9ec6e5c25e849dcab5353828b8974881.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Third Session : Presentation on (Export/Import Documentation Incoterms and procedures of Export /Import by Rajan Sharma
Third Session : Presentation on (Export/Import Documentation Incoterms and procedures of Export /Import by Rajan Sharma
 Objective of this Class: Acquaint the participants with the following: a. Document required for export and Import b. Import and export procedure c. Choosing the right means and mode of transportation d. International Incoterms and its implication in business contract and negotiation. e. Packing , warehousing and distribution. f. Problems in shipping out of Nepal
Objective of this Class: Acquaint the participants with the following: a. Document required for export and Import b. Import and export procedure c. Choosing the right means and mode of transportation d. International Incoterms and its implication in business contract and negotiation. e. Packing , warehousing and distribution. f. Problems in shipping out of Nepal
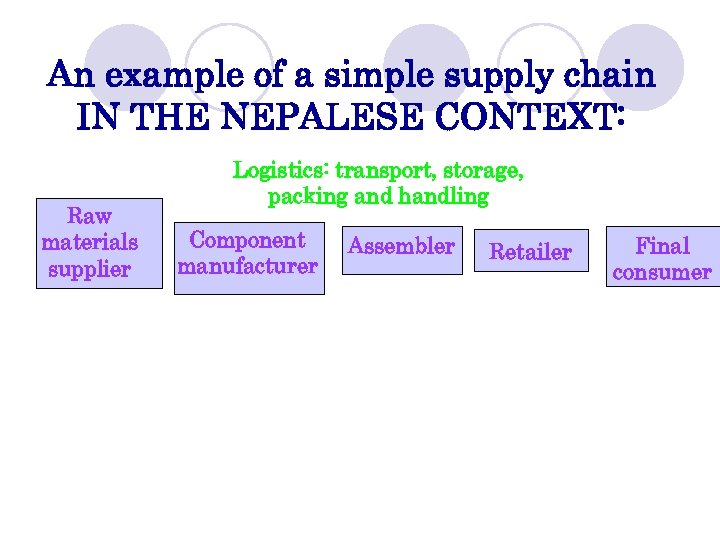 An example of a simple supply chain IN THE NEPALESE CONTEXT: Raw materials supplier Logistics: transport, storage, packing and handling Component manufacturer Assembler Retailer Final consumer
An example of a simple supply chain IN THE NEPALESE CONTEXT: Raw materials supplier Logistics: transport, storage, packing and handling Component manufacturer Assembler Retailer Final consumer
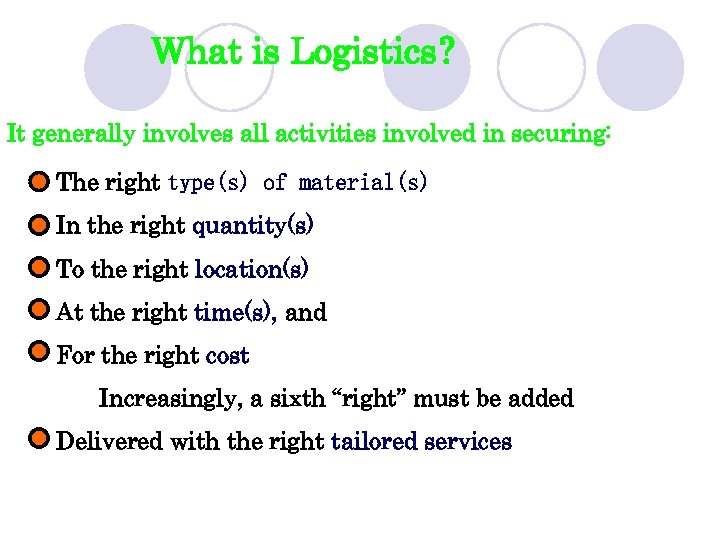 What is Logistics? It generally involves all activities involved in securing: The right type(s) of material(s) In the right quantity(s) To the right location(s) At the right time(s), and For the right cost Increasingly, a sixth “right” must be added Delivered with the right tailored services
What is Logistics? It generally involves all activities involved in securing: The right type(s) of material(s) In the right quantity(s) To the right location(s) At the right time(s), and For the right cost Increasingly, a sixth “right” must be added Delivered with the right tailored services
