32ed9d56abf249b15ae4fe7f4b7c679d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Thurs. Dec. 9 • • Powerpoint presentations due this week Review sheet for Exam 3 Review in lecture today EXAM 3 during finals – 12: 15 Lecture: Sun. Dec. 12, 3: 15 pm – 1: 40 Lecture: Mon. Dec. 13, 1 pm If the school closes due to weather during our last exam…you’re off the hook! Otherwise, you’re ON the hook - STUDY
Thurs. Dec. 9 • • Powerpoint presentations due this week Review sheet for Exam 3 Review in lecture today EXAM 3 during finals – 12: 15 Lecture: Sun. Dec. 12, 3: 15 pm – 1: 40 Lecture: Mon. Dec. 13, 1 pm If the school closes due to weather during our last exam…you’re off the hook! Otherwise, you’re ON the hook - STUDY
 Movie “No Grapes” • • Goal of the film? Raise awareness? Strength of the evidence? Weak! Not very scientific, did present some facts but no sources • Didn’t prove that the pesticides caused any of the illnesses • Risk Assessment: Apply the Principles of Toxicology, then weigh costs and benefits
Movie “No Grapes” • • Goal of the film? Raise awareness? Strength of the evidence? Weak! Not very scientific, did present some facts but no sources • Didn’t prove that the pesticides caused any of the illnesses • Risk Assessment: Apply the Principles of Toxicology, then weigh costs and benefits
 Risk Assessment - Captan • • Type of substance? Chemical Type of effects? Cancer, birth defects, acute poisoning, death – Low acute toxicity if eaten or breathed – Can irritate skin; Permanent damage to eyes – Kills fish; causes stunted growth – Evidence of teratogenecity in some studies • Movement in the environment? • Breaks down quickly; Does not bioaccumulate or biomagnify npic. orst. edu/factsheets/captangen. pdf
Risk Assessment - Captan • • Type of substance? Chemical Type of effects? Cancer, birth defects, acute poisoning, death – Low acute toxicity if eaten or breathed – Can irritate skin; Permanent damage to eyes – Kills fish; causes stunted growth – Evidence of teratogenecity in some studies • Movement in the environment? • Breaks down quickly; Does not bioaccumulate or biomagnify npic. orst. edu/factsheets/captangen. pdf
 Risk Assessment – Captan on grapes • Amount – how much is too much • Exposure – how much do we get exposed to from grapes? • 34 different pesticides used • Can’t be washed off • #12 out of top 12 “dirtiest” fruits/veggies http: //www. whatsonmyfood. org/food. jsp? food=GR
Risk Assessment – Captan on grapes • Amount – how much is too much • Exposure – how much do we get exposed to from grapes? • 34 different pesticides used • Can’t be washed off • #12 out of top 12 “dirtiest” fruits/veggies http: //www. whatsonmyfood. org/food. jsp? food=GR
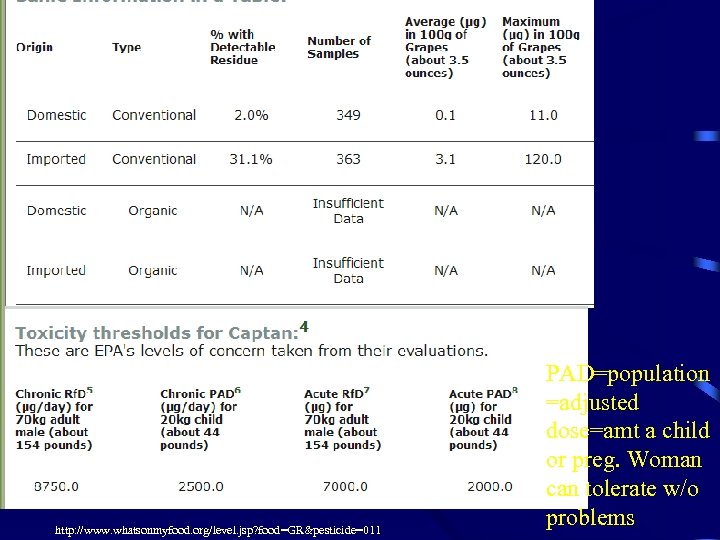 http: //www. whatsonmyfood. org/level. jsp? food=GR&pesticide=011 PAD=population =adjusted dose=amt a child or preg. Woman can tolerate w/o problems
http: //www. whatsonmyfood. org/level. jsp? food=GR&pesticide=011 PAD=population =adjusted dose=amt a child or preg. Woman can tolerate w/o problems
 Risk Assessment – Captan on grapes 1. 2000 ug is max dose for a small child, there is an average of 3. 1 ug per serving of grapes 2. How many servings of grapes would the child need to eat to get cancer? 3. About 710 4. Captan does not bioaccumulate – need to eat this every day 5. What dose does a field worker get everyday?
