458ef325318b0bdee3b3716ec18e4dbb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 68
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Tier 2 Use of computer as a simulation tool PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 1
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Tier 2 Use of computer as a simulation tool PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 1
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Statement of intent Use of computer as simulation tool It contain a series of closed problems with their solution. It is explained the assumption made, and the methods apply to solve them. ü To review the process to create a simulation flowsheet. ü To give the student some tips to simulate. ü To run some simulations in a computer. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 2
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Statement of intent Use of computer as simulation tool It contain a series of closed problems with their solution. It is explained the assumption made, and the methods apply to solve them. ü To review the process to create a simulation flowsheet. ü To give the student some tips to simulate. ü To run some simulations in a computer. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 2
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Contents Table of content Ø Solving closed problem. Ø Resolution of problems with a spreadsheet (excel). Ø Using advance mathematic software (matlab). Ø Separation NH 4 – H 20 using specialize software (aspen tech). Ø Using tools optimization. PAPRICAN as sensitivity ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE analysis and UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 3
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Contents Table of content Ø Solving closed problem. Ø Resolution of problems with a spreadsheet (excel). Ø Using advance mathematic software (matlab). Ø Separation NH 4 – H 20 using specialize software (aspen tech). Ø Using tools optimization. PAPRICAN as sensitivity ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE analysis and UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 3
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Solving Closed problem PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 4
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Solving Closed problem PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 4
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Closed Problems Closed problems are the type with only one right answer. These are the same types of problems that are usually found at the end of chapters in text books, and they reinforce concepts learned in the corresponding chapters. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 5
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Closed Problems Closed problems are the type with only one right answer. These are the same types of problems that are usually found at the end of chapters in text books, and they reinforce concepts learned in the corresponding chapters. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 5
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Algorithm 1. Write out the problem statement. 2. Draw and label a sketch. 3. List assumptions and approximations involved in solving the problem. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 6
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Algorithm 1. Write out the problem statement. 2. Draw and label a sketch. 3. List assumptions and approximations involved in solving the problem. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 6
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION Closed problems PIECE Algorithm 4. Check to see if the problem is either under – specified or over – specified. 5. Relate problem to a problem or experience. 6. Develop, derive, integrate or manipulate an equation from which the desired variable can be determined. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE similar UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 7
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION Closed problems PIECE Algorithm 4. Check to see if the problem is either under – specified or over – specified. 5. Relate problem to a problem or experience. 6. Develop, derive, integrate or manipulate an equation from which the desired variable can be determined. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE similar UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 7
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Algorithm 7. Substitute numerical values and calculate the desired variable. 8. Examine and evaluate the answer to see it makes sense. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 8
