 Thyroid Cancer an M. A. Khachatry
Thyroid Cancer an M. A. Khachatry
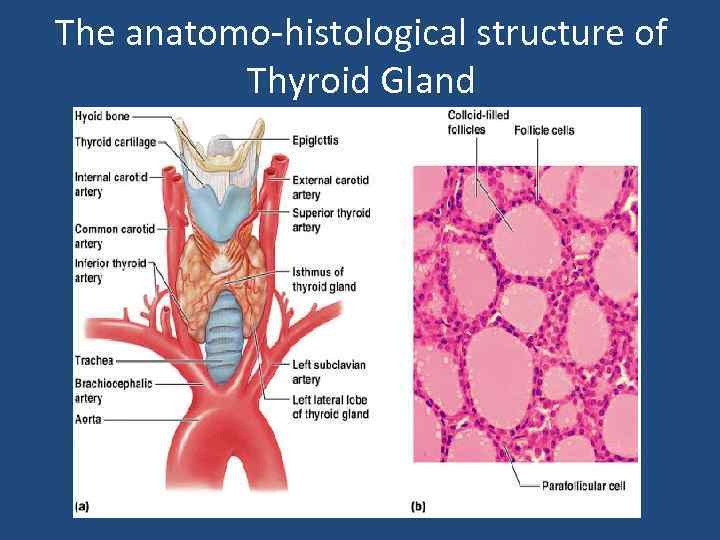 The anatomo-histological structure of Thyroid Gland
The anatomo-histological structure of Thyroid Gland
 Thyroid Cancer • • Papillary C-r Folliculary C-r Medullary C-r Anaplastic C-r
Thyroid Cancer • • Papillary C-r Folliculary C-r Medullary C-r Anaplastic C-r
 Characteristics of Papillary Thyroid Cancer • • 80% of TC Common in females Peak onset ages 30 -50 Follicular cell genesis Well-differentiated Minimally invasive Lymphogenic spread
Characteristics of Papillary Thyroid Cancer • • 80% of TC Common in females Peak onset ages 30 -50 Follicular cell genesis Well-differentiated Minimally invasive Lymphogenic spread
 Causes/ Risk Factors • • Family history/genetic defect maybe involved Radiation Men Older persons AACE/AME/ETA Thyroid Nodule Guidelines, Endocr Pract. 2010; 16(Suppl 1
Causes/ Risk Factors • • Family history/genetic defect maybe involved Radiation Men Older persons AACE/AME/ETA Thyroid Nodule Guidelines, Endocr Pract. 2010; 16(Suppl 1