Risk Assessment – Captan on grapes 1. 2000 ug is max dose for a small child, there is an average of 3. 1 ug per serving of grapes 2. How many servings of grapes would the child need to eat to get cancer? 3. About 710 4. Captan does not bioaccumulate – need to eat this every day 5. What dose does a field worker get everyday?
 Risk Assessment – Captan on grapes • • Who is harmed? Farm workers, farm neighbors, consumers Benefits? Fungicide – kills fungus that kills the crops cheaper grapes, sell more, make more money Who benefits? Company owners, consumers Are benefits greater than the costs? How to compare? Put $ value on everything
Risk Assessment – Captan on grapes • • Who is harmed? Farm workers, farm neighbors, consumers Benefits? Fungicide – kills fungus that kills the crops cheaper grapes, sell more, make more money Who benefits? Company owners, consumers Are benefits greater than the costs? How to compare? Put $ value on everything
 Risk management • Govt minimizes risk by setting max. limits (standards) for environmental toxins. • Weighing costs and benefits in $ terms • Value of a life = money saved or earned by allowing the toxin/#lives lost “How much expense is society willing to incur for each potential life that could be saved? Widening a dangerous road may save some lives, but how much are taxpayers willing to spend to do it? ” http: //www. lifehappens. org/life-insurance/human-life-value
Risk management • Govt minimizes risk by setting max. limits (standards) for environmental toxins. • Weighing costs and benefits in $ terms • Value of a life = money saved or earned by allowing the toxin/#lives lost “How much expense is society willing to incur for each potential life that could be saved? Widening a dangerous road may save some lives, but how much are taxpayers willing to spend to do it? ” http: //www. lifehappens. org/life-insurance/human-life-value
 If you can’t always buy organic…buy lowpesticide foods =personal risk management http: //www. food news. org/wallet guide. php
If you can’t always buy organic…buy lowpesticide foods =personal risk management http: //www. food news. org/wallet guide. php
