243b93425405af8ef4a9bb82fa7f438c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66
 Thinking and Language
Thinking and Language
 Lateral Thinking Puzzles- Think outside the bo • Cleopatra and Mark Antony are found dead, naked in a shattered glass house. How did this happen? • A father and son were in a car accident. The father was dead on impact, and the son severely injured and rushed to the hospital. The surgeon refused to work to operate on the injured boy, saying, “I can’t operate on him, he is my son!” How is this possible? • Hunters came upon a cabin in the woods, where inside they found two dead. At first glance, it was obvious how they died. How did they die? • Tom is found dead in the living room, with a bar across his back. How did he die? • Adults are holding children, waiting their turn. The children are handed to a man, who holds them while a woman shoots them.
Lateral Thinking Puzzles- Think outside the bo • Cleopatra and Mark Antony are found dead, naked in a shattered glass house. How did this happen? • A father and son were in a car accident. The father was dead on impact, and the son severely injured and rushed to the hospital. The surgeon refused to work to operate on the injured boy, saying, “I can’t operate on him, he is my son!” How is this possible? • Hunters came upon a cabin in the woods, where inside they found two dead. At first glance, it was obvious how they died. How did they die? • Tom is found dead in the living room, with a bar across his back. How did he die? • Adults are holding children, waiting their turn. The children are handed to a man, who holds them while a woman shoots them.
 Cognition • Another term for thinking, knowing and remembering Does the way we think really matter? Maybe by studying the way we think, we can eventually think better.
Cognition • Another term for thinking, knowing and remembering Does the way we think really matter? Maybe by studying the way we think, we can eventually think better.
 In order to think about the world, we form……. . Concepts • A mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas or people. • Give order w/o defining everything Money, exercise equipment etc • Concepts are similar to Piaget’s idea of…. Schemas These animals all look different, but they fall under our concept of “dogs”.
In order to think about the world, we form……. . Concepts • A mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas or people. • Give order w/o defining everything Money, exercise equipment etc • Concepts are similar to Piaget’s idea of…. Schemas These animals all look different, but they fall under our concept of “dogs”.
 What is a schema? • A schema is a set of ideas about something. Our stereotypes come from our schemas. • What is your schema for an office?
What is a schema? • A schema is a set of ideas about something. Our stereotypes come from our schemas. • What is your schema for an office?
 • People were asked what they remembered about this picture. • 29 out of 30 recalled Chair, desk, and walls • Only 8 subjects recalled it had a skull • 9 subjects recalled it had books which it did not • Memory for location is influenced by the person’s schema for that location.
• People were asked what they remembered about this picture. • 29 out of 30 recalled Chair, desk, and walls • Only 8 subjects recalled it had a skull • 9 subjects recalled it had books which it did not • Memory for location is influenced by the person’s schema for that location.
 Spelling words wrong • https: //www. youtub e. com/watch? v=bn J 8 Upvd. TQY
Spelling words wrong • https: //www. youtub e. com/watch? v=bn J 8 Upvd. TQY
 We base our concepts on …. Prototypes • A mental image or best (typical) example of a category. • If a new object is similar to our prototype, we are better able to recognize it. • Which bird is a prototypical bird?
We base our concepts on …. Prototypes • A mental image or best (typical) example of a category. • If a new object is similar to our prototype, we are better able to recognize it. • Which bird is a prototypical bird?
 How do we solve problems?
How do we solve problems?
