2f4d725b98536386d27eb6ee37e55663.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Three kinds of colonies that England created in what was to become the U. S. o Royal colonies o Charter colonies o Proprietary colonies **Trustee (only GA colony for a while)
Three kinds of colonies that England created in what was to become the U. S. o Royal colonies o Charter colonies o Proprietary colonies **Trustee (only GA colony for a while)
 Royal Colony o Royal- Britain directly ruled o Parliament appointed a governor and a council know as the Upper House. The colonists elected an assembly called the Lower House. Royal Colonies were directly controlled by the Crown (king/queen).
Royal Colony o Royal- Britain directly ruled o Parliament appointed a governor and a council know as the Upper House. The colonists elected an assembly called the Lower House. Royal Colonies were directly controlled by the Crown (king/queen).
 Change to Royal colony o Most of the 13 colonies were originally charter colonies but by the eve of the Revolution 8 of them were royal colonies. o Virginia, which began as a charter colony, was the first to have its charter revoked and become a royal colony (1624).
Change to Royal colony o Most of the 13 colonies were originally charter colonies but by the eve of the Revolution 8 of them were royal colonies. o Virginia, which began as a charter colony, was the first to have its charter revoked and become a royal colony (1624).
 Proprietary Colony o Sometimes the king granted charters to an individual proprietor who could govern the land as he saw fit. These were called proprietary colonies. o Maryland was a proprietary colony governed by Lord Baltimore. o Pennsylvania and Delaware were under the domain of William Penn
Proprietary Colony o Sometimes the king granted charters to an individual proprietor who could govern the land as he saw fit. These were called proprietary colonies. o Maryland was a proprietary colony governed by Lord Baltimore. o Pennsylvania and Delaware were under the domain of William Penn
 Charter Colony o Charter- contract between the people who came and the crown o Virginia for example was originally a charter colony, and its first colonists were employees of the Virginia Company that would make $$ for England
Charter Colony o Charter- contract between the people who came and the crown o Virginia for example was originally a charter colony, and its first colonists were employees of the Virginia Company that would make $$ for England
 Most American colonists believed… o …they had many rights and exercised much self-government. o … they had the rights of all Englishmen. o …distance from the "old country" meant they were free to create new, more democratic government. o …in the charter colonies, selfgovernment was especially strong.
Most American colonists believed… o …they had many rights and exercised much self-government. o … they had the rights of all Englishmen. o …distance from the "old country" meant they were free to create new, more democratic government. o …in the charter colonies, selfgovernment was especially strong.
 SS Standard #12 Compares and contrasts political, economic and socio-religious development of the New England, Middle Atlantic, and Southern colonies. Discusses how the different physical and religious environments provided opportunities for or placed constraints on human activities.
SS Standard #12 Compares and contrasts political, economic and socio-religious development of the New England, Middle Atlantic, and Southern colonies. Discusses how the different physical and religious environments provided opportunities for or placed constraints on human activities.
 Political Differences o Which colonies had different types of colony status? (Which had more independence from Britain vs. less independence from Britain? )
Political Differences o Which colonies had different types of colony status? (Which had more independence from Britain vs. less independence from Britain? )
 Colony Independence from British Crown o Charter colonies had more independence than Proprietary colonies because they were making $$$ for the English crown. o But, Royal colonies had the least independence of all. When the crown was angry with what a Charter or Proprietary colony did, the colony usually was made a Royal colony.
Colony Independence from British Crown o Charter colonies had more independence than Proprietary colonies because they were making $$$ for the English crown. o But, Royal colonies had the least independence of all. When the crown was angry with what a Charter or Proprietary colony did, the colony usually was made a Royal colony.
 Economic Differences o How did each region of colonies make a living? (Were they mostly farmers? Skilled craftsmen? Or did they earn their living in other ways? )
Economic Differences o How did each region of colonies make a living? (Were they mostly farmers? Skilled craftsmen? Or did they earn their living in other ways? )
 Socio-Religious Differences o Socio- How did they value/treat other humans? o Religious – What type of religions were allowed in each region? Was there religious tolerance?
Socio-Religious Differences o Socio- How did they value/treat other humans? o Religious – What type of religions were allowed in each region? Was there religious tolerance?
