7aaaf754b4baf705cffbeb1d9470bd92.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50
 TILSA Alignment Tool Dissemination Workshop July 25 and 26, 2005 WYNDHAM Hotel Boston, Massachusetts Funded by the U. S. Department of Education through a contract to the state of Oklahoma and subcontracts to CCSSO, WCER, Hum. RRO, and Tindal.
TILSA Alignment Tool Dissemination Workshop July 25 and 26, 2005 WYNDHAM Hotel Boston, Massachusetts Funded by the U. S. Department of Education through a contract to the state of Oklahoma and subcontracts to CCSSO, WCER, Hum. RRO, and Tindal.
 Alignment Powerful Tool for Focusing Instruction, Curricula, and Assessment
Alignment Powerful Tool for Focusing Instruction, Curricula, and Assessment
 Agenda July 25, 2005 8: 30 to Noon Speakers: Norman L. Webb Lauress L. Wise Gerald Tindal Noon Lunch 1: 00 to 5: 00 PM Concurrent sessions Session A: Using the WAT Session B: Interpreting reports and coordinating an alignment study
Agenda July 25, 2005 8: 30 to Noon Speakers: Norman L. Webb Lauress L. Wise Gerald Tindal Noon Lunch 1: 00 to 5: 00 PM Concurrent sessions Session A: Using the WAT Session B: Interpreting reports and coordinating an alignment study
 Agenda July 26, 2005 8: 30 to 12: 30 PM Concurrent sessions Session A: Using the WAT Session B: Interpreting reports and coordinating an alignment study 12: 30 Lunch 1: 30 to 3: 00 Plenary Technical issues with the CD alignment system General questions and closing
Agenda July 26, 2005 8: 30 to 12: 30 PM Concurrent sessions Session A: Using the WAT Session B: Interpreting reports and coordinating an alignment study 12: 30 Lunch 1: 30 to 3: 00 Plenary Technical issues with the CD alignment system General questions and closing
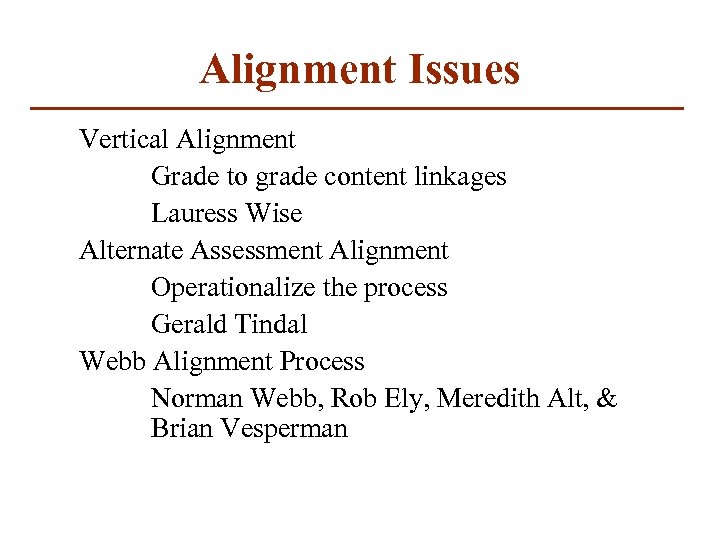 Alignment Issues Vertical Alignment Grade to grade content linkages Lauress Wise Alternate Assessment Alignment Operationalize the process Gerald Tindal Webb Alignment Process Norman Webb, Rob Ely, Meredith Alt, & Brian Vesperman
Alignment Issues Vertical Alignment Grade to grade content linkages Lauress Wise Alternate Assessment Alignment Operationalize the process Gerald Tindal Webb Alignment Process Norman Webb, Rob Ely, Meredith Alt, & Brian Vesperman
 Workshop Expectations Set up of an alignment study Responsibilities of a group leader Responsibilities of reviewers Coding procedures Special features How to conduct an alignment analysis of standards and assessments with the WAT
Workshop Expectations Set up of an alignment study Responsibilities of a group leader Responsibilities of reviewers Coding procedures Special features How to conduct an alignment analysis of standards and assessments with the WAT
 Alignment The degree to which expectations and assessments are in agreement and serve in conjunction with one another to guide the system toward students learning what is expected.
Alignment The degree to which expectations and assessments are in agreement and serve in conjunction with one another to guide the system toward students learning what is expected.