 Symptoms and Signs • Few or no symptoms • Small lump(nodule) • Painless during palpation
Symptoms and Signs • Few or no symptoms • Small lump(nodule) • Painless during palpation
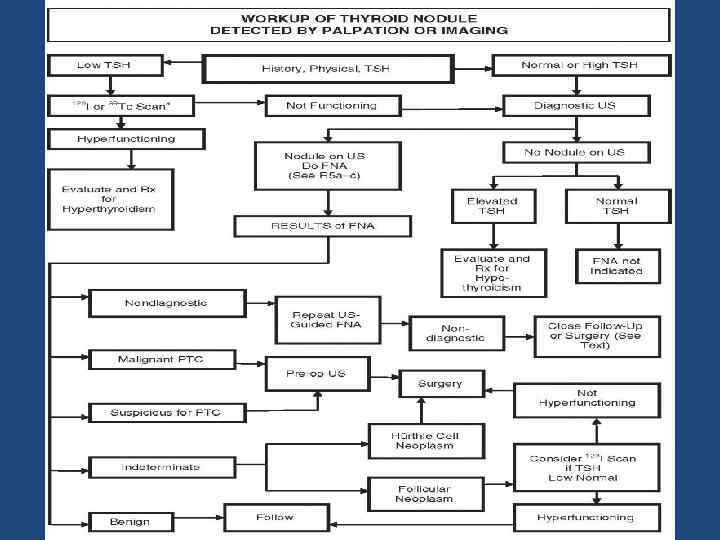
 Exams and Tests • • • History Physical examination US FNA Thyroid function tests
Exams and Tests • • • History Physical examination US FNA Thyroid function tests
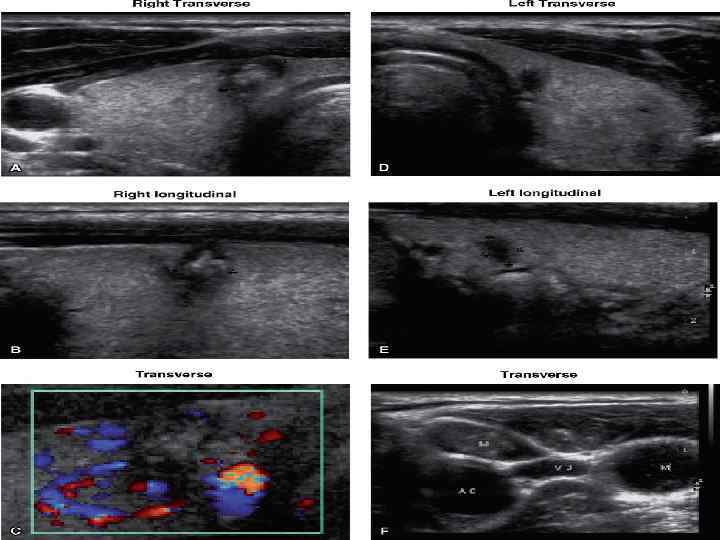
 PTC US Features • • Hypoechogenicity Inhomogeneous echo pattern Microcalcifications Absence of peripheral halo Irregular borders, blurred margins Often intranodular hypervascularity Regional lymphadenopathy
PTC US Features • • Hypoechogenicity Inhomogeneous echo pattern Microcalcifications Absence of peripheral halo Irregular borders, blurred margins Often intranodular hypervascularity Regional lymphadenopathy
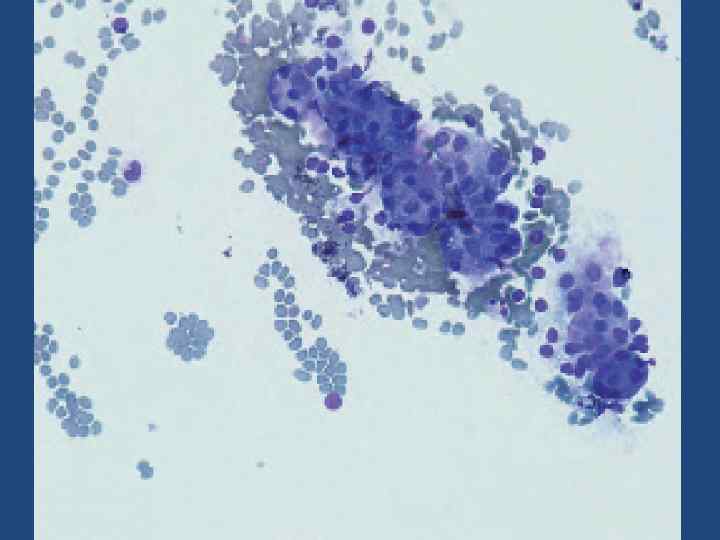
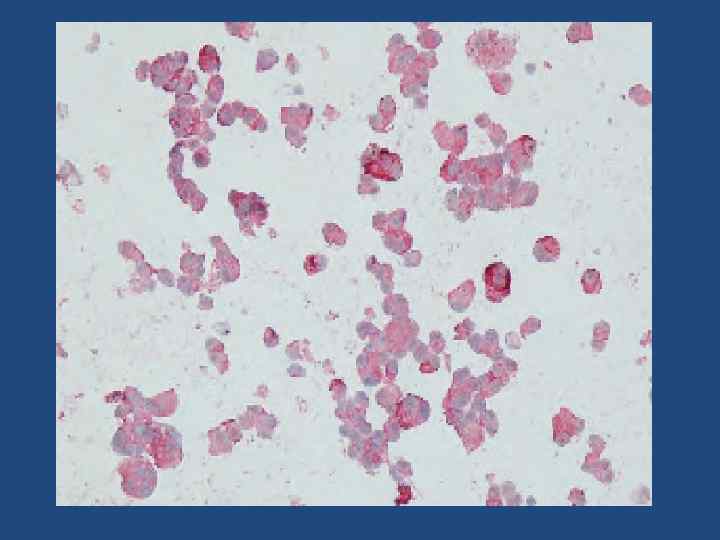
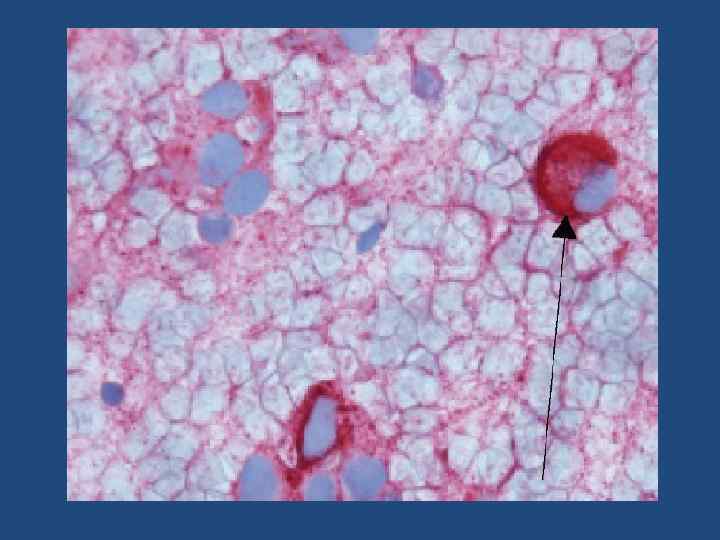
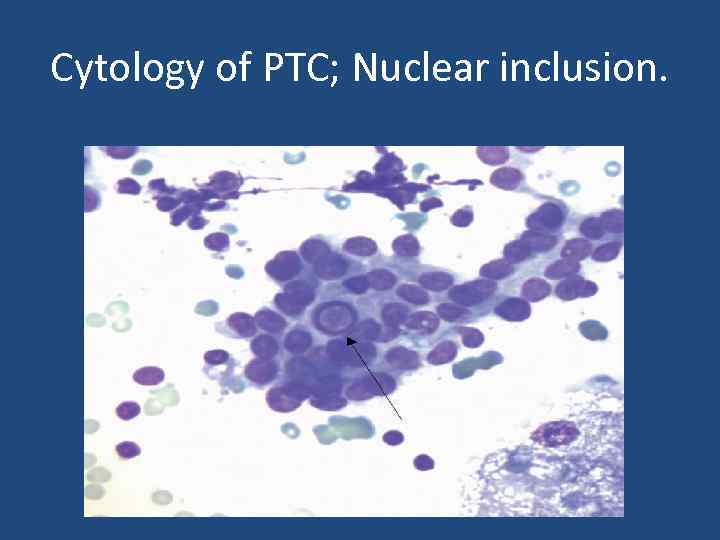 Cytology of PTC; Nuclear inclusion.