 Trial and Error
Trial and Error
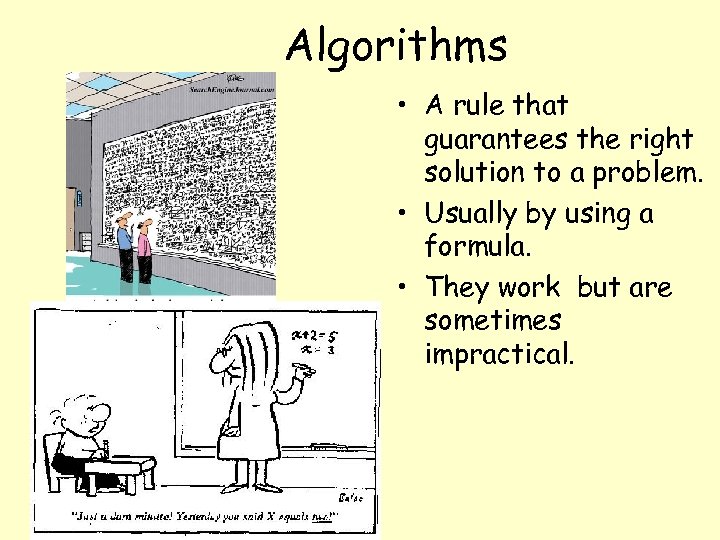 Algorithms • A rule that guarantees the right solution to a problem. • Usually by using a formula. • They work but are sometimes impractical.
Algorithms • A rule that guarantees the right solution to a problem. • Usually by using a formula. • They work but are sometimes impractical.
 Find another word using all the letters: SPLOYOCHYG. • Using each letter in each position there would be 907, 200 permutations • Algorithms are slow, but eventually accurate. Computers use algorithms.
Find another word using all the letters: SPLOYOCHYG. • Using each letter in each position there would be 907, 200 permutations • Algorithms are slow, but eventually accurate. Computers use algorithms.
 Big Bang Algorithms • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=k 0 xgj. U h. EG 3 U
Big Bang Algorithms • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=k 0 xgj. U h. EG 3 U
 Heuristics Who would you trust to baby-sit your child? • A rule-of-thumb strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently. A short cut (that can be prone to errors). Quick but there can be errors • Who would you trust to baby sit your child? Your answer is based on your heuristic of their appearances.
Heuristics Who would you trust to baby-sit your child? • A rule-of-thumb strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently. A short cut (that can be prone to errors). Quick but there can be errors • Who would you trust to baby sit your child? Your answer is based on your heuristic of their appearances.
 Unscramble this word using a heuristic • euqne • Since q and u always go together, you put them together as a shortcut. Then you figure out the rest.
Unscramble this word using a heuristic • euqne • Since q and u always go together, you put them together as a shortcut. Then you figure out the rest.
 Insight • A sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem. • No real strategy involved
Insight • A sudden and often novel realization of the solution to a problem. • No real strategy involved
 What are some obstacles to problem solving?
What are some obstacles to problem solving?
 Confirmation Bias • A tendency to search for information that confirms one’s preconceptions. For example, if you believe that during a full moon there is an increase in admissions to the emergency room where you work, you will take notice of admissions during a full moon, but be inattentive to the moon when admissions occur during other nights of the month.
Confirmation Bias • A tendency to search for information that confirms one’s preconceptions. For example, if you believe that during a full moon there is an increase in admissions to the emergency room where you work, you will take notice of admissions during a full moon, but be inattentive to the moon when admissions occur during other nights of the month.
 Match Problem Can you arrange these six matches into four equilateral triangles?
Match Problem Can you arrange these six matches into four equilateral triangles?
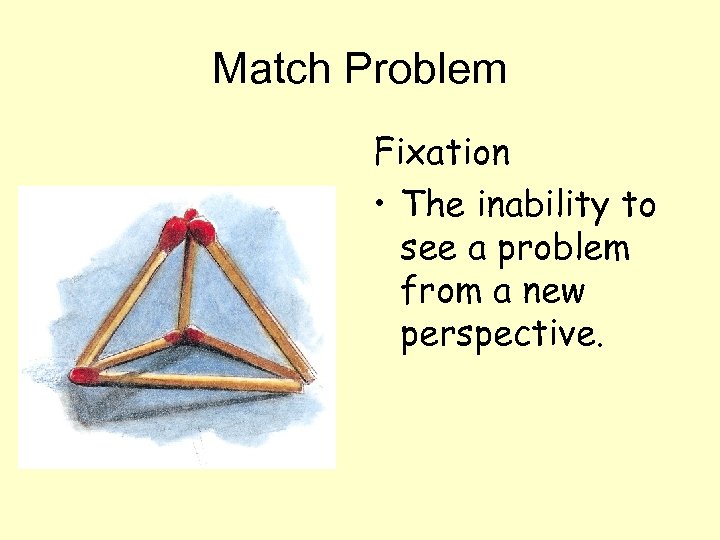 Match Problem Fixation • The inability to see a problem from a new perspective.
