9369f27f172db0f63ea1e12438df88bd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 56


Tibia Fractures, Open

Frequency

Etiology

Presentation

Classification
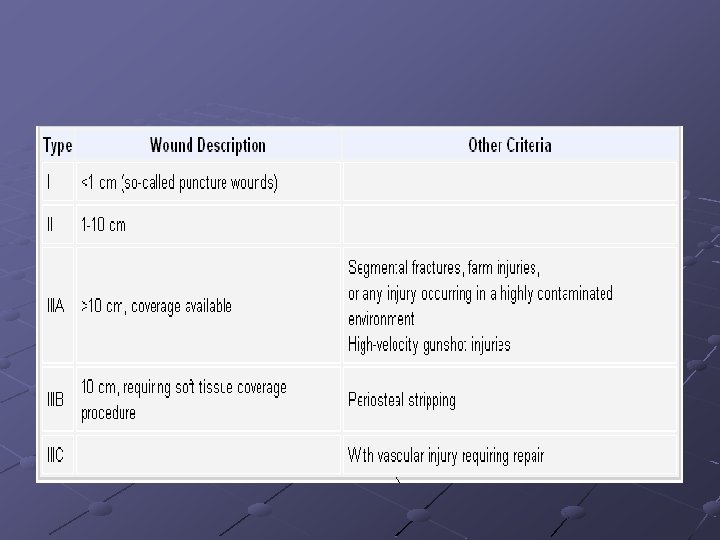

Indications

Contraindications

Medical Therapy

Surgical Therapy

Complications


Introduction

Problem

Frequency

Etiology

Pathophysiology

Presentation and examination

Indications

Contraindications

Laboratory Studies

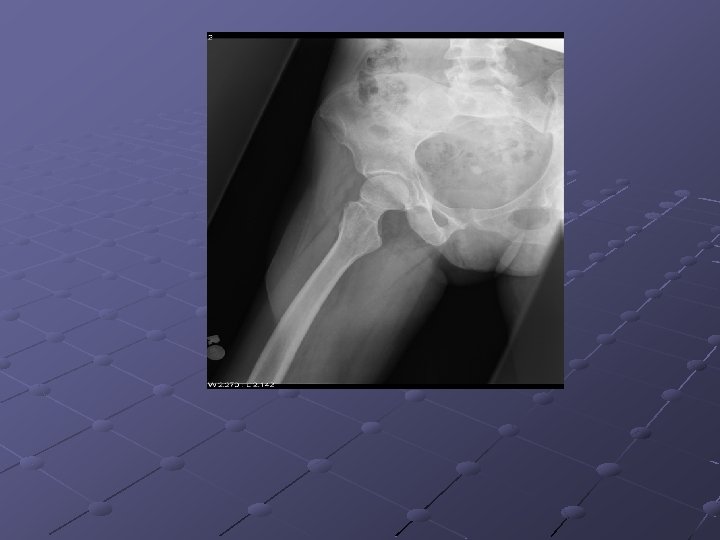
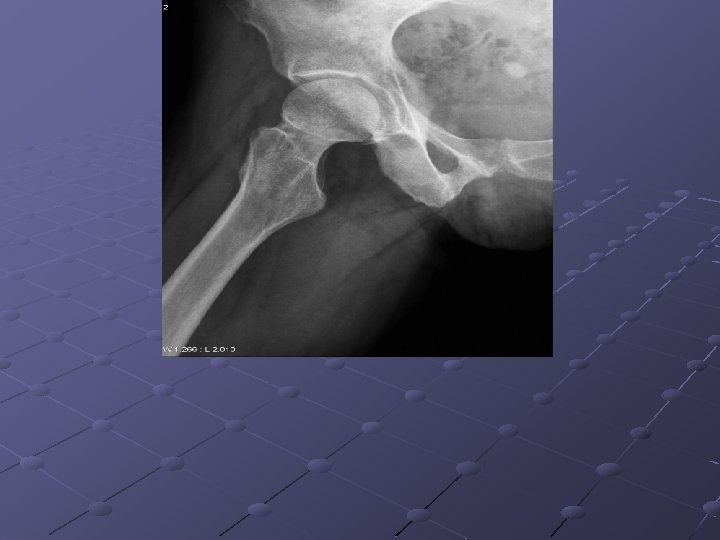
Imaging Studies

