9d9b85163c6ce6100430ab3a12c6fc95.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39

 Three Minute Review TREATMENT • history of treatment • 2 major approaches – Biological – Psychotherapy • Psychopharmacology – Antipsychotic Drugs • deinstitutionalization • dopamine • differences between older and newer generation drugs – Anti-anxiety drugs • e. g. , Valium • GABA
Three Minute Review TREATMENT • history of treatment • 2 major approaches – Biological – Psychotherapy • Psychopharmacology – Antipsychotic Drugs • deinstitutionalization • dopamine • differences between older and newer generation drugs – Anti-anxiety drugs • e. g. , Valium • GABA
 – Antidepressants • • • tricyclics (reduce reuptake of serotonin & NE) MAOIs (reduce breakdown of serotonin & NE) SSRIs (reduce reuptake of serotonin only) See Fig. 17. 3 of Gray (p. 666) monoamine hypothesis and issues with it maybe they work because of effects on sleep cycle • Light therapy for SAD • Electroconvulsive Therapy – why resort to something so extreme? – how has it improved since Cuckoo’s Nest era? • Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) – magnetic fields disrupt neural firing locally • Psychosurgery – history and current status
– Antidepressants • • • tricyclics (reduce reuptake of serotonin & NE) MAOIs (reduce breakdown of serotonin & NE) SSRIs (reduce reuptake of serotonin only) See Fig. 17. 3 of Gray (p. 666) monoamine hypothesis and issues with it maybe they work because of effects on sleep cycle • Light therapy for SAD • Electroconvulsive Therapy – why resort to something so extreme? – how has it improved since Cuckoo’s Nest era? • Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) – magnetic fields disrupt neural firing locally • Psychosurgery – history and current status
 Psychotherapy • eclectic - mixed bag • Psychodynamic – transference • Humanistic – client-centred, reflection, empathy, unconditional positive regard • Cognitive Therapy – problem-centred, change thought patterns
Psychotherapy • eclectic - mixed bag • Psychodynamic – transference • Humanistic – client-centred, reflection, empathy, unconditional positive regard • Cognitive Therapy – problem-centred, change thought patterns
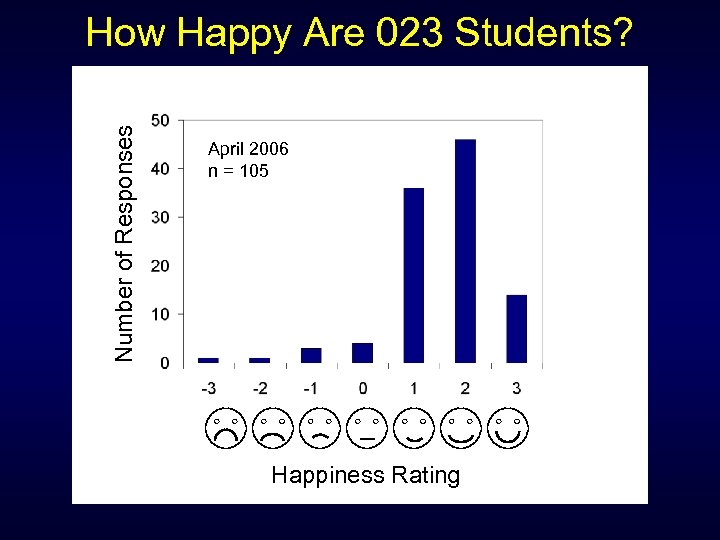 Number of Responses How Happy Are 023 Students? April 2006 n = 105 Happiness Rating
Number of Responses How Happy Are 023 Students? April 2006 n = 105 Happiness Rating
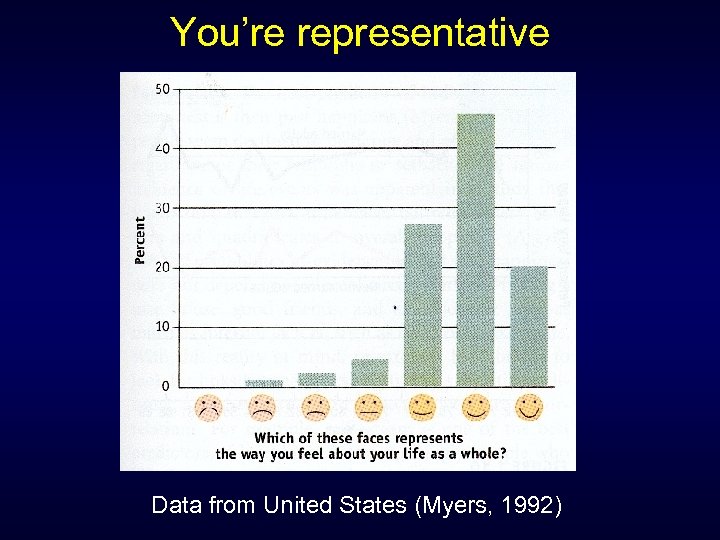 You’re representative Data from United States (Myers, 1992)
You’re representative Data from United States (Myers, 1992)
 Very Common Responses • Relationships social life, more time with family and friends and partner finding a partner (or a better partner) • Money Common: more emphasis on basics and stability rather than luxury level – “Money can’t buy happiness, it can pay rent!” Less common: winning the lottery – “Money can’t buy you happiness, but I’m happiest when I can buy what I want. ” • Better grades end of exams • Reduced stress less stress, less work, less worrying, slower pace, more spare time better study habits, organization less parental pressure to perform family illnesses, deaths, conflicts
Very Common Responses • Relationships social life, more time with family and friends and partner finding a partner (or a better partner) • Money Common: more emphasis on basics and stability rather than luxury level – “Money can’t buy happiness, it can pay rent!” Less common: winning the lottery – “Money can’t buy you happiness, but I’m happiest when I can buy what I want. ” • Better grades end of exams • Reduced stress less stress, less work, less worrying, slower pace, more spare time better study habits, organization less parental pressure to perform family illnesses, deaths, conflicts