Cytology of PTC; Nuclear inclusion.
 Primary treatment • No prospective clinical trials have clearly determined the “best treatment” of patients with PTC • Appropiate surgical planning 202 ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Vol. 7 No. 3 May/June 2001
Primary treatment • No prospective clinical trials have clearly determined the “best treatment” of patients with PTC • Appropiate surgical planning 202 ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Vol. 7 No. 3 May/June 2001
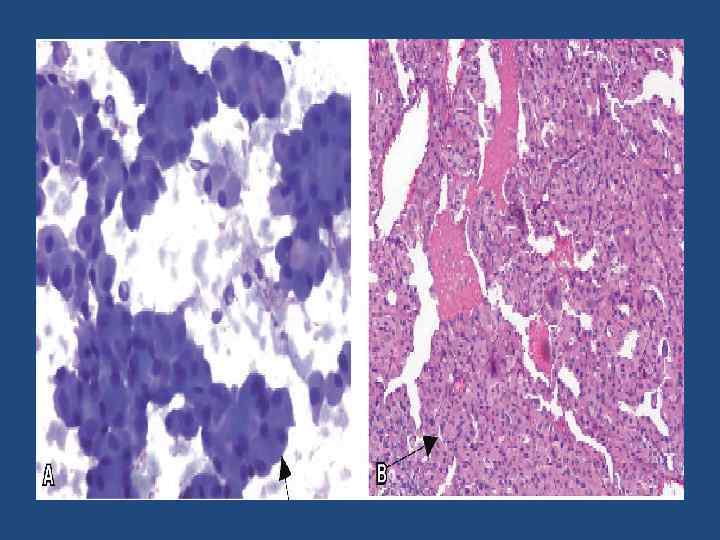
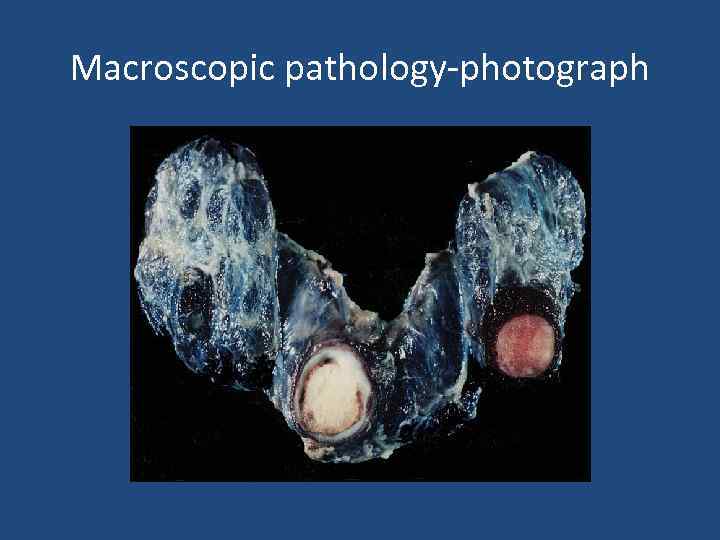 Macroscopic pathology-photograph
Macroscopic pathology-photograph
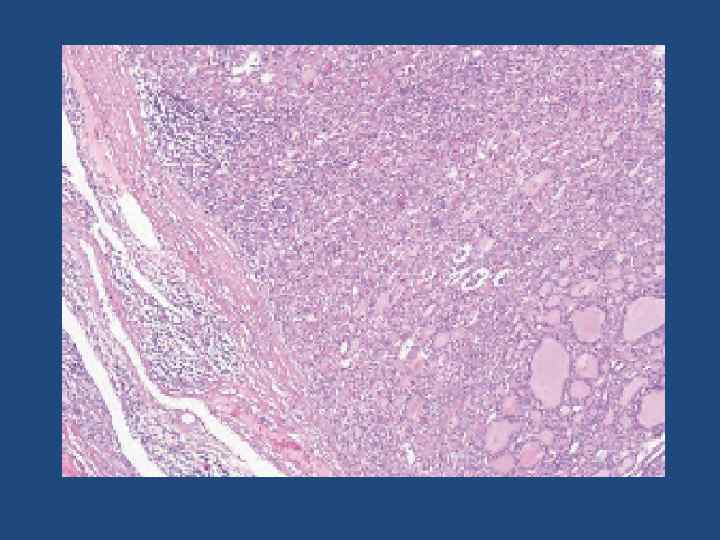
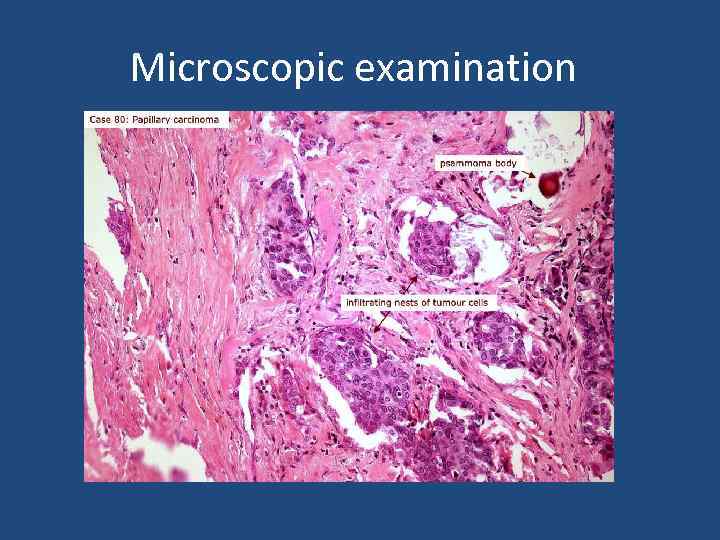 Microscopic examination
Microscopic examination
 Adjuvant Therapy • Thyroid Hormone-suppresive therapy • Radioiodine Remnant Ablation(131 J) 202 ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Vol. 7 No. 3 May/June 2001
Adjuvant Therapy • Thyroid Hormone-suppresive therapy • Radioiodine Remnant Ablation(131 J) 202 ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Vol. 7 No. 3 May/June 2001
