 This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. This icon indicates teacher’s notes in the Notes field. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. 1 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not editable. This icon indicates teacher’s notes in the Notes field. For more detailed instructions, see the Getting Started presentation. 1 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
 Decimal rules 2 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
Decimal rules 2 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
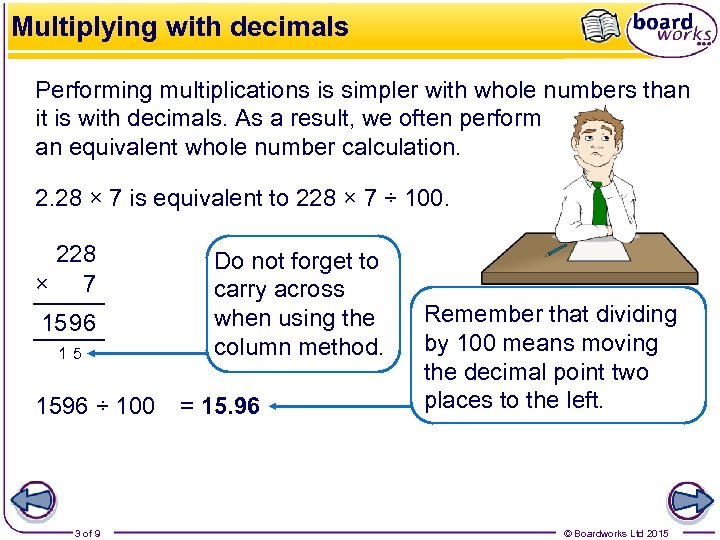 Multiplying with decimals Performing multiplications is simpler with whole numbers than it is with decimals. As a result, we often perform an equivalent whole number calculation. 2. 28 × 7 is equivalent to 228 × 7 ÷ 100. 228 × 7 15 96 15 1596 ÷ 100 3 of 9 Do not forget to carry across when using the column method. = 15. 96 Remember that dividing by 100 means moving the decimal point two places to the left. © Boardworks Ltd 2015
Multiplying with decimals Performing multiplications is simpler with whole numbers than it is with decimals. As a result, we often perform an equivalent whole number calculation. 2. 28 × 7 is equivalent to 228 × 7 ÷ 100. 228 × 7 15 96 15 1596 ÷ 100 3 of 9 Do not forget to carry across when using the column method. = 15. 96 Remember that dividing by 100 means moving the decimal point two places to the left. © Boardworks Ltd 2015
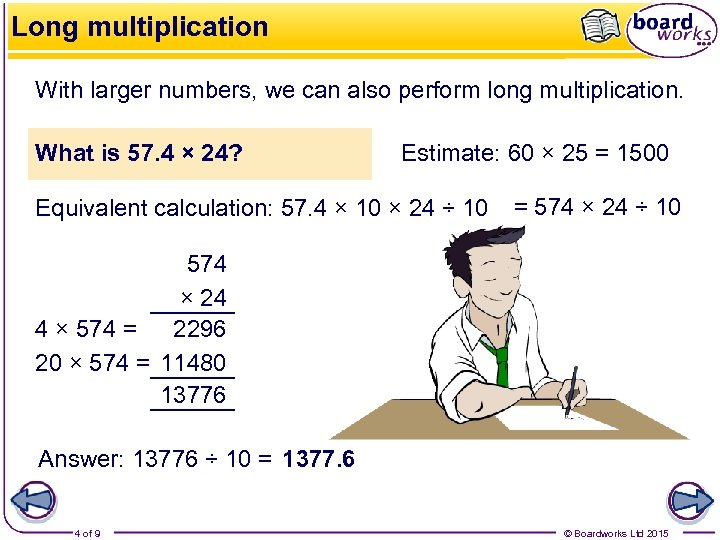 Long multiplication With larger numbers, we can also perform long multiplication. What is 57. 4 × 24? Estimate: 60 × 25 = 1500 Equivalent calculation: 57. 4 × 10 × 24 ÷ 10 = 574 × 24 ÷ 10 574 × 24 4 × 574 = 2296 20 × 574 = 11480 13776 Answer: 13776 ÷ 10 = 1377. 6 4 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
Long multiplication With larger numbers, we can also perform long multiplication. What is 57. 4 × 24? Estimate: 60 × 25 = 1500 Equivalent calculation: 57. 4 × 10 × 24 ÷ 10 = 574 × 24 ÷ 10 574 × 24 4 × 574 = 2296 20 × 574 = 11480 13776 Answer: 13776 ÷ 10 = 1377. 6 4 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
 Long multiplication 5 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
Long multiplication 5 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
 Short division by a decimal We are dividing by a single digit which means it is most efficient to use short division to complete the calculation. Calculate 57. 23 ÷ 0. 8 to 2 decimal places. 07 1. 5 3 7 8 55712. 4 33060 We need to find the value of this digit to see whether we need to round up or down. 57. 23 ÷ 0. 8 = 71. 54 (to 2 d. p. ) How would we complete a calculation when dividing by a two-digit number? 6 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