 What does Each Incoterm determine ? 1. When and where the seller provides the goods to the buyer and when and where the buyer is obliged to pay the contracted price 2. Obligations for export/import licences, duties, taxes, etc. 3. Obligations to arrange and pay for transportation and insurance 4. Conditions for delivery by the seller and acceptance by the buyer 5. Allocation of responsibility for risk of loss or damage 6. Allocation of costs associated with movement of the goods 7. Provisions regarding notices of delivery or dispatch of the goods 8. Proof of delivery, transport documents or electronic messages 9. Requirements of seller to check quantity & conformance of goods with the contract and to provide suitable packaging and markings 10. Obligations of mutual assistance, information and documentation
What does Each Incoterm determine ? 1. When and where the seller provides the goods to the buyer and when and where the buyer is obliged to pay the contracted price 2. Obligations for export/import licences, duties, taxes, etc. 3. Obligations to arrange and pay for transportation and insurance 4. Conditions for delivery by the seller and acceptance by the buyer 5. Allocation of responsibility for risk of loss or damage 6. Allocation of costs associated with movement of the goods 7. Provisions regarding notices of delivery or dispatch of the goods 8. Proof of delivery, transport documents or electronic messages 9. Requirements of seller to check quantity & conformance of goods with the contract and to provide suitable packaging and markings 10. Obligations of mutual assistance, information and documentation
 Incoterms are grouped into four categories: “E” Terms - Ex-works “F” Terms - Main carriage not paid by seller “C” Terms - Main carriage paid by seller “D” Terms - Delivered on arrival
Incoterms are grouped into four categories: “E” Terms - Ex-works “F” Terms - Main carriage not paid by seller “C” Terms - Main carriage paid by seller “D” Terms - Delivered on arrival