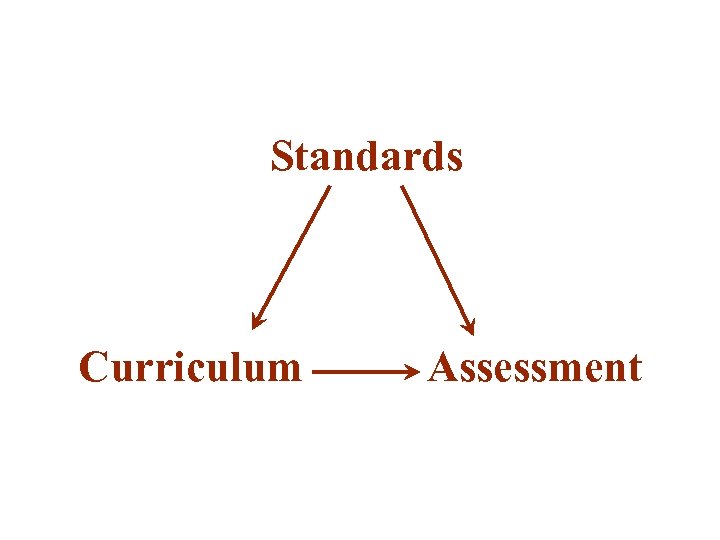 Standards Curriculum Assessment
Standards Curriculum Assessment
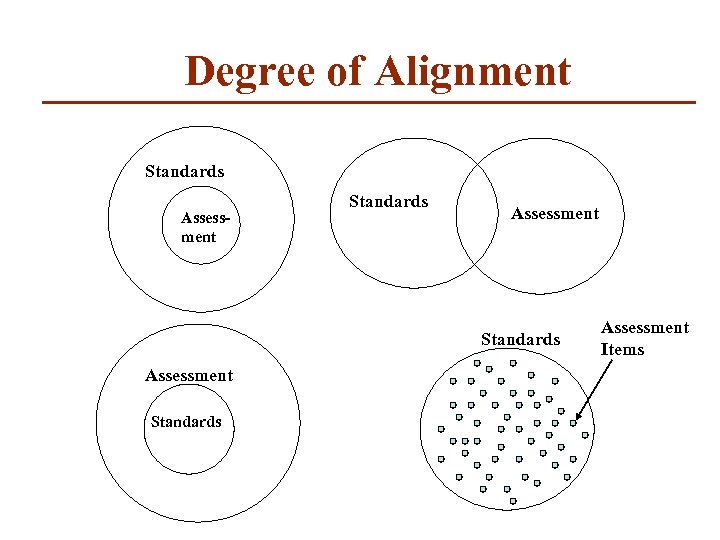 Degree of Alignment Standards Assessment Items
Degree of Alignment Standards Assessment Items
 Alignment Process • Identify Standards and Assessments • Select 6 -8 Reviewers (Content Experts) • Train Reviewers on DOK Levels • Part I: Code DOK Levels of the • Standards/Objectives Part II: Code DOK Levels and Corresponding Objectives of Assessment Items
Alignment Process • Identify Standards and Assessments • Select 6 -8 Reviewers (Content Experts) • Train Reviewers on DOK Levels • Part I: Code DOK Levels of the • Standards/Objectives Part II: Code DOK Levels and Corresponding Objectives of Assessment Items
 Specific Criteria Content Focus A. Categorical Concurrence B. Depth-of-Knowledge Consistency C. Range-of-Knowledge Correspondence D. Balance of Representation and Source of Challenge
Specific Criteria Content Focus A. Categorical Concurrence B. Depth-of-Knowledge Consistency C. Range-of-Knowledge Correspondence D. Balance of Representation and Source of Challenge
 Depth of Knowledge Level 1 Recall of a fact, information, or procedure. Level 2 Skill/Concept Use information or conceptual knowledge, two or more steps, etc. Level 3 Strategic Thinking Requires reasoning, developing plan or a sequence of steps, some complexity, more than one possible answer. Level 4 Extended Thinking Requires an investigation, time to think and process multiple conditions of the problem.
Depth of Knowledge Level 1 Recall of a fact, information, or procedure. Level 2 Skill/Concept Use information or conceptual knowledge, two or more steps, etc. Level 3 Strategic Thinking Requires reasoning, developing plan or a sequence of steps, some complexity, more than one possible answer. Level 4 Extended Thinking Requires an investigation, time to think and process multiple conditions of the problem.
 Items by Objectives Report Lo w Medium High 0 5. 20202 48 root I 1 7 8 1 9 3 8 4 5 1. 1. 2 2 7 7 7 7 8 1 9 3 8 3 8 4 5 1. 2. 1 9 1 9 2 9 3 2 3 2 3 2 4 0 4 3 1. 3. 2 9 3 6 3 8 4 5 1. 4. 2 5 3 5 3 5 4 1 1. 5. 2 2 7 8 8 1 0 2 5 1 0 8 8 1 0 1 0 4 3 4 5 4 5 2 5 2 9 3 6 4 1 4 5 1 9 1 9
Items by Objectives Report Lo w Medium High 0 5. 20202 48 root I 1 7 8 1 9 3 8 4 5 1. 1. 2 2 7 7 7 7 8 1 9 3 8 3 8 4 5 1. 2. 1 9 1 9 2 9 3 2 3 2 3 2 4 0 4 3 1. 3. 2 9 3 6 3 8 4 5 1. 4. 2 5 3 5 3 5 4 1 1. 5. 2 2 7 8 8 1 0 2 5 1 0 8 8 1 0 1 0 4 3 4 5 4 5 2 5 2 9 3 6 4 1 4 5 1 9 1 9
 What alignment is good enough?
What alignment is good enough?