Imaging Studies

Imaging Studies

Outcome and Prognosis

Future and Controversies


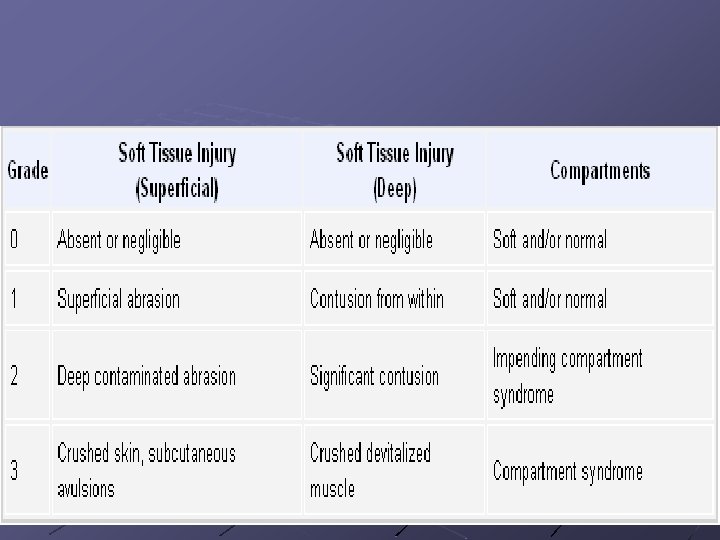
Problem

Frequency

Etiology

Indications


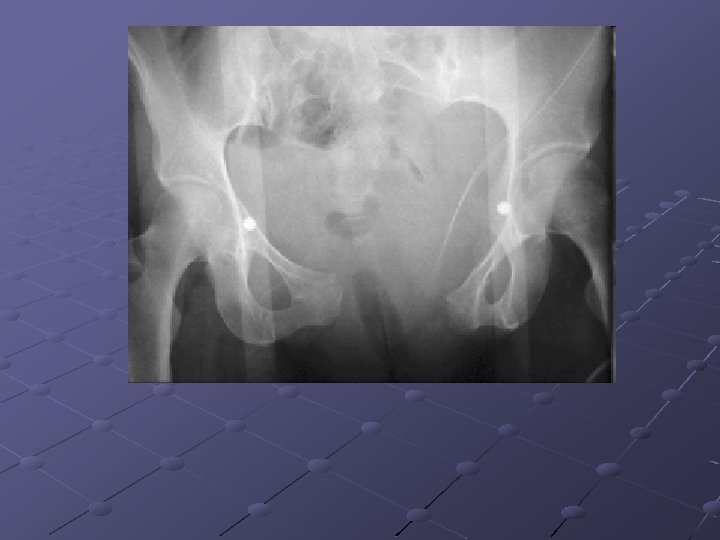
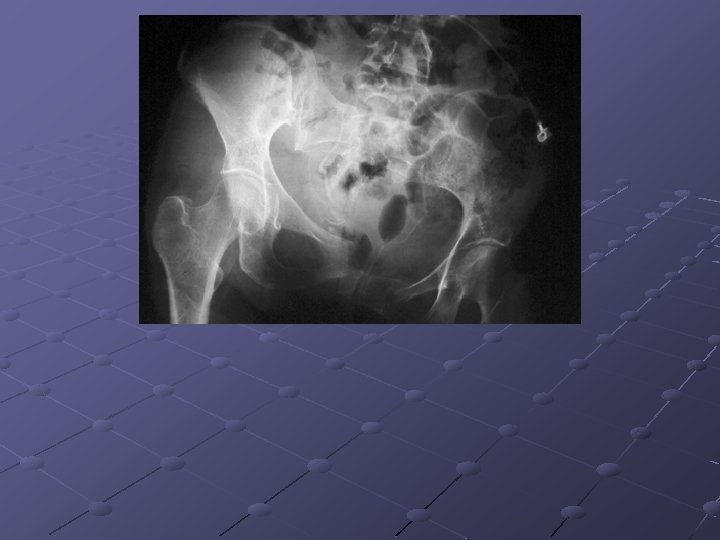
Laboratory Studies

