level 3 theme 1 Thinking about intelligence and giftedness.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 29

THINKING ABOUT INTELLIGENCE AND GIFTEDNESS © 2011 by The Johns Hopkins University. All rights reserved.

2 Outcomes Participants will be able to: v Describe various theories of intelligence giftedness v Articulate cognitive characteristics and needs of gifted students v Describe implications of giftedness for curriculum and instruction in schools and

3 Intelligence What are some general theories of cognitive development?

Theories of Gifted Cognitive Development 4 v Stimulus-Response Theory • v The reaction time of gifted individuals is faster Piagetian Developmental Theory • • Gifted development is faster within stages Extended adult period of development is present in the gifted

Theories of Gifted Cognitive Development (cont. ) 5 v Psychometric Theory • v Reasoning tests represent accurately the high cognitive level of function in the gifted Cognitive Theory • The gifted have superior analytic, creative, and metacognitive skills and processes

Talent Development Theories 6 Domain-specific development, a confluence of circumstances v Drive and dedication in a society–supported field of endeavor v Nurturing environment for the specific talent v Outstanding instruction and mentorship v Role of parents

Talent Development Theories (cont. ) 7 Evolving systems v Organization of knowledge, affect, and purpose Catalytic process that converts abilities to talents v v v Internal factors External factors Learning, training, and practice
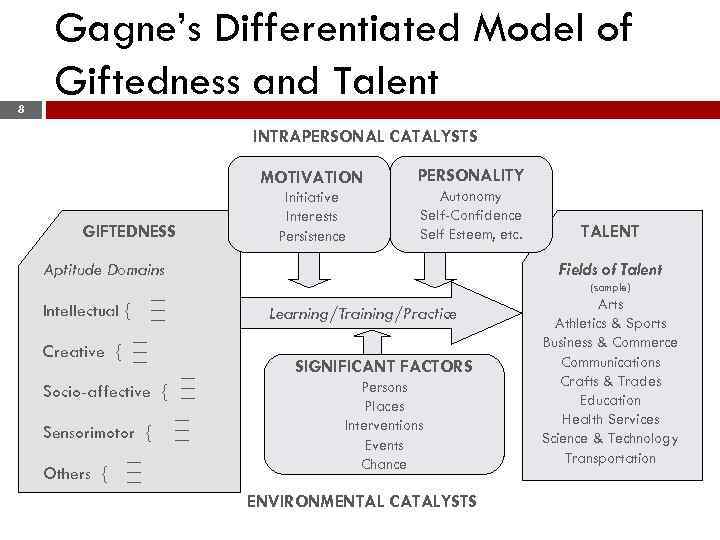
8 Gagne’s Differentiated Model of Giftedness and Talent INTRAPERSONAL CATALYSTS MOTIVATION Initiative Interests Persistence GIFTEDNESS PERSONALITY Autonomy Self-Confidence Self Esteem, etc. Fields of Talent Aptitude Domains Creative { Learning/Training/Practice ___ ___ Socio-affective { Sensorimotor { Others { (sample) ___ ___ Intellectual { ___ ___ TALENT ___ ___ ___ SIGNIFICANT FACTORS Persons Places Interventions Events Chance ENVIRONMENTAL CATALYSTS Arts Athletics & Sports Business & Commerce Communications Crafts & Trades Education Health Services Science & Technology Transportation

9 Giftedness What are some conceptualizations of giftedness?

Conceptions of Giftedness 10 v A child is gifted whose performance in a potentially valuable line of human activity is consistently remarkable v Talent is the capacity for superior achievement in any socially valuable area of human endeavor, such academic fields as languages, social sciences, natural sciences, mathematics, and such artistic fields as music, graphic and plastic arts, performing arts, mechanical arts, and the field of human relations

Conceptions of Giftedness (cont. ) 11 v Genius is the result of being labeled as such in a society and thus has no independent existence v Composite set of factors treated equally (creativity, motivation, and above average intelligence) v Extraordinary ability/performance in seven different intelligence areas, including verbal, logical mathematical, spatial visual, musical, kinesthetic, intrapersonal, and interpersonal
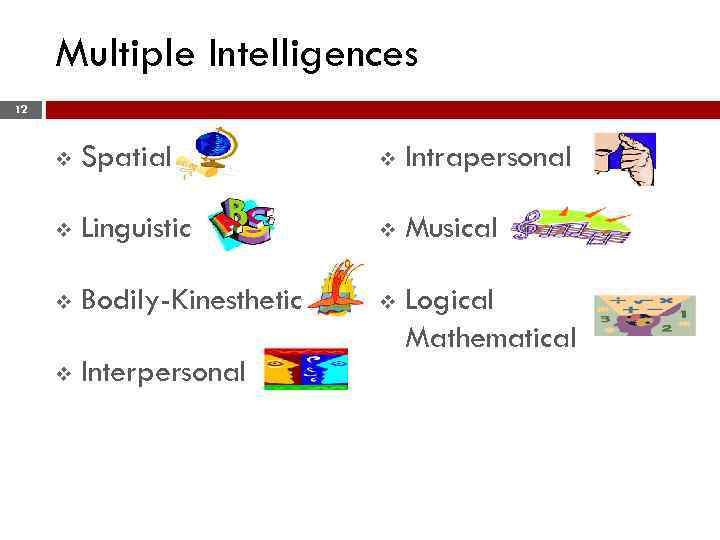
Multiple Intelligences 12 v Spatial v Intrapersonal v Linguistic v Musical v Bodily-Kinesthetic v v Interpersonal Logical Mathematical

13 Definitions of Giftedness

From the United States Department of Education 14 v Children and youth with outstanding talent perform or show potential for performing at remarkably high levels of accomplishment when compared with others of their age, experience, or environment. v These children and youth exhibit high performance capability in intellectual, creative, and/or artistic areas, possess an unusual leadership capacity, or excel in specific academic fields. They require services or activities not ordinarily provided by the schools. v Outstanding talents are present in children and youth from all cultural groups, across the economic strata, and in all areas of human endeavor.