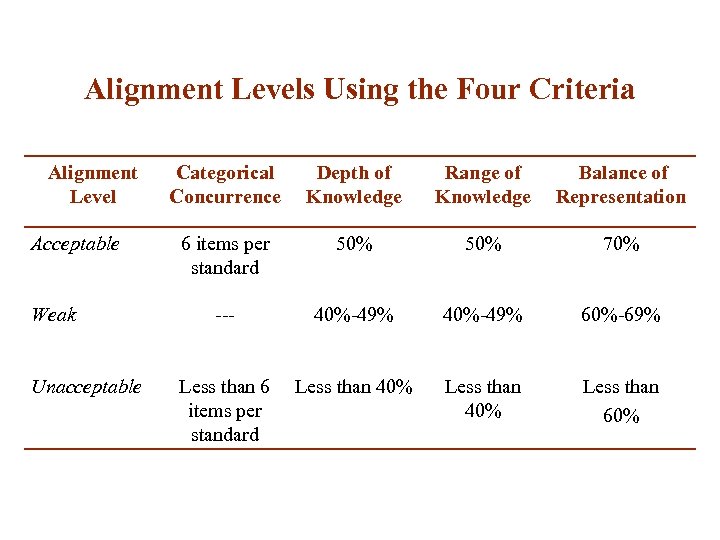 Alignment Levels Using the Four Criteria Alignment Level Acceptable Weak Unacceptable Categorical Concurrence Depth of Knowledge Range of Knowledge Balance of Representation 6 items per standard 50% 70% --- 40%-49% 60%-69% Less than 40% Less than 6 Less than 40% items per standard
Alignment Levels Using the Four Criteria Alignment Level Acceptable Weak Unacceptable Categorical Concurrence Depth of Knowledge Range of Knowledge Balance of Representation 6 items per standard 50% 70% --- 40%-49% 60%-69% Less than 40% Less than 6 Less than 40% items per standard
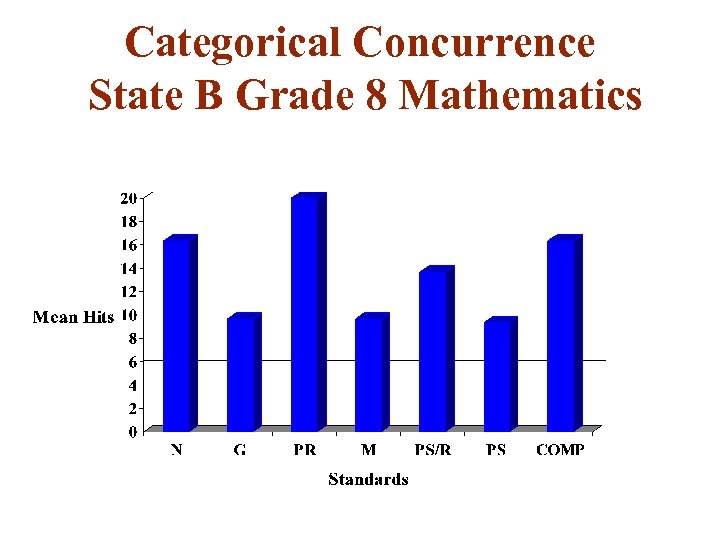 Categorical Concurrence State B Grade 8 Mathematics
Categorical Concurrence State B Grade 8 Mathematics
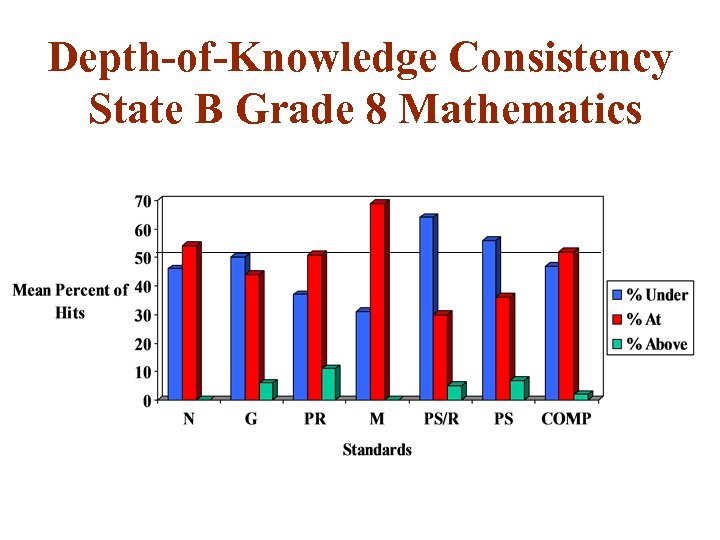 Depth-of-Knowledge Consistency State B Grade 8 Mathematics
Depth-of-Knowledge Consistency State B Grade 8 Mathematics
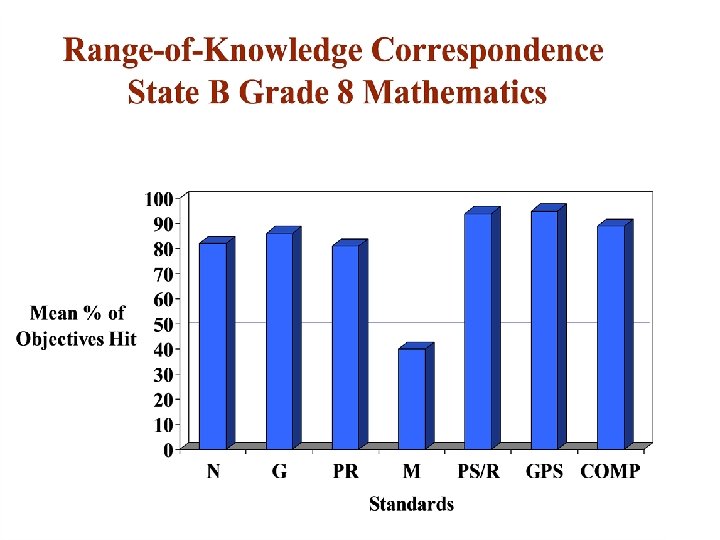
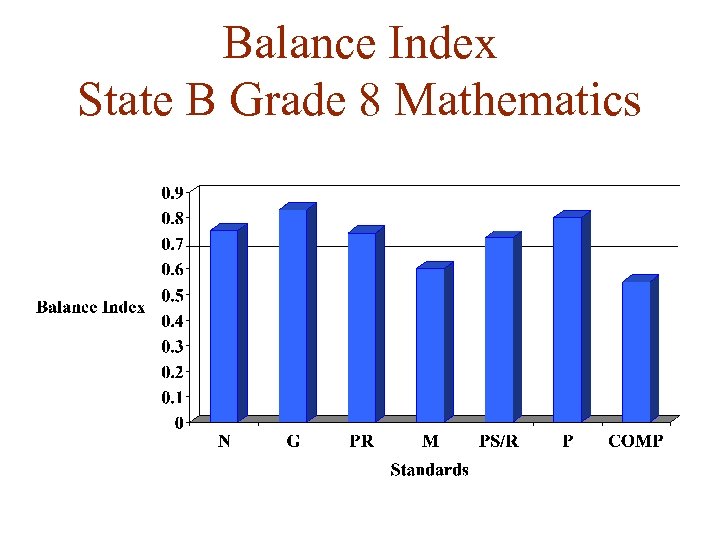 Balance Index State B Grade 8 Mathematics
Balance Index State B Grade 8 Mathematics
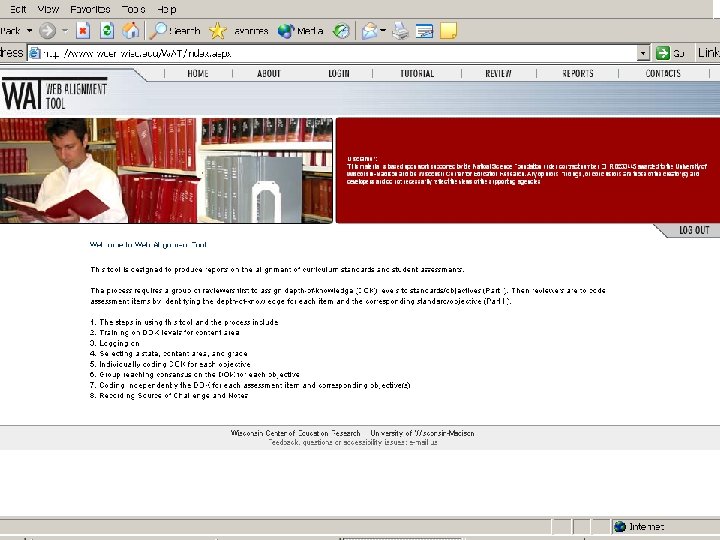
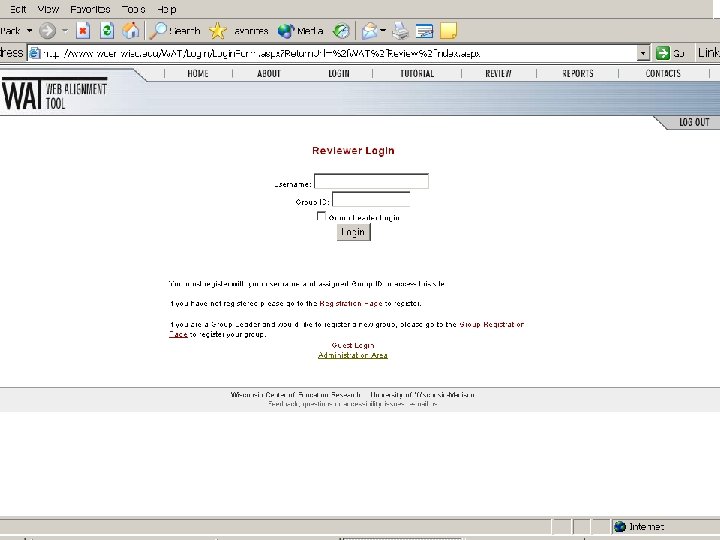
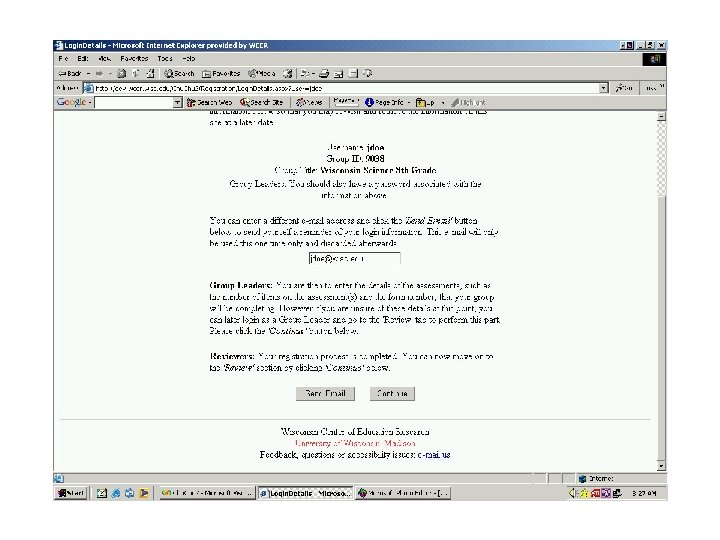
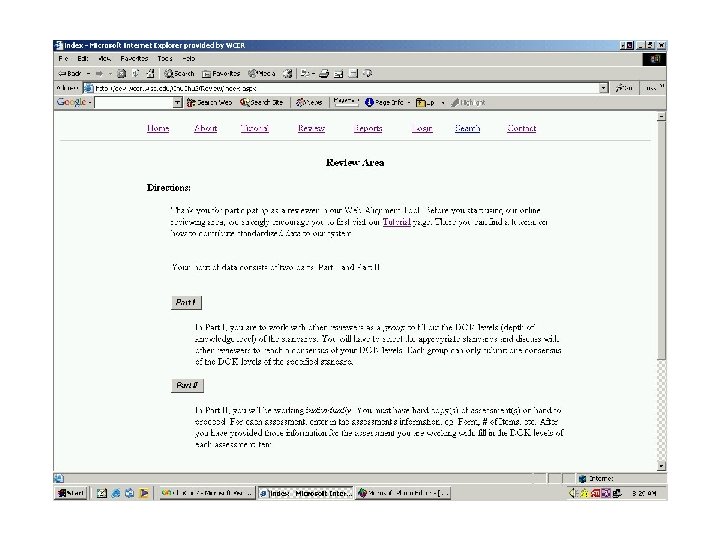