Match Problem Fixation • The inability to see a problem from a new perspective.
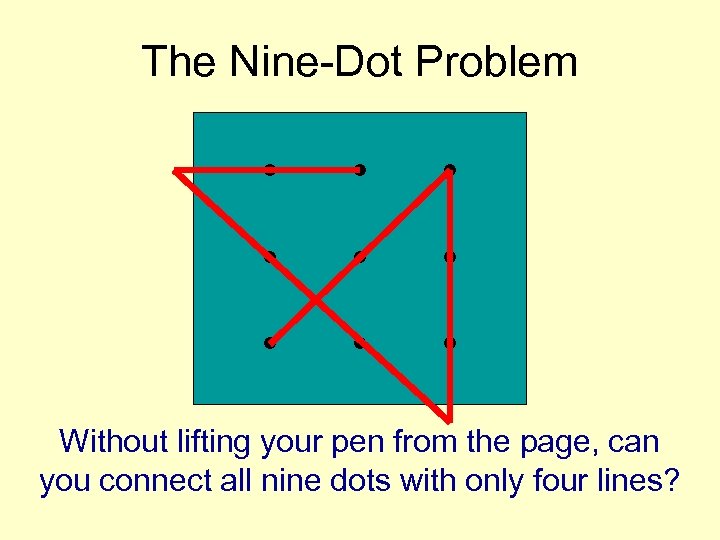 The Nine-Dot Problem . . Without lifting your pen from the page, can you connect all nine dots with only four lines?
The Nine-Dot Problem . . Without lifting your pen from the page, can you connect all nine dots with only four lines?
 Mental Set • A tendency to approach a problem in a particular way, especially if it has worked in the past. • May or may not be a good thing.
Mental Set • A tendency to approach a problem in a particular way, especially if it has worked in the past. • May or may not be a good thing.
 Functional Fixedness • The tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions. What are some things I can do with this quarter (other than spend it)? Paperclip?
Functional Fixedness • The tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions. What are some things I can do with this quarter (other than spend it)? Paperclip?
 Divergent thinking, Convergent thinking • Divergent thinking is thinking outside the box. It means you are creative in coming up with solutions nobody else came up with. (shocks to build muscle) • Convergent thinking is more conforming but just as good. Sometimes the standard way is the best. (lifting weights to build muscle)
Divergent thinking, Convergent thinking • Divergent thinking is thinking outside the box. It means you are creative in coming up with solutions nobody else came up with. (shocks to build muscle) • Convergent thinking is more conforming but just as good. Sometimes the standard way is the best. (lifting weights to build muscle)
 Types of Heuristics (That often lead to errors)
Types of Heuristics (That often lead to errors)
 Representativeness Heuristic • A rule of thumb for judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they match our prototype. • Can cause us to ignore important information. Below is Linda. She loves books and hates loud noises. Is Linda a librarian or a beautician?
Representativeness Heuristic • A rule of thumb for judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they match our prototype. • Can cause us to ignore important information. Below is Linda. She loves books and hates loud noises. Is Linda a librarian or a beautician?
 Representativeness Heuristic Who went to Harvard? Dan is a smart dude, but did not go to Harvard (but he looks like he did). • If I tell you that Sonia Dara is a Sports Illustrated swimsuit model, you would make certain quick judgments (heuristics) about her…like about her interests or intelligence. • She is an economics major at Harvard University. • Judging a situation based on how similar the aspects are to the prototypes the person holds in their mind. • Like thinking everyone from Rye is preppy, or someone with glasses is nerdy, or a blonde is not smart.
Representativeness Heuristic Who went to Harvard? Dan is a smart dude, but did not go to Harvard (but he looks like he did). • If I tell you that Sonia Dara is a Sports Illustrated swimsuit model, you would make certain quick judgments (heuristics) about her…like about her interests or intelligence. • She is an economics major at Harvard University. • Judging a situation based on how similar the aspects are to the prototypes the person holds in their mind. • Like thinking everyone from Rye is preppy, or someone with glasses is nerdy, or a blonde is not smart.
