring, maceration • Plantar: - Moccasin: scaling, pruritus, erythema - Vesicobullous: pruritus, vesicles, scaling, erythema • Combinations of interdigital and plantar • Athlete’s foot is the layman’s term and can be found in reference to any of these forms 3
 Causative Organisms • Trichophyton rubrum (60 -80%) -Plantar, mocassin -Plantar small vesicles, may also affect distal subungual nail, other body sites • Trichophyton mentagrophytes (10 -20%), -Peri-plantar large vesicles, and may spread to white superficial nail • Epidermophyton floccosum (3 -10%) 4
Causative Organisms • Trichophyton rubrum (60 -80%) -Plantar, mocassin -Plantar small vesicles, may also affect distal subungual nail, other body sites • Trichophyton mentagrophytes (10 -20%), -Peri-plantar large vesicles, and may spread to white superficial nail • Epidermophyton floccosum (3 -10%) 4
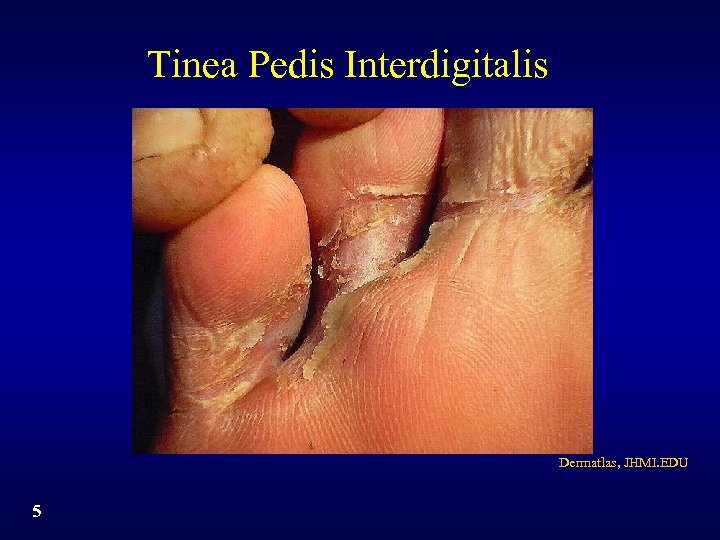 Tinea Pedis Interdigitalis Dermatlas, JHMI. EDU 5
Tinea Pedis Interdigitalis Dermatlas, JHMI. EDU 5
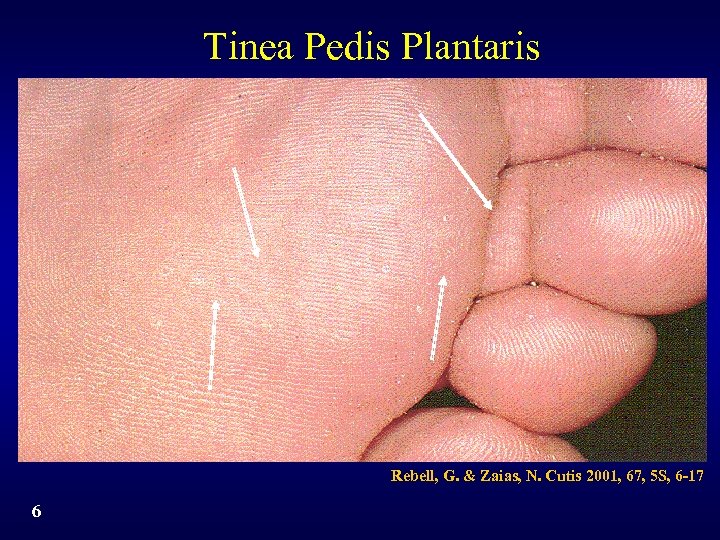 Tinea Pedis Plantaris Rebell, G. & Zaias, N. Cutis 2001, 67, 5 S, 6 -17 6
Tinea Pedis Plantaris Rebell, G. & Zaias, N. Cutis 2001, 67, 5 S, 6 -17 6
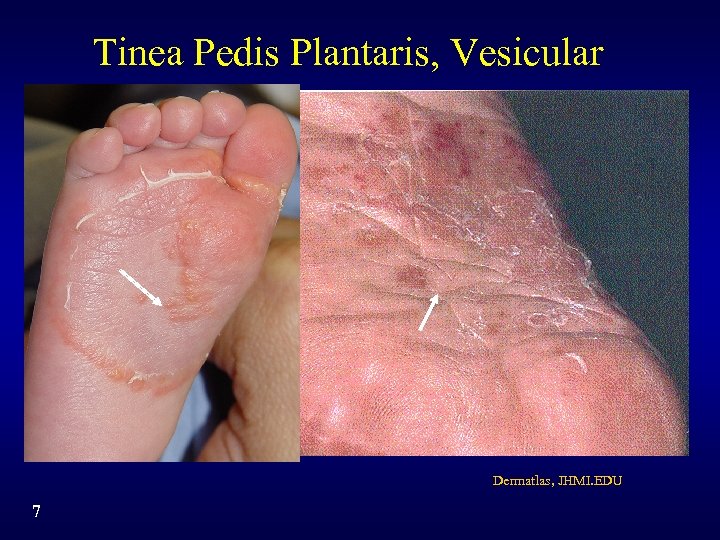 Tinea Pedis Plantaris, Vesicular Dermatlas, JHMI. EDU 7
Tinea Pedis Plantaris, Vesicular Dermatlas, JHMI. EDU 7
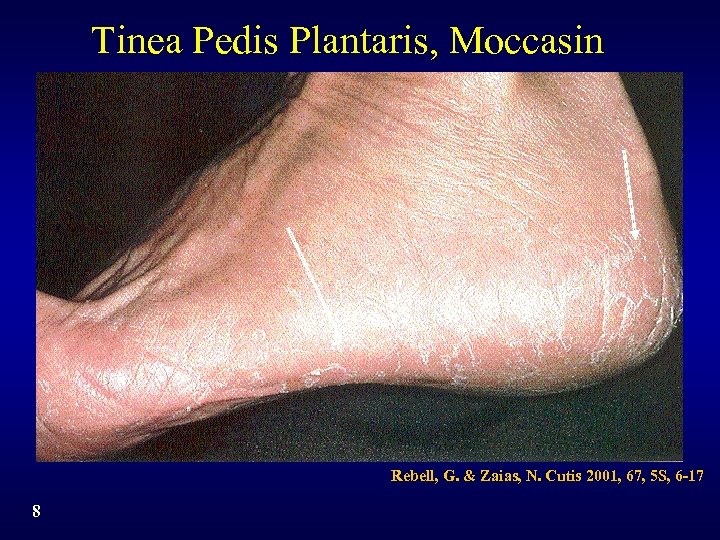 Tinea Pedis Plantaris, Moccasin Rebell, G. & Zaias, N. Cutis 2001, 67, 5 S, 6 -17 8
Tinea Pedis Plantaris, Moccasin Rebell, G. & Zaias, N. Cutis 2001, 67, 5 S, 6 -17 8
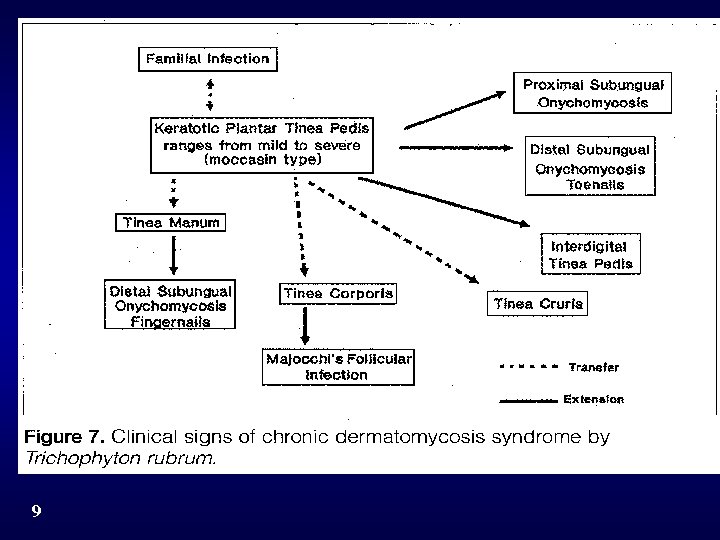 Rebell, G. & Zaias, N. Cutis 2001, 67, 5 S, 6 -17 9
Rebell, G. & Zaias, N. Cutis 2001, 67, 5 S, 6 -17 9
 Predisposing Factors • • • 10 Closed communities: army barracks, boarding schools Public baths, swimming pools Local trauma on dermatophyte carrying individual Occlusive footgear Immersion Warm weather Exposure to hair of infected animals (rats in Vietnam) Infected family members (~17% in one study) Familial predisposition