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Algorithm 7. Substitute numerical values and calculate the desired variable. 8. Examine and evaluate the answer to see it makes sense. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 8
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Some advice when running a simulation 1. Are you designing trays? Pressure drop is important and surface tension plays a key role in pressure drop calculation. 2. Do you have azeotropes? Do you suspect they may exist? Check them out before proposing a modification that will violate the second law of thermodynamics. 3. Trace components should not be brushed aside. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 9
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Some advice when running a simulation 1. Are you designing trays? Pressure drop is important and surface tension plays a key role in pressure drop calculation. 2. Do you have azeotropes? Do you suspect they may exist? Check them out before proposing a modification that will violate the second law of thermodynamics. 3. Trace components should not be brushed aside. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 9
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Some advice when running a simulation 4. Check your pure component and mixture densities. 5. Check your pure-component and mixture enthalpies and heat capacities if you are going to do any calculations related to energy balance. 6. Are you going to design heat exchangers? It is good idea to check your transport properties. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 10
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Some advice when running a simulation 4. Check your pure component and mixture densities. 5. Check your pure-component and mixture enthalpies and heat capacities if you are going to do any calculations related to energy balance. 6. Are you going to design heat exchangers? It is good idea to check your transport properties. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 10
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Some Advice when running a simulation 7. Talk with people. (chemist, vendor, other engineers doing the same). 8. Beware of using estimated parameters and interaction parameters when screening process alternatives. 9. Go see the plant. Plant personnel are usually helpful. Their insight and your knowledge of modeling can form a strong bond for problem solving. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 11
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Some Advice when running a simulation 7. Talk with people. (chemist, vendor, other engineers doing the same). 8. Beware of using estimated parameters and interaction parameters when screening process alternatives. 9. Go see the plant. Plant personnel are usually helpful. Their insight and your knowledge of modeling can form a strong bond for problem solving. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 11
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Some Advice when running a simulation Simulation is a means, not an end, no matter how much effort you put into the model. Once, after finishing a large simulation model with several hundreds of unit operations, one of us had to spend many hours fixing the model, because air leakage into equipment was not taken into account. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 12
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Some Advice when running a simulation Simulation is a means, not an end, no matter how much effort you put into the model. Once, after finishing a large simulation model with several hundreds of unit operations, one of us had to spend many hours fixing the model, because air leakage into equipment was not taken into account. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 12
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Commercial Simulation Software Packages There are many of them, some of them are: ü ü ü ü PAPRICAN Excel (spreadsheet) Matlab (matrix laboratory) Fortran (programming language) Aspen tech Win. GEMS CADSIM plus PAPDYN G 2 (Gensym) IDEAS (Simons) ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 13
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Closed problems Commercial Simulation Software Packages There are many of them, some of them are: ü ü ü ü PAPRICAN Excel (spreadsheet) Matlab (matrix laboratory) Fortran (programming language) Aspen tech Win. GEMS CADSIM plus PAPDYN G 2 (Gensym) IDEAS (Simons) ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 13
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Problem resolution with spreadsheets PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 14