 Coding Process Tips • One Primary Objective and up to Two Secondary Objectives (if necessary) • Source of Challenge (a correct/incorrect response for the wrong reason) • Notes (any insights to share) • Consider Full Range of Standards • Use generic objectives sparingly
Coding Process Tips • One Primary Objective and up to Two Secondary Objectives (if necessary) • Source of Challenge (a correct/incorrect response for the wrong reason) • Notes (any insights to share) • Consider Full Range of Standards • Use generic objectives sparingly
 Structure of the Automated Alignment Process Registration Group Leader Reviewers Standards/Goals/Objectives Entry Process Training on Depth-of-Knowledge Levels Phase I Consensus Process on Assigning DOK Levels to Objectives Phase II Coding of Assessment Tasks Phase III Analysis of Coding Phase IV Reporting
Structure of the Automated Alignment Process Registration Group Leader Reviewers Standards/Goals/Objectives Entry Process Training on Depth-of-Knowledge Levels Phase I Consensus Process on Assigning DOK Levels to Objectives Phase II Coding of Assessment Tasks Phase III Analysis of Coding Phase IV Reporting
 Web Sites http: //facstaff. wcer. wisc. edu/normw/ Alignment Tool http: //www. wcer. wisc. edu/WAT/index. aspx Survey of the Enacted Curriculum http: //www. SECsurvey. org