Predisposing Factors • • • 10 Closed communities: army barracks, boarding schools Public baths, swimming pools Local trauma on dermatophyte carrying individual Occlusive footgear Immersion Warm weather Exposure to hair of infected animals (rats in Vietnam) Infected family members (~17% in one study) Familial predisposition
 Complicating Factors: • Immunosuppression • Atopy • Diabetes • Compromised circulation • Localized trauma • Geriatric population 11
Complicating Factors: • Immunosuppression • Atopy • Diabetes • Compromised circulation • Localized trauma • Geriatric population 11
 Complications: Cellulitis • Tinea pedis unrecognized • Treatment not given • Treatment is inadequate • Reinfection from the nail 12
Complications: Cellulitis • Tinea pedis unrecognized • Treatment not given • Treatment is inadequate • Reinfection from the nail 12
 Epidemiology • • • 15 -70 % of population at large 40 % of patients attending a general clinic Those seeking help often have nail involvement Many undiagnosed cases Dermatophytes isolated from: - 2 -40% “normal feet” - Public showers - Swimming pools - Shoes and Socks 13
Epidemiology • • • 15 -70 % of population at large 40 % of patients attending a general clinic Those seeking help often have nail involvement Many undiagnosed cases Dermatophytes isolated from: - 2 -40% “normal feet” - Public showers - Swimming pools - Shoes and Socks 13
 Recurrence Topical terbinafine and clotrimazole in interdigital tinea pedis: A multicenter comparison of cure and relapse rates with 1 - and 4 - week treatment regimens. Bergstresser PR et al, JAAD 1993; 28: 648 -51 Long-term outcome of patients with interdigital tinea pedis treated with terbinafine or clotrimazole. Elewski, B. et al. JAAD 1995; 32: 290 -2 14
Recurrence Topical terbinafine and clotrimazole in interdigital tinea pedis: A multicenter comparison of cure and relapse rates with 1 - and 4 - week treatment regimens. Bergstresser PR et al, JAAD 1993; 28: 648 -51 Long-term outcome of patients with interdigital tinea pedis treated with terbinafine or clotrimazole. Elewski, B. et al. JAAD 1995; 32: 290 -2 14