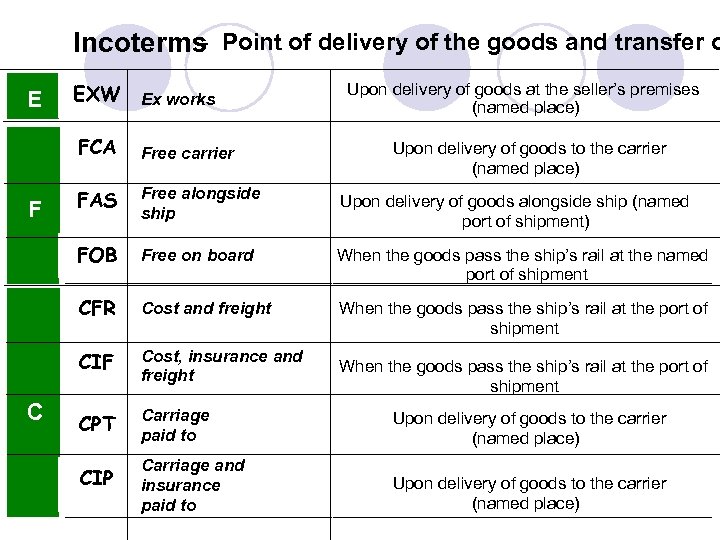 – Incoterms Point of delivery of the goods and transfer o E EXW Ex works Upon delivery of goods at the seller’s premises (named place) FCA Free alongside ship Upon delivery of goods alongside ship (named port of shipment) Free on board When the goods pass the ship’s rail at the named port of shipment CFR Cost and freight When the goods pass the ship’s rail at the port of shipment CIF C FAS FOB F Free carrier Cost, insurance and freight CPT Carriage paid to Upon delivery of goods to the carrier (named place) CIP Carriage and insurance paid to Upon delivery of goods to the carrier (named place) When the goods pass the ship’s rail at the port of shipment
– Incoterms Point of delivery of the goods and transfer o E EXW Ex works Upon delivery of goods at the seller’s premises (named place) FCA Free alongside ship Upon delivery of goods alongside ship (named port of shipment) Free on board When the goods pass the ship’s rail at the named port of shipment CFR Cost and freight When the goods pass the ship’s rail at the port of shipment CIF C FAS FOB F Free carrier Cost, insurance and freight CPT Carriage paid to Upon delivery of goods to the carrier (named place) CIP Carriage and insurance paid to Upon delivery of goods to the carrier (named place) When the goods pass the ship’s rail at the port of shipment
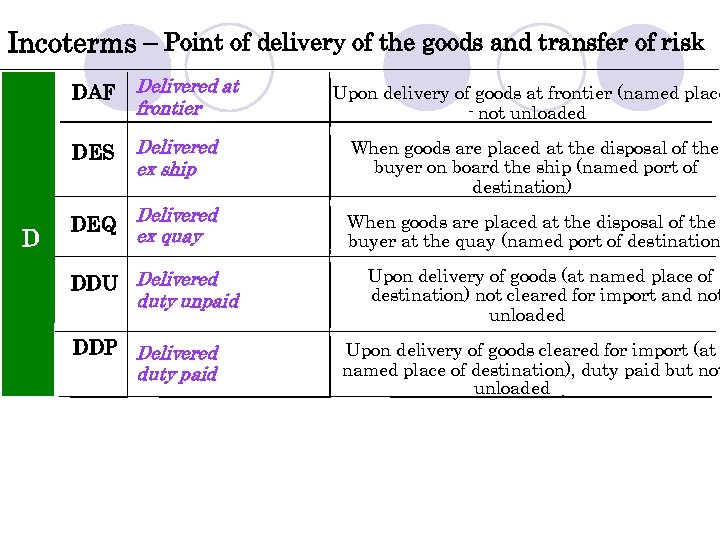 Incoterms – Point of delivery of the goods and transfer of risk DAF DES D Delivered at frontier Delivered ex ship When goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer on board the ship (named port of destination) DEQ Delivered ex quay When goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer at the quay (named port of destination DDU Delivered duty unpaid DDP Delivered duty paid Upon delivery of goods at frontier (named place - not unloaded Upon delivery of goods (at named place of destination) not cleared for import and not unloaded Upon delivery of goods cleared for import (at named place of destination), duty paid but not unloaded