Web Sites http: //facstaff. wcer. wisc. edu/normw/ Alignment Tool http: //www. wcer. wisc. edu/WAT/index. aspx Survey of the Enacted Curriculum http: //www. SECsurvey. org
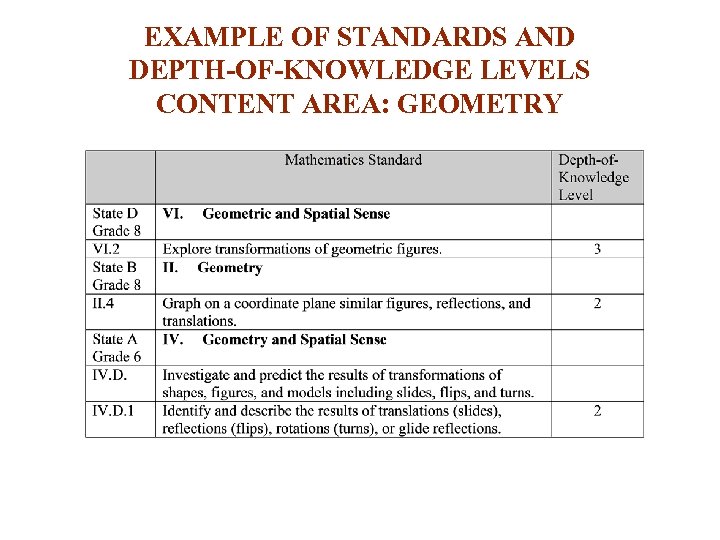 EXAMPLE OF STANDARDS AND DEPTH-OF-KNOWLEDGE LEVELS CONTENT AREA: GEOMETRY
EXAMPLE OF STANDARDS AND DEPTH-OF-KNOWLEDGE LEVELS CONTENT AREA: GEOMETRY
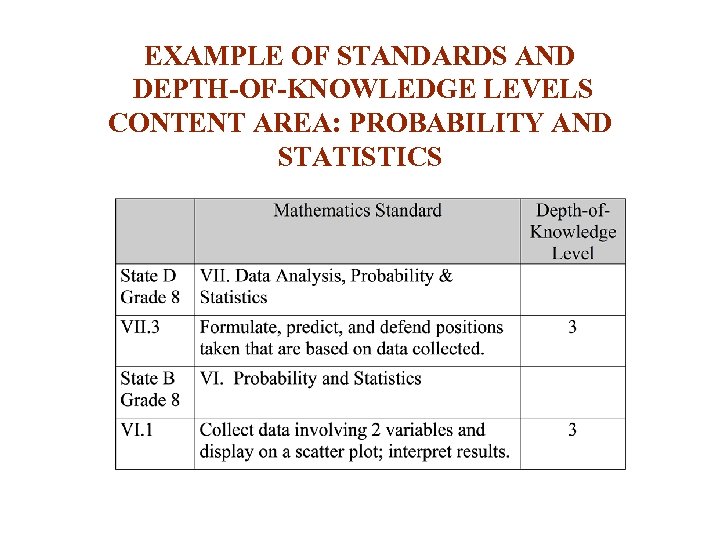 EXAMPLE OF STANDARDS AND DEPTH-OF-KNOWLEDGE LEVELS CONTENT AREA: PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS
EXAMPLE OF STANDARDS AND DEPTH-OF-KNOWLEDGE LEVELS CONTENT AREA: PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS





 New Cubes Your school is planning a casino night to raise funds to construct a wall aquarium in your school. As a mathematics student, you are given the job of developing a dice game for this event. A regular pair of “number dice” consists of two cubes, each with its faces numbered 1 through 6. Often, dice games are played by rolling the two dice and then finding the sum of the two numbers turned upward. 1. Show that, with a regular pair of number dice, the probability of rolling a sum of 7 is greater than the probability of rolling any other sum.