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Problem resolution with spreadsheets PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 14
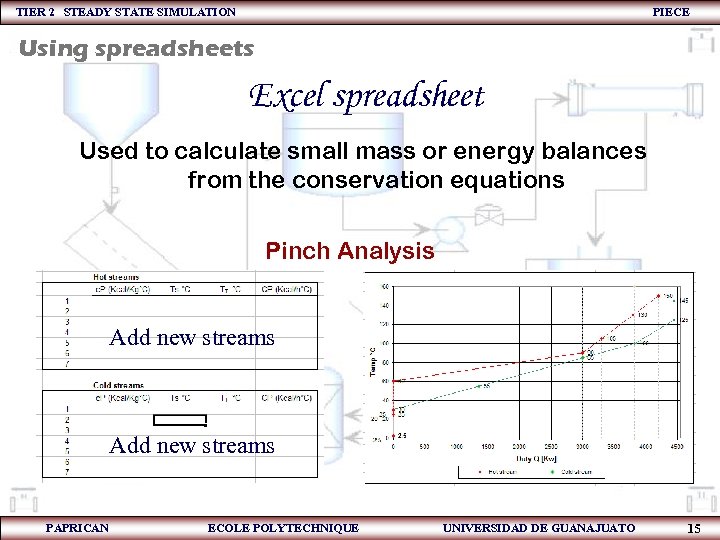 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Using spreadsheets Excel spreadsheet Used to calculate small mass or energy balances from the conservation equations Pinch Analysis Add new streams PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 15
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Using spreadsheets Excel spreadsheet Used to calculate small mass or energy balances from the conservation equations Pinch Analysis Add new streams PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 15
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Solving problems with Advance mathematics software PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 16
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Solving problems with Advance mathematics software PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 16
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Matlab Is a mathematic specialized software, which allows one to make use of complicate equations, with rigorous iterative convergence methods in an easier way. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 17
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Matlab Is a mathematic specialized software, which allows one to make use of complicate equations, with rigorous iterative convergence methods in an easier way. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 17
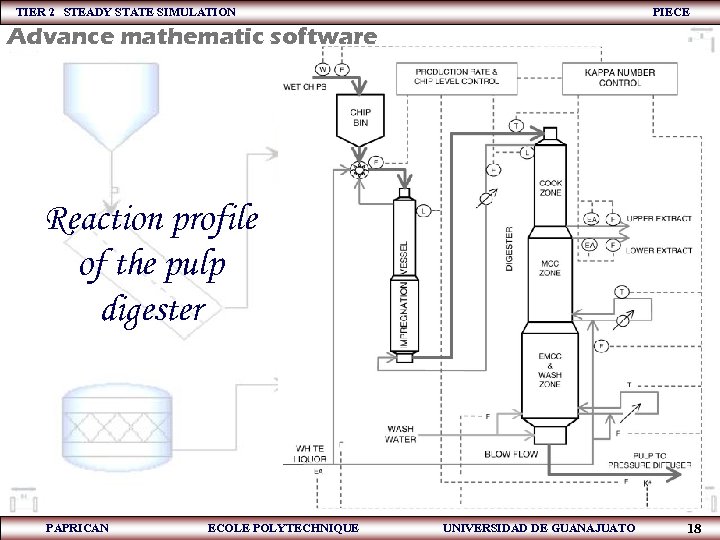 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Reaction profile of the pulp digester PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 18
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Reaction profile of the pulp digester PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 18
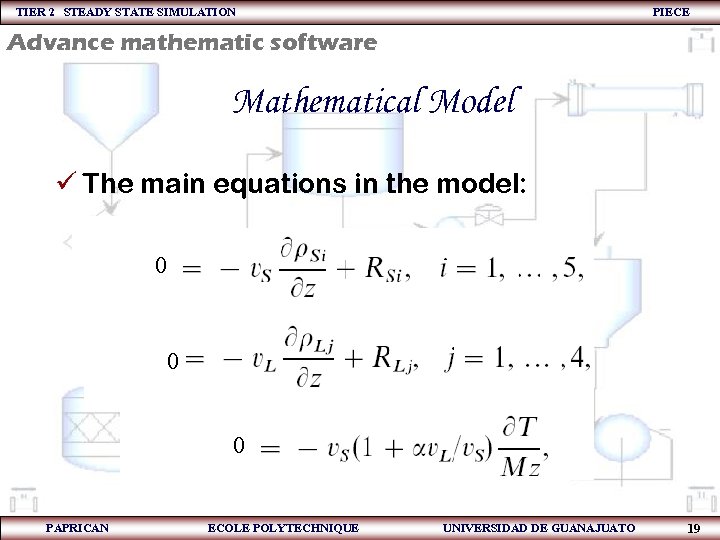 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Mathematical Model ü The main equations in the model: 0 0 0 PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 19
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Mathematical Model ü The main equations in the model: 0 0 0 PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 19
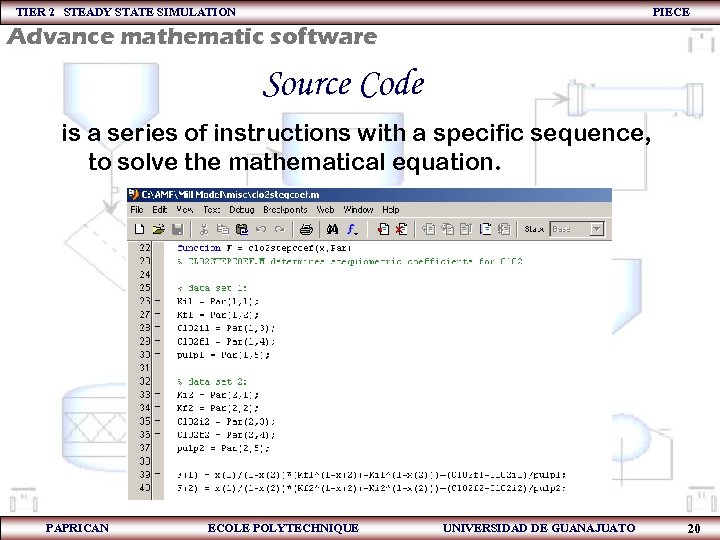 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Source Code is a series of instructions with a specific sequence, to solve the mathematical equation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 20
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Source Code is a series of instructions with a specific sequence, to solve the mathematical equation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 20
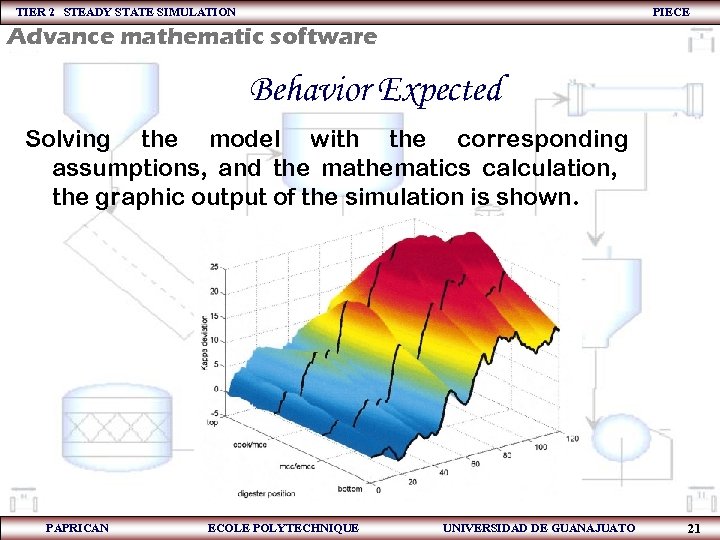 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Behavior Expected Solving the model with the corresponding assumptions, and the mathematics calculation, the graphic output of the simulation is shown. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 21
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Advance mathematic software Behavior Expected Solving the model with the corresponding assumptions, and the mathematics calculation, the graphic output of the simulation is shown. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 21
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Using specialized software to simulate a process PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 22
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Using specialized software to simulate a process PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 22
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Using specialized software What do more advanced simulation package offer? The use of specialized software, allows one to solve complicated problems, using relationships such as mass and energy balances, phase and chemical equilibrium, and reaction kinetics, with thermodynamic data, and rigorous equipment models. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 23
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Using specialized software What do more advanced simulation package offer? The use of specialized software, allows one to solve complicated problems, using relationships such as mass and energy balances, phase and chemical equilibrium, and reaction kinetics, with thermodynamic data, and rigorous equipment models. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 23