 Fairly Common Responses • Physical appearance esp. weight loss Psychological factors self-esteem, confidence, less self criticism, less concern about others’ opinions, overcoming shyness, more assertive, less anxious Career more certainty about life, direction, career successful career or education (e. g. , med school) summer job (esp. lab work) “working helps me to feel fulfilled” • Health • • good health more sleep sports, exercise (some specific) better eating habits
Fairly Common Responses • Physical appearance esp. weight loss Psychological factors self-esteem, confidence, less self criticism, less concern about others’ opinions, overcoming shyness, more assertive, less anxious Career more certainty about life, direction, career successful career or education (e. g. , med school) summer job (esp. lab work) “working helps me to feel fulfilled” • Health • • good health more sleep sports, exercise (some specific) better eating habits
 Somewhat Common Responses • Living conditions moving away from home moving closer to home “better roommate (only one month left!!!!!)” • Others’ behavior/mood – changed behavior of others in life, fewer problems with others in life, family stability, family members being happy • Finding meaning, making a contribution – “be in a more personal environment where I could make a constructive contribution” – “I can’t choose #3 because although my life is comparatively wonderful, overall there are huge problems with the world” – “Making some noticeable change in the community with regards to our relationship with the environment”
Somewhat Common Responses • Living conditions moving away from home moving closer to home “better roommate (only one month left!!!!!)” • Others’ behavior/mood – changed behavior of others in life, fewer problems with others in life, family stability, family members being happy • Finding meaning, making a contribution – “be in a more personal environment where I could make a constructive contribution” – “I can’t choose #3 because although my life is comparatively wonderful, overall there are huge problems with the world” – “Making some noticeable change in the community with regards to our relationship with the environment”
 One of a Kind • I could be rich, Hugh Hefner’s son, Bill Gates nephew, dating both the Olson twins • if I was rich, I make med school, I find Natalie Portman, I win at life • a new Batman costume two extra hours in each day • being older • winning the lottery… warm weather… world peace • more laughter, less hate • live in the now! • Nothing. I’m still alive • Life is great! I’ve been very blessed • Life isn’t searching for more but making the best of what you have. The glass is half full! I’ve learned to be grateful rather than angry.
One of a Kind • I could be rich, Hugh Hefner’s son, Bill Gates nephew, dating both the Olson twins • if I was rich, I make med school, I find Natalie Portman, I win at life • a new Batman costume two extra hours in each day • being older • winning the lottery… warm weather… world peace • more laughter, less hate • live in the now! • Nothing. I’m still alive • Life is great! I’ve been very blessed • Life isn’t searching for more but making the best of what you have. The glass is half full! I’ve learned to be grateful rather than angry.