 Who would you go to for math tutoring? • Our heuristic thinking will tell us to go to the person who looks like he /she knows what that are doing.
Who would you go to for math tutoring? • Our heuristic thinking will tell us to go to the person who looks like he /she knows what that are doing.
 Availability Heuristic Although diseases kill many more people than accidents, it has been shown that people will judge accidents and diseases to be equally fatal. This is because accidents are more dramatic and are often written up in the paper or seen on the news on TV. , and are more available in memory than diseases. • Estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in our memory. • If it comes to mind easily (maybe a vivid event) we presume it is common.
Availability Heuristic Although diseases kill many more people than accidents, it has been shown that people will judge accidents and diseases to be equally fatal. This is because accidents are more dramatic and are often written up in the paper or seen on the news on TV. , and are more available in memory than diseases. • Estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in our memory. • If it comes to mind easily (maybe a vivid event) we presume it is common.
 Availability Heuristic and Fear • Genetic factors influence what we fear: snakes, spiders • People often overestimate a fear due to availability heuristic. Such as tornadoes
Availability Heuristic and Fear • Genetic factors influence what we fear: snakes, spiders • People often overestimate a fear due to availability heuristic. Such as tornadoes
 Overconfidence • The tendency to be more confident than correct. • To overestimate the accuracy of your beliefs and judgments. Considering “overconfidence” do you want to risk 1 million dollars on an audience poll?
Overconfidence • The tendency to be more confident than correct. • To overestimate the accuracy of your beliefs and judgments. Considering “overconfidence” do you want to risk 1 million dollars on an audience poll?
 Framing • • 90% of the population will be saved with this medication…. . or 10% of the population will die despite this medication. You should not drink more than two drinks per day…. or You should not drink more than 730 drinks a year. • Label a food low-fat and people eat more • The way a problem/issue is presented can drastically affect the way we view it.
Framing • • 90% of the population will be saved with this medication…. . or 10% of the population will die despite this medication. You should not drink more than two drinks per day…. or You should not drink more than 730 drinks a year. • Label a food low-fat and people eat more • The way a problem/issue is presented can drastically affect the way we view it.
 Framing • https: //www. youtube. c om/watch? v=pw. JDYS q. V 4 Nw
Framing • https: //www. youtube. c om/watch? v=pw. JDYS q. V 4 Nw
 Belief Perseverance • Clinging to your initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited. .
Belief Perseverance • Clinging to your initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited. .

 Language
Language
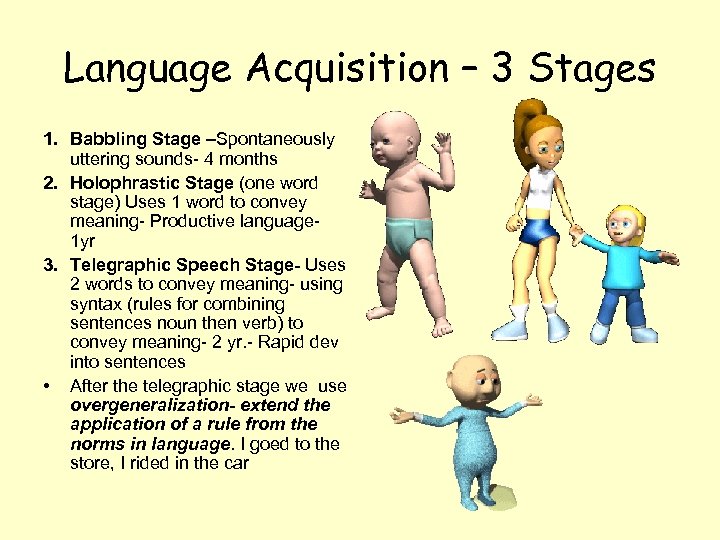 Language Acquisition – 3 Stages 1. Babbling Stage –Spontaneously uttering sounds- 4 months 2. Holophrastic Stage (one word stage) Uses 1 word to convey meaning- Productive language 1 yr 3. Telegraphic Speech Stage- Uses 2 words to convey meaning- using syntax (rules for combining sentences noun then verb) to convey meaning- 2 yr. - Rapid dev into sentences • After the telegraphic stage we use overgeneralization- extend the application of a rule from the norms in language. I goed to the store, I rided in the car
Language Acquisition – 3 Stages 1. Babbling Stage –Spontaneously uttering sounds- 4 months 2. Holophrastic Stage (one word stage) Uses 1 word to convey meaning- Productive language 1 yr 3. Telegraphic Speech Stage- Uses 2 words to convey meaning- using syntax (rules for combining sentences noun then verb) to convey meaning- 2 yr. - Rapid dev into sentences • After the telegraphic stage we use overgeneralization- extend the application of a rule from the norms in language. I goed to the store, I rided in the car
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=2 pgpn 9 f WJNU
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=2 pgpn 9 f WJNU
 How do we learn language?