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Using specialized software Advantage of specialized software ü Interactive interface. ü Different forms to enter data. ü Verification of incoming data against ranges. ü Check degrees of freedom. ü Sensitivity analysis. ü Optimization capabilities. ü Easy way to display results. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 24
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Using specialized software Advantage of specialized software ü Interactive interface. ü Different forms to enter data. ü Verification of incoming data against ranges. ü Check degrees of freedom. ü Sensitivity analysis. ü Optimization capabilities. ü Easy way to display results. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 24
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Solution of some problems using specialized software Ø NH 4 – H 2 O separation. Ø Sensitivity analysis of C 2 H 5 Cl manufacture. Ø Optimization of C 2 H 5 Cl manufacture. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 25
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Solution of some problems using specialized software Ø NH 4 – H 2 O separation. Ø Sensitivity analysis of C 2 H 5 Cl manufacture. Ø Optimization of C 2 H 5 Cl manufacture. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 25
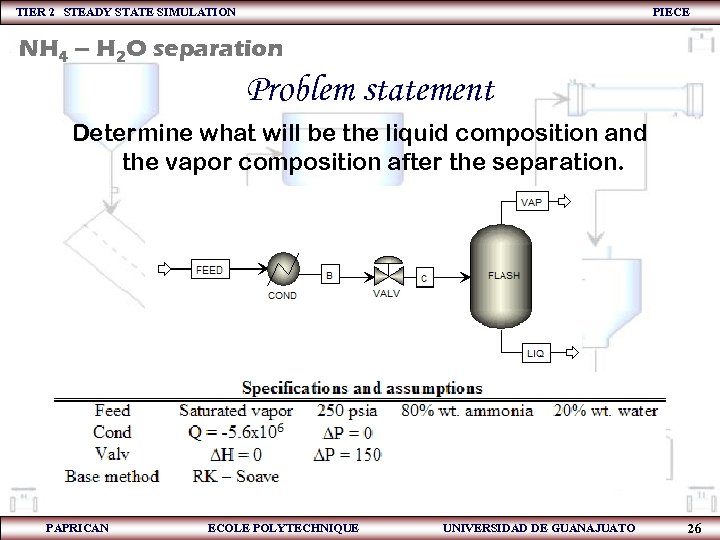 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Problem statement Determine what will be the liquid composition and the vapor composition after the separation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 26
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Problem statement Determine what will be the liquid composition and the vapor composition after the separation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 26
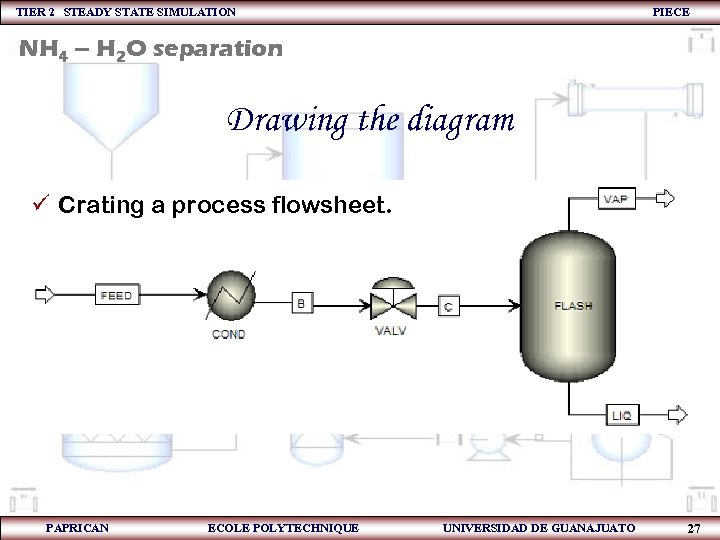 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Drawing the diagram ü Crating a process flowsheet. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 27
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Drawing the diagram ü Crating a process flowsheet. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 27
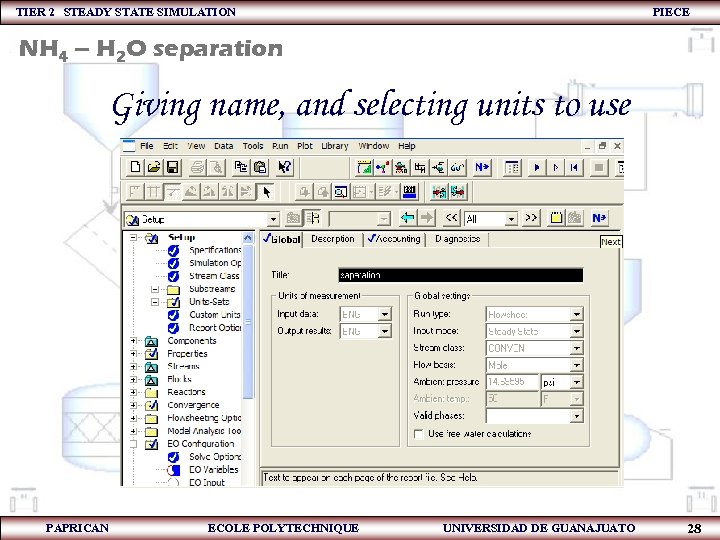 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Giving name, and selecting units to use PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 28
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Giving name, and selecting units to use PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 28
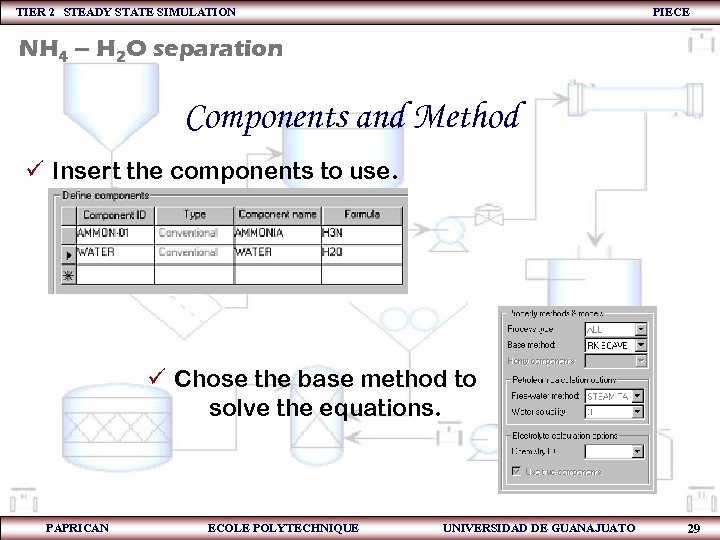 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Components and Method ü Insert the components to use. ü Chose the base method to solve the equations. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 29
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Components and Method ü Insert the components to use. ü Chose the base method to solve the equations. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 29
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation RK-Soave Use this method for non-polar, mildly polar mixtures. This property method is particularly suitable in the high temperature and high pressure regions. It is recommended for gas – processing, refinery, and petrochemical applications. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 30
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation RK-Soave Use this method for non-polar, mildly polar mixtures. This property method is particularly suitable in the high temperature and high pressure regions. It is recommended for gas – processing, refinery, and petrochemical applications. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 30
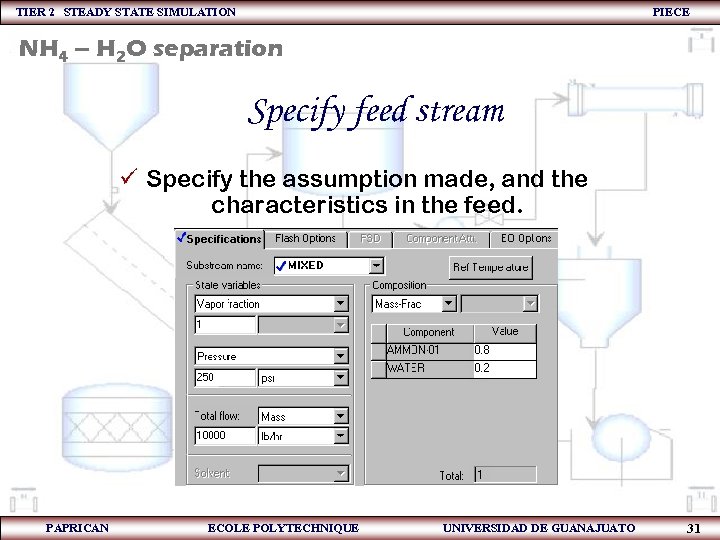 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Specify feed stream ü Specify the assumption made, and the characteristics in the feed. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 31
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Specify feed stream ü Specify the assumption made, and the characteristics in the feed. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 31
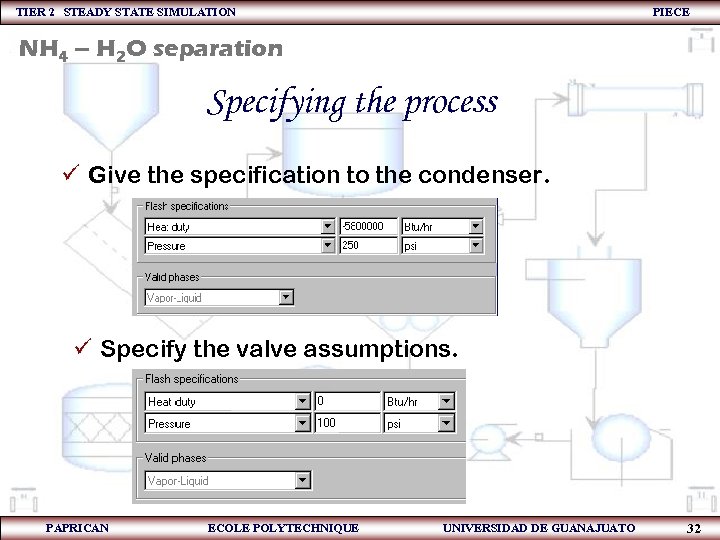 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Specifying the process ü Give the specification to the condenser. ü Specify the valve assumptions. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 32
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Specifying the process ü Give the specification to the condenser. ü Specify the valve assumptions. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 32
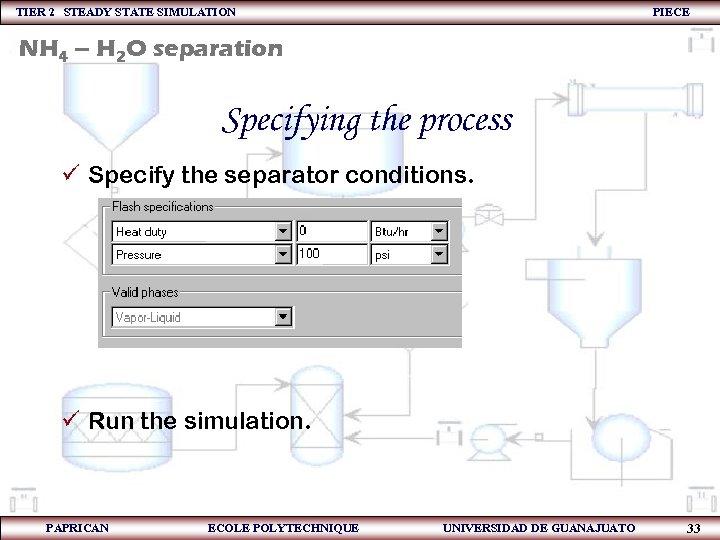 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Specifying the process ü Specify the separator conditions. ü Run the simulation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 33