 Negative versus positive topics in psychology journal articles 1887 to 2001 9, 760 on “anger” 65, 531 on “anxiety” 79, 154 on “depression” 20, 868 on “fear” 207, 110 on “treatment” 1, 021 on “joy” 4, 129 on “life satisfaction” 3, 522 on “happiness” 781 on “courage 31, 019 on “prevention” Slide courtesy of David Myers
Negative versus positive topics in psychology journal articles 1887 to 2001 9, 760 on “anger” 65, 531 on “anxiety” 79, 154 on “depression” 20, 868 on “fear” 207, 110 on “treatment” 1, 021 on “joy” 4, 129 on “life satisfaction” 3, 522 on “happiness” 781 on “courage 31, 019 on “prevention” Slide courtesy of David Myers
 People want more • Popularity of self-help books suggests a large number of people want to go from okay to well Mental Health Spectrum Poor OK Most of Psychology is here Great Why not here?
People want more • Popularity of self-help books suggests a large number of people want to go from okay to well Mental Health Spectrum Poor OK Most of Psychology is here Great Why not here?
 What is LEAST important? Does money make us as happy as we expect it will?
What is LEAST important? Does money make us as happy as we expect it will?
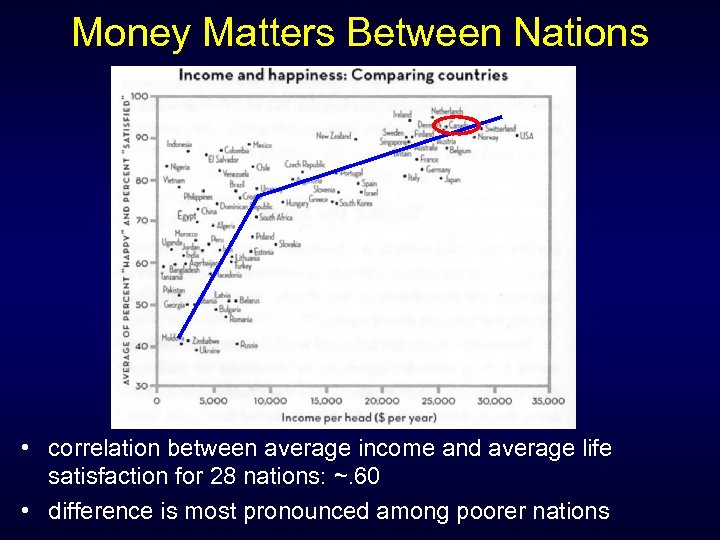 Money Matters Between Nations • correlation between average income and average life satisfaction for 28 nations: ~. 60 • difference is most pronounced among poorer nations
Money Matters Between Nations • correlation between average income and average life satisfaction for 28 nations: ~. 60 • difference is most pronounced among poorer nations
 Gross National Happiness? Optional video link on course web site
Gross National Happiness? Optional video link on course web site
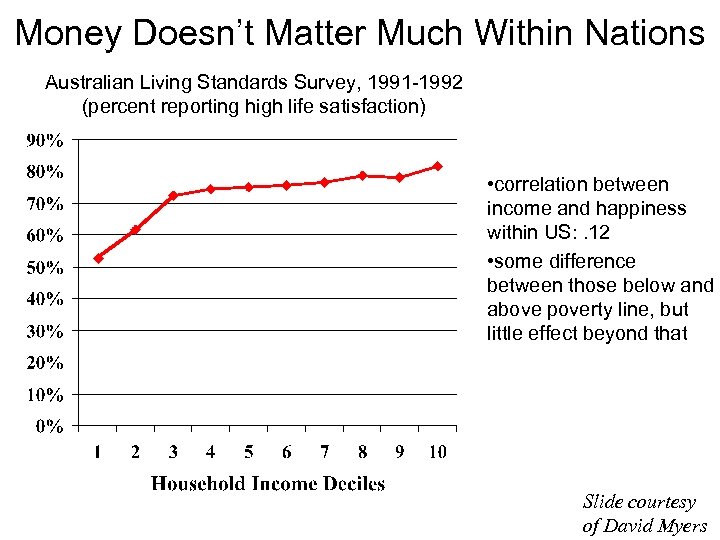 Money Doesn’t Matter Much Within Nations Australian Living Standards Survey, 1991 -1992 (percent reporting high life satisfaction) • correlation between income and happiness within US: . 12 • some difference between those below and above poverty line, but little effect beyond that Slide courtesy of David Myers
Money Doesn’t Matter Much Within Nations Australian Living Standards Survey, 1991 -1992 (percent reporting high life satisfaction) • correlation between income and happiness within US: . 12 • some difference between those below and above poverty line, but little effect beyond that Slide courtesy of David Myers