Incoterms – Point of delivery of the goods and transfer of risk DAF DES D Delivered at frontier Delivered ex ship When goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer on board the ship (named port of destination) DEQ Delivered ex quay When goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer at the quay (named port of destination DDU Delivered duty unpaid DDP Delivered duty paid Upon delivery of goods at frontier (named place - not unloaded Upon delivery of goods (at named place of destination) not cleared for import and not unloaded Upon delivery of goods cleared for import (at named place of destination), duty paid but not unloaded
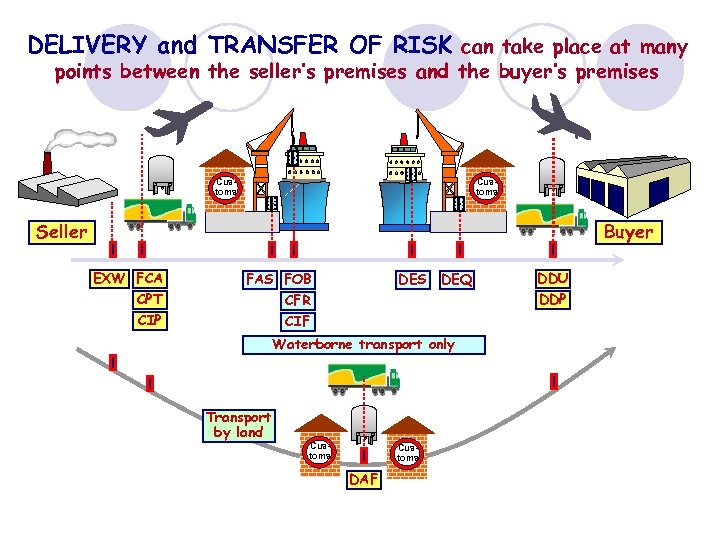 DELIVERY and TRANSFER OF RISK can take place at many points between the seller’s premises and the buyer’s premises Customs Seller Buyer EXW FCA CPT CIP FAS FOB CFR CIF DES DEQ Waterborne transport only Transport by land Customs DAF DDU DDP
DELIVERY and TRANSFER OF RISK can take place at many points between the seller’s premises and the buyer’s premises Customs Seller Buyer EXW FCA CPT CIP FAS FOB CFR CIF DES DEQ Waterborne transport only Transport by land Customs DAF DDU DDP
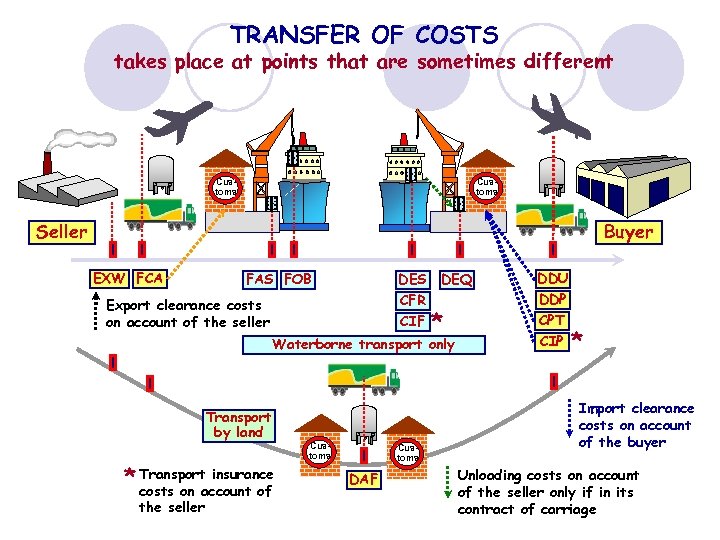 TRANSFER OF COSTS takes place at points that are sometimes different Customs Seller Buyer EXW FCA FAS FOB DES CFR CIF Export clearance costs on account of the seller DEQ * Waterborne transport only Transport by land * Transport insurance costs on account of the seller Customs DAF DDU DDP CPT CIP * Import clearance costs on account of the buyer Unloading costs on account of the seller only if in its contract of carriage
TRANSFER OF COSTS takes place at points that are sometimes different Customs Seller Buyer EXW FCA FAS FOB DES CFR CIF Export clearance costs on account of the seller DEQ * Waterborne transport only Transport by land * Transport insurance costs on account of the seller Customs DAF DDU DDP CPT CIP * Import clearance costs on account of the buyer Unloading costs on account of the seller only if in its contract of carriage
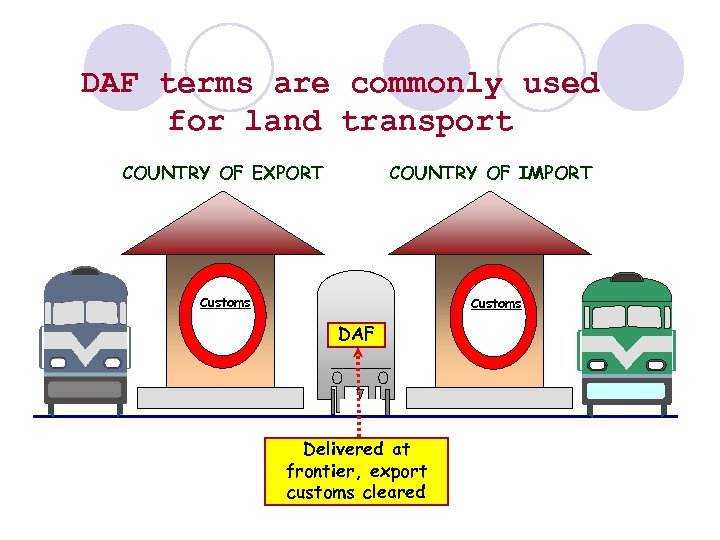 DAF terms are commonly used for land transport COUNTRY OF EXPORT COUNTRY OF IMPORT Customs DAF Delivered at frontier, export customs cleared
DAF terms are commonly used for land transport COUNTRY OF EXPORT COUNTRY OF IMPORT Customs DAF Delivered at frontier, export customs cleared