How do we learn language?
 Social Learning Theory • B. F. Skinner from the Behaviorist School • Critical Period for Lang. Dev • Baby imitates others. • If they are reinforced they keep saying the word. • If they are punished, they stop saying the word. • https: //www. youtube. com/wa tch? v=zq. UJUFOu. I 5 k
Social Learning Theory • B. F. Skinner from the Behaviorist School • Critical Period for Lang. Dev • Baby imitates others. • If they are reinforced they keep saying the word. • If they are punished, they stop saying the word. • https: //www. youtube. com/wa tch? v=zq. UJUFOu. I 5 k
 Chomsky’s Theory (nativist theory) • • • We learn language too quickly for it to be through reinforcement and punishment Language acquisition deviceprewired, inborn ability to learn language. Universal grammar –Common grammatical building blocks that all languages share, usually start with nouns then verbs then adjectives But if inborn with support = interactionist view • Critical period for language development
Chomsky’s Theory (nativist theory) • • • We learn language too quickly for it to be through reinforcement and punishment Language acquisition deviceprewired, inborn ability to learn language. Universal grammar –Common grammatical building blocks that all languages share, usually start with nouns then verbs then adjectives But if inborn with support = interactionist view • Critical period for language development
 Benjamin Whorf’s Linguistic Determinism • The idea that language determines the way we think. Language determinism doesn’t determine but they influence our thinking and what we think about people, objects, ideas • The Hopi tribe has no past tense in their language, so Whorf says they rarely think of the past.
Benjamin Whorf’s Linguistic Determinism • The idea that language determines the way we think. Language determinism doesn’t determine but they influence our thinking and what we think about people, objects, ideas • The Hopi tribe has no past tense in their language, so Whorf says they rarely think of the past.
 Language • Our spoken written or gestured words and the way we combine them to communicate meaning.
Language • Our spoken written or gestured words and the way we combine them to communicate meaning.
 Language development • How many words do you think you know now? Probably around 80, 000. After age 1 you average about 13 words a day.
Language development • How many words do you think you know now? Probably around 80, 000. After age 1 you average about 13 words a day.
 Phonemes How many phonemes does Bubbles have? • In a spoken language, the smallest distinctive sound unit. • Chug has three phonemes, ch, u, g. Think “phones” make sound.
Phonemes How many phonemes does Bubbles have? • In a spoken language, the smallest distinctive sound unit. • Chug has three phonemes, ch, u, g. Think “phones” make sound.
 Morphemes • In a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning. • Can be a word or part of a word (prefix or suffix). • Americanisms has ____ morphemes.
Morphemes • In a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning. • Can be a word or part of a word (prefix or suffix). • Americanisms has ____ morphemes.
 Grammar • A system of rules in a language that enables us to communicate and understand others. Verb tense etc.
Grammar • A system of rules in a language that enables us to communicate and understand others. Verb tense etc.