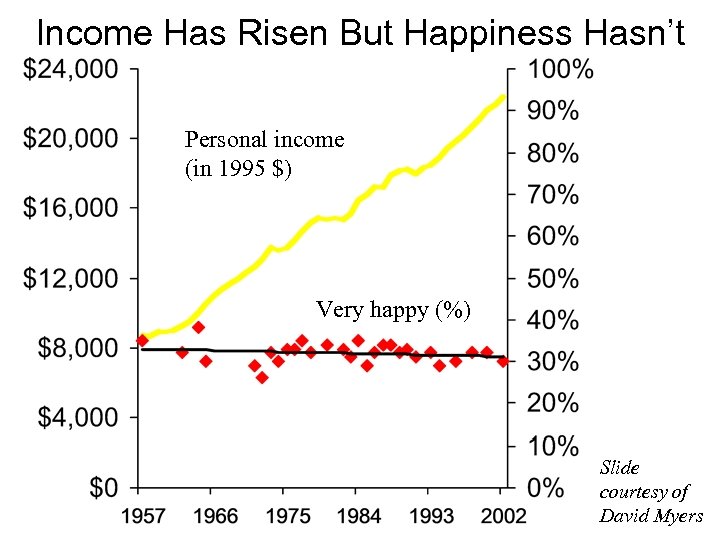 Income Has Risen But Happiness Hasn’t Personal income (in 1995 $) Very happy (%) Slide courtesy of David Myers
Income Has Risen But Happiness Hasn’t Personal income (in 1995 $) Very happy (%) Slide courtesy of David Myers
 Hedonic Treadmill Happiness = Reality / Expectations
Hedonic Treadmill Happiness = Reality / Expectations
 Social Comparison Would you rather: 1. earn $50, 000/year when your co -workers get $25, 000/year OR 2. earn $100, 000/year when your co-workers get $250, 000/year? Would you rather: 1. have 2 weeks vacation when your co-workers have 1 week OR 2. have 4 weeks vacation when your co-workers have 8 weeks? The paradox of German reunification
Social Comparison Would you rather: 1. earn $50, 000/year when your co -workers get $25, 000/year OR 2. earn $100, 000/year when your co-workers get $250, 000/year? Would you rather: 1. have 2 weeks vacation when your co-workers have 1 week OR 2. have 4 weeks vacation when your co-workers have 8 weeks? The paradox of German reunification
 If Only I Could Win the Lottery… • … I’d probably be about as happy as I am now • Happiness of lottery winners: 4. 0 • Happiness of others: 3. 8 • many life disruptions – 70% quit jobs lose job satisfaction and co-workers – most move, many are not socially acceptable to new neighbors – family quarrels
If Only I Could Win the Lottery… • … I’d probably be about as happy as I am now • Happiness of lottery winners: 4. 0 • Happiness of others: 3. 8 • many life disruptions – 70% quit jobs lose job satisfaction and co-workers – most move, many are not socially acceptable to new neighbors – family quarrels
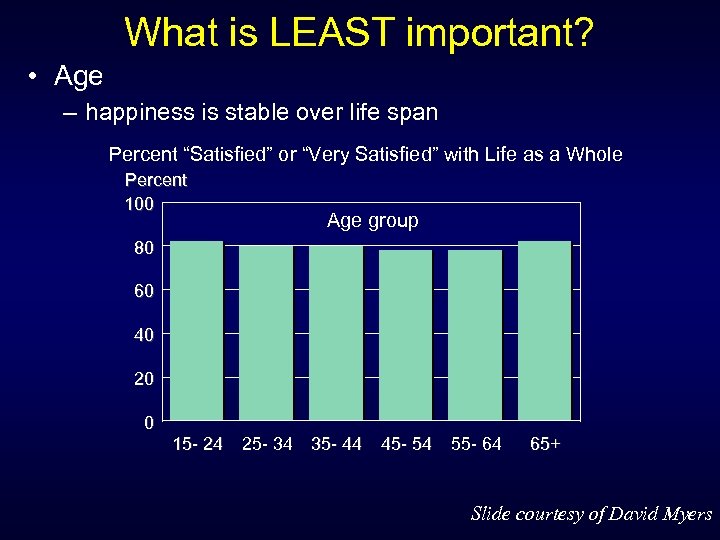 What is LEAST important? • Age – happiness is stable over life span Percent “Satisfied” or “Very Satisfied” with Life as a Whole Percent 100 Age group 80 60 40 20 0 15 - 24 25 - 34 35 - 44 45 - 54 55 - 64 65+ Slide courtesy of David Myers
What is LEAST important? • Age – happiness is stable over life span Percent “Satisfied” or “Very Satisfied” with Life as a Whole Percent 100 Age group 80 60 40 20 0 15 - 24 25 - 34 35 - 44 45 - 54 55 - 64 65+ Slide courtesy of David Myers