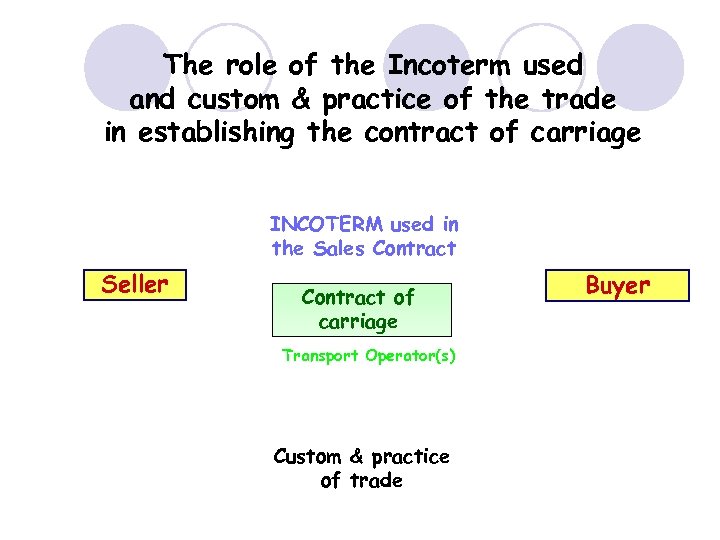 The role of the Incoterm used and custom & practice of the trade in establishing the contract of carriage INCOTERM used in the Sales Contract Seller Contract of carriage Transport Operator(s) Custom & practice of trade Buyer
The role of the Incoterm used and custom & practice of the trade in establishing the contract of carriage INCOTERM used in the Sales Contract Seller Contract of carriage Transport Operator(s) Custom & practice of trade Buyer
 Freight Forwarders Responsibility and Duties: Duties and responsibilities of the freight forwarding agent when contracted by the shipper(who may be the exporter or importer depending on the Incoterm used): Advise on the most appropriate mode of transport. Arrange reservation of space on a vessel, train or aeroplane. Take delivery of the goods. Pack products into containers or onto pallets. Store goods in transit (before loading on board). Insure the cargo. Weigh and measure the goods. Prepare loading and, if necessary, transhipments. Transport the goods to a named port or airport of origin.
Freight Forwarders Responsibility and Duties: Duties and responsibilities of the freight forwarding agent when contracted by the shipper(who may be the exporter or importer depending on the Incoterm used): Advise on the most appropriate mode of transport. Arrange reservation of space on a vessel, train or aeroplane. Take delivery of the goods. Pack products into containers or onto pallets. Store goods in transit (before loading on board). Insure the cargo. Weigh and measure the goods. Prepare loading and, if necessary, transhipments. Transport the goods to a named port or airport of origin.
 Freight Forwarders… cont. . Duties and responsibilities of the freight forwarding agent when contracted by the importer (whether or not the importer is the shipper): Follow-up on the movement of the goods. Receive and control documents related to the goods. Ensure customs documents are prepared in advance. Take delivery of the goods. Check on goods storage during transhipments. Assist with customs clearance. Deliver the goods to the consignee.