 With this new info about pesticides on grapes, my opinion is now… 1. I will eat as many grapes as I want 2. I will limit my consumption of grapes 3. I will only eat organically grown grapes 4. I will get more information before I eat any more grapes 5. I will not eat grapes at all
With this new info about pesticides on grapes, my opinion is now… 1. I will eat as many grapes as I want 2. I will limit my consumption of grapes 3. I will only eat organically grown grapes 4. I will get more information before I eat any more grapes 5. I will not eat grapes at all
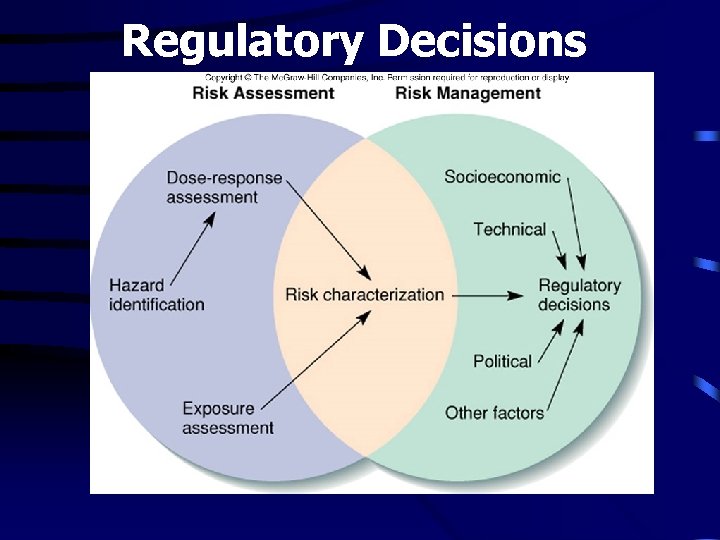 Regulatory Decisions
Regulatory Decisions
 Review for Exam 3 • Multiple choice • Matching • Essay
Review for Exam 3 • Multiple choice • Matching • Essay
 Essay questions #16 – Soil erosion – Define it, how does ag. Cause it #21 – Four effects of ag. on biodiversity #23 – Pros and cons of GM foods #24 – Effect of GM crops on wild species #25 – Neg economic effects of GM crops #29 – What is sustainable agriculture, how does it reduce the problems of modern ag. ? #4 (Nov. 30) – Apply the Princ. Of Toxicology to deciding if a substance is harmful #13 (Dec. 2) – 3 different ways to measure toxicity – pros and cons #16 (Dec. 2) Same as #4 above #17 (dec. 7) – Risk management: How to assess and manage risk for some nasty substance
Essay questions #16 – Soil erosion – Define it, how does ag. Cause it #21 – Four effects of ag. on biodiversity #23 – Pros and cons of GM foods #24 – Effect of GM crops on wild species #25 – Neg economic effects of GM crops #29 – What is sustainable agriculture, how does it reduce the problems of modern ag. ? #4 (Nov. 30) – Apply the Princ. Of Toxicology to deciding if a substance is harmful #13 (Dec. 2) – 3 different ways to measure toxicity – pros and cons #16 (Dec. 2) Same as #4 above #17 (dec. 7) – Risk management: How to assess and manage risk for some nasty substance
 Please select a Team. 5 pts. for winning team! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Team Team 1 2 3 4 5 6
Please select a Team. 5 pts. for winning team! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Team Team 1 2 3 4 5 6
 Team Scores
Team Scores
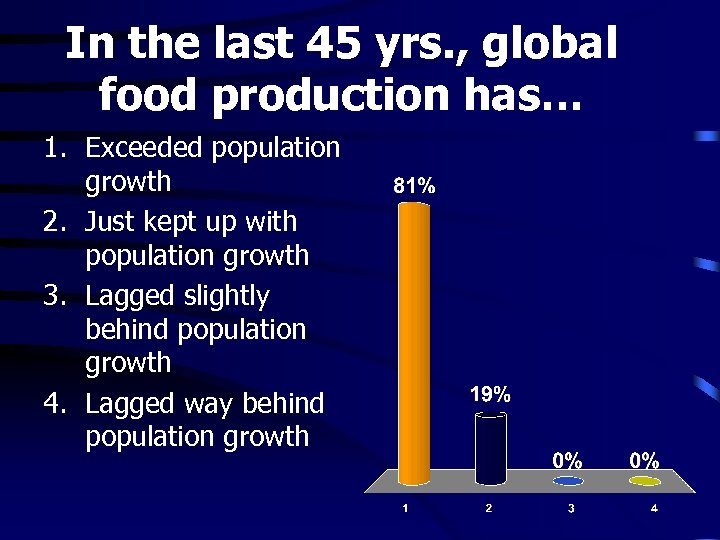 In the last 45 yrs. , global food production has… 1. Exceeded population growth 2. Just kept up with population growth 3. Lagged slightly behind population growth 4. Lagged way behind population growth