 Semantics • The set of rules by which we derive meaning in a language. • Adding ed at the end of words means past tense. The words one chooses for meaning: Boston massacre
Semantics • The set of rules by which we derive meaning in a language. • Adding ed at the end of words means past tense. The words one chooses for meaning: Boston massacre
 Semantic Examples Ø Crash can mean auto accident, a drop in the Stock Market, to attend a party without being invited, ocean waves hitting the shore or the sound of a cymbals being struck together. Ø A child’s alphabet block could be described as a wooden cube, learning aid, toy or block. Ø Some see the glass half empty and others see the glass half full.
Semantic Examples Ø Crash can mean auto accident, a drop in the Stock Market, to attend a party without being invited, ocean waves hitting the shore or the sound of a cymbals being struck together. Ø A child’s alphabet block could be described as a wooden cube, learning aid, toy or block. Ø Some see the glass half empty and others see the glass half full.
 Syntax • The rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences. • “Happy to be home, the bed looked like a comfortable place to take a nap. ” • In English, adjectives come before nouns, but not in Spanish!! Is this the White House or the House White?
Syntax • The rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences. • “Happy to be home, the bed looked like a comfortable place to take a nap. ” • In English, adjectives come before nouns, but not in Spanish!! Is this the White House or the House White?
 Koko Sign language • https: //www. youtub e. com/watch? v=Go e. com/watch? v=SN rg. Ft. Cq. PEs u. Z 4 OE 6 v. Ck
Koko Sign language • https: //www. youtub e. com/watch? v=Go e. com/watch? v=SN rg. Ft. Cq. PEs u. Z 4 OE 6 v. Ck
 Chapter 8 Quiz Language and Thought
Chapter 8 Quiz Language and Thought
 Don’t forget to write your answers on a separate piece of paper to grade when you’re done! 1. Phonemes are: a) The rules of grammar that dictate letter combinations in a language b) The smallest unit of sound in a language c) The smallest unit of meaning in a language d) Semantically the same as morphemes
Don’t forget to write your answers on a separate piece of paper to grade when you’re done! 1. Phonemes are: a) The rules of grammar that dictate letter combinations in a language b) The smallest unit of sound in a language c) The smallest unit of meaning in a language d) Semantically the same as morphemes
 2. Because it has all the features commonly associated with the concept bird, a robin is considered a(n): a) prototype b) heuristic c) algorithm d) phenotype
2. Because it has all the features commonly associated with the concept bird, a robin is considered a(n): a) prototype b) heuristic c) algorithm d) phenotype
 3. Compared to convergent thinkers, to solve a problem divergent thinkers are more likely to: a) Process information to arrive at the single best answer b) Think creatively and generate multiple answers c) Problem solve in a systematic step-by-step fashion d) Frequently suffer from functional fixedness
3. Compared to convergent thinkers, to solve a problem divergent thinkers are more likely to: a) Process information to arrive at the single best answer b) Think creatively and generate multiple answers c) Problem solve in a systematic step-by-step fashion d) Frequently suffer from functional fixedness
 4. Unlike B. F. Skinner, Noam Chomsky believes that children a) Learn to speak by mimicking the sounds around them b) Speak more quickly if their parents correct their mispronunciations earlier c) Are hard-wired for language acquisition d) Learn language more quickly if positive rewards are given to them
4. Unlike B. F. Skinner, Noam Chomsky believes that children a) Learn to speak by mimicking the sounds around them b) Speak more quickly if their parents correct their mispronunciations earlier c) Are hard-wired for language acquisition d) Learn language more quickly if positive rewards are given to them
 5. Which of the following is a good example of functional fixedness? a) Failing to use a dime as a screwdriver when you have lost your screwdriver b) Not being able to solve a physics problem because you apply the same rule you always do c) Using a blanket as a pillow d) Adding water to a cake mix when it calls for milk
5. Which of the following is a good example of functional fixedness? a) Failing to use a dime as a screwdriver when you have lost your screwdriver b) Not being able to solve a physics problem because you apply the same rule you always do c) Using a blanket as a pillow d) Adding water to a cake mix when it calls for milk