Freight Forwarders… cont. . Duties and responsibilities of the freight forwarding agent when contracted by the importer (whether or not the importer is the shipper): Follow-up on the movement of the goods. Receive and control documents related to the goods. Ensure customs documents are prepared in advance. Take delivery of the goods. Check on goods storage during transhipments. Assist with customs clearance. Deliver the goods to the consignee.
 Export Documents: l l l l Letter of Credit/Advance payment certificate and Covering letter of bank Invoice (Description of Goods and value per unit and total. Packing list (Volume and weight break of each Pc) Certificate of origin and GSP Pan /Vat/Company registration certificate copy Authority Letter CTD ATA CARNET
Export Documents: l l l l Letter of Credit/Advance payment certificate and Covering letter of bank Invoice (Description of Goods and value per unit and total. Packing list (Volume and weight break of each Pc) Certificate of origin and GSP Pan /Vat/Company registration certificate copy Authority Letter CTD ATA CARNET
 l l l l l Yellow paper (Custom declaration) Currency declaration Form Handicraft Certificate (for handicraft Goods) Visa in case of garments export Plant Quarantine certificate in case of Plants/Food items Permission from department of Forestry in cage of Forest product Certificate from Agriculture department in case of agro products. Sample goods and special goods permission from department of Customs ie: diplomatic /Personal effects Human remains: Fumigation certificate for Agro products or wooden goods.
l l l l l Yellow paper (Custom declaration) Currency declaration Form Handicraft Certificate (for handicraft Goods) Visa in case of garments export Plant Quarantine certificate in case of Plants/Food items Permission from department of Forestry in cage of Forest product Certificate from Agriculture department in case of agro products. Sample goods and special goods permission from department of Customs ie: diplomatic /Personal effects Human remains: Fumigation certificate for Agro products or wooden goods.
 Documents for Import Goods: l l l l l Letter of credit with Covering letters from bank NTWCL Invoice Packing List Certificate of origin Bank forms, Custom declaration AWB/HBL or MBL ( Transport Documents) Permission Certificate from department of custom Permission Certificate from department of commerce
Documents for Import Goods: l l l l l Letter of credit with Covering letters from bank NTWCL Invoice Packing List Certificate of origin Bank forms, Custom declaration AWB/HBL or MBL ( Transport Documents) Permission Certificate from department of custom Permission Certificate from department of commerce
 l Authority permission by importer (consignee) l Insurance covering paper l Delivery Order paper from transporter l CTD In case of Land Shipment: Mode and Means of Shipment and how to choose the right mode and means of transport. l Air/Air l Air/Sea l Land/sea. l Airplane, Trucking, Train, Ship :
l Authority permission by importer (consignee) l Insurance covering paper l Delivery Order paper from transporter l CTD In case of Land Shipment: Mode and Means of Shipment and how to choose the right mode and means of transport. l Air/Air l Air/Sea l Land/sea. l Airplane, Trucking, Train, Ship :
 Payment methods l Letter of credit l Telegraphic transfer l Advance payment l Cash against documents
Payment methods l Letter of credit l Telegraphic transfer l Advance payment l Cash against documents
 Factors to be considered in the means and mode of transport: l Time l Cost l Place of delivery l Loading point l Tran-shipment point l Customs point and infrastructure and cost.
Factors to be considered in the means and mode of transport: l Time l Cost l Place of delivery l Loading point l Tran-shipment point l Customs point and infrastructure and cost.