In the last 45 yrs. , global food production has… 1. Exceeded population growth 2. Just kept up with population growth 3. Lagged slightly behind population growth 4. Lagged way behind population growth
 The era of modern agriculture began with… 1. The invention of the plow 2. The invention of the steam engine 3. The end of the Civil War 4. The end of WWII 5. The beginning of the industrial era
The era of modern agriculture began with… 1. The invention of the plow 2. The invention of the steam engine 3. The end of the Civil War 4. The end of WWII 5. The beginning of the industrial era
 Food security means… 1. Keeping food supplies safe 2. Allowing food to be distributed to people in need 3. Having access to the right variety of foods 4. Maintaining a 2 -year storage of food supplies at all times
Food security means… 1. Keeping food supplies safe 2. Allowing food to be distributed to people in need 3. Having access to the right variety of foods 4. Maintaining a 2 -year storage of food supplies at all times
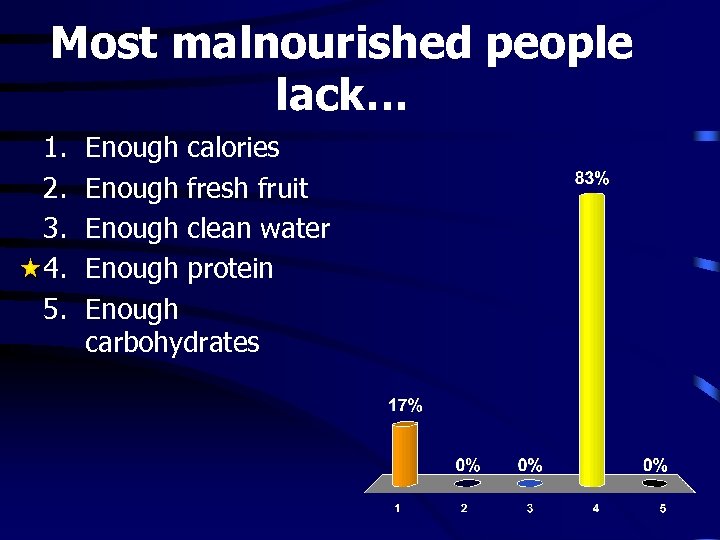 Most malnourished people lack… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Enough calories Enough fresh fruit Enough clean water Enough protein Enough carbohydrates
Most malnourished people lack… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Enough calories Enough fresh fruit Enough clean water Enough protein Enough carbohydrates
 Soil type is NOT determined by… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Temperature Bacteria and fungi Glaciers Slope of the land Fertilizer use
Soil type is NOT determined by… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Temperature Bacteria and fungi Glaciers Slope of the land Fertilizer use
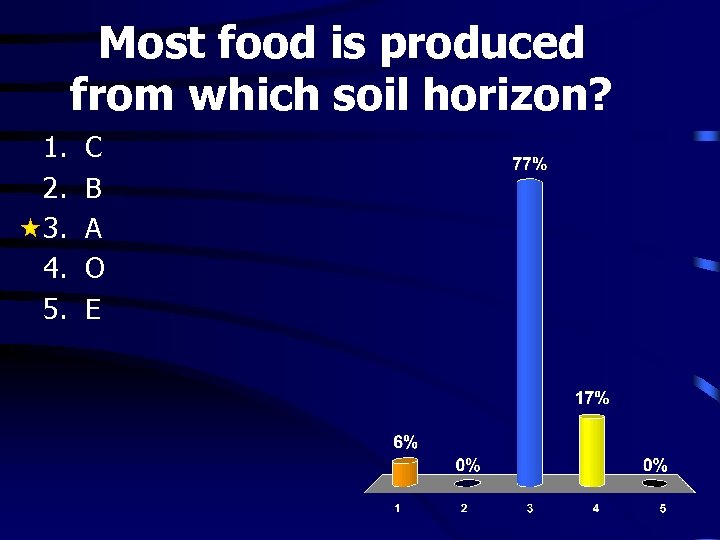 Most food is produced from which soil horizon? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C B A O E
Most food is produced from which soil horizon? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C B A O E
 Soil erosion is caused by… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Gummy bears Tic-tacs Milky way bars Kit-kats Wind and water
Soil erosion is caused by… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Gummy bears Tic-tacs Milky way bars Kit-kats Wind and water