Short division by a decimal We are dividing by a single digit which means it is most efficient to use short division to complete the calculation. Calculate 57. 23 ÷ 0. 8 to 2 decimal places. 07 1. 5 3 7 8 55712. 4 33060 We need to find the value of this digit to see whether we need to round up or down. 57. 23 ÷ 0. 8 = 71. 54 (to 2 d. p. ) How would we complete a calculation when dividing by a two-digit number? 6 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
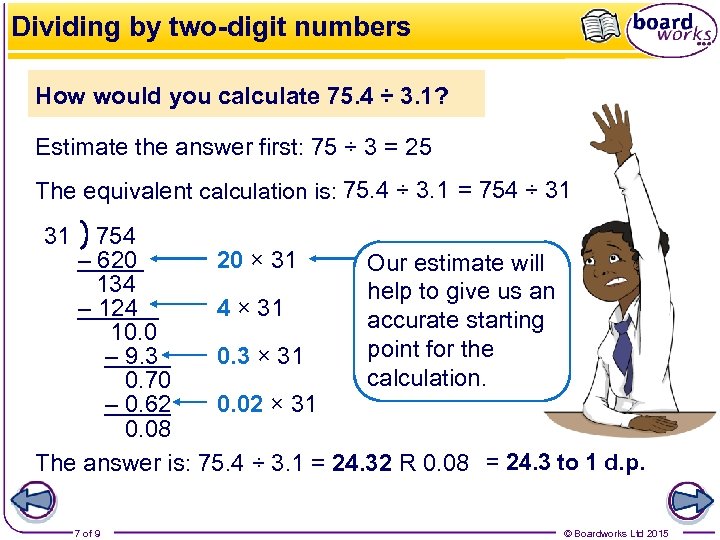 Dividing by two-digit numbers How would you calculate 75. 4 ÷ 3. 1? Estimate the answer first: 75 ÷ 3 = 25 The equivalent calculation is: 75. 4 ÷ 3. 1 = 754 ÷ 31 31 754 – 620 20 × 31 Our estimate will 134 help to give us an – 124 4 × 31 accurate starting 10. 0 point for the – 9. 3 0. 3 × 31 calculation. 0. 70 – 0. 62 0. 02 × 31 0. 08 The answer is: 75. 4 ÷ 3. 1 = 24. 32 R 0. 08 = 24. 3 to 1 d. p. 7 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
Dividing by two-digit numbers How would you calculate 75. 4 ÷ 3. 1? Estimate the answer first: 75 ÷ 3 = 25 The equivalent calculation is: 75. 4 ÷ 3. 1 = 754 ÷ 31 31 754 – 620 20 × 31 Our estimate will 134 help to give us an – 124 4 × 31 accurate starting 10. 0 point for the – 9. 3 0. 3 × 31 calculation. 0. 70 – 0. 62 0. 02 × 31 0. 08 The answer is: 75. 4 ÷ 3. 1 = 24. 32 R 0. 08 = 24. 3 to 1 d. p. 7 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
 Long division 8 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
Long division 8 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
 File storage Rachel wants to buy a memory stick that she’s going to use to store music she downloads. She’s found three different types: a 1 GB stick costing $6. 99 a $12. 79 stick with 2 GB of memory a 4 GB stick for $20. 49. If we know that there are 1024 MB in 1 GB, how much would it cost to fill the three memory sticks? Rachel buys the 4 GB stick and uses 75% of the space. How much has it cost her to buy and fill the stick? 9 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015
File storage Rachel wants to buy a memory stick that she’s going to use to store music she downloads. She’s found three different types: a 1 GB stick costing $6. 99 a $12. 79 stick with 2 GB of memory a 4 GB stick for $20. 49. If we know that there are 1024 MB in 1 GB, how much would it cost to fill the three memory sticks? Rachel buys the 4 GB stick and uses 75% of the space. How much has it cost her to buy and fill the stick? 9 of 9 © Boardworks Ltd 2015