 Packing /Marks and Numbers : It protects your product your during transportation. It breaks down your product to sellable units (e. g. transforming staple goods into consumer units), or it simply makes the product accessible to consumers. It conveys a message to the buyer/consumer (e. g. advertisement or instruction for use etc. ). l Distribution l Warehousing (storage)
Packing /Marks and Numbers : It protects your product your during transportation. It breaks down your product to sellable units (e. g. transforming staple goods into consumer units), or it simply makes the product accessible to consumers. It conveys a message to the buyer/consumer (e. g. advertisement or instruction for use etc. ). l Distribution l Warehousing (storage)
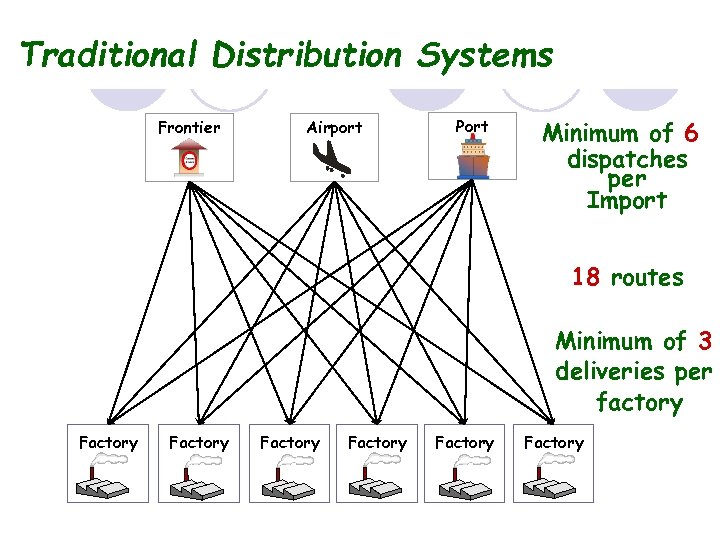 Traditional Distribution Systems Frontier Airport Port Minimum of 6 dispatches per Import 18 routes Minimum of 3 deliveries per factory Factory Factory
Traditional Distribution Systems Frontier Airport Port Minimum of 6 dispatches per Import 18 routes Minimum of 3 deliveries per factory Factory Factory
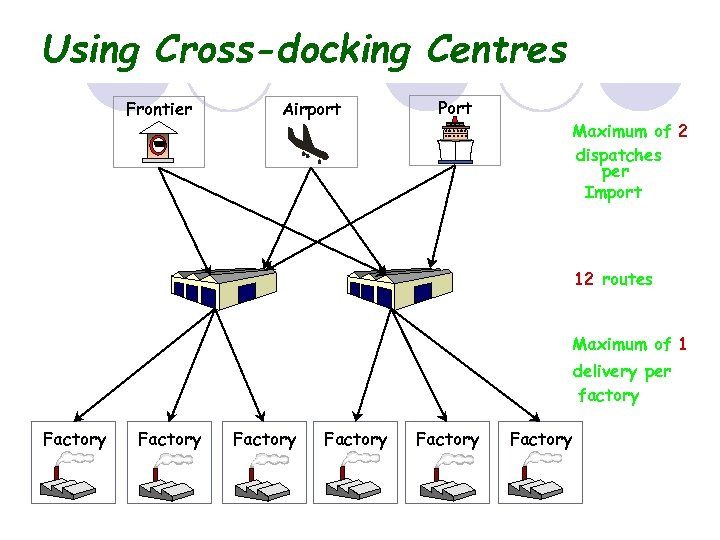 (B) Cross-docking centres Using cross-docking. Centres Frontier Airport Port Customs Douane Maximum of 2 dispatches per Import 12 routes Maximum of 1 delivery per factory Factory Factory
(B) Cross-docking centres Using cross-docking. Centres Frontier Airport Port Customs Douane Maximum of 2 dispatches per Import 12 routes Maximum of 1 delivery per factory Factory Factory
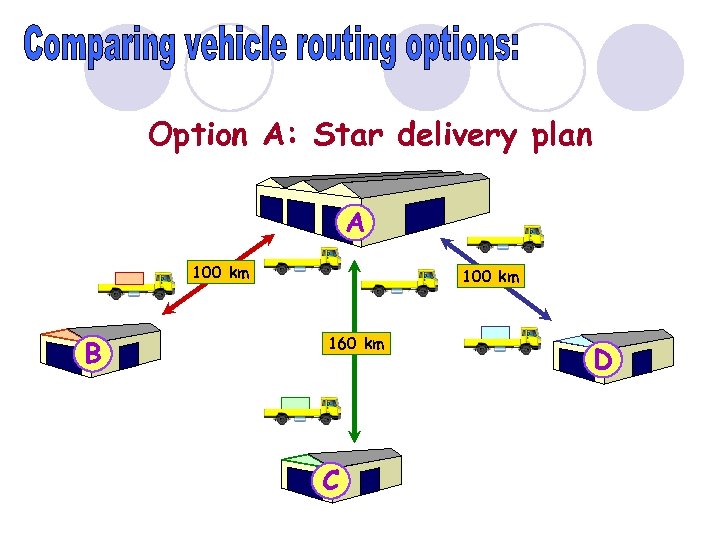 Option A: Star delivery plan A 100 km B 100 km 160 km C D
Option A: Star delivery plan A 100 km B 100 km 160 km C D
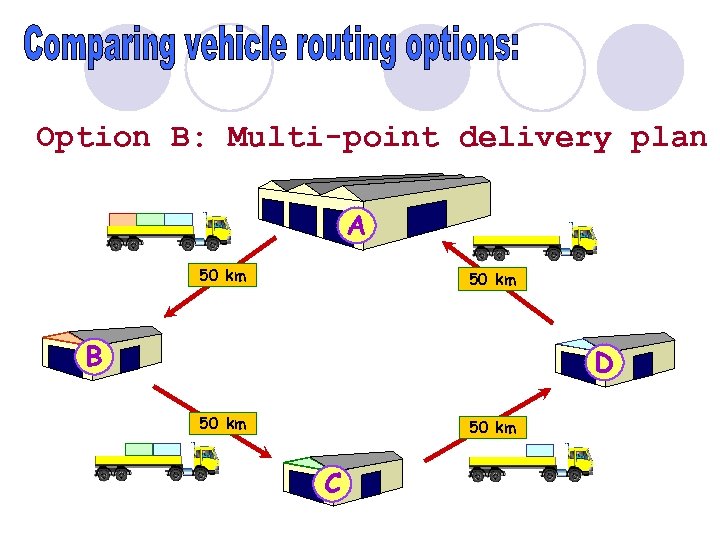 Option B: Multi-point delivery plan A 50 km B D 50 km C
Option B: Multi-point delivery plan A 50 km B D 50 km C