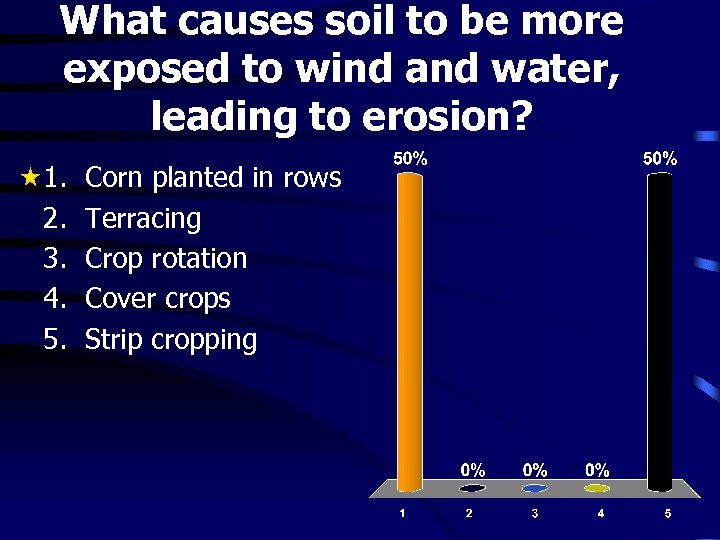 What causes soil to be more exposed to wind and water, leading to erosion? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Corn planted in rows Terracing Crop rotation Cover crops Strip cropping
What causes soil to be more exposed to wind and water, leading to erosion? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Corn planted in rows Terracing Crop rotation Cover crops Strip cropping
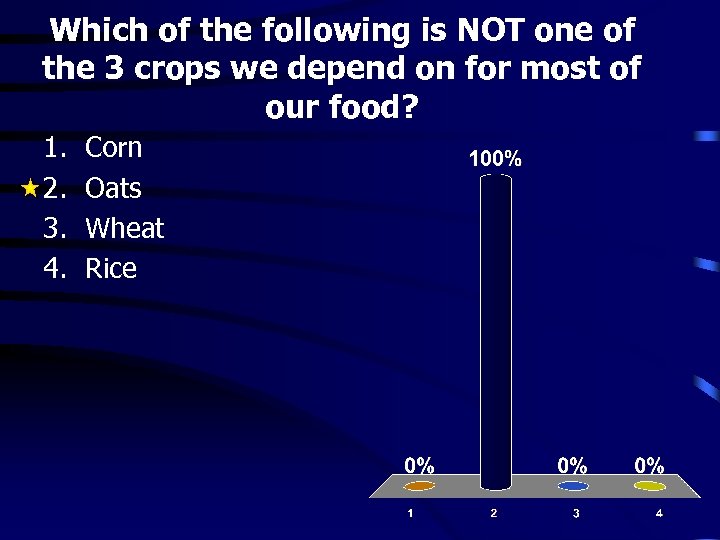 Which of the following is NOT one of the 3 crops we depend on for most of our food? 1. 2. 3. 4. Corn Oats Wheat Rice
Which of the following is NOT one of the 3 crops we depend on for most of our food? 1. 2. 3. 4. Corn Oats Wheat Rice
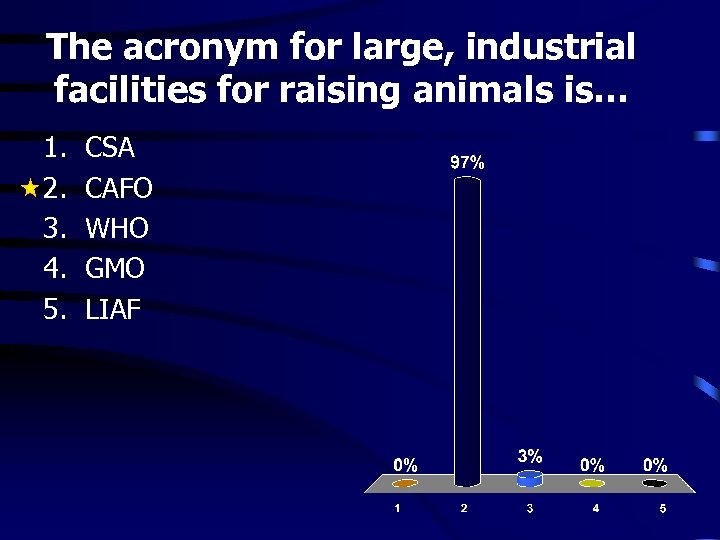 The acronym for large, industrial facilities for raising animals is… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. CSA CAFO WHO GMO LIAF
The acronym for large, industrial facilities for raising animals is… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. CSA CAFO WHO GMO LIAF
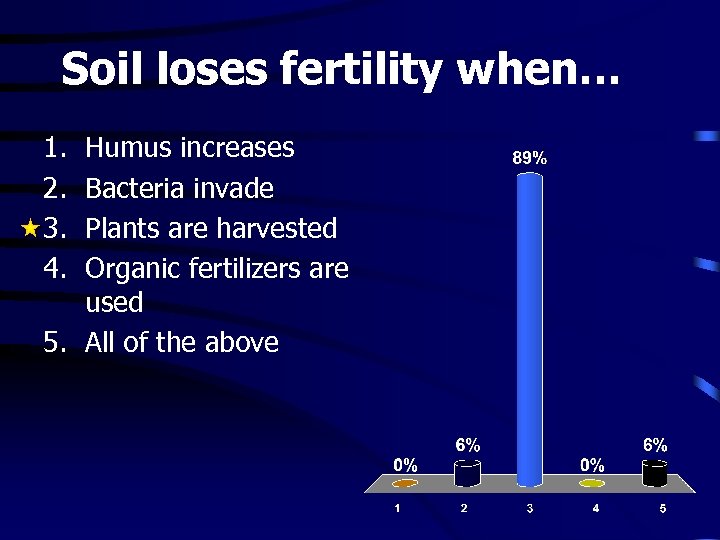 Soil loses fertility when… 1. 2. 3. 4. Humus increases Bacteria invade Plants are harvested Organic fertilizers are used 5. All of the above
Soil loses fertility when… 1. 2. 3. 4. Humus increases Bacteria invade Plants are harvested Organic fertilizers are used 5. All of the above
 Chemical fertilizers are a problem because they… 1. Deplete the ozone layer 2. Wash into water and become endocrine disruptors 3. Wash into water and create harmful algae growth 4. Evaporate into the air and cause cancer
Chemical fertilizers are a problem because they… 1. Deplete the ozone layer 2. Wash into water and become endocrine disruptors 3. Wash into water and create harmful algae growth 4. Evaporate into the air and cause cancer
 Modern agriculture threatens biodiversity because… 1. It destroys habitat 2. It creates greenhouse gases 3. It causes water pollution which degrades habitat 4. GM crops might interbreed with wild species 5. All of the above
Modern agriculture threatens biodiversity because… 1. It destroys habitat 2. It creates greenhouse gases 3. It causes water pollution which degrades habitat 4. GM crops might interbreed with wild species 5. All of the above