 Follicular Thyroid Cancer The Second Most Common Type of Thyroid Cancer
Follicular Thyroid Cancer The Second Most Common Type of Thyroid Cancer
 Characteristics of Folliculary Thyroid Cancer More malignant Common in females Peak onset ages 40 -60 Follicular cell genesis Well-differentiated Invasion into vascular structures (veins and arteries) • haematogenic spread • • •
Characteristics of Folliculary Thyroid Cancer More malignant Common in females Peak onset ages 40 -60 Follicular cell genesis Well-differentiated Invasion into vascular structures (veins and arteries) • haematogenic spread • • •
 Symptoms and Signs • Few or no symptoms • Small lump(nodule) • Painless during palpation
Symptoms and Signs • Few or no symptoms • Small lump(nodule) • Painless during palpation
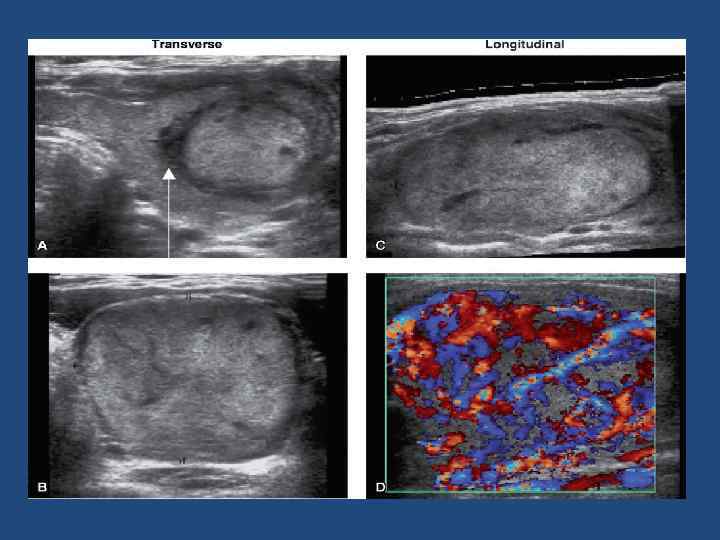
 Common Features of Follicular Adenomas • • Solitary Egg shape Thin, hypoechoic capsule Homogeneous echogenicity Hyper-, iso-, hypoechoic, or mixed May have cystic degeneration “Spoke-and-wheel-like” vascularity