New Cubes Your school is planning a casino night to raise funds to construct a wall aquarium in your school. As a mathematics student, you are given the job of developing a dice game for this event. A regular pair of “number dice” consists of two cubes, each with its faces numbered 1 through 6. Often, dice games are played by rolling the two dice and then finding the sum of the two numbers turned upward. 1. Show that, with a regular pair of number dice, the probability of rolling a sum of 7 is greater than the probability of rolling any other sum.

 Coordination of an Alignment Institute Identify • Content areas • Grade levels • Number of test forms • Number of reviewers • Computer facilities • Standards and their structure
Coordination of an Alignment Institute Identify • Content areas • Grade levels • Number of test forms • Number of reviewers • Computer facilities • Standards and their structure
 Coordination of an Alignment Institute Ask if • Tests include field test items • Items have different point values • Alternate assessments will be included • English Language Learners will be included
Coordination of an Alignment Institute Ask if • Tests include field test items • Items have different point values • Alternate assessments will be included • English Language Learners will be included
 WAT Adoption to State Needs • • Assessment development (front end alignment) District and local assessments Test to test comparison analysis Curriculum to standard analysis
WAT Adoption to State Needs • • Assessment development (front end alignment) District and local assessments Test to test comparison analysis Curriculum to standard analysis
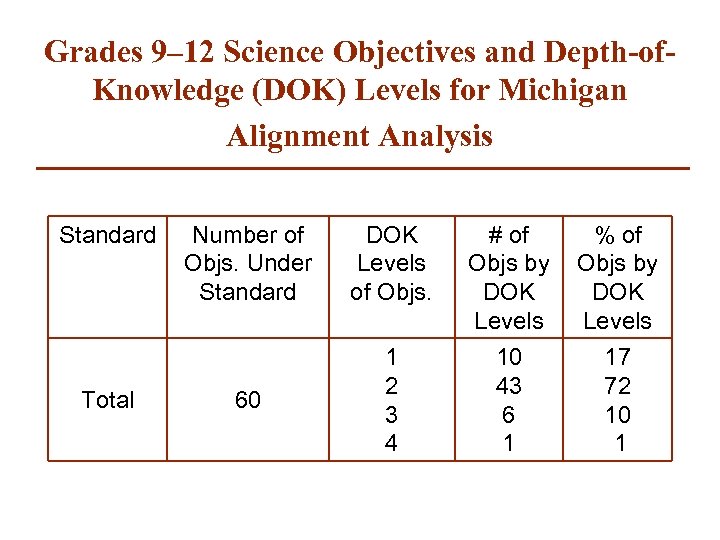 Grades 9– 12 Science Objectives and Depth-of. Knowledge (DOK) Levels for Michigan Alignment Analysis Standard Total Number of Objs. Under Standard DOK Levels of Objs. # of Objs by DOK Levels % of Objs by DOK Levels 60 1 2 3 4 10 43 6 1 17 72 10 1