 Document required for exporting to EU l GSP l (Derogation) l Other necessary quality certification l Health and Sanitization certificate l HACCP l Environment issues l Child labor issues
Document required for exporting to EU l GSP l (Derogation) l Other necessary quality certification l Health and Sanitization certificate l HACCP l Environment issues l Child labor issues
 Export procedure l Preparing shipment l Haulage , choosing the means and mode of transport, sending pre-alert, issuing the right transport document, negotiation with bank, l Other document compliance.
Export procedure l Preparing shipment l Haulage , choosing the means and mode of transport, sending pre-alert, issuing the right transport document, negotiation with bank, l Other document compliance.
 Import Procedure: l Product finding l Price negotiation l adding document cost, haulage cost, customs cost, tax in the exporting country, l Arranging shipping, information flow, transshipment point procedure , import procedure of the country. dealing with customs etc.
Import Procedure: l Product finding l Price negotiation l adding document cost, haulage cost, customs cost, tax in the exporting country, l Arranging shipping, information flow, transshipment point procedure , import procedure of the country. dealing with customs etc.
 Problems: l L/C Compliance l Transport Document Compliance l Shipment date l L/C expiry l Delivery problem/Delivery order l Discrepancy due to transportation problem l Bank release.
Problems: l L/C Compliance l Transport Document Compliance l Shipment date l L/C expiry l Delivery problem/Delivery order l Discrepancy due to transportation problem l Bank release.
 Thank You for your Attention. Any Questions ? ? ?
Thank You for your Attention. Any Questions ? ? ?