Common Features of Follicular Adenomas • • Solitary Egg shape Thin, hypoechoic capsule Homogeneous echogenicity Hyper-, iso-, hypoechoic, or mixed May have cystic degeneration “Spoke-and-wheel-like” vascularity
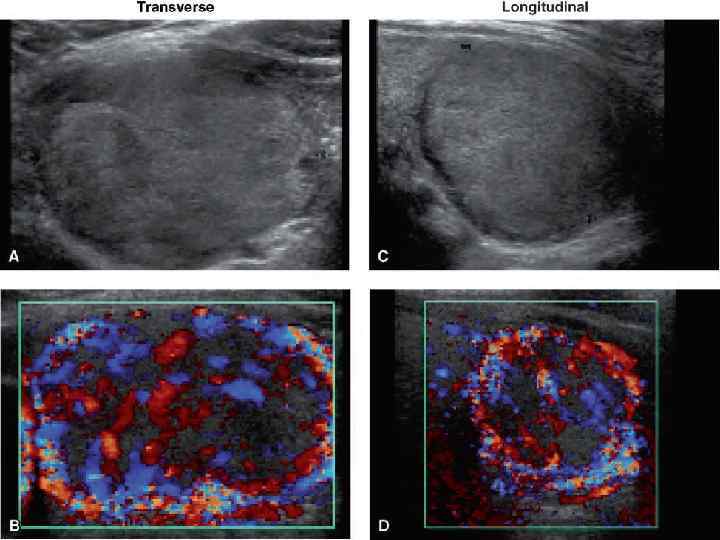
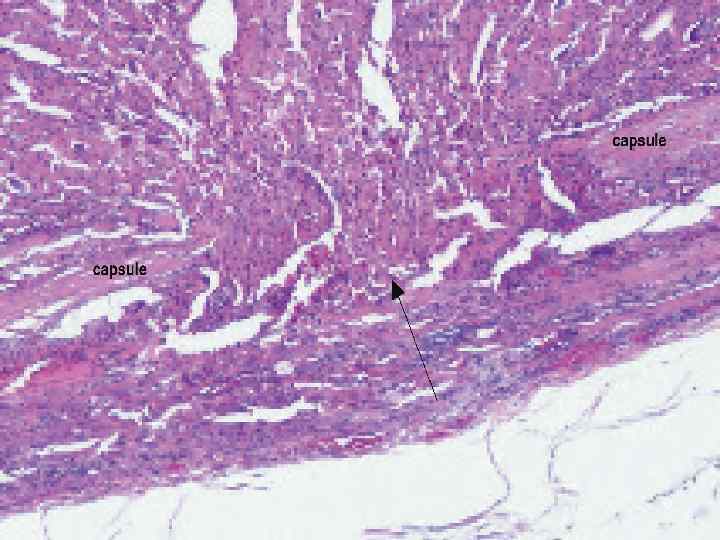
 Common Features of Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas • • Solitary Egg shape Thick, uneven hypoechoic capsule Homogeneous echogenicity Hyper-, iso-, hypoechoic, or mixed May have cystic degeneration Hypervascular “Spoke-and-wheel-like” vascularity less prominent
Common Features of Follicular Thyroid Carcinomas • • Solitary Egg shape Thick, uneven hypoechoic capsule Homogeneous echogenicity Hyper-, iso-, hypoechoic, or mixed May have cystic degeneration Hypervascular “Spoke-and-wheel-like” vascularity less prominent
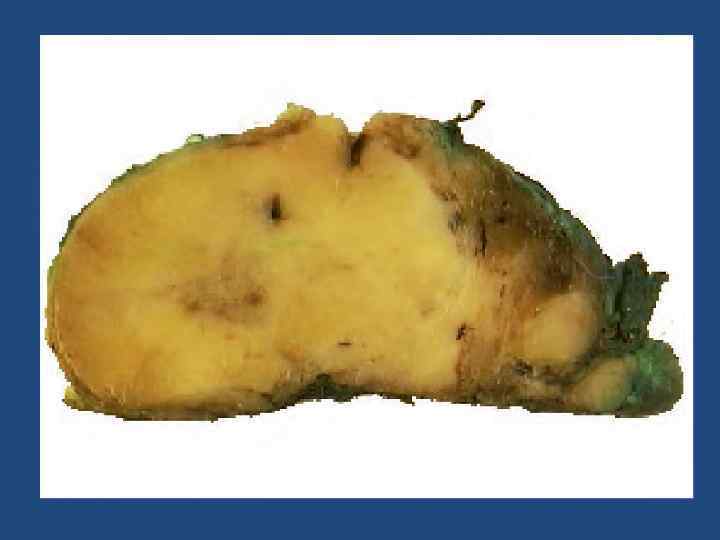

 Treatment of FTC and follicular adenoma/neoplasia • Thyroidectomy • Thyroid Hormone-suppresive therapy • Radioiodine Remnant Ablation(131 J) • Follow up( TG measurment <2 ng/ml) Thyroid Carcinoma Guidelines, Endocr Pract. 2001; 7(No. 3) 217