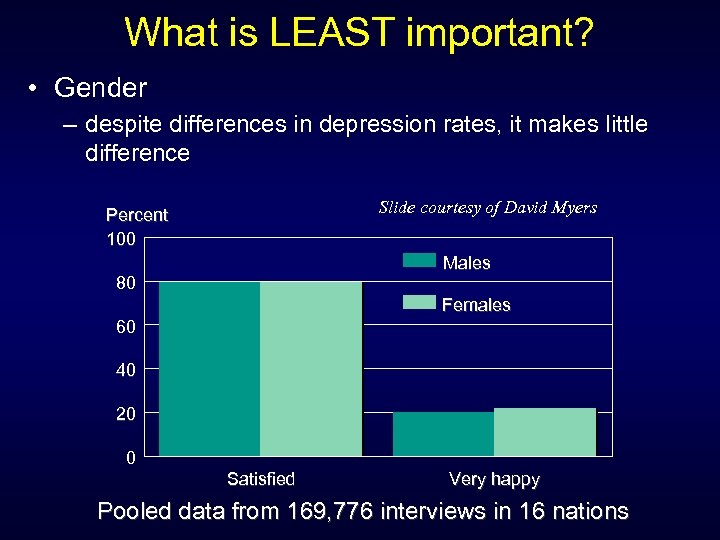 What is LEAST important? • Gender – despite differences in depression rates, it makes little difference Slide courtesy of David Myers Percent 100 Males 80 Females 60 40 20 0 Satisfied Very happy Pooled data from 169, 776 interviews in 16 nations
What is LEAST important? • Gender – despite differences in depression rates, it makes little difference Slide courtesy of David Myers Percent 100 Males 80 Females 60 40 20 0 Satisfied Very happy Pooled data from 169, 776 interviews in 16 nations
 What is LEAST important? • Intelligence – no correlation between IQ and happiness – teeny correlation between education level and happiness • Physical Attractiveness – teeny correlation between attractiveness and happiness, esp. for women • Parenthood – parents less happy with toddlers and teenagers
What is LEAST important? • Intelligence – no correlation between IQ and happiness – teeny correlation between education level and happiness • Physical Attractiveness – teeny correlation between attractiveness and happiness, esp. for women • Parenthood – parents less happy with toddlers and teenagers
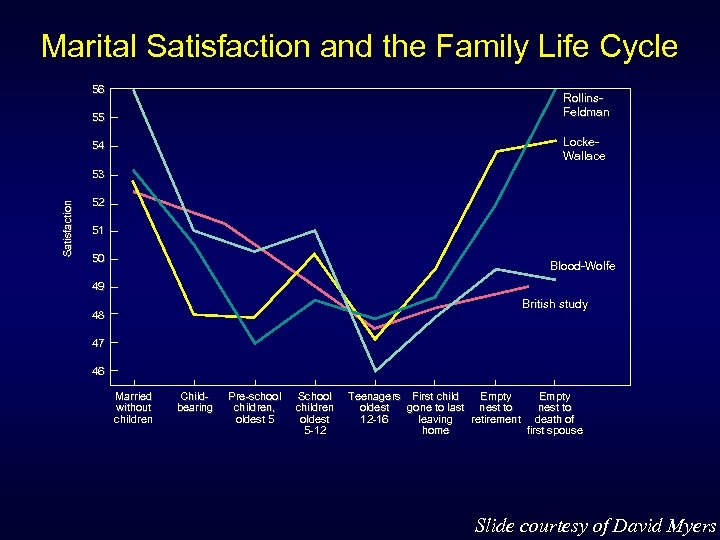 Marital Satisfaction and the Family Life Cycle 56 Rollins. Feldman 55 Locke. Wallace 54 Satisfaction 53 52 51 50 Blood-Wolfe 49 British study 48 47 46 Married without children Childbearing Pre-school children, oldest 5 School children oldest 5 -12 Teenagers First child Empty oldest gone to last nest to 12 -16 leaving retirement death of home first spouse Slide courtesy of David Myers
Marital Satisfaction and the Family Life Cycle 56 Rollins. Feldman 55 Locke. Wallace 54 Satisfaction 53 52 51 50 Blood-Wolfe 49 British study 48 47 46 Married without children Childbearing Pre-school children, oldest 5 School children oldest 5 -12 Teenagers First child Empty oldest gone to last nest to 12 -16 leaving retirement death of home first spouse Slide courtesy of David Myers
 What is VERY important? • Love and Marriage – clear correlation – cause and effect unclear • relationships --> happiness? • happiness --> relationships?
