fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Thunderstorm Tracking and Nowcasting using 3 D Lightning and Radar Data in Southern Germany Vera Meyer [1] - vera. meyer@zamg. ac. at, H. Höller [2], H. -D. Betz [3] , K. Schmidt [2] [1] Central Institute for Meteorology and Geodynamics, Hohe Warte, Vienna [2] Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt, Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre, Oberpfaffenhofen, Deutschland [3] Physics Department, University of Munich, Germany 1 Convection Week 2011, Session 3
Thunderstorm Tracking and Nowcasting using 3 D Lightning and Radar Data in Southern Germany Vera Meyer [1] - vera. meyer@zamg. ac. at, H. Höller [2], H. -D. Betz [3] , K. Schmidt [2] [1] Central Institute for Meteorology and Geodynamics, Hohe Warte, Vienna [2] Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt, Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre, Oberpfaffenhofen, Deutschland [3] Physics Department, University of Munich, Germany 1 Convection Week 2011, Session 3
 PROJECT Regio. Ex. AKT www. regioexakt. de Regional Risk of Convective Extreme Weather Events: User-oriented concepts for optimised thunderstorm nowcasting, with focus on the needs of Munich Airport Coordinator: Dr. Nikolai Dotzek MUNICH AIRPORT HEAVY RAIN 15 Juni 2007 40, 5 l/m² zw. 18. 00 – 21. 00 h intense rain hail lightning strikes wind gusts etc. 2 HAIL DAMAGE Boeing 737, Geneva 15 August 2003 MOTIVATION
PROJECT Regio. Ex. AKT www. regioexakt. de Regional Risk of Convective Extreme Weather Events: User-oriented concepts for optimised thunderstorm nowcasting, with focus on the needs of Munich Airport Coordinator: Dr. Nikolai Dotzek MUNICH AIRPORT HEAVY RAIN 15 Juni 2007 40, 5 l/m² zw. 18. 00 – 21. 00 h intense rain hail lightning strikes wind gusts etc. 2 HAIL DAMAGE Boeing 737, Geneva 15 August 2003 MOTIVATION
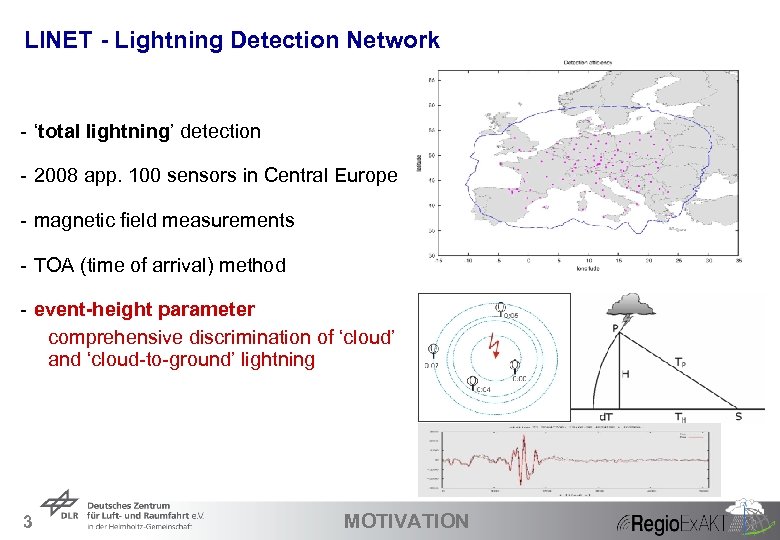 LINET - Lightning Detection Network - ‘total lightning’ detection - 2008 app. 100 sensors in Central Europe - magnetic field measurements - TOA (time of arrival) method - event-height parameter comprehensive discrimination of ‘cloud’ and ‘cloud-to-ground’ lightning 3 MOTIVATION
LINET - Lightning Detection Network - ‘total lightning’ detection - 2008 app. 100 sensors in Central Europe - magnetic field measurements - TOA (time of arrival) method - event-height parameter comprehensive discrimination of ‘cloud’ and ‘cloud-to-ground’ lightning 3 MOTIVATION
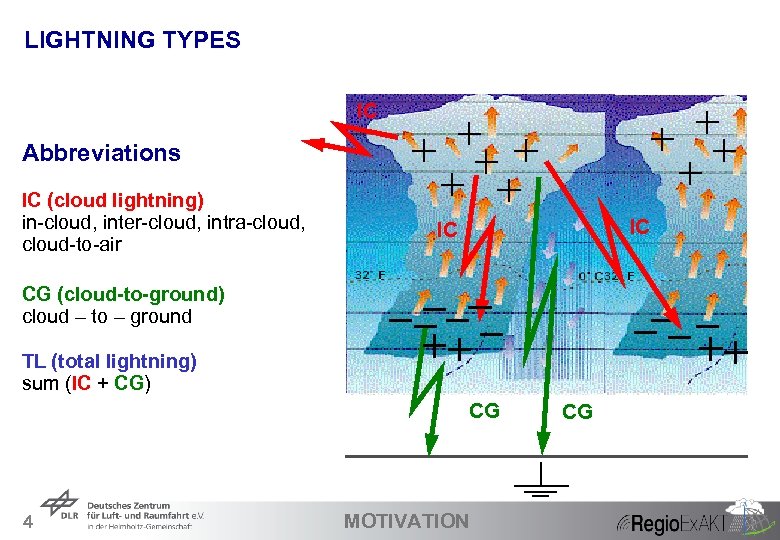 LIGHTNING TYPES IC Abbreviations IC (cloud lightning) in-cloud, inter-cloud, intra-cloud, cloud-to-air -15 °C IC IC 0 °C CG (cloud-to-ground) cloud – to – ground TL (total lightning) sum (IC + CG) CG 4 MOTIVATION CG
LIGHTNING TYPES IC Abbreviations IC (cloud lightning) in-cloud, inter-cloud, intra-cloud, cloud-to-air -15 °C IC IC 0 °C CG (cloud-to-ground) cloud – to – ground TL (total lightning) sum (IC + CG) CG 4 MOTIVATION CG
 LINET 3 D-Visualisierung high-precision lightning detection. ‚NORMAL STORM‘ ‚SEVERE STORM‘ cloud lightning cloud-to- ground lightning 5 MOTIVATION
LINET 3 D-Visualisierung high-precision lightning detection. ‚NORMAL STORM‘ ‚SEVERE STORM‘ cloud lightning cloud-to- ground lightning 5 MOTIVATION
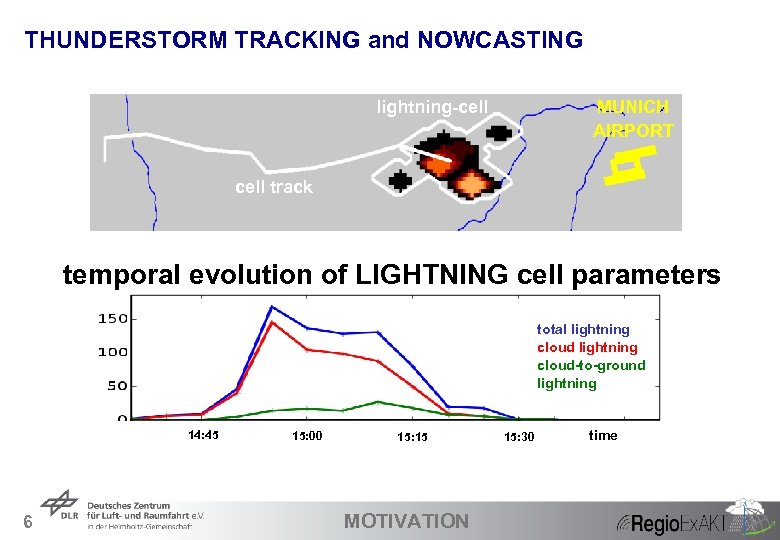 THUNDERSTORM TRACKING and NOWCASTING lightning-cell MUNICH AIRPORT cell track temporal evolution of LIGHTNING cell parameters total lightning cloud-to-ground lightning 14: 45 6 15: 00 15: 15 MOTIVATION 15: 30 time
THUNDERSTORM TRACKING and NOWCASTING lightning-cell MUNICH AIRPORT cell track temporal evolution of LIGHTNING cell parameters total lightning cloud-to-ground lightning 14: 45 6 15: 00 15: 15 MOTIVATION 15: 30 time
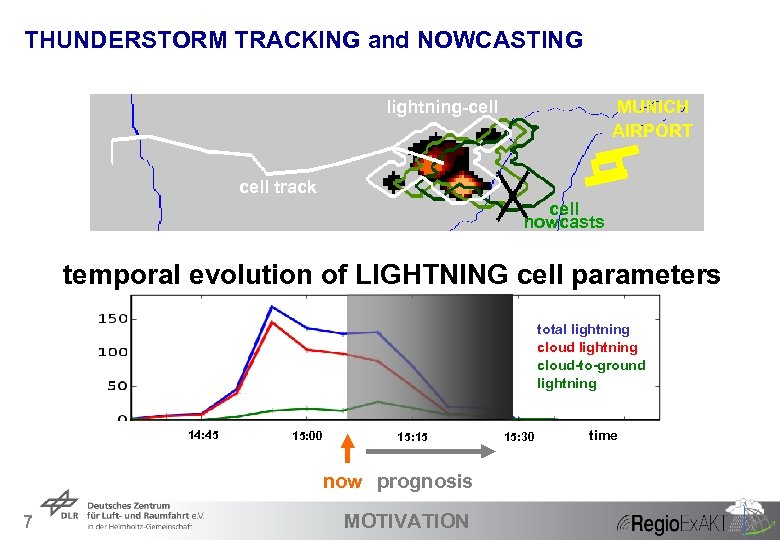 THUNDERSTORM TRACKING and NOWCASTING lightning-cell MUNICH AIRPORT cell track cell nowcasts temporal evolution of LIGHTNING cell parameters total lightning cloud-to-ground lightning 14: 45 15: 00 15: 15 now prognosis 7 MOTIVATION 15: 30 time