Grades 9– 12 Science Objectives and Depth-of. Knowledge (DOK) Levels for Michigan Alignment Analysis Standard Total Number of Objs. Under Standard DOK Levels of Objs. # of Objs by DOK Levels % of Objs by DOK Levels 60 1 2 3 4 10 43 6 1 17 72 10 1
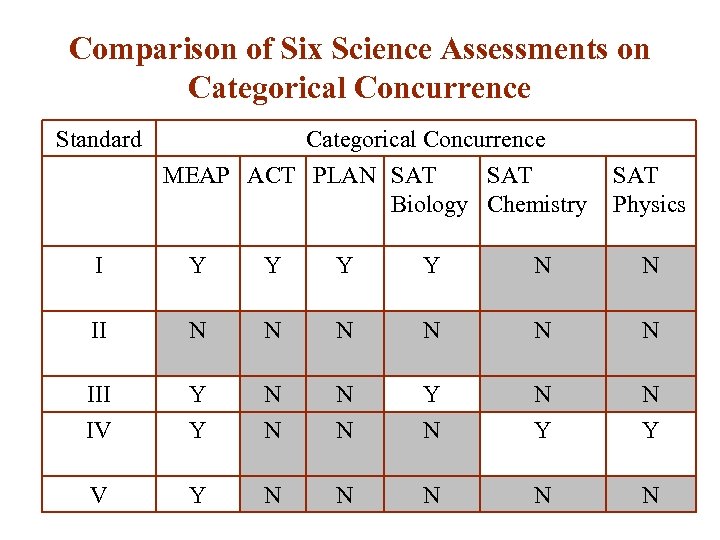 Comparison of Six Science Assessments on Categorical Concurrence Standard Categorical Concurrence MEAP ACT PLAN SAT Biology Chemistry SAT Physics I II Y Y N N N N III IV Y Y Y N N Y N N N V
Comparison of Six Science Assessments on Categorical Concurrence Standard Categorical Concurrence MEAP ACT PLAN SAT Biology Chemistry SAT Physics I II Y Y N N N N III IV Y Y Y N N Y N N N V
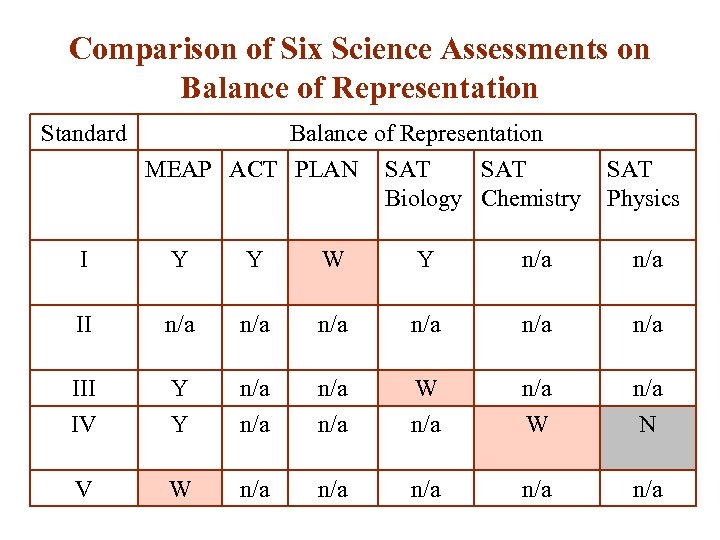 Comparison of Six Science Assessments on Balance of Representation Standard Balance of Representation MEAP ACT PLAN I III IV V SAT Biology Chemistry SAT Physics Y Y W Y n/a n/a Y Y W n/a n/a W n/a N n/a n/a n/a
Comparison of Six Science Assessments on Balance of Representation Standard Balance of Representation MEAP ACT PLAN I III IV V SAT Biology Chemistry SAT Physics Y Y W Y n/a n/a Y Y W n/a n/a W n/a N n/a n/a n/a
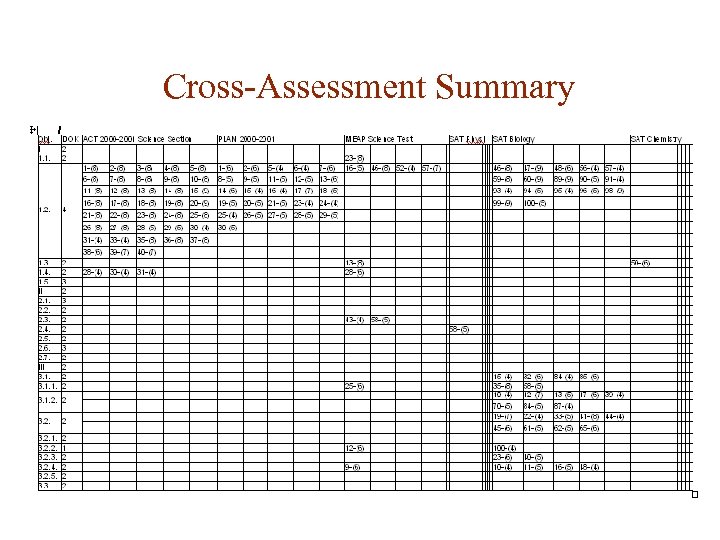 Cross-Assessment Summary
Cross-Assessment Summary
 Three Analytic Methods • Common Framework • Expert Consensus • Common Criteria
Three Analytic Methods • Common Framework • Expert Consensus • Common Criteria
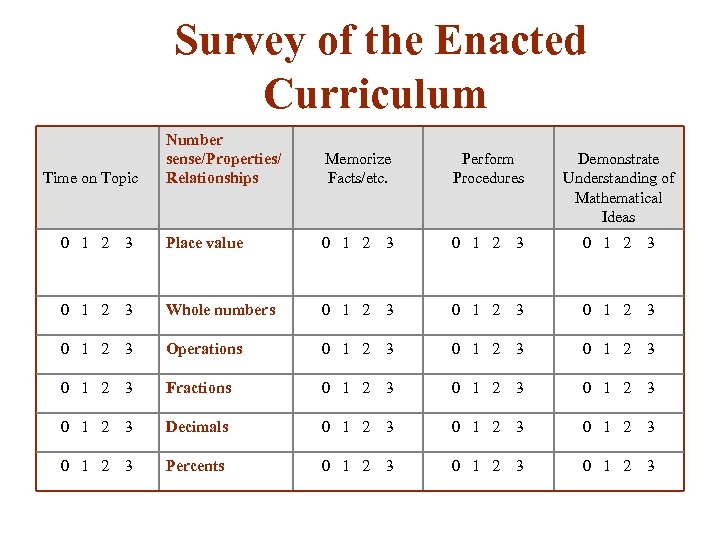 Survey of the Enacted Curriculum Number sense/Properties/ Relationships Memorize Facts/etc. Perform Procedures Demonstrate Understanding of Mathematical Ideas 0 1 2 3 Place value 0 1 2 3 Whole numbers 0 1 2 3 Operations 0 1 2 3 Fractions 0 1 2 3 Decimals 0 1 2 3 Percents 0 1 2 3 Time on Topic
Survey of the Enacted Curriculum Number sense/Properties/ Relationships Memorize Facts/etc. Perform Procedures Demonstrate Understanding of Mathematical Ideas 0 1 2 3 Place value 0 1 2 3 Whole numbers 0 1 2 3 Operations 0 1 2 3 Fractions 0 1 2 3 Decimals 0 1 2 3 Percents 0 1 2 3 Time on Topic