 Some farmers don’t like certain GM crops because the crops… 1. Are more vulnerable to insects 2. Can become herbicide-tolerant 3. Are too sensitive to weather 4. Cause excessive soil erosion 5. All of the above
Some farmers don’t like certain GM crops because the crops… 1. Are more vulnerable to insects 2. Can become herbicide-tolerant 3. Are too sensitive to weather 4. Cause excessive soil erosion 5. All of the above
 When is organic food not sustainable? 1. When it uses manure for fertilizer 2. When it uses cover crops 3. When it uses strip cropping 4. When it is shipped far away 5. All of the above
When is organic food not sustainable? 1. When it uses manure for fertilizer 2. When it uses cover crops 3. When it uses strip cropping 4. When it is shipped far away 5. All of the above
 According to the Princ. Of Toxicol. , toxicity of a substance is affected by. . 1. Stability/persistence 2. Type of solvent needed 3. Ability to bioaccumulate 4. Ability to biomagnify 5. Amount (dose) 6. Exposure 7. All of the above
According to the Princ. Of Toxicol. , toxicity of a substance is affected by. . 1. Stability/persistence 2. Type of solvent needed 3. Ability to bioaccumulate 4. Ability to biomagnify 5. Amount (dose) 6. Exposure 7. All of the above
 If the effect of a substance is shortterm, the effect is called. . 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Toxic Hazardous Carcinogenic Chronic Acute
If the effect of a substance is shortterm, the effect is called. . 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Toxic Hazardous Carcinogenic Chronic Acute
 Substance A has an LD 50 of 0. 1 ounce. Substance B has an LD 50 of 5 ounces. Which is more toxic? 1. 2. 3. 4. Substance A Substance B They are the same Can’t tell without knowing the type of effects 5. All of the above
Substance A has an LD 50 of 0. 1 ounce. Substance B has an LD 50 of 5 ounces. Which is more toxic? 1. 2. 3. 4. Substance A Substance B They are the same Can’t tell without knowing the type of effects 5. All of the above
 Mercury is an example of… 1. A substance that has both positive and negative health effects 2. A known carcinogen 3. An endocrine disruptor 4. A neurotoxin 5. All of the above