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Specifying the process ü Specify the separator conditions. ü Run the simulation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 33
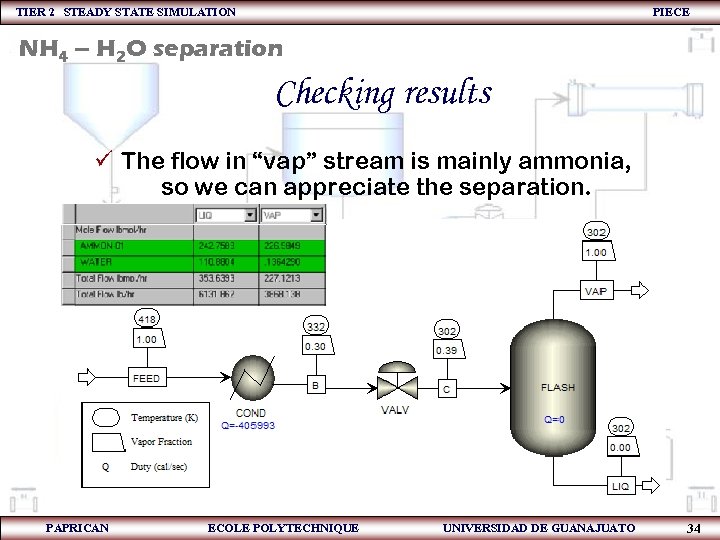 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Checking results ü The flow in “vap” stream is mainly ammonia, so we can appreciate the separation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 34
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation Checking results ü The flow in “vap” stream is mainly ammonia, so we can appreciate the separation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 34
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation What can be done with simulation ü Steady state simulation is useful to predict the behave of a process in the plant. ü What if, situations can be check with simulation. ü Sensitivity analysis and optimization problems. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 35
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE NH 4 – H 2 O separation What can be done with simulation ü Steady state simulation is useful to predict the behave of a process in the plant. ü What if, situations can be check with simulation. ü Sensitivity analysis and optimization problems. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 35
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis of C 2 H 5 Cl manufacture PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 36
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis of C 2 H 5 Cl manufacture PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 36
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Sensitivity Analysis Is a useful tool to know the respond of the output variable when the input is varied in a range. With this information one can appreciate which variable cause the biggest change in the process. Is easier to make a decision in the parameter we obtain best results. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 37
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Sensitivity Analysis Is a useful tool to know the respond of the output variable when the input is varied in a range. With this information one can appreciate which variable cause the biggest change in the process. Is easier to make a decision in the parameter we obtain best results. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 37
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Ethyl chloride manufacture One of the routes to produce ethyl chloride is by the gas phase reaction of HCl with ethylene over a copper chloride catalyst: Objective: Observe the effect in “recycle” stream, “recycle” composition and “product” stream when the flow in “w” stream vary from 5 to 13 kmol/h. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 38
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Ethyl chloride manufacture One of the routes to produce ethyl chloride is by the gas phase reaction of HCl with ethylene over a copper chloride catalyst: Objective: Observe the effect in “recycle” stream, “recycle” composition and “product” stream when the flow in “w” stream vary from 5 to 13 kmol/h. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 38
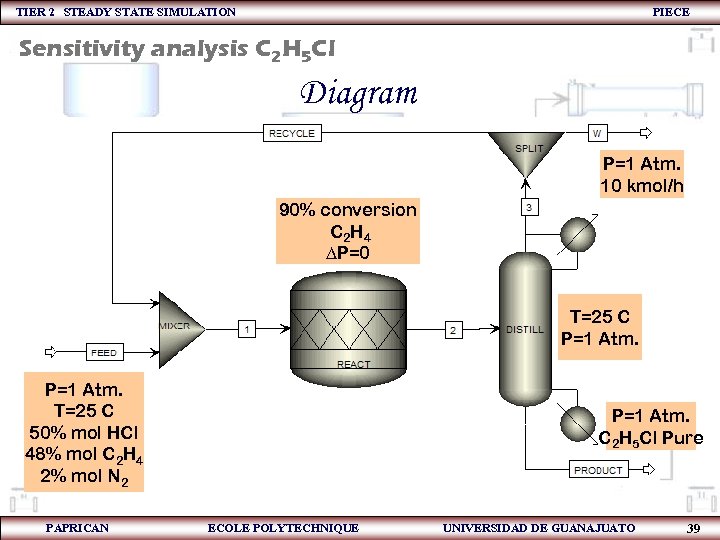 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Diagram P=1 Atm. 10 kmol/h 90% conversion C 2 H 4 DP=0 T=25 C P=1 Atm. T=25 C 50% mol HCl 48% mol C 2 H 4 2% mol N 2 PAPRICAN P=1 Atm. C 2 H 5 Cl Pure ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 39
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Diagram P=1 Atm. 10 kmol/h 90% conversion C 2 H 4 DP=0 T=25 C P=1 Atm. T=25 C 50% mol HCl 48% mol C 2 H 4 2% mol N 2 PAPRICAN P=1 Atm. C 2 H 5 Cl Pure ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 39
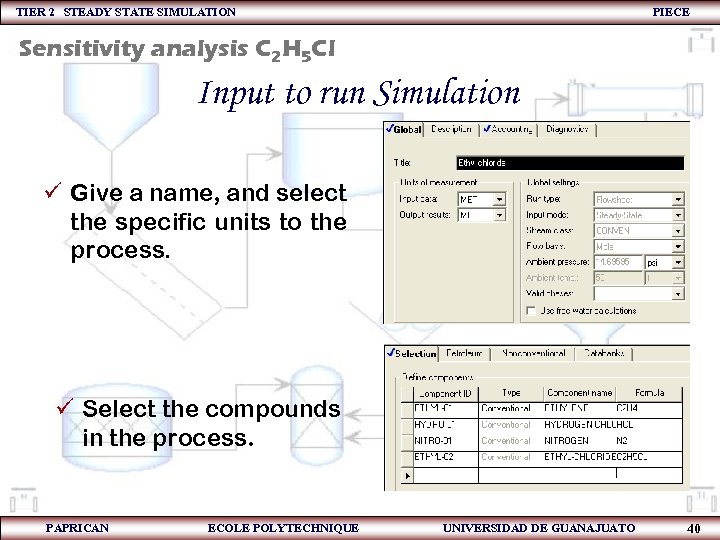 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run Simulation ü Give a name, and select the specific units to the process. ü Select the compounds in the process. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 40
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run Simulation ü Give a name, and select the specific units to the process. ü Select the compounds in the process. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 40
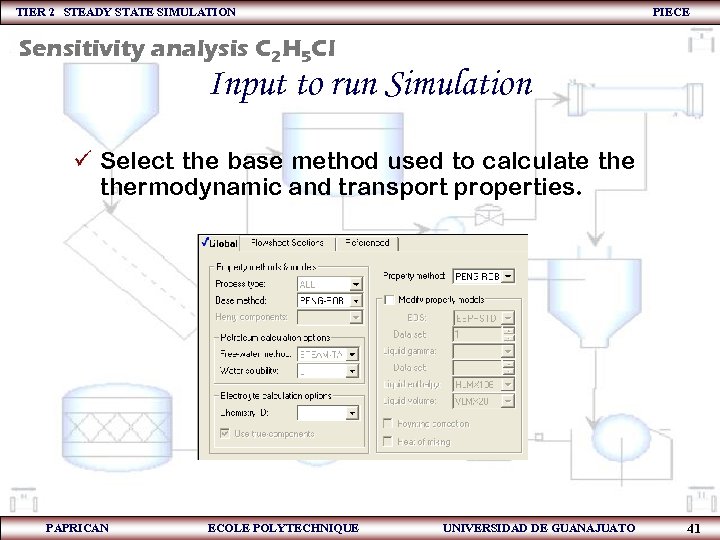 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run Simulation ü Select the base method used to calculate thermodynamic and transport properties. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 41
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run Simulation ü Select the base method used to calculate thermodynamic and transport properties. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 41
