THREE DOMAINS OF BLOOM’S TAXONOMY MAJOR: “










bloomstaxonomy.pptx
- Размер: 1.1 Мб
- Автор:
- Количество слайдов: 15
Описание презентации THREE DOMAINS OF BLOOM’S TAXONOMY MAJOR: “ по слайдам
 THREE DOMAINS OF BLOOM’S TAXONOMY MAJOR: “ 6 M 073900 -PETROCHE MISTRY” DONE BY OTZHAN ULZHAN SERIKKANOV ASLAN AMRENOVA NAZERKE BAISENGIROVA AISULU YESSEMALIYEVA ALINA UMBETKALIYEVA KAMILL
THREE DOMAINS OF BLOOM’S TAXONOMY MAJOR: “ 6 M 073900 -PETROCHE MISTRY” DONE BY OTZHAN ULZHAN SERIKKANOV ASLAN AMRENOVA NAZERKE BAISENGIROVA AISULU YESSEMALIYEVA ALINA UMBETKALIYEVA KAMILL
 TAXONOMY comes from the Greek word “ taxis =arrangements” and “ nomos =science” Science of arrangements means ‘a set of classification principles’, or ‘structure’ Domain simply means ‘ category ‘.
TAXONOMY comes from the Greek word “ taxis =arrangements” and “ nomos =science” Science of arrangements means ‘a set of classification principles’, or ‘structure’ Domain simply means ‘ category ‘.
 WHO IS BENJAMIN BLOOM? was a Jewish-American educational psychologist. Contributions: 1. Classification of Educational Objectives 2. Theory of Mastery-Learning 3(Feb. 1913 – Sep. 1999) BENJAMIN SAMUEL BLOOM
WHO IS BENJAMIN BLOOM? was a Jewish-American educational psychologist. Contributions: 1. Classification of Educational Objectives 2. Theory of Mastery-Learning 3(Feb. 1913 – Sep. 1999) BENJAMIN SAMUEL BLOOM
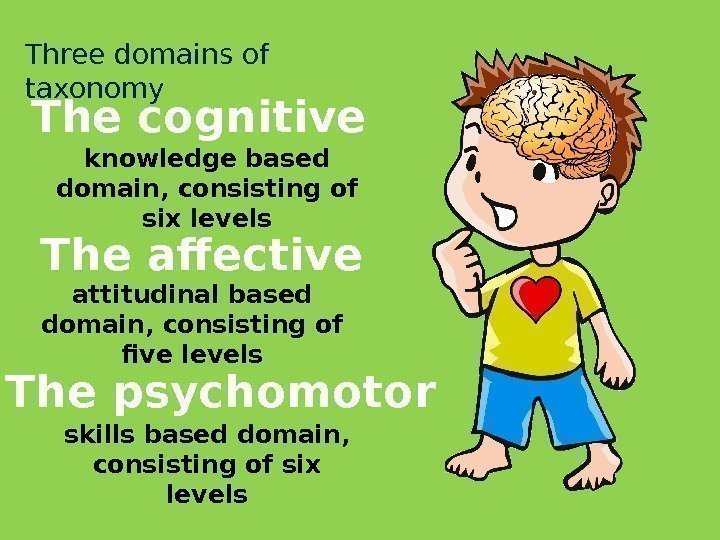
 Three domains of taxonomy knowledge based domain, consisting of six levels attitudinal based domain, consisting of five levels skills based domain, consisting of six levels. The cognitive The affective The psychomotor
Three domains of taxonomy knowledge based domain, consisting of six levels attitudinal based domain, consisting of five levels skills based domain, consisting of six levels. The cognitive The affective The psychomotor
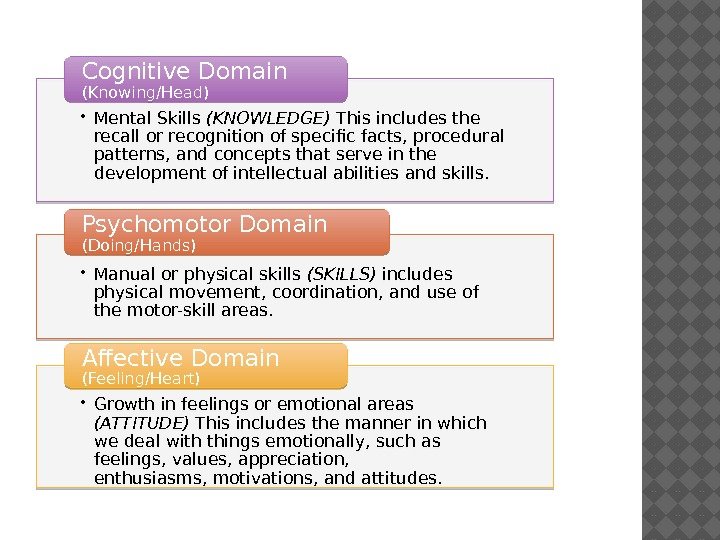
 • Mental Skills (KNOWLEDGE) This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts, procedural patterns, and concepts that serve in the development of intellectual abilities and skills. Cognitive Domain (Knowing/Head) • Manual or physical skills (SKILLS) includes physical movement, coordination, and use of the motor-skill areas. Psychomotor Domain (Doing/Hands) • Growth in feelings or emotional areas (ATTITUDE) This includes the manner in which we deal with things emotionally, such as feelings, values, appreciation, enthusiasms, motivations, andattitudes. Affective Domain (Feeling/Heart)