Imaging Studies

Imaging Studies

Imaging Studies

Medical Therapy

Surgical Therapy

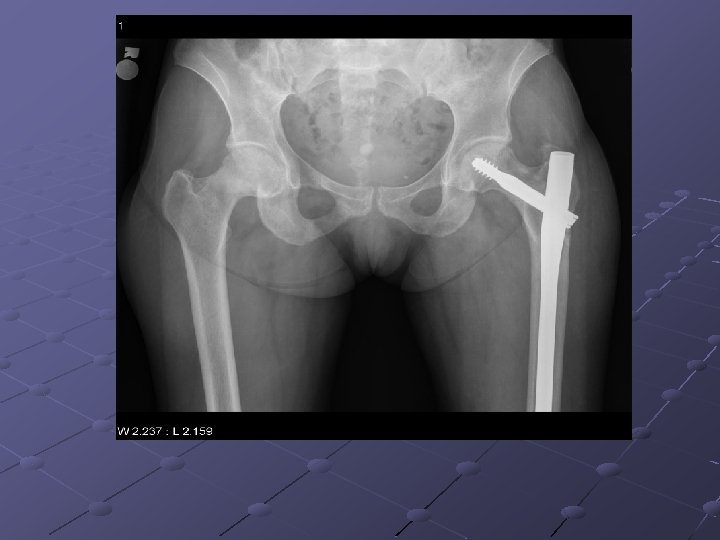
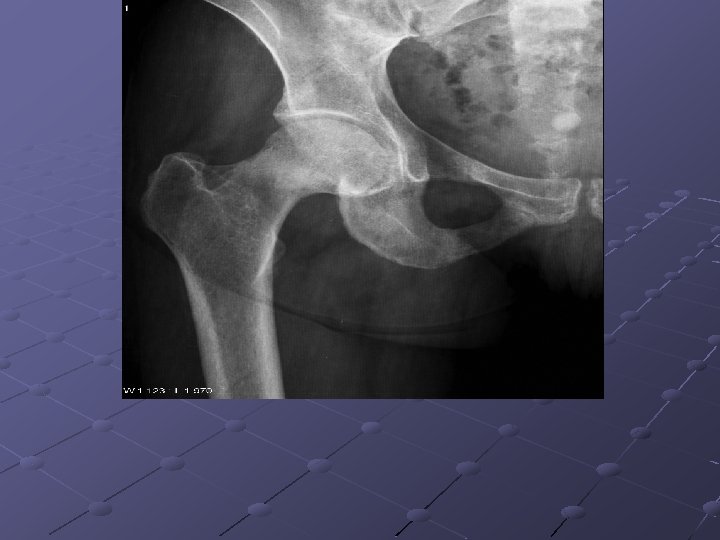
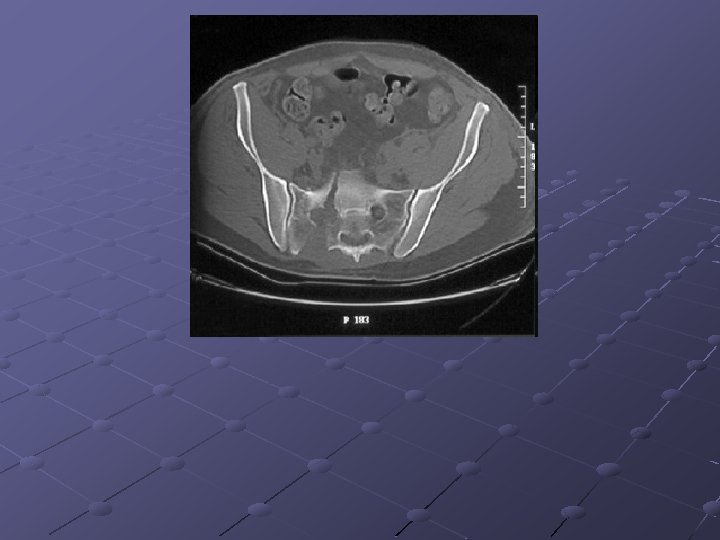
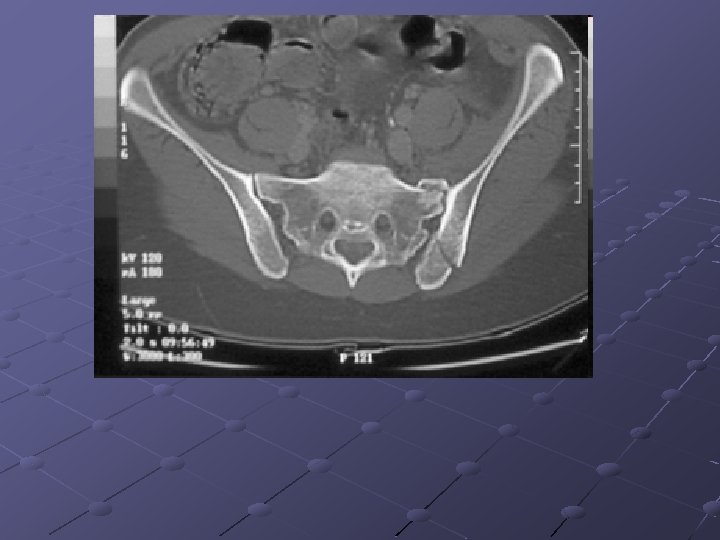
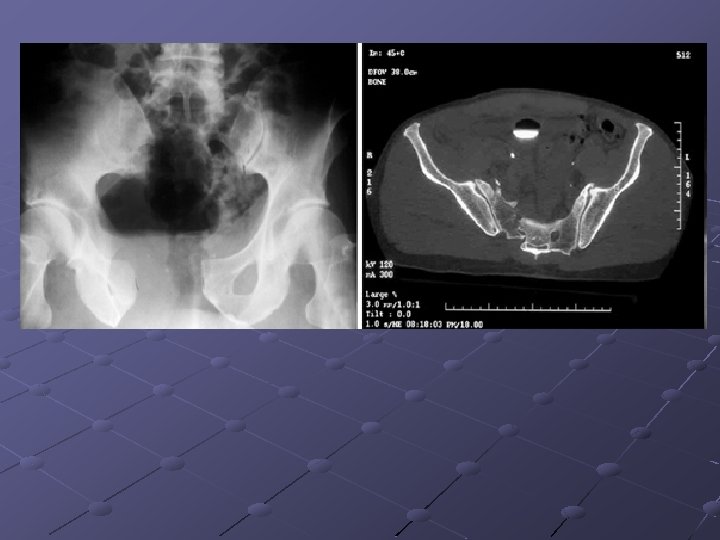
Pubic ramus fractures occur as parasymphysial fractures, midramus fractures, and pubic root fractures in association with distraction and compression injuries of the pelvis (Routt, Orthop Clin North Am, 1997). Displacement of pubic rami fractures may cause impingement or laceration of the bladder, vagina, and perineum, and, for these reasons, operative management may be considered. Operative treatment of pubic rami fractures is indicated to provide additional pelvic ring stability in association with posterior pelvic ring fixation. Stabilization of pubic rami fractures also may be considered in fractures involving the obturator neurovascular canal with accompanying neurologic injury. Treatment options for pubic rami fractures include external fixation, percutaneous screw fixation, and open reduction and internal fixation. External fixation with either multiple pins (Kellam, 1989) or single pins in each hemipelvis (Tucker, 2001) may be used successfully in conjunction with stabilization of posterior ring injuries to impart additional stability to the pelvic fixation construct. External fixation for pubic ramus fractures is indicated to impart additional stability after posterior pelvic ring repair and also when percutaneous or open treatment is contraindicated. Intramedullary fixation of pubic ramus fractures has been described for treatment of pubic rami fractures (Simonian, J Orthop Trauma 1994; 8(6): 476 -82; Tile, 1995). Intramedullary pubic ramus fixation with a 4. 5 -mm cortical screw has demonstrated fixation strength equivalent to plate fixation and has demonstrated good results in clinical settings (Routt, 2000; Simonian, J Orthop Trauma 1994; 8(6): 483 -9). Intramedullary stabilization of ramus fractures may be performed with either a percutaneous or open technique with either antegrade or retrograde screw placement in the pubic ramus. Extramedullary plate fixation is another option to stabilize pubic rami fractures after open reduction and usually is achieved with 3. 5 -mm pelvic reconstruction plates.

Iliac wing fractures

Crescent fractures

Sacroiliac joint disruptions

Sacral fractures

Complications

Outcome and Prognosis
9369f27f172db0f63ea1e12438df88bd.ppt