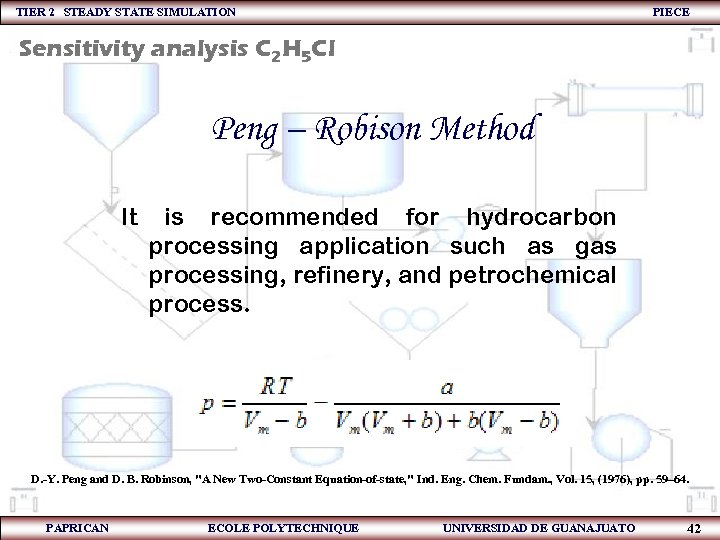 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Peng – Robison Method It is recommended for hydrocarbon processing application such as gas processing, refinery, and petrochemical process. D. -Y. Peng and D. B. Robinson, "A New Two-Constant Equation-of-state, " Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. , Vol. 15, (1976), pp. 59– 64. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 42
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Peng – Robison Method It is recommended for hydrocarbon processing application such as gas processing, refinery, and petrochemical process. D. -Y. Peng and D. B. Robinson, "A New Two-Constant Equation-of-state, " Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. , Vol. 15, (1976), pp. 59– 64. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 42
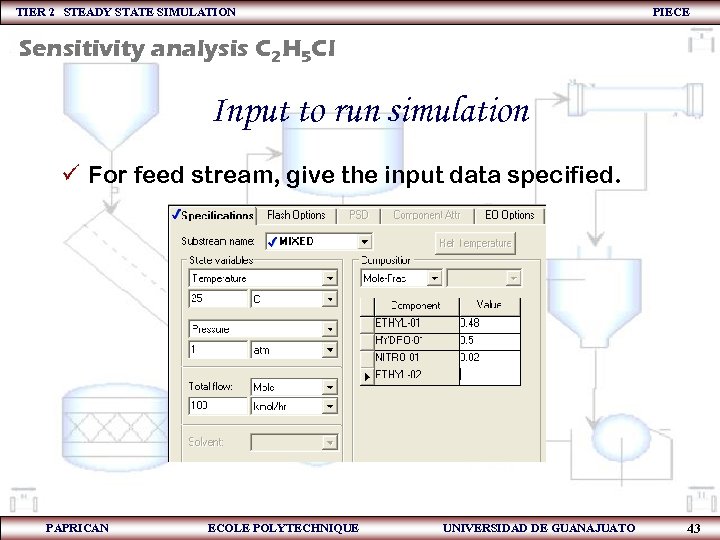 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For feed stream, give the input data specified. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 43
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For feed stream, give the input data specified. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 43
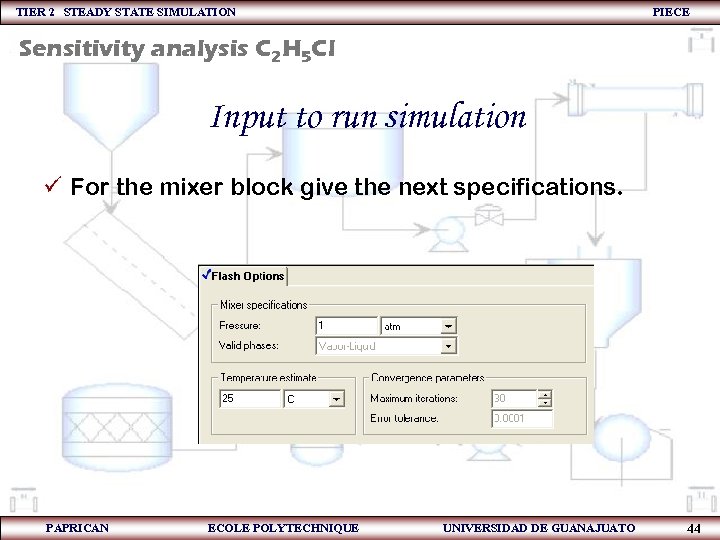 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For the mixer block give the next specifications. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 44
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For the mixer block give the next specifications. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 44
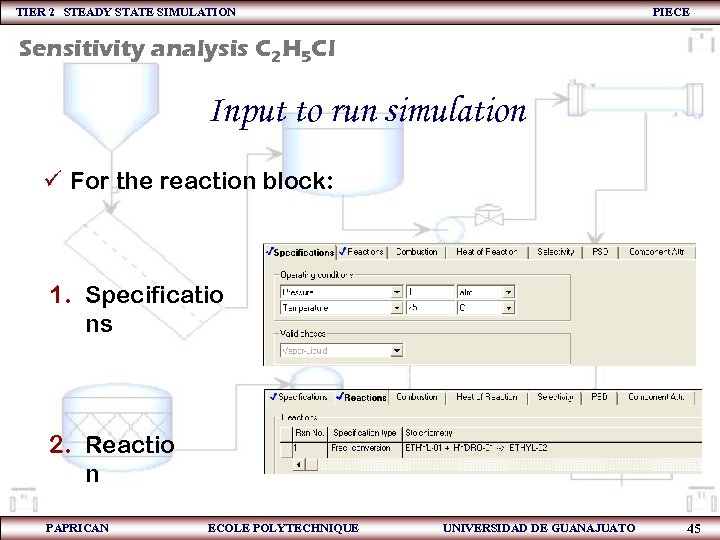 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For the reaction block: 1. Specificatio ns 2. Reactio n PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 45
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For the reaction block: 1. Specificatio ns 2. Reactio n PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 45
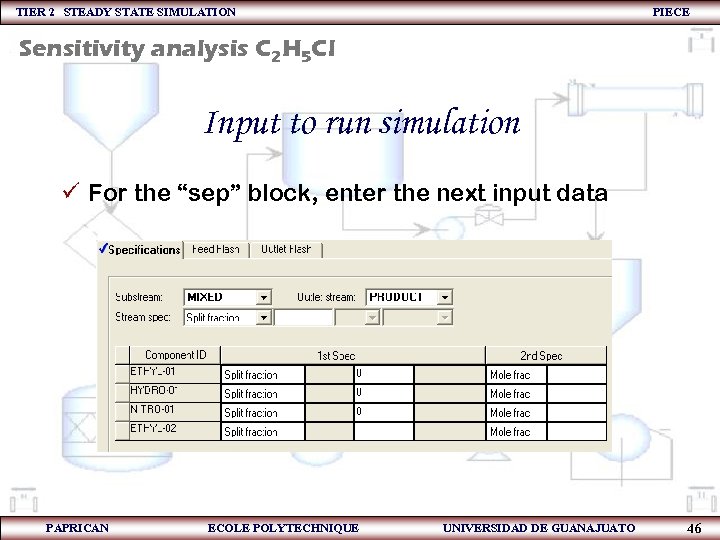 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For the “sep” block, enter the next input data PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 46
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For the “sep” block, enter the next input data PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 46
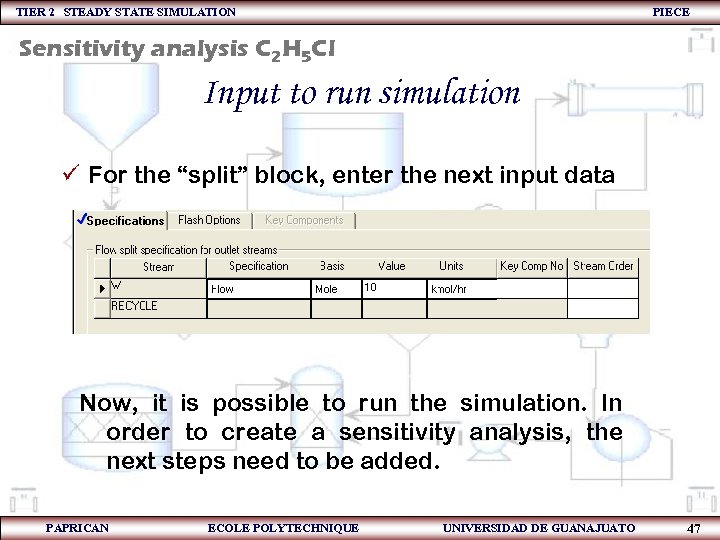 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For the “split” block, enter the next input data Now, it is possible to run the simulation. In order to create a sensitivity analysis, the next steps need to be added. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 47
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to run simulation ü For the “split” block, enter the next input data Now, it is possible to run the simulation. In order to create a sensitivity analysis, the next steps need to be added. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 47
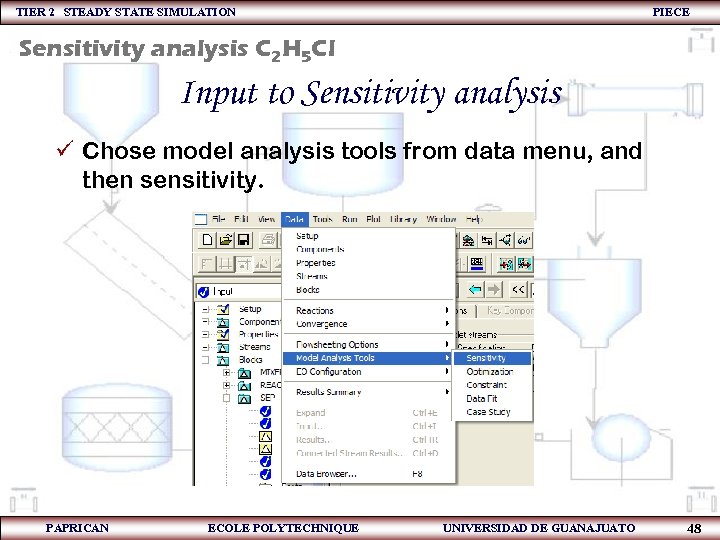 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to Sensitivity analysis ü Chose model analysis tools from data menu, and then sensitivity. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 48
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to Sensitivity analysis ü Chose model analysis tools from data menu, and then sensitivity. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 48
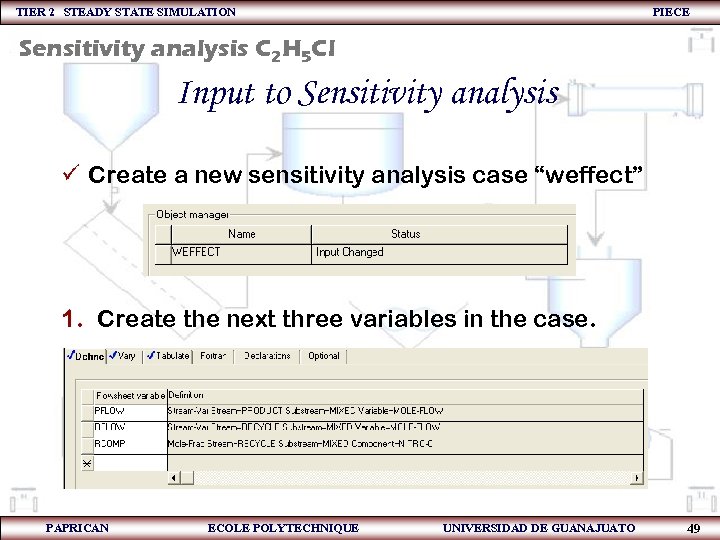 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to Sensitivity analysis ü Create a new sensitivity analysis case “weffect” 1. Create the next three variables in the case. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 49
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to Sensitivity analysis ü Create a new sensitivity analysis case “weffect” 1. Create the next three variables in the case. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 49
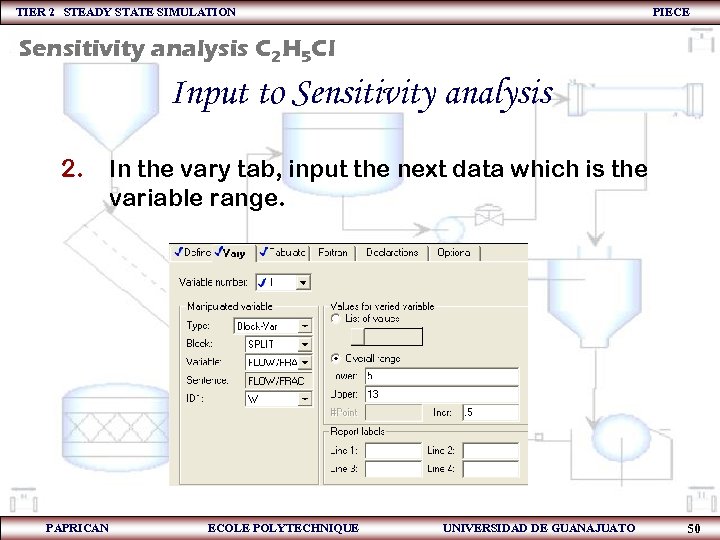 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to Sensitivity analysis 2. PAPRICAN In the vary tab, input the next data which is the variable range. ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 50
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to Sensitivity analysis 2. PAPRICAN In the vary tab, input the next data which is the variable range. ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 50
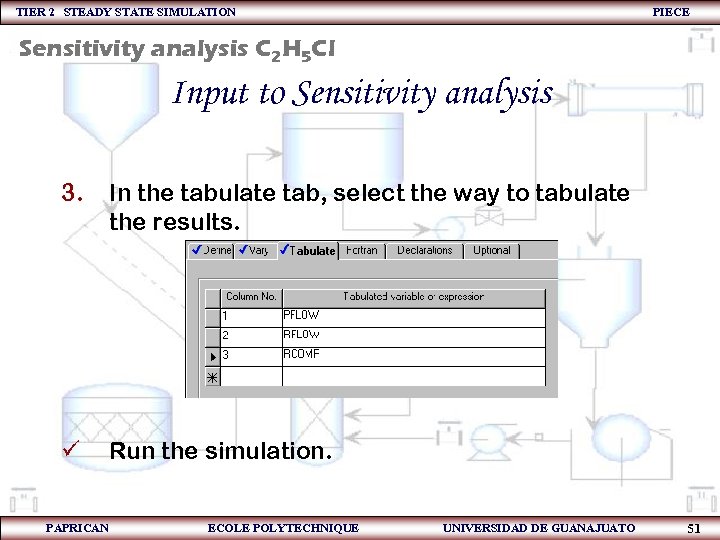 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to Sensitivity analysis 3. In the tabulate tab, select the way to tabulate the results. ü Run the simulation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 51
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Input to Sensitivity analysis 3. In the tabulate tab, select the way to tabulate the results. ü Run the simulation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 51