Treatment of FTC and follicular adenoma/neoplasia • Thyroidectomy • Thyroid Hormone-suppresive therapy • Radioiodine Remnant Ablation(131 J) • Follow up( TG measurment <2 ng/ml) Thyroid Carcinoma Guidelines, Endocr Pract. 2001; 7(No. 3) 217
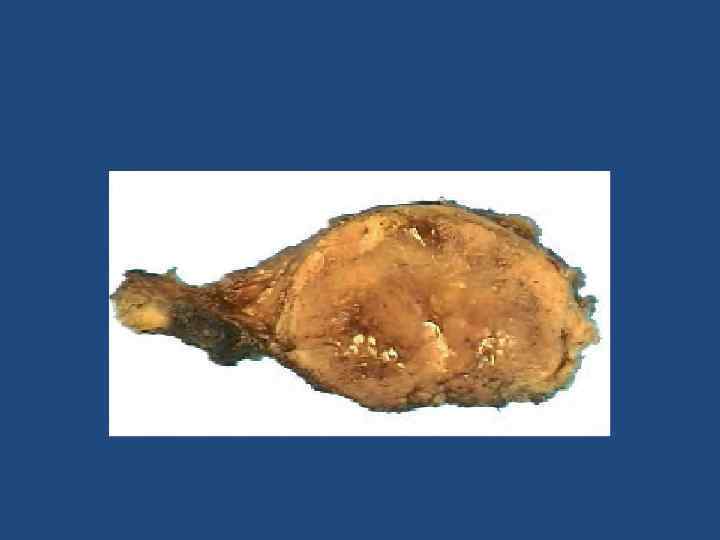
 Medullary thyroid cancer Characteristics of Medullary Thyroid Cancer • 75% are sporadic and 25% are hereditary • C cell genesis • Common in females • Differentiated • Spread-local lymch nodes, lungs, bone, liver, brain(rare) • High serum calcitonin level • Diarrhea
Medullary thyroid cancer Characteristics of Medullary Thyroid Cancer • 75% are sporadic and 25% are hereditary • C cell genesis • Common in females • Differentiated • Spread-local lymch nodes, lungs, bone, liver, brain(rare) • High serum calcitonin level • Diarrhea
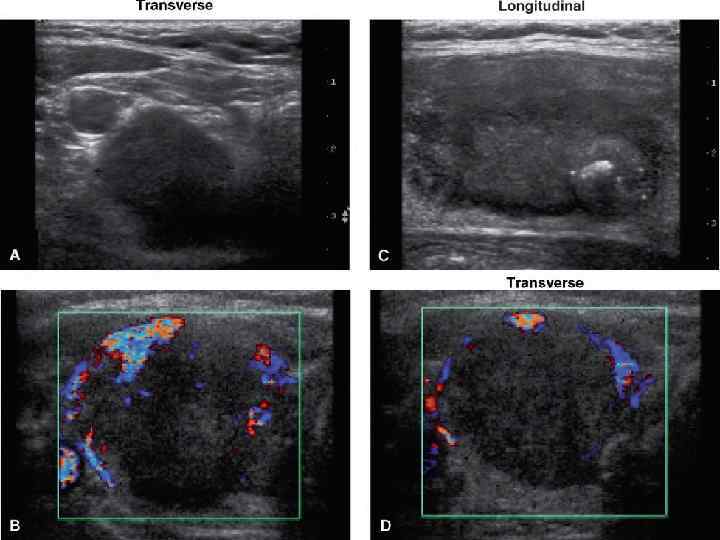