 6. Having been told that Syd is an engineer and Fran is an elementary school teacher, when Arnold meets the couple for the first time, he assumes that Syd is the husband Fran is the wife, rather than the opposite, which is the case. This best illustrates: a) Confirmation bias b) The mere exposure effect c) The anchoring effect d) The representativeness heuristic
6. Having been told that Syd is an engineer and Fran is an elementary school teacher, when Arnold meets the couple for the first time, he assumes that Syd is the husband Fran is the wife, rather than the opposite, which is the case. This best illustrates: a) Confirmation bias b) The mere exposure effect c) The anchoring effect d) The representativeness heuristic
 7. Which of the following is a holophrase one-year-old Amanda is likely to say? a) b) c) d) “Mmmmm” “Gaga” “Eat apple” “Bottle”
7. Which of the following is a holophrase one-year-old Amanda is likely to say? a) b) c) d) “Mmmmm” “Gaga” “Eat apple” “Bottle”
 9. According to the nativist theory, language is acquired a) By parents reinforcing correct language use b) Using an inborn ability to learn language at a certain developmental stage c) Best in the language and culture native to the child and parents d) Only if formal language instruction is provided in the child’s native language
9. According to the nativist theory, language is acquired a) By parents reinforcing correct language use b) Using an inborn ability to learn language at a certain developmental stage c) Best in the language and culture native to the child and parents d) Only if formal language instruction is provided in the child’s native language
 10. In light of their views on language acquisition, which theorist would expect apes to progress the furthest in language development? a) b) c) d) B. F. Skinner Noam Chomsky Jean Piaget Herb Terrance
10. In light of their views on language acquisition, which theorist would expect apes to progress the furthest in language development? a) b) c) d) B. F. Skinner Noam Chomsky Jean Piaget Herb Terrance
 12. In cultures that depend on hunting and gathering for subsistence, _____ style is more adaptive. a) b) c) d) A field dependent A risk-averse A field independent An algorithmic
12. In cultures that depend on hunting and gathering for subsistence, _____ style is more adaptive. a) b) c) d) A field dependent A risk-averse A field independent An algorithmic
 13. Corey was serving on a jury in a criminal case, and the jury reached a unanimous “not guilty” verdict. Several months later, some additional evidence came to light that strongly suggested that the defendant was, in fact, guilty of the crime in question. Corey is still not convinced by the new evidence, and claims he wouldn’t have voted guilty, even if the new information had been presented during the trial. In this example, Corey is showing evidence of a) b) c) d) The conjunction fallacy The availability heuristic Belief perseverance Mental set
13. Corey was serving on a jury in a criminal case, and the jury reached a unanimous “not guilty” verdict. Several months later, some additional evidence came to light that strongly suggested that the defendant was, in fact, guilty of the crime in question. Corey is still not convinced by the new evidence, and claims he wouldn’t have voted guilty, even if the new information had been presented during the trial. In this example, Corey is showing evidence of a) b) c) d) The conjunction fallacy The availability heuristic Belief perseverance Mental set
 14. Dr. Grath believes that both an innate predisposition and a supportive environment contribute to language development. Dr. Grath’s views are MOST consistent with those of a) b) c) d) Behavioral theories Nativist theories Whorfian theories Interactionist theories
14. Dr. Grath believes that both an innate predisposition and a supportive environment contribute to language development. Dr. Grath’s views are MOST consistent with those of a) b) c) d) Behavioral theories Nativist theories Whorfian theories Interactionist theories
 15. Fast mapping is a) The development of a mental representation of one’s environment b) The pacing activity associated with genetics, allowing for anticipation of motivational events c) The type of play a child engages in at an early age d) Mapping words to underlying concepts after only one exposure
15. Fast mapping is a) The development of a mental representation of one’s environment b) The pacing activity associated with genetics, allowing for anticipation of motivational events c) The type of play a child engages in at an early age d) Mapping words to underlying concepts after only one exposure
 Chapter 8 Answer Key 1) B 2) A 3) B 4) C 5) A 6) D 7) D 8) B 9) B 10) A 11)A 12)C 13)C 14)D 15)D
Chapter 8 Answer Key 1) B 2) A 3) B 4) C 5) A 6) D 7) D 8) B 9) B 10) A 11)A 12)C 13)C 14)D 15)D