What is VERY important? • Love and Marriage – clear correlation – cause and effect unclear • relationships --> happiness? • happiness --> relationships?
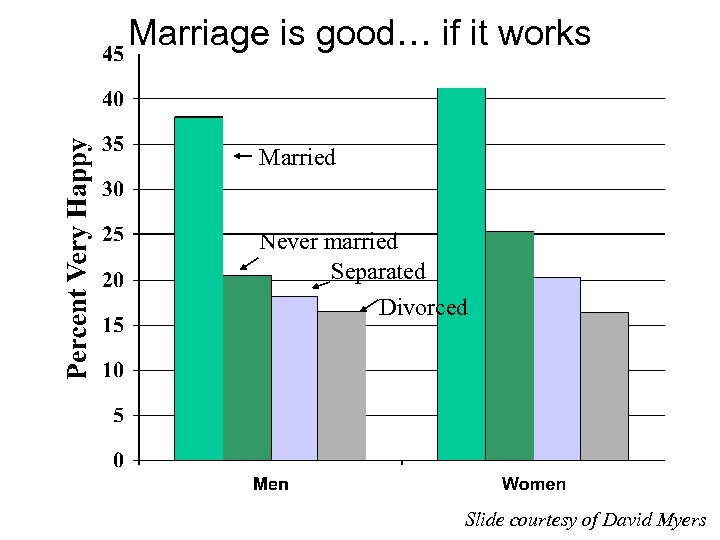 Marriage is good… if it works Married Never married Separated Divorced Slide courtesy of David Myers
Marriage is good… if it works Married Never married Separated Divorced Slide courtesy of David Myers
 Friends Are Very Important
Friends Are Very Important
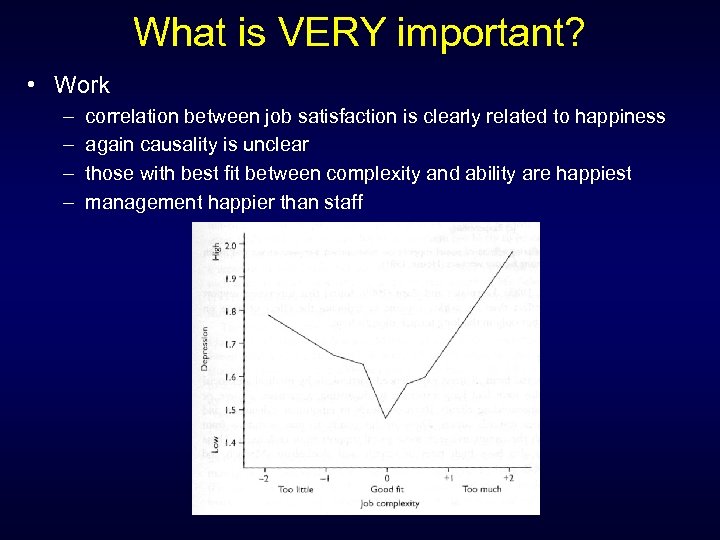 What is VERY important? • Work – – correlation between job satisfaction is clearly related to happiness again causality is unclear those with best fit between complexity and ability are happiest management happier than staff
What is VERY important? • Work – – correlation between job satisfaction is clearly related to happiness again causality is unclear those with best fit between complexity and ability are happiest management happier than staff
 What is VERY important? • Personality – past happiness predicts future happiness very well – is there a happiness “set point”? – key factors • • self-esteem extroversion optimism sense of control over one’s life
What is VERY important? • Personality – past happiness predicts future happiness very well – is there a happiness “set point”? – key factors • • self-esteem extroversion optimism sense of control over one’s life
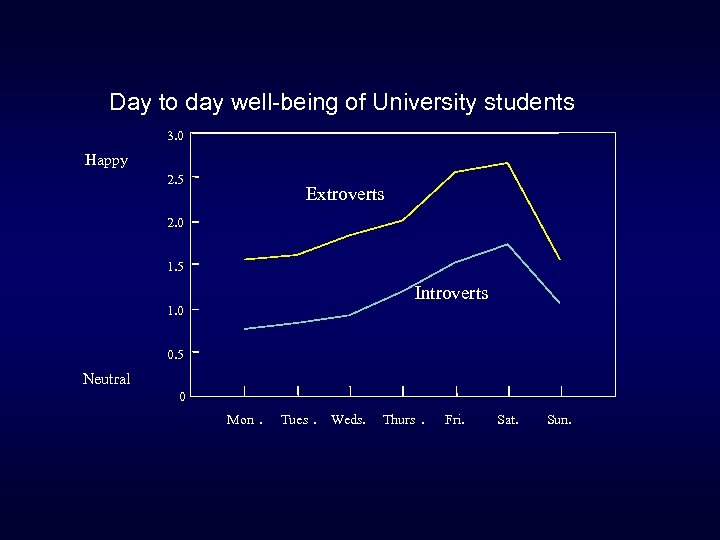 Day to day well-being of University students 3. 0 Happy 2. 5 Extroverts 2. 0 1. 5 Introverts 1. 0 0. 5 Neutral 0 Mon. Tues. Weds. Thurs. Fri. Sat. Sun.
Day to day well-being of University students 3. 0 Happy 2. 5 Extroverts 2. 0 1. 5 Introverts 1. 0 0. 5 Neutral 0 Mon. Tues. Weds. Thurs. Fri. Sat. Sun.
 What is SOMEWHAT important? • Health – correlation between health and happiness: . 32 – spurious -- related to neuroticism • neurotics are less happy • neurotics are less healthy • Social activity • Religion – social aspect – healthier lifestyle – spirituality
What is SOMEWHAT important? • Health – correlation between health and happiness: . 32 – spurious -- related to neuroticism • neurotics are less happy • neurotics are less healthy • Social activity • Religion – social aspect – healthier lifestyle – spirituality