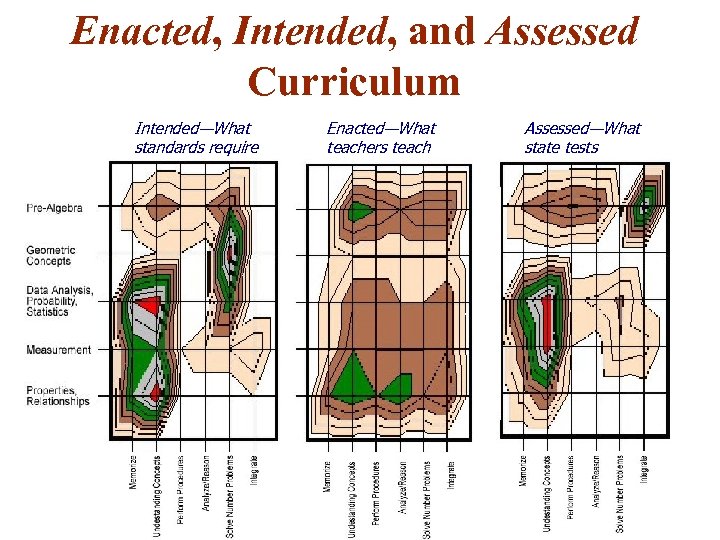 Enacted, Intended, and Assessed Curriculum Intended—What standards require Enacted—What teachers teach Assessed—What state tests
Enacted, Intended, and Assessed Curriculum Intended—What standards require Enacted—What teachers teach Assessed—What state tests
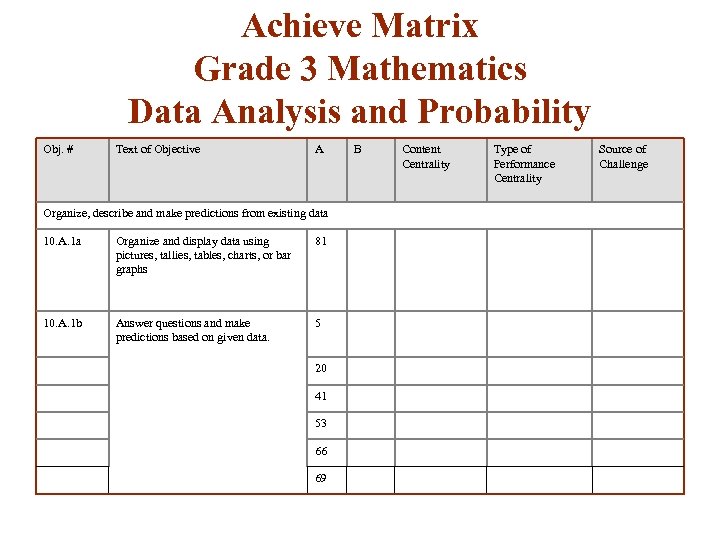 Achieve Matrix Grade 3 Mathematics Data Analysis and Probability Obj. # Text of Objective A B Content Centrality Type of Performance Centrality Source of Challenge Organize, describe and make predictions from existing data 10. A. 1 a Organize and display data using pictures, tallies, tables, charts, or bar graphs 81 10. A. 1 b Answer questions and make predictions based on given data. 5 20 41 53 66 69
Achieve Matrix Grade 3 Mathematics Data Analysis and Probability Obj. # Text of Objective A B Content Centrality Type of Performance Centrality Source of Challenge Organize, describe and make predictions from existing data 10. A. 1 a Organize and display data using pictures, tallies, tables, charts, or bar graphs 81 10. A. 1 b Answer questions and make predictions based on given data. 5 20 41 53 66 69
 Achieve Alignment Criteria Item-Standard Match • Content Centrality • Performance Centrality • Source of Challenge Instrument-Standard Match • Level of Challenge • Balance • Range
Achieve Alignment Criteria Item-Standard Match • Content Centrality • Performance Centrality • Source of Challenge Instrument-Standard Match • Level of Challenge • Balance • Range
 Alignment Process • Identify Standards and Assessments • Select 6 -8 Reviewers (Content Experts) • Train Reviewers on DOK Levels • Part I: Code DOK Levels of the • Standards/Objectives Part II: Code DOK Levels and Corresponding Objectives of Assessment Items
Alignment Process • Identify Standards and Assessments • Select 6 -8 Reviewers (Content Experts) • Train Reviewers on DOK Levels • Part I: Code DOK Levels of the • Standards/Objectives Part II: Code DOK Levels and Corresponding Objectives of Assessment Items