 Study Details • 193 evaluable patients with interdigital tinea pedis • Treatment twice daily with: -terbinafine cr or clotrimazole cr -1 or 4 weeks Observation for up to 18 months [Elewski] • Mycology “Cure” 15
Study Details • 193 evaluable patients with interdigital tinea pedis • Treatment twice daily with: -terbinafine cr or clotrimazole cr -1 or 4 weeks Observation for up to 18 months [Elewski] • Mycology “Cure” 15
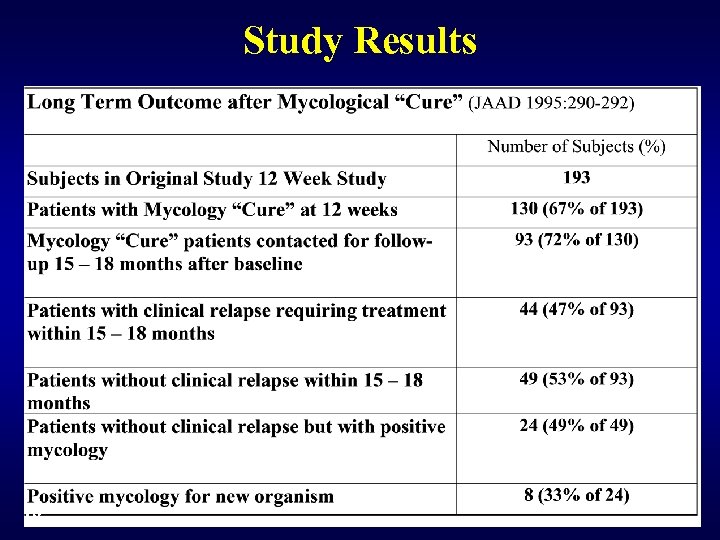 Study Results 16
Study Results 16
 Diagnosis • Clinical: by clinical signs and symptoms • Mycology: KOH (direct examination) and culture. • Mycology [KOH] helps confirm diagnosis and avoid: - Delay of indicated treatment - Prescribing inappropriate treatment 17
Diagnosis • Clinical: by clinical signs and symptoms • Mycology: KOH (direct examination) and culture. • Mycology [KOH] helps confirm diagnosis and avoid: - Delay of indicated treatment - Prescribing inappropriate treatment 17
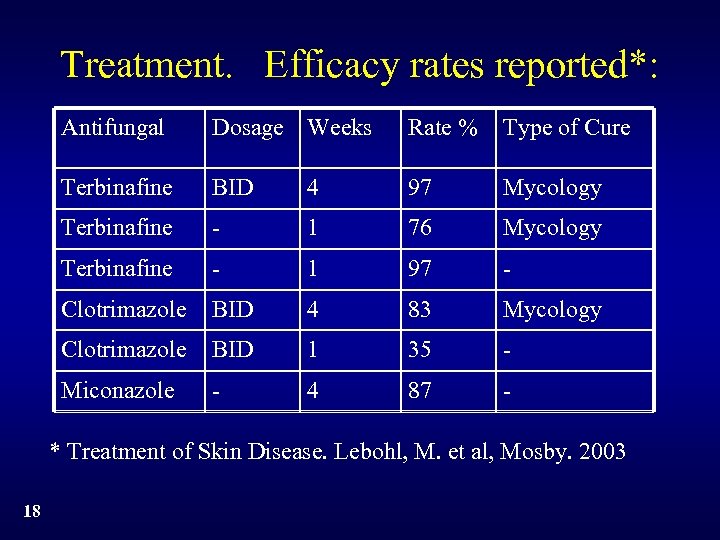 Treatment. Efficacy rates reported*: Antifungal Dosage Weeks Rate % Type of Cure Terbinafine BID 4 97 Mycology Terbinafine - 1 76 Mycology Terbinafine - 1 97 - Clotrimazole BID 4 83 Mycology Clotrimazole BID 1 35 - Miconazole - 4 87 - * Treatment of Skin Disease. Lebohl, M. et al, Mosby. 2003 18
Treatment. Efficacy rates reported*: Antifungal Dosage Weeks Rate % Type of Cure Terbinafine BID 4 97 Mycology Terbinafine - 1 76 Mycology Terbinafine - 1 97 - Clotrimazole BID 4 83 Mycology Clotrimazole BID 1 35 - Miconazole - 4 87 - * Treatment of Skin Disease. Lebohl, M. et al, Mosby. 2003 18
 Part II: Clinical Trials • Dose ranging studies • Clinical trials for safety and efficacy 19
Part II: Clinical Trials • Dose ranging studies • Clinical trials for safety and efficacy 19