 New England o Daily New England life o Turkey – eaten in Europe; B. Franklin proposes it as national bird, not Bald Eagle o 90% of colonists live outside town/city o Horse – good transportation, cost 20 pounds (half year’s salary) o Transportation done in summer and winter (spring & fall too muddy)
New England o Daily New England life o Turkey – eaten in Europe; B. Franklin proposes it as national bird, not Bald Eagle o 90% of colonists live outside town/city o Horse – good transportation, cost 20 pounds (half year’s salary) o Transportation done in summer and winter (spring & fall too muddy)
 New England colonies o cold climate, short growing season, rocky, hilly land o Small farms for family use (very little demand for slaves to work fields) o $ fishing, ship-building, trade, skilled workers …blacksmiths, coppers (barrel makers), silversmiths, furniture makers
New England colonies o cold climate, short growing season, rocky, hilly land o Small farms for family use (very little demand for slaves to work fields) o $ fishing, ship-building, trade, skilled workers …blacksmiths, coppers (barrel makers), silversmiths, furniture makers
 New England colonies (cont. ) o Farms = small; Church life = important o So, people live close together o Most urbanized region (Boston, Providence, Newport) o Most New England colonies founded for religious reasons, so, reading Bible is important (Education = important; 1671 all but one N. E. colony has school laws) o Almost all = English background
New England colonies (cont. ) o Farms = small; Church life = important o So, people live close together o Most urbanized region (Boston, Providence, Newport) o Most New England colonies founded for religious reasons, so, reading Bible is important (Education = important; 1671 all but one N. E. colony has school laws) o Almost all = English background
 New England Colonies o Economic Differences – How did New England colonists make a living? o _______________ o Socio-Religious Differences – How did New Englanders treat other people? What religions were present or accepted? o ________________________________
New England Colonies o Economic Differences – How did New England colonists make a living? o _______________ o Socio-Religious Differences – How did New Englanders treat other people? What religions were present or accepted? o ________________________________
 Furniture making in Mid. Atlantic colonies
Furniture making in Mid. Atlantic colonies
 Middle Atlantic colonies o Temperate climate (longer growing season than New England) o Fertile rolling hills allows growing of variety of crops (surplus sold for $$; some interested in slave labor to work land for profit) o $ agriculture (#1 econ. Activity), mining, Forests provide wood for: barrel production, ship building, Conestoga wagons and furniture making
Middle Atlantic colonies o Temperate climate (longer growing season than New England) o Fertile rolling hills allows growing of variety of crops (surplus sold for $$; some interested in slave labor to work land for profit) o $ agriculture (#1 econ. Activity), mining, Forests provide wood for: barrel production, ship building, Conestoga wagons and furniture making
 Middle Atlantic colonies (cont. ) o Farms = bigger than New England; Church life o o = important So, people don’t live as close together as New England, but still close enough to attend Church 2 largest American cities (Philadelphia, New York) mix of cities, towns, rural areas No formal education laws, education left to private tutors or Church schools Most diverse in terms of people (English, Dutch, German, Scots-Irish), religion, economy