Normative Concept of Talent and Giftedness 15 10– 15% 70– 80% 10– 15% Non Competence Talent Expertise Mental Handicap Intellectual Ability/ Average IQ Giftedness
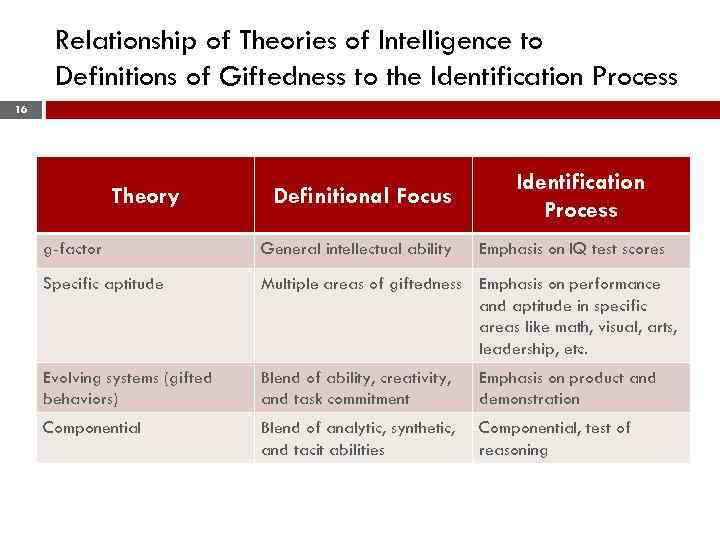
Relationship of Theories of Intelligence to Definitions of Giftedness to the Identification Process 16 Theory Definitional Focus Identification Process g-factor General intellectual ability Emphasis on IQ test scores Specific aptitude Multiple areas of giftedness Emphasis on performance and aptitude in specific areas like math, visual, arts, leadership, etc. Evolving systems (gifted behaviors) Blend of ability, creativity, and task commitment Emphasis on product and demonstration Componential Blend of analytic, synthetic, and tacit abilities Componential, test of reasoning

What Do We Know about Giftedness That Matters in Identification? 17 v Multidimensional v Genetic and environmental components v Manifested in one area or several v Degrees of giftedness within and across areas v Qualitative differences apparent, especially at extreme levels v Focus on evidence of advanced behavior v Non-intellective factors matter in predicting program success (e. g. , creativity, motivation, persistence)

18 Characteristics of Gifted Learners What are the cognitive characteristics of gifted learners?

Cognitive Characteristics 19 v Rapid learning rate v Advanced cognitive development in one or more academic areas v Complex thinking v Lengthy attention span v Divergent thinking

Cognitive Characteristics (cont. ) 20 v Keen sense of justice v Capacity for reflection v Early language or reading development v Exceptional reasoning ability v Intellectual curiosity

Specific Academic Aptitude– Math 21 v Spontaneous formation of problems v Use of multiple strategies to solve problems v Early interest in numbers v Strong understanding of quantitative relationships v Advanced spatial reasoning v Enjoyment of mathematical reasoning

Specific Academic Aptitude– Science 22 v Strong curiosity about scientific topics v Inquisitive about how things work and why things happen v Ease in developing spontaneous speculations/hypotheses v Able to analyze data and spot patterns

Specific Academic Aptitude– Science 23 v Intense interest in one particular area of science v Enjoyment in measuring and investigating things v May have scientific hobbies and/or extensive collections v Think logically, seeking plausible explanations for phenomena

Specific Academic Aptitude– Verbal Ability 24 v Early letter and word recognition v Early reading v Loves to read and does so unprompted v Facility with writing, drawing, and oral communication

Specific Academic Aptitude– Verbal Ability 25 v Enjoys memorizing verbal content like poems or text from books v Enjoys word puzzles, games, and relationships v Asks complex questions

26 Case Study Activity: Milton Think about the general and specific characteristics of gifted learners and highlight examples in the Case Study. Think about particular needs Milton has related to these characteristics.

27 Discussion Questions v In what ways should the core curriculum be adapted in response to the needs of gifted learners? v How might differences among gifted learners impact curriculum adaptations?

28 Session Reflection How can teachers best address the characteristics and needs of gifted learners in classrooms?

29 When will we also teach them what they are? We should say to each of them: Do you know what you are? You are a marvel. You are unique. In all the years that have passed, there has never been another child like you…You have the capacity for anything. Yes, you are a marvel. ─ Pablo Casals
level 3 theme 1 Thinking about intelligence and giftedness.pptx