Mercury is an example of… 1. A substance that has both positive and negative health effects 2. A known carcinogen 3. An endocrine disruptor 4. A neurotoxin 5. All of the above
 Persistent Organic Pollutants… 1. Do not breakdown in the environment 2. Do not biomagnify 3. Contain little carbon 4. Are all neurotoxins 5. Affect humans but not wildlife 6. All of the above
Persistent Organic Pollutants… 1. Do not breakdown in the environment 2. Do not biomagnify 3. Contain little carbon 4. Are all neurotoxins 5. Affect humans but not wildlife 6. All of the above
 A substance that causes suffocation is called a(n) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Allergen Mutagen Asphyxiant Teratogen Pillow
A substance that causes suffocation is called a(n) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Allergen Mutagen Asphyxiant Teratogen Pillow
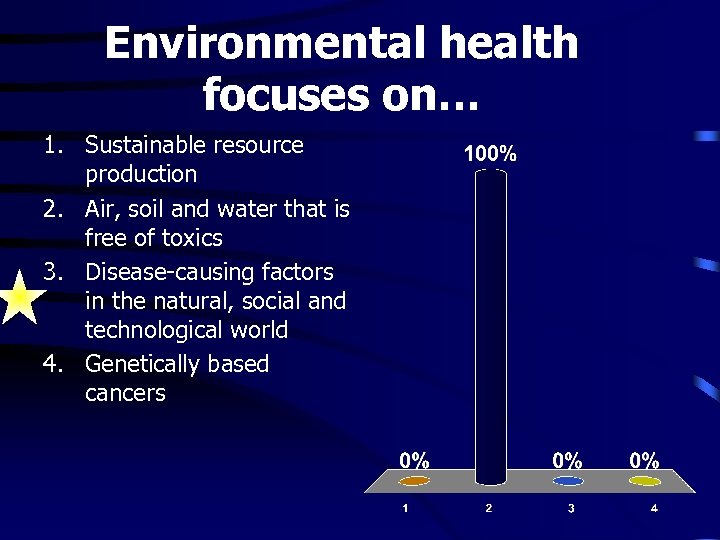 Environmental health focuses on… 1. Sustainable resource production 2. Air, soil and water that is free of toxics 3. Disease-causing factors in the natural, social and technological world 4. Genetically based cancers
Environmental health focuses on… 1. Sustainable resource production 2. Air, soil and water that is free of toxics 3. Disease-causing factors in the natural, social and technological world 4. Genetically based cancers
 Team Scores 11 11 10. 8 8. 75 Team 2 6 5 1 8. 67 Team 4
Team Scores 11 11 10. 8 8. 75 Team 2 6 5 1 8. 67 Team 4
 II. Principles of Toxicology A. There are different types of env. risks (chemical, biological, physical) B. Different substances had different effects (asphyxiant, allergen, neurotoxin, mutagen, carcinogen, teratogen) C. Toxicity is affected by many factors (stability, movement, biomagnification, amount/dose, duration of exposure, type of organism, etc. ) D. Identifying effects is difficult E. Risk management: Weigh costs and benefits, minimize risks
II. Principles of Toxicology A. There are different types of env. risks (chemical, biological, physical) B. Different substances had different effects (asphyxiant, allergen, neurotoxin, mutagen, carcinogen, teratogen) C. Toxicity is affected by many factors (stability, movement, biomagnification, amount/dose, duration of exposure, type of organism, etc. ) D. Identifying effects is difficult E. Risk management: Weigh costs and benefits, minimize risks