• Mental Skills (KNOWLEDGE) This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts, procedural patterns, and concepts that serve in the development of intellectual abilities and skills. Cognitive Domain (Knowing/Head) • Manual or physical skills (SKILLS) includes physical movement, coordination, and use of the motor-skill areas. Psychomotor Domain (Doing/Hands) • Growth in feelings or emotional areas (ATTITUDE) This includes the manner in which we deal with things emotionally, such as feelings, values, appreciation, enthusiasms, motivations, andattitudes. Affective Domain (Feeling/Heart)
 Means of expressing qualitatively different kinds of thinking Been adapted for classroom use as a planning tool Continues to be one of the most universally applied models Provides a way to organize thinking skills into six levels, from the most basic to the more complex levels of thinking. Bloom’s Taxonomy. Benjamin Bloom,
Means of expressing qualitatively different kinds of thinking Been adapted for classroom use as a planning tool Continues to be one of the most universally applied models Provides a way to organize thinking skills into six levels, from the most basic to the more complex levels of thinking. Bloom’s Taxonomy. Benjamin Bloom,
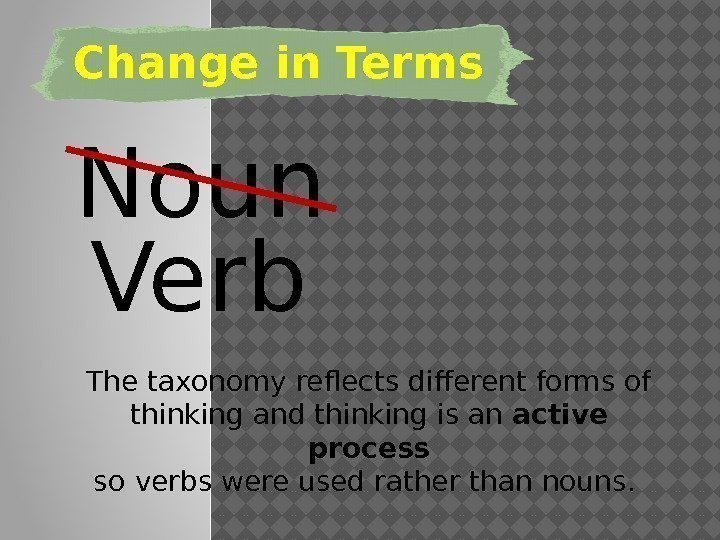
 Change in Terms Noun Verb The taxonomy reflects different forms of thinking and thinking is an active process so verbs were used rather than nouns.
Change in Terms Noun Verb The taxonomy reflects different forms of thinking and thinking is an active process so verbs were used rather than nouns.
 COGNITIVE This domain includes content knowledge and the development of intellectual skills. This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts and concepts that serve developing intellectual abilities and skills.
COGNITIVE This domain includes content knowledge and the development of intellectual skills. This includes the recall or recognition of specific facts and concepts that serve developing intellectual abilities and skills.
 TABLE OF THE REVISED COGNITIVE DOMAIN
TABLE OF THE REVISED COGNITIVE DOMAIN
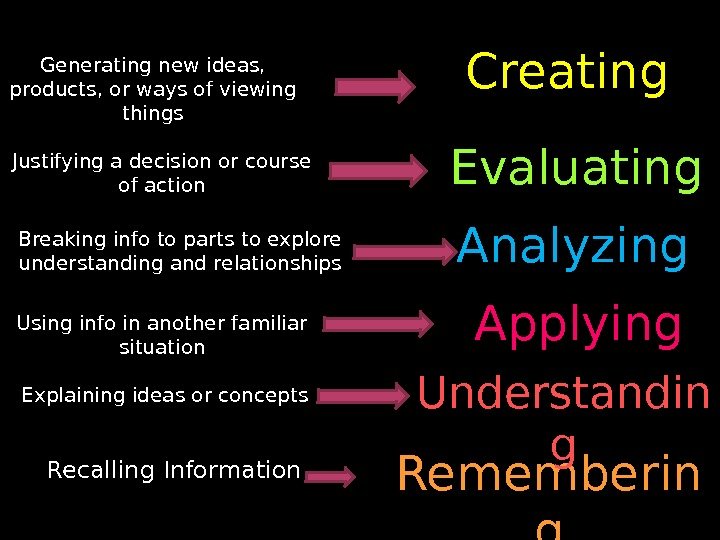
 Rememberin g. Understandin g. Applying. Analyzing. Evaluating Creating Recalling Information. Explaining ideas or concepts. Using info in another familiar situation. Breaking info to parts to explore understanding and relationships. Justifying a decision or course of action. Generating new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things
Rememberin g. Understandin g. Applying. Analyzing. Evaluating Creating Recalling Information. Explaining ideas or concepts. Using info in another familiar situation. Breaking info to parts to explore understanding and relationships. Justifying a decision or course of action. Generating new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things
 Affective The affective domain includes the manner in which we deal with things emotionally, such as feelings, values, appreciation, enthusiasms, motivations, and attitudes.