 US Common Features of MTC Hypoechoic Well marginated, sharply circumscribed Upper/mid lobe Centrally located separate coarse or microcalcifi cations • Regional lymphadenopathy • •
US Common Features of MTC Hypoechoic Well marginated, sharply circumscribed Upper/mid lobe Centrally located separate coarse or microcalcifi cations • Regional lymphadenopathy • •
 Hereditory MTC • • 25% of MTC MEN type IIA MEN type IIB Isolated familial MTC
Hereditory MTC • • 25% of MTC MEN type IIA MEN type IIB Isolated familial MTC
 MEN type IIA • MTC (generally bilateral) • pheochromocytoma or adrenal medullary hyperplasia (also bilateral) • Hyperparathyroidism
MEN type IIA • MTC (generally bilateral) • pheochromocytoma or adrenal medullary hyperplasia (also bilateral) • Hyperparathyroidism
 MEN type IIB • MTC • Pheochromocytoma • Marfanoid habitus, mucosal neuromas involving the lips, tongue, eyes, and pharynx, and ganglioneuromatosis of the gastrointestinal tract.
MEN type IIB • MTC • Pheochromocytoma • Marfanoid habitus, mucosal neuromas involving the lips, tongue, eyes, and pharynx, and ganglioneuromatosis of the gastrointestinal tract.