 Dose Ranging Studies For Tinea Pedis • Dose ranging studies for topical antifungals often recommended by FDA but usually not conducted • Dose ranging studies for topical antifungals to select the best safety/efficacy dose: -Drug strength -Frequency of application -Duration of treatment 20
Dose Ranging Studies For Tinea Pedis • Dose ranging studies for topical antifungals often recommended by FDA but usually not conducted • Dose ranging studies for topical antifungals to select the best safety/efficacy dose: -Drug strength -Frequency of application -Duration of treatment 20
 Clinical Safety and Efficacy Trials • Assessment • Outcomes 21
Clinical Safety and Efficacy Trials • Assessment • Outcomes 21
 Assessment • Mycology: -Direct microscopic examination (KOH) -Mycology culture • Clinical. Signs and symptoms: -Erythema -Scaling -Pruritus, etc. 22
Assessment • Mycology: -Direct microscopic examination (KOH) -Mycology culture • Clinical. Signs and symptoms: -Erythema -Scaling -Pruritus, etc. 22
 Outcomes • Mycology “Cure” (MC): • Negative KOH and negative culture • Effective treatment: • MC, no symptoms, only residual signs • Complete Cure: • MC, and no signs or symptoms 23
Outcomes • Mycology “Cure” (MC): • Negative KOH and negative culture • Effective treatment: • MC, no symptoms, only residual signs • Complete Cure: • MC, and no signs or symptoms 23
 Clinical Safety and Efficay Studies Inclusion/exclusion criteria often do not mimic the populations expected to actually use the product • Include: healthy patients with interdigital tinea pedis • Exclude harder cases: -Onychomycosis -Mocassin type, keratotic feet -Diabetic -Immunosuppressed -Compromised circulation 24
Clinical Safety and Efficay Studies Inclusion/exclusion criteria often do not mimic the populations expected to actually use the product • Include: healthy patients with interdigital tinea pedis • Exclude harder cases: -Onychomycosis -Mocassin type, keratotic feet -Diabetic -Immunosuppressed -Compromised circulation 24