THUNDERSTORM TRACKING and NOWCASTING lightning-cell MUNICH AIRPORT cell track cell nowcasts temporal evolution of LIGHTNING cell parameters total lightning cloud-to-ground lightning 14: 45 15: 00 15: 15 now prognosis 7 MOTIVATION 15: 30 time
 INTRODUCTION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) 8 INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) 8 INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) identification tracking prediction 9 INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) identification tracking prediction 9 INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) identification tracking prediction cell evolution 10 INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) identification tracking prediction cell evolution 10 INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) - develop a nowcasting method based on lightning information - develop a method to compare lightning-cell information with information from other data sources (radar) verify lightning-cell properties in case-studies evaluate the statistical information content of 3 D lightning information 11 INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) - develop a nowcasting method based on lightning information - develop a method to compare lightning-cell information with information from other data sources (radar) verify lightning-cell properties in case-studies evaluate the statistical information content of 3 D lightning information 11 INTRODUCTION
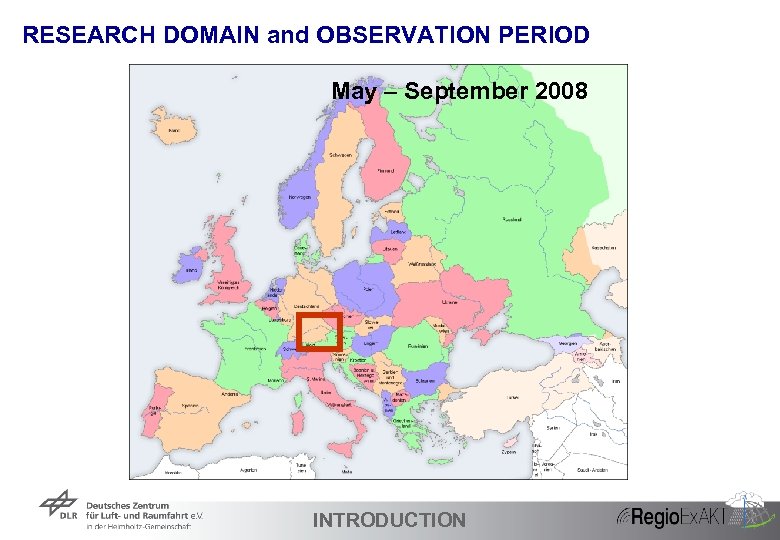 RESEARCH DOMAIN and OBSERVATION PERIOD May – September 2008 12 INTRODUCTION
RESEARCH DOMAIN and OBSERVATION PERIOD May – September 2008 12 INTRODUCTION
 NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM – tracking and monitoring of electrically charged convective cells combines cell informations from independently tracked lightning- and radar-cells 13 METHOD
NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM – tracking and monitoring of electrically charged convective cells combines cell informations from independently tracked lightning- and radar-cells 13 METHOD
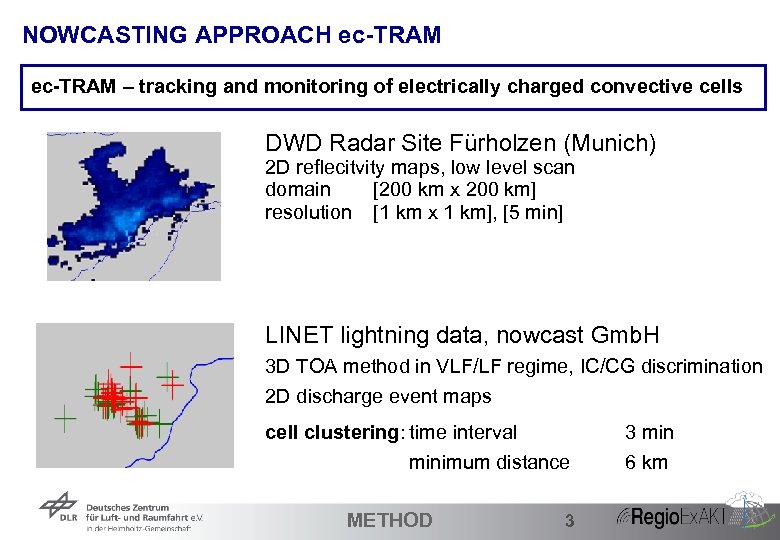 NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM – tracking and monitoring of electrically charged convective cells DWD Radar Site Fürholzen (Munich) 2 D reflecitvity maps, low level scan domain [200 km x 200 km] resolution [1 km x 1 km], [5 min] LINET lightning data, nowcast Gmb. H 3 D TOA method in VLF/LF regime, IC/CG discrimination 2 D discharge event maps cell clustering: time interval minimum distance 14 METHOD 3 3 min 6 km
NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM – tracking and monitoring of electrically charged convective cells DWD Radar Site Fürholzen (Munich) 2 D reflecitvity maps, low level scan domain [200 km x 200 km] resolution [1 km x 1 km], [5 min] LINET lightning data, nowcast Gmb. H 3 D TOA method in VLF/LF regime, IC/CG discrimination 2 D discharge event maps cell clustering: time interval minimum distance 14 METHOD 3 3 min 6 km
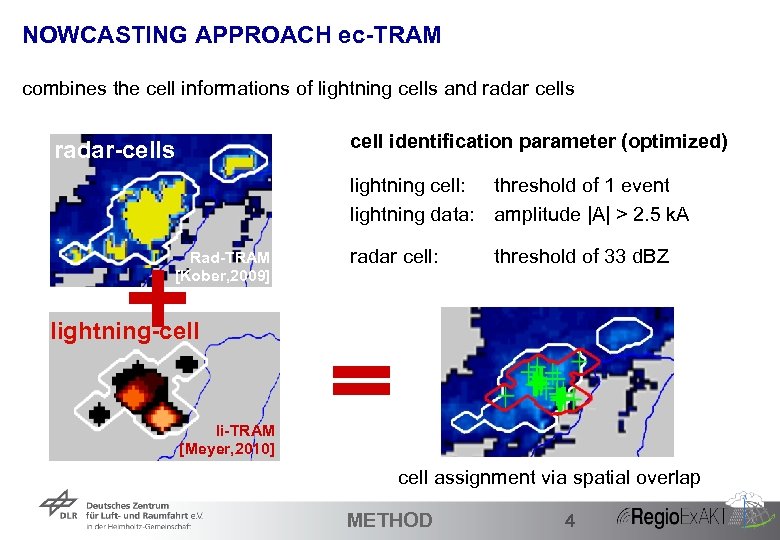 NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM combines the cell informations of lightning cells and radar cells cell identification parameter (optimized) radar-cells lightning cell: threshold of 1 event lightning data: amplitude |A| > 2. 5 k. A Rad-TRAM [Kober, 2009] radar cell: threshold of 33 d. BZ lightning-cell li-TRAM [Meyer, 2010] cell assignment via spatial overlap 15 METHOD 4
NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM combines the cell informations of lightning cells and radar cells cell identification parameter (optimized) radar-cells lightning cell: threshold of 1 event lightning data: amplitude |A| > 2. 5 k. A Rad-TRAM [Kober, 2009] radar cell: threshold of 33 d. BZ lightning-cell li-TRAM [Meyer, 2010] cell assignment via spatial overlap 15 METHOD 4
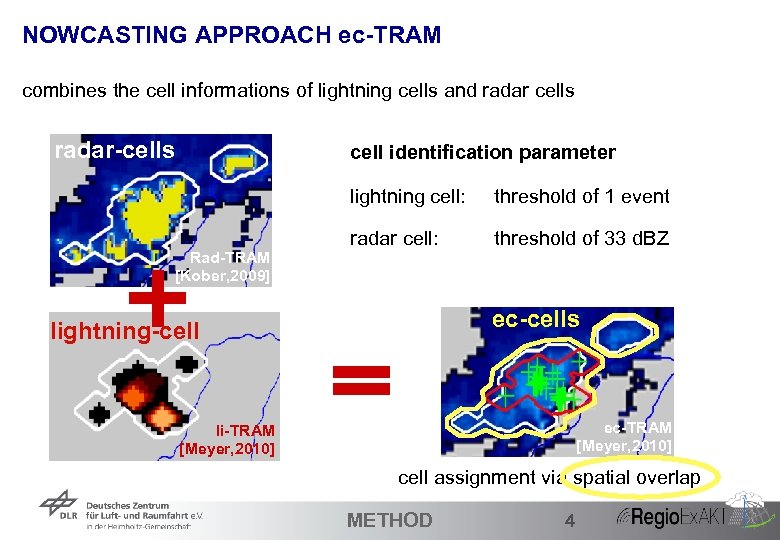 NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM combines the cell informations of lightning cells and radar cells radar-cells cell identification parameter lightning cell: Rad-TRAM [Kober, 2009] threshold of 1 event radar cell: threshold of 33 d. BZ ec-cells lightning-cell ec-TRAM [Meyer, 2010] li-TRAM [Meyer, 2010] cell assignment via spatial overlap 16 METHOD 4
NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM combines the cell informations of lightning cells and radar cells radar-cells cell identification parameter lightning cell: Rad-TRAM [Kober, 2009] threshold of 1 event radar cell: threshold of 33 d. BZ ec-cells lightning-cell ec-TRAM [Meyer, 2010] li-TRAM [Meyer, 2010] cell assignment via spatial overlap 16 METHOD 4
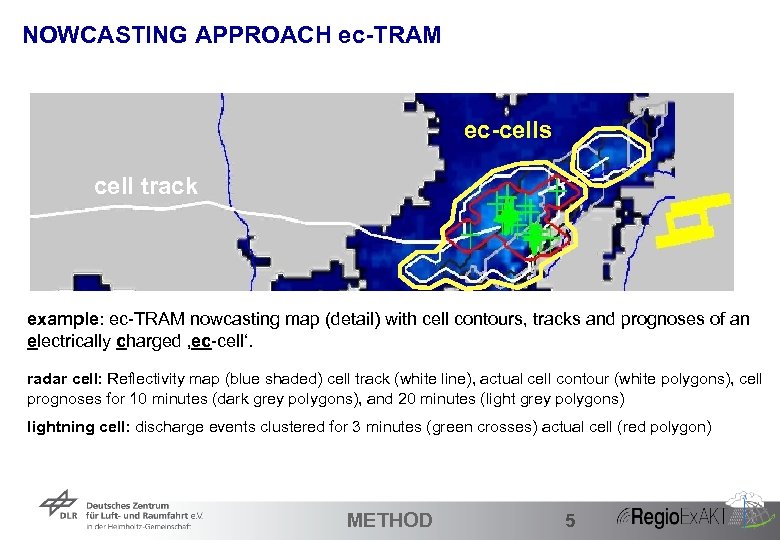 NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM ec-cells cell track example: ec-TRAM nowcasting map (detail) with cell contours, tracks and prognoses of an electrically charged ‚ec-cell‘. radar cell: Reflectivity map (blue shaded) cell track (white line), actual cell contour (white polygons), cell prognoses for 10 minutes (dark grey polygons), and 20 minutes (light grey polygons) lightning cell: discharge events clustered for 3 minutes (green crosses) actual cell (red polygon) 17 METHOD 5
NOWCASTING APPROACH ec-TRAM ec-cells cell track example: ec-TRAM nowcasting map (detail) with cell contours, tracks and prognoses of an electrically charged ‚ec-cell‘. radar cell: Reflectivity map (blue shaded) cell track (white line), actual cell contour (white polygons), cell prognoses for 10 minutes (dark grey polygons), and 20 minutes (light grey polygons) lightning cell: discharge events clustered for 3 minutes (green crosses) actual cell (red polygon) 17 METHOD 5
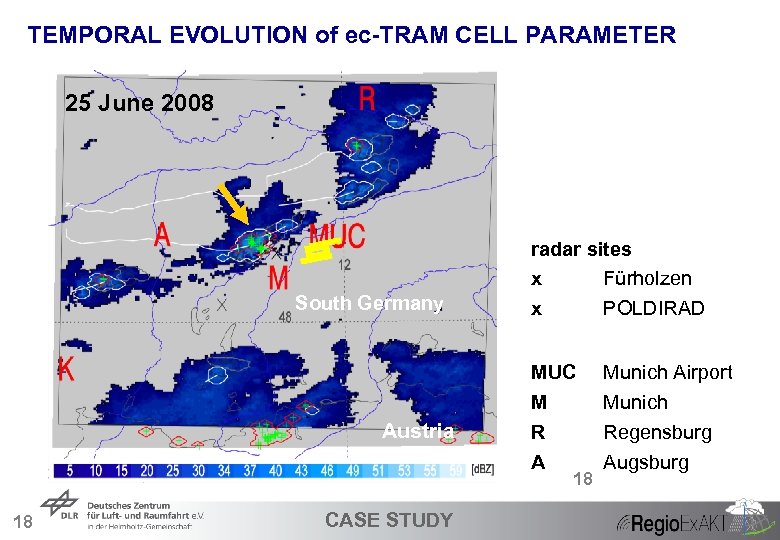 TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER 25 June 2008 F P South Germany Austria radar sites x Fürholzen x POLDIRAD MUC M R A 18 18 CASE STUDY Munich Airport Munich Regensburg Augsburg
TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER 25 June 2008 F P South Germany Austria radar sites x Fürholzen x POLDIRAD MUC M R A 18 18 CASE STUDY Munich Airport Munich Regensburg Augsburg
 19 19
19 19
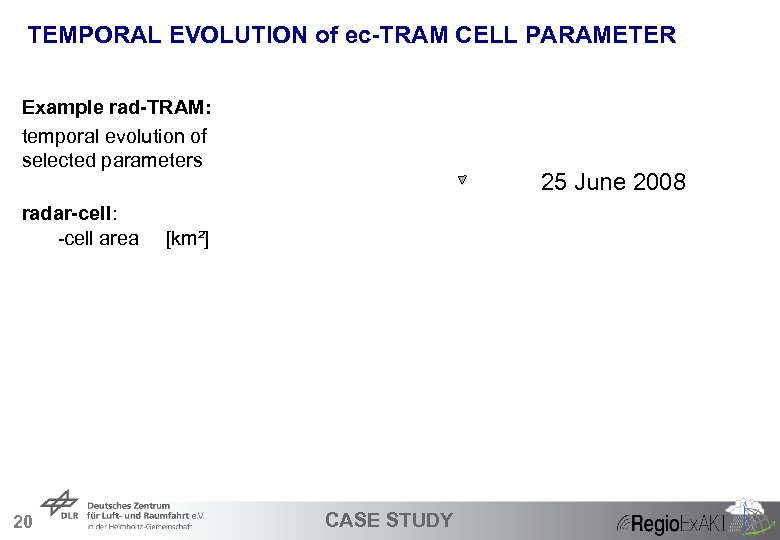 TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER Example rad-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area 20 25 June 2008 [km²] CASE STUDY
TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER Example rad-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area 20 25 June 2008 [km²] CASE STUDY
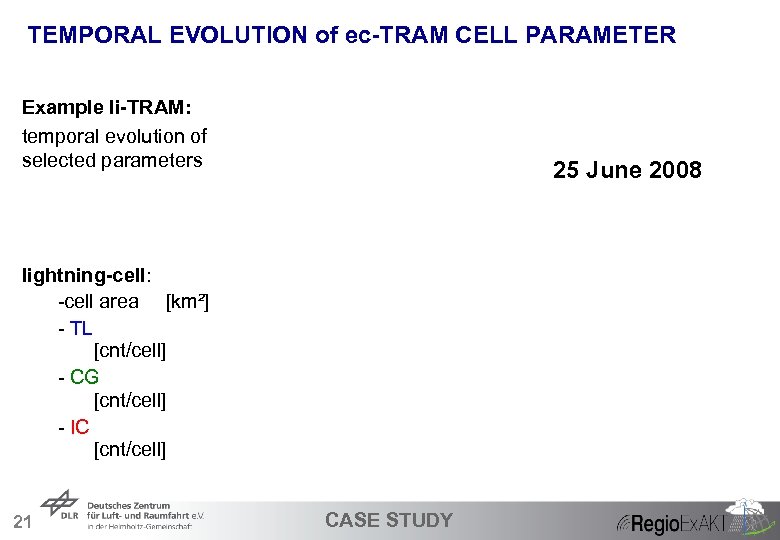 TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER Example li-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters 25 June 2008 lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 21 CASE STUDY
TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER Example li-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters 25 June 2008 lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 21 CASE STUDY
![TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²]](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-22.jpg) TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 22 25 June 2008 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters 22 CASE STUDY
TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 22 25 June 2008 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters 22 CASE STUDY
![Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-23.jpg) Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 23 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER onset 23 CASE STUDY
Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 23 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER onset 23 CASE STUDY
![Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-24.jpg) Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 24 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER cell splitting 24 CASE STUDY
Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 24 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER cell splitting 24 CASE STUDY
![Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-25.jpg) Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 25 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER intensification 25 CASE STUDY
Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 25 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER intensification 25 CASE STUDY
![Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-26.jpg) Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 26 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER decease 26 CASE STUDY
Example ec-TRAM: temporal evolution of selected parameters radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area [km²] - TL [cnt/cell] - CG [cnt/cell] - IC [cnt/cell] 26 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] TEMPORAL EVOLUTION of ec-TRAM CELL PARAMETER decease 26 CASE STUDY
 VERIFICATION of LIGHTNING-CELL PROPERTIES in CASE-STUDIES lifetime series of ec-cell parameters were complemented with 3 D polarimetric radar data (POLDIRAD) - not shown lightning-cell parameters were found to -evolve reasonably according to the current state of knowledge -be in very good agreement with other case studies [Klemp 1987, Williams 1989 and 1999, Goodman 1988, Carey 1996, Lopez 1997, Mazur 1998, Altaraz 2003, Motley 2006, . . . ] à reflect the actual storm dynamic (intensification / weakening) à li-TRAM has reasonable, consistent tracking performances (comparable to rad-TRAM) [Meyer, 2010] 27 VERIFICATION
VERIFICATION of LIGHTNING-CELL PROPERTIES in CASE-STUDIES lifetime series of ec-cell parameters were complemented with 3 D polarimetric radar data (POLDIRAD) - not shown lightning-cell parameters were found to -evolve reasonably according to the current state of knowledge -be in very good agreement with other case studies [Klemp 1987, Williams 1989 and 1999, Goodman 1988, Carey 1996, Lopez 1997, Mazur 1998, Altaraz 2003, Motley 2006, . . . ] à reflect the actual storm dynamic (intensification / weakening) à li-TRAM has reasonable, consistent tracking performances (comparable to rad-TRAM) [Meyer, 2010] 27 VERIFICATION
![PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-28.jpg) PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 28 2 CASE STUDIES
PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 28 2 CASE STUDIES
![PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-29.jpg) PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell growth 3 2 I cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 29 2 CASE STUDIES
PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell growth 3 2 I cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 29 2 CASE STUDIES
![PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-30.jpg) PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 mature stage cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 30
PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 mature stage cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 30
![PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-31.jpg) PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell dissipation 4 5 6 E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 31 2 CASE STUDIES
PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell dissipation 4 5 6 E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 31 2 CASE STUDIES
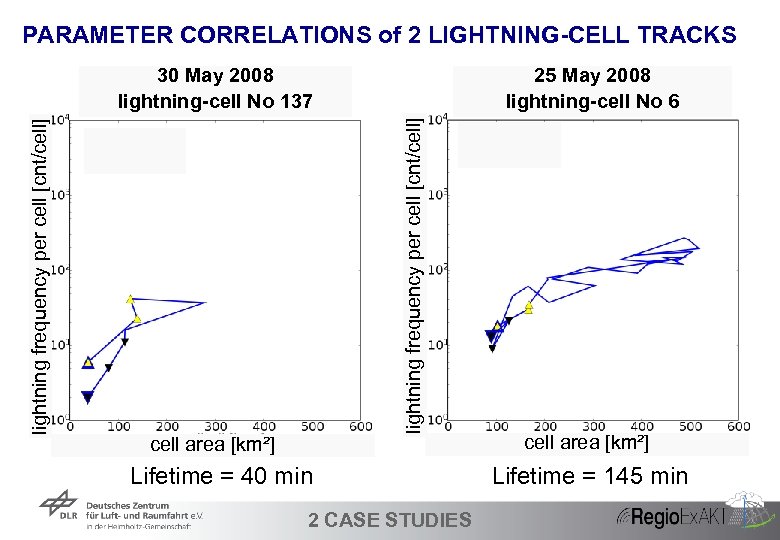 PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 32 2 CASE STUDIES cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min
PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 32 2 CASE STUDIES cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min
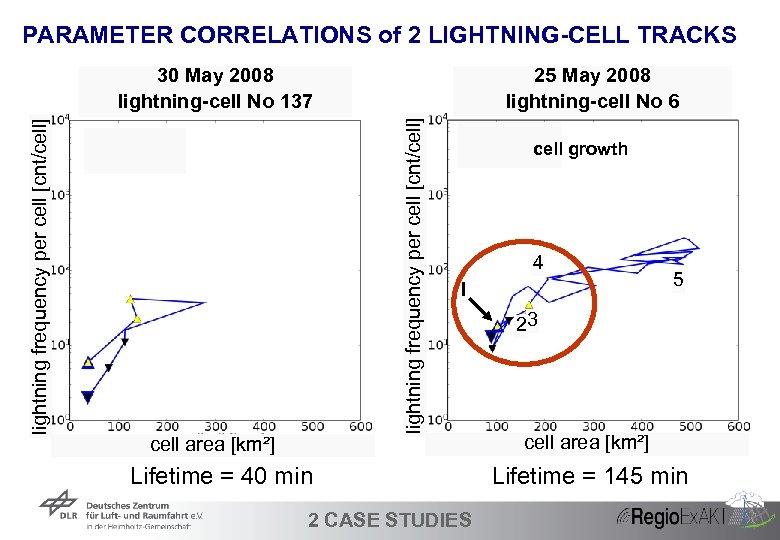 PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] cell growth 4 I Lifetime = 40 min 33 2 CASE STUDIES 5 23 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min
PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] cell growth 4 I Lifetime = 40 min 33 2 CASE STUDIES 5 23 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min
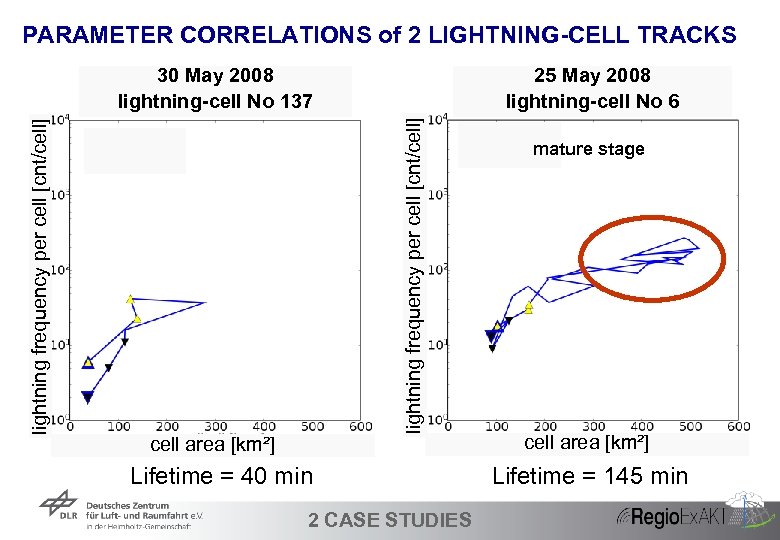 PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 34 2 CASE STUDIES mature stage cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min
PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 34 2 CASE STUDIES mature stage cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min
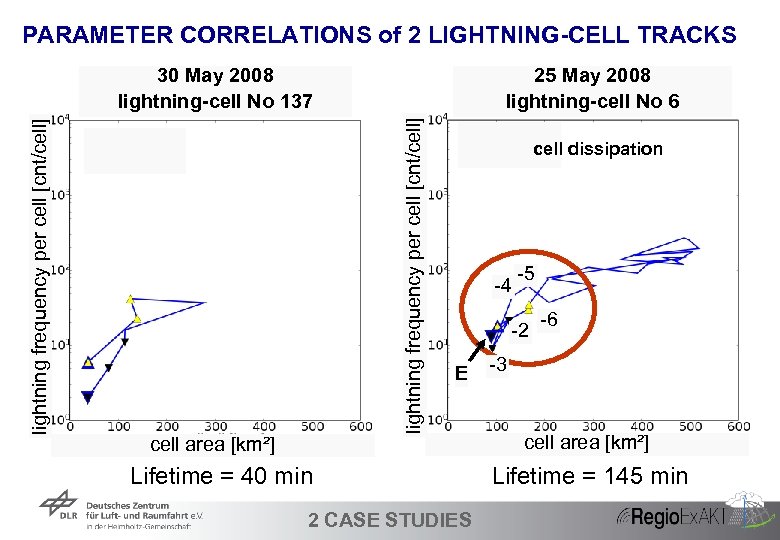 PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] cell dissipation -4 -2 E Lifetime = 40 min 35 -5 2 CASE STUDIES -6 -3 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min
PARAMETER CORRELATIONS of 2 LIGHTNING-CELL TRACKS 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 cell area [km²] cell dissipation -4 -2 E Lifetime = 40 min 35 -5 2 CASE STUDIES -6 -3 cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min
![lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean TL MEAN lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean TL MEAN](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-36.jpg) lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean TL MEAN IC mean IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 PARAMETER MEANS lightning frequency versus cell area -10 km² area intervals -10 200 completely assessed lightning-cell entries cell area [km²] 36 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS
lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean TL MEAN IC mean IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 PARAMETER MEANS lightning frequency versus cell area -10 km² area intervals -10 200 completely assessed lightning-cell entries cell area [km²] 36 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS
![lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean TL MEAN lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean TL MEAN](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-37.jpg) lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean TL MEAN IC mean IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] 37 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS
lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean TL MEAN IC mean IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] 37 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS
![TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²]](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-38.jpg) TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] 38 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS IC MEAN height fit 1 + 2 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS cell area [km²]
TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] 38 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS IC MEAN height fit 1 + 2 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS cell area [km²]
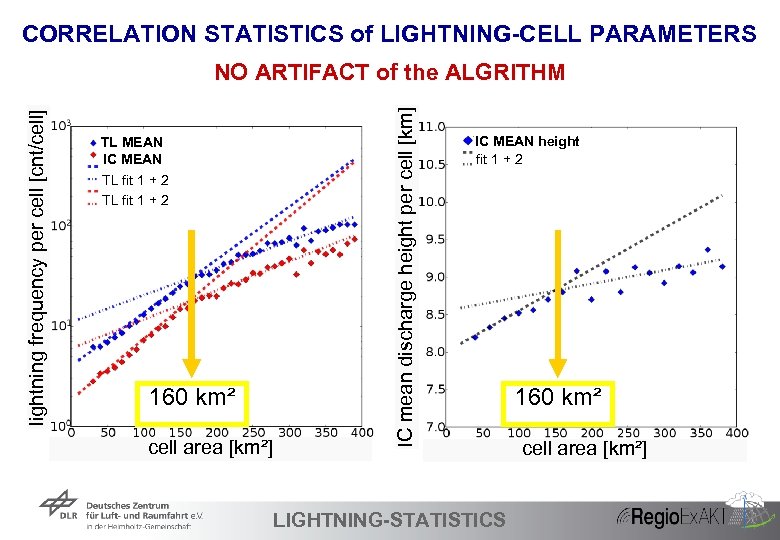 CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] 39 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] NO ARTIFACT of the ALGRITHM IC mean height IC MEAN height fit 1 + 2 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS 160 km² cell area [km²]
CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] 39 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] NO ARTIFACT of the ALGRITHM IC mean height IC MEAN height fit 1 + 2 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS 160 km² cell area [km²]
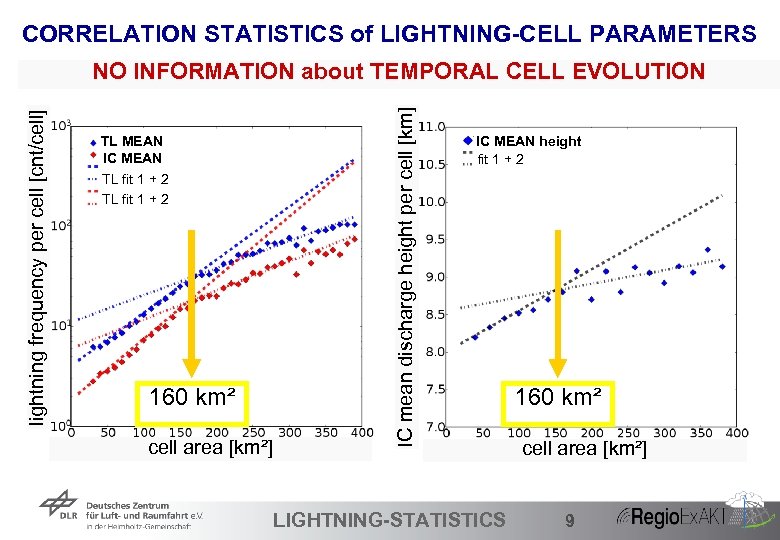 CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean MEAN IC mean MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] 40 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] NO INFORMATION about TEMPORAL CELL EVOLUTION IC mean height IC MEANheight fit 1 + 2 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS 160 km² cell area [km²] 9
CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS TL mean MEAN IC mean MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² cell area [km²] 40 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] NO INFORMATION about TEMPORAL CELL EVOLUTION IC mean height IC MEANheight fit 1 + 2 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS 160 km² cell area [km²] 9
![CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-41.jpg) CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 41 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min LIGHTNING-STATISTICS 10
CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 41 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min LIGHTNING-STATISTICS 10
![CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-42.jpg) CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 42 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min LIGHTNING-STATISTICS 10
CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 40 min 42 25 May 2008 lightning-cell No 6 lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] 30 May 2008 lightning-cell No 137 I E cell area [km²] Lifetime = 145 min LIGHTNING-STATISTICS 10
![frequency [-] FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION of LIFE-TIMES short-lived cells long-lived cells lightning-cell lifetime [min] 43 frequency [-] FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION of LIFE-TIMES short-lived cells long-lived cells lightning-cell lifetime [min] 43](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-43.jpg) frequency [-] FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION of LIFE-TIMES short-lived cells long-lived cells lightning-cell lifetime [min] 43 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS
frequency [-] FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION of LIFE-TIMES short-lived cells long-lived cells lightning-cell lifetime [min] 43 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS
![LIFETIME REGIMES short-lived [ 15 min – 75 min ] ‚SINGLE CELLS‘ - lowly LIFETIME REGIMES short-lived [ 15 min – 75 min ] ‚SINGLE CELLS‘ - lowly](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-44.jpg) LIFETIME REGIMES short-lived [ 15 min – 75 min ] ‚SINGLE CELLS‘ - lowly organized - simply structured: - simple life-cycles: long-lived 1 updraft + 1 downdraft growth – short maturity – decease [ ≥ 80 min ] ‚MULITCELLS‘, ‚SUPERCELLS‘ - highly organized - complexly structured - complex life-cycles: growth – elongated (fluctuating) maturity – decease 44 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS
LIFETIME REGIMES short-lived [ 15 min – 75 min ] ‚SINGLE CELLS‘ - lowly organized - simply structured: - simple life-cycles: long-lived 1 updraft + 1 downdraft growth – short maturity – decease [ ≥ 80 min ] ‚MULITCELLS‘, ‚SUPERCELLS‘ - highly organized - complexly structured - complex life-cycles: growth – elongated (fluctuating) maturity – decease 44 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS
![CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning relative frequency lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning relative frequency lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell]](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-45.jpg) CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning relative frequency lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] RELATIVE AMOUNT to STATISTICAL MEAN long-lived cells shortlived cell area [km²] 45 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS cell area [km²]
CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning relative frequency lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] RELATIVE AMOUNT to STATISTICAL MEAN long-lived cells shortlived cell area [km²] 45 LIGHTNING-STATISTICS cell area [km²]
![lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning cell type lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning cell type](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-46.jpg) lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning cell type short-lived cells shortlived h wt o gr e as e ec d cell area [km²] 46 DISCUSSION
lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning cell type short-lived cells shortlived h wt o gr e as e ec d cell area [km²] 46 DISCUSSION
![lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning long-lived cells lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning long-lived cells](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-47.jpg) lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning long-lived cells cell type y urit t ma h wt o long-lived cells gr e as e ec d cell area [km²] 47 DISCUSSION
lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS total lightning long-lived cells cell type y urit t ma h wt o long-lived cells gr e as e ec d cell area [km²] 47 DISCUSSION
![TL lightning totalmean IC mean TL fit 1 + 2 SCATTER! cell area [km²] TL lightning totalmean IC mean TL fit 1 + 2 SCATTER! cell area [km²]](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-48.jpg) TL lightning totalmean IC mean TL fit 1 + 2 SCATTER! cell area [km²] 48 48 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] Lightning frequency per cell [1/km²] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS DISCUSSION IC mean height fit 1 + 2 SCATTER! cell area [km²]
TL lightning totalmean IC mean TL fit 1 + 2 SCATTER! cell area [km²] 48 48 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] Lightning frequency per cell [1/km²] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS DISCUSSION IC mean height fit 1 + 2 SCATTER! cell area [km²]
![CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] INFORMATION about STORM TYPE CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] INFORMATION about STORM TYPE](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-49.jpg) CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] INFORMATION about STORM TYPE (lifetime, intensity) and TEMPORAL EVOLUTION! long-lived cell type short-lived shortlived cell area [km²] 49 DISCUSSION long-lived cells
CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] INFORMATION about STORM TYPE (lifetime, intensity) and TEMPORAL EVOLUTION! long-lived cell type short-lived shortlived cell area [km²] 49 DISCUSSION long-lived cells
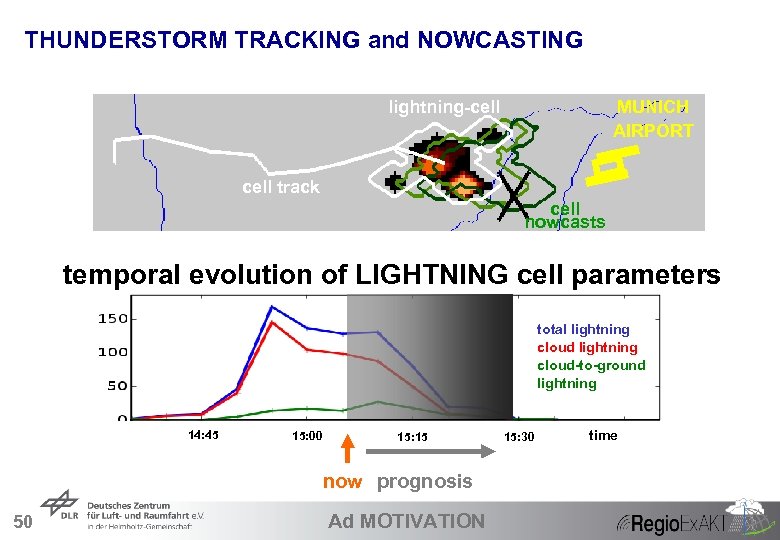 THUNDERSTORM TRACKING and NOWCASTING lightning-cell MUNICH AIRPORT cell track cell nowcasts temporal evolution of LIGHTNING cell parameters total lightning cloud-to-ground lightning 14: 45 15: 00 15: 15 now prognosis 50 Ad MOTIVATION 15: 30 time
THUNDERSTORM TRACKING and NOWCASTING lightning-cell MUNICH AIRPORT cell track cell nowcasts temporal evolution of LIGHTNING cell parameters total lightning cloud-to-ground lightning 14: 45 15: 00 15: 15 now prognosis 50 Ad MOTIVATION 15: 30 time
![TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 cell area [km²] 51 IC TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 cell area [km²] 51 IC](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-51.jpg) TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 cell area [km²] 51 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS DISCUSSION IC MEAN height fit 1 + 2 3 D information from 2 D cell tracking! cell area [km²]
TL MEAN IC MEAN TL fit 1 + 2 cell area [km²] 51 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] CORRELATION STATISTICS of LIGHTNING-CELL PARAMETERS DISCUSSION IC MEAN height fit 1 + 2 3 D information from 2 D cell tracking! cell area [km²]
 CONCLUSION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) 3 D lightning information with in-cloud and cloud-to-ground lightning discrimination provides useful information about the storm dynamic and developement and have the capacity to nowcast cell trends from the cell history 52 CONCLUSION and OUTLOOK 11
CONCLUSION GOAL: to assess the usability of 3 D total-lightning data for thunderstorm nowcasting separately and in combination with other data sources (radar) 3 D lightning information with in-cloud and cloud-to-ground lightning discrimination provides useful information about the storm dynamic and developement and have the capacity to nowcast cell trends from the cell history 52 CONCLUSION and OUTLOOK 11
 OUTLOOK - test the usability of (specified) normalized cell life-cycles to derive trend prognoses - use cell trends from cell history to add trend prognoses to local prognoses - test the quality of trend prognoses - investigate cell parameter correlations with other data sources (3 D radar, satellite, . . . ) 53 CONCLUSION and OUTLOOK 11