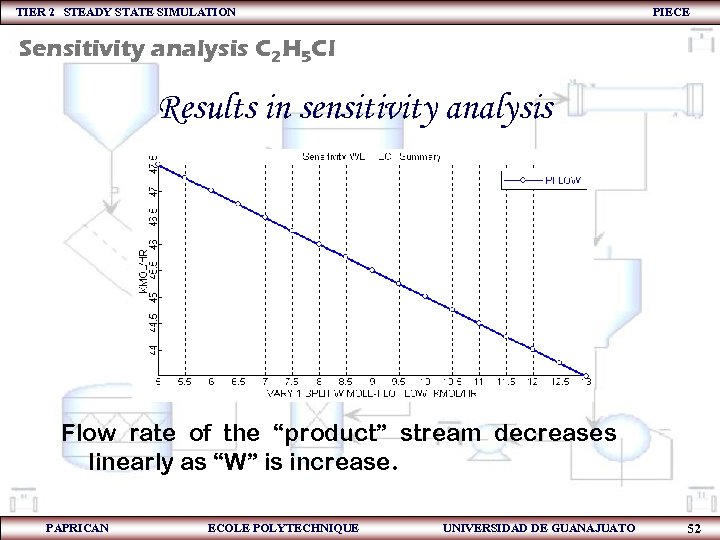 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Results in sensitivity analysis Flow rate of the “product” stream decreases linearly as “W” is increase. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 52
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Results in sensitivity analysis Flow rate of the “product” stream decreases linearly as “W” is increase. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 52
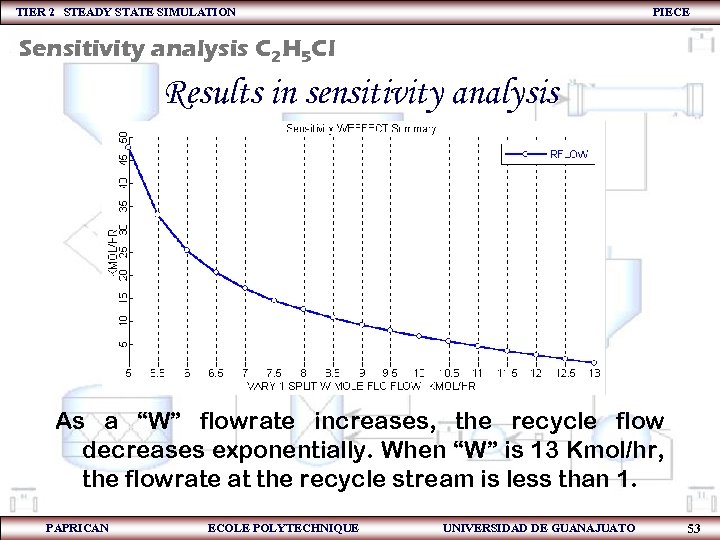 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Results in sensitivity analysis As a “W” flowrate increases, the recycle flow decreases exponentially. When “W” is 13 Kmol/hr, the flowrate at the recycle stream is less than 1. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 53
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Results in sensitivity analysis As a “W” flowrate increases, the recycle flow decreases exponentially. When “W” is 13 Kmol/hr, the flowrate at the recycle stream is less than 1. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 53
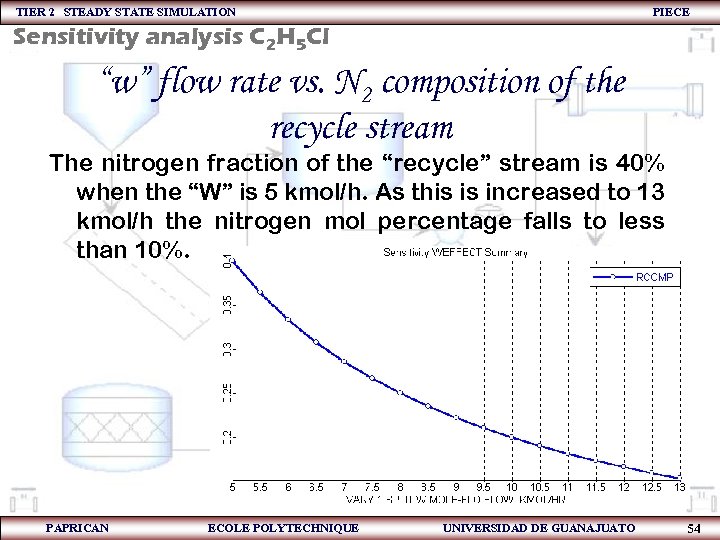 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl “w” flow rate vs. N 2 composition of the recycle stream The nitrogen fraction of the “recycle” stream is 40% when the “W” is 5 kmol/h. As this is increased to 13 kmol/h the nitrogen mol percentage falls to less than 10%. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 54
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl “w” flow rate vs. N 2 composition of the recycle stream The nitrogen fraction of the “recycle” stream is 40% when the “W” is 5 kmol/h. As this is increased to 13 kmol/h the nitrogen mol percentage falls to less than 10%. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 54
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Conclusion from the simulation With this kind of analysis, one can appreciate how sensitive is the process to the change in one variable, in this case “W” flowrate. In which cases the process behaves with a benefit to the production. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 55
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Sensitivity analysis C 2 H 5 Cl Conclusion from the simulation With this kind of analysis, one can appreciate how sensitive is the process to the change in one variable, in this case “W” flowrate. In which cases the process behaves with a benefit to the production. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 55
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 56
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 56
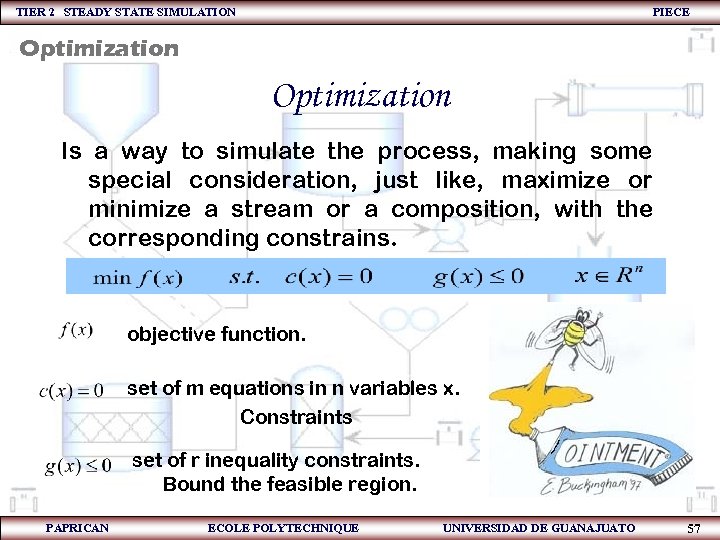 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Is a way to simulate the process, making some special consideration, just like, maximize or minimize a stream or a composition, with the corresponding constrains. objective function. set of m equations in n variables x. Constraints set of r inequality constraints. Bound the feasible region. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 57
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Is a way to simulate the process, making some special consideration, just like, maximize or minimize a stream or a composition, with the corresponding constrains. objective function. set of m equations in n variables x. Constraints set of r inequality constraints. Bound the feasible region. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 57
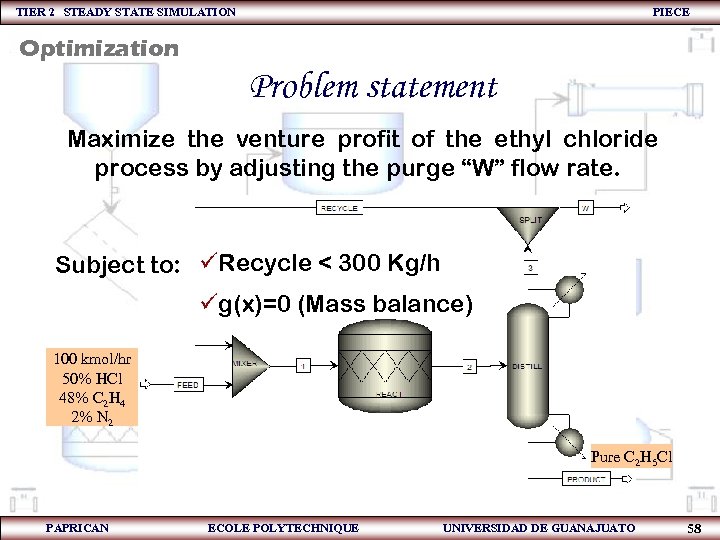 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Problem statement Maximize the venture profit of the ethyl chloride process by adjusting the purge “W” flow rate. Subject to: üRecycle < 300 Kg/h üg(x)=0 (Mass balance) 100 kmol/hr 50% HCl 48% C 2 H 4 2% N 2 Pure C 2 H 5 Cl PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 58
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Problem statement Maximize the venture profit of the ethyl chloride process by adjusting the purge “W” flow rate. Subject to: üRecycle < 300 Kg/h üg(x)=0 (Mass balance) 100 kmol/hr 50% HCl 48% C 2 H 4 2% N 2 Pure C 2 H 5 Cl PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 58
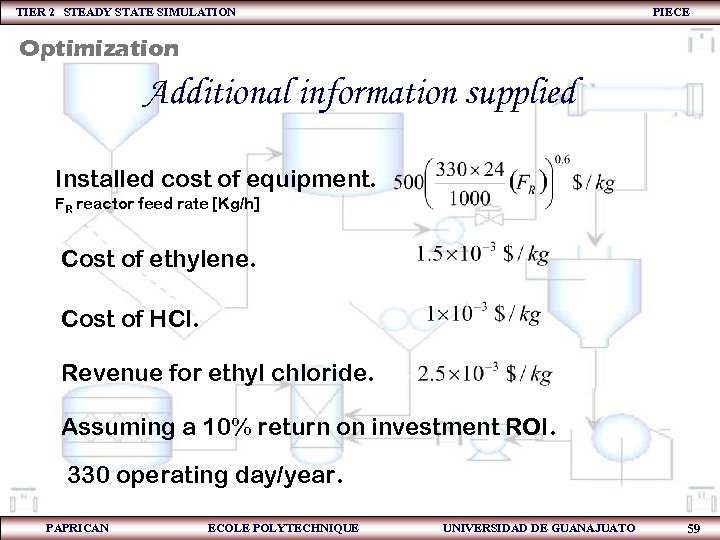 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Additional information supplied Installed cost of equipment. FR reactor feed rate [Kg/h] Cost of ethylene. Cost of HCl. Revenue for ethyl chloride. Assuming a 10% return on investment ROI. 330 operating day/year. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 59