Affective The affective domain includes the manner in which we deal with things emotionally, such as feelings, values, appreciation, enthusiasms, motivations, and attitudes.
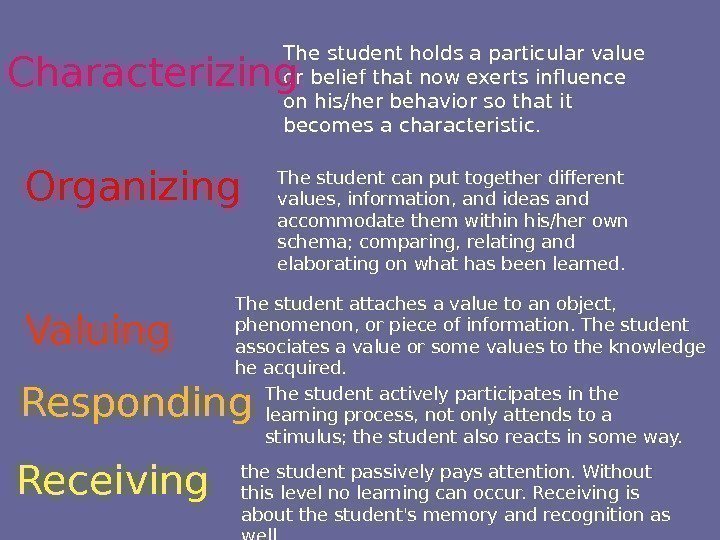
 The student holds a particular value or belief that now exerts influence on his/her behavior so that it becomes a characteristic. the student passively pays attention. Without this level no learning can occur. Receiving is about the student’s memory and recognition as well. The student actively participates in the learning process, not only attends to a stimulus; the student also reacts in some way. The student attaches a value to an object, phenomenon, or piece of information. The student associates a value or some values to the knowledge he acquired. The student can put together different values, information, and ideas and accommodate them within his/her own schema; comparing, relating and elaborating on what has been learned. Receiving Responding Valuing. Organizing. Characterizing
The student holds a particular value or belief that now exerts influence on his/her behavior so that it becomes a characteristic. the student passively pays attention. Without this level no learning can occur. Receiving is about the student’s memory and recognition as well. The student actively participates in the learning process, not only attends to a stimulus; the student also reacts in some way. The student attaches a value to an object, phenomenon, or piece of information. The student associates a value or some values to the knowledge he acquired. The student can put together different values, information, and ideas and accommodate them within his/her own schema; comparing, relating and elaborating on what has been learned. Receiving Responding Valuing. Organizing. Characterizing
 Psychomotor The psychomotor domain () includes physical movement, coordination, and use of the motor-skill areas. Development of these skills requires practice and is measured in terms of speed, precision, distance, procedures, or techniques in execution.
Psychomotor The psychomotor domain () includes physical movement, coordination, and use of the motor-skill areas. Development of these skills requires practice and is measured in terms of speed, precision, distance, procedures, or techniques in execution.
 The ability to use sensory cues to guide motor activity. This ranges from sensory stimulation, through cue selection, to translation. Readiness to act. It includes mental, physical, and emotional sets. These three sets are dispositions that predetermine a person’s response to different situations (sometimes called mindsets). The early stages in learning a complex skill that includes imitation and trial and error. Adequacy of performance is achieved by practicing. This is the intermediate stage in learning a complex skill. Learned responses have become habitual and the movements can be performed with some confidence and proficiency. Proficiency is indicated by a quick, accurate, and highly coordinated performance, requiring a minimum of energy. This category includes performing without hesitation, and automatic performance. Skills are well developed and the individual can modify movement patterns to fit special requirements. Creating new movement patterns to fit a particular situation or specific problem. Learning outcomes emphasize creativity based upon highly developed skills. Perception (awareness)Set Guided Response Mechanism (basic proficiency) Complex Overt Response (Expert)Adaptation Origination
The ability to use sensory cues to guide motor activity. This ranges from sensory stimulation, through cue selection, to translation. Readiness to act. It includes mental, physical, and emotional sets. These three sets are dispositions that predetermine a person’s response to different situations (sometimes called mindsets). The early stages in learning a complex skill that includes imitation and trial and error. Adequacy of performance is achieved by practicing. This is the intermediate stage in learning a complex skill. Learned responses have become habitual and the movements can be performed with some confidence and proficiency. Proficiency is indicated by a quick, accurate, and highly coordinated performance, requiring a minimum of energy. This category includes performing without hesitation, and automatic performance. Skills are well developed and the individual can modify movement patterns to fit special requirements. Creating new movement patterns to fit a particular situation or specific problem. Learning outcomes emphasize creativity based upon highly developed skills. Perception (awareness)Set Guided Response Mechanism (basic proficiency) Complex Overt Response (Expert)Adaptation Origination
 Thank you for your time and attention
Thank you for your time and attention