OUTLOOK - test the usability of (specified) normalized cell life-cycles to derive trend prognoses - use cell trends from cell history to add trend prognoses to local prognoses - test the quality of trend prognoses - investigate cell parameter correlations with other data sources (3 D radar, satellite, . . . ) 53 CONCLUSION and OUTLOOK 11
 OTHER possible APPLICATIONS - parameterization of TL frequency with IC/CG ratio and mean IC height for modelling [Price and Rind 1992, Allen and Pickering 2002] - simulation of thunderstorm life-cycles with realistic discharge characteristics ? 160 km²? 54 CONCLUSION and OUTLOOK
OTHER possible APPLICATIONS - parameterization of TL frequency with IC/CG ratio and mean IC height for modelling [Price and Rind 1992, Allen and Pickering 2002] - simulation of thunderstorm life-cycles with realistic discharge characteristics ? 160 km²? 54 CONCLUSION and OUTLOOK
![IC mean height fit 1 + 2 THANK YOU 160 km² cell area [km²] IC mean height fit 1 + 2 THANK YOU 160 km² cell area [km²]](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-55.jpg) IC mean height fit 1 + 2 THANK YOU 160 km² cell area [km²] 55 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] TL mean IC mean TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² vera. meyer@zamg. ac. at cell area [km²]
IC mean height fit 1 + 2 THANK YOU 160 km² cell area [km²] 55 IC mean discharge height per cell [km] lightning frequency per cell [cnt/cell] TL mean IC mean TL fit 1 + 2 160 km² vera. meyer@zamg. ac. at cell area [km²]
 Literature K. Kober and A. Tafferner. Tracking and nowcasting of convective cells unsing remote sensing data from radar and satellite. Meteorologiesche Zeitschrift, 10(1): 75 -84, 2009 V. Meyer, H. Höller, K. Schmidt, and H. -D. Betz. Temporal evolution of total lightning and radar parameters of thunderstorms in southern Germany and its benefit for nowcasting. Proceedings: 5 th European Conference on Severe Storms, 2009 V. Meyer (2010): Thunderstorm Tracking and Monitorin on the Basis of Three Dimenional Lightning Data and Conventional and Polarimetric Radar Data. Dissertation, LMU München: Faculty of Physics http: //edoc. ub. uni-muenchen. de/12102/ 56 vera. meyer@zamg. ac. at
Literature K. Kober and A. Tafferner. Tracking and nowcasting of convective cells unsing remote sensing data from radar and satellite. Meteorologiesche Zeitschrift, 10(1): 75 -84, 2009 V. Meyer, H. Höller, K. Schmidt, and H. -D. Betz. Temporal evolution of total lightning and radar parameters of thunderstorms in southern Germany and its benefit for nowcasting. Proceedings: 5 th European Conference on Severe Storms, 2009 V. Meyer (2010): Thunderstorm Tracking and Monitorin on the Basis of Three Dimenional Lightning Data and Conventional and Polarimetric Radar Data. Dissertation, LMU München: Faculty of Physics http: //edoc. ub. uni-muenchen. de/12102/ 56 vera. meyer@zamg. ac. at
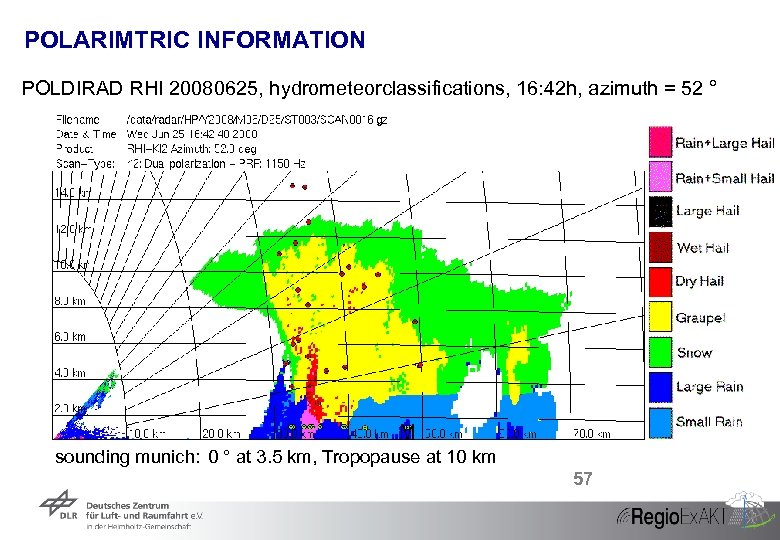 POLARIMTRIC INFORMATION POLDIRAD RHI 20080625, hydrometeorclassifications, 16: 42 h, azimuth = 52 ° sounding munich: 0 ° at 3. 5 km, Tropopause at 10 km 57 57
POLARIMTRIC INFORMATION POLDIRAD RHI 20080625, hydrometeorclassifications, 16: 42 h, azimuth = 52 ° sounding munich: 0 ° at 3. 5 km, Tropopause at 10 km 57 57
![ZEITLICHE ENTWICKLUNG VON ec-ZELL PARAMETERN example: radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area - ZEITLICHE ENTWICKLUNG VON ec-ZELL PARAMETERN example: radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area -](https://present5.com/presentation/fe5d7eec7ea14bc63f5fa1b5dba9a7ae/image-58.jpg) ZEITLICHE ENTWICKLUNG VON ec-ZELL PARAMETERN example: radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area - TL - CG - IC [km²] [cnt/cell] polar. radar data - hydrometeors d. BZ cell graupel/hail light rain H = 4 km ground heavy rain 58 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] 25 June 2008
ZEITLICHE ENTWICKLUNG VON ec-ZELL PARAMETERN example: radar-cell: -cell area [km²] lightning-cell: -cell area - TL - CG - IC [km²] [cnt/cell] polar. radar data - hydrometeors d. BZ cell graupel/hail light rain H = 4 km ground heavy rain 58 area [km²], discharge frequency [cnt/cell] 25 June 2008