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Additional information supplied Installed cost of equipment. FR reactor feed rate [Kg/h] Cost of ethylene. Cost of HCl. Revenue for ethyl chloride. Assuming a 10% return on investment ROI. 330 operating day/year. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 59
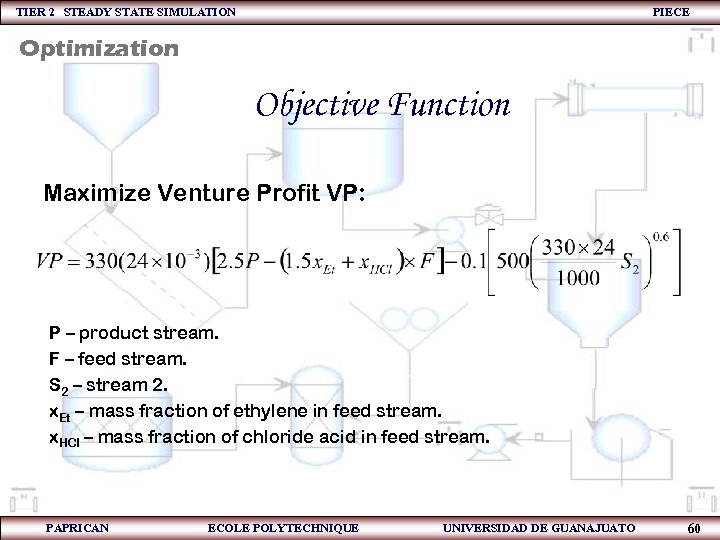 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Objective Function Maximize Venture Profit VP: P – product stream. F – feed stream. S 2 – stream 2. x. Et – mass fraction of ethylene in feed stream. x. HCl – mass fraction of chloride acid in feed stream. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 60
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Objective Function Maximize Venture Profit VP: P – product stream. F – feed stream. S 2 – stream 2. x. Et – mass fraction of ethylene in feed stream. x. HCl – mass fraction of chloride acid in feed stream. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 60
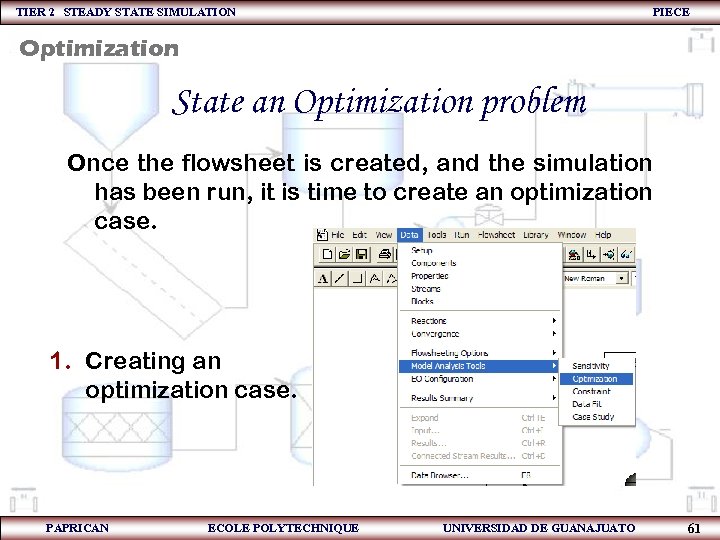 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization State an Optimization problem Once the flowsheet is created, and the simulation has been run, it is time to create an optimization case. 1. Creating an optimization case. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 61
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization State an Optimization problem Once the flowsheet is created, and the simulation has been run, it is time to create an optimization case. 1. Creating an optimization case. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 61
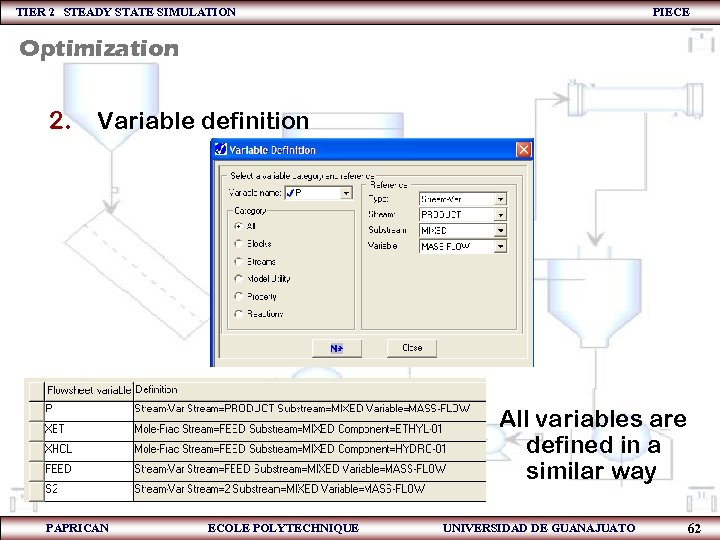 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization 2. Variable definition All variables are defined in a similar way PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 62
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization 2. Variable definition All variables are defined in a similar way PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 62
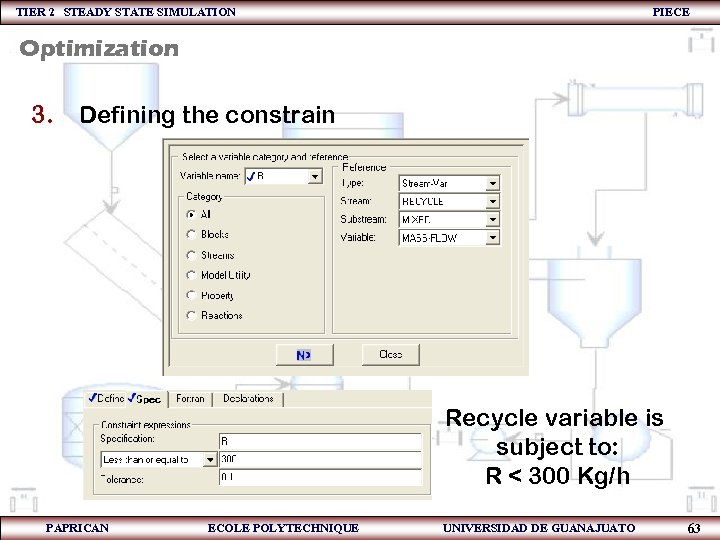 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization 3. Defining the constrain Recycle variable is subject to: R < 300 Kg/h PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 63
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization 3. Defining the constrain Recycle variable is subject to: R < 300 Kg/h PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 63
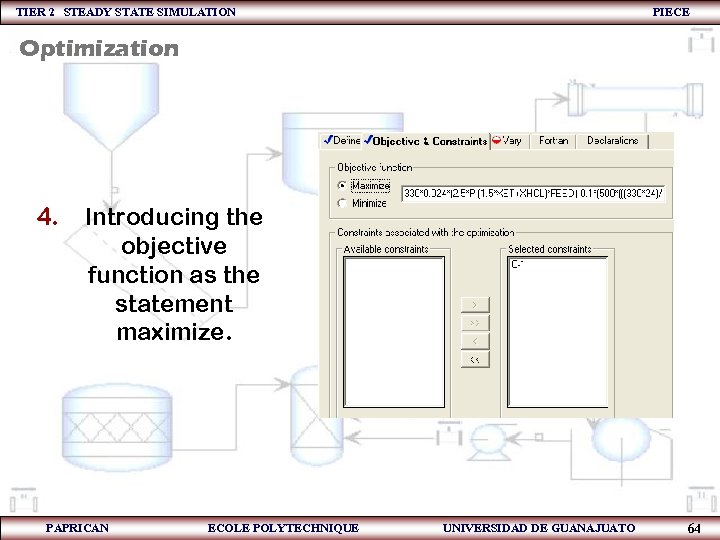 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization 4. Introducing the objective function as the statement maximize. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 64
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization 4. Introducing the objective function as the statement maximize. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 64
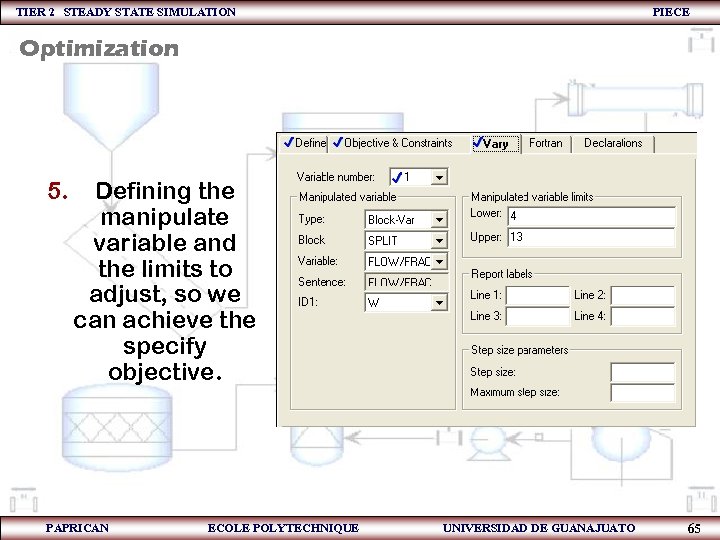 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization 5. Defining the manipulate variable and the limits to adjust, so we can achieve the specify objective. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 65
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization 5. Defining the manipulate variable and the limits to adjust, so we can achieve the specify objective. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 65
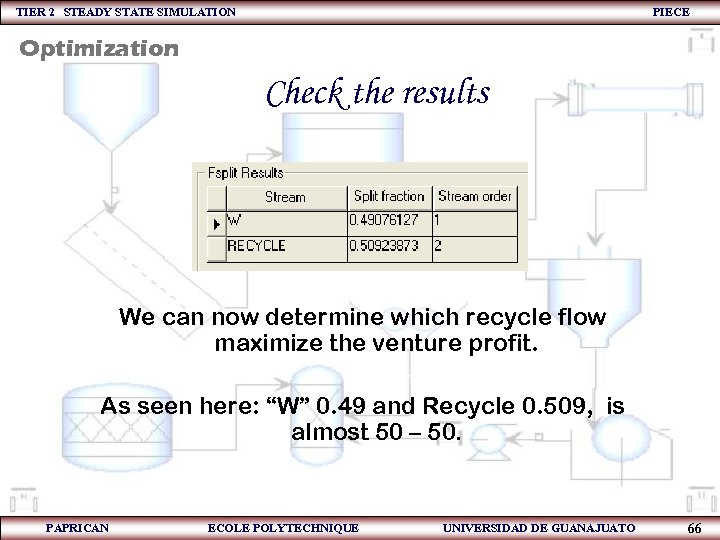 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Check the results We can now determine which recycle flow maximize the venture profit. As seen here: “W” 0. 49 and Recycle 0. 509, is almost 50 – 50. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 66
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Check the results We can now determine which recycle flow maximize the venture profit. As seen here: “W” 0. 49 and Recycle 0. 509, is almost 50 – 50. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 66
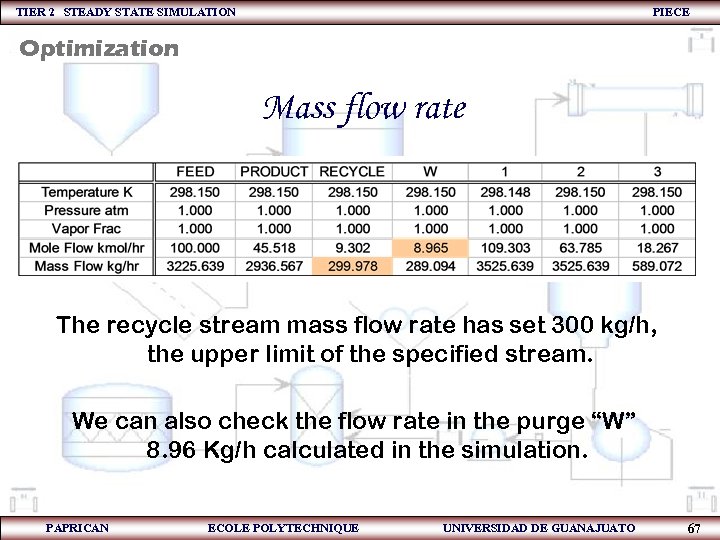 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Mass flow rate The recycle stream mass flow rate has set 300 kg/h, the upper limit of the specified stream. We can also check the flow rate in the purge “W” 8. 96 Kg/h calculated in the simulation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 67
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE Optimization Mass flow rate The recycle stream mass flow rate has set 300 kg/h, the upper limit of the specified stream. We can also check the flow rate in the purge “W” 8. 96 Kg/h calculated in the simulation. PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 67
 TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE End of Tier 2 PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 68
TIER 2 STEADY STATE SIMULATION PIECE End of Tier 2 PAPRICAN ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE UNIVERSIDAD DE GUANAJUATO 68