Middle Atlantic colonies (cont. ) o Farms = bigger than New England; Church life o o = important So, people don’t live as close together as New England, but still close enough to attend Church 2 largest American cities (Philadelphia, New York) mix of cities, towns, rural areas No formal education laws, education left to private tutors or Church schools Most diverse in terms of people (English, Dutch, German, Scots-Irish), religion, economy
 Middle Atlantic Colonists o Economic Differences – How did Middle Atlantic colonists make a living? o _______________ o Socio-Religious Differences – How did Mid-Atlantic colonists treat other people? What religions were present or accepted? o ________________________________
Middle Atlantic Colonists o Economic Differences – How did Middle Atlantic colonists make a living? o _______________ o Socio-Religious Differences – How did Mid-Atlantic colonists treat other people? What religions were present or accepted? o ________________________________
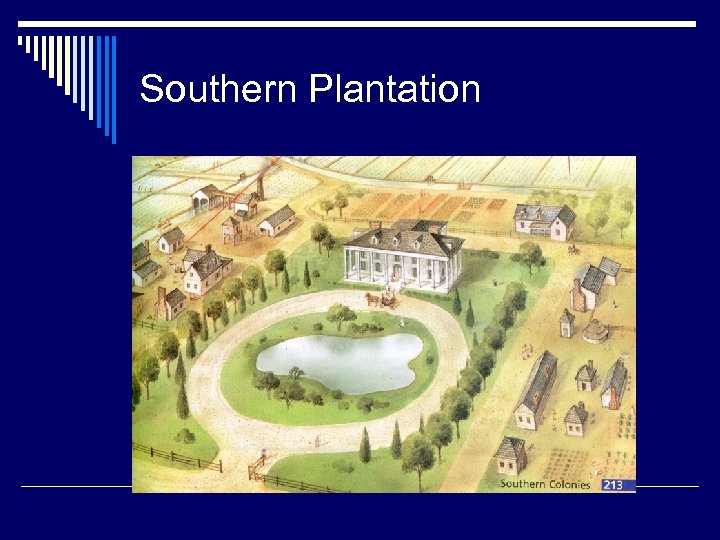 Southern Plantation
Southern Plantation
 Southern colonies o Warm climate, rich soil, large coastal plain (longest growing season ) o Plantations – large scale farms with many laborers doing same task at same time (plantations must grow a cash crop that’s in high demand; great interest in slave labor to work land for profit) o $ agriculture (#1 economic activity), VA/MD- tobacco; SC/GA- rice & indigo (for blue dye)
Southern colonies o Warm climate, rich soil, large coastal plain (longest growing season ) o Plantations – large scale farms with many laborers doing same task at same time (plantations must grow a cash crop that’s in high demand; great interest in slave labor to work land for profit) o $ agriculture (#1 economic activity), VA/MD- tobacco; SC/GA- rice & indigo (for blue dye)
 Southern colonies (cont. ) o Plantations are very large farms, so people live far apart o Region with fewest American cities (Charleston was only southern city during colonial times) o Very few schools, NO education requirement (only children of wealthy have tutors or board at a private school) o Ethnic Background: English, African, Scots-Irish
Southern colonies (cont. ) o Plantations are very large farms, so people live far apart o Region with fewest American cities (Charleston was only southern city during colonial times) o Very few schools, NO education requirement (only children of wealthy have tutors or board at a private school) o Ethnic Background: English, African, Scots-Irish
 Southern Colonists o Economic Differences – How did Southern colonists make a living? o _______________ o Socio-Religious Differences – How did Southerners treat other people? What religions were present or accepted? o ________________________________
Southern Colonists o Economic Differences – How did Southern colonists make a living? o _______________ o Socio-Religious Differences – How did Southerners treat other people? What religions were present or accepted? o ________________________________
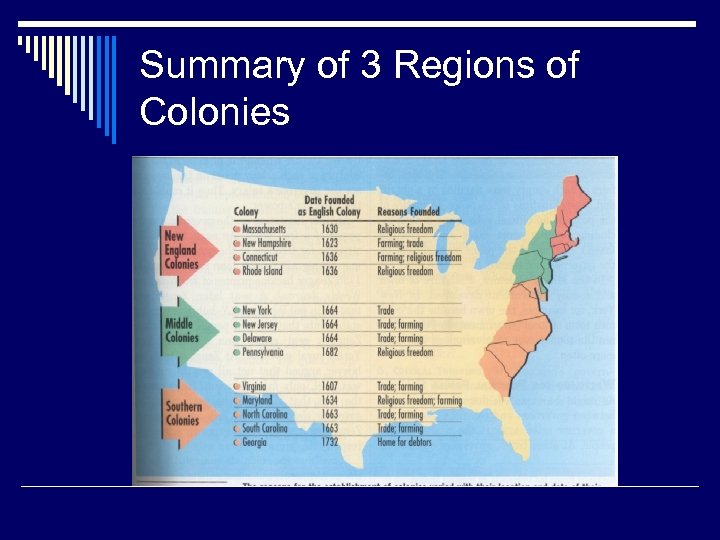 Summary of 3 Regions of Colonies
Summary of 3 Regions of Colonies
 13 Topic: Development o Standard: Compares the development of early Georgia with that of other colonies.
13 Topic: Development o Standard: Compares the development of early Georgia with that of other colonies.
 Compare GA colony with other colonies o Using slide #20, how is GA colony similar to other colonies? o ________________________________ o ________________
Compare GA colony with other colonies o Using slide #20, how is GA colony similar to other colonies? o ________________________________ o ________________
 Compare GA colony to other colonies o Using slide #20, how is GA colony different than other colonies? o ____________________________________ o __________________
Compare GA colony to other colonies o Using slide #20, how is GA colony different than other colonies? o ____________________________________ o __________________