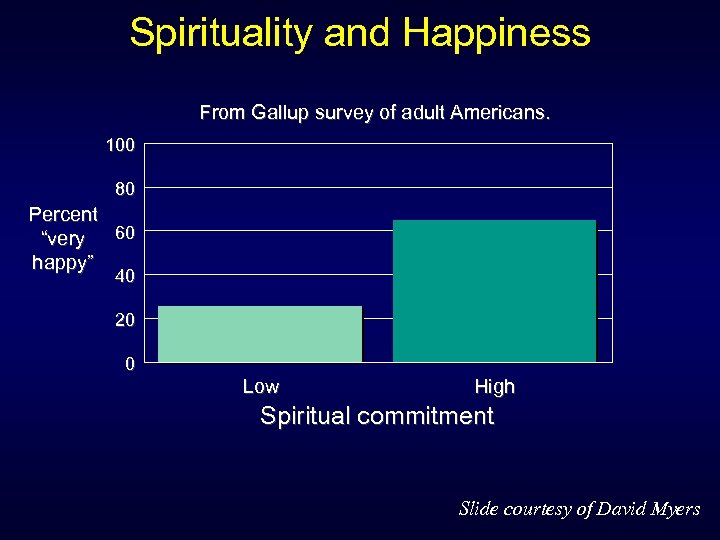 Spirituality and Happiness From Gallup survey of adult Americans. 100 80 Percent 60 “very happy” 40 20 0 Low High Spiritual commitment Slide courtesy of David Myers
Spirituality and Happiness From Gallup survey of adult Americans. 100 80 Percent 60 “very happy” 40 20 0 Low High Spiritual commitment Slide courtesy of David Myers
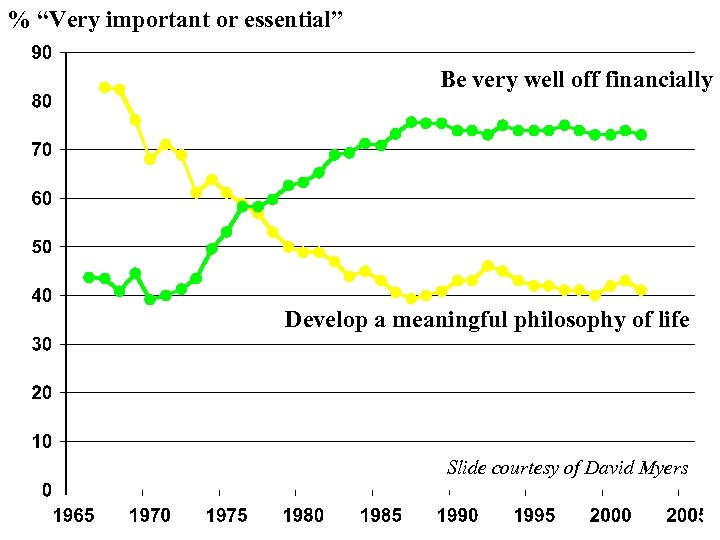 % “Very important or essential” Be very well off financially Develop a meaningful philosophy of life Slide courtesy of David Myers
% “Very important or essential” Be very well off financially Develop a meaningful philosophy of life Slide courtesy of David Myers
 What is SOMEWHAT important? • Leisure – correlation between satisfaction with leisure activities and happiness: . 4 – some activities have positive effect • social clubs, volunteer work, music, dancing, sports, holidays – some activities have negative effect • excessive TV-watching
What is SOMEWHAT important? • Leisure – correlation between satisfaction with leisure activities and happiness: . 4 – some activities have positive effect • social clubs, volunteer work, music, dancing, sports, holidays – some activities have negative effect • excessive TV-watching
 The Tyranny of Choice • maximizers – obsessed with finding the best – less satisfied – more prone to depression • satisficers – willing to accept “good enough” Optional Scientific American article including Maximization Test on course web site
The Tyranny of Choice • maximizers – obsessed with finding the best – less satisfied – more prone to depression • satisficers – willing to accept “good enough” Optional Scientific American article including Maximization Test on course web site
 Choose Wisely
Choose Wisely
 Finding Flow • moments of complete engagement in a task – – intense concentration clear goals and feedback lose sense of time lose self consciousness • optimal when abilities closely match challenges • surfing the peak of the optimal level of arousal curve? • would you really be happy lying on the beach drinking pina coladas all day long for the long term?