 Treatment • Total thyroidectomy and central(? evidence grade C) compartment lymph node dissection • No radioiodine Remnant Ablation(131 J) • Calcitonin measurment(postoperation) Thyroid Carcinoma Guidelines, Endocr Pract. 2001; 7(No. 3) 217
Treatment • Total thyroidectomy and central(? evidence grade C) compartment lymph node dissection • No radioiodine Remnant Ablation(131 J) • Calcitonin measurment(postoperation) Thyroid Carcinoma Guidelines, Endocr Pract. 2001; 7(No. 3) 217
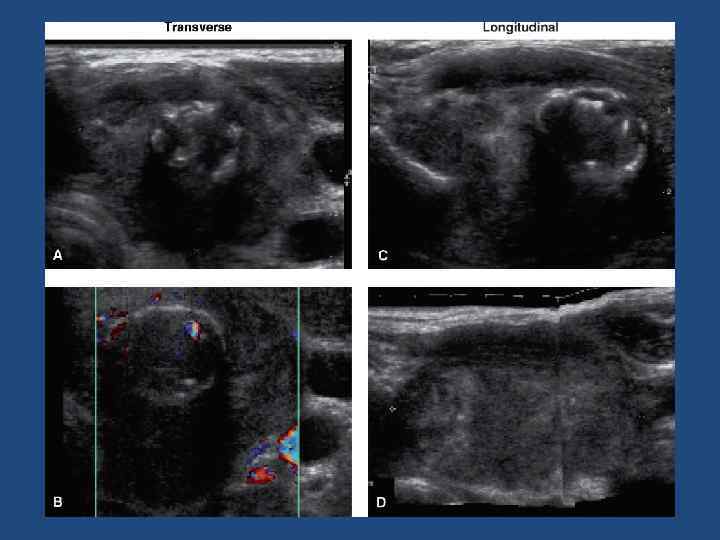
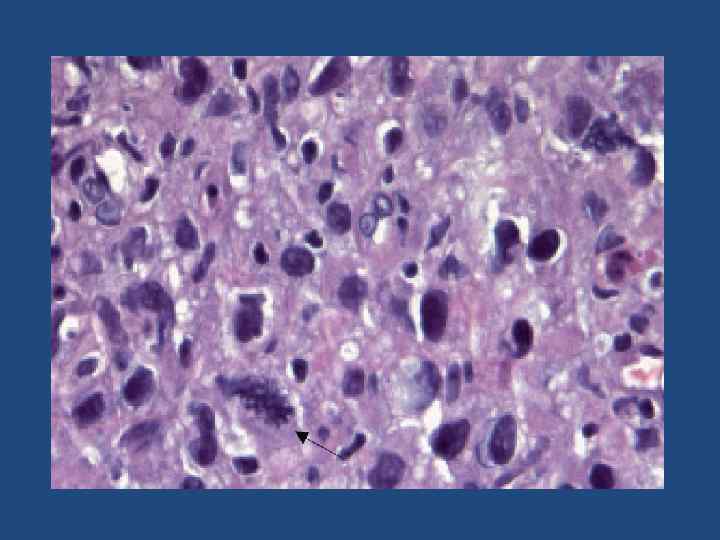
 Anaplastic TC Undifferentiated Highly aggressive Male=female Manifestations(thyroid mass, dyspnea, dysphagia, and cervical pain. Other manifestations include superior vena cava syndrome, ball-valve tracheal obstruction, hyperthyroidism • MTS lung, bone, brain, and, rarely, skin and bowel • •
Anaplastic TC Undifferentiated Highly aggressive Male=female Manifestations(thyroid mass, dyspnea, dysphagia, and cervical pain. Other manifestations include superior vena cava syndrome, ball-valve tracheal obstruction, hyperthyroidism • MTS lung, bone, brain, and, rarely, skin and bowel • •
 Common Features • • Large size Hypoechoic Inhomogeneous Multilobular Rapid growth Clinical symptoms Elderly patient
Common Features • • Large size Hypoechoic Inhomogeneous Multilobular Rapid growth Clinical symptoms Elderly patient
 Treatment • Thyroidectomy • External radiotherapy • Chemotherapy? (doxorubicin) Thyroid Carcinoma Guidelines, Endocr Pract. 2001; 7(No. 3) 217
Treatment • Thyroidectomy • External radiotherapy • Chemotherapy? (doxorubicin) Thyroid Carcinoma Guidelines, Endocr Pract. 2001; 7(No. 3) 217
 M. A. Khachatryan
M. A. Khachatryan