Finding Flow • moments of complete engagement in a task – – intense concentration clear goals and feedback lose sense of time lose self consciousness • optimal when abilities closely match challenges • surfing the peak of the optimal level of arousal curve? • would you really be happy lying on the beach drinking pina coladas all day long for the long term?

 Top Ten Things to Remember 1. How to spell “Psychology” 2. There’s much more to psychology than Freud. 3. Evolutionary principles and neuroscience can explain a lot about human behavior. 4. Microsleeps are deadly. If you are sleepy while driving, take a break. 5. Beware “the banality of evil. ” If someone asks you to do something that you know in your gut is wrong, you can refuse. 6. If someone needs help, do something instead of waiting for others to take action. 7. Children’s early development is very important: physical development, critical periods, and attachment. 8. Be aware of your prejudices, including the implicit ones, to avoid discrimination. 9. Mental disorders are common, understandable and treatable. 10. You have to power to improve your happiness (e. g. , life choices) and success (e. g. , internal locus of control)
Top Ten Things to Remember 1. How to spell “Psychology” 2. There’s much more to psychology than Freud. 3. Evolutionary principles and neuroscience can explain a lot about human behavior. 4. Microsleeps are deadly. If you are sleepy while driving, take a break. 5. Beware “the banality of evil. ” If someone asks you to do something that you know in your gut is wrong, you can refuse. 6. If someone needs help, do something instead of waiting for others to take action. 7. Children’s early development is very important: physical development, critical periods, and attachment. 8. Be aware of your prejudices, including the implicit ones, to avoid discrimination. 9. Mental disorders are common, understandable and treatable. 10. You have to power to improve your happiness (e. g. , life choices) and success (e. g. , internal locus of